DPT 5226 - Foundational Concepts in Therapeutic Exercise
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Which of the following is INACCURATE?
a) inability to drive is a participation restriction
b) adhesive capsulitis is a physical therapy diagnosis
c) reaching and lifting are examples of activity limitation
d) pain is an example of impairment
b) adhesive capsulitis is a mainstream diagnosis
What does muscle performance involve?
• strength
• endurance
• power
muscle performance =
strength, power and/or endurance
most bodily movements are _______
rotational
muscle performance - What is endurance?
ability of a muscle to repeatedly contract against a load without undue fatigue, either in a dynamic or static muscle (e.g. posture) action
muscle performance - What is power?
• rate of performing work (work/time)
• torque or work = force x moment arm or distance
muscle performance - What is strength?
• max tension a muscle generates during a single contraction
• measured based on muscle force (tension), torque (rotational force), work (linear force), power (work/time)
muscle torque - resistance training vs. ergonomics - How can torque be altered?
• by modifying force magnitude (e.g. the load lifted or resistance applied)
• by modifying the moment arm length
• by modifying the joint angle
torque or work =
force x moment arm
What does the SAID principle stand for?
Specific Adaptations to Imposed Demands principle
What is the SAID principle?
• you get what you give
• specificity - important for rehab
• implications for fitness/performance
What is an example for the SAID principle?
order/sequence and progression matter
• impairments before function, but function ASAP
