Renal 2 - Terrestrial Osmoregulation: The Kidney
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Water Loss
Greatest challenge to terrestrial organisms is water loss
Sources of Water Loss
– Respiratory Water Loss → breathing: when we breathe we lose water
– Evaporative Water Loss (EWL) → ex. loss through skin
– Excretory Water Loss → necessary removal of waste products (ex. uric acid/urea)
Excretory Water Loss
Necessary to remove waste products
– Nitrogen from catabolism of proteins
Composition of urine can be modified
– Composition, concentration, and volume
Urine Concentration Modification
During times of drought
– Water is retained by production of highly concentrated urine
During times of water loading
– Excess water is removed by production of large amounts of dilute urine
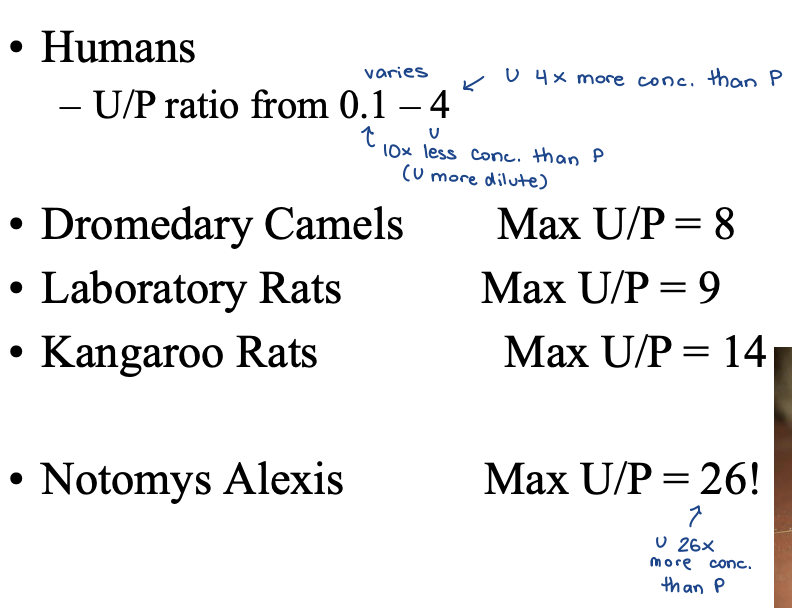
Concentrations can be represented by the U/P ratio
U/P Ratio
Osmotic pressure of the urine divided by osmotic pressure of the plasma
U/P = 1 urine is isosmotic to plasma
U/P < 1, urine is hypo-osmotic (dilute) → water loading
U/P > 1, urine is hyperosmotic (concentrated) → drought
Mammals U/P ratios
Concentrating Ability
mammalian kidney
can increase conc in urine but is very selective so that certain things - K+, Na+, etc - are reabsorbed in blood and waste is excreted
urine production
regulate H2O
regulate solute concentration
