Men Reproductive System
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
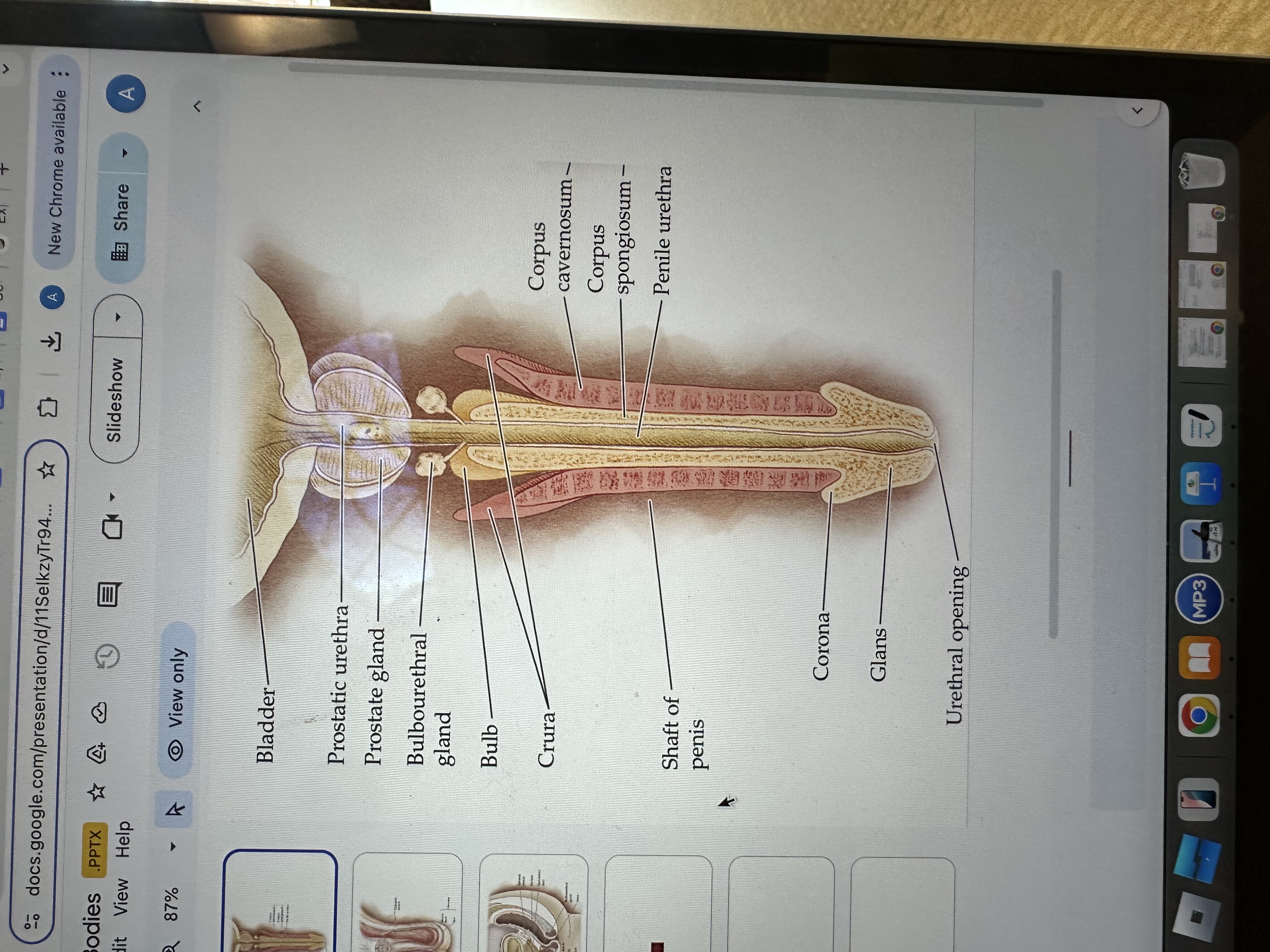
Glans of the Penis
The glans is the sensitive bulbous structure at the tip of the penis, also known as the head.
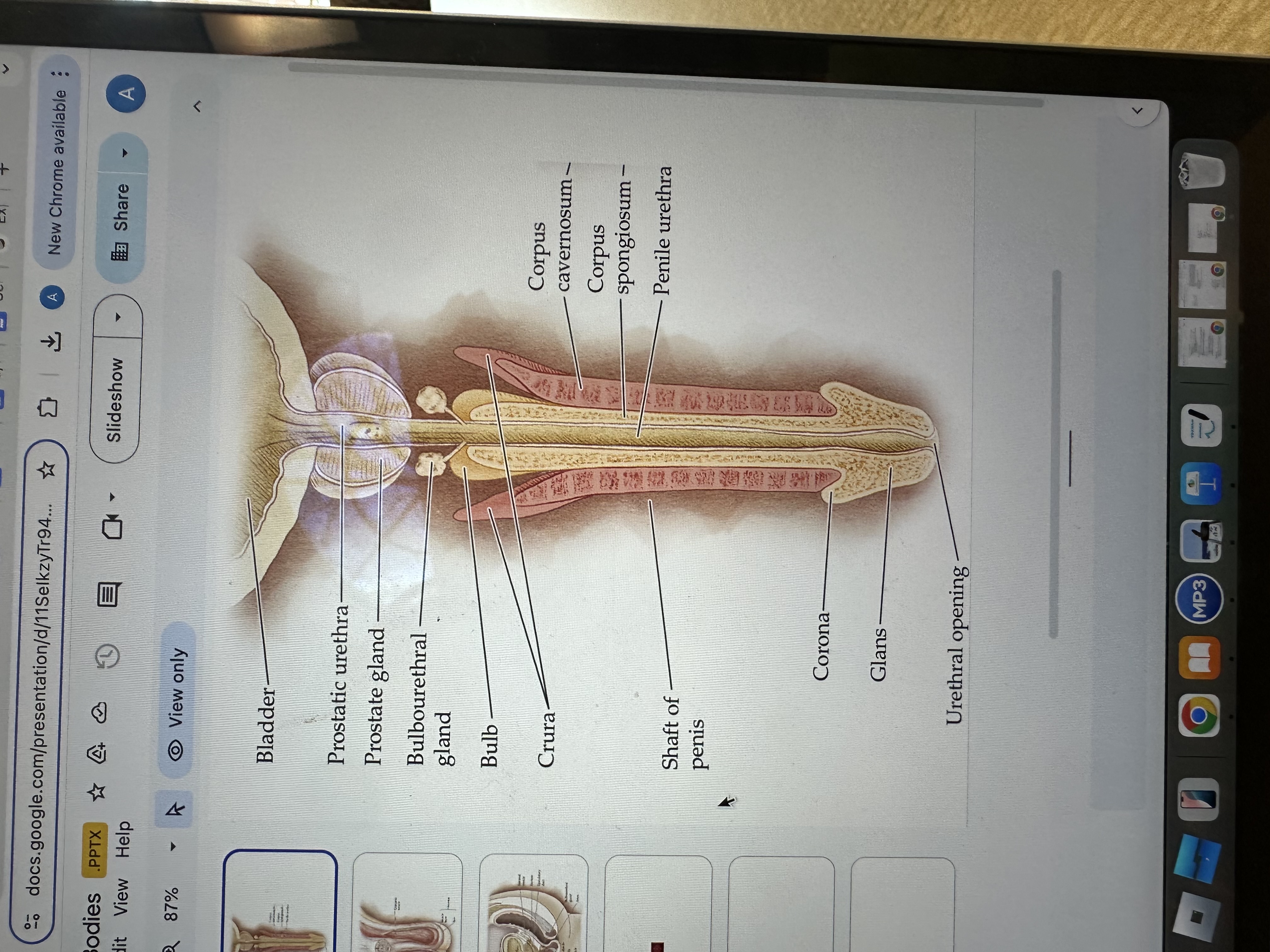
Urethral opening
The urethral opening is the external opening through which urine and semen exit the body, located at the tip of the penis.
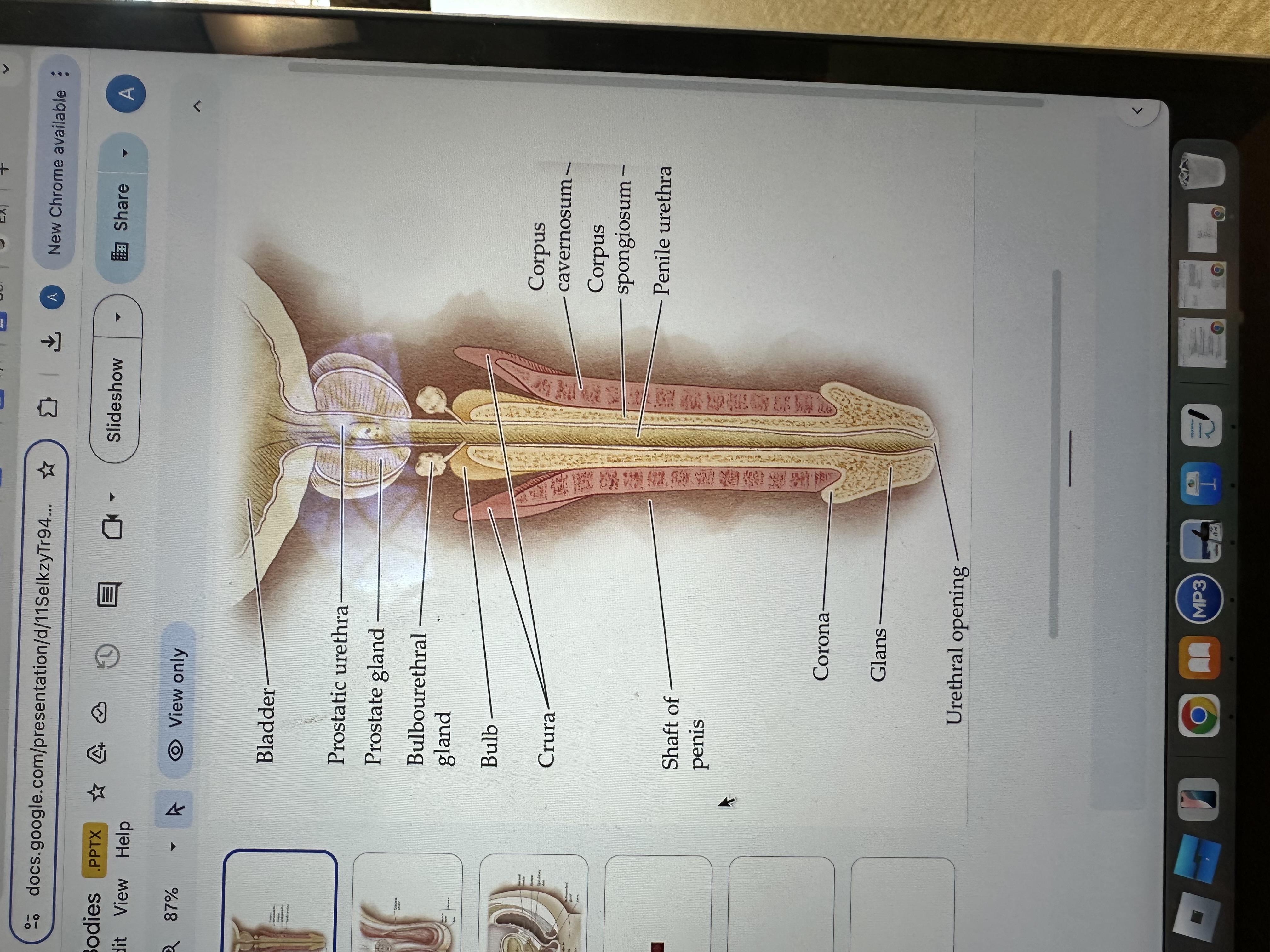
Corona of the penis
The corona is the rounded ridge that forms the edge of the glans, separating it from the shaft of the penis.
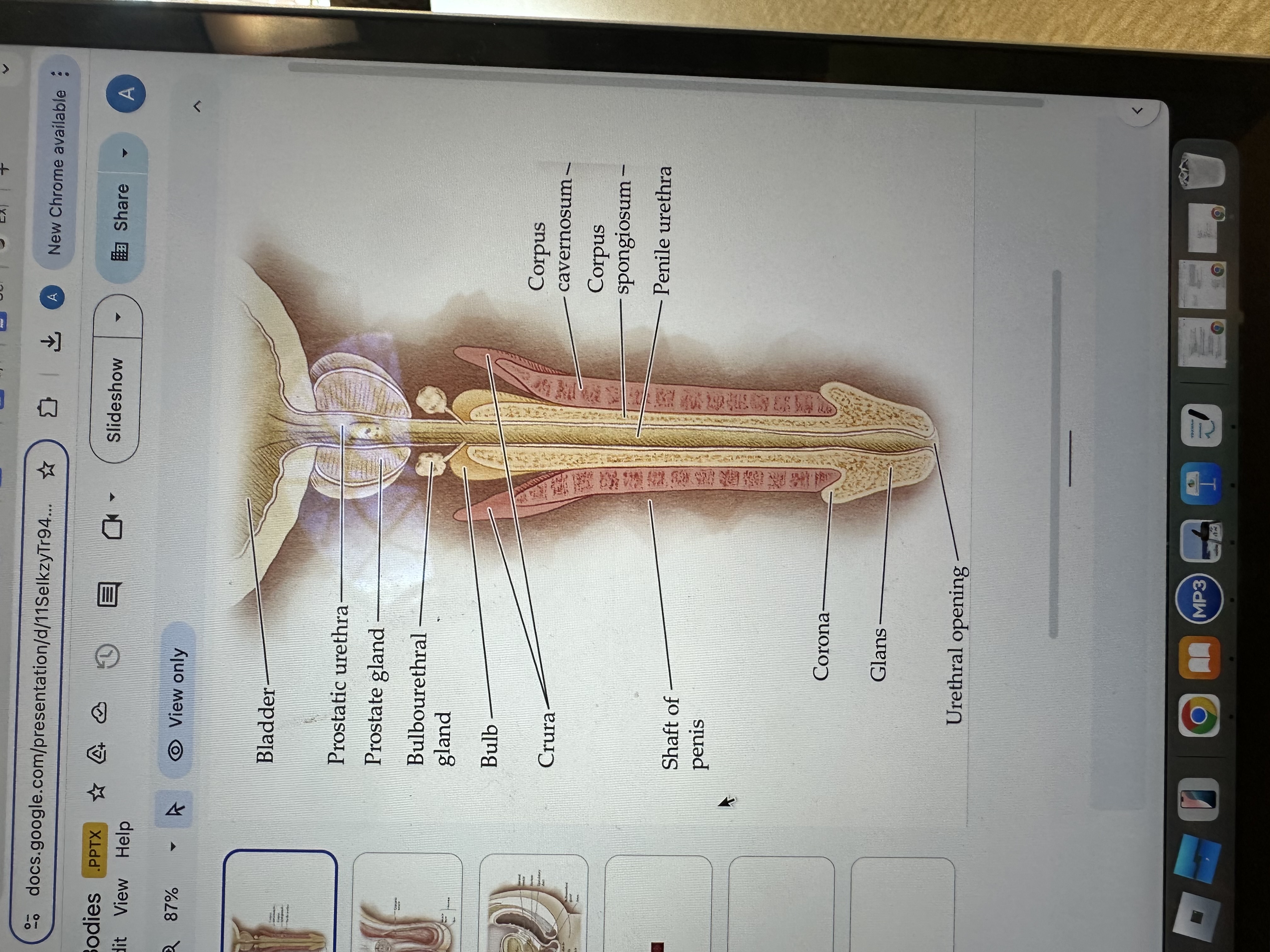
Shaft of penis
The shaft of the penis is the elongated portion that extends from the glans to the base, providing structure and support.
