Nervous System III - Special Senses
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
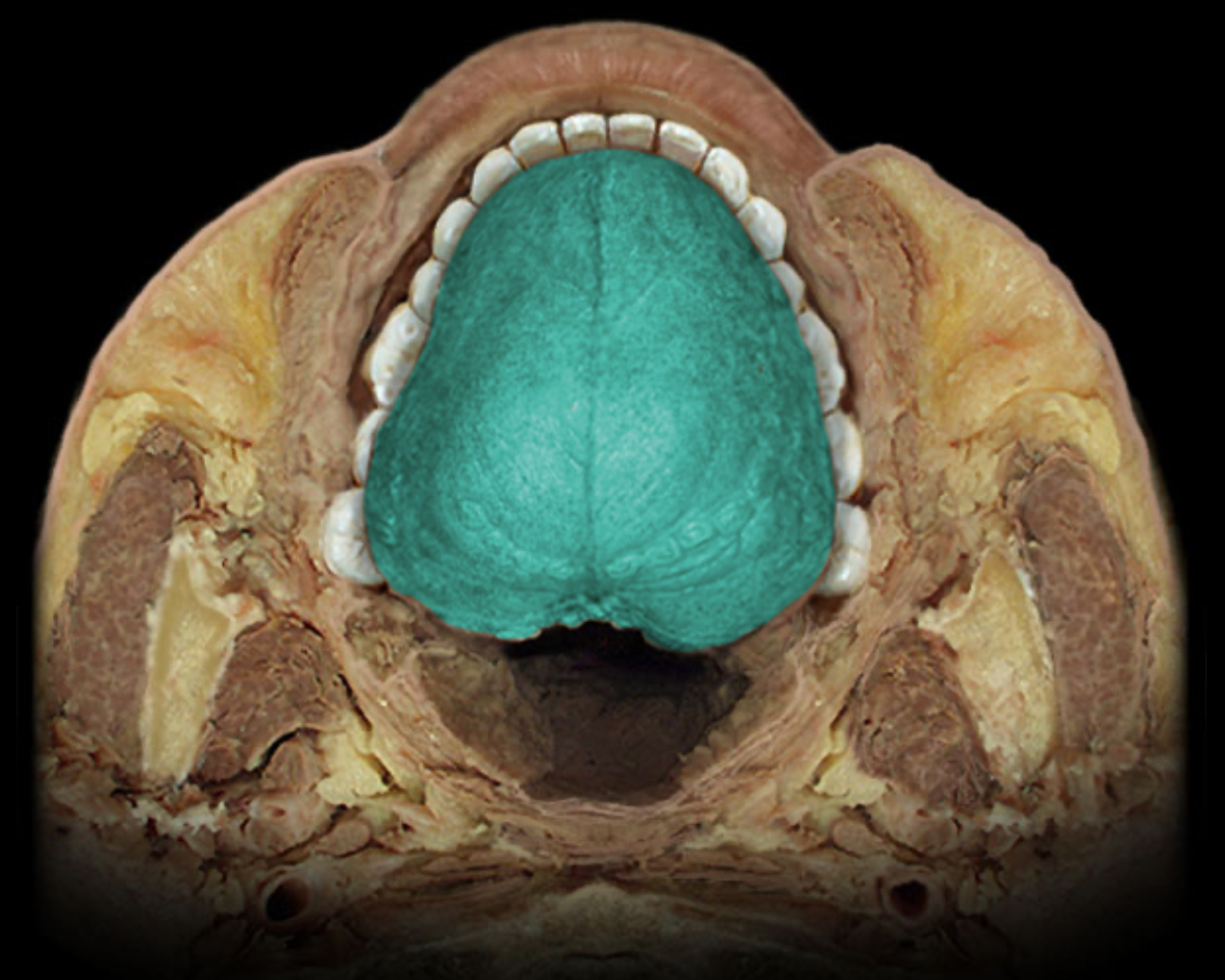
Dorsum of tongue
Location:
Superior surface of tongue
Description:
Mucous membrane contains taste buds
Dense concentration of papillae gives dorsal surface "felt-like" appearance
Divided by V-shaped sulcus terminalis into anterior (oral) part and posterior (pharyngeal)
Anterior part has median furrow
Posterior part is nodular due to presence of lingual tonsils
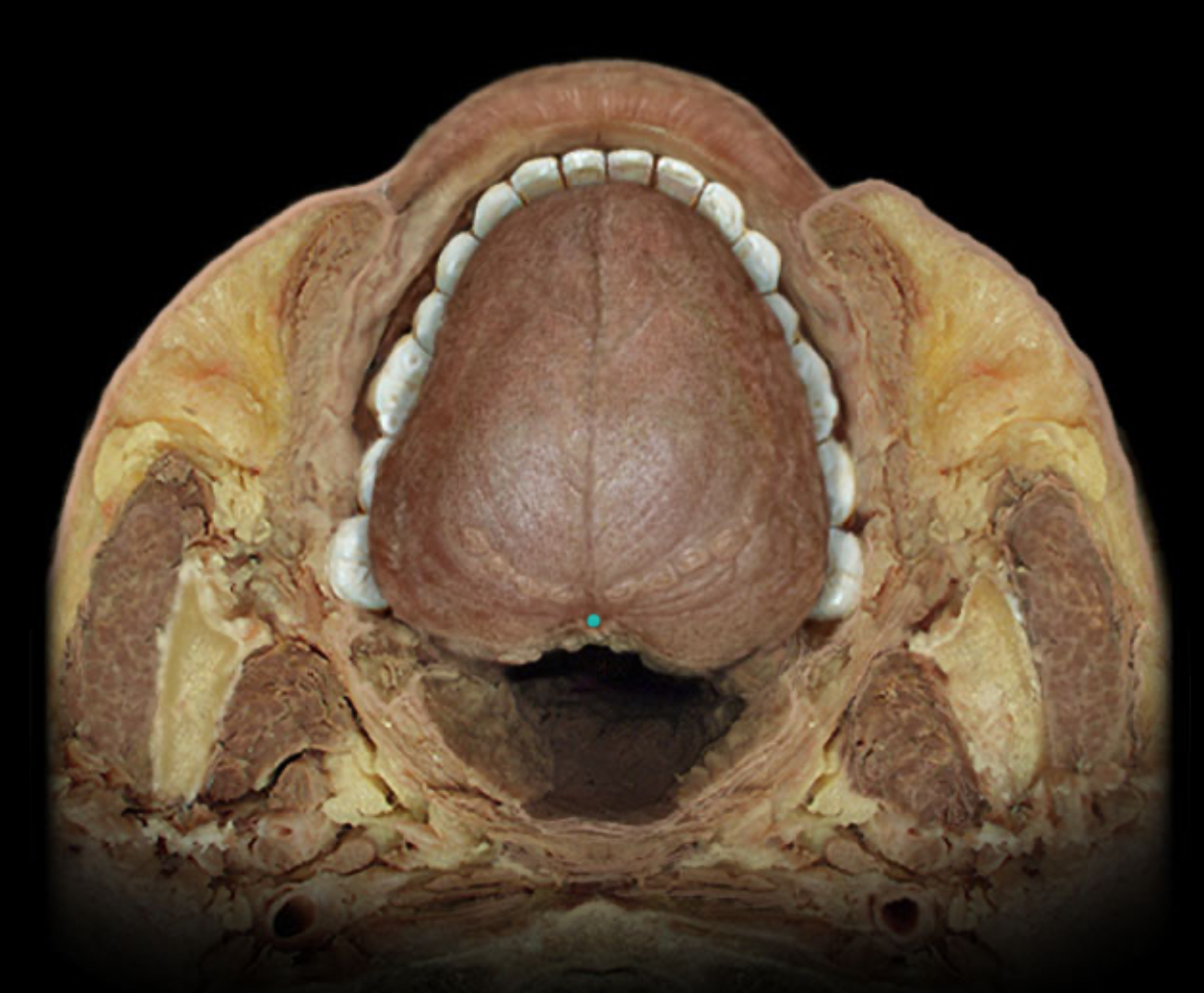
Foramen cecum of tongue
Location:
Tongue (dorsum)
Description:
Small pit located at the apex of the terminal sulcus
Comment:
Remnant of embryonic thyroglossal duct
General sensory distribution of glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX)
Location:
Middle ear
Posterior 1/3 of tongue
Pharynx
Comment:
General sensation includes pain, touch, and temperature
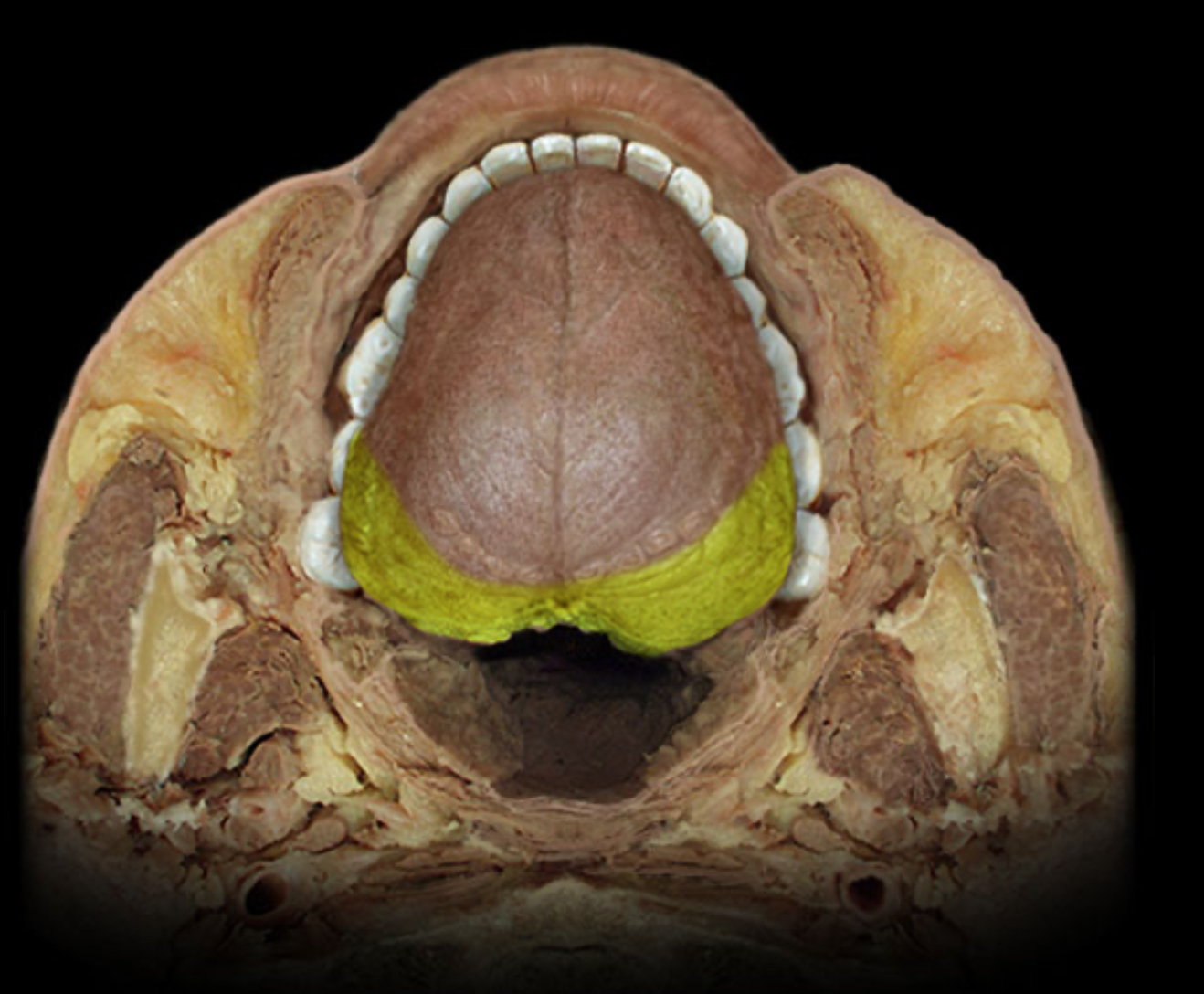
Lingual tonsil
Location:
Tongue (posterior part)
Description:
Collection of lymphoid nodules in submucosal connective tissue
Not surrounded by connective tissue capsule
Function:
Traps foreign material and facilitates identification by lymphocytes
Produces lymphocytes
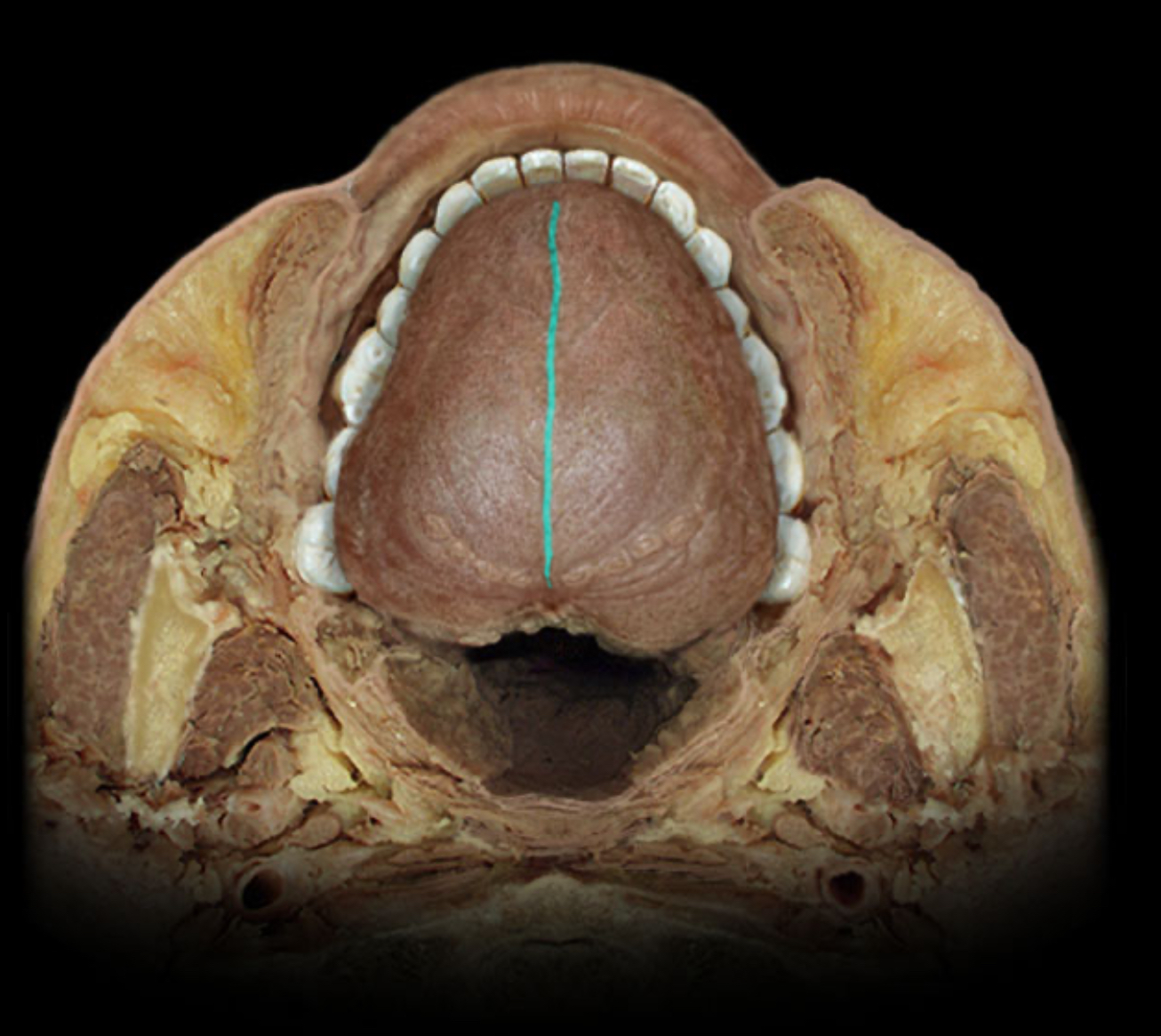
Median sulcus of tongue
Location:
Tongue (dorsum)
Description:
Shallow median longitudinal groove on anterior part of tongue
Comment:
Indicates position of underlying midline fibrous septum
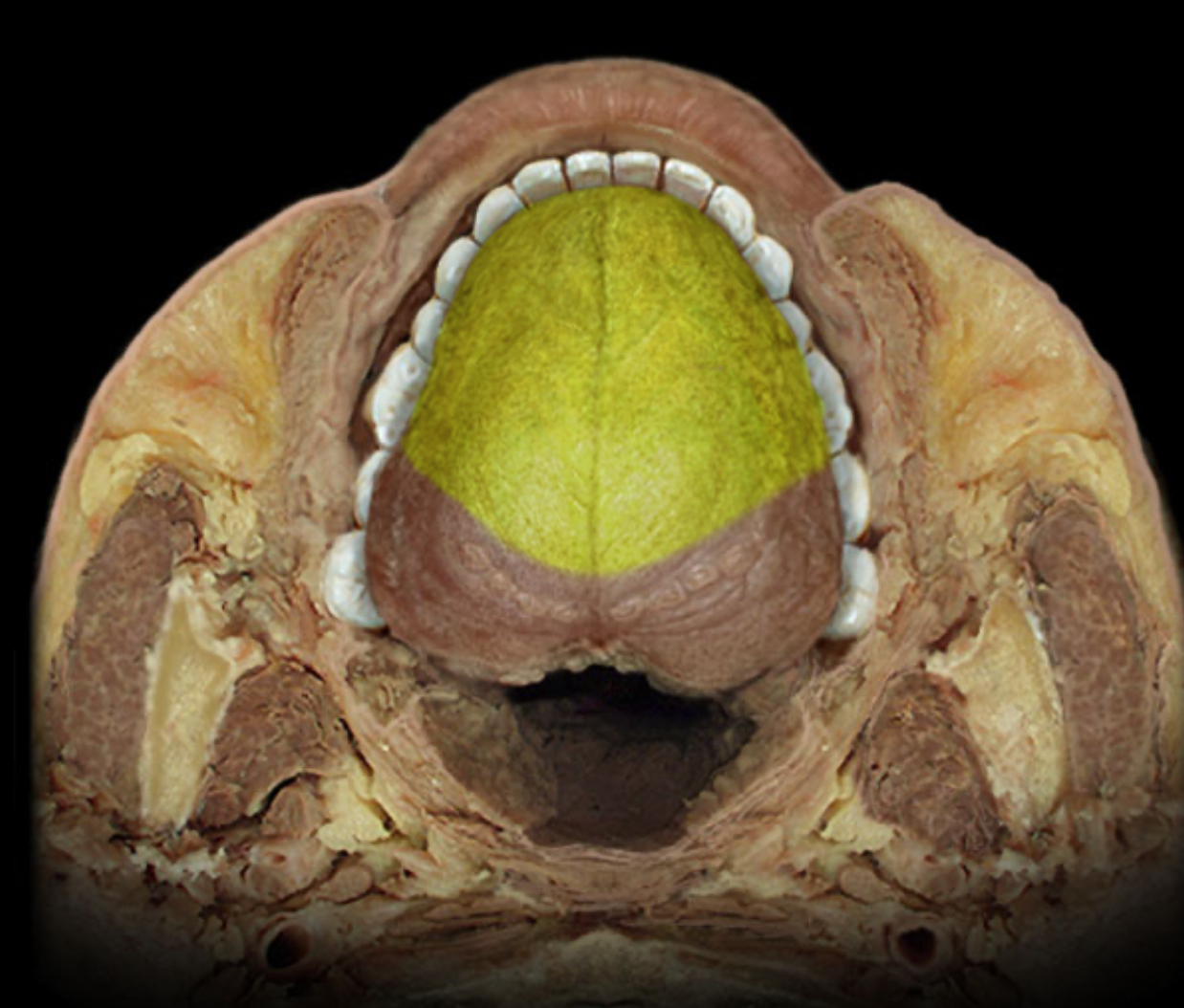
Special sensory distribution of chorda tympani
Location:
