Med Chem
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Creation of drugs:
1) molecular target
2) clinical trials
3) regulatory review
Ways to administer drugs:
1) Orally
2) Rectally
3)Inhalation
4) Injection
5) Topical
Injection types:
Intravenous- into blood, by passes stomach content (most effective)
Intramuscular- into the muscle (large volumes can be injected and when immediate response is not required)
Subcutaneous- under the skin (slow absorption)
Bioavailability
the fraction of the administered dose that reaches the bloodstream
What effects bioavailiblity?
higher solubility = more bioavailability
Functional groups
Polarity-
nonpolar good at passing blood-brain barrier (Ex. esters, ether, phenyl rings)
Polar- good at entering the blood stream (Ex. hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino groups)
Tolerance
The body's adaptation to a drug, which causes a need for a higher dosage in order to achieve the original effect
Addiction
when the dependency on a drug leads to withdrawal symptoms if its withheld.
Dosage Regime
refers to the specific quantity of the drug to be taken at one time, and the frequency of administration
First-pass effect
pharmacological phenomenon in which a medication undergoes metabolism at a specific location in the body cause bioavailability to become reduced
Therapeutic window
describes the dosage range between a minimum effective therapeutic concentration, and the minimum toxic concentration
wide range is most desirable
Therapeutic index (TI = TD50/LD50)
ratio of the dose that produces toxicity to the dose that produces a clinically effective response in a population
Low TI VERY DANGEROUS
High TI less dangerous
Receptors
often proteins, binding of the drug inhibits normal biological activity, so development of the disease is interrupted
Inhibitors
binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity
ED50 (effective dose)
is the dose producing the therapeutic effect in 50% of the population
LD50 (lethal dose)
the dose that is lethal for 50% of the population
TD50 (toxic dose)
the dose that is toxic for 50% of the population
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
are medicines that are widely used to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and bring down a high temperature
Analgesics
pain reliever
Mild analgesics
block the sensation of pain at the source (aspirin)
or block Prostaglandins
Prostaglandins
hormone like cells that release from cells damaged, allowing the body to detect pain
mediate the inflammatory response by causing dilation of blood vessels
Inflammatory response
the immune system's response to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, toxic compounds, or irradiation
Antipyretic
fever reducer (aspirin)
Anticoagulant
“blood thinners”, prevents the clotting of blood (aspirin)
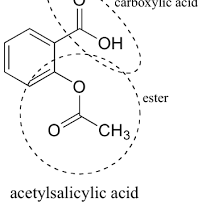
Aspirin
-derivative of salicylic acid - esterified to become less irritable to the body
Effects:
Analgesic
Anti-inflammatory (relief from swelling)
Antipyretic
Anticoagulant
can cause bleeding when taken with alcohol
allergic reactions
Reye’s disease in children
Functional Group:
Carboxylic acid
phenyl group
ester
combine it with NaOH or NaHCO3 to form an ionic salt which increases solubility - increases bioavailability
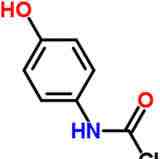
Paracetamol/ acetaminophen
Effects:
Antipyretic
Analgesic
NOT AN ANTI-INFLAMMATORY
Can cause liver damage and kidney damage
overdose
increase tolerance
skin reactions
Functional groups
Hydroxyl
phenyl group
amide
less side effects than aspirin and has narrower therapeutic window
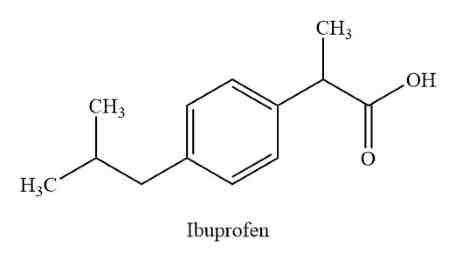
Ibuprofen
Similar properties to aspirin ( only has carboxylic acid)
is not a blood thinner
antipyretic
IR Spectrum of aspirin and salicylic acid
Similarities:
C-O( alcohol/ ester)
C=O ( carboxylic acid)
O-H( carboxylic acid)
C-H
Differences:
Aspirin has an ester group and salicylic acid has an OH group attached to the benzene ring
recrystallization
used on aspirin
purifying a substance by causing it to crystalize from a hot saturated solution
Synergy
An interaction between two or more drugs that causes the total effect of the drugs to be greater than the sum of the individual effects of each drug.