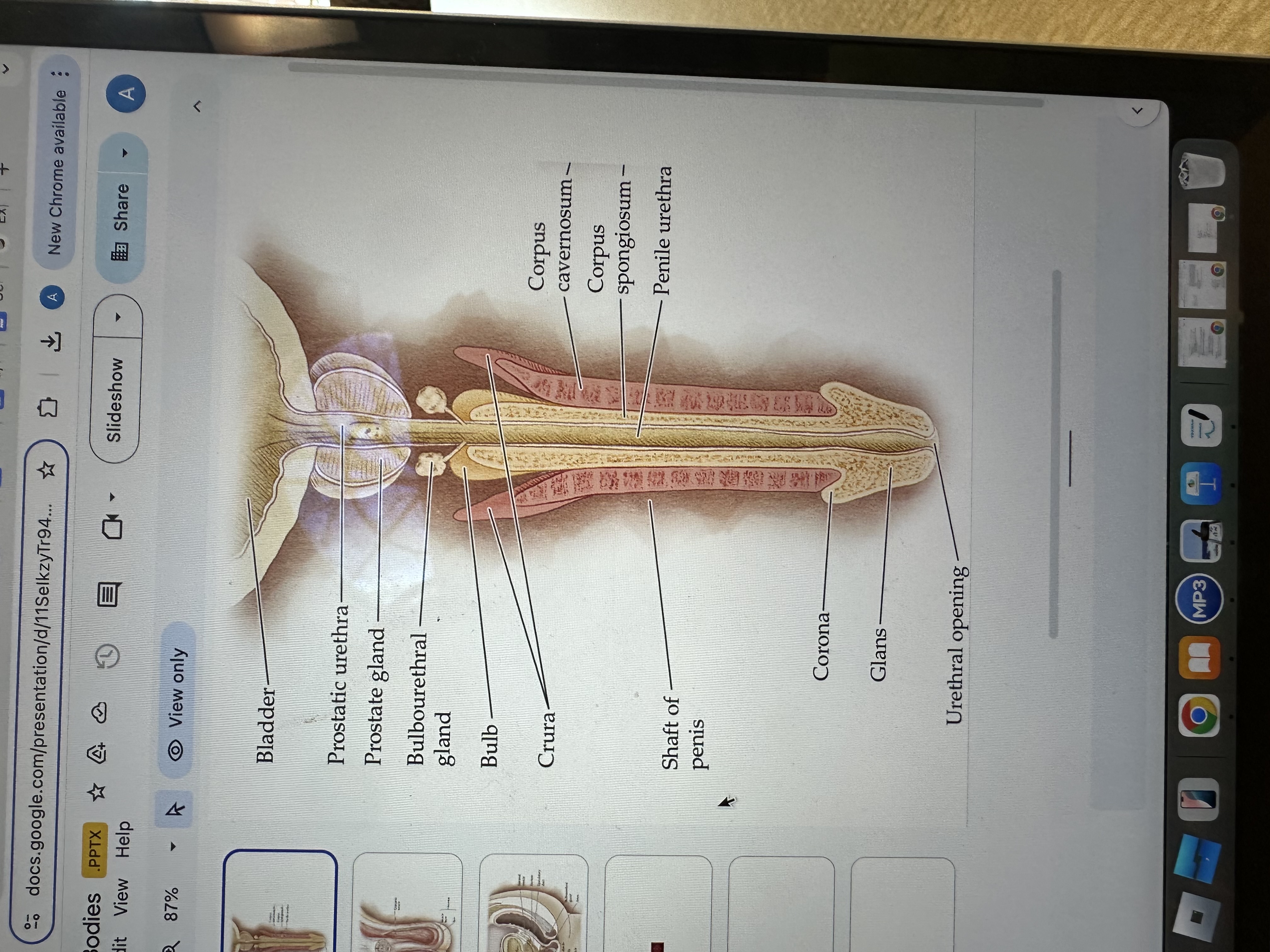
Penile Urethra
The penile urethra is the portion of the urethra that runs through the penis, facilitating the passage of urine and semen out of the body.
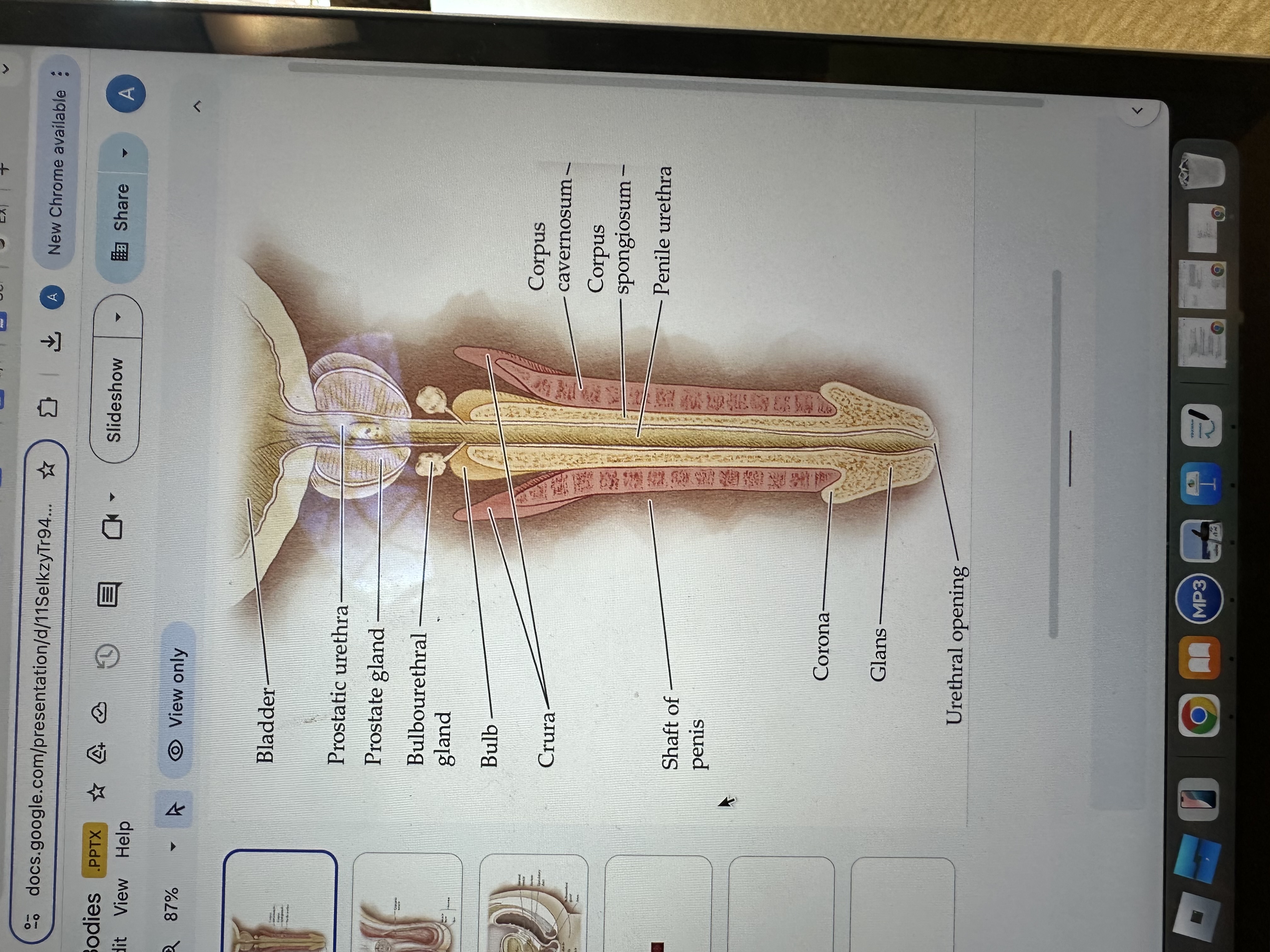
Corpus spongiosum
The corpus spongiosum is the erectile tissue surrounding the penile urethra, preventing it from collapsing during erection, and helping maintain the flow of semen and urine.
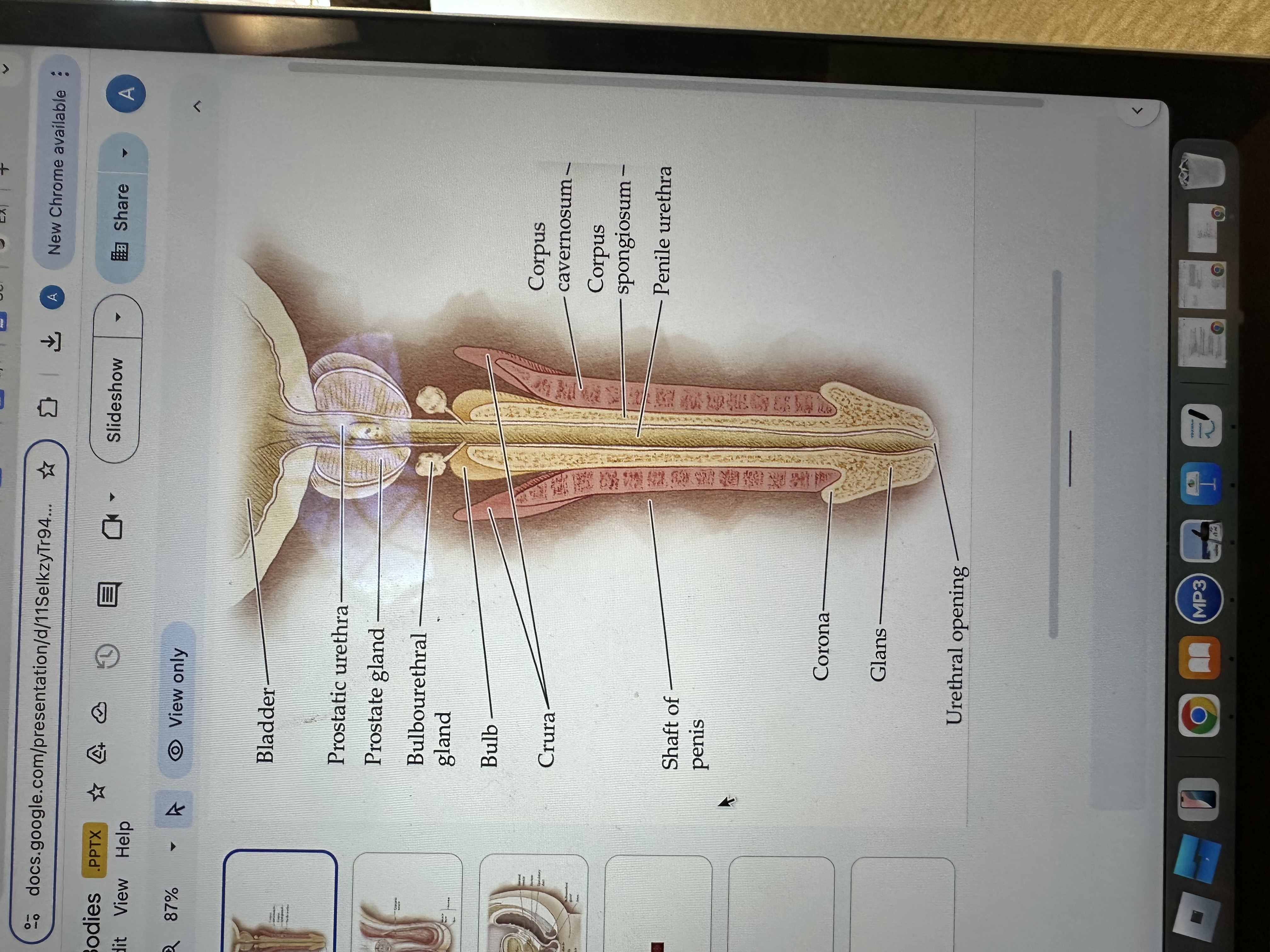
Corpus cavernosum
The corpus cavernosum refers to two columns of erectile tissue along the penis that fill with blood during sexual arousal, facilitating erection.
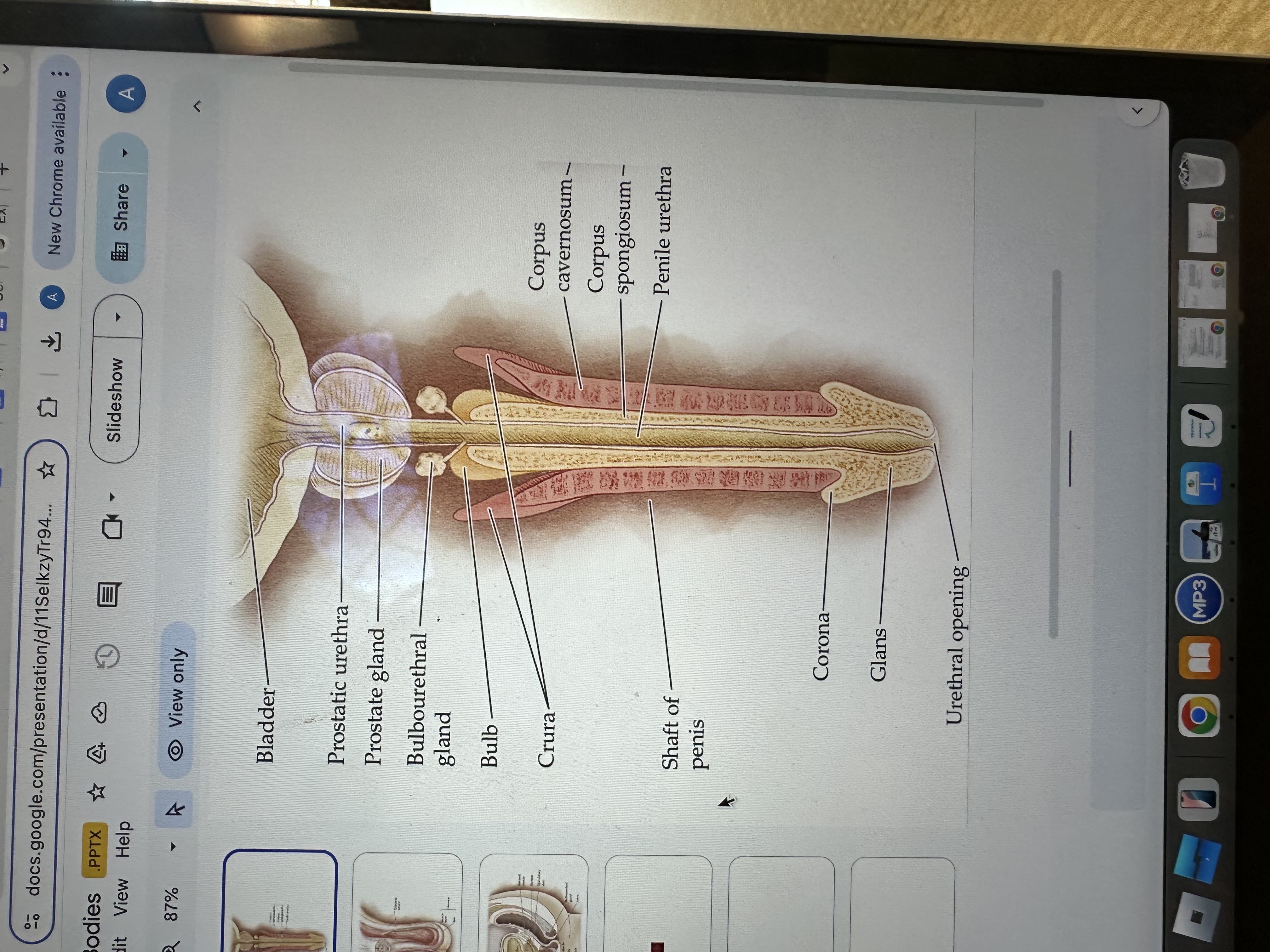
Crura of the penis
The crura are elongated structures at the base of the penis made of erectile tissue, anchoring it to the pubic bone and contributing to the erection by filling with blood.
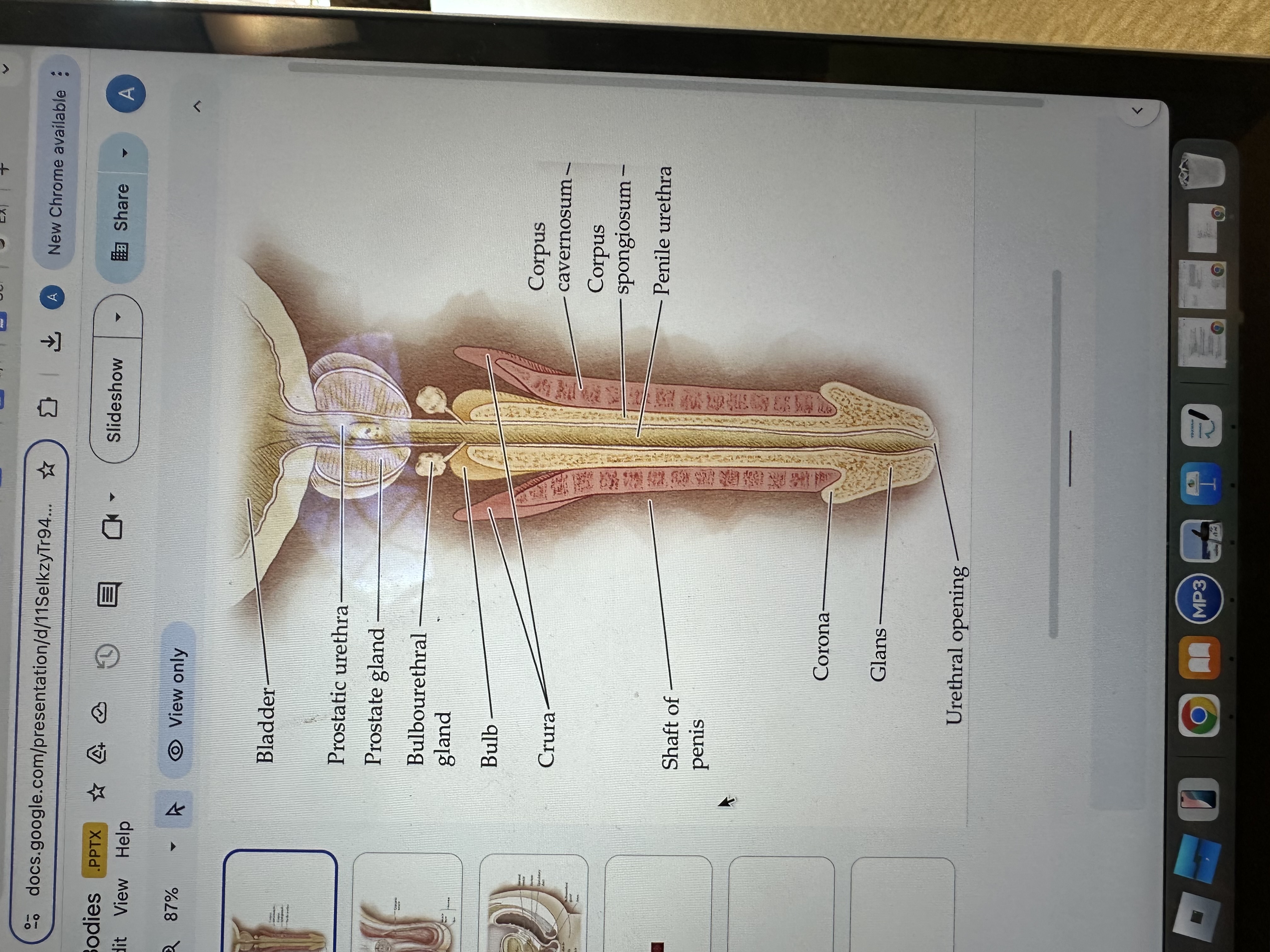
Bulb
The bulb is the rounded, enlarged base of the corpus spongiosum, contributing to the structure and erectile function of the penis.