Anterior 2/3 of tongue (information from taste buds)
Comment:
Special sensation includes smell, vision, taste, hearing, and balance
Chorda tympani is branch of facial nerve (CN VII) that joins lingual nerve (a branch of CN V3) in infratemporal fossa
Chorda tympani also contains preganglionic parasympathetic axons to submandibular ganglion
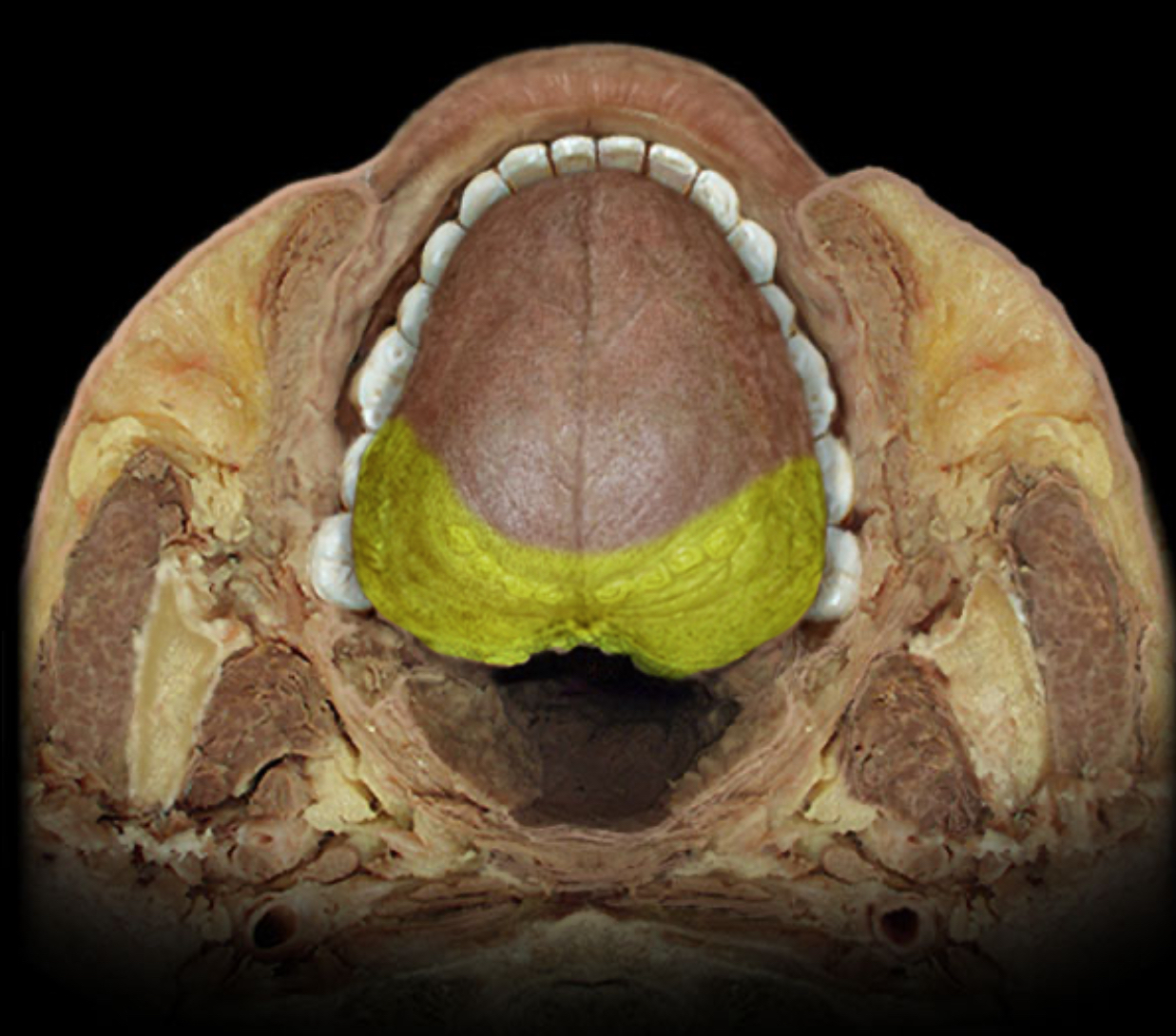
Special sensory distribution of glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX)
Location:
Posterior 1/3 of tongue (information from taste buds)
Comment:
Special sensation includes smell, vision, taste, hearing, and balance
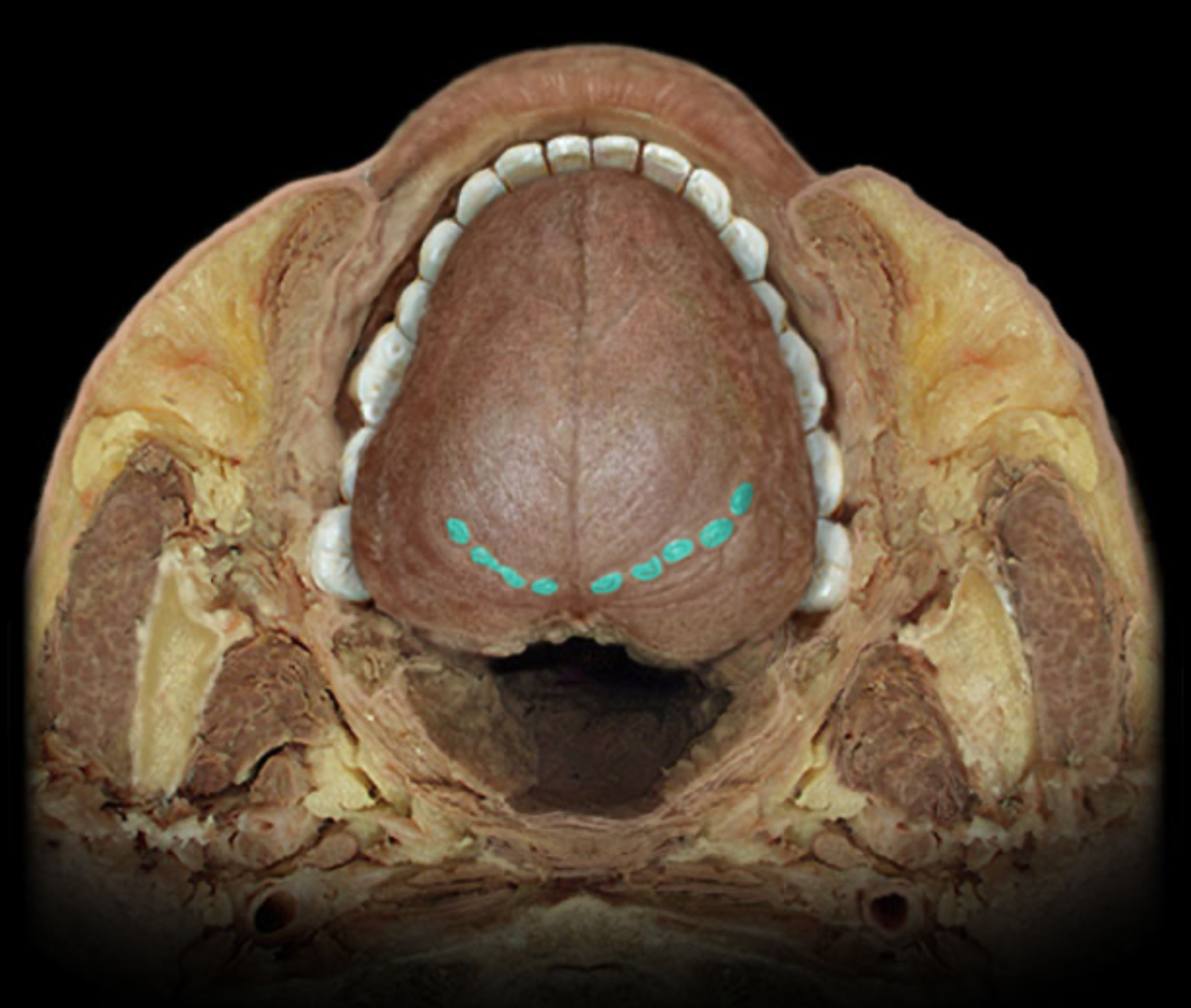
Terminal sulcus of tongue
Location:
Tongue (dorsum)
Description:
"V"-shaped groove on posterior part of tongue
Comment:
Separates anterior (oral) and posterior (pharyngeal) parts of tongue
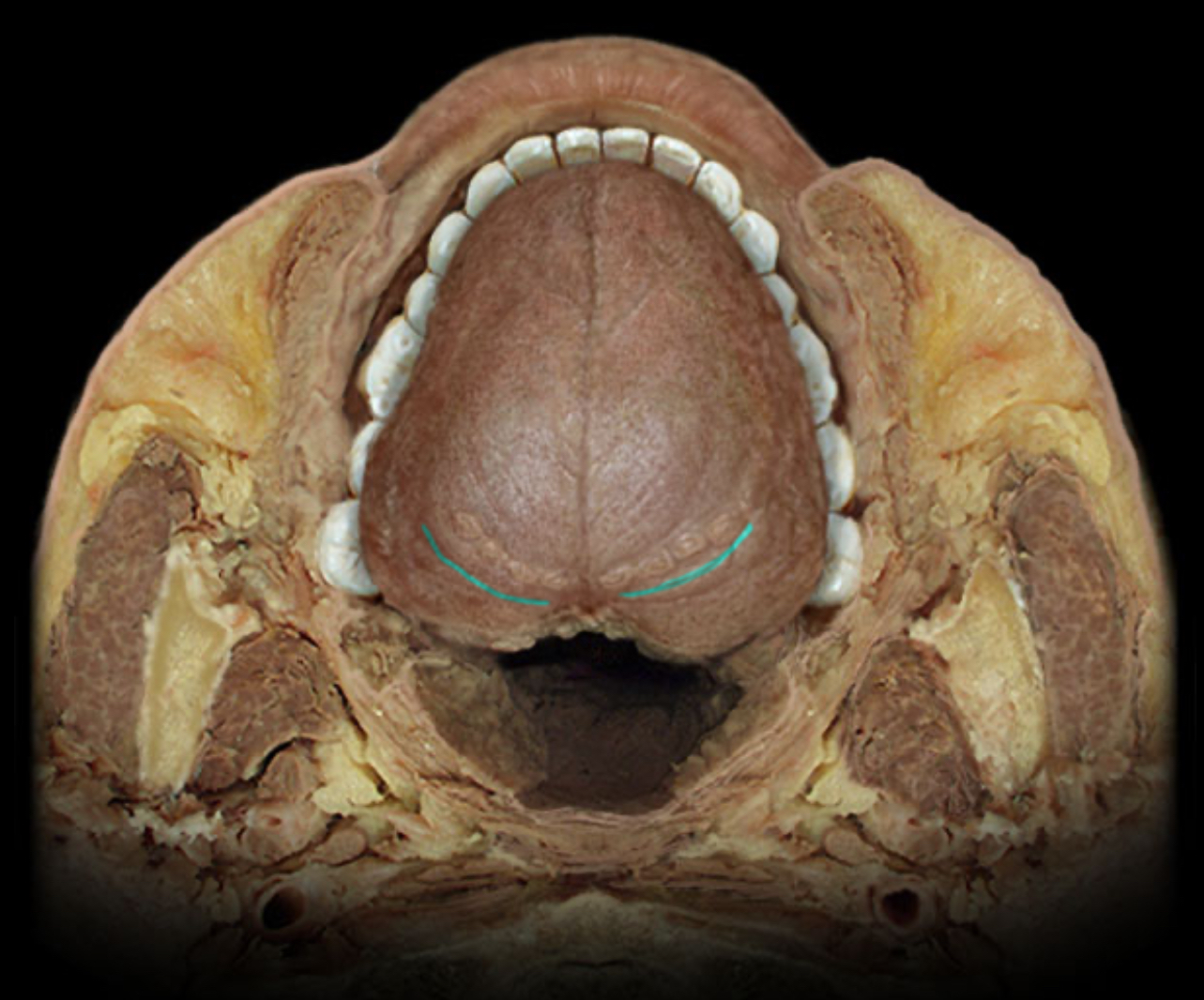
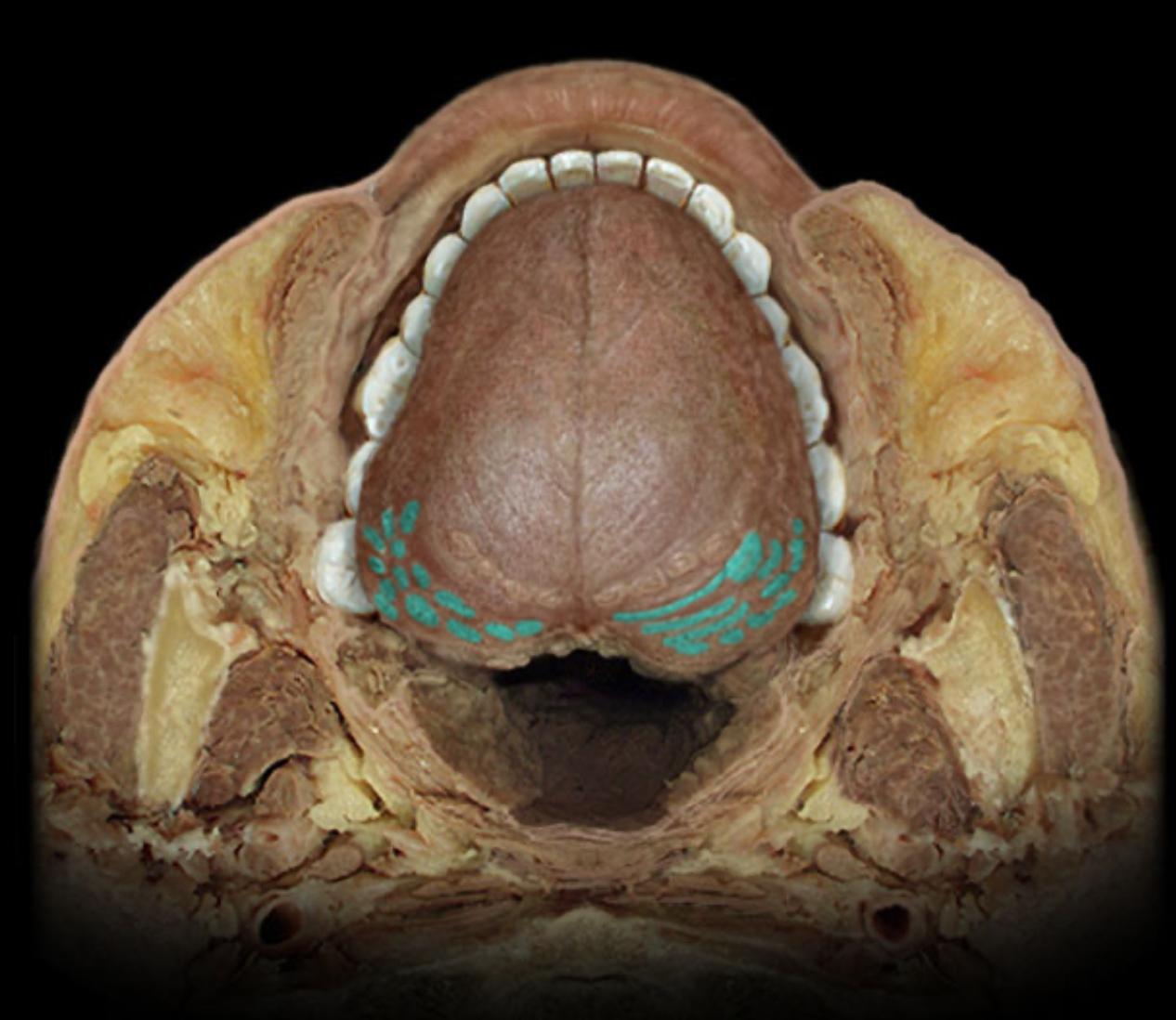
Vallate papilla
Location:
Tongue (dorsum)
Description:
8-12 large, flat-topped papillae located just anterior to terminal sulcus
Contains numerous taste buds
Also known as:
Circumvallate papilla
Comment:
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) receives special sensory information (taste) from taste buds in these papillae
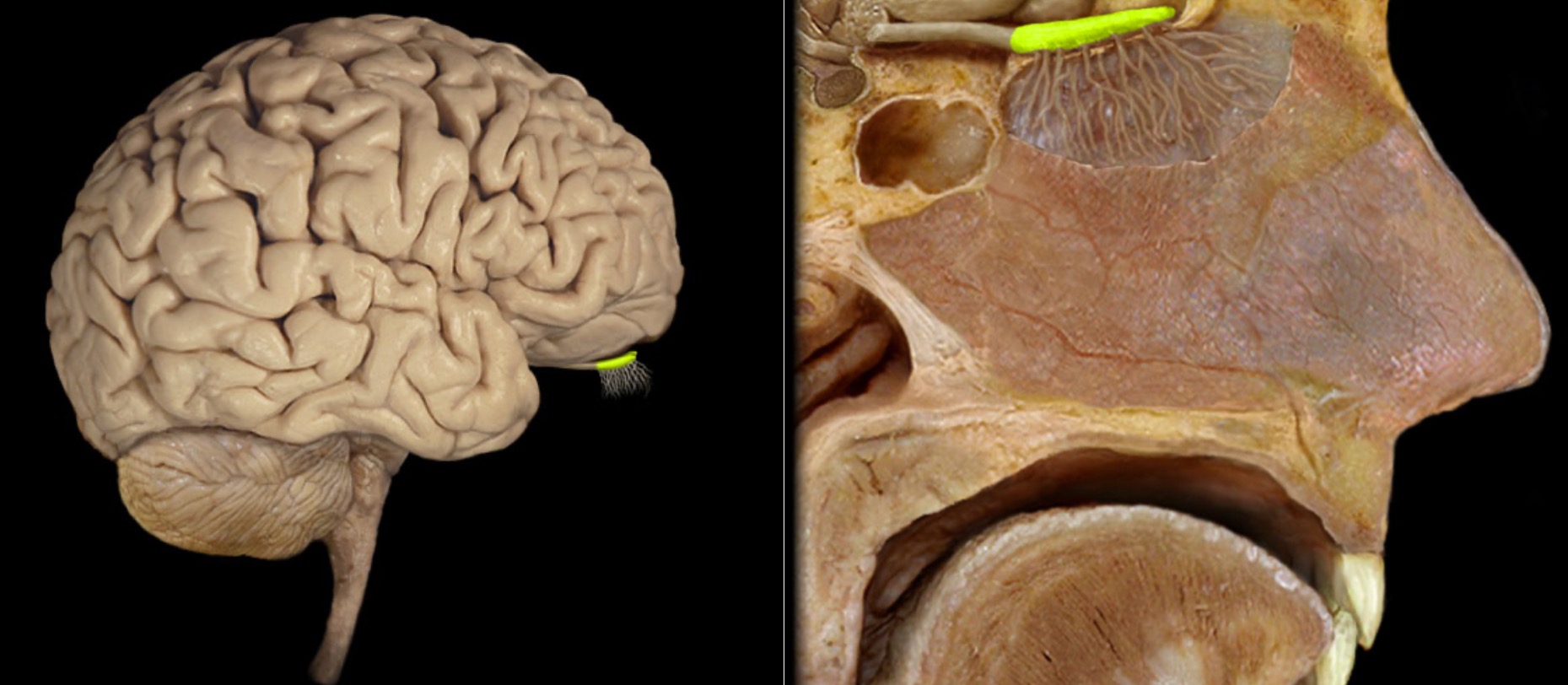
Olfactory bulb
Location:
Lies on cribriform plate of ethmoid bone in anterior cranial fossa
Ventral aspect of frontal lobe of brain
Description:
Expanded anterior end of olfactory tract
Site of synapse for olfactory neurons (CN I) after their axons pass through cribriform plate