for there to be increased conc urine have to move solutes from an area in blood plasma thats less conc to an area that’s more conc
kidney
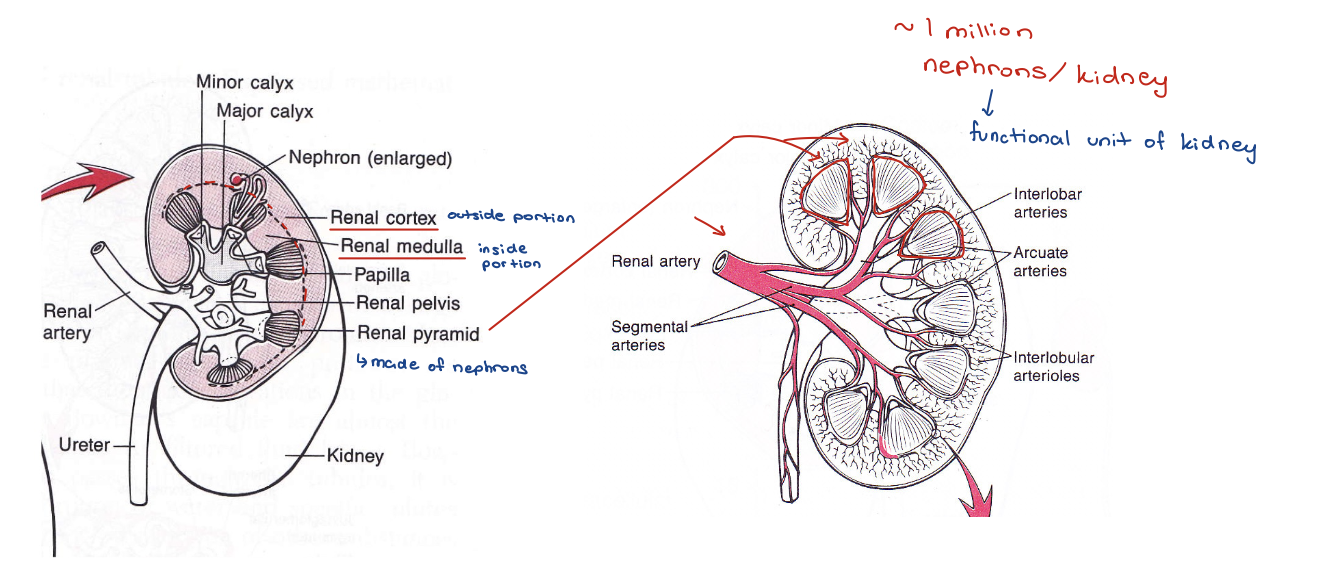
nephron
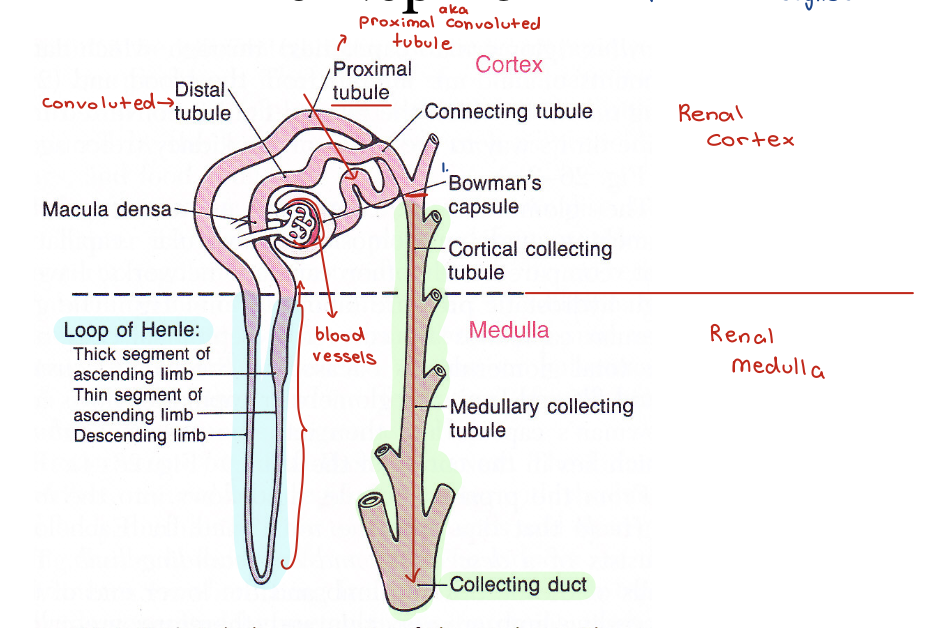
Bowman’s Capsule (BC)
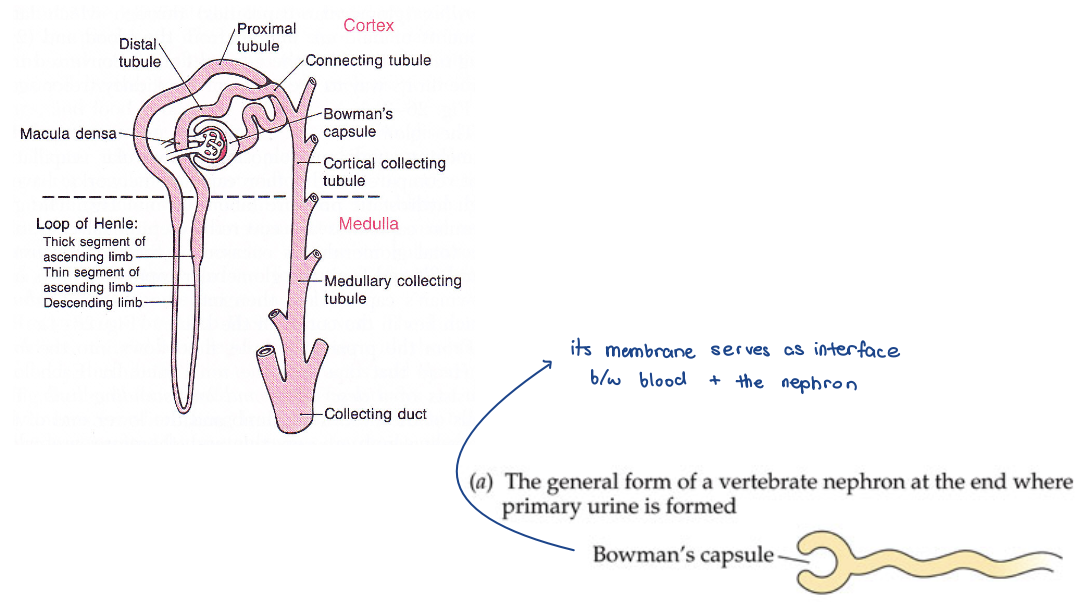
Glomerulus
the blood vessels adjacent to BC
beginning of nephron and all of the vasculature
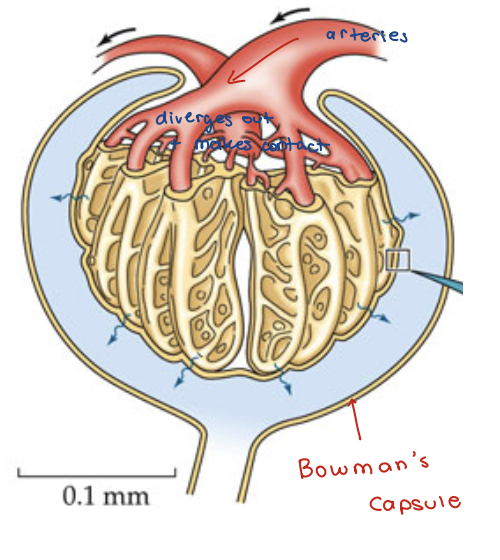
hydrostatic pressures
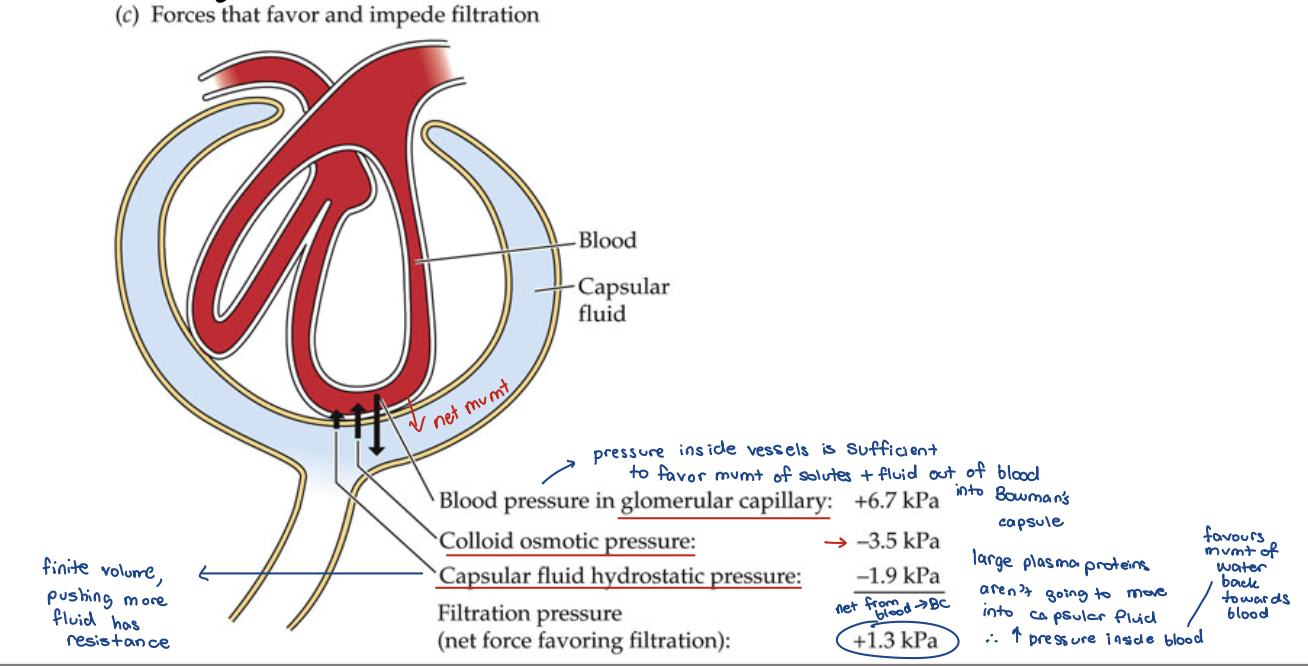
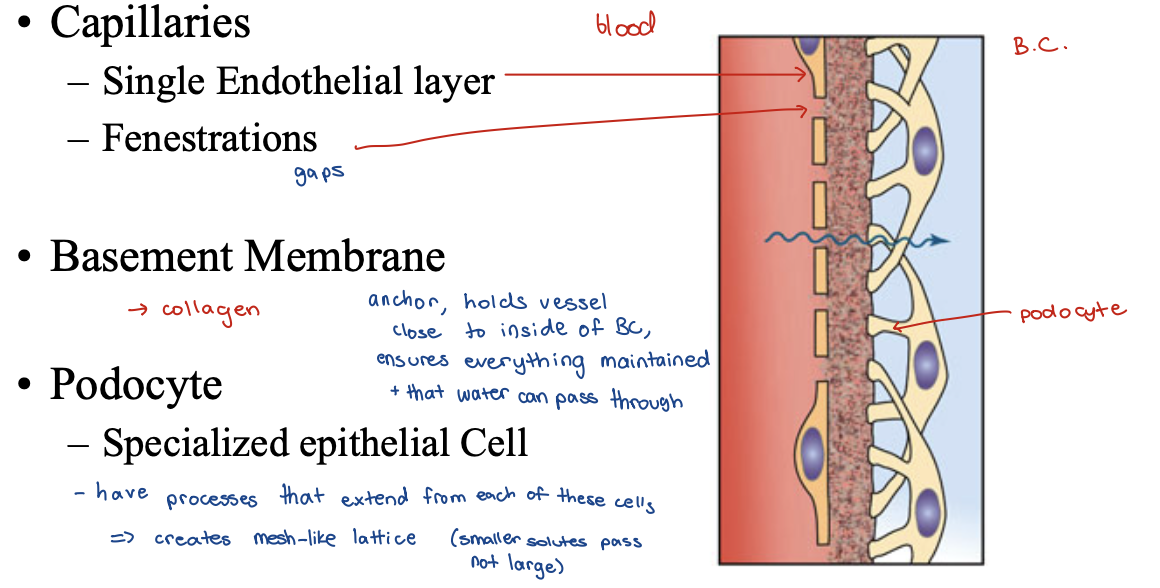
Ultrafiltration
Hydrostatic Pressure outside tubule greater than in tubule lumen
Large solutes can NOT pass
Pressure created by Systole (contraction of heart)
ultra filter
primary urine
isosmotic to blood plasma
Aqueous solution first introduced into kidney tubules
consists of H2O, urea, ions (Na, Cl, K)
Inorganic ions and organic solutes pass into the capsular fluid
Large plasma proteins do not pass
Blood osmotic pressure is higher than capsular fluid
definitive urine
what is excreted
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Rate of production of primary urine
amt produced going from blood to nephrons = GFR
~ 120 ml/min
Full blood volume filtered every ~30 min!!
Urine Concentration
GFR is relatively constant
How are organisms able to retain water in periods of drought and excrete excess water after water loading?