DOMS
delayed onset muscle soreness
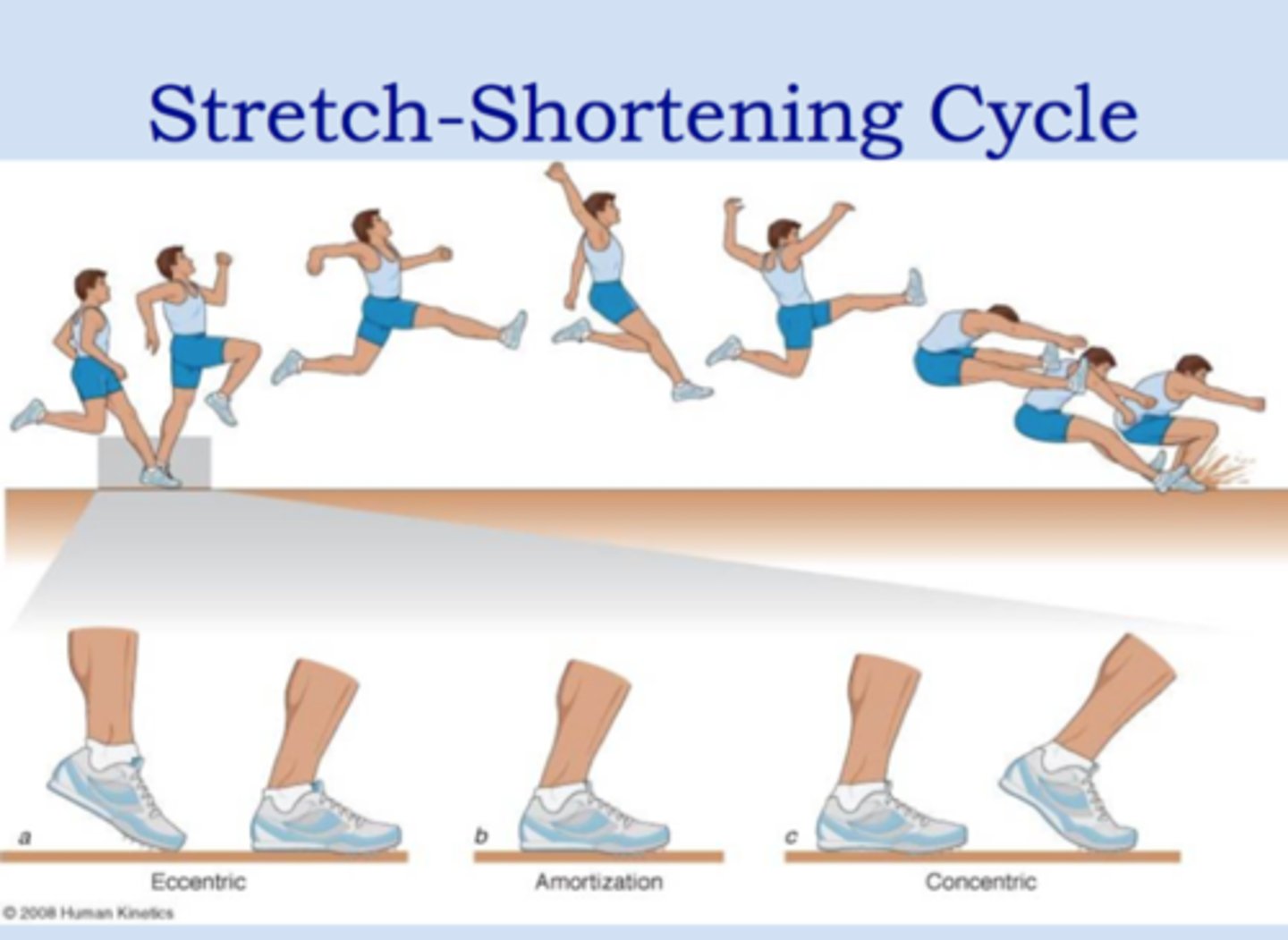
stretch shortening cycle
• combination of eccentric action followed by a concentric action
• resulting concentric contraction that follows in an SSC is more powerful than a traditional concentric action alone (elastic potentiation)
• basis for certain PNF techniques and plyometrics... plyos are not limited to the lower limbs and performance training
training load and DOMS
• successful training = progressive load; adequate recovery; avoiding excessive overload.... necessary for performance (aerobic, strength, power)
• it's ok if it hurts a "lil" bit 2-4 days after resistance training, but...
• minimize DOMS as much as possible (to enhance exercise adherence)
• start small... avoid eccentric mm actions at initial stages of rehab
stretch shortening cycle - What is elastic potentiation?
the resulting concentric contraction that follows in an SSC is more powerful than a traditional concentric action alone
PNF
proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation
Is plyometrics only used in lower limbs?
NO
What are examples of plyometrics exercises?
• plyo wall push-ups
• lunge plyometrics
• scissors jumps @30/50/70% max
• fast feet
Would you use plyometrics in the shelf stage?
no, you want to think about improving ROM (isometrics)
muscle force-velocity relationship
• light resistance = high velocity
• increasing concentric resistance/load = decreasing velocity (when v = 0, mm contraction is max isometric... further load = eccentric mm action)
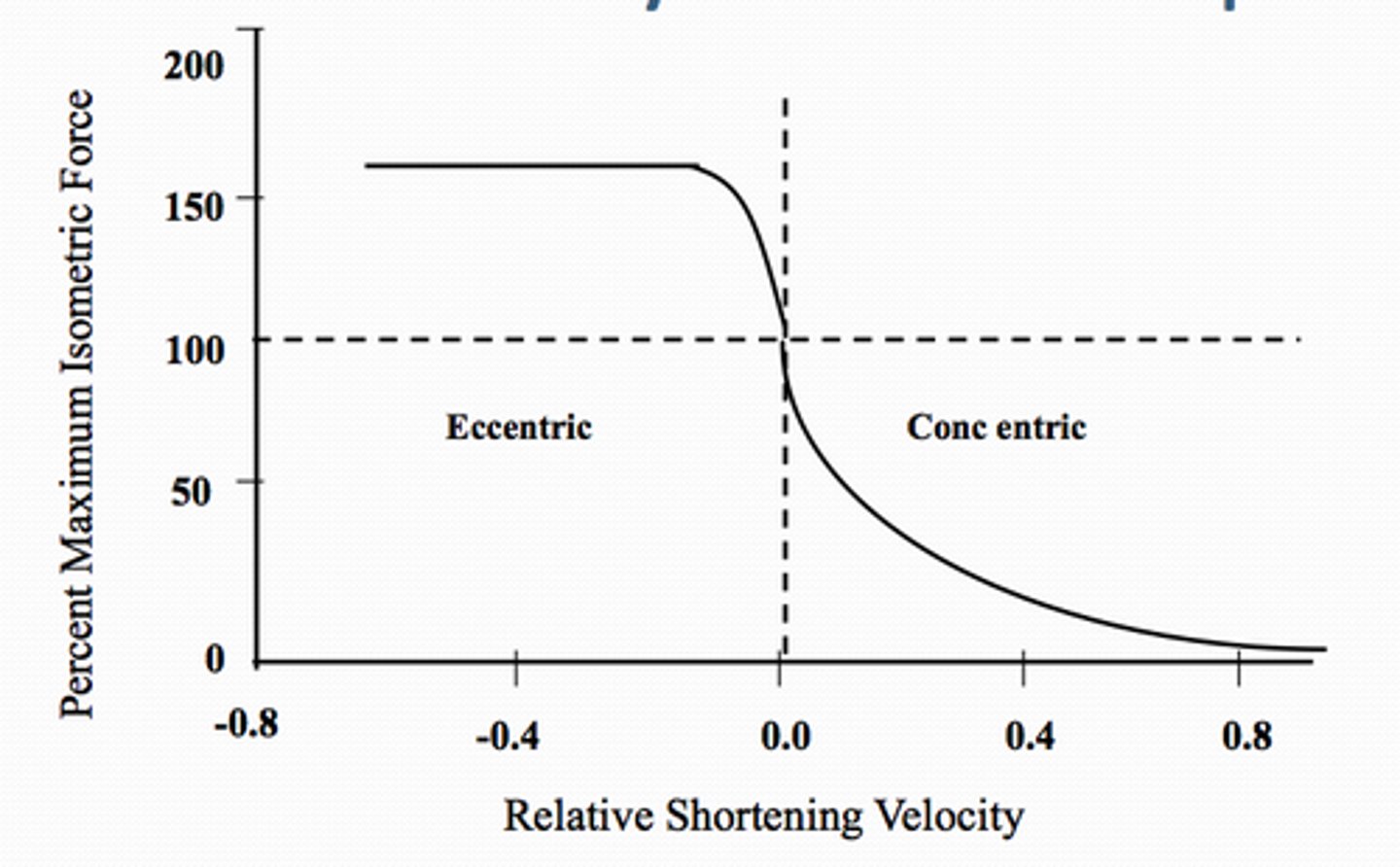
muscle force-velocity relationship - What are the implications?
• strength vs. endurance training