Antibiotics
chemicals produced from microorganisms that act against other microorganisms
Bacterocidal
kills bacteria directly
Bacteriostatic
inhibits bacteria’s cell division
Penicillin G
administered by injection because its not acid resistance
Penicillin V
taken orally because acid resistance
Cloxacillin
penicillinase and acid resistant
Beta-lactam
90 degree Four-membered ring containing a cyclic amide group, most active part, responsible for its antibacterial properties
the 90-degree bond angles can easily break and bind to the transpeptidase disrupting the formation of the cell wall, causing the cell to burst
What in penicillin is unique?
5 ring sulfur and beta-lactam ring
Disadvantages of overprescription (penicillin):
destruction of harmless bacteria in digestive tract
leads to genetic resistance
makes penicillin less effective
Reasons to modify side chains of penicillin
become more resistnat to stomach acid
increase tolerance to penicillinase
prevent deactivation by penicillinase
Trans-peptidase
a bacterial enzyme that cross-links the peptidoglycan chains to form rigid cell walls
Penicillinase
enzyme produced by resistant bacteria, that can open penicillin ring and render it inactive
Opiates (strong analgesics)
prevent transmission of pain impulses at the brain, rather than the source
Narcotic
sleep inducing, effects mood and behavior
Blood-brain barrier
protects the brain by restricting chemicals that can enter the blood
nonpolar
the more lipid soluble the more likely a substance can enter the brain
Semi-Synthetic
derivatives of natural antibiotics with slightly different but advantageous characteristics
esterase
a group of hydrolases that have wide substrate tolerances and are able to catalyze a broad spectrum of reactions even in organic solvents
active metabolite
are the active forms of drugs after they have been processed in the body
codeine is converted into morphine in the body and it is the morphine that binds much more strongly to the opioid receptors than codeine, producing an analgesic effect
omeprazole/esomeprazole are converted into different forms that are able to bind to proton pumps
aspirin is converted into the active form – salicylic acid.
Codeine
0.5 % raw opium (prepared from morphine)- methylation
Effects
Used with OTC drugs
cough medication
treatment of diarrhea
dizziness, anxiety, mood change, confusion
Functional Groups:
2 methyl Ethers
phenyl
1 hydroxyl -makes it less polar allowing it to cross more easily
Alkenyl
Tertiary amine
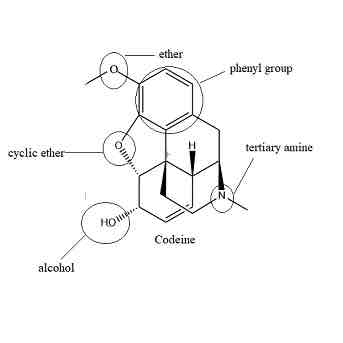
Morphine
10 % raw opium
Effects
relief of severe pain
better bioavailability (100%) when inserted through IV
Addictive, Anxiety, mood change, allergic reaction
Functional Groups
Ether
Alkenyl
2 Hydroxyls (slightly polar)- limits ability to cross blood-brain barrier
Tertiary amide
phenyl
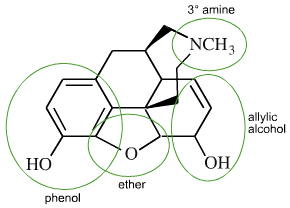
Heroin (diamorphine)
Synthesized from morphine (acetylation twice)
Effects:
relief of server pain (illegal in many places)
Addictive, anxiety, fear, mood changes, withdrawal
Functional Groups
2- esters - least polar ( can move across barrier easiest)
ether
tertiary amide
phenyl
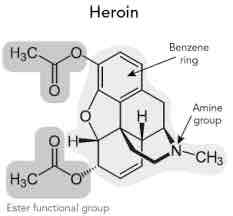
Methadone
reduces drug craving and withdrawal symptoms
Parietal Cells
maintain the pH in stomach (1-2) by releasing HCl
Dyspepsia
acid indigestion- uncomfortable feeling in stomach
Heartburn- acid rises to esophagus
Ulceration- damage the lining
What causes dyspepsia?