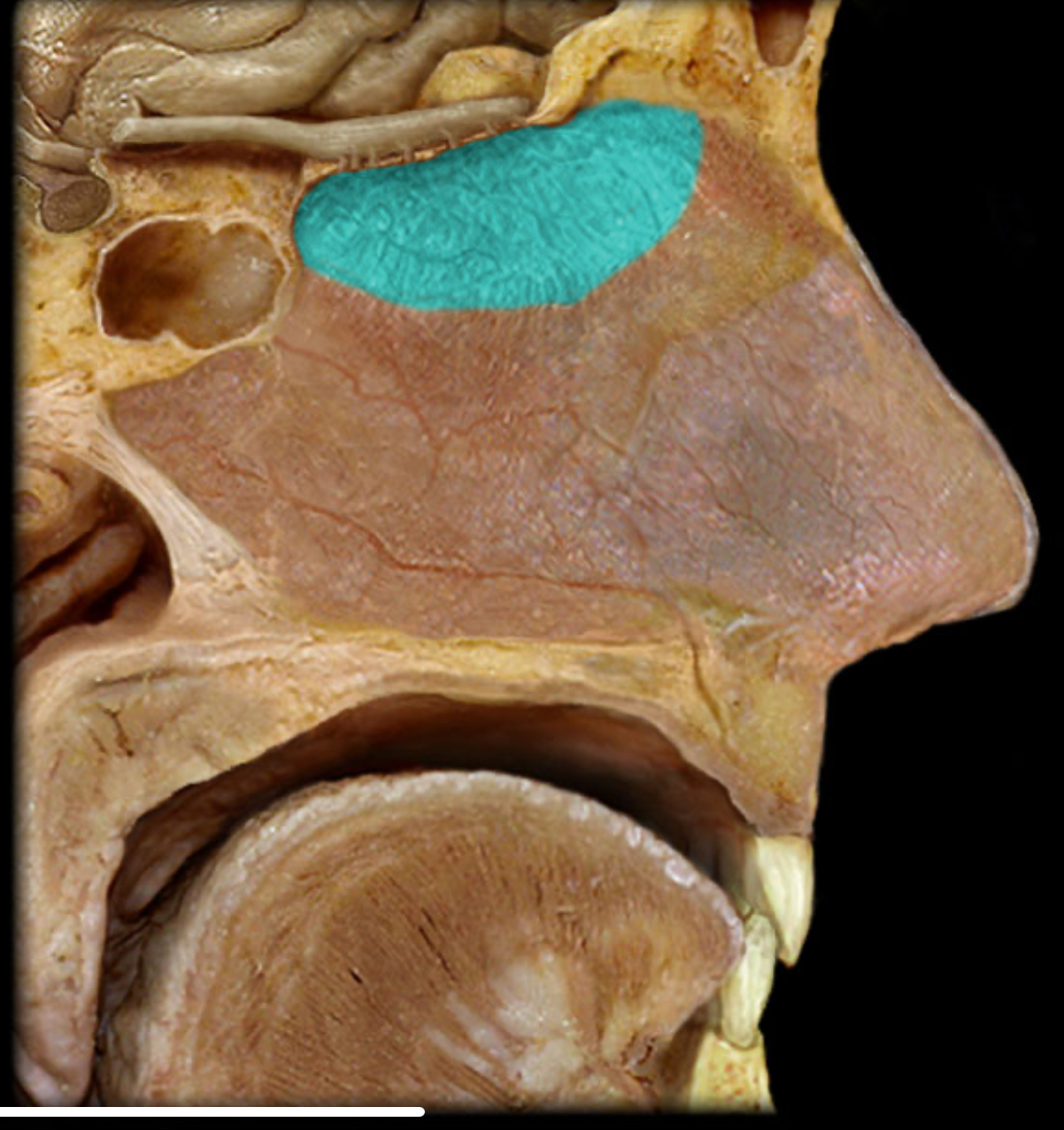
Olfactory mucosa
Location:
Nasal cavity (superior nasal septum and superior nasal concha and roof between)
Description:
Contains olfactory neurons
Comment:
Primary function: olfaction
Olfactory nn. (CN I)
Location:
Mucosa of anterosuperior nasal cavity (olfactory epithelium)
Anterior cranial fossa
Composition:
Special sensation
Special sensation:
Olfaction (smell)
CNS connection:
Olfactory bulb
Cranial foramina:
Cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
Comment:
Special sensation includes smell, vision, taste, hearing, and balance
Olfactory nerve formed by proximal process (axons) of olfactory neurons
Olfactory axons project through cribriform plate to synapse in olfactory bulb
Olfactory nerve also known as CN I
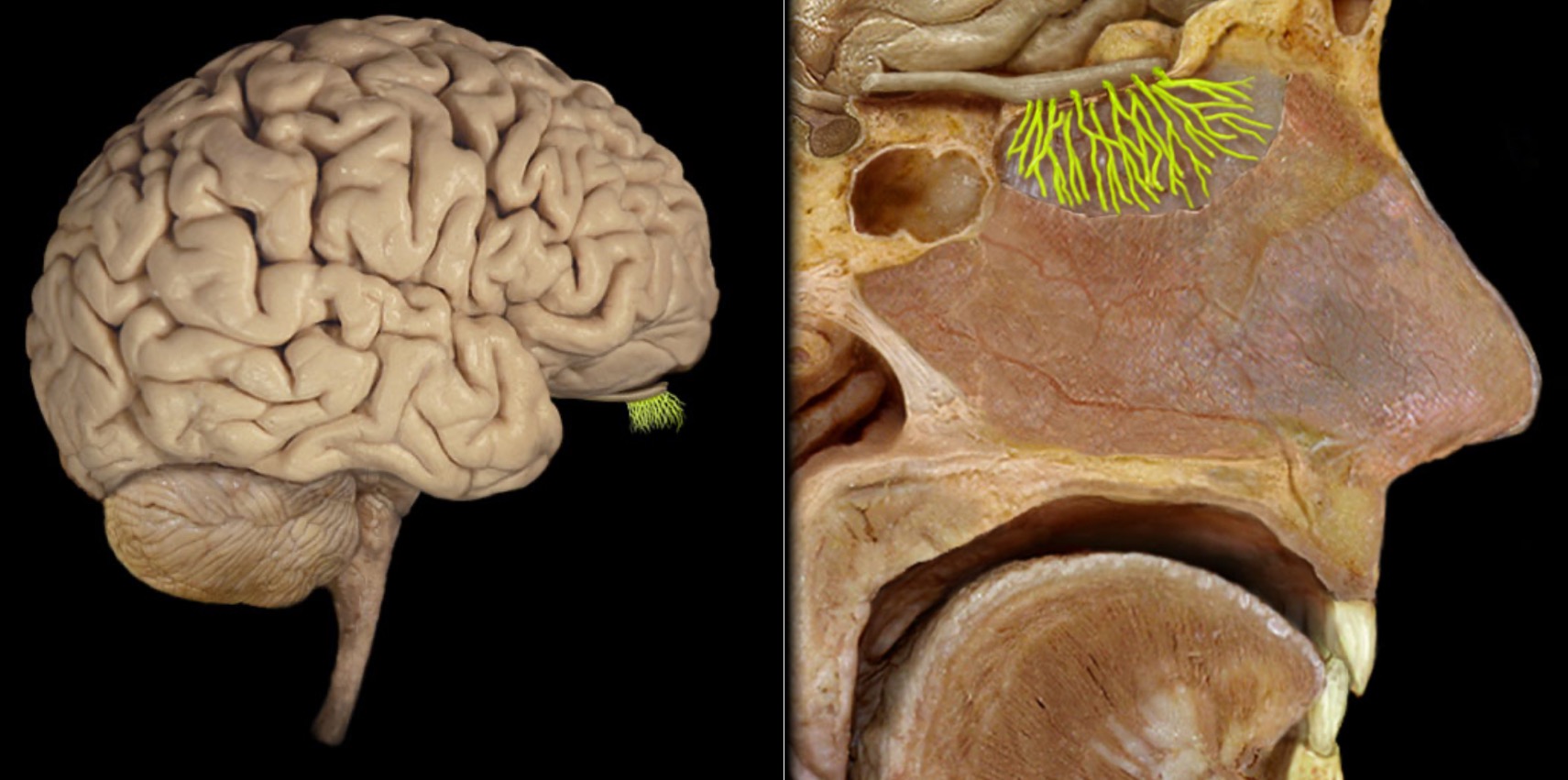
Olfactory tract
Location:
Ventral aspect of frontal lobe
Between olfactory bulb and medial aspect of temporal lobe
Description:
Bundles of afferent and efferent axons
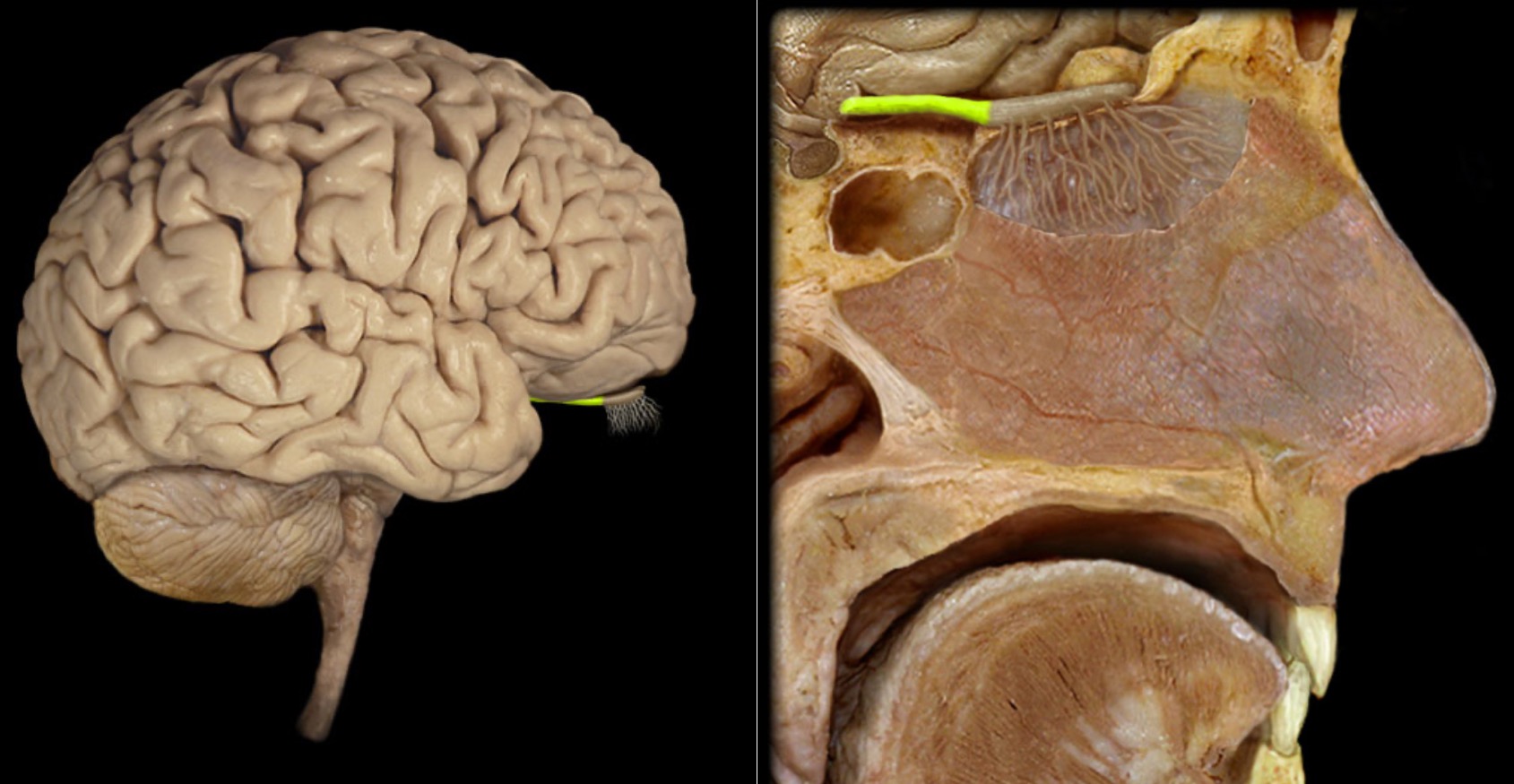
Respiratory nasal mucosa
Location:
Nasal cavity (inferior two-thirds)
Description:
Non-olfactory region of nasal mucosa
Comment:
Primary function: warm and humidify inhaled air
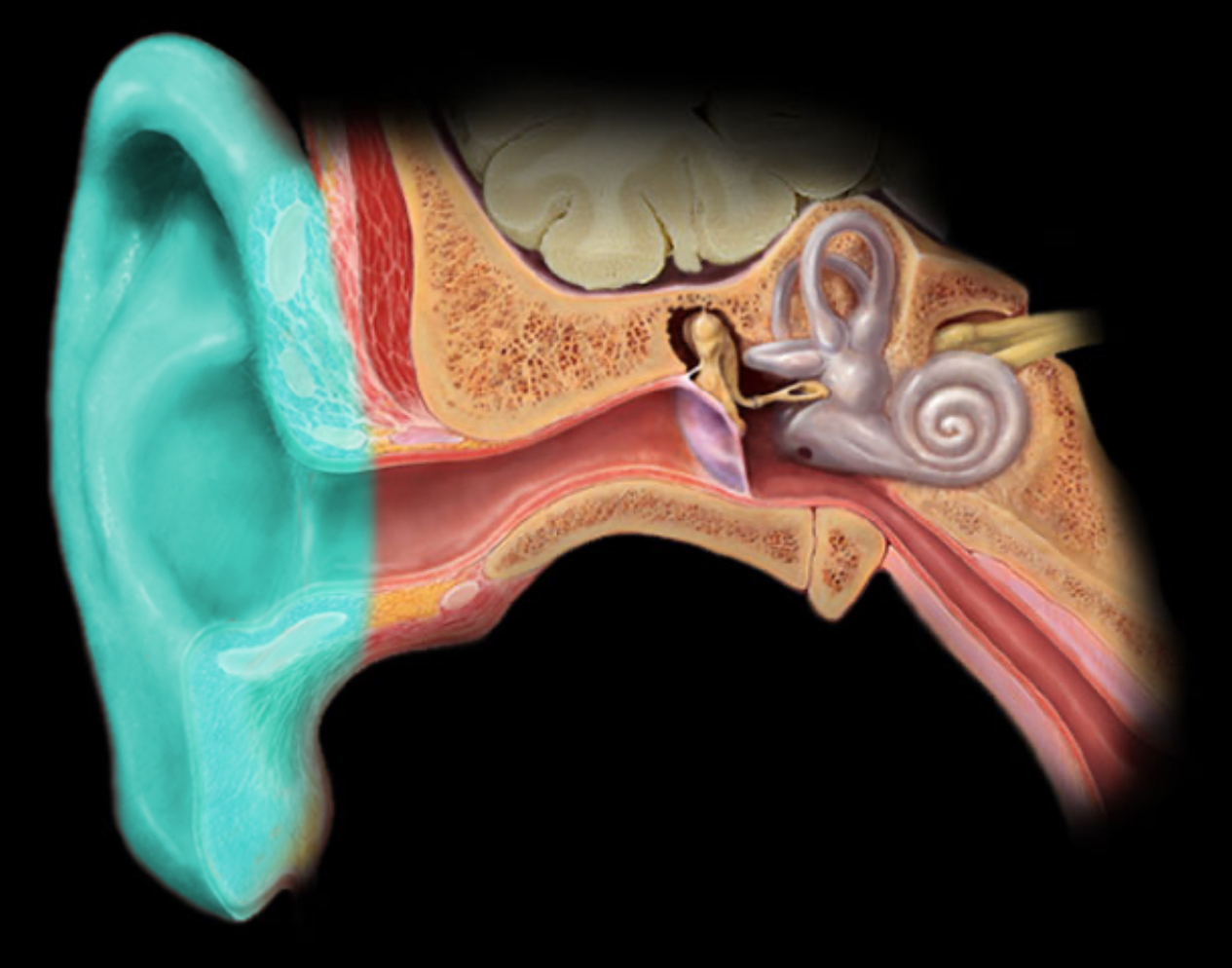
Auricle of ear
Location:
Head (lateral)
Description:
Appendage of skin, cartilage, and connective tissue
Contains part of external acoustic meatus
Also known as:
External ear or pinna
Comment:
Acts like a funnel to collect and modify sound waves
Latin: auri = an ear
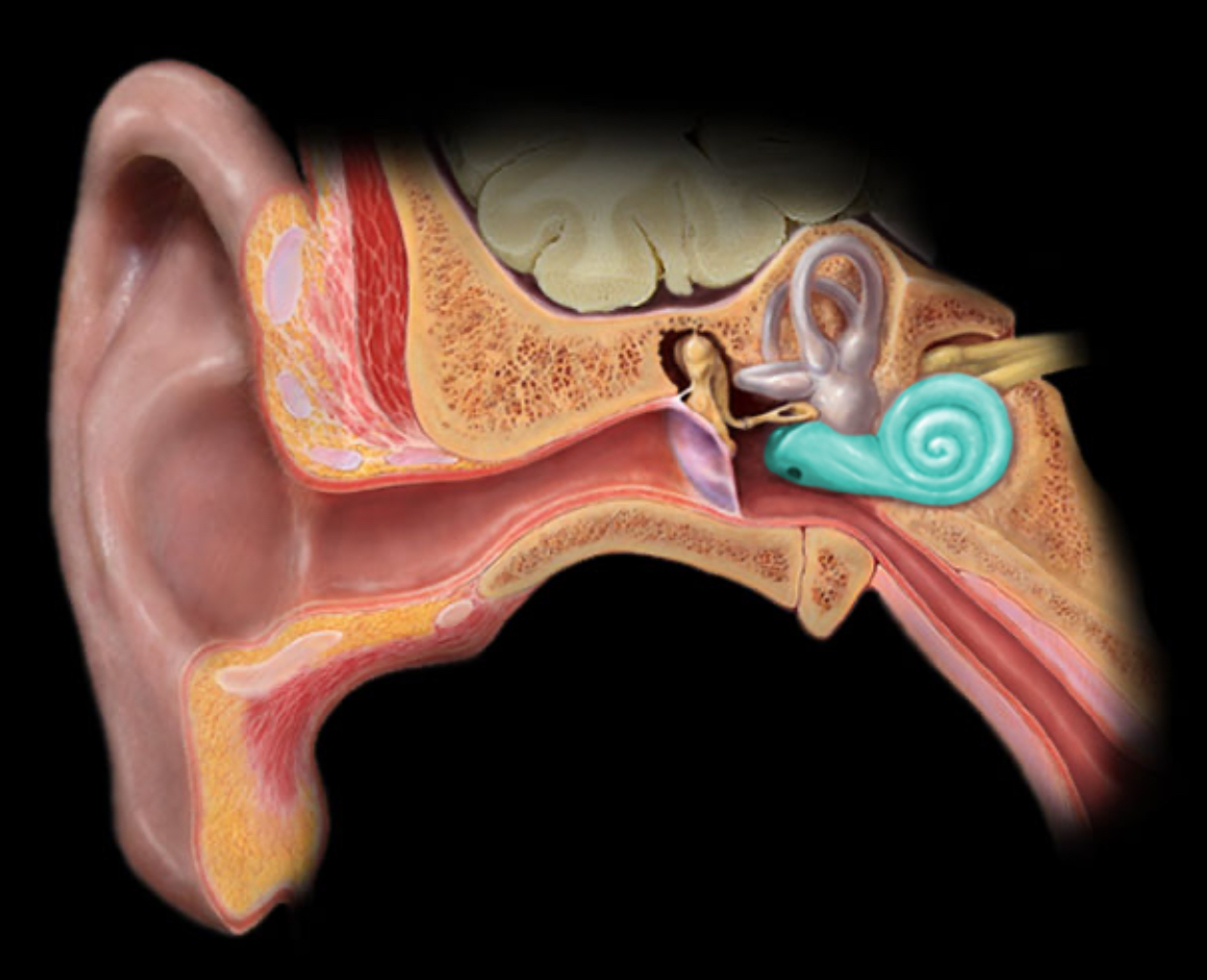