• Other aspects of nephron function accomplish this
Loops of Henle - image
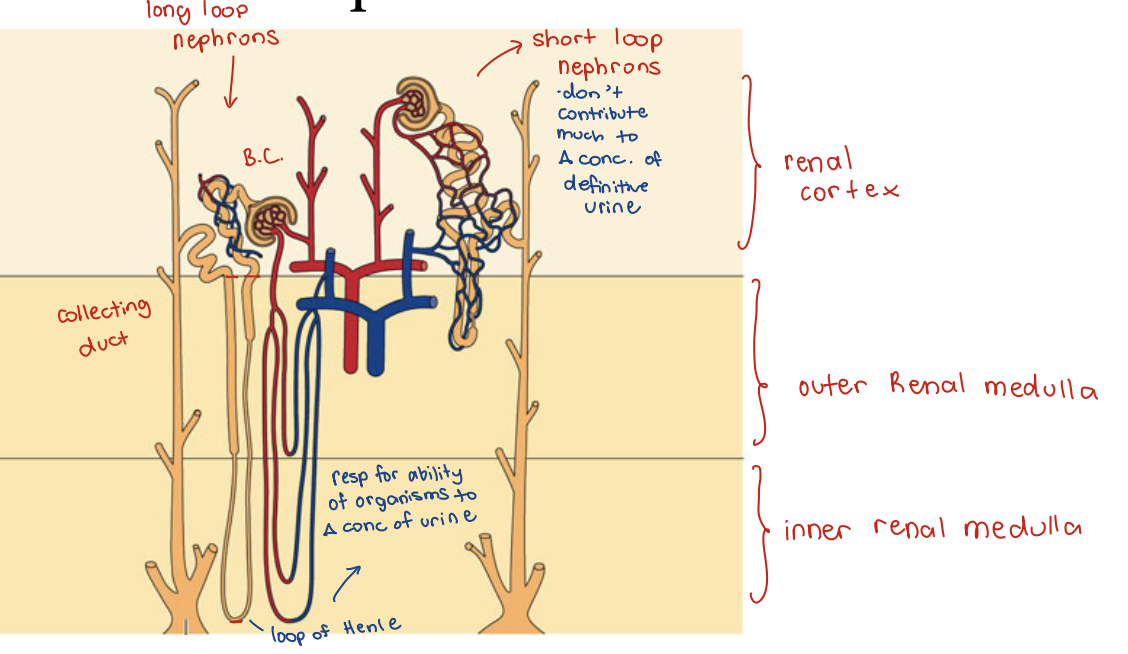
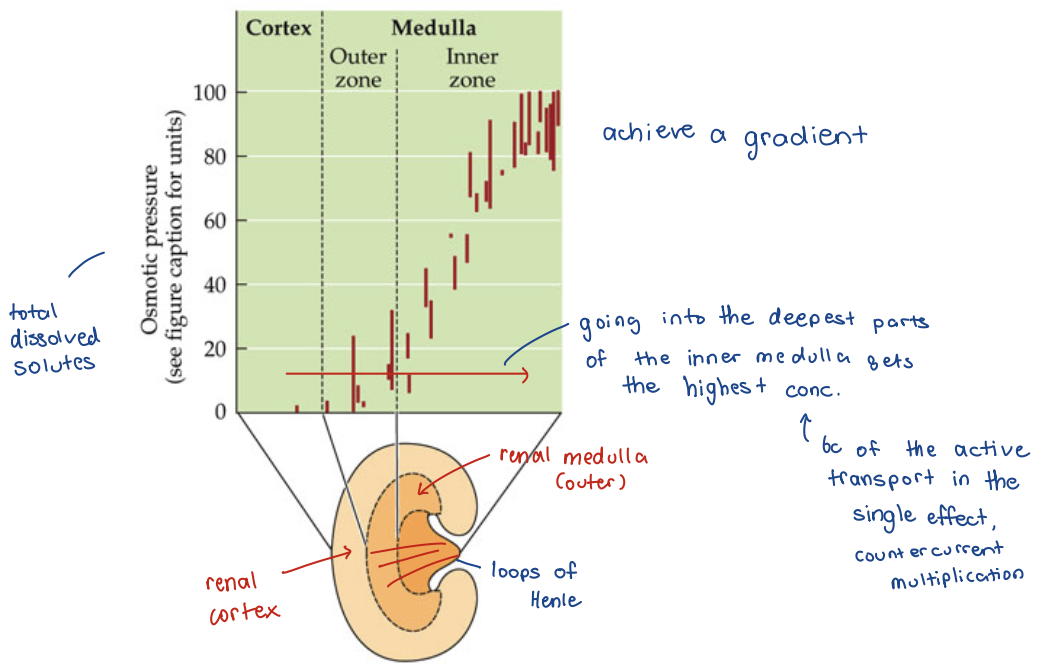
Loops of Henle
Renal component that allows for concentration of urine
U/P Ratio
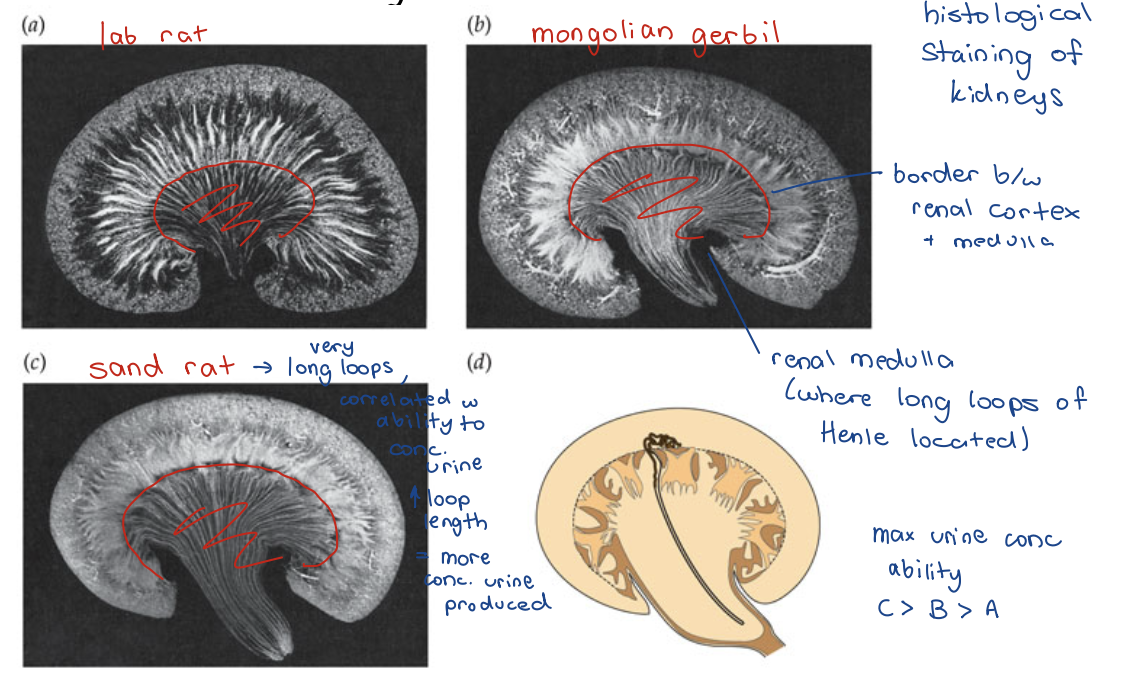
Max urine concentration correlates with abundance of long loops of Henle
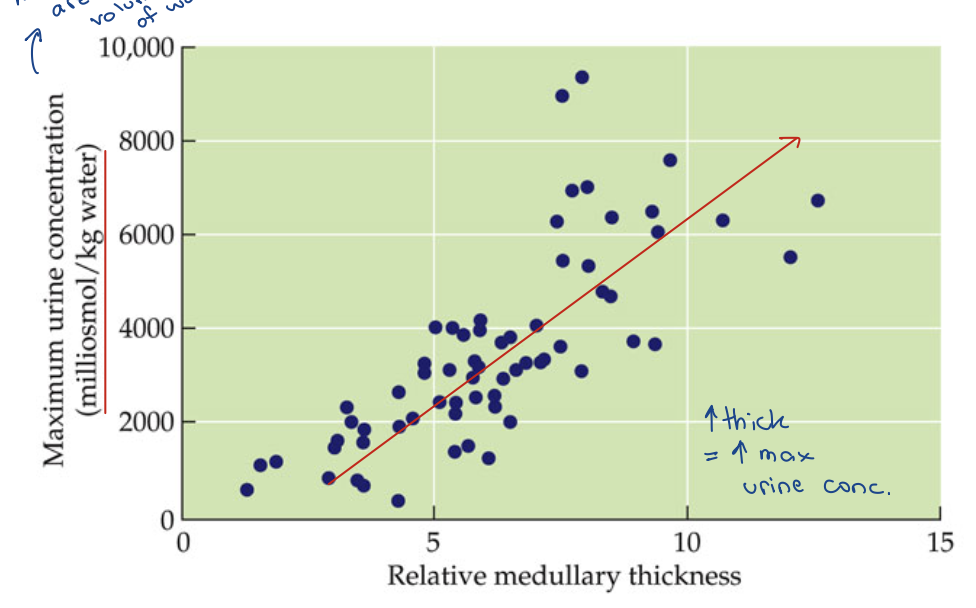
Renal Medullary Thickness
Renal Medullary Thickness - graph
Concentration in Loop of Henle
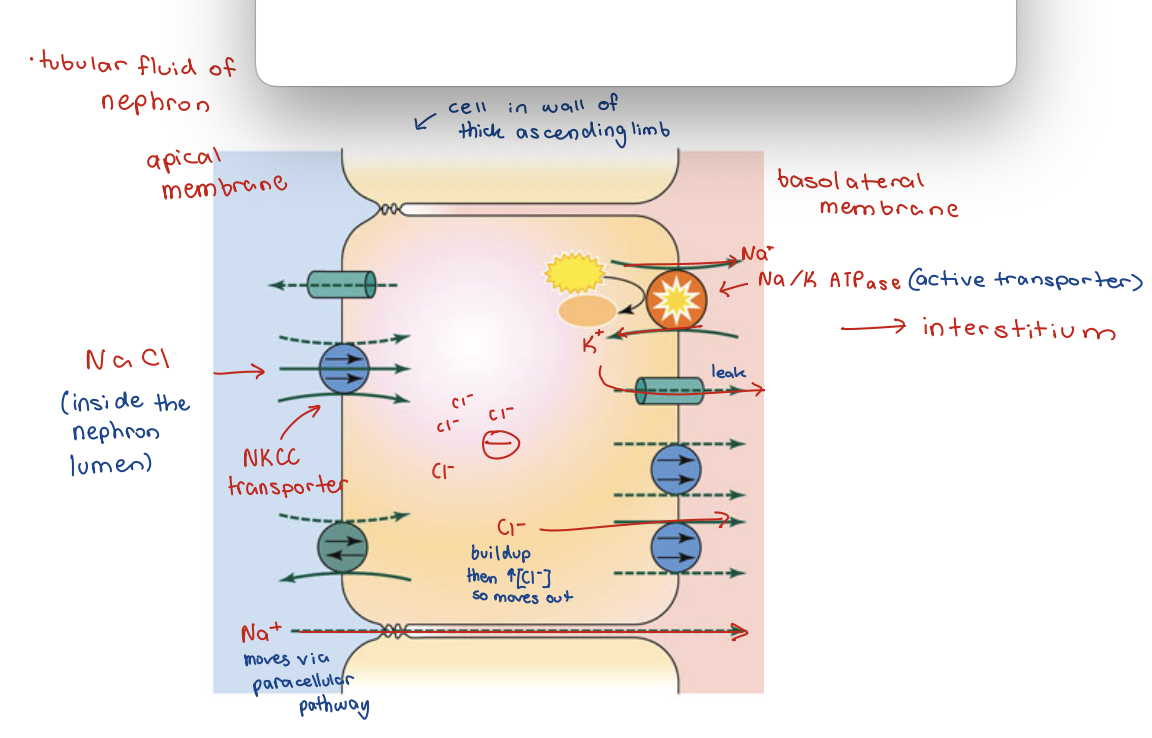
active NaCl transport on the thick segment of the ascending limb
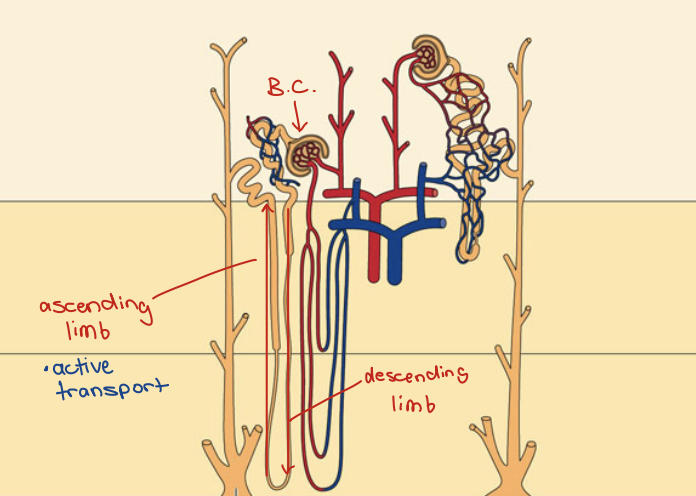
Loops of Henle - descending thin segments