excess alcohol, smoking, caffeine, and stress which leads to increase acid buildup
Histamine
activates the partietal cells that release gastric juices
H2- receptor antagonist (Zantac/ ranitidine)
Zantac interacts with H2 receptors; prevents histamine interacting with H2 receptors; prevents secretion of acid into stomach
-does not really prevent healing of ulcers
Proton pump inhibitor (omeprazole or esomeprazole)
reduce the production of acid by blocking the enzyme in the wall of the stomach that neutralizes acid
-inhibit initial producing of HCl
-prevents and heals ulcers
Antacids
weak bases that neutralize acids
-strong bases can not be used ( to corrosive)
Types of antacids:
Magnesium Compounds may cause diarrhea
Aluminum Compounds may cause constipation and they also may interfere with the adsorption of phosphates in the formation of bones.
Carbonates may generate carbon dioxide leading to bloating and flatulence.
Formulas for antacids
CaCO3 + 2 HCl = CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
NaHCO3 + HCl = NaCl + H2O + CO2
Al(OH)3 + 3 HCl = AlCl3 + 3 H2O (best)
Mg(OH)2 + 2 HCl = MgCl2 + 2 H2O
MgO + 2 HCl = MgCl2 + H2O
Buffers
resist changes in pH of a solution upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base
pH equations
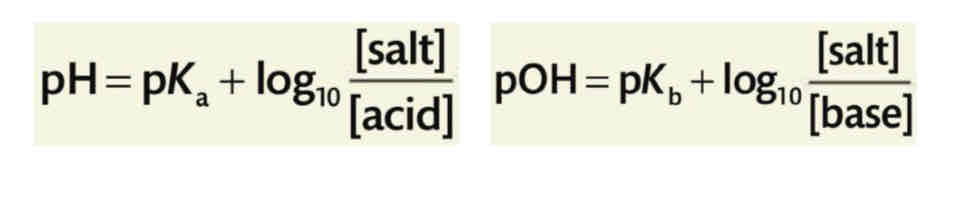
Alginates
float on the stomach contents to form a neutralizing layer preventing reflux of stomach acids up into the esophagus. Hence they help to prevent acid reflux or heart burn.
Anti-foaming agents
such as simethicone(dimethicone) prevent the formation of gases and reduce flatulence
Superbugs
strains of bacteria that are resistant to several types of antibiotics.
Viruses
are submicroscopic, non-cellular parasitic, infectious particles that can only reproduce inside a living host cell
reproduce rapidly with mutations( change in genetic material)
Bacteria
reproduces by cell division/ fission, living cell, and has a cell wall
Virus reproduction
1. Virus attaches to host cell
2. Viral DNA injected into cell
3. Viral DNA replicated using metabolic processes of host
4. New protein coats for viruses are made
5. Mature virions assembled in cell
6. Cell ruptures and releases mature viruses
prophylactic
prevents disease
How the body fights viruses
- Helper T-Cells (white blood cells) - fight infections- must recognize viral/abnormal cells before new viruses are released
- A secondary viral infection is fought by memory B-cells releasing antibodies to mark viruses
Antivirals
medications that help your body fight off certain viruses that can cause disease.