• muscle force/tension hierarchy (eccentric > isometric > concentric)
muscle length-tension relationship
• mm length and strength relationships
• capacity to produce force depends on the length at which the muscle is held (max force delivered near the muscle's normal resting length)
muscle length-tension relationship - What are the implications?
muscular insufficiency
muscle insufficiency
• relevant to multi-joint muscles ONLY
• active vs. passive insufficiency
muscle insufficiency - What is active insufficiency?
• relates to mm tension/force generation
• "too" short over pry and/or sec joints
• too much slack
• prime movers (in the direction of motion)
muscle insufficiency - What is passive insufficiency?
• relates to allowable ROM
• "too" long over pry and/or sec joints
• too much opposing length/stretch in antagonists
• good for stretching - the MI paradox
Is there more tension when opposing elbow flexion when the elbow is flexed or extended?
when the elbow is extended
When is passive insufficiency beneficial?
when stretching
When is passive insufficiency bad?
when loading
True or false. Maximal shoulder flexion CANNOT be achieved simultaneous with maximal elbow flexion.
true, they are blocked because of the triceps
How MUST muscles be stretched?
over primary and secondary joints (plus tertiary, if applicable)
closed kinetic chain (CKC)
the terminal joints meet considerable external resistance which prohibits or restrains its free motion
open kinetic chain (OKC)
when the end segment is free to move
CKC exercises
combine the forces of weight bearing and the effect of gravity to simulate functional activities
How do we examine and evaluate muscle performance?