Highly permeable to water Loops of Henle
Moderately permeable to most solutes
Loops of Henle - ascending thin segment
Impermeable to water
Moderately permeable to most solutes
Loops of Henle - ascending thick segment
Impermeable to water
Active transport of NaCl
Active NaCl Transport
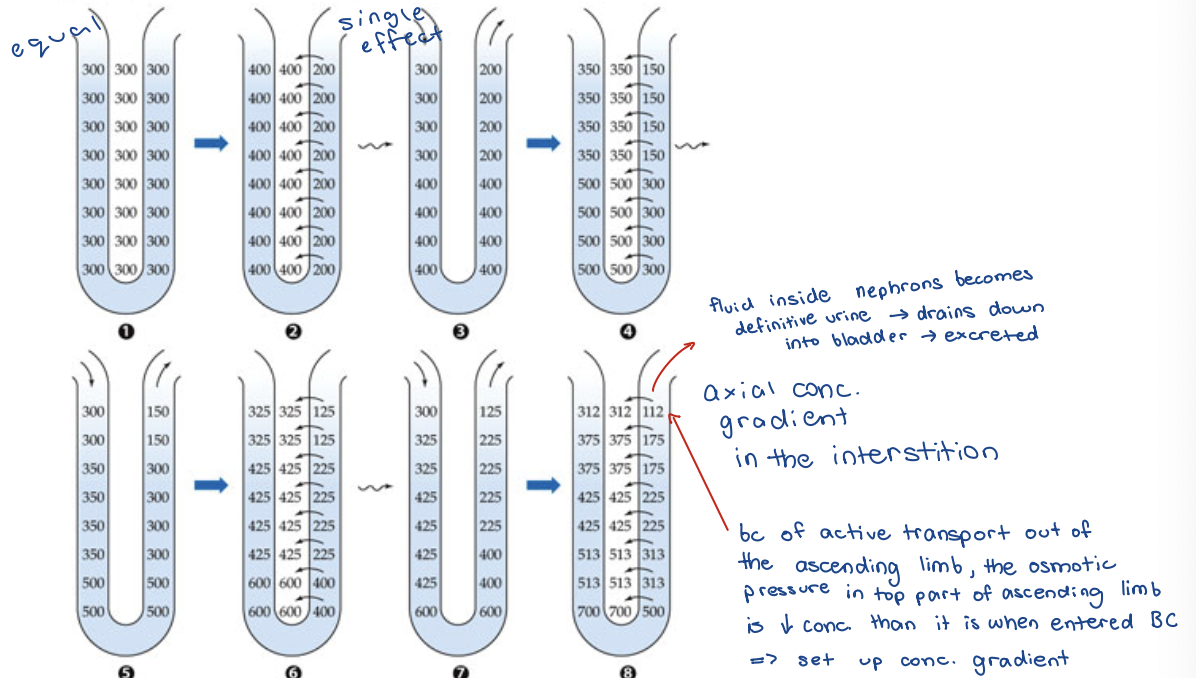
Osmotic Pressures in Loop of Henle
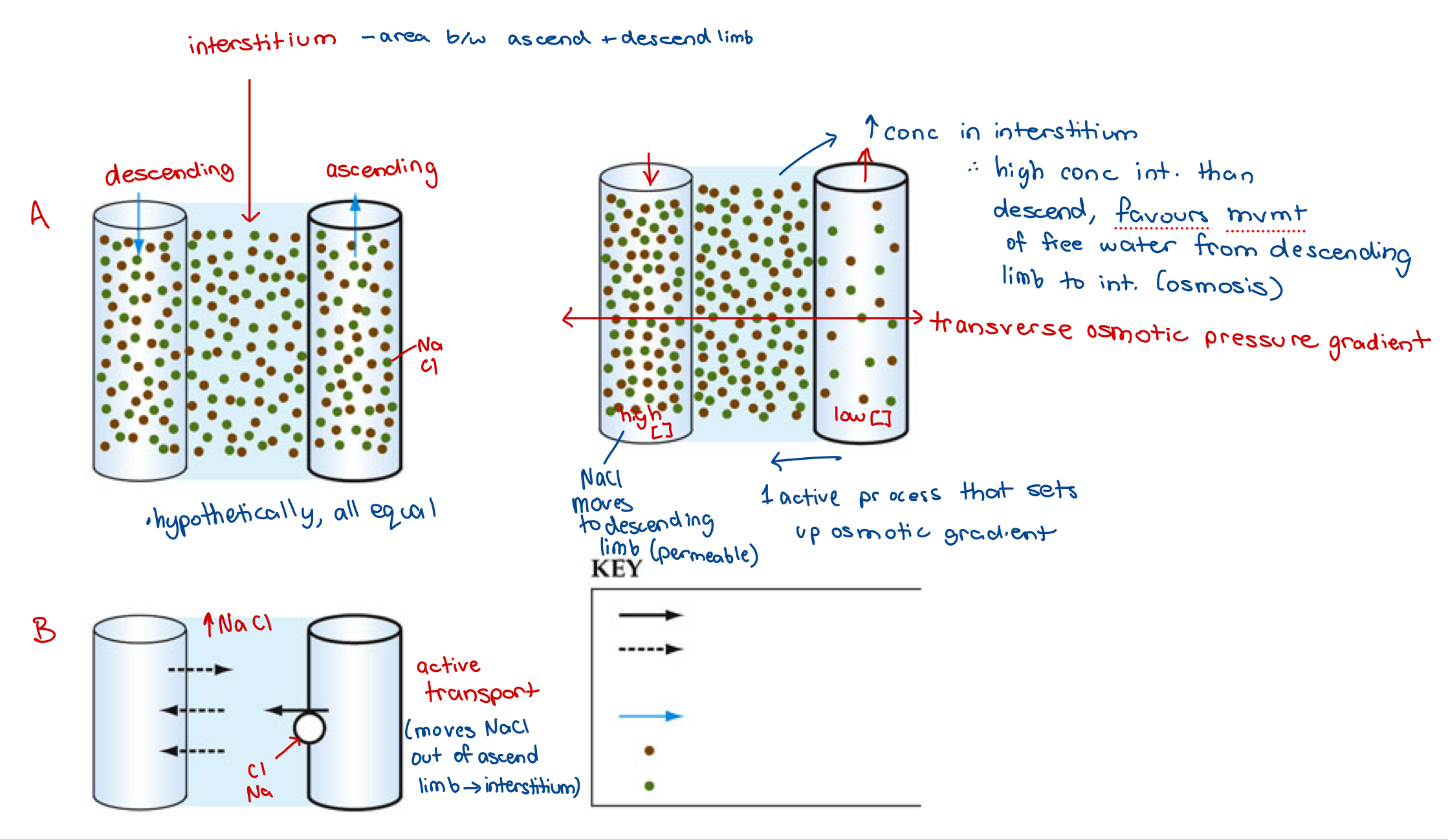
single effect
countercurrent multiplication
single effect
horizontal/transverse osmotic pressure gradient
initial change in pressure because of active transport
Countercurrent Multiplication
axial/vertical osmotic pressure gradient
osmotic pressure differences are multiplied due to fluids moving in opposite directions