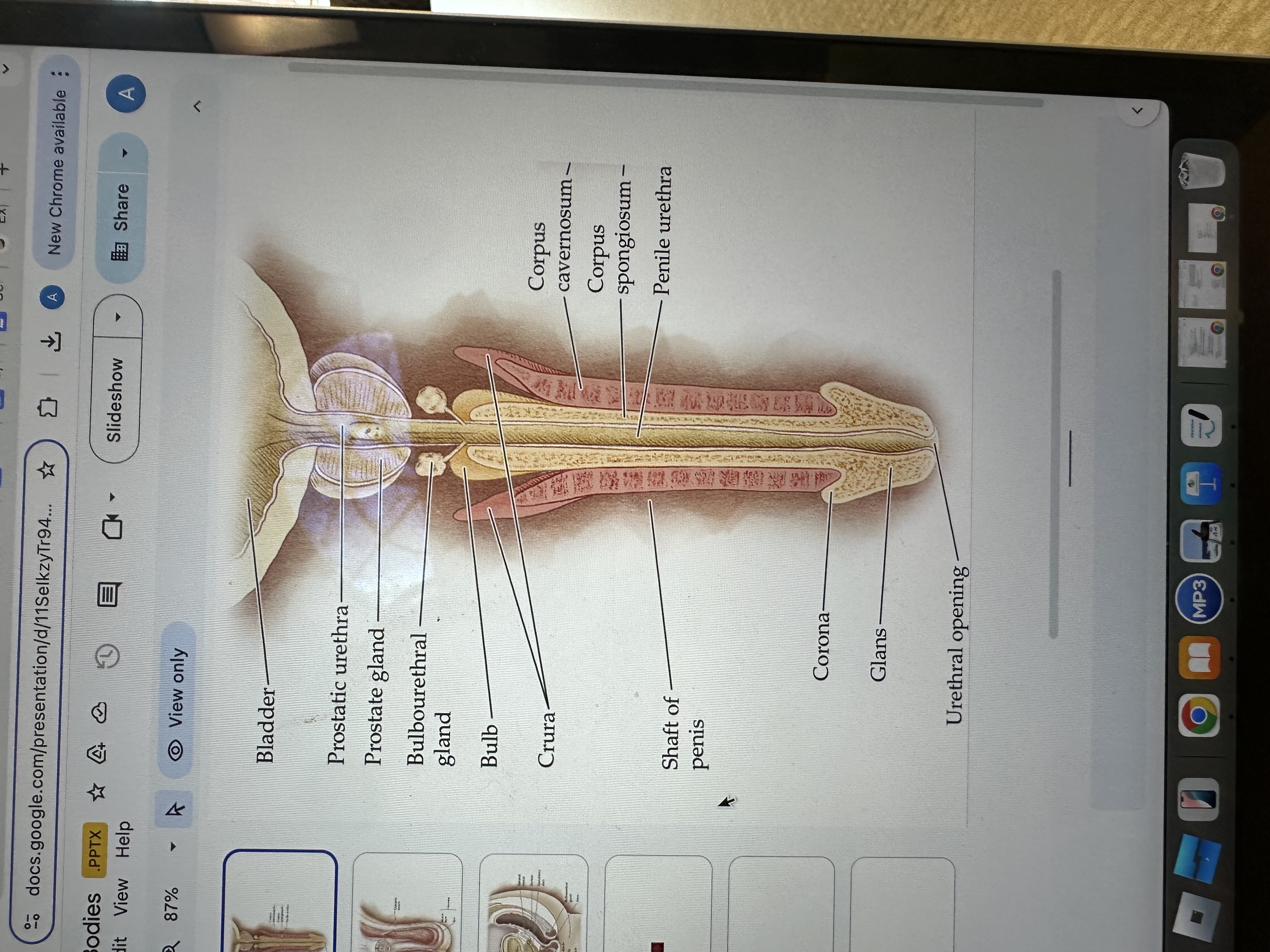
Bulbourethral gland
The bulbourethral glands, also known as Cowper's glands, are responsible for producing a clear, viscous fluid that lubricates the urethra and neutralizes acidity prior to ejaculation.
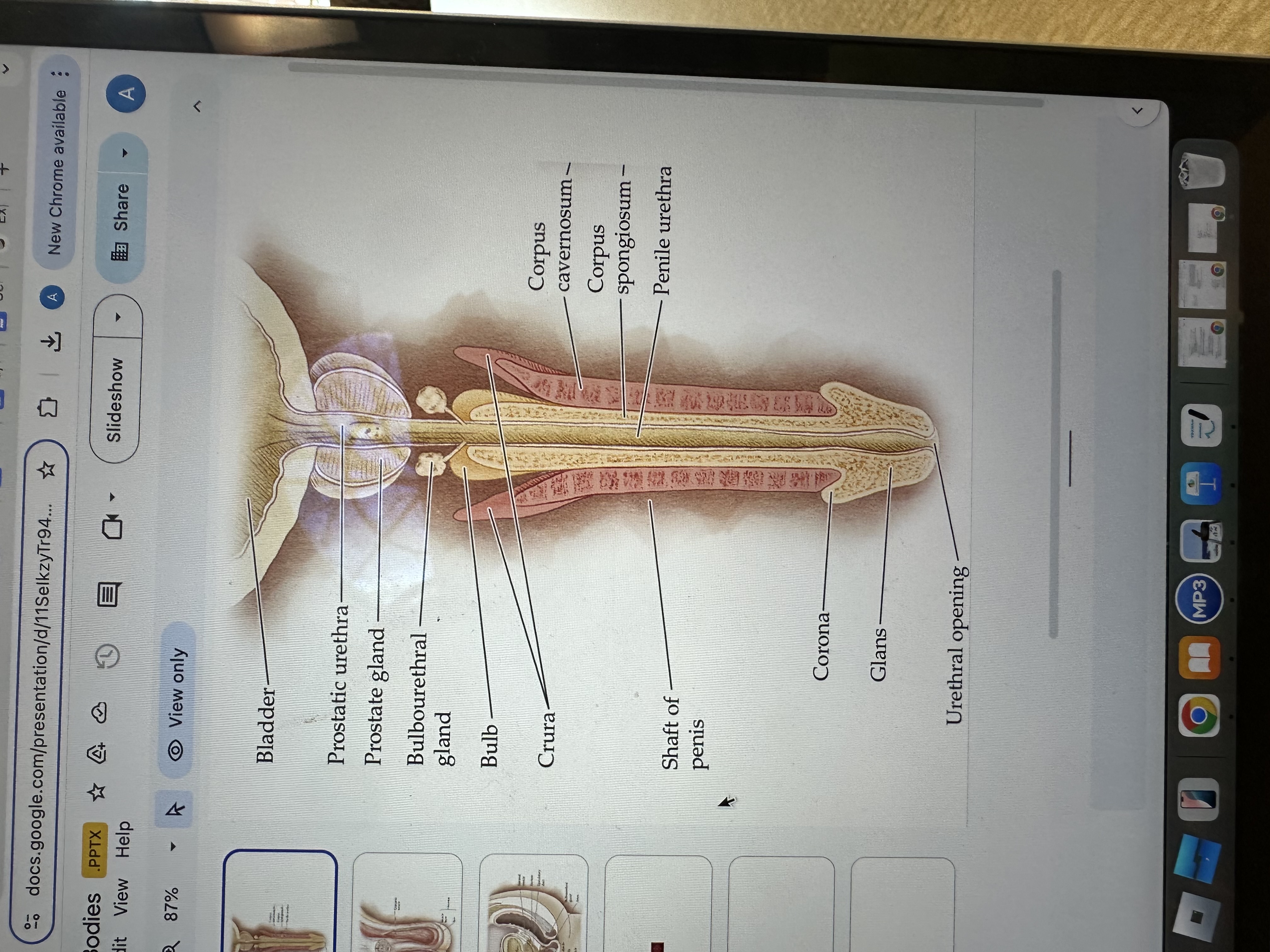
Prostate gland
The prostate gland is a small, walnut-shaped gland located below the bladder that produces seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm.
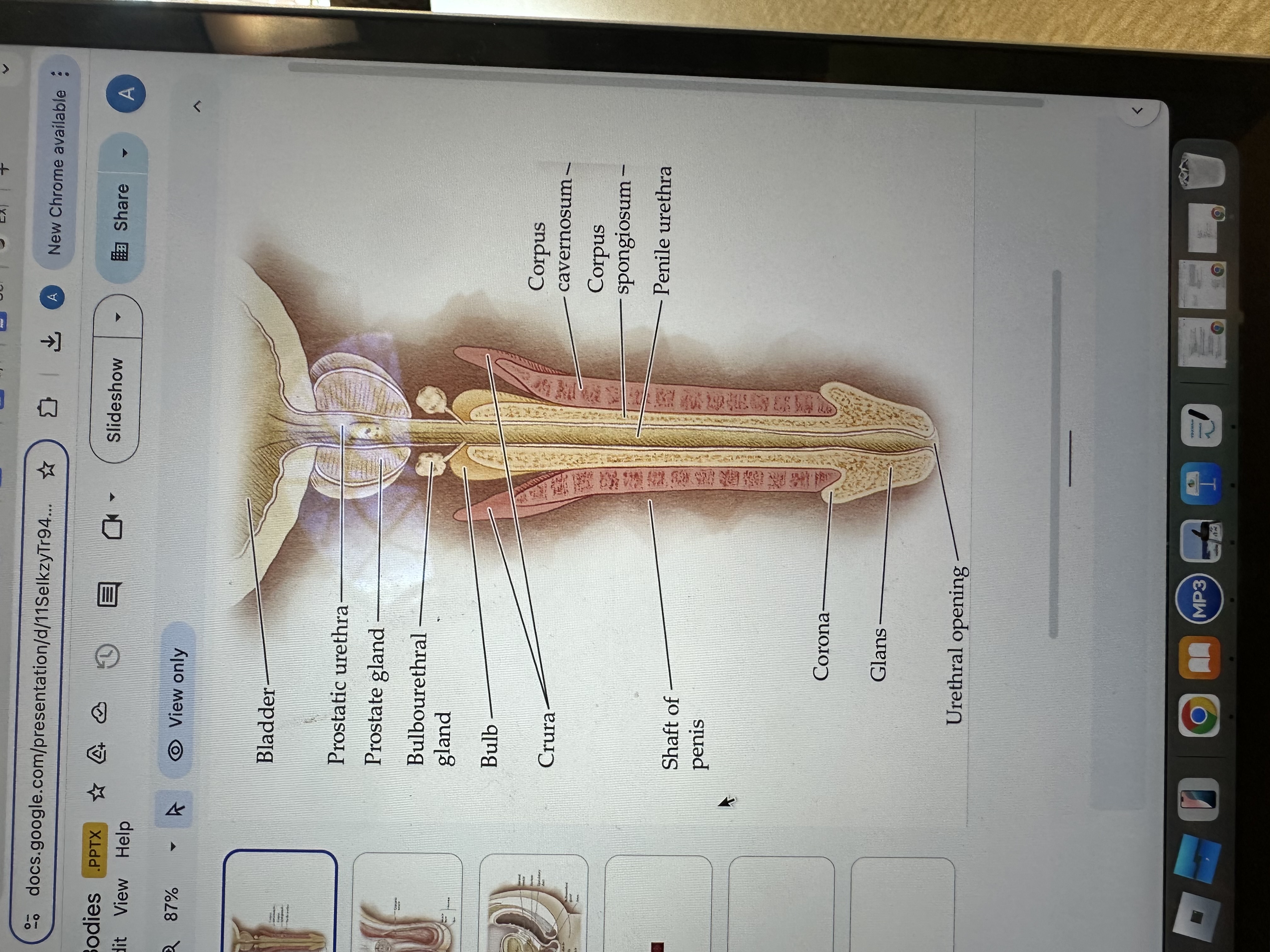
Prostatic urethra
The prostatic urethra is the portion of the urethra that runs through the prostate gland, allowing the passage of urine and semen, and is surrounded by prostatic tissue.
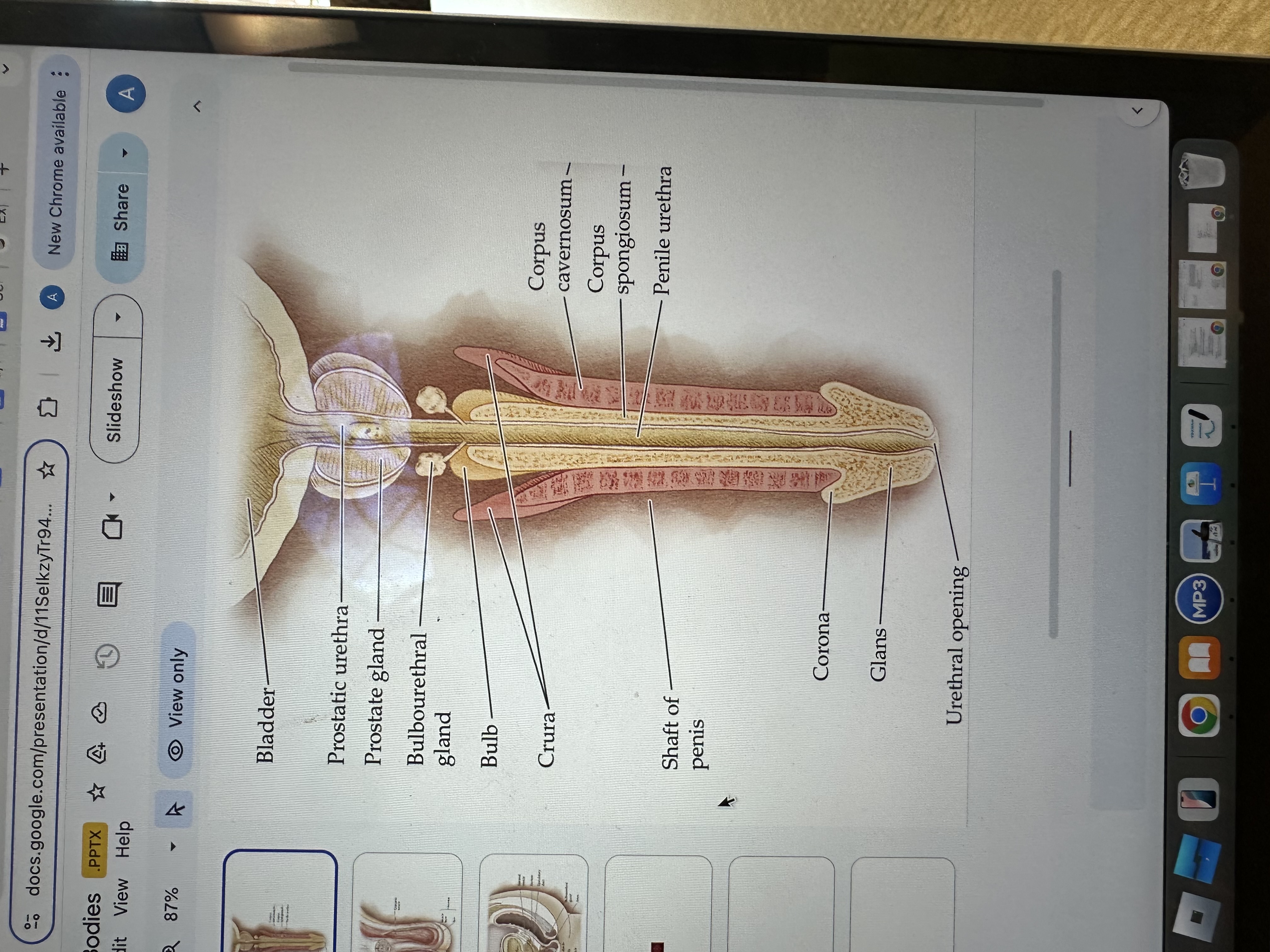
Bladder
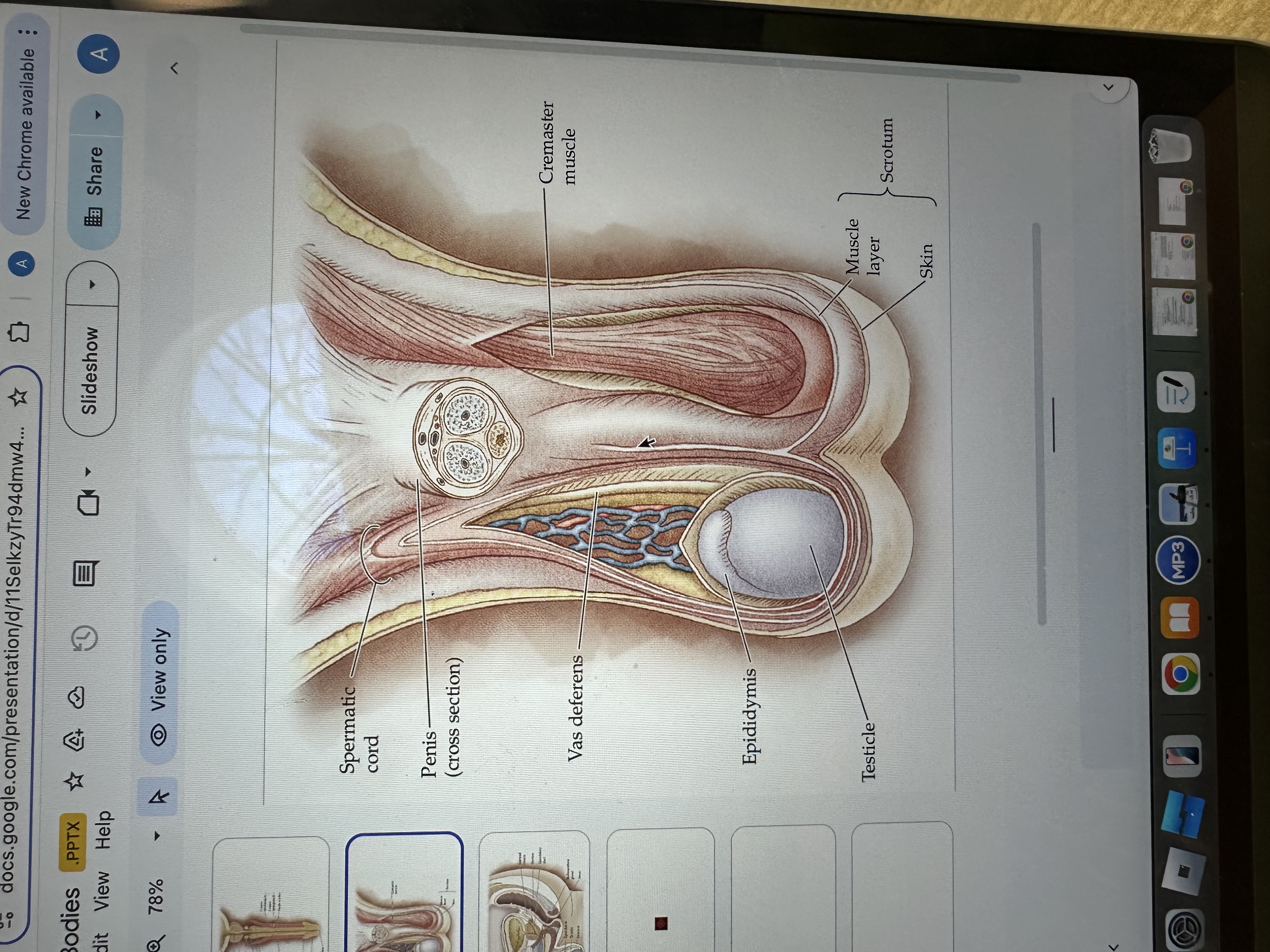
Skin
