Marine Ecosystems Review
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential concepts regarding marine ecosystems, including interactions, productivity, and ecological roles.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is the difference between a community of organisms and a population of organisms?
community= different populations of species in an area,
population= same species in an area.
What are the three types of symbiosis and their symbols? give examples
Parasitism (+,-), exp= sea lice and fish
Commensalism (+,0), remora fish and manta rays or sharks
Mutualism (+,+). boxer crabs and anenomies
What is the difference between an ectoparasite and an endoparasite?
Ectoparasites live outside their host (e.g. sea lice),
endoparasites live inside (e.g. tapeworms).
What are the two ways autotrophs can make their own food?
Through photosynthesis and chemosynthesis.
What is a heterotroph? what types are there?
An organism that feeds on autotrophs.
primary, secondary, tertiary, quarternary
What does 'productivity' measure in marine ecosystems?
The rate of production of new biomass per unit area by autotrophs
through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis?
Reactants: Carbon dioxide and water.
products: glucose and oxygen

Where does chemosynthesis typically occur in the ocean?
Usually near hydrothermal vents at depths
2000-7700m.
What is cellular respiration? what are the reactants and products?
A process in which all living things release chemical energy stored in organic molecules.
C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
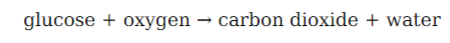
In what ways can productivity be measured?
using rate of photosynthesis from producers
using rate of increase in producer biomass
using satellite imagery to measure chlorophyll
What is eutrophication?
When nutrient levels increase too rapidly, causing phytoplankton to bloom excessively.
algae bloom
How much energy is typically passed from one trophic level to the next?
10%.
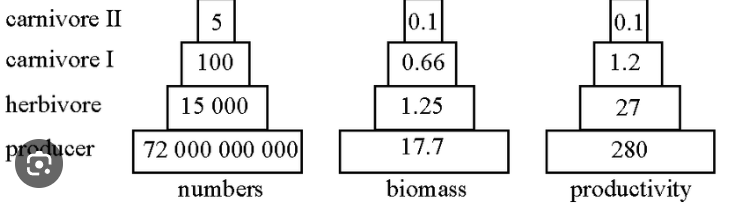
What are the three types of ecological pyramids?
Pyramids of number- number of organism in each trophic level
biomass= biomass of organisms in each trophic level
energy= rate of production of biomass
What is a nutrient?
substance needed for growth, repair, energy, or normal metabolism.
How do nutrients enter the bodies of producers?
assimilation and absorption.
How do nutrients enter the bodies of consumers?
feeding.
what is the importance of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium?
Carbon: carbohydrates, organic compounds
Nitrogen: amino acids, proteins, DNA, RNA
Phosphorus: DNA, bones
Calcium: bones, shells, coral skeletons
Magnesium: Chlorophyll
What do carbohydrates do inside living organisms?
Provide energy (starch) and storage
provide cellulose: the basis of cell walls in plants.
What do lipids do inside living organisms?
energy storage, form cell membranes, and act as signaling molecules.
What do proteins do inside living organisms?
enzymes
hormones’
bones and muscles, cartilage, and blood
cell wall
What are the levels of the modern classification system?
Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species.
What is a keystone species?
A species that significantly affects biodiversity in an ecosystem, e.g., kelp, seagrass.
What role do phytoplankton play in marine ecosystems?
Producers that remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
What are three examples of echinoderms?
Seastars, sea cucumbers, sea urchins.
What is the class name of bony fish?
Osteichthyes.
What is the class name of cartilaginous fish?
Chondrichthyes.
What are the basic characteristics of the splash zone on a rocky shoreline?
Area just above the high tide mark, exposed to air, and sprayed with seawater.
What is coral bleaching?
When corals expel their zooxanthellae due to stress from factors like temperature and pH.
What benefits do healthy coral reefs provide?
Coastal protection, food sources, medicinal compounds, and tourism opportunities.
What are the main challenges mangrove trees face in their environments?
Climate change, overharvesting, and storm damage.