• manual muscle testing
• 1RM
• dynamometers
• others (e.g. push ups)
manual muscle testing
oxford grading using standard positioning specific to muscles/joints
dynamometers
isometric (handheld, grip) and isokinetic
Your goal is to improve the strength of your patient's biceps femoris (strength grade 2/5). The BEST starting position would be:
a) prone with knee extended
b) sidelying 20° hip flexion with 90° knee flexion
c) sidelying 20° hip flexion with 45° knee flexion
d) sidelying full hip extension with knee extension
c) sidelying 20° hip flexion with 45° knee flexion
this is best for isometric contraction
muscle contraction - static
isometric
muscle contraction - static - isometric
muscle contracts but does not shorten or change joint angle
muscle contraction - dynamic
• isokinetic
• isotonic
muscle contraction - dynamic - isokinetic
• equal velocity through the ROM
• load varies
• use a machine in the gym to get this
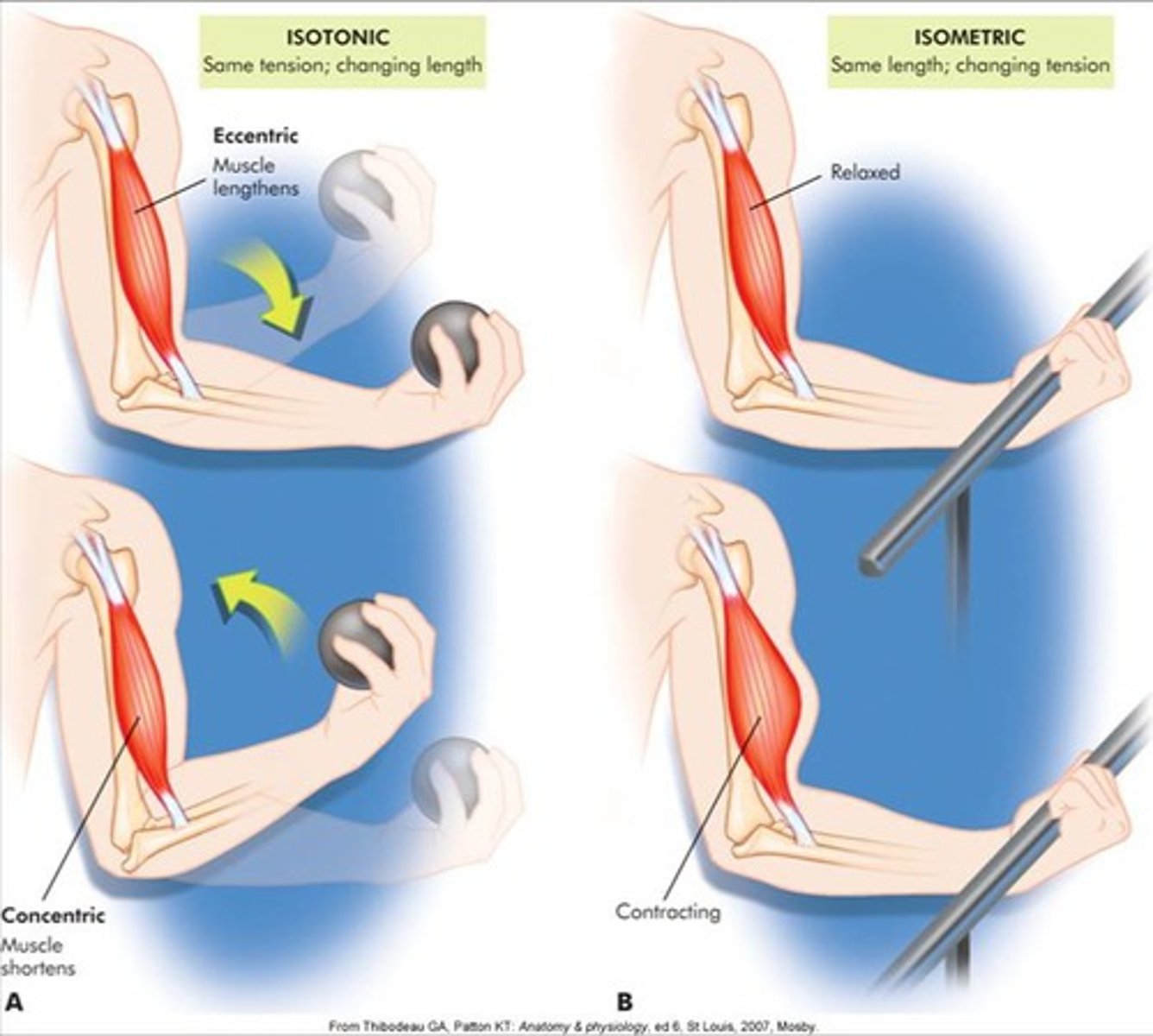
muscle contraction - dynamic - isotonic
• muscle length changes
• velocity changes, load is the same
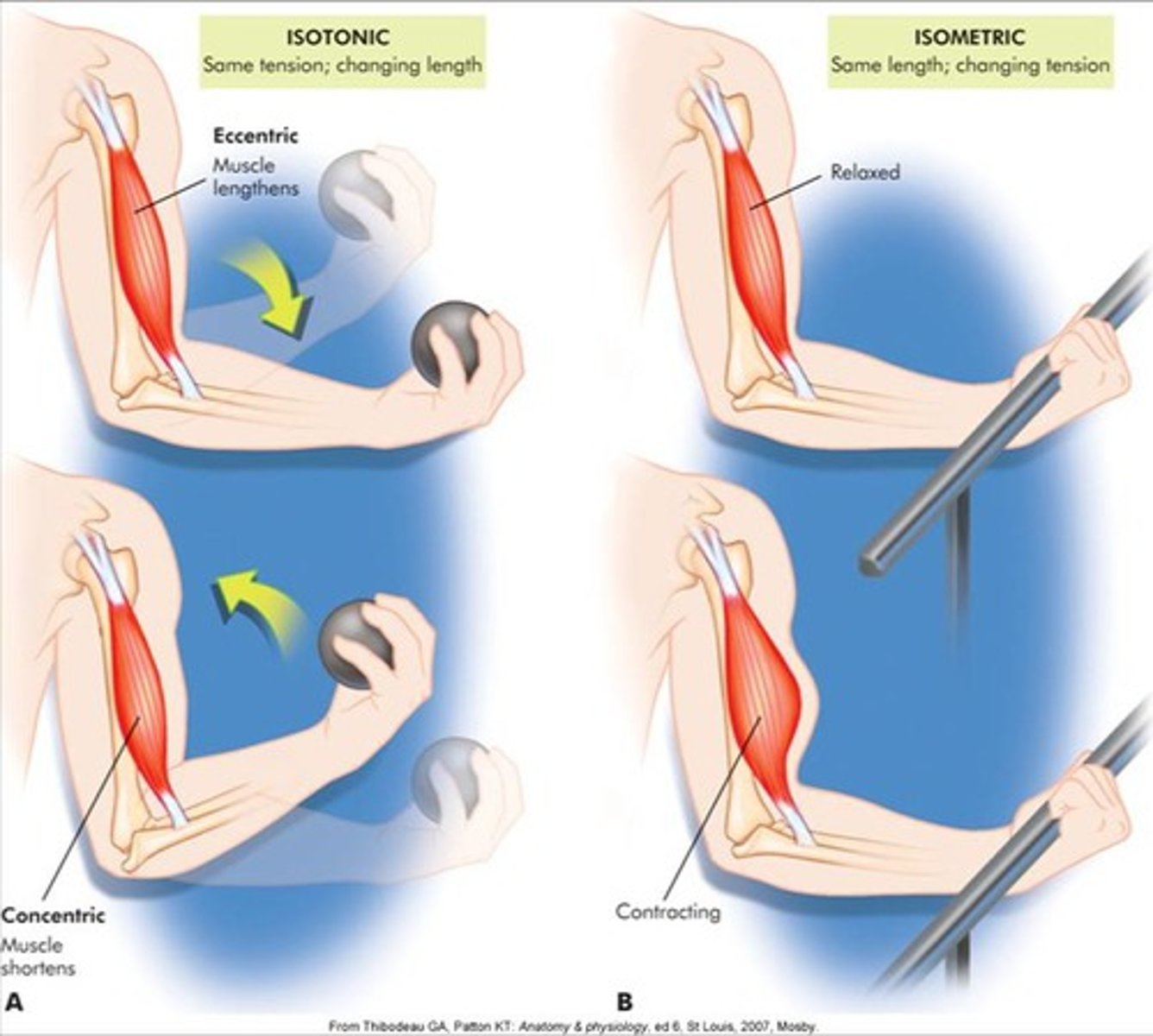
eccentrics
• generates the greatest muscle tension
• key component of functional movement (e.g. deceleration)
• implications for high injury risk (e.g. hamstring strains)
What are 2 considerations we need to have when we figure out what muscle is working?
• movement dynamics
• force dynamics
What muscle is working? - movement dynamics
• What joint is moving (primary jt. of motion)?
• Any secondary joints of motion?
• Is there an effect of gravity and/or external resistance?