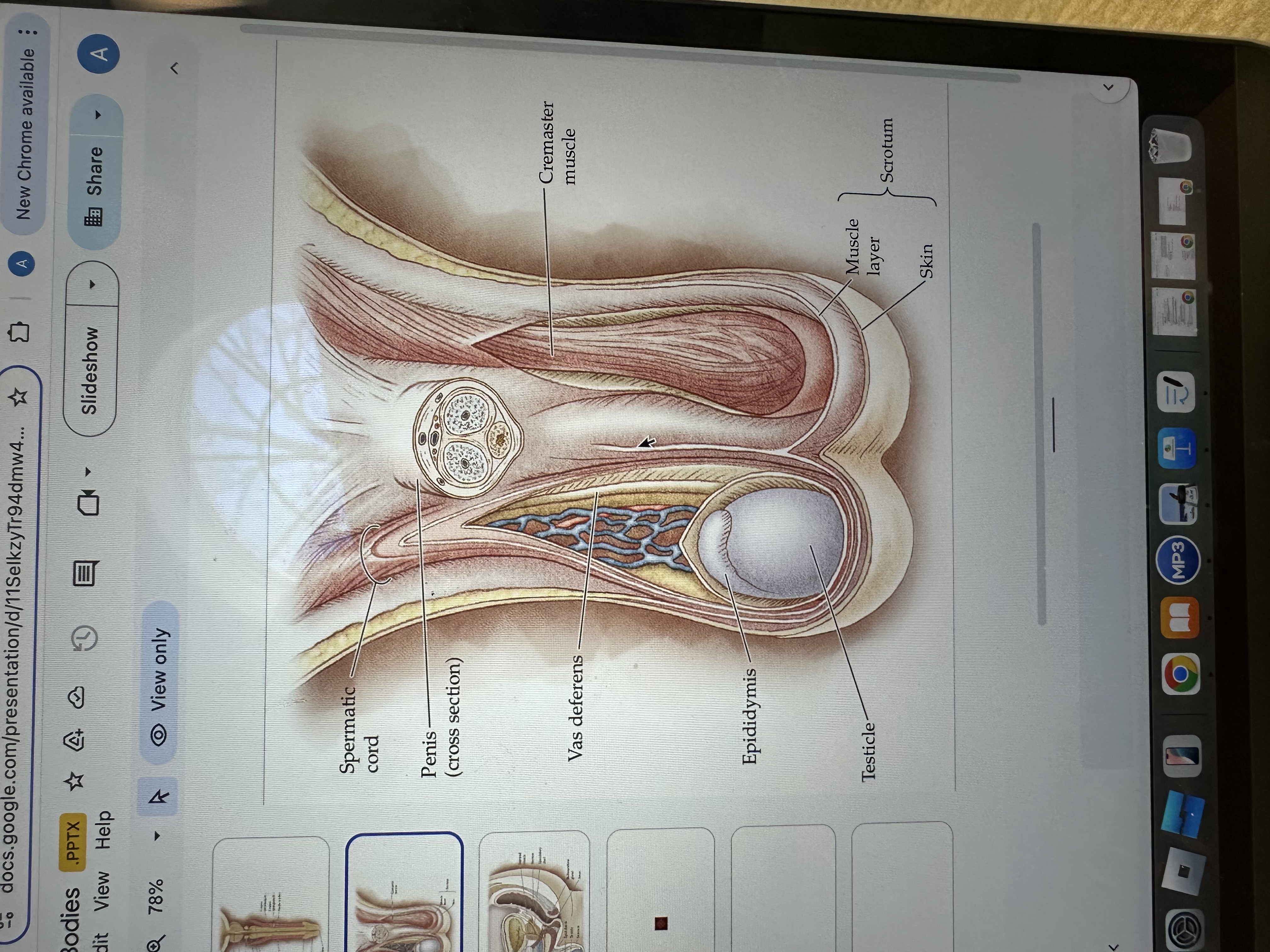
Scrotum
The scrotum is a pouch of skin that contains and protects the testes, helping to regulate their temperature for optimal sperm production.
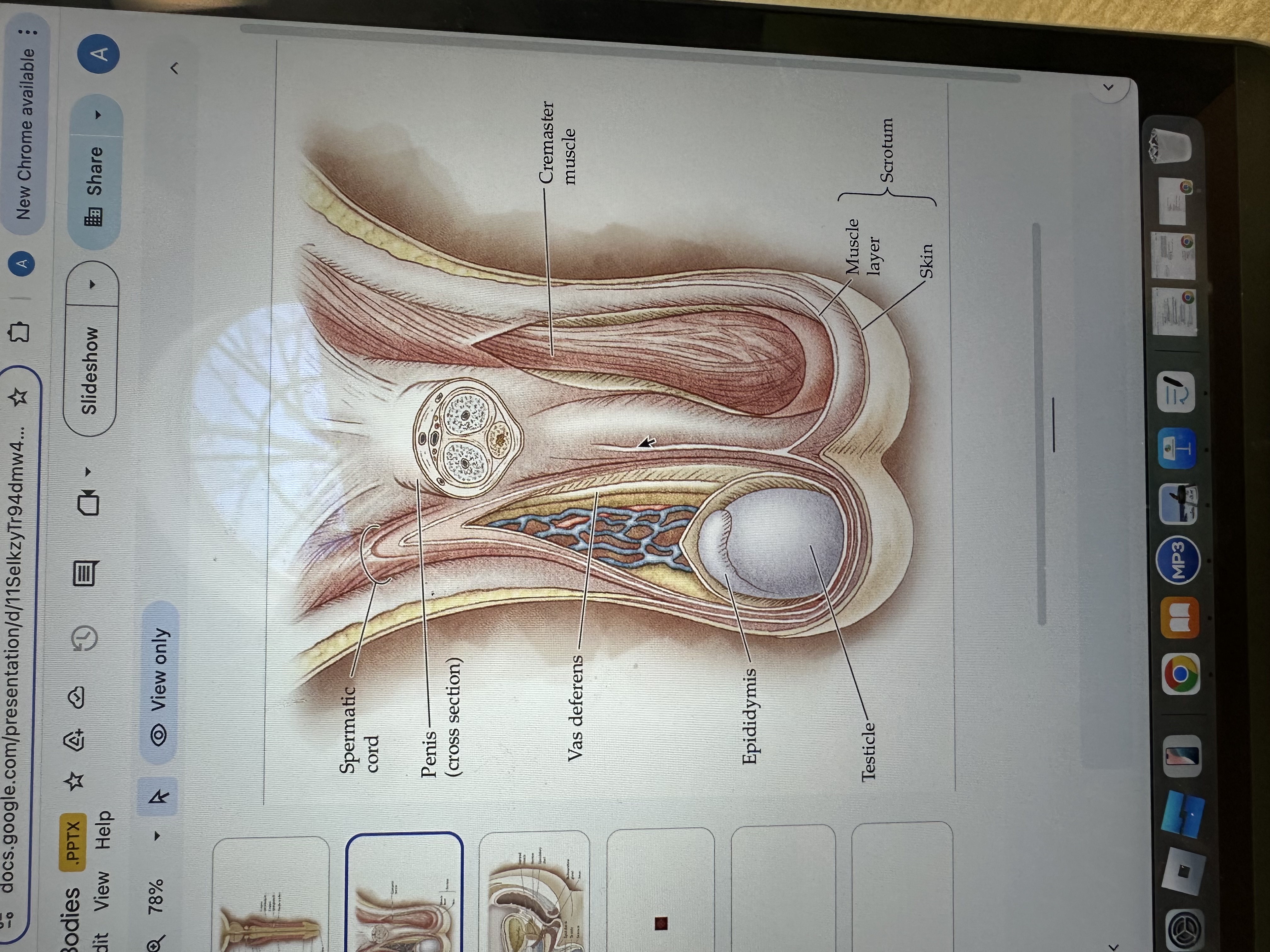
Muscle layer
The muscle layer in the penis provides structural support and facilitates erection by contracting and relaxing during sexual stimulation.
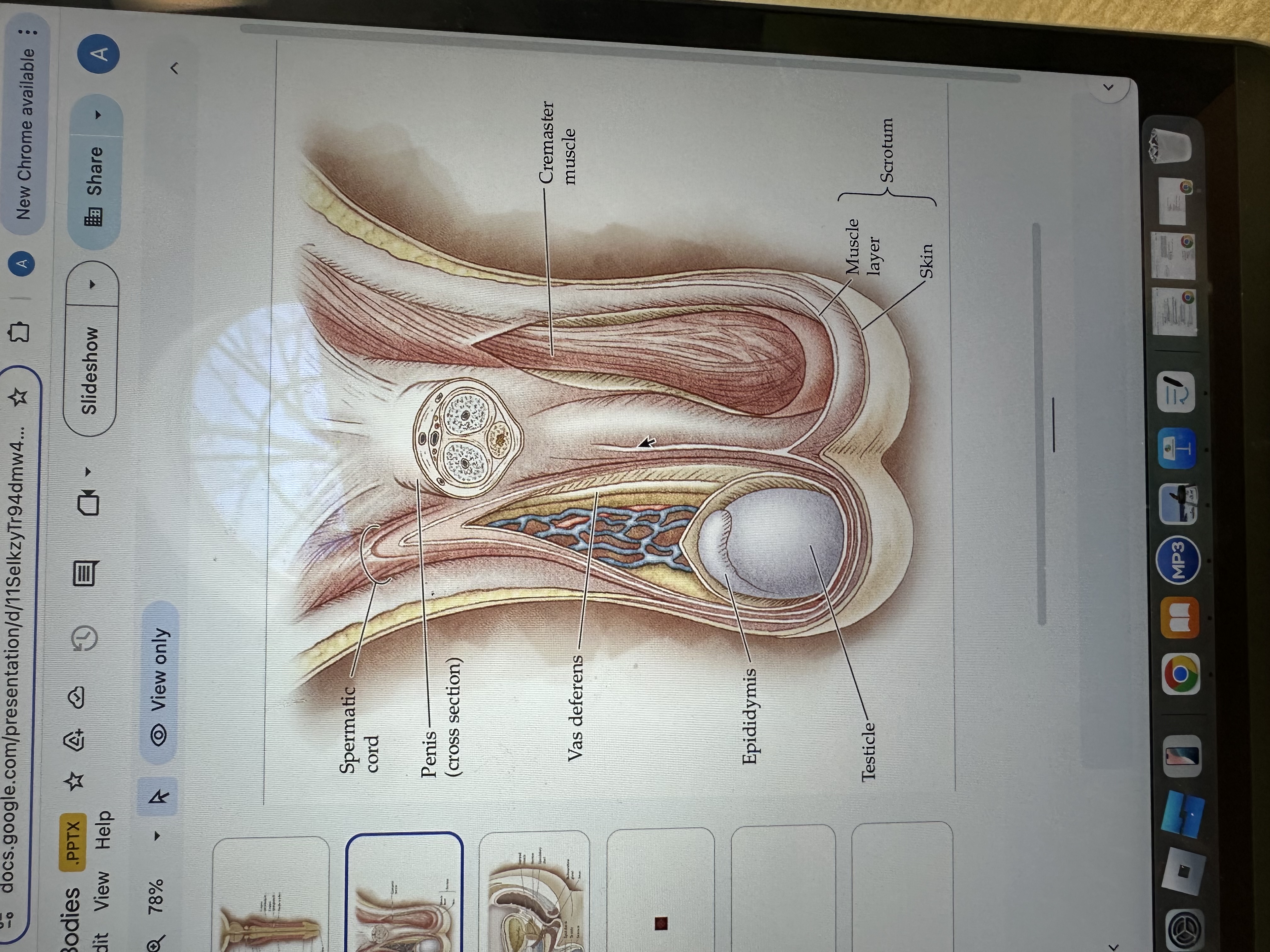
Testicles
Testicles are the male reproductive organs that produce sperm and hormones, primarily testosterone. They are located in the scrotum, which helps regulate their temperature for optimal function.
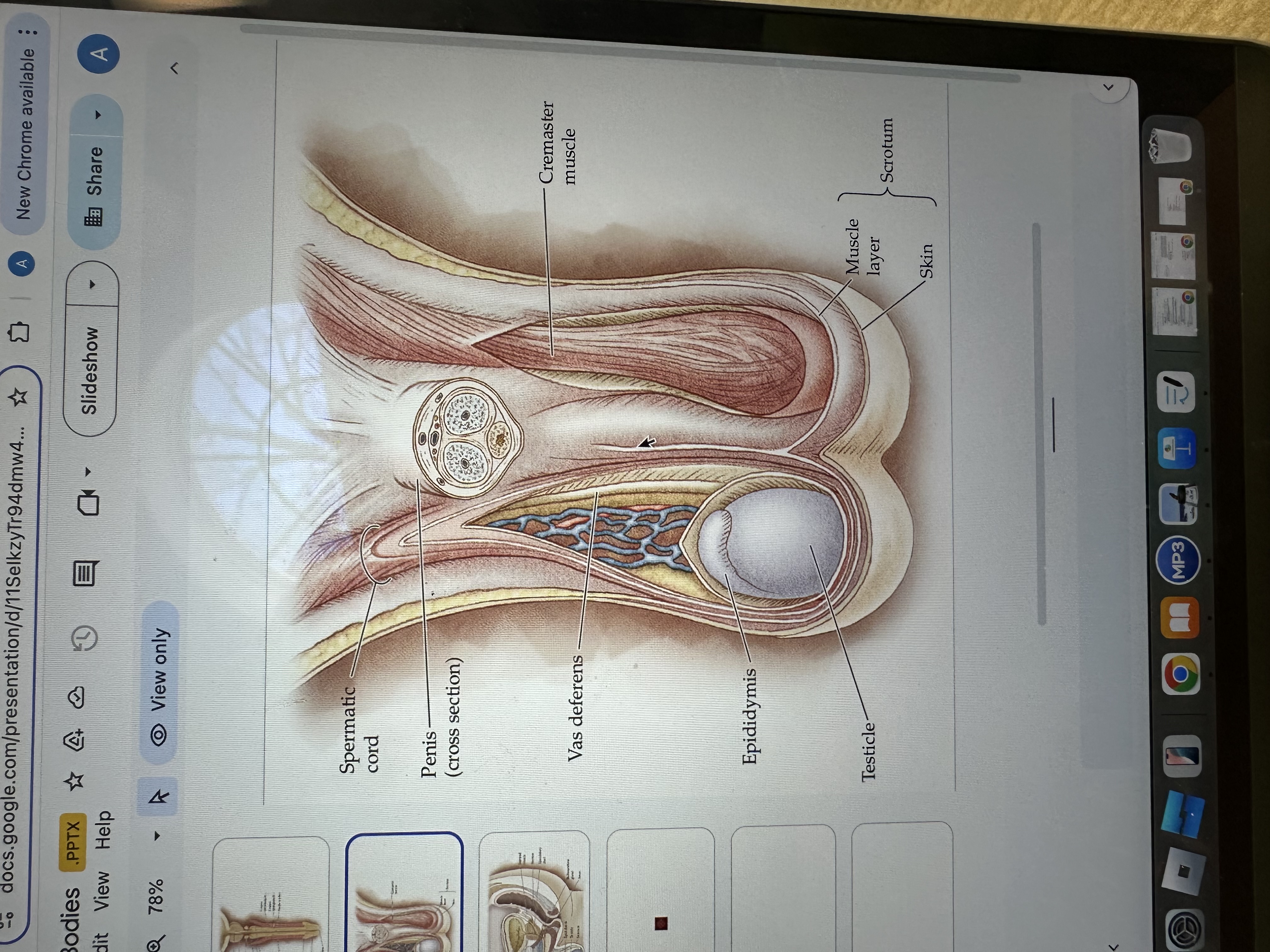
Epididymis
The epididymis is a coiled tube located at the back of each testis where sperm mature and are stored before ejaculation.