what happens when single effect has occurred but fluid inside limbs are moving
osmotic pressure process 1
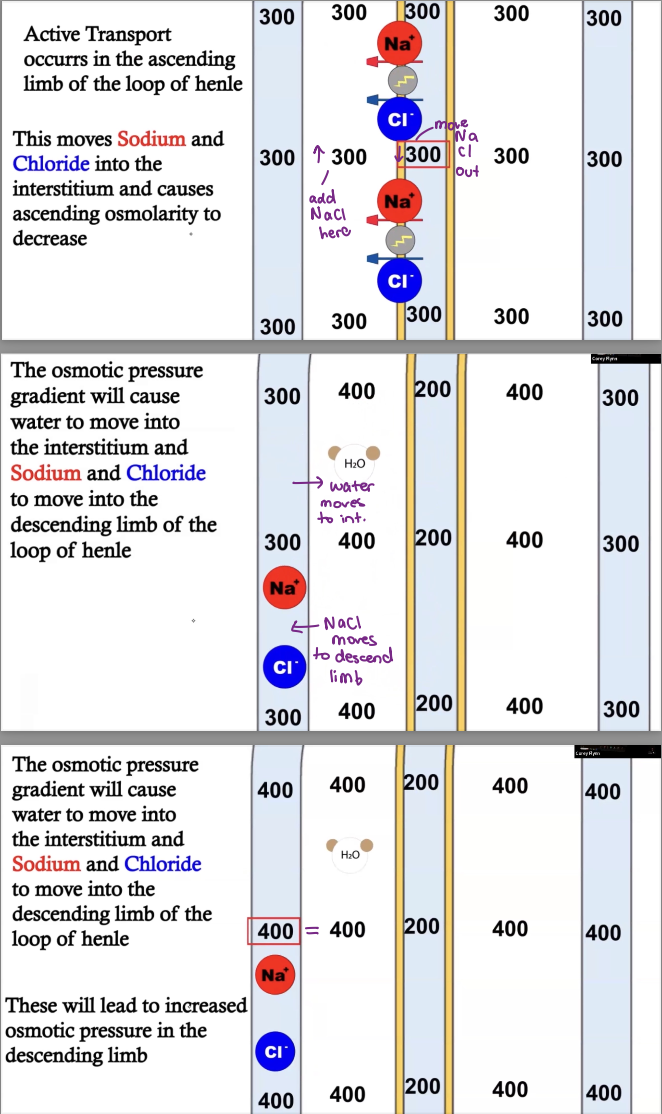
osmotic pressure process 2
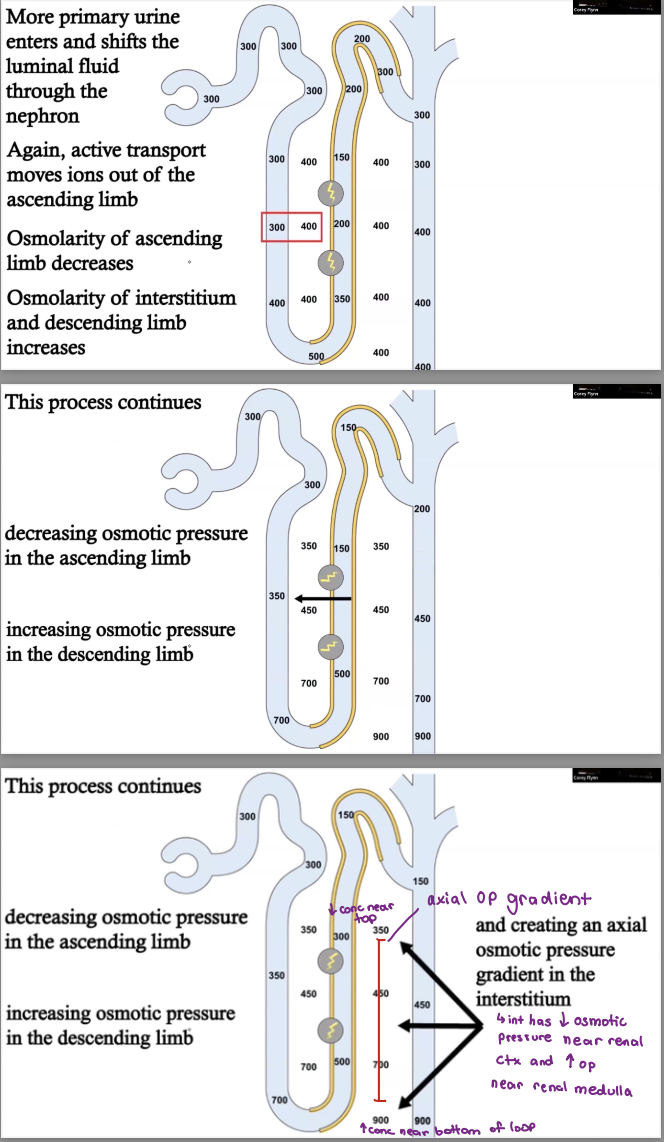
Osmotic Pressure Gradient
urine concentration
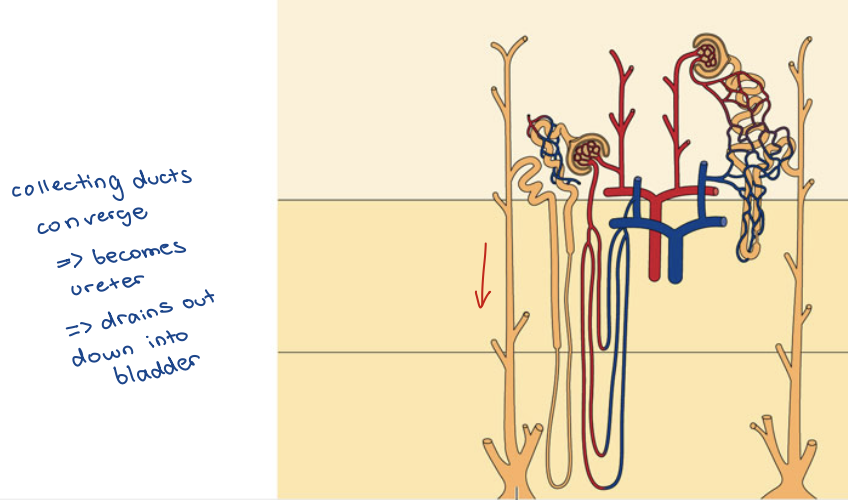
Collecting Ducts
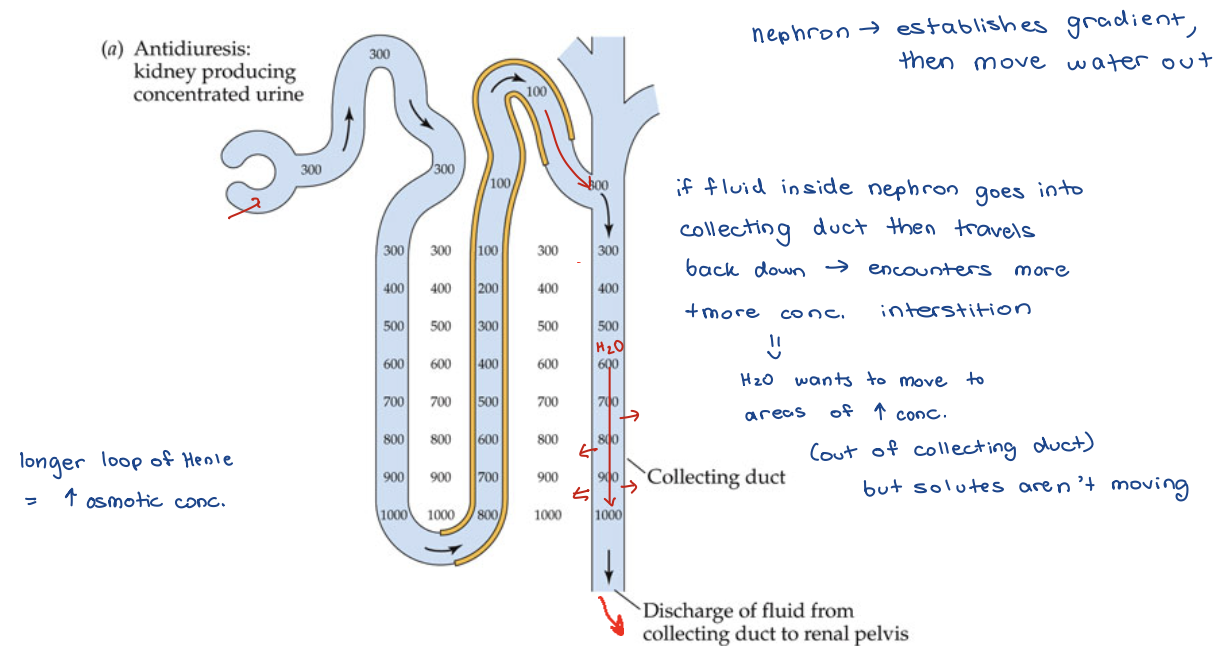
Antidiuresis – Concentrated Urine
Diuresis – Dilute Urine
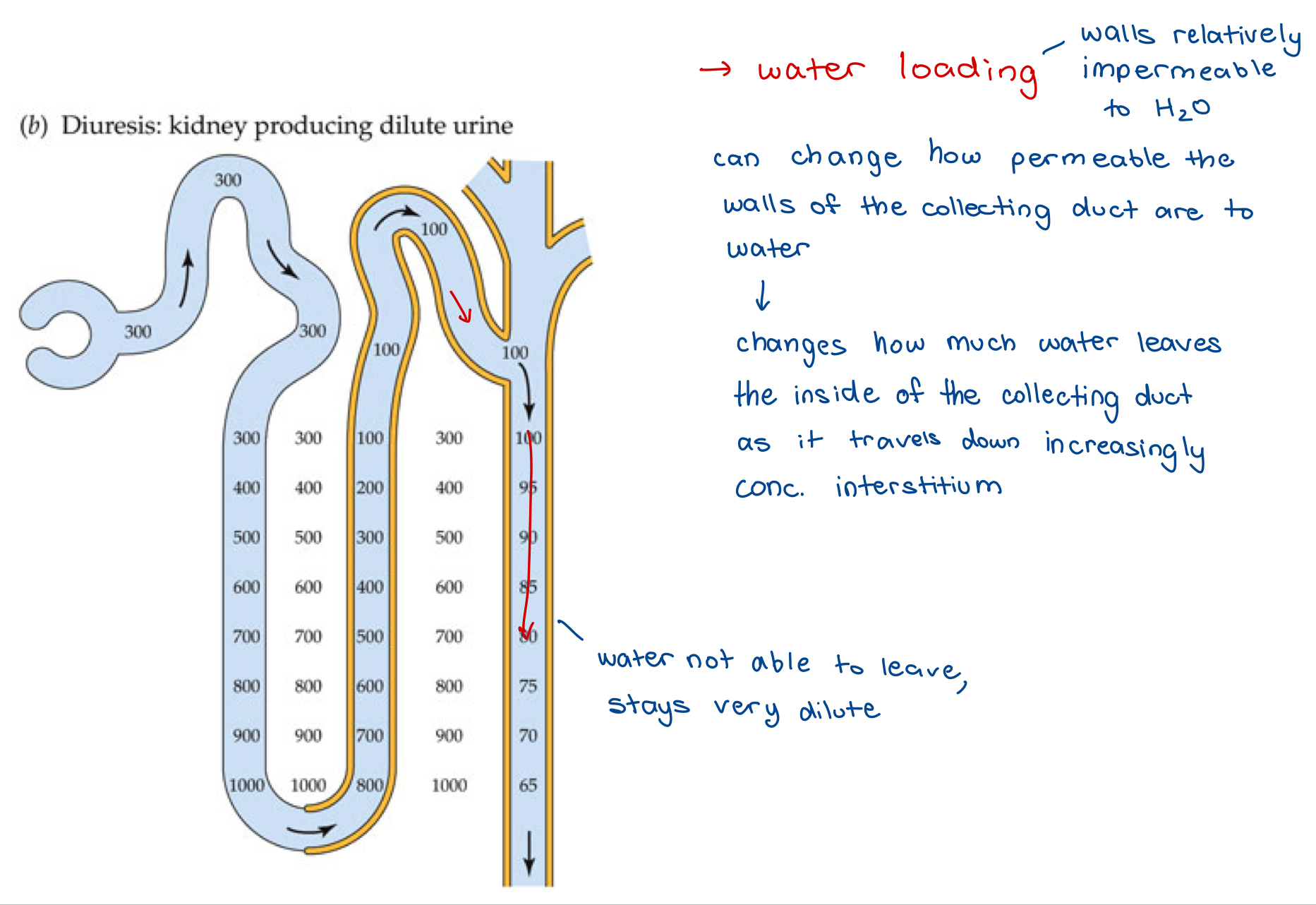
Hormonal Control of Urine [ ]
Water retention of collecting duct under hormonal control
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) - aka
– Arginine vasopressin