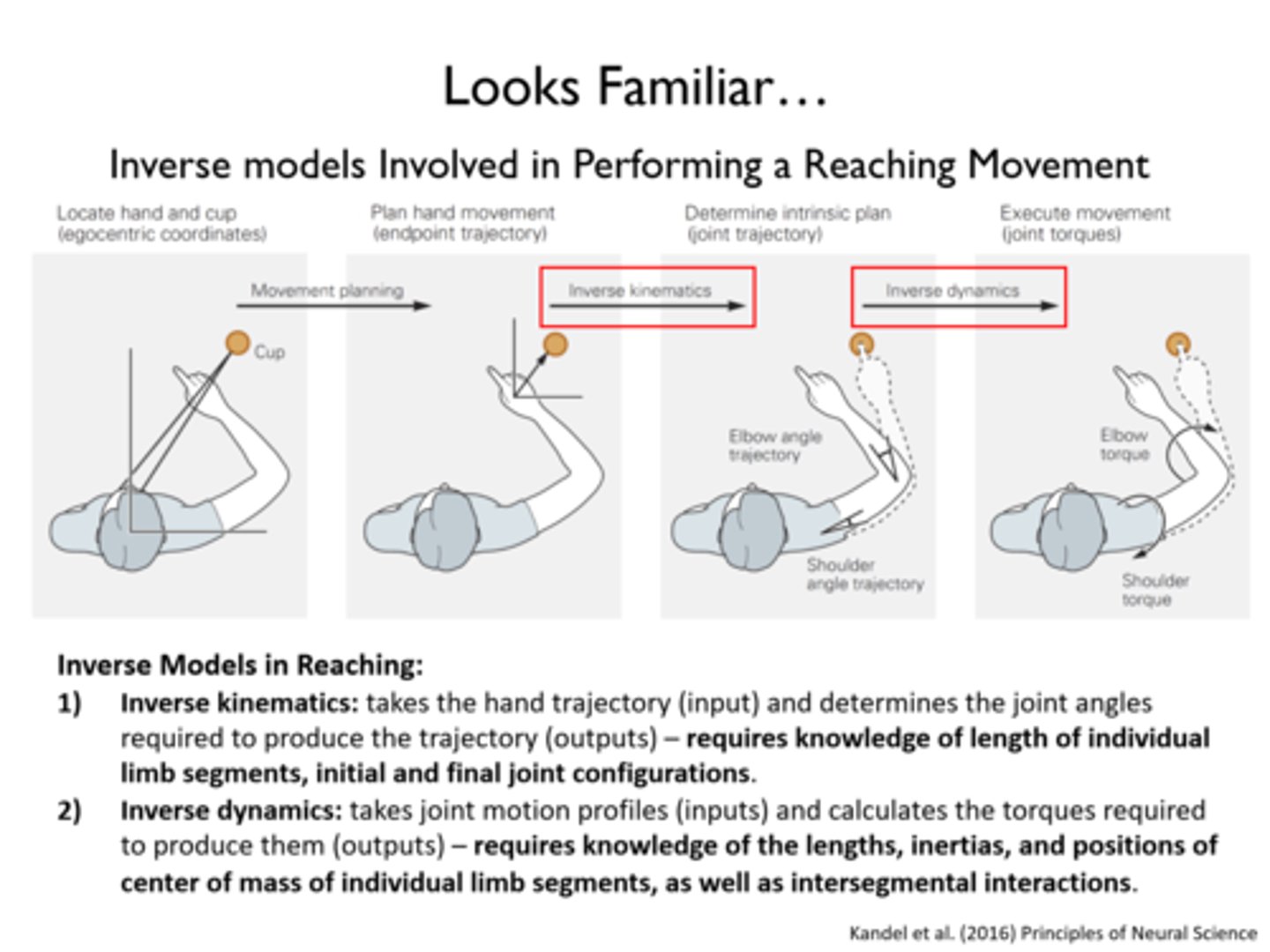
What muscle is working? - force dynamics
• Is the muscle lengthening or shortening?
• What type of contraction is occurring? (Is it eccentric or concentric?)
force dynamics - The Muscle Action Algorithm
• gravity overpowers muscle torque? ... muscle yields
• resistance overpowers muscle torque? ... muscle yields
• gravity overpowered by muscle torque? ... muscle dominates
• resistance overpowered by muscle torque? ... muscle dominates
• forces counterbalances?
Does the direction of motion of a limb dictate what muscle (group) is active?
• NO
• e.g. eccentric elbow extension with a dumbbell
MA and considerations for rehab
THINK
• foundational concepts
• exercise specificity
• exercise progression
MA and considerations for rehab - exercise progression
• Isoms >> [PROM >>] >> AAEx >> FAEx >> RAEx (manual) >> RAEx (equipment)
• Fxl re-education and work/sport specific skill training should be incorporated into the above continuum ASAP
squat vs. leg extension exercises
• greater torque/hypertrophy is generated in the RF during leg extension
• squat-related exs tend to impact distal quad fibers more, and leg extension exs tend to impact proximal
• squat-related exs significantly improves quad power
• combo of squat-like exercises and leg extension exercise is necessary to maximize loading and performance training in the quads group of mms