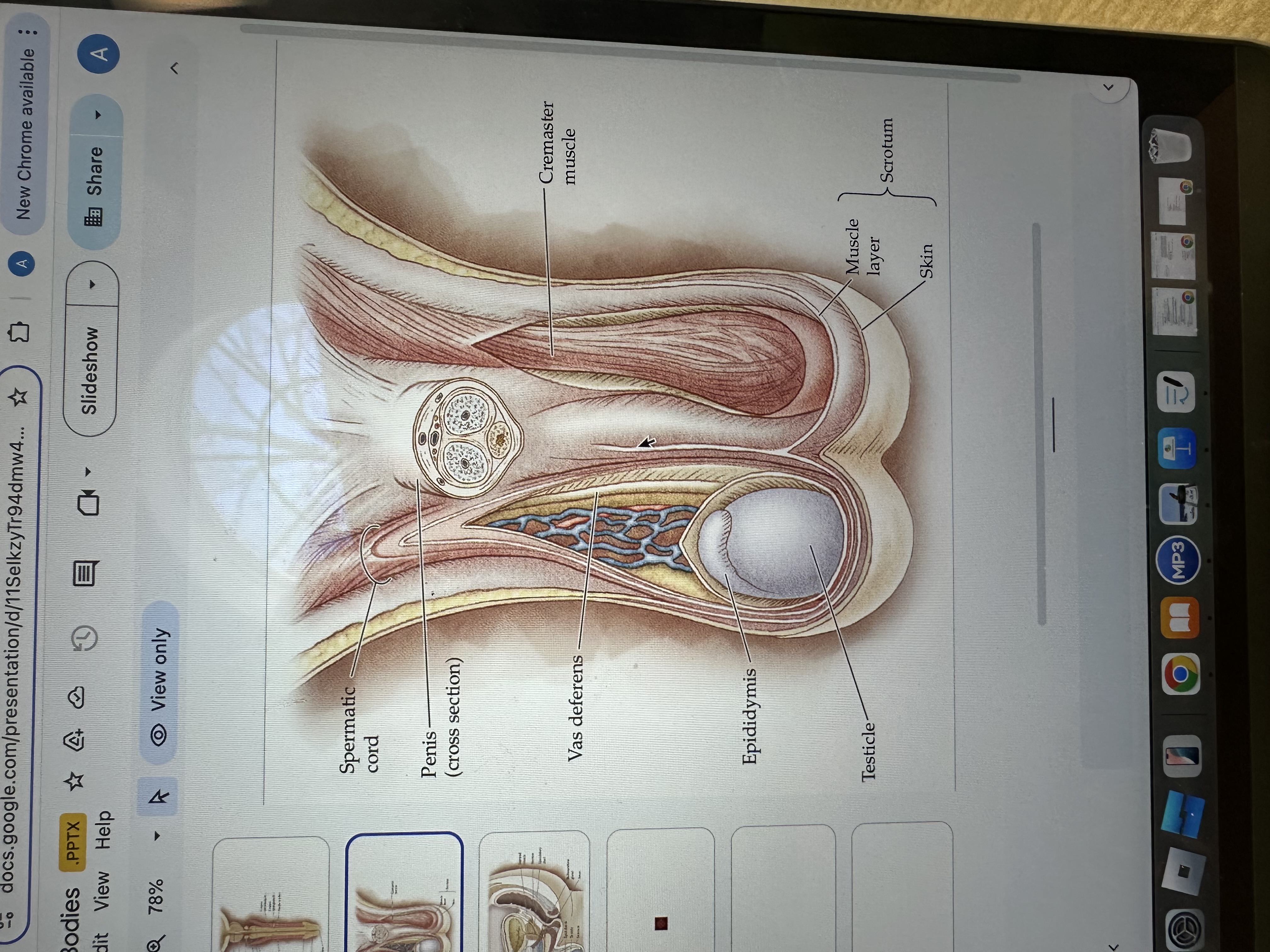
Vas deferens
The vas deferens is a muscular tube that transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct in preparation for ejaculation.
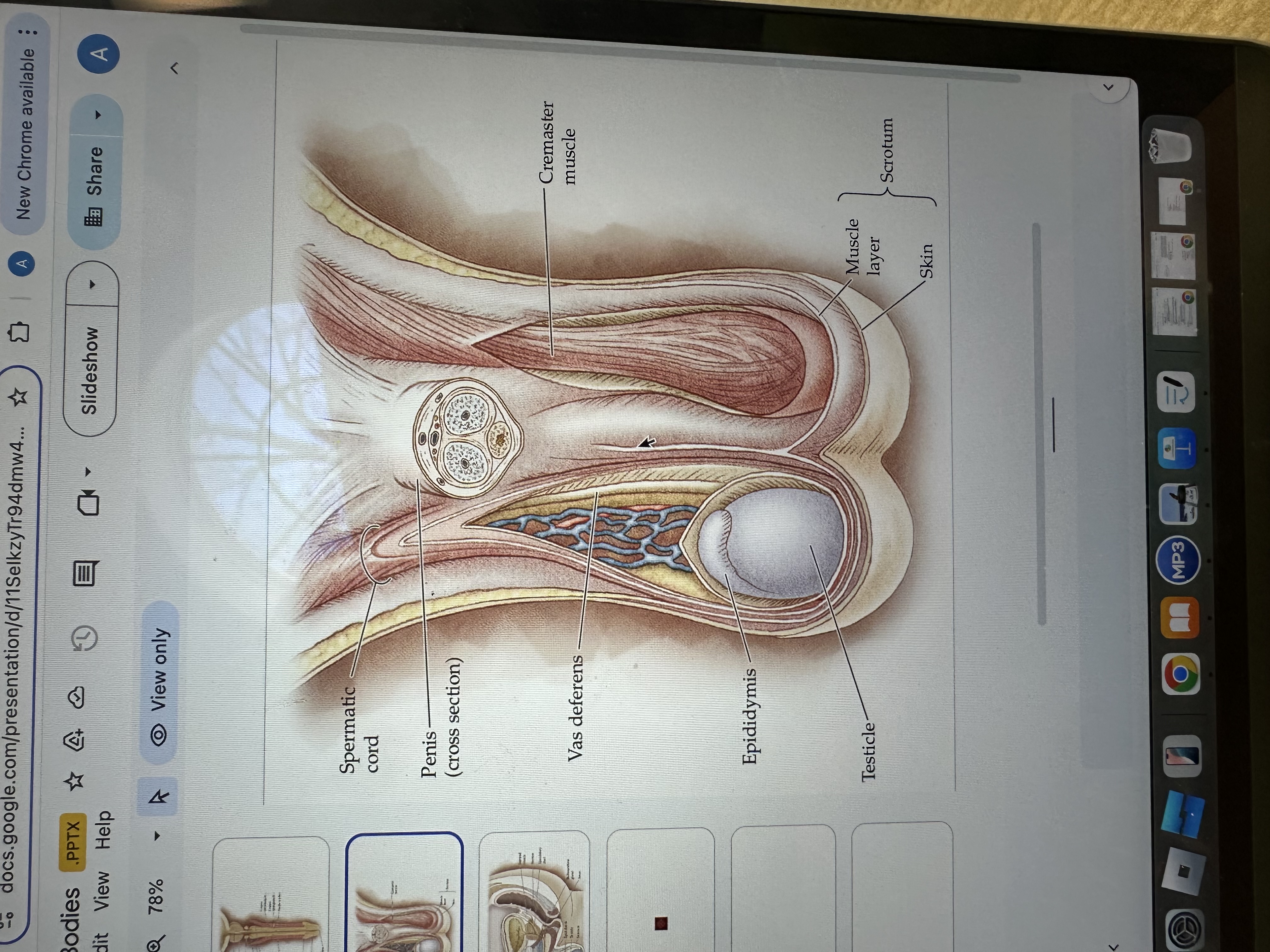
Cremaster Muscle
The cremaster muscle is a thin layer of muscle that surrounds the testes and can raise or lower them to regulate temperature for optimal sperm production.
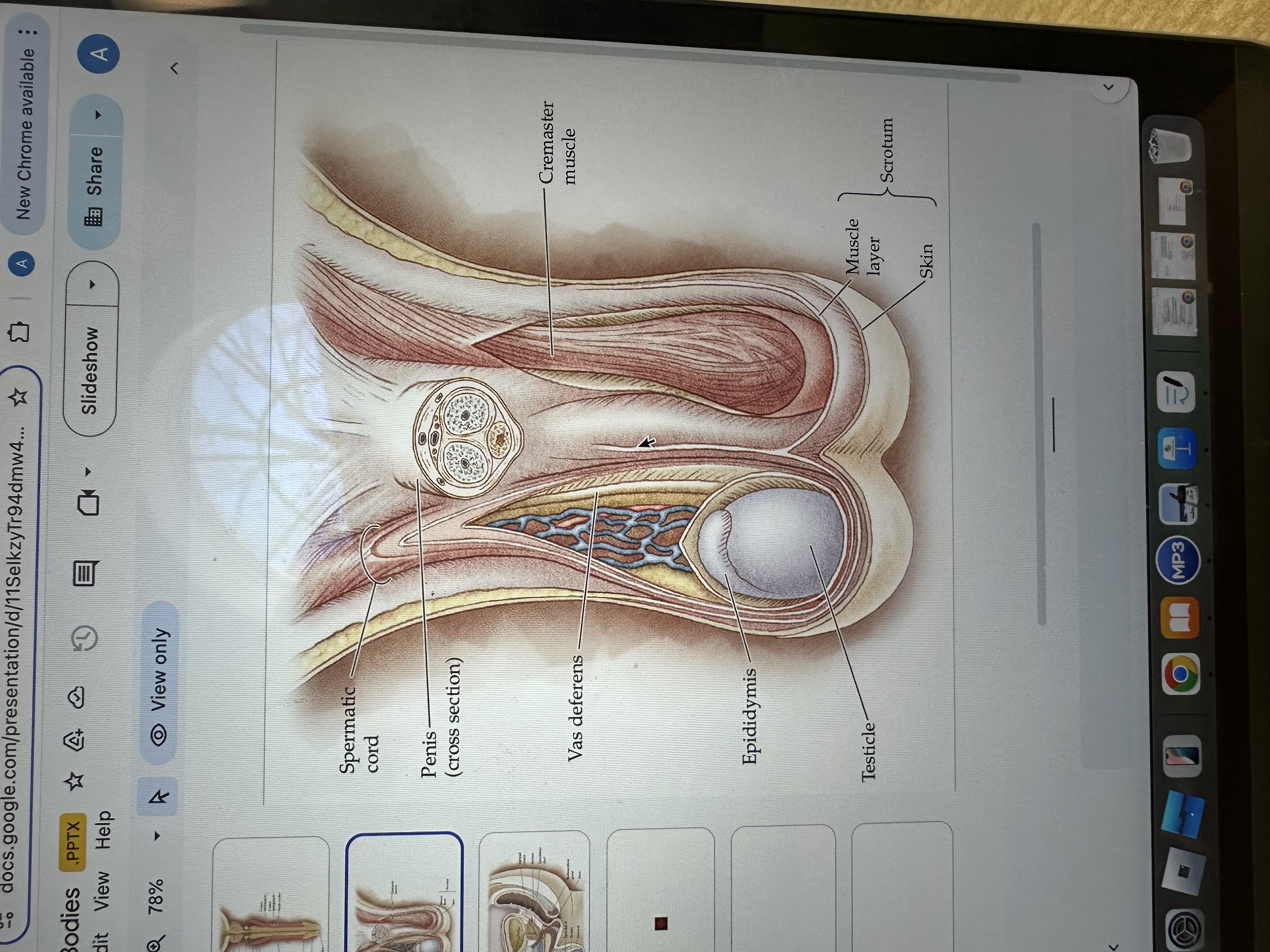
Penis
The penis is the male external sexual organ that facilitates sexual intercourse and serves as a conduit for urine and semen.
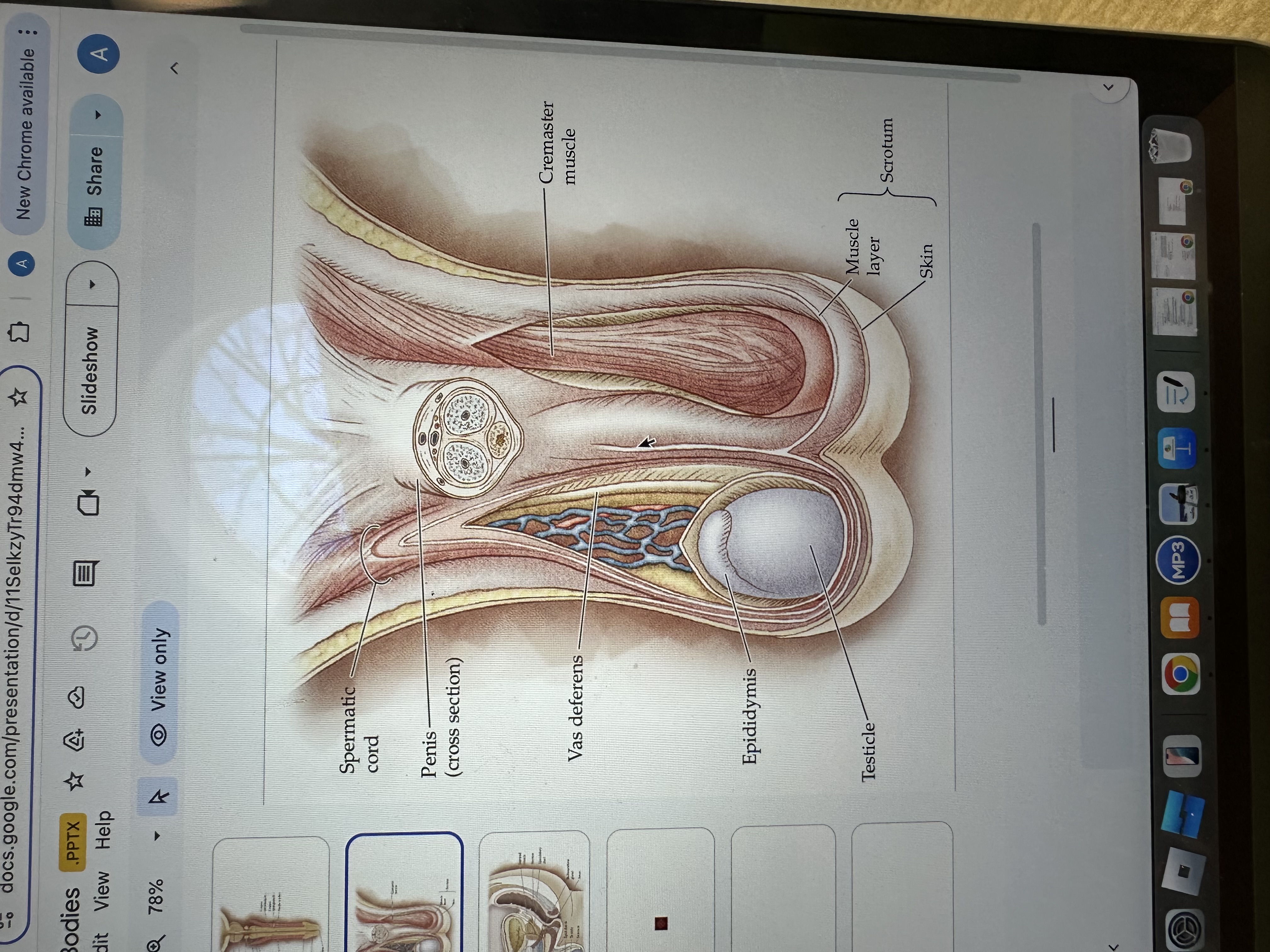
Spermatic cord
The spermatic cord is a bundle of ducts, blood vessels, nerves, and tissue that extends from the abdomen to each testis, anchoring the testis in place and providing connections for blood supply and sperm transport.