Use of antiviral medicines
1.Alter the genetic material within the cell, ex: acyclovir prevents cold sore replication
2.Inhibit the activity of enzymes within the host cells that are needed to make new viruses, ex: indinavir – prevents HIV protease to make new viruses
3.Prevent them from binding to the host cell surface and gaining access into the host
4.Prevent the virus from leaving the host cell so it cannot infect others
Latent Viruses
viruses that inject their genetic material into a host cell, but the material is not expressed until a later date
Influenza
common viral disease
contains RNA, RNA polymerase and a lipid envelope with neuraminidase (NA) and hemagglutinin (HA) proteins.
Hemagglutinin (H)
allows viruses to bind to host cells at sialic acid (glycoprotein)
Neuraminidase (N)
breaks down mucous surrounding cells allowing it access to target cells
>After viruses replicate in the host cell the NA must break the link between sialic acid so the virus can break free from the cell
If the NA fails to work, the virus is unable to infect other host cells
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
neuraminidase inhibitors
They bind to the active site of the NA enzyme and prevents it from Un anchoring the virus from the cell
Contains: ester, carbonyl group
taken orally
total synthesis makes a lot of waste
Uses shikimic acid (synthetic route)
shikmic acid
is renewable and can be extracted from Chinese star anise (low yielding process and star anise not always available) or from glucose fermentation using genetically modified bacteria (uses low temperatures and an aqueous medium – greener process).
zanamivir (Relenza)
neuraminidase inhibitors
bind to the active site of the NA enzyme and prevents it from unanchoring the virus from the cell
Contains alcohol, carboxyl
dry powder for oral inhalation since it is highly polar and cannot pass through the cell membrane
retrovirus
type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell
can mutate much easier
HIV
>infects T-cells due to specific receptor proteins on their surface to which the virus attaches to gain entry.
>Once inside the viral enzyme, reverse transcriptase converts RNA into DNA so it is integrated into the cell’s DNA.
>T-cells then make more HIV viruses or remain latent, copying the viral DNA whenever they replicate.
Death of T-cells occurs when viruses leave, causing a weakened immune system
AZT (azidothymidine)
early anti-retroviral drug designed to target the reverse transcriptase enzyme, preventing DNA synthesis.
Multi-drug resistance (MDR)
bacteria have developed, so “cocktails” of antibiotics need to be prescribed to hopefully combine their effects to overcome the infections.
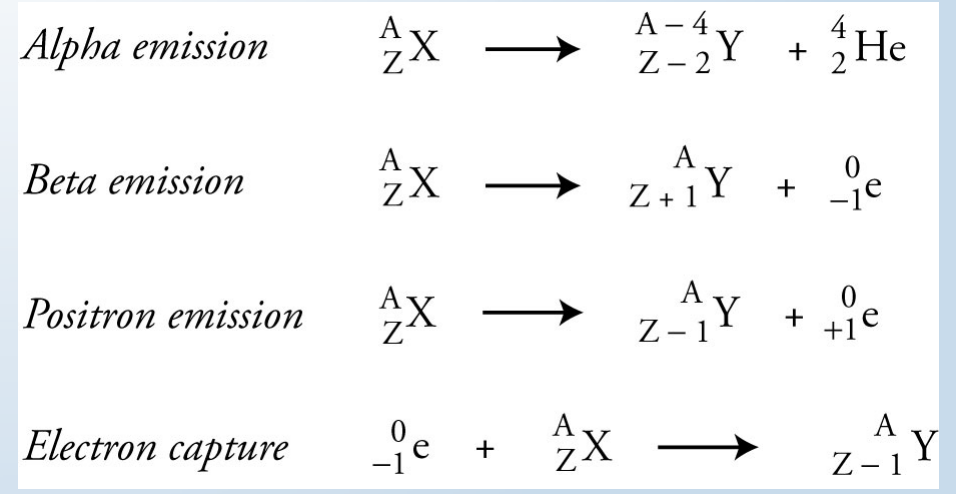
Radioactive isotopes
used in medicine as a form of treatment and diagnosis.
decay by emission of alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays (called ionizing radiation).