– Vasopressin
Modulates permeability of collecting ducts to water (by changing amt of Aquaporin that are in the walls of the collecting duct)
– ADH causes insertion of an aquaporin (Aquaporin-2), which is a water channel protein in membrane that allows H2O to pass through
Antidiuretic Hormone - receptors
Release is stimulated by low levels of blood plasma
Detected by baroreceptors (detect change in blood volume due to stretch of blood vessels)
– Located in Pulmonary Venous System, Cardiac Atria, Aortic Arch, and carotid sinus
Detected by osmoreceptors (detect change in blood osmolarity)
– Located in hypothalamus
Antidiuretic Hormone
Modulates permeability of collecting ducts to water
ADH causes insertion (or removal) of an aquaporin
Aquaporin-2
Aquaporin 2 (AQP2)
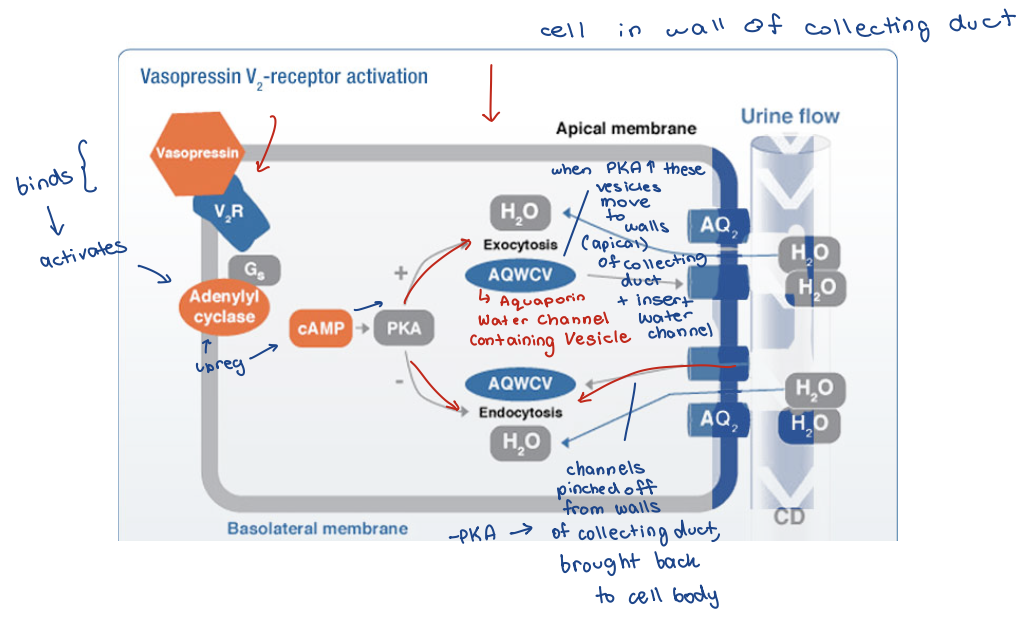
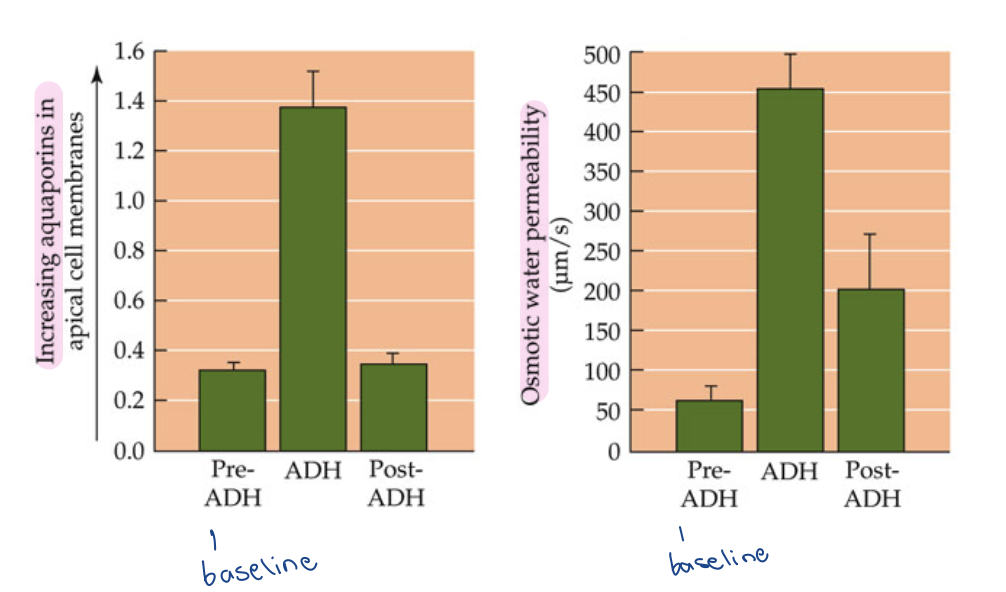
ADH control of AQP2 density
urea
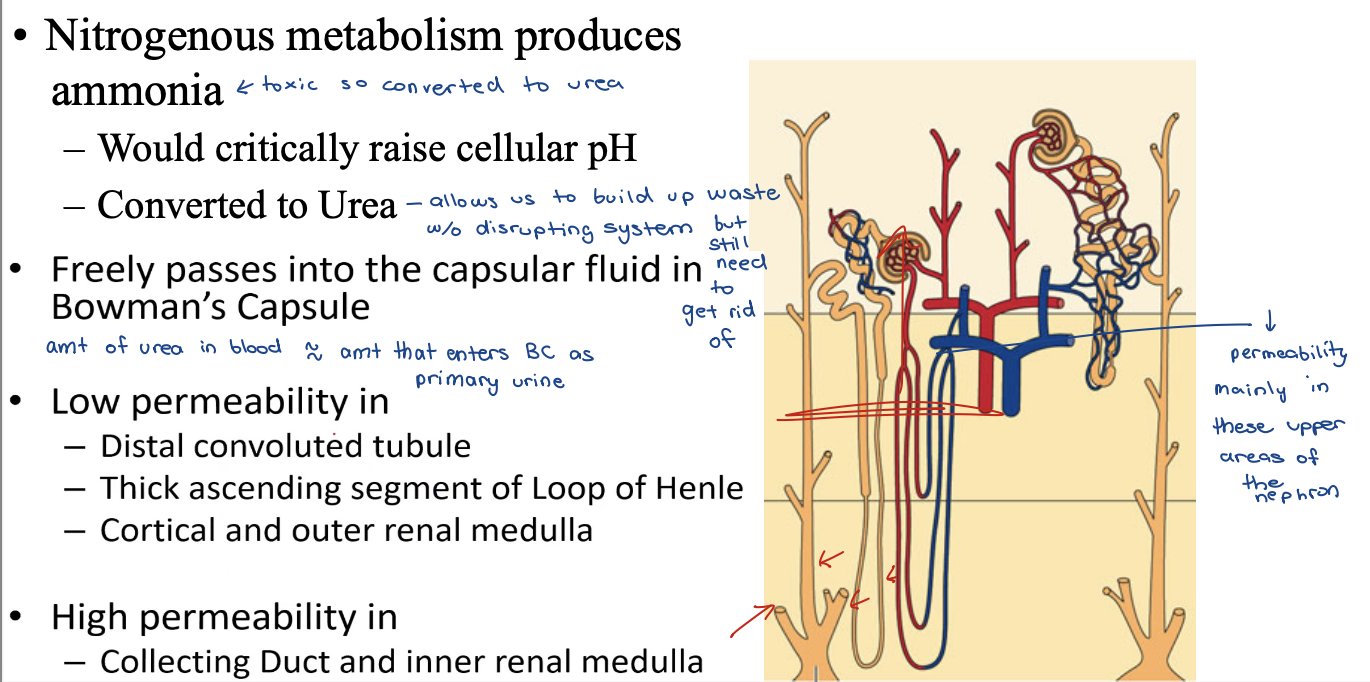
urea low permeability in
distal convoluted tubule
thick ascending segment of Loop of Henle
cortical and outer renal medulla
urea high permeability in
collecting duct and inner renal medulla
Urea Permeability - image
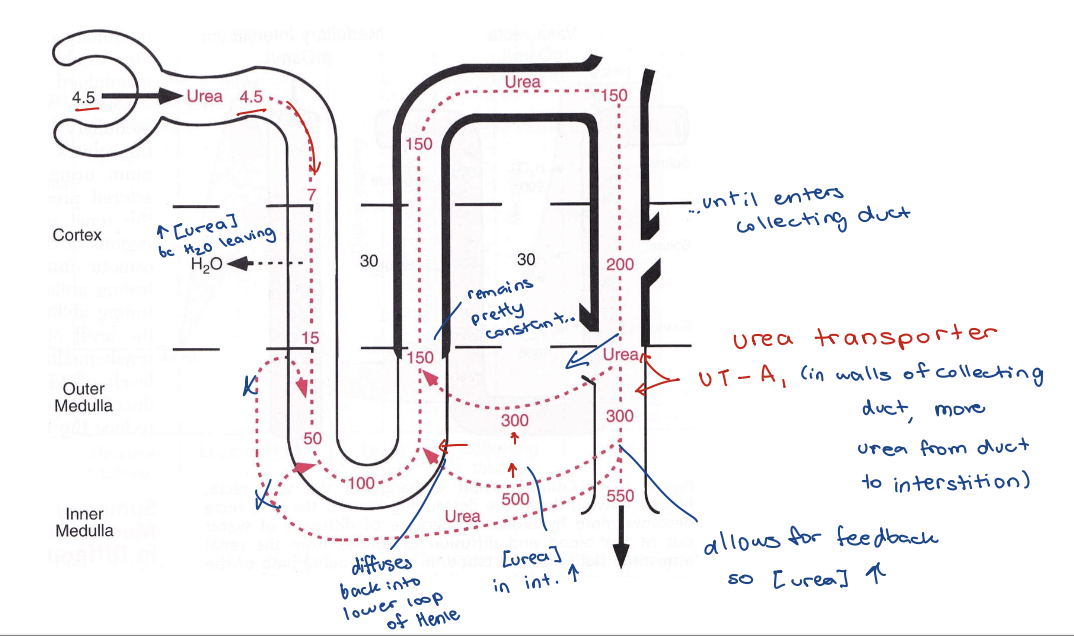
Urea Permeability
Urea transporter protein
– Facilitates diffusion from collecting duct into interstitial fluid
– Upregulated by ADH
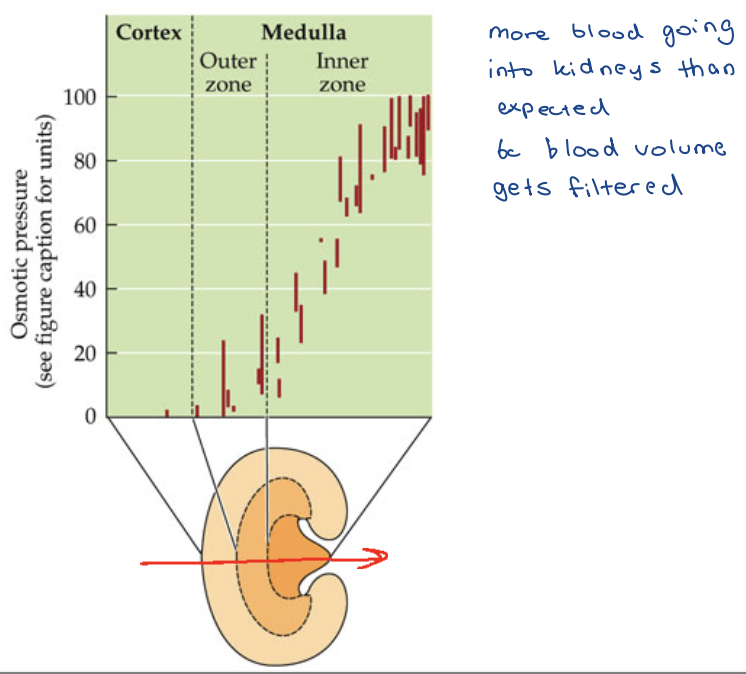