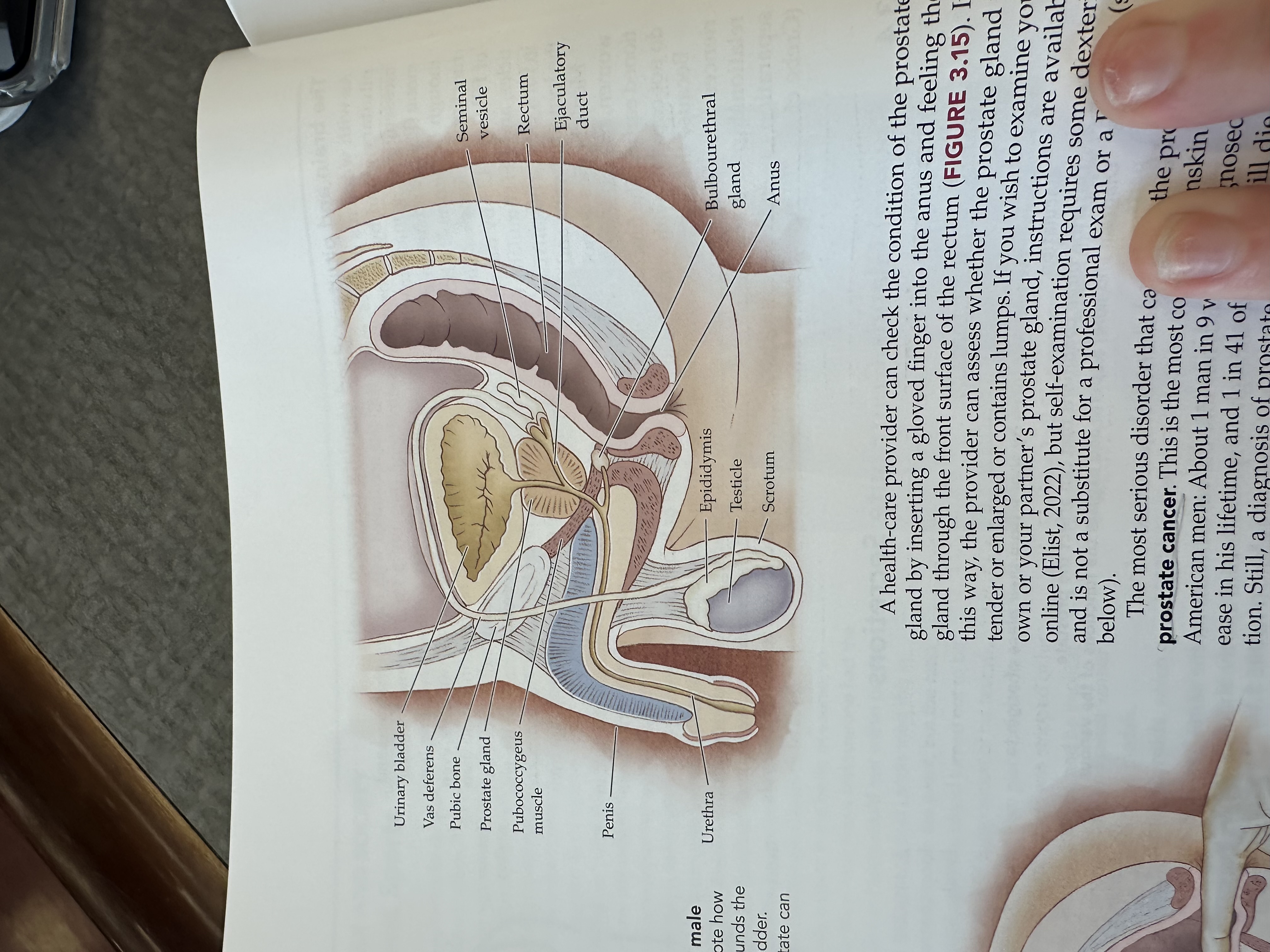
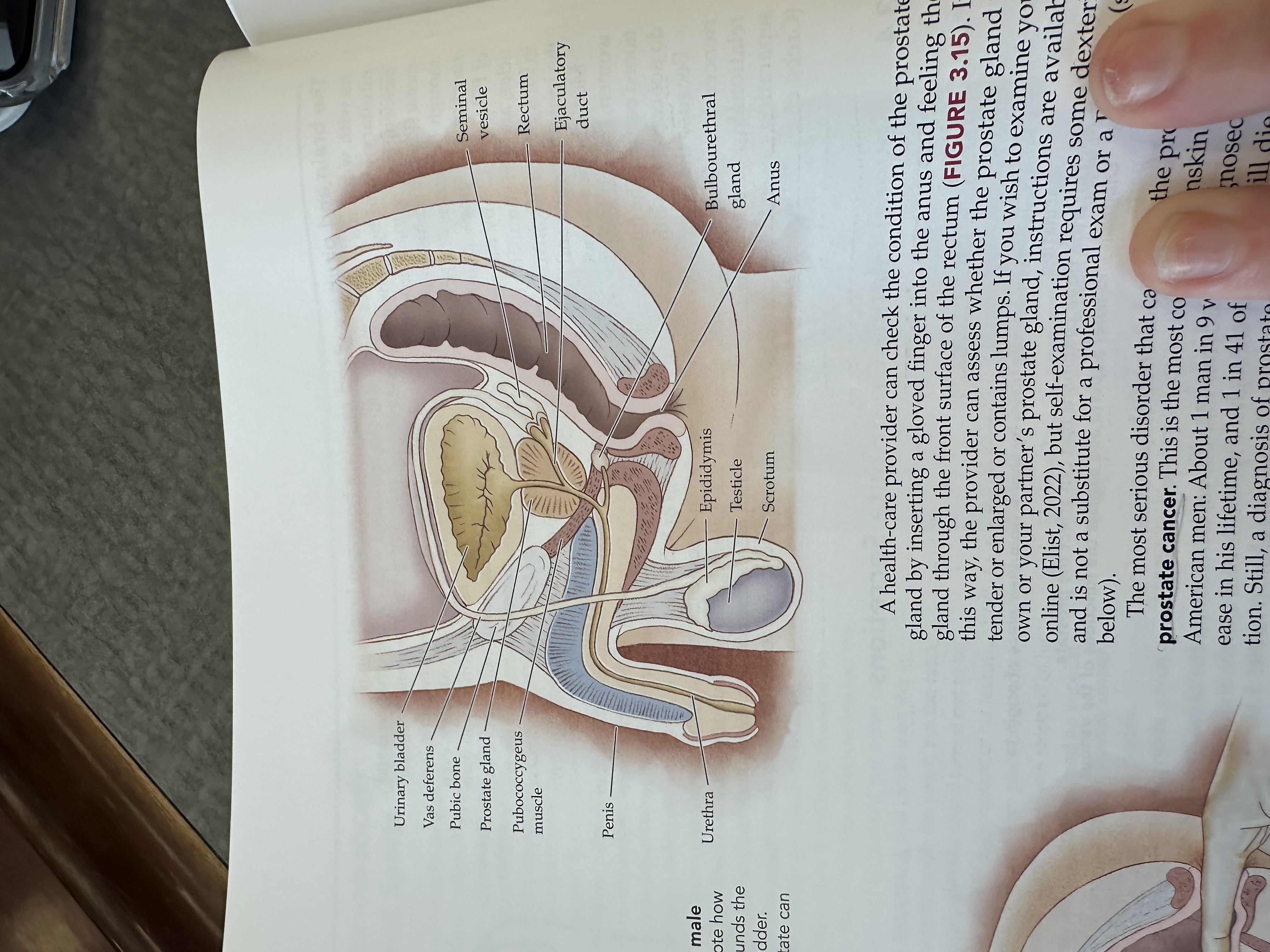
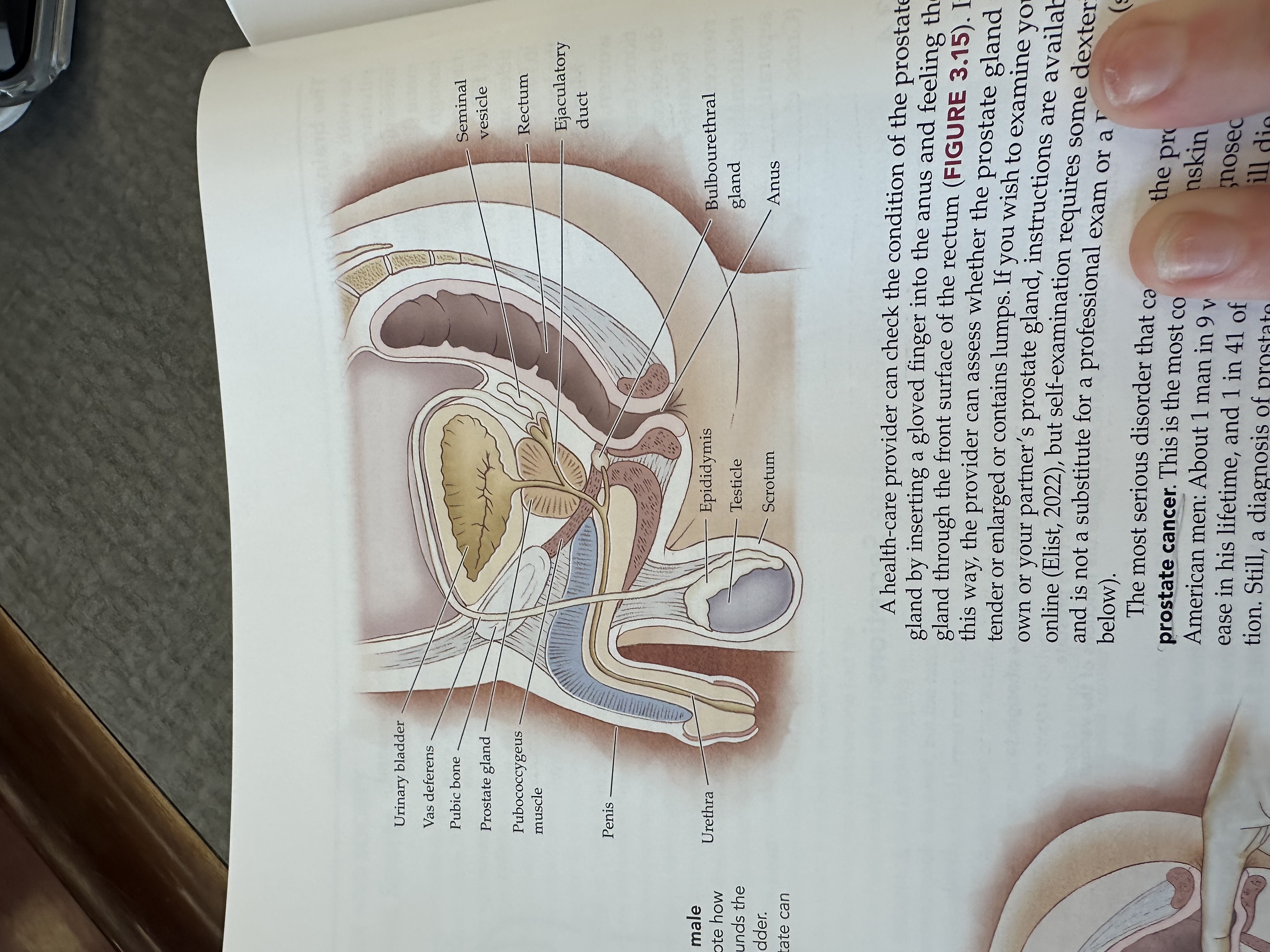
Pubic bone
The pubic bone is one of the bones that make up the pelvis, providing structural support and serving as an attachment point for muscles, with important roles in supporting reproductive organs.
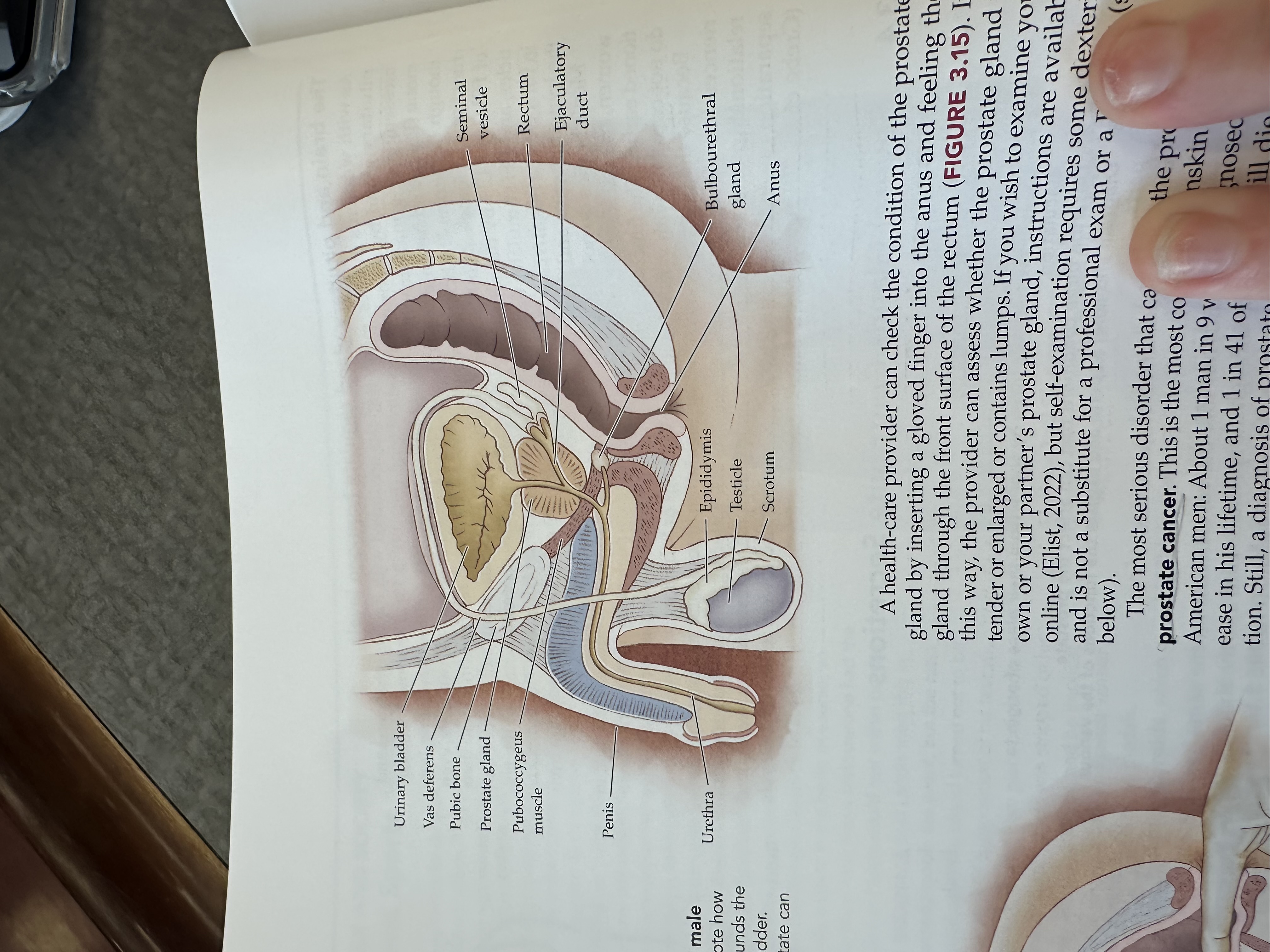
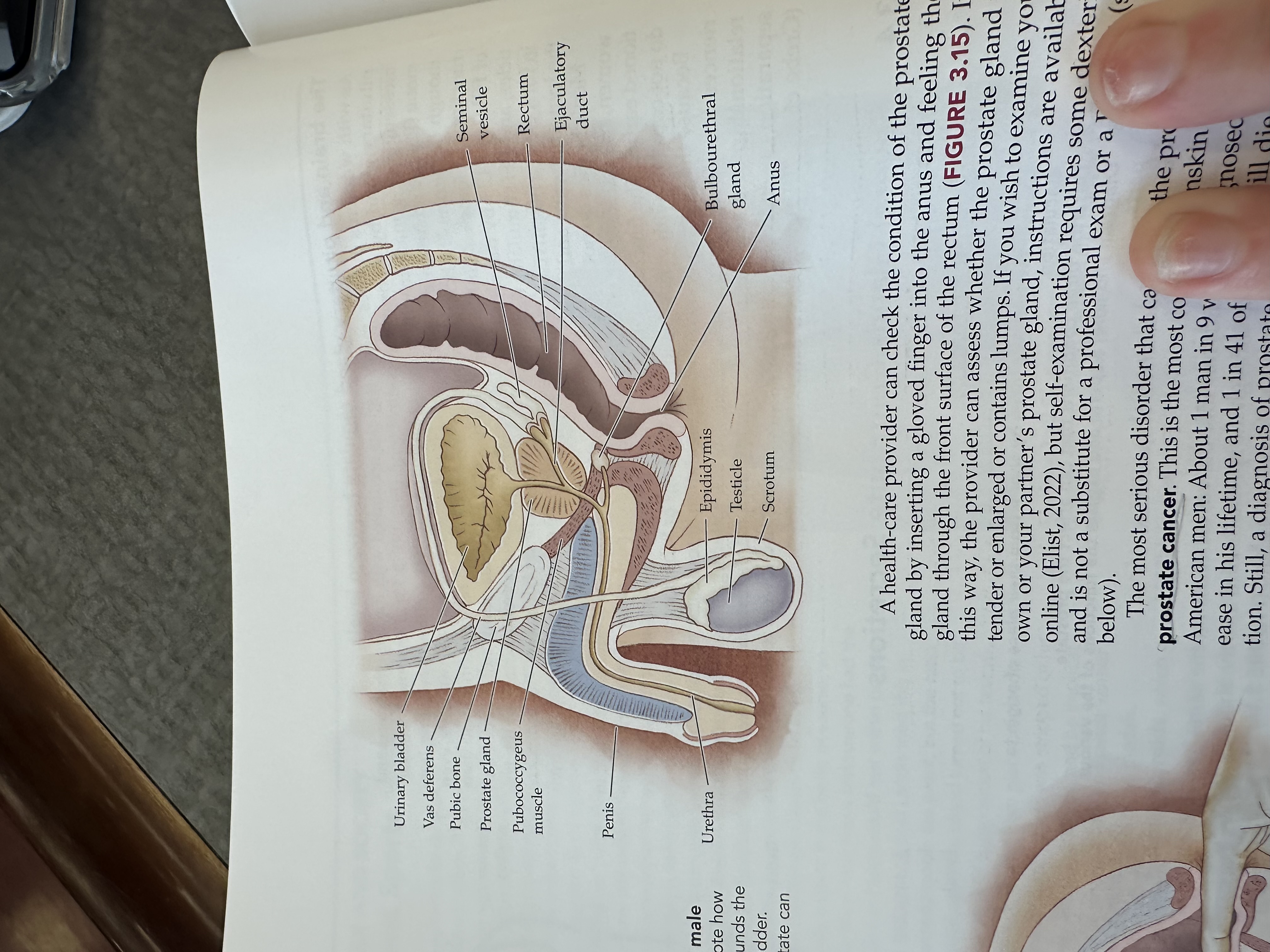
Urinary bladder
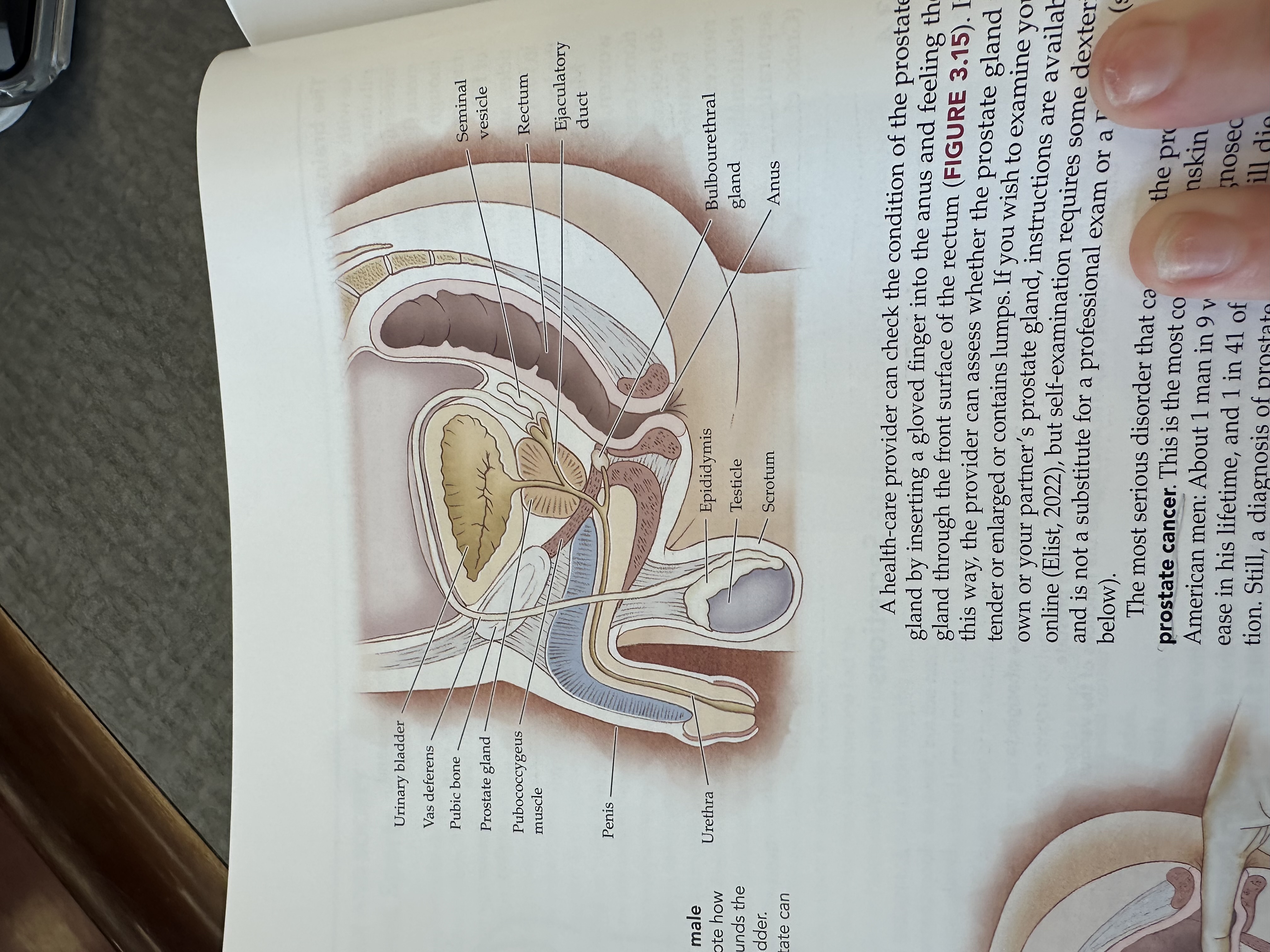
Gas deferens