Cochlea
Location:
Temporal bone (petrous part)
Description:
Coiled membranous tube surrounded by bone
Contains three fluid-filled chambers
Comment:
Organ of hearing
Contains spiral organ (of Corti) in cochlear duct
Semicircular canals
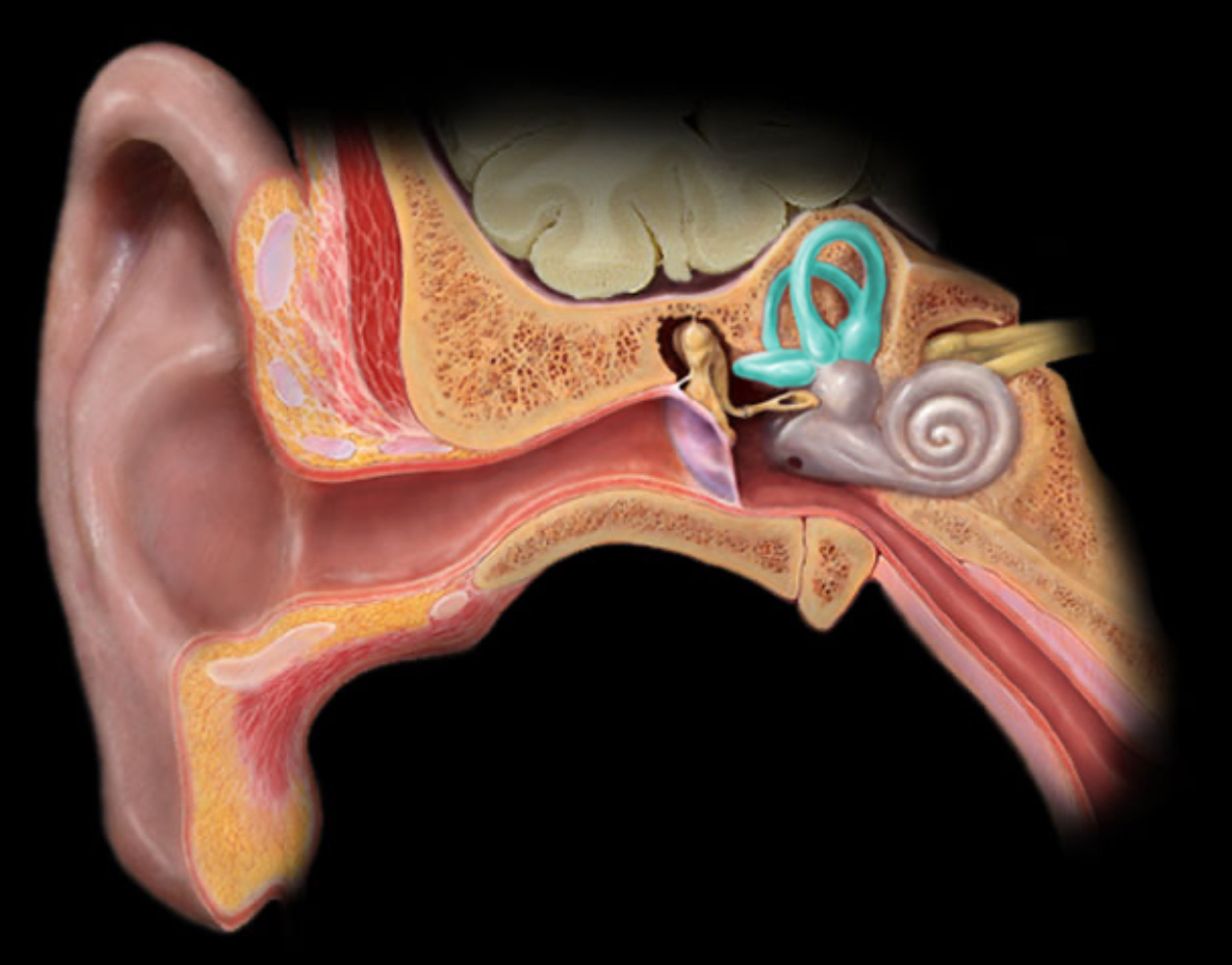
Location:
Temporal bone (petrous part)
Description:
The three semicircular canals are part of the bony labyrinth
Each semicircular canal contains a membranous semicircular duct
Orientation of ducts in perpendicular (X, Y, and Z) planes
Comment:
The membranous semicircular ducts are part of the vestibular apparatus, i.e. organs of equilibrium
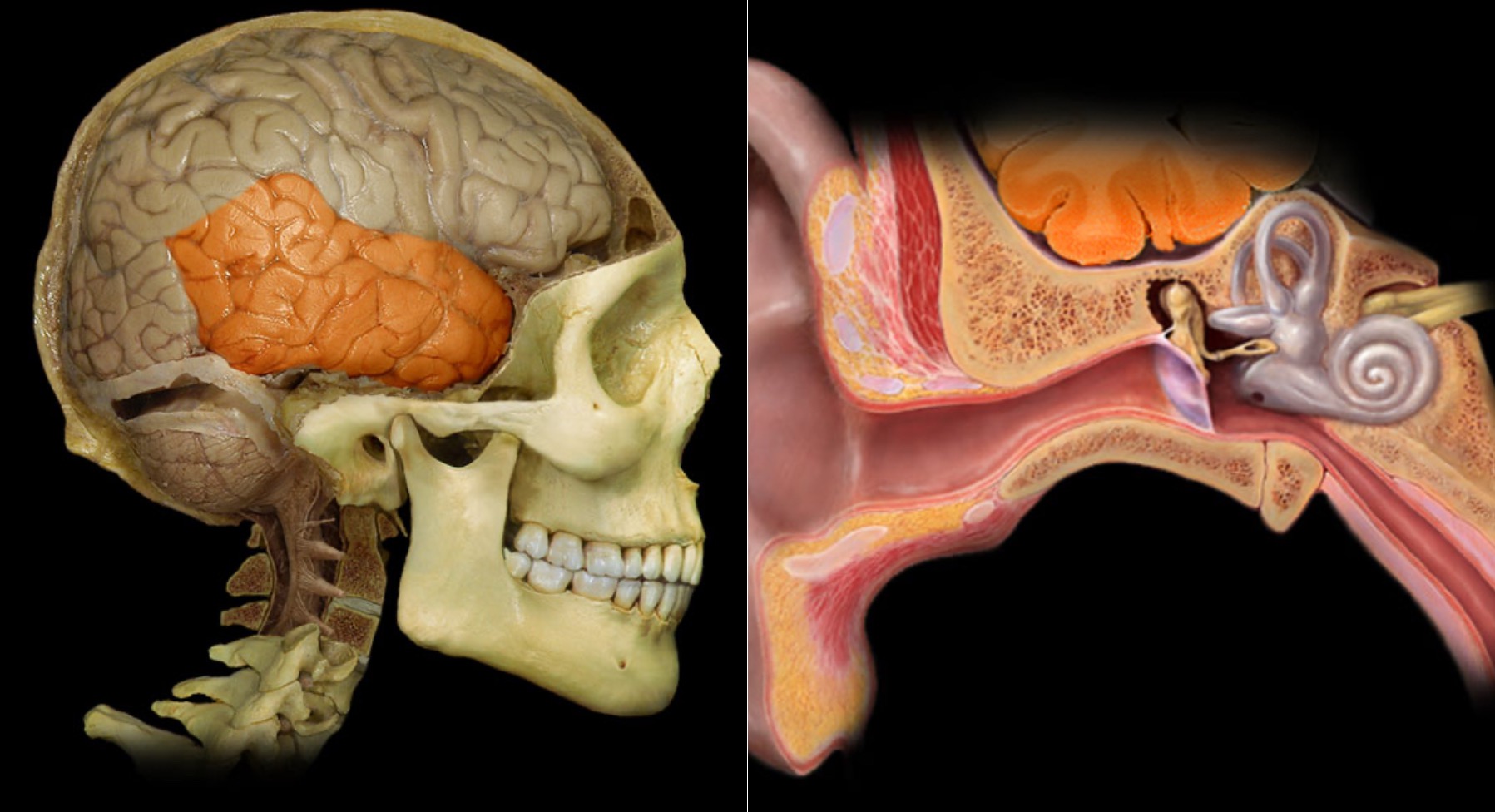
Temporal lobe
Location:
Lateral and inferior portion of each cerebral hemisphere
Inferior to lateral sulcus
Description:
Lateral surface has three parallel gyri
Function:
Primary hearing and smell areas
Memory
Speech perception and recognition (i.e., Wernicke's area - usually in left hemisphere)
Comment:
Named for overlying bone
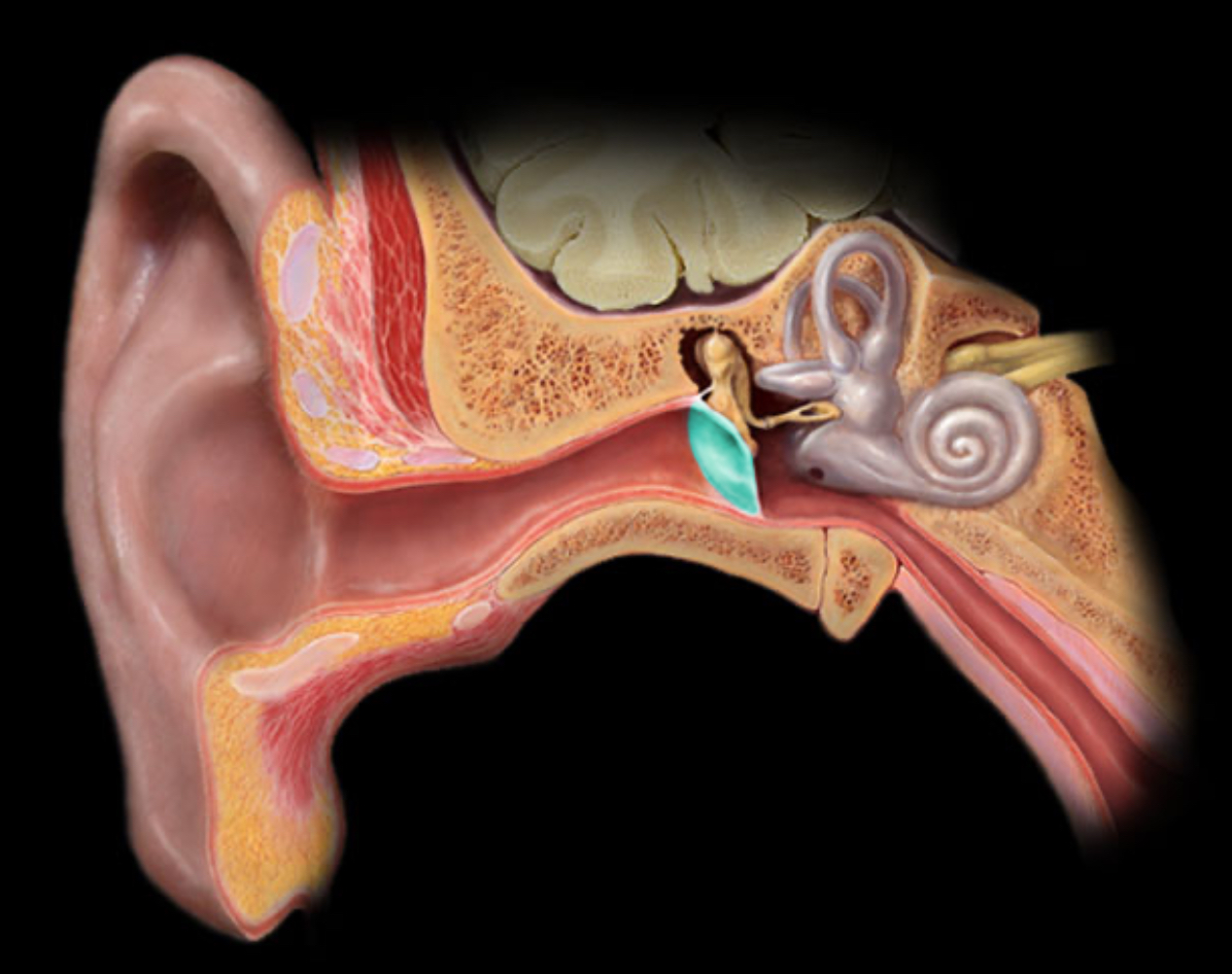
Tympanic membrane
Location:
Temporal bone (petrous part)
Description:
Thin, semi-transparent, oval membrane
Separates external acoustic meatus (external ear) from tympanic cavity (middle ear)
Also known as:
"Ear drum"
Comment:
Attached to malleus (ossicle)
Vestibular of ear
Location:
Temporal bone (petrous part)
Description:
The vestibule is part of the bony labyrinth
The vestibule contains the utricle and saccule
The utricle and saccule are membranous sacs at base of semicircular ducts
Comment:
The membranous utricle and saccule are part of the vestibular apparatus, i.e. organs of equilibrium
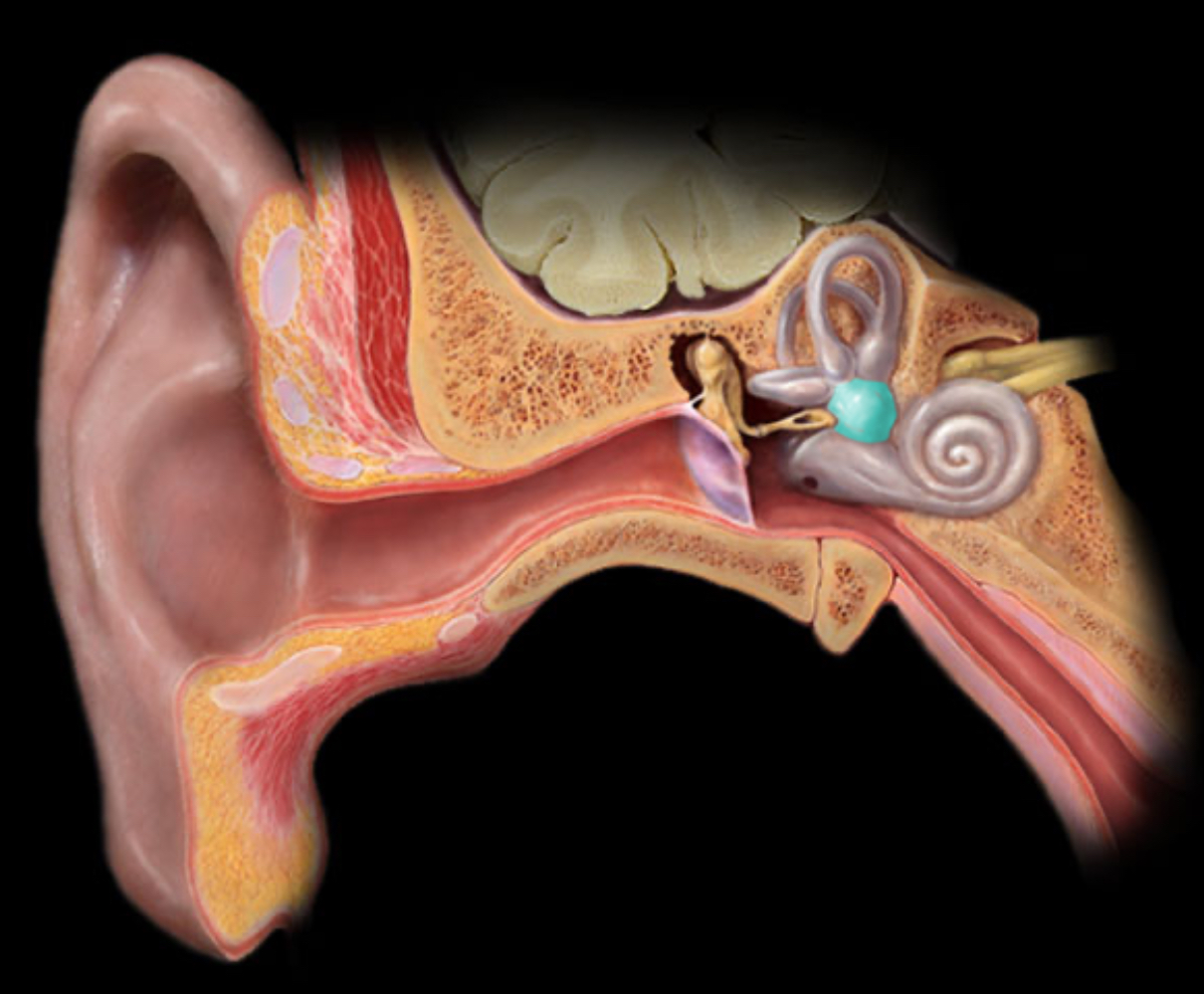
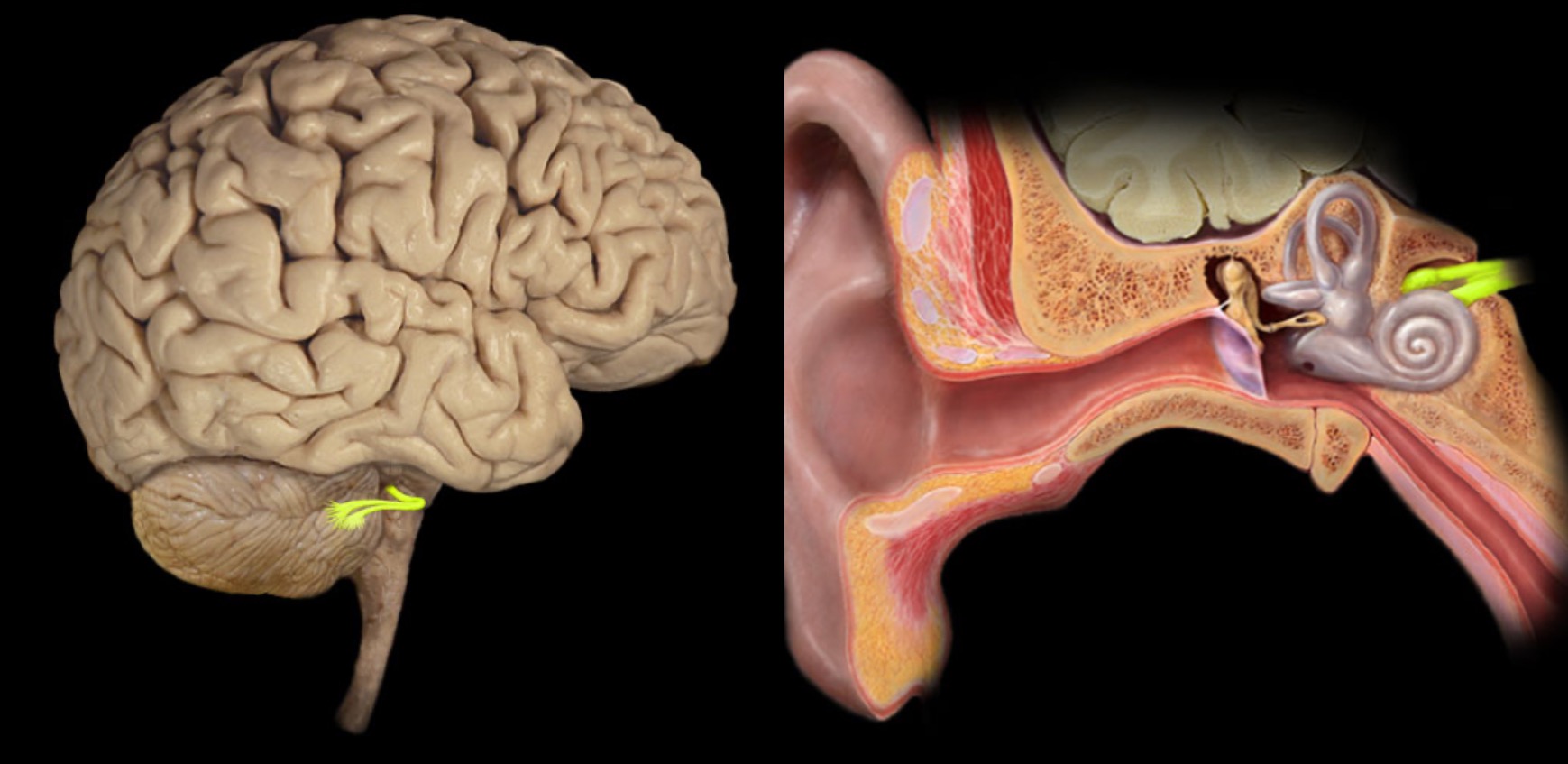
Vestibulocochlear n. (CN VIII)
Location:
Posterior cranial fossa
Petrous portion of temporal bone
Composition:
Special sensation
Special sensation:
Hearing (cochlea)
Balance (semicircular canals and vestibule)
Sensory ganglion:
Cochlear (spiral) ganglion (cochlear part of CN VIII)
Vestibular ganglion (vestibular part of CN VIII)
CNS connection:
Pons (vestibular nuclei)
Medulla oblongata (cochlear and vestibular nuclei)
Cranial foramina:
Internal acoustic meatus
Comment:
Special sensation includes smell, vision, taste, hearing, and balance
Vestibulocochlear nerve has two distinct functional components: vestibular (balance) and cochlear (hearing)
Vestibulocochlear nerve also known as CN VIII
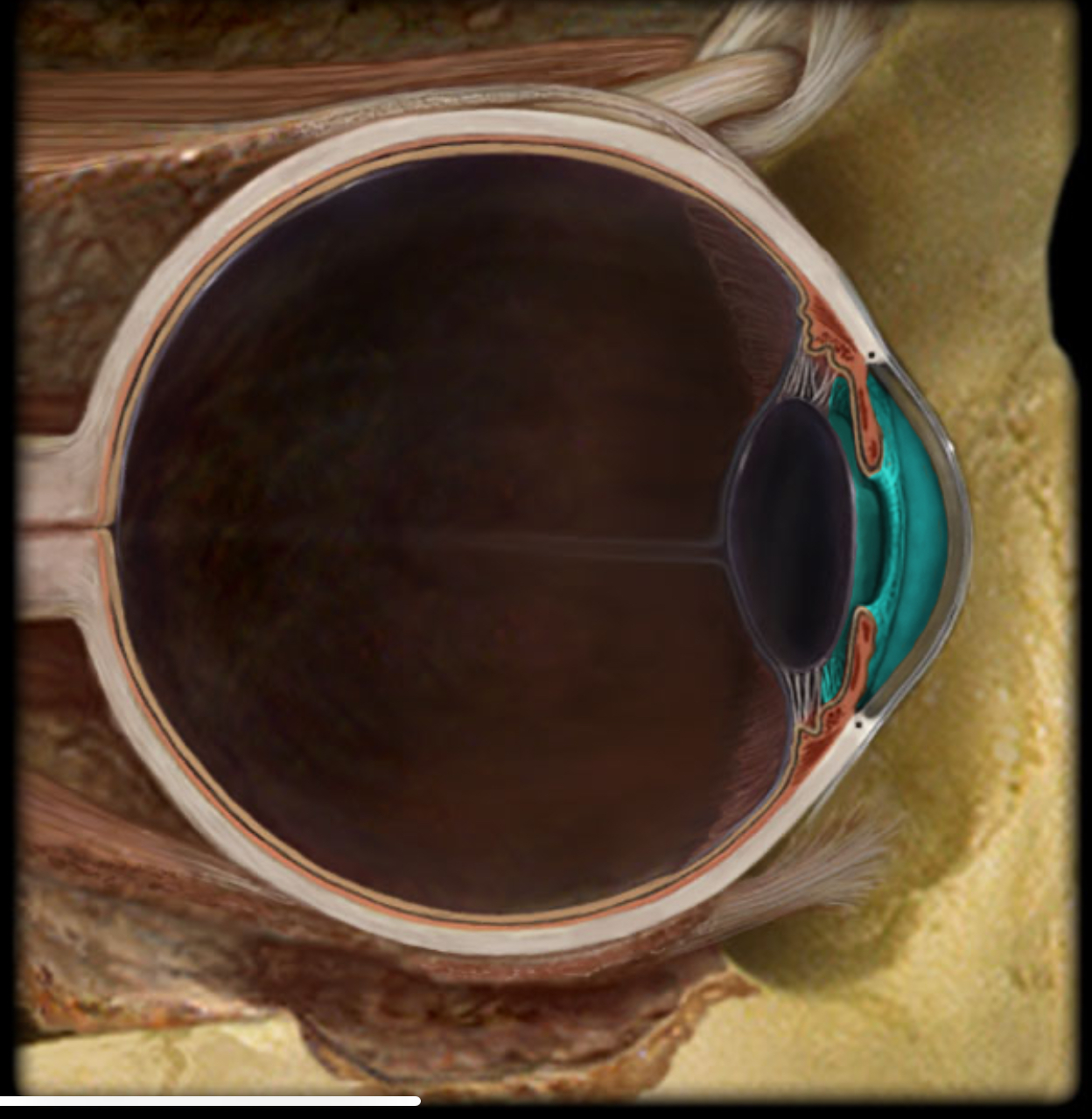
Anterior cavity
Location:
Eye
Between cornea and lens
Description:
Cavity in eye
Divided by iris into anterior and posterior chambers
Filled with aqueous humor
Comment:
Aqueous humor produced in posterior chamber; passes through pupil; enters anterior chamber; reabsorbed into venous system through scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm)
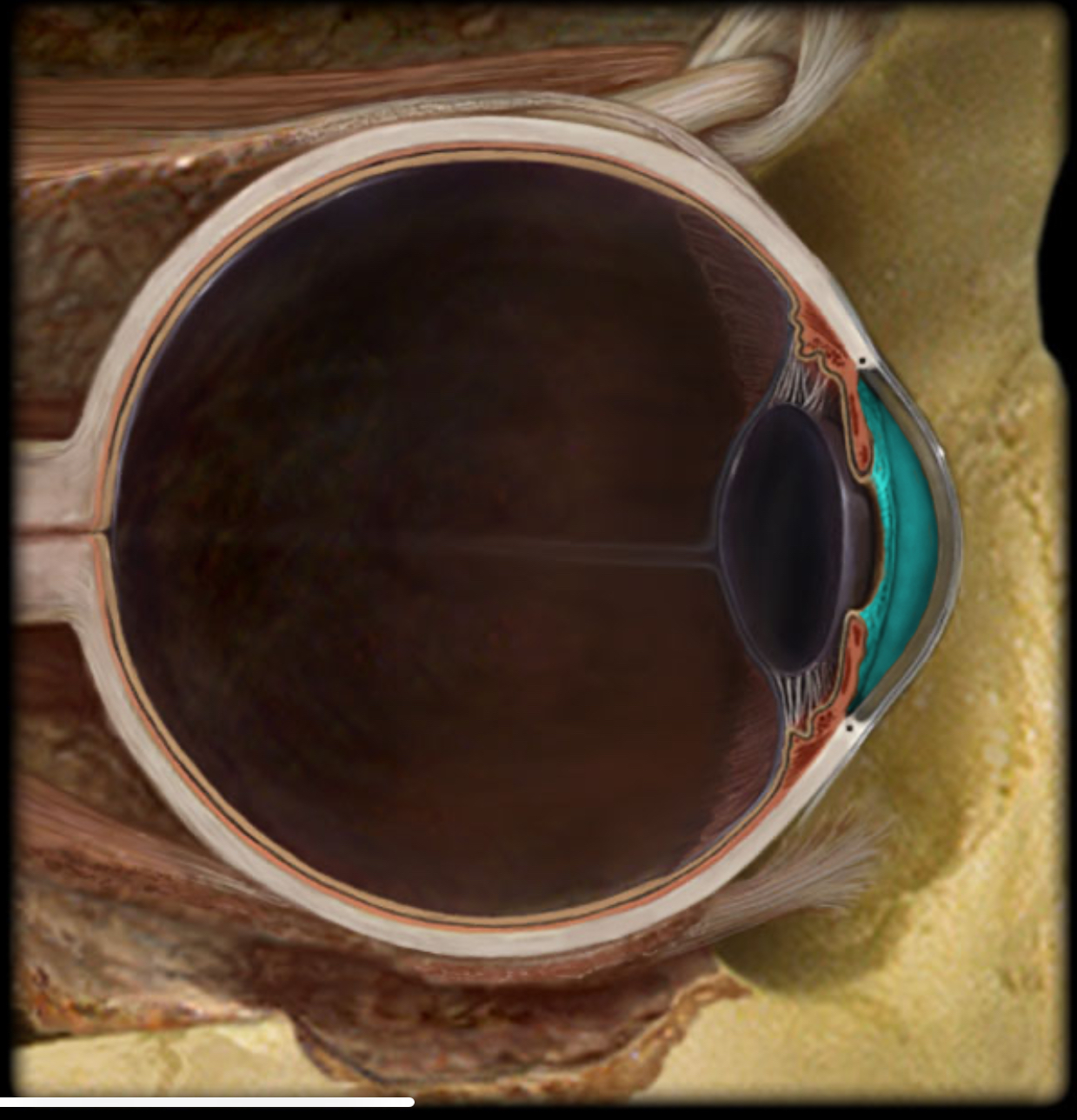
Anterior chamber
Location:
Anterior cavity of eye
Between cornea and iris
Description:
Subdivision of anterior cavity
Filled with aqueous humor
Comment:
Aqueous humor produced in posterior chamber; passes through pupil; enters anterior chamber; reabsorbed into venous system through scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm)