Renal Medulla Blood Supply
Capillaries are permeable
As blood flows from cortex to medulla
Plasma would
– Lose water to interstitium
– Take up NaCl
– Take up Urea
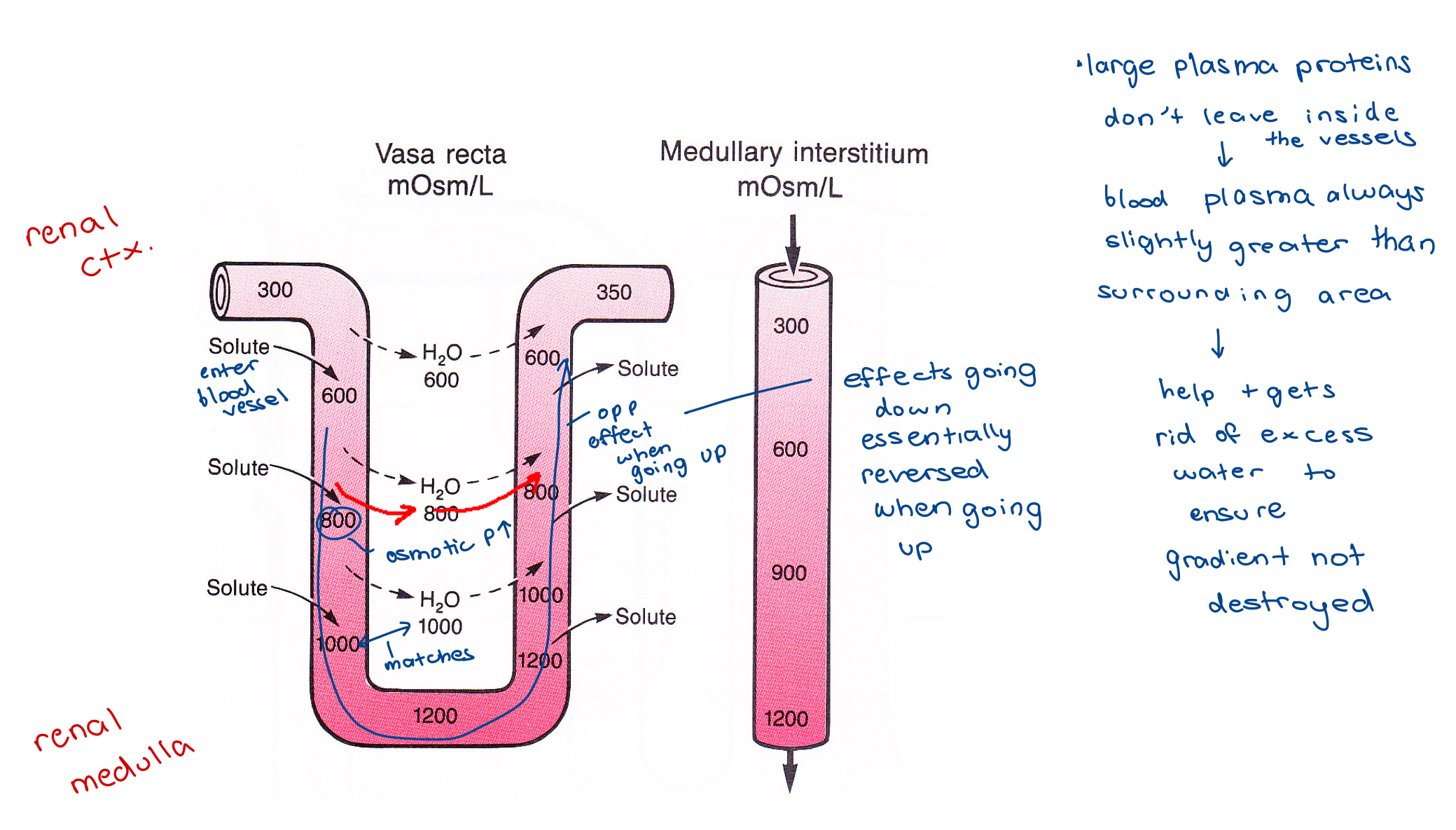
The Vasa Recta - image
blood vessels that serve the deepest part of the inner RM
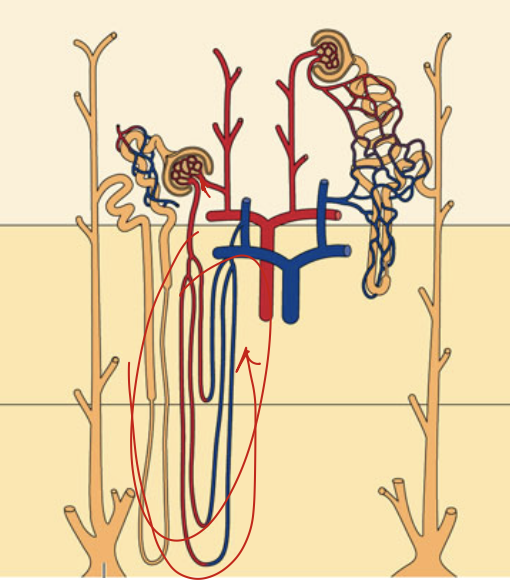
The Vasa Recta
Does NOT destroy osmotic pressure gradients
bc it turns around and comes back towards the renal cortex
Very Little Blood Flow
– Only 1% - 2% of total renal blood flow
remaining to glomeruli to get filtered through nephron to ensure tight control
Countercurrent Exchangers
– Minimizes washout of solutes
the vasa recta - osmolarity