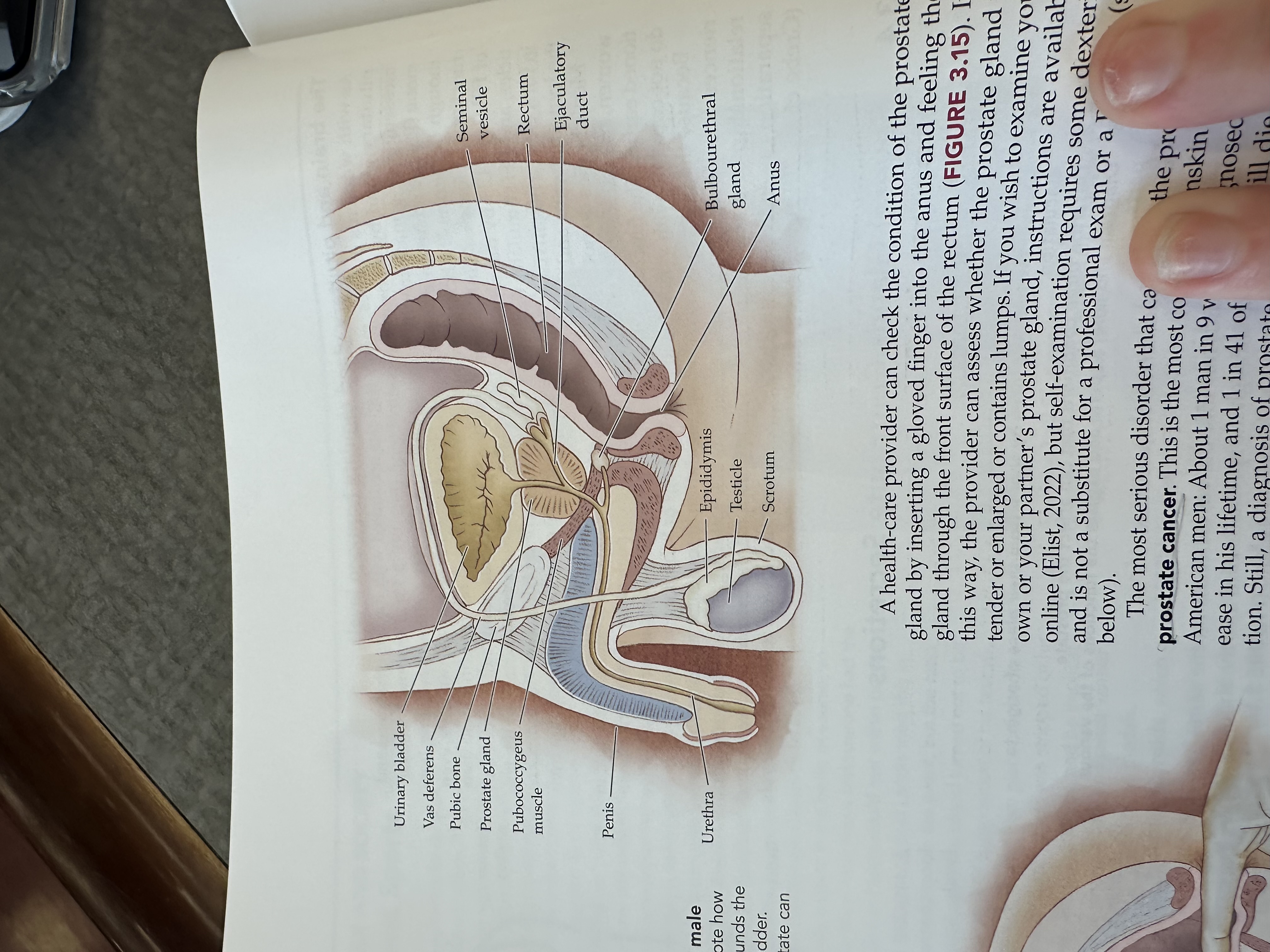
Prostate gland
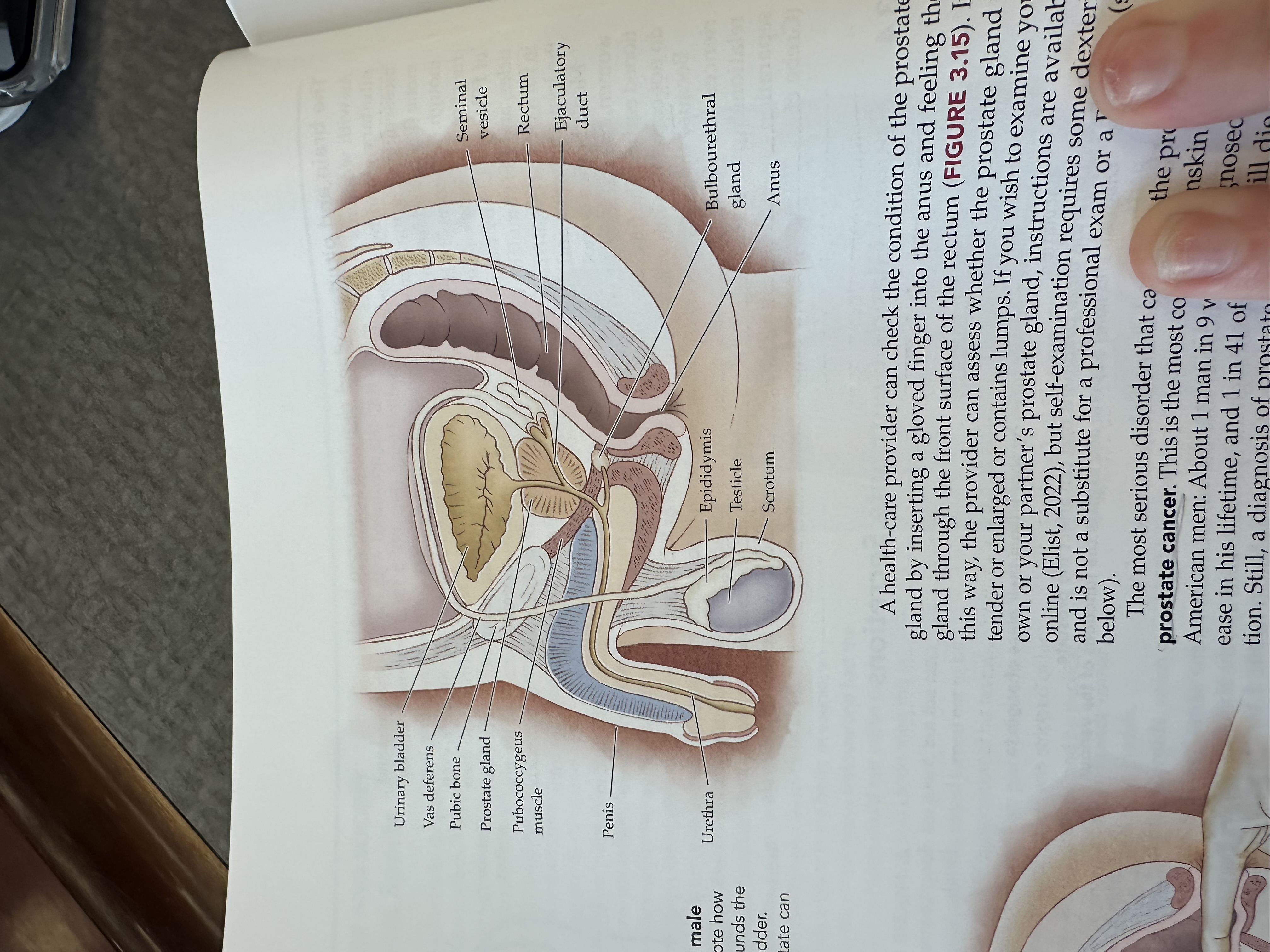
Pubococcygeus muscle
The pubococcygeus muscle is a part of the pelvic floor muscles, supporting the pelvic organs and playing a role in urinary and fecal continence.
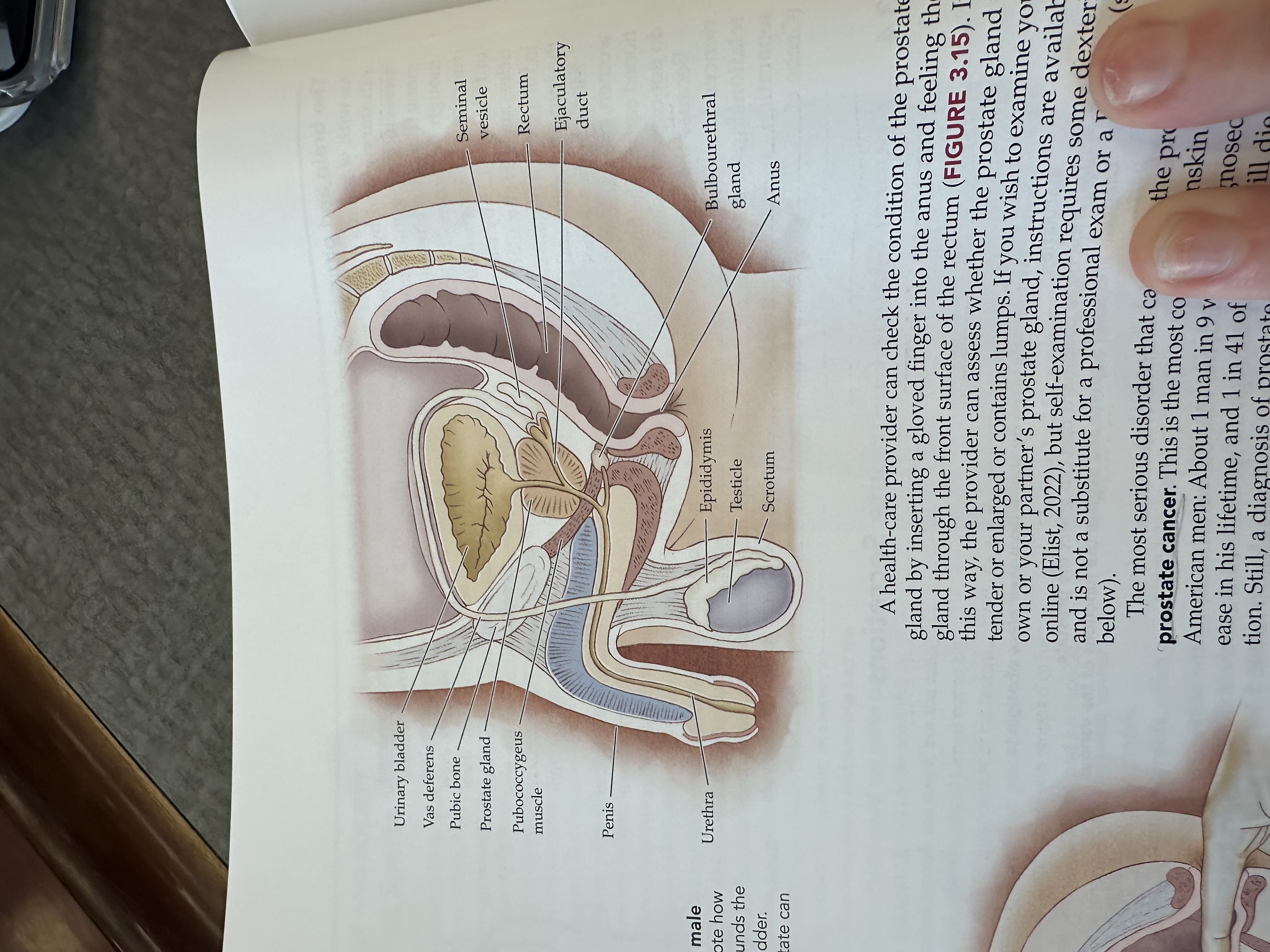
Penis
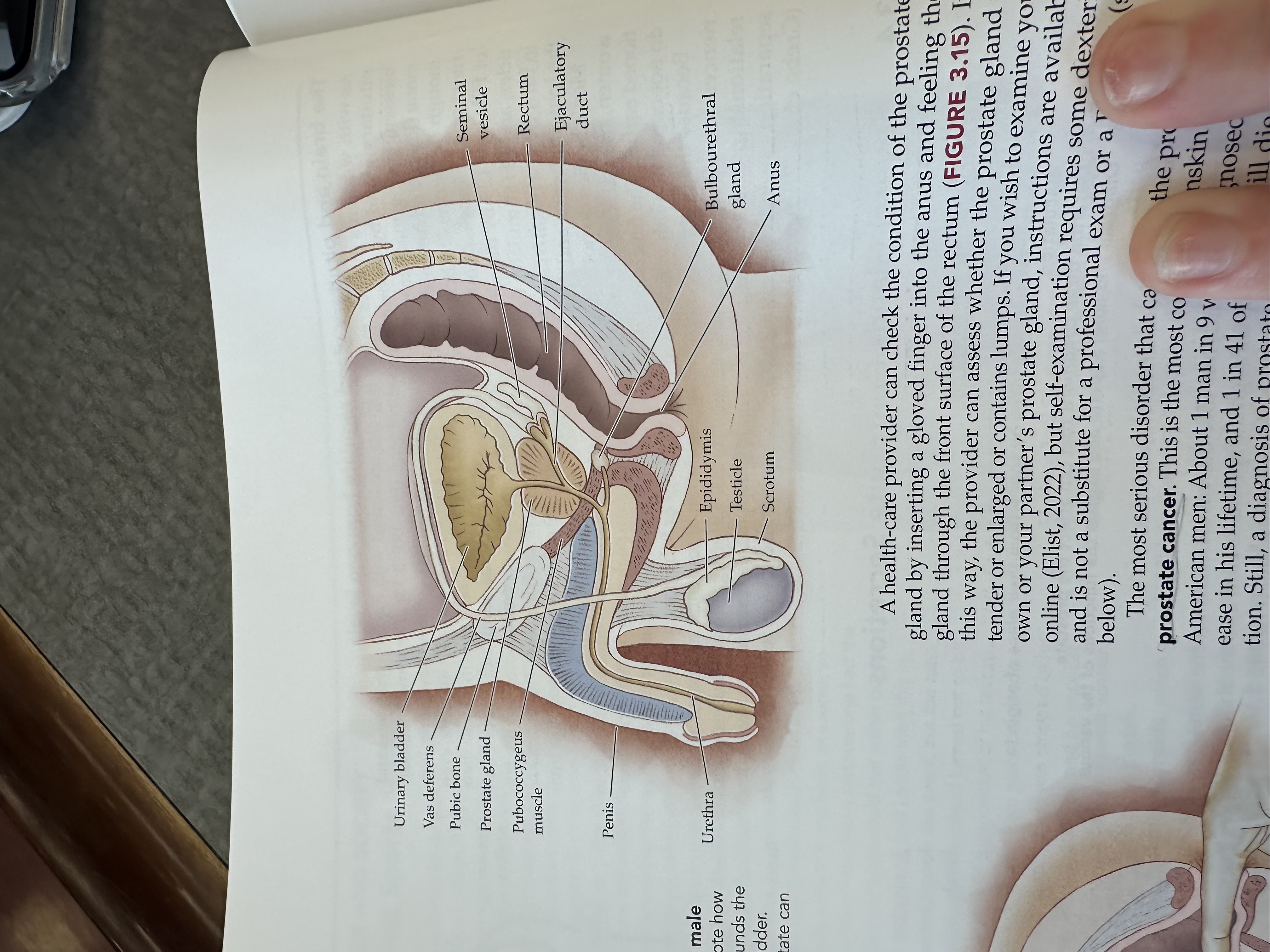
Urethra
Epididymis
Testicles
Scrotum
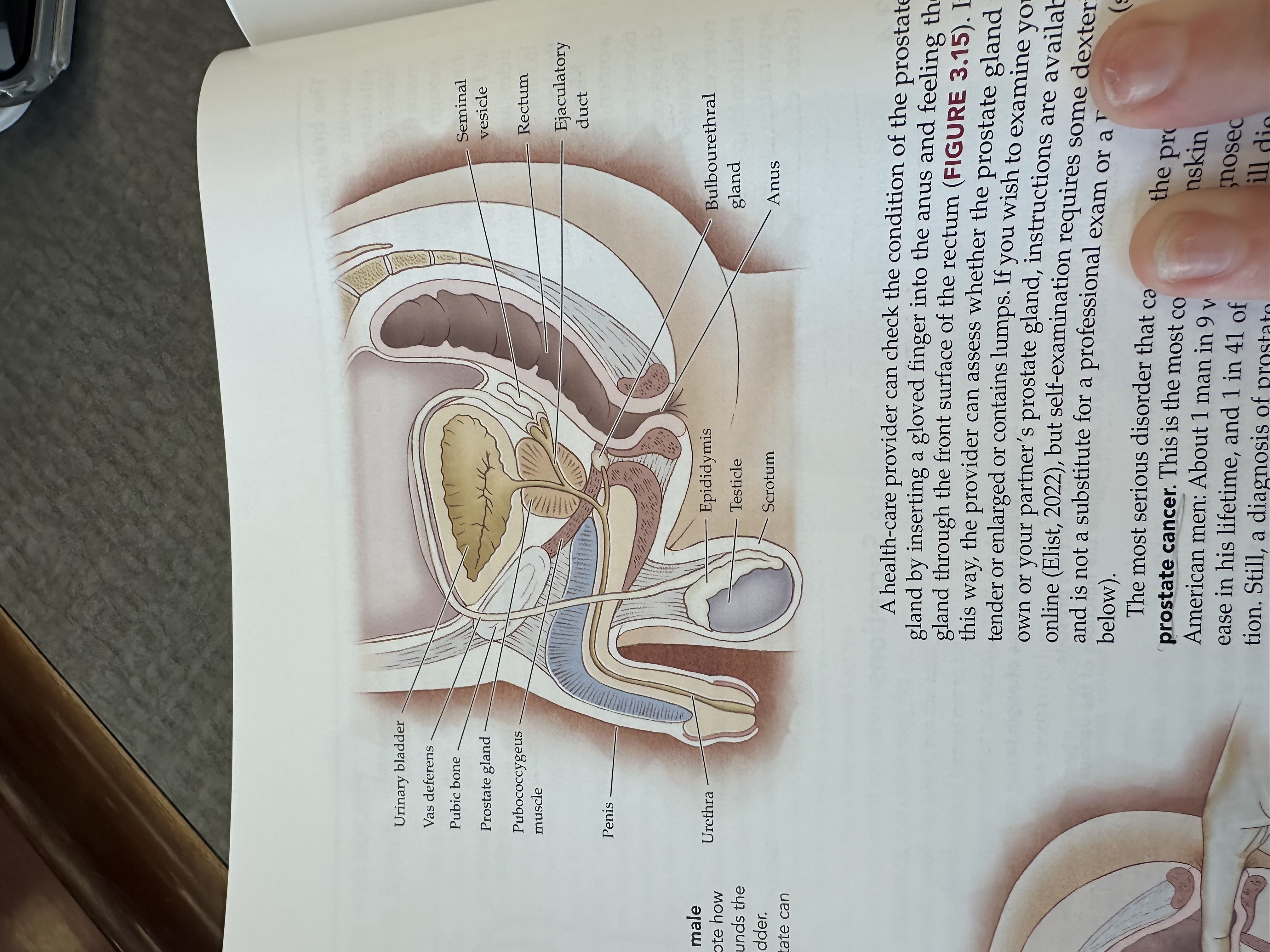
Bulbouretheral gland