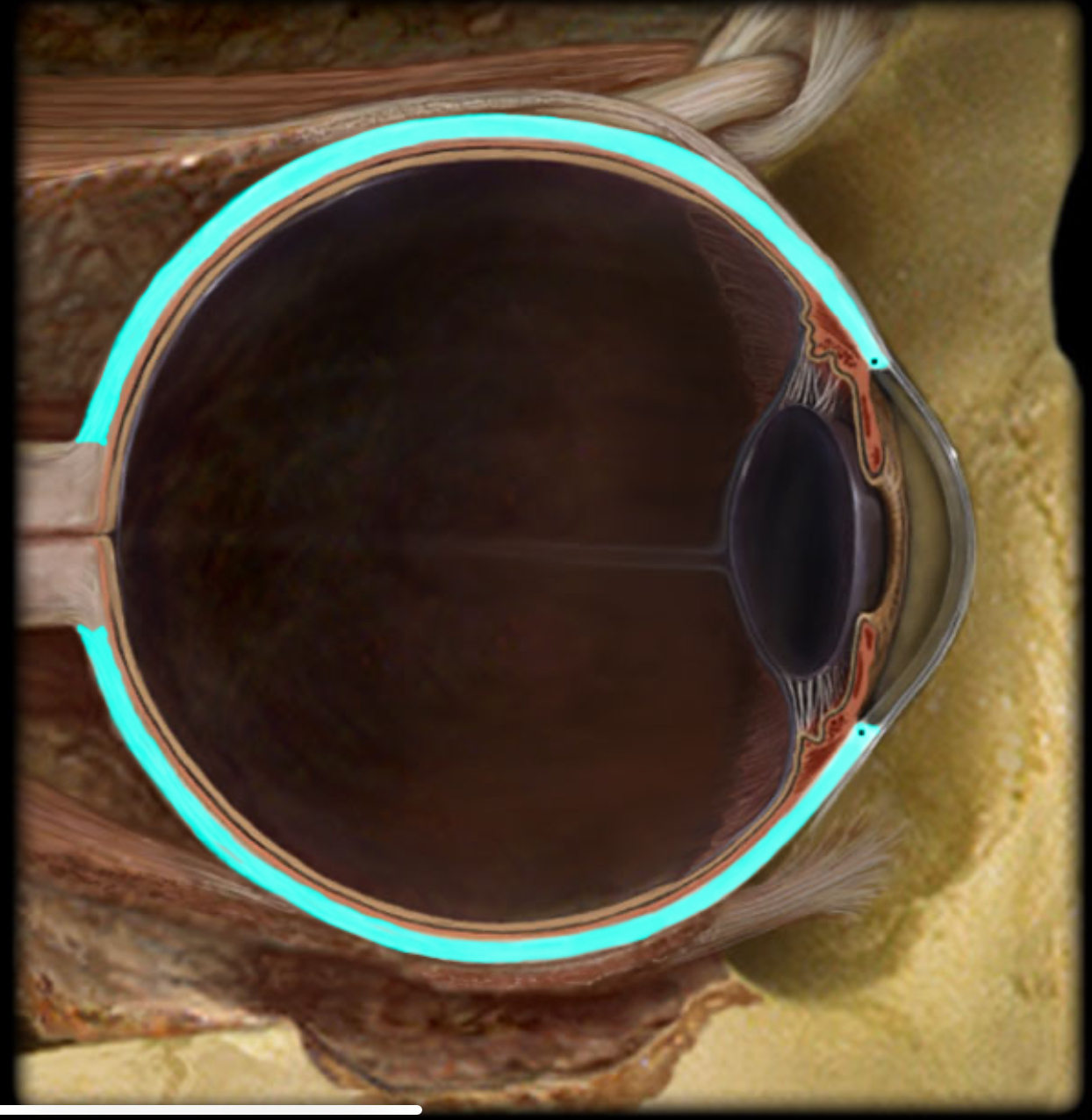
Choroid
Location:
Eye (vascular layer)
Description:
Highly vascular layer
Contains dark brown pigment - melanin
Function:
Blood supply to outer part of neural retina
Prevent light reflection within eye
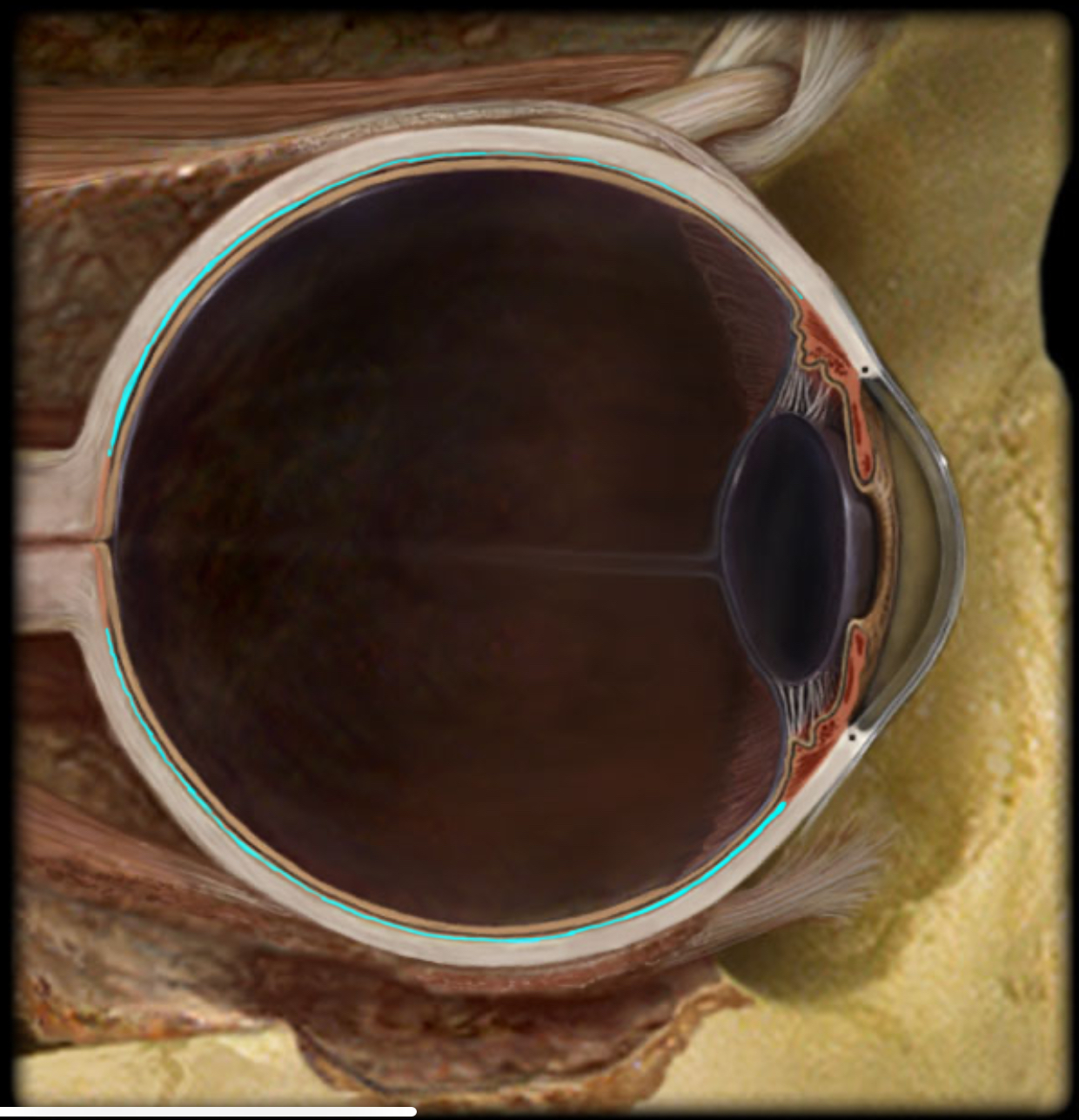
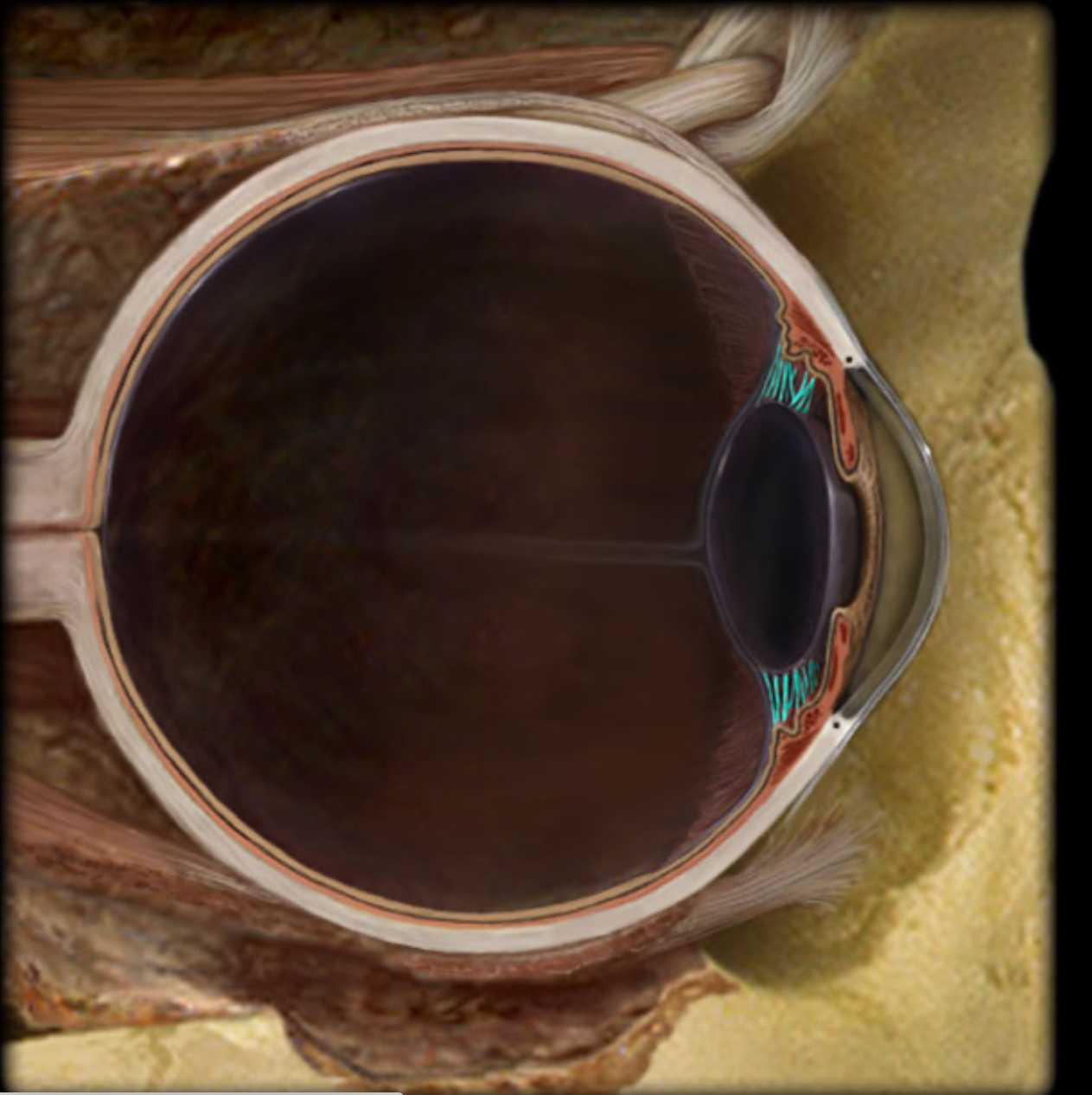
Ciliary body
Location:
Eye
Part of vascular (middle) layer, between choroid and iris
Description:
Composed of ciliary muscle and ciliary processes
Function:
Anular ciliary smooth muscle controls tension of suspensory ligaments to adjust thickness of lens
Ciliary processes produce aqueous humor
Comment:
Aqueous humor produced by ciliary processes flows from posterior chamber to posterior chamber of anterior cavity where it is resorbed into venous system through the scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm)
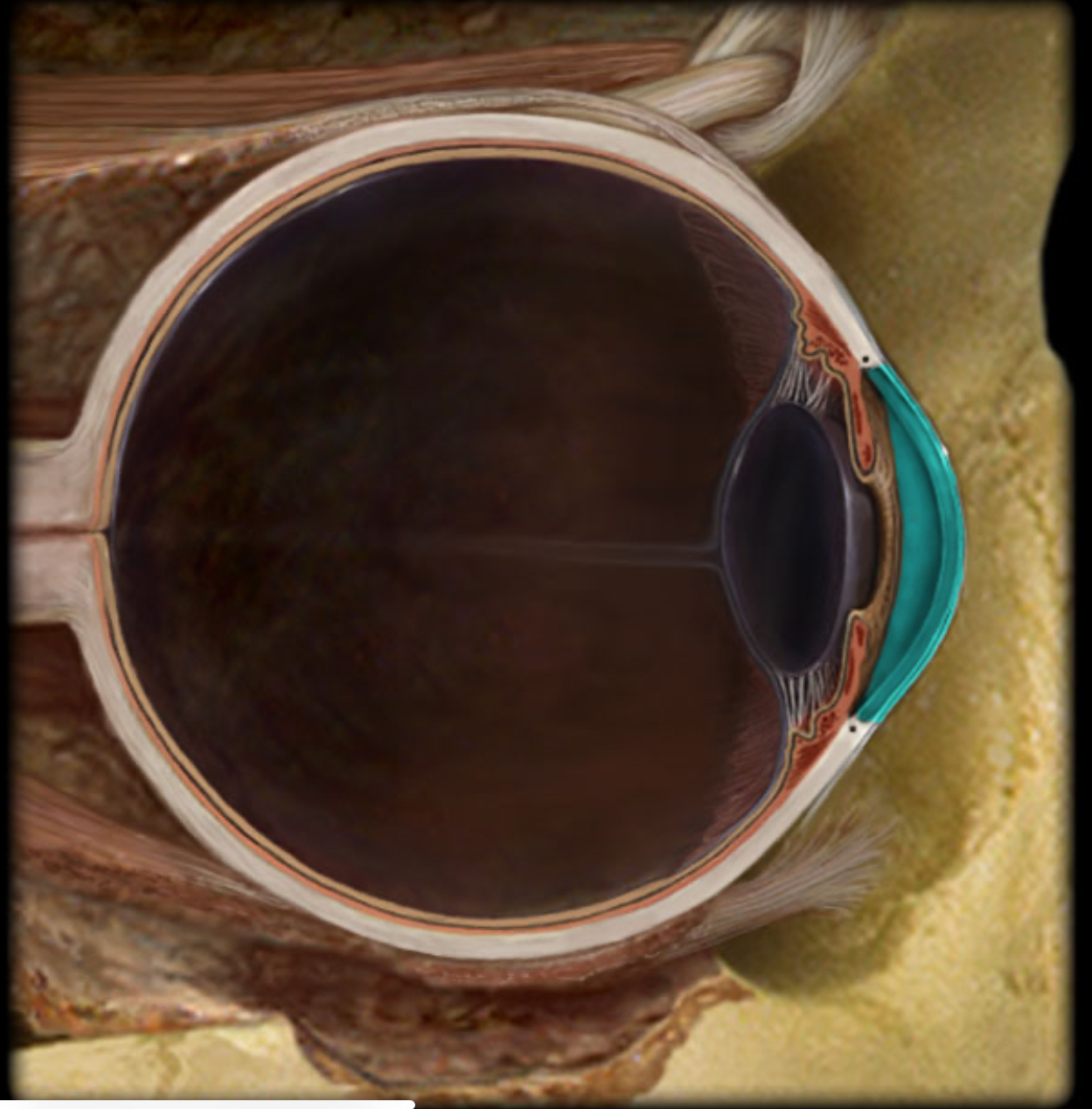
Cornea
Location:
Eye
Description:
Transparent connective tissue layer of anterior 1/6th of eye
Function:
Site for light refraction
Protection of anterior eye
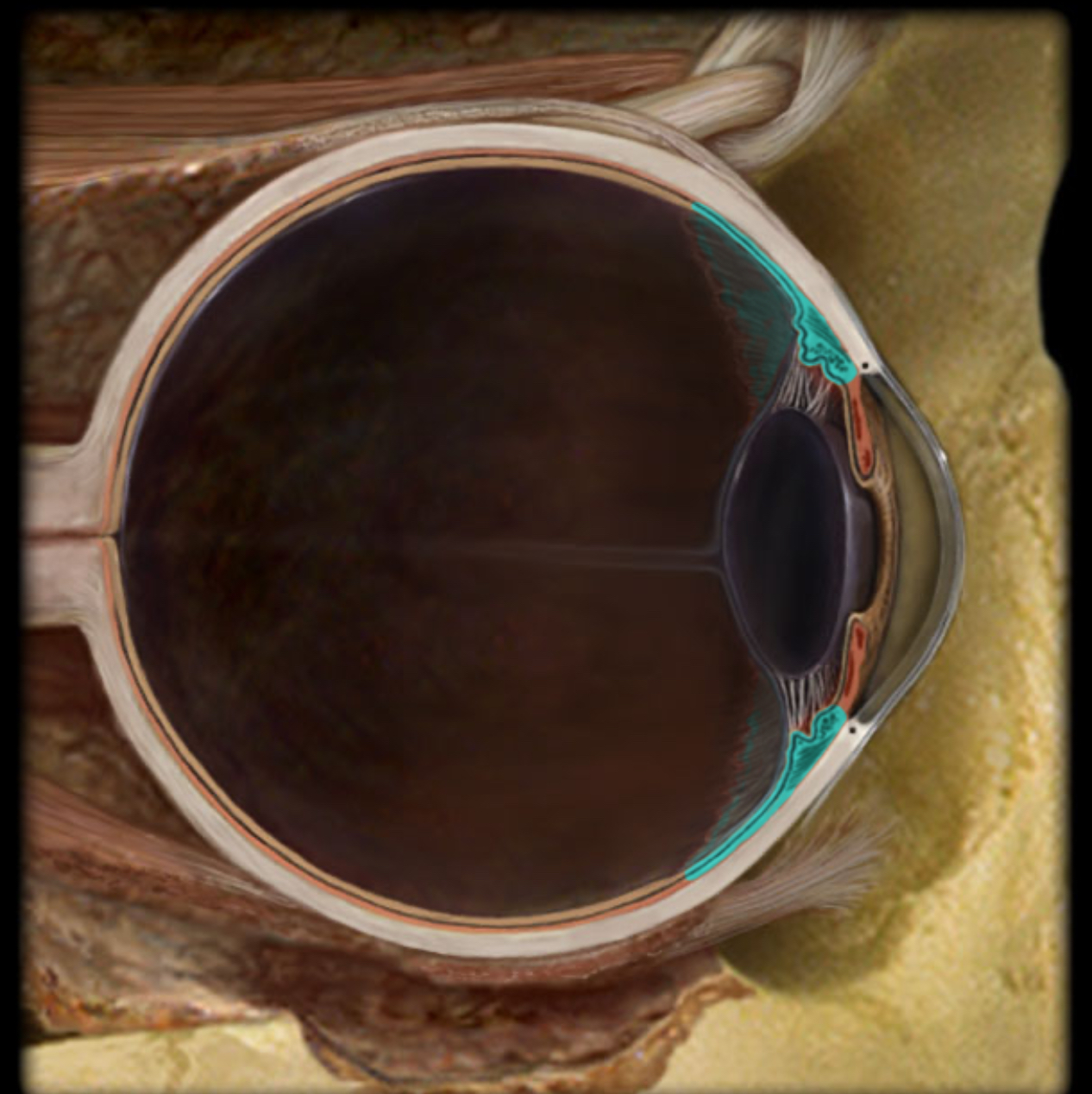
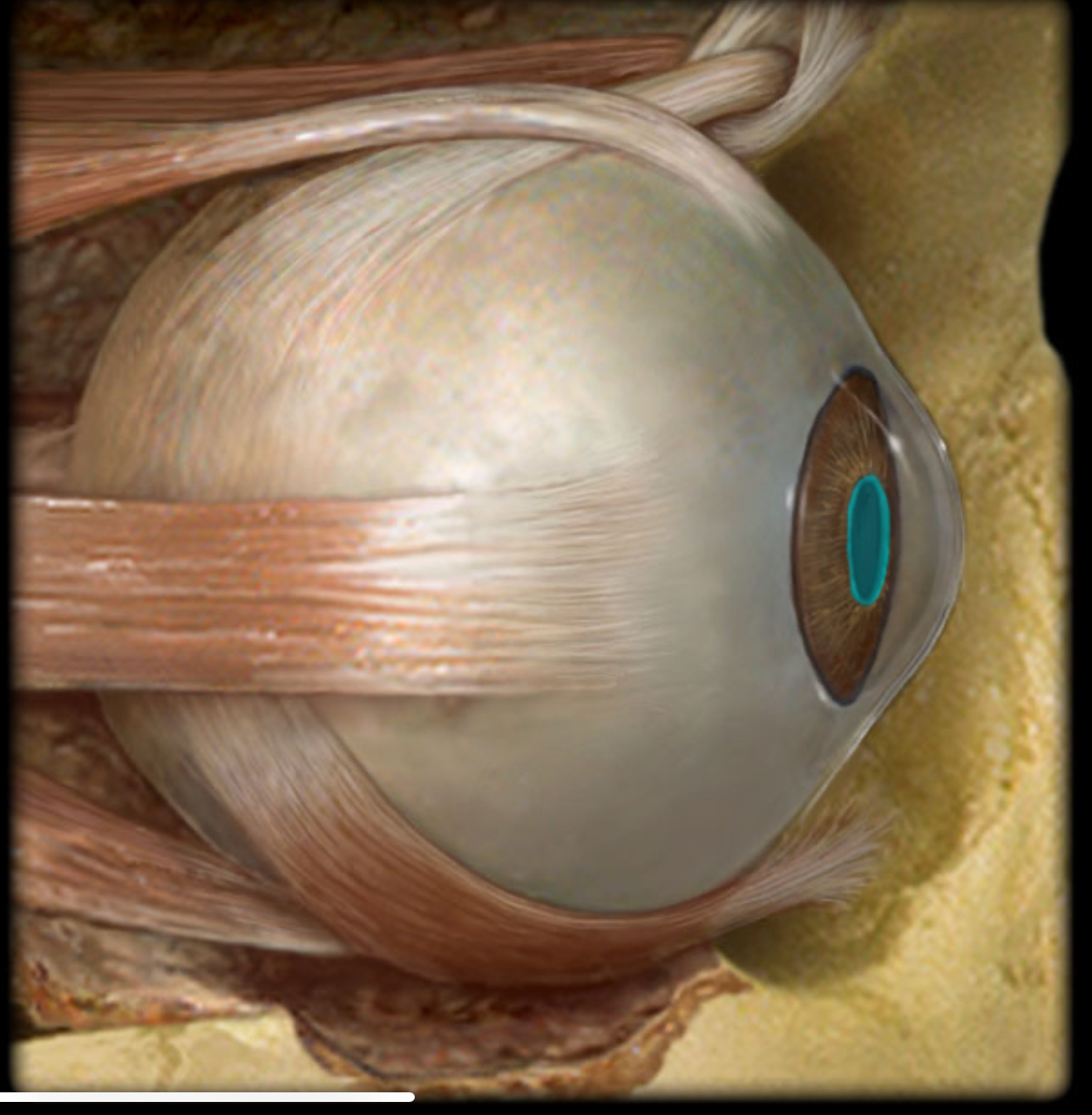
Iris
Location:
Eye (posterior to cornea)
Description:
Colored part of eye
Diaphragm that regulates pupil size
Contains pupillary constrictor and dilator muscles
Function:
Controls size of pupil (pupil constricts and dilates in response to light)
Comment:
Pupillary constrictor receives parasympathetic innervation, pupillary dilator receives sympathetic innervation