Ionizing radiation
causes the formation of ions (by ejection of electrons) when they interact with matter.
can damage cells, usually due to the damage caused to DNA.
Low-level waste (radioactive waste)
has low activity and usually contains isotopes with short half lives. And includes gloves, clothing, tools, syringes, excrement
small amt of radiation for a short time
stored on site or shipped to a central site until safe OR incinerated OR buried underground in individual concrete lined vaults (up to 500 years).
intermediate-level radioactive waste
a category that is sometimes used but not universally.
High-level waste
has high activity and usually contains isotopes with longer half-lives. And includes fuel rods and other materials from nuclear reactors.
kept underwater in storage ponds and then transferred to dry casks and stored in concrete bunkers. Permanent store is a major problem since the future and stability of the containers is unknown.
Waste Solvent
used as mediums in which many reactions occur, in the extraction and purification of compounds and contribute about 80-90% of the mass of substances used in pharmaceutical production and make a large contribution to the energy used, and to the cost.
toxic to humans
Ways to make waster solvent greener:
prevention of solvent use is paramount; using a solvent that is recyclable or reused is preferable; energy use to purify the solvent is considered, and disposal method for solvents is also considered (incineration, underground injection, reuse, etc.)
the release of antibiotics into the environment
1. incorrect disposal of unwanted medicines, ex. Flushing them down the toilet
2. agriculture – drugs given to animals will be present in animal waste that enters groundwater, rivers, and lakes
Water treatment does remove some of the materials but long term exposure to man can result in damage.
Antibiotics can damage aquatic organisms and also increases the resistance of bacteria to antibiotics
Green Chemistry
approach to chemical research and industrial processes that seeks to minimize the production of hazardous substances and their release to the environment.
12 Principles of Green Chemistry:
1. Prevention – it is easier to prevent waste than clean it up or treat it
2. Atom economy – synthetic methods should try to maximize incorporation of all materials into the final product (less waste)
3. Less hazardous chemical synthesis – design use to generate substances that possess little to no toxicity to humans or environment
4. Designing safer chemicals – products should do what they are designed to do and minimize their toxicity
5. Safer solvents and auxiliaries – Use of ancillary materials should not be used or made innocuous when used
6. Design for energy efficiency - Energy requirements for processes should be assessed for environmental and economic impact (attempt to occur at ambient temperature and pressure)
7. Use of renewable feedstocks – a raw material or feedstock should be renewable whenever technically and economically practical.
8. Reduce derivatives – unnecessary derivations should be minimized or avoided as they generate added waste.
9. Catalysis – Catalytic reagents are superior to stoichiometric reagents
10. Design for degradation – Chemical products should be designed to break down into innocuous products that do not persist in the environment.
11. Real time analysis for pollution prevention – methodologies need to be developed for real time monitoring and control of hazardous wastes
12. Inherently safer chemistry for accident prevention – choose substances to minimize accidents, releases, fires, and explosions.
chiral auxiliary
stereoisomers -have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space.
causes different functions / effects
breathalyzer (ethanol)
the ethanol is oxidized, reduces the dichromate causing a color change from orange to green
Percent error formula
| Actual - experimental / actual| X 100
ABSOLUTE VALUE
Half life equation
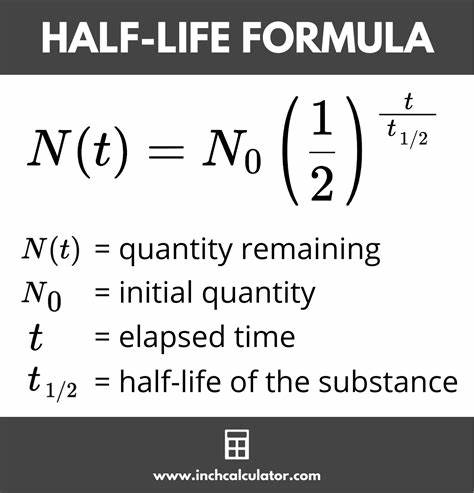
Nuclear chemistry