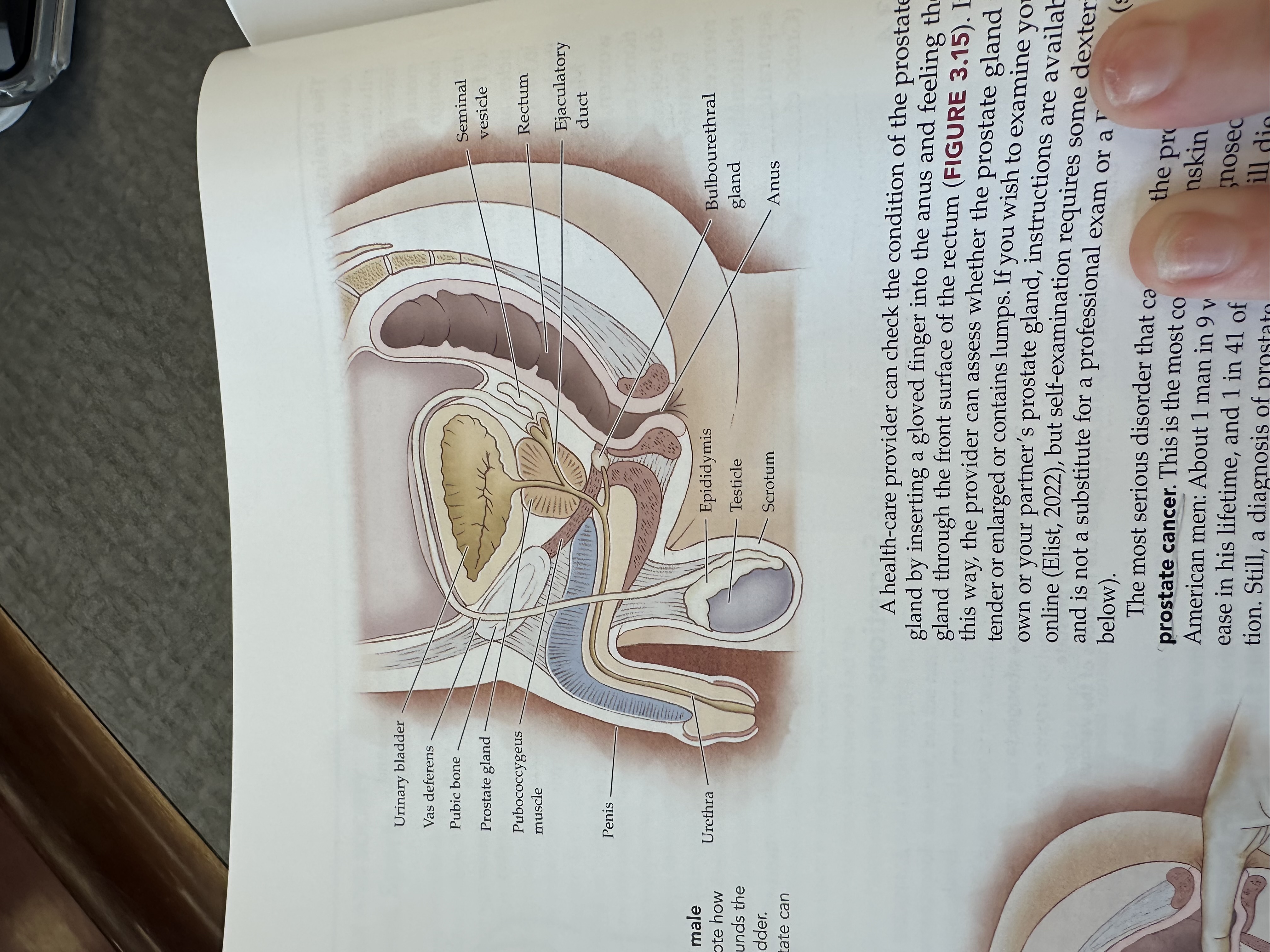
Anus
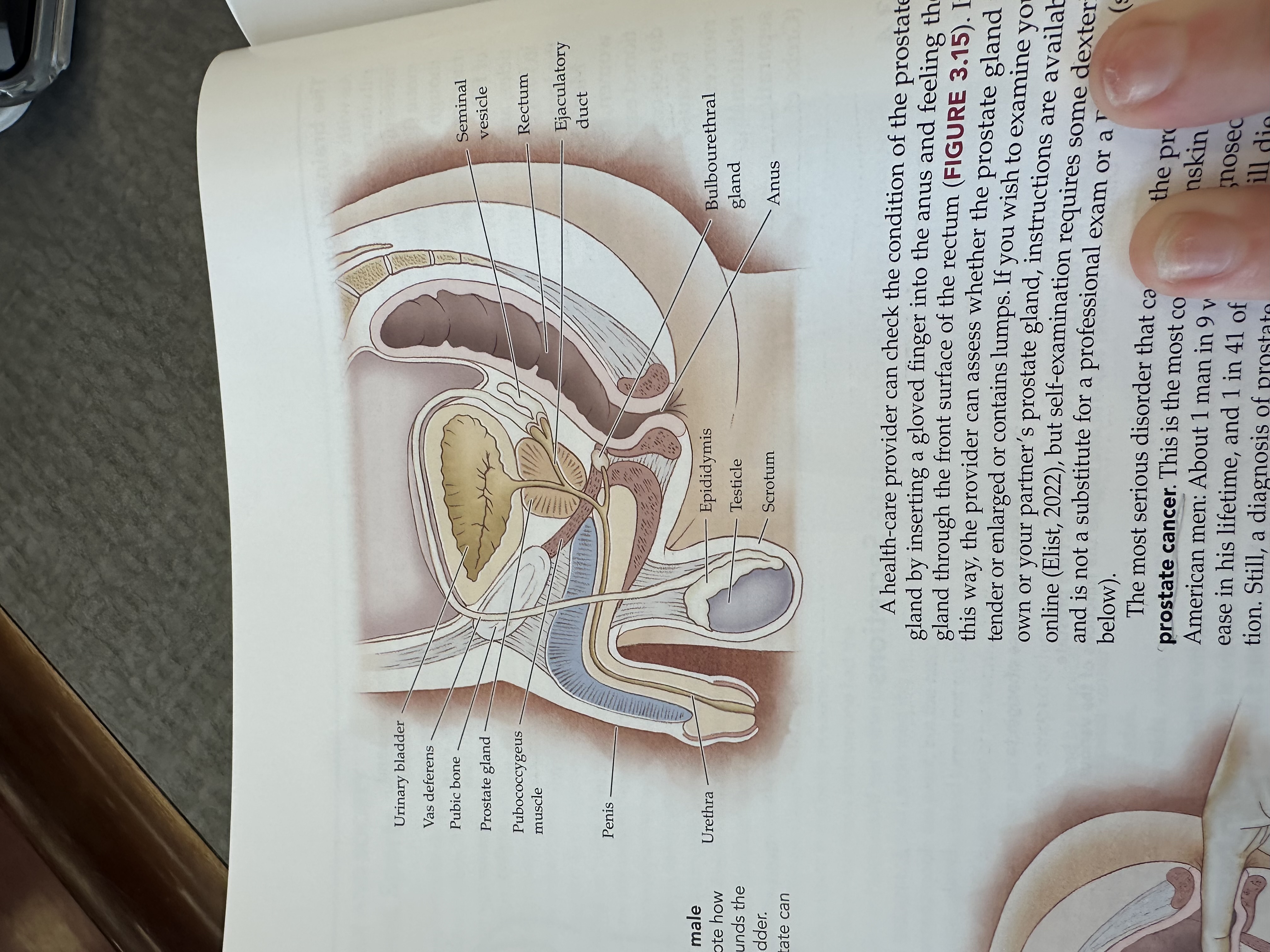
Ejaculatory duct
The ejaculatory duct is a tube that carries sperm from the vas deferens and seminal fluid from the prostate gland into the prostatic urethra during ejaculation.

Rectum
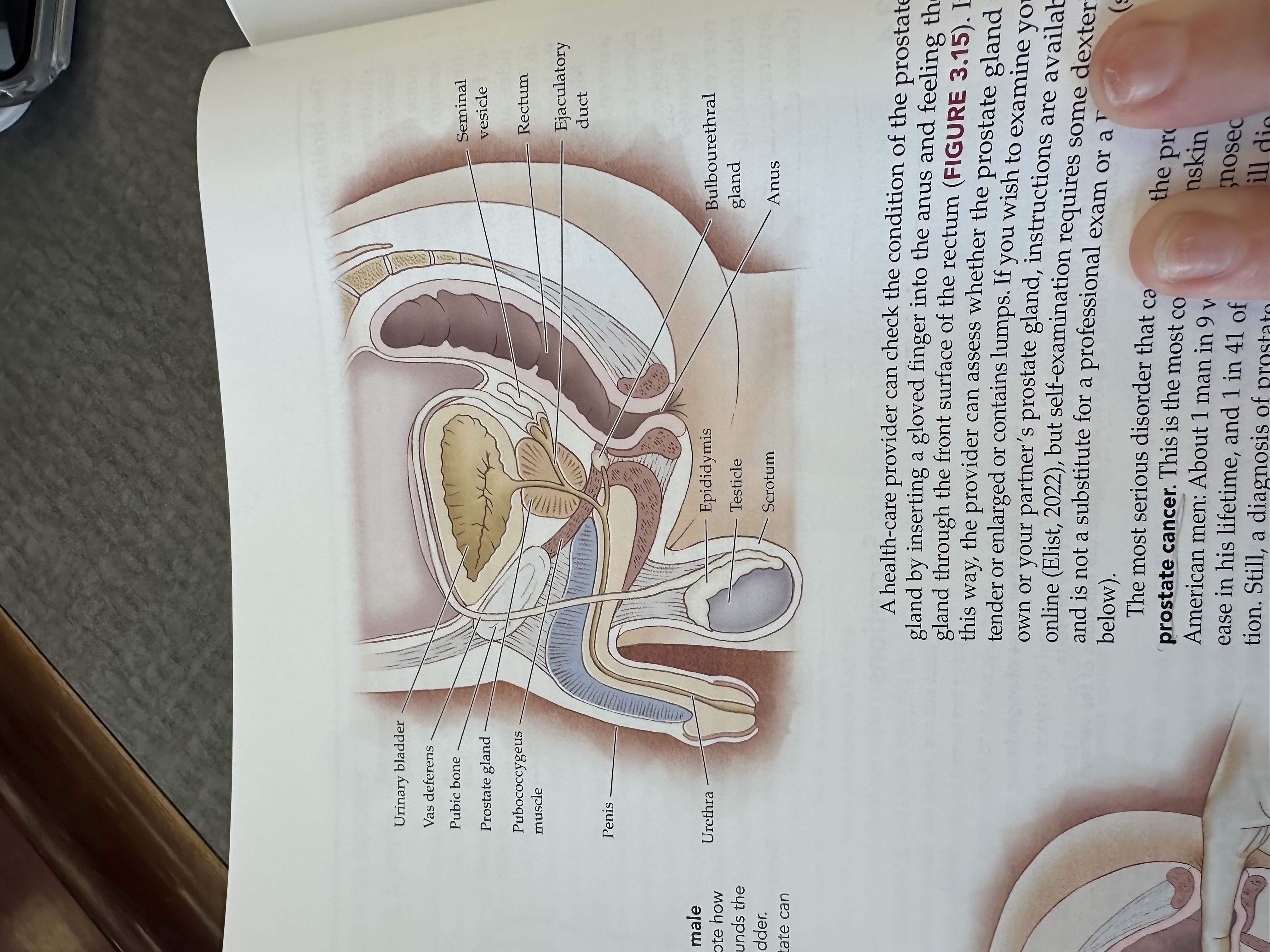
Seminal vesicle
The seminal vesicle is a pair of glands located behind the bladder that produce a fluid rich in sugar that nourishes sperm and forms a significant portion of semen.