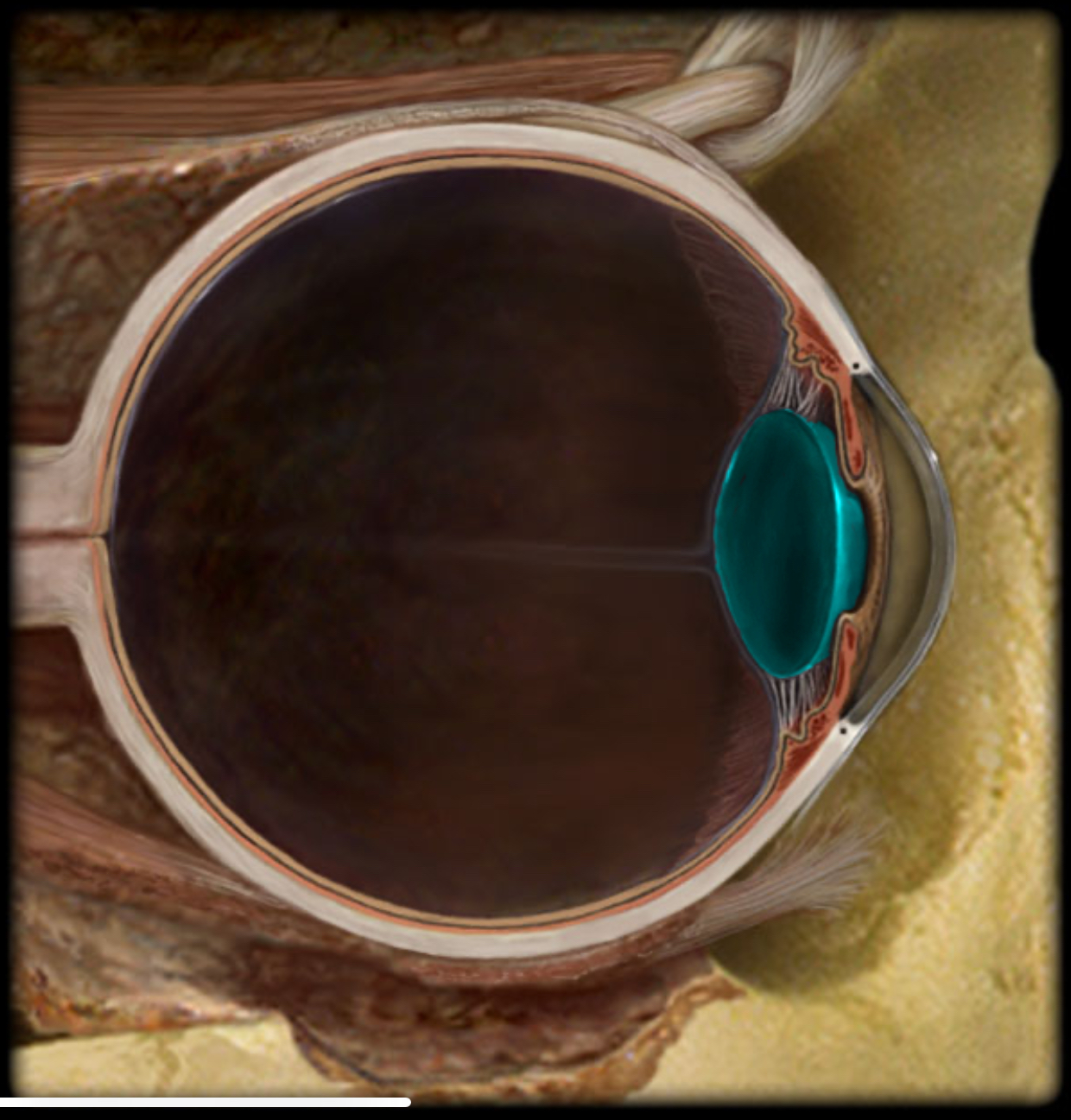
Lens
Location:
Eye (posterior to iris)
Description:
Biconvex lens
Composed of cells called lens fibers
Function:
Light refraction
Focuses light onto neural retina
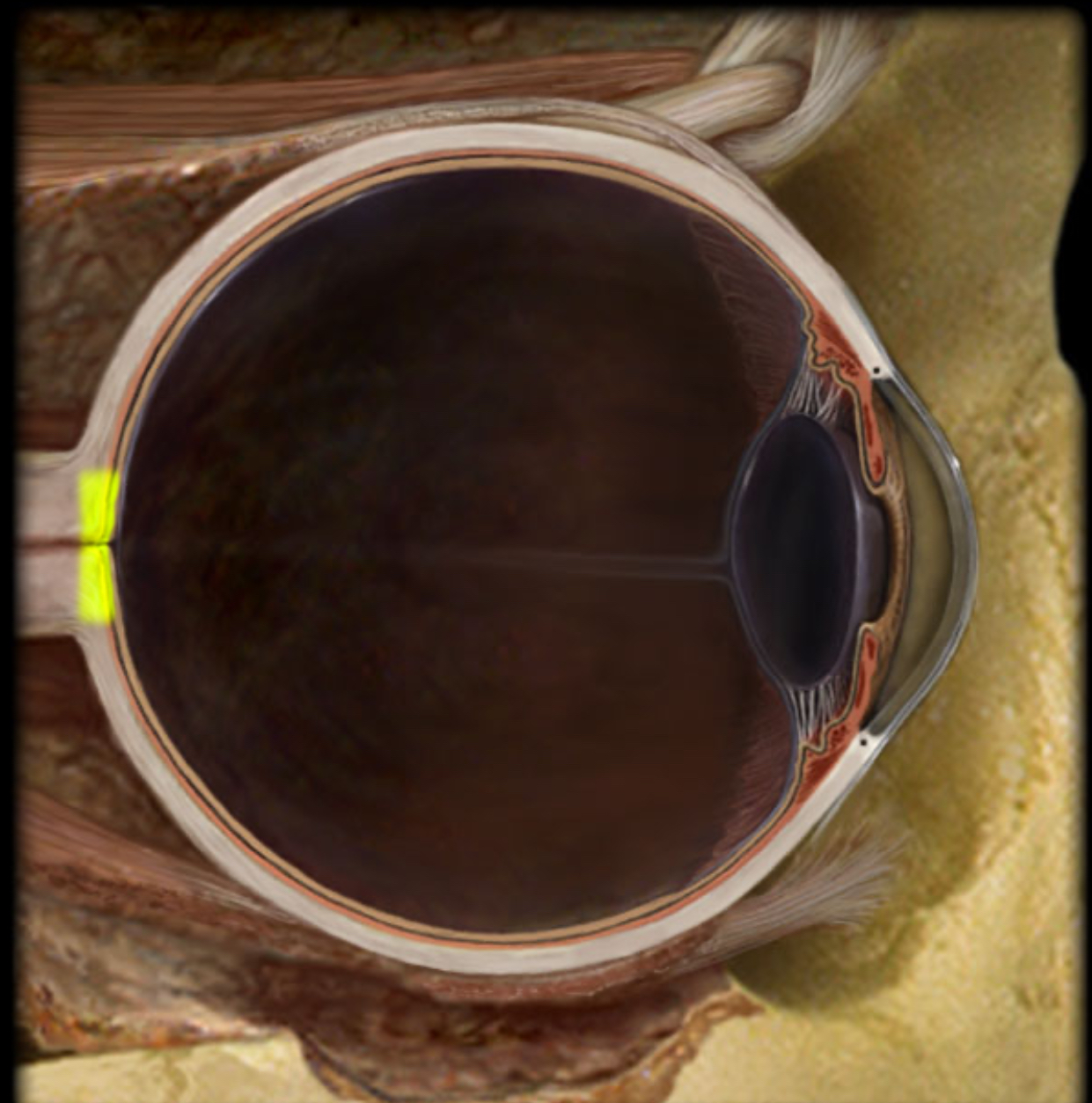
Optic disk
Location:
Retina
At junction with optic nerve
Description:
Circular to oval area
Composed of optic fibers (axons of retinal ganglion cells) that form optic nerve
Central retinal artery enters eye through optic disk
Comment:
Lack of photoreceptors in disk creates “blind spot” in visual field
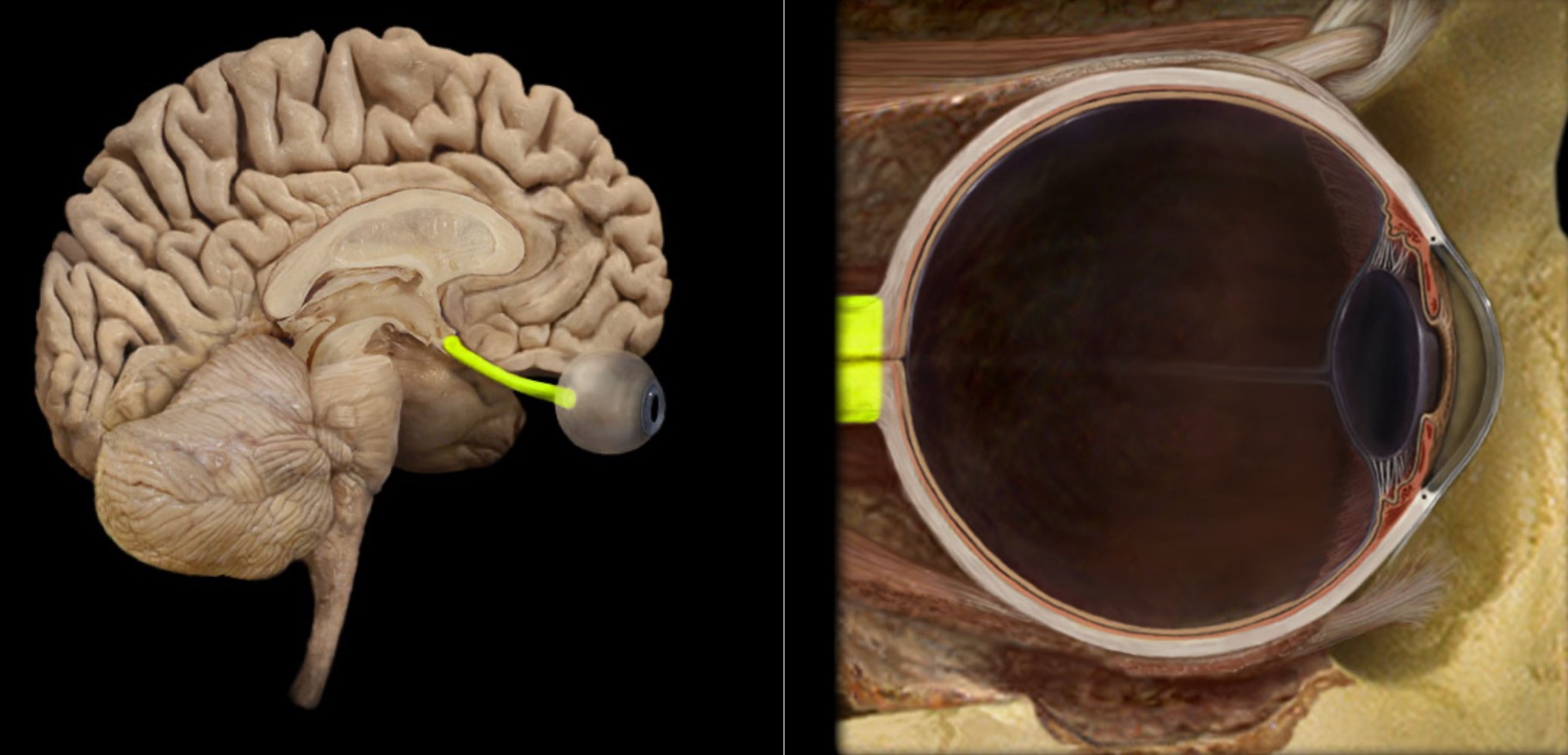
Optic n. (CN II)
Location:
Orbit
Middle cranial fossa
Composition:
Special sensation
Special sensation:
Vision
CNS connection:
Lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus
Cranial foramina:
Optic canal
Comment:
Special sensation includes smell, vision, taste, hearing, and balance
Optic nerve formed by axons of retinal ganglion cells
Retinal ganglion cell axon pathway: optic nerve > optic chiasm > optic tract > brainstem nuclei (including lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus)
Optic nerve also known as CN II
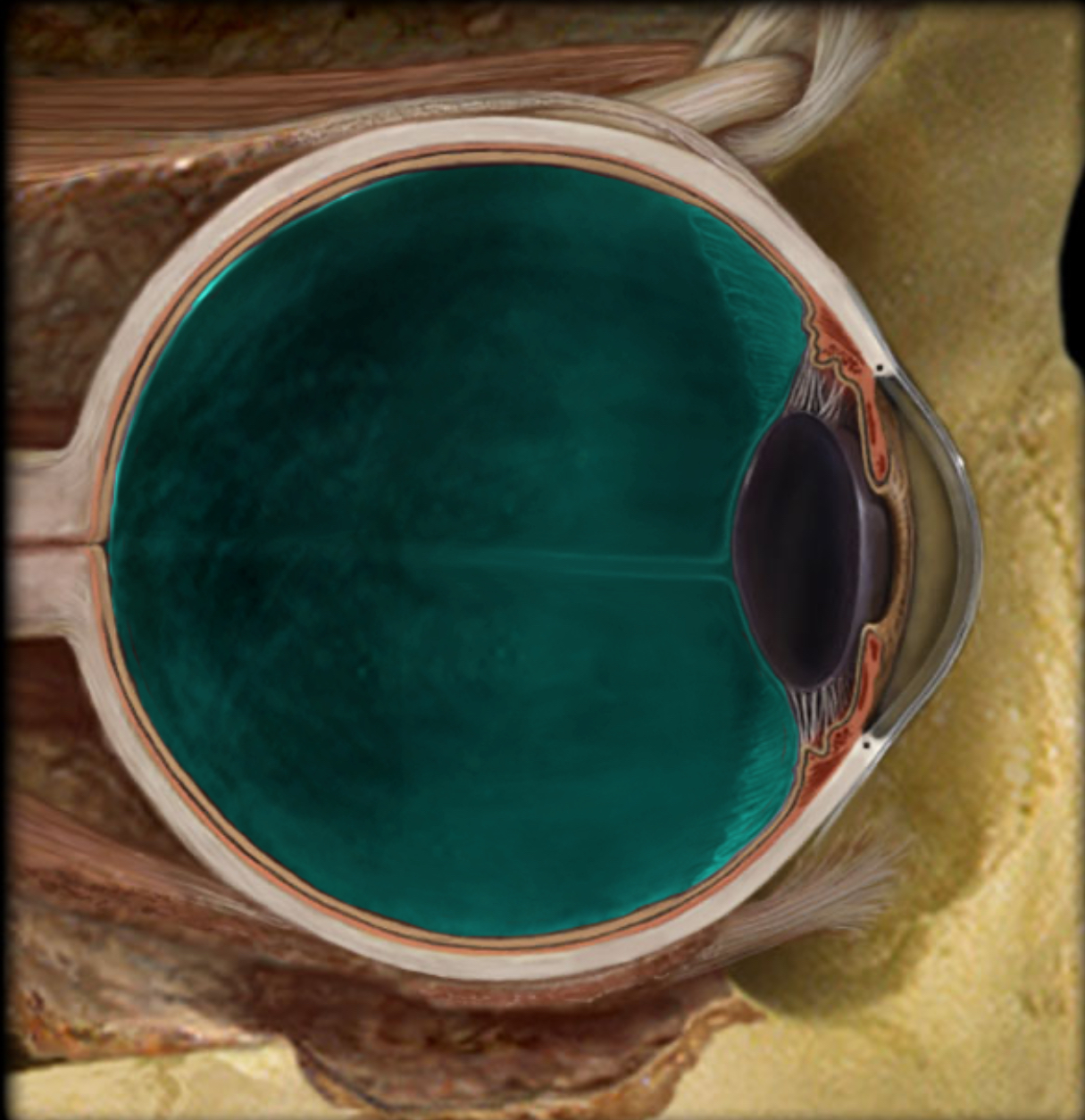
Posterior cavity
Location:
Eye
Posterior to lens and its suspensory ligaments
Description:
Cavity in eye
Occupied by vitreous body (humor)
Function:
Maintain normal intraocular pressure and shape of the eye
Maintain lens and retina in place
Refraction of light
Also known as:
Vitreous chamber
Posterior chamber
Location:
Anterior cavity of eye
Between iris, ciliary body, and lens
Description:
Subdivision of anterior cavity
Filled with aqueous humor
Comment:
Aqueous humor produced in posterior chamber; passes through pupil; enters anterior chamber; reabsorbed into venous system through scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm)
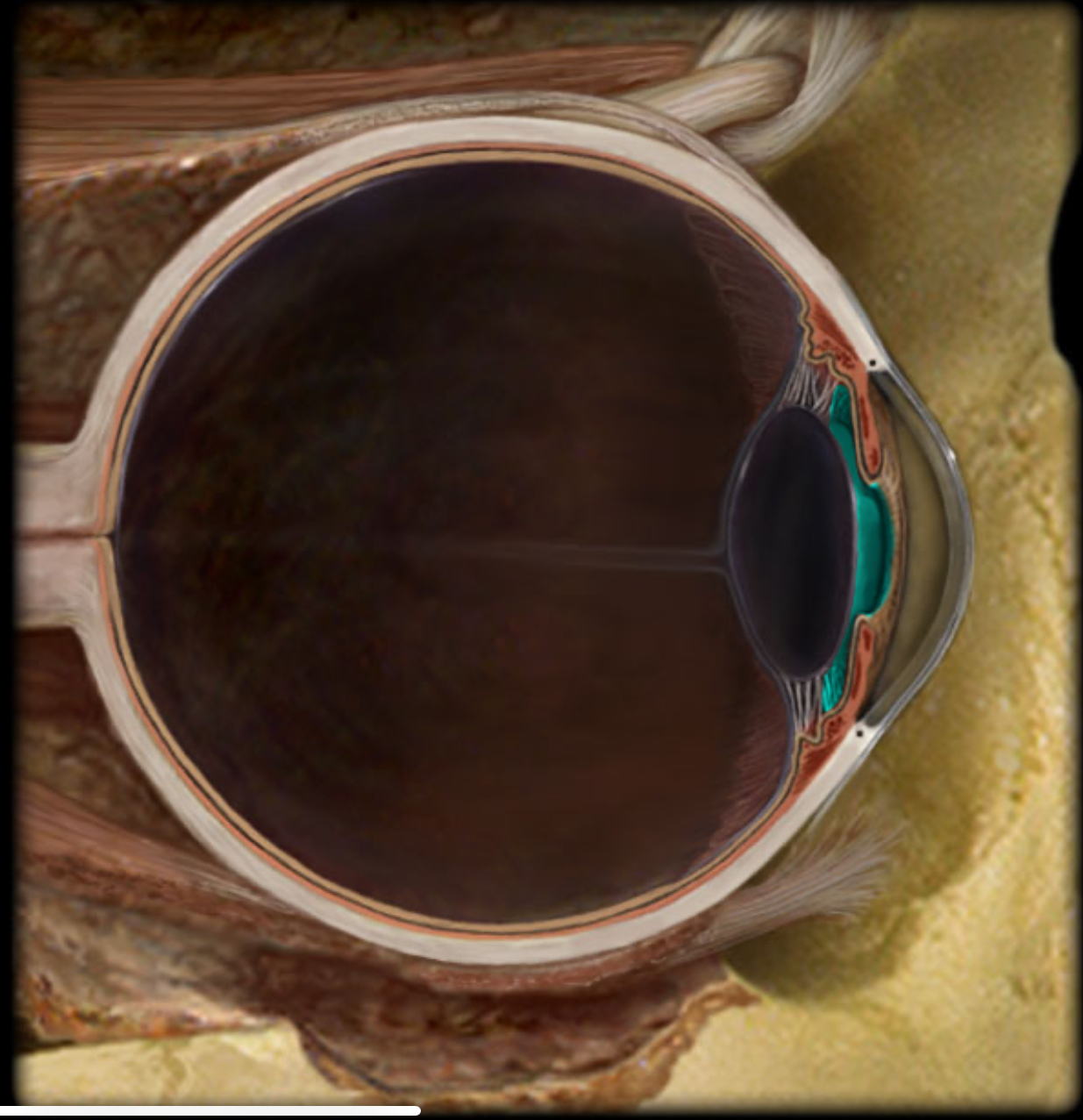
Pupil
Location:
Iris
Description:
Opening in center of iris
Function:
Allows light to enter eye
Comment:
Size of pupil controlled by pupillary constrictor and dilator muscles within iris
Retina
Location:
Eye
Description:
Inner tunic
Composed of two layers
Outer pigmented layer immediately inside choroid
Inner neural layer contains photoreceptors and associated neurons
Comment:
Photoreceptors are primary sensory neurons that respond to light
Axons of retinal ganglion cells form optic nerve (CN I), which connects eye to brain
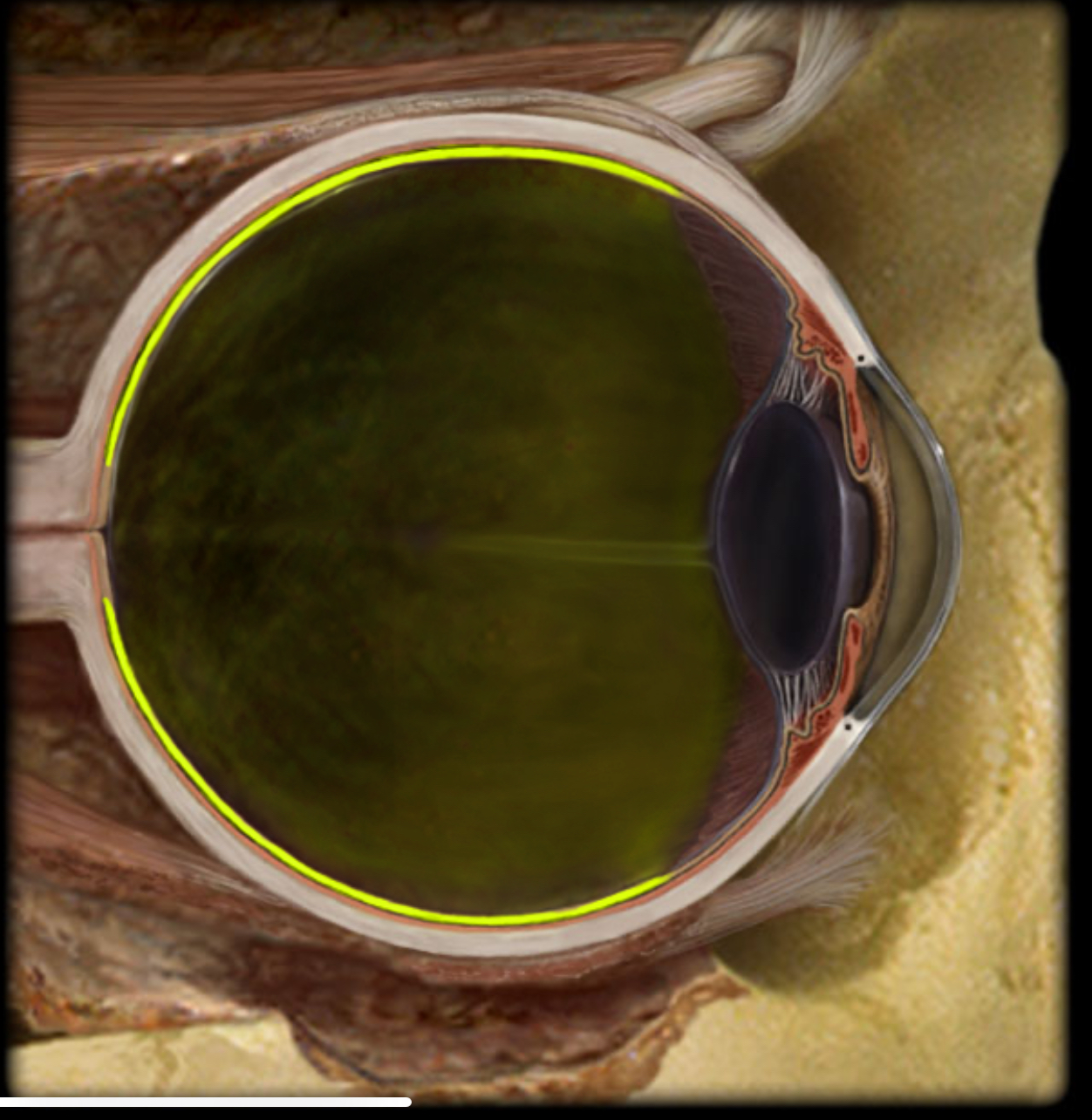
Sclera
Location:
Eye (fibrous layer)
Description:
Outer layer of posterior 5/6th of eye
Dense collagenous connective tissue
Function:
Protects eye
Maintains shape of eye
Comment:
"White" of the eye
Suspensory ligaments of lens
Location:
Eye
Between ciliary body and lens
Description:
Transparent, elastic fibers
Suspends lens from ciliary body
Connects ciliary muscle to lens
Function:
Permits thickness of lens to change with contraction/relaxation of ciliary muscle
Contraction of ciliary muscle > relaxes suspensory ligaments > lens thickens
Relaxation of ciliary muscle > tenses supsensory ligaments > lens gets thinner
Also known as:
Zonular fibers or zonule of Zinn