Populations Exam 4
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Foodborne Illnesses
Any illness resulting from the consumption of contaminated food, bacteria, viruses, parasites, chemical or natural toxins, poisonous mushrooms.
PulseNet
National program - Conducts molecular surveillance using DNA fingerprinting to serotype and subtype pathogens
Steps to diagnosis foodborne illness

risk factors for foodborne illness
Crowding
Eating chicken!
Poor hygiene
Childcare centers
Healthcare facilities, especially long-term care facilities
Eating raw/undercooked meats or fish
Ingesting raw/unpasteurized mild or dairy products
Working with animals or animal products
Traveling to developing countries
Abusing drugs
Having children in daycare or school
Investigation must go through a 72 hour meal history
s/sx foodborne illness
depends on causative agent, GI bugs cause - nausea, vomiting, abd cramps, diarrhea -> must be 2 or more persons not in same household
foodborne illness criteria
must be 2 or more persons not in same household
foodborne illness danger s/sx
Bloody diarrhea
Stiff neck with HA and fever
Excessive diarrhea/vomiting
When do I go back to work? vomiting and diarrhea
gone for 24 hours
Norovius return to work
72 hours
When do I go back to work? sore throat
restricted 24 hours antibiotics, neg throat culture or free from Strep infection
reportable food borne illnesses (big 5)
salmonella, shigella, E coli, hep A, norovirus
Norovirus
most common - 93% of viral gastroenteritis (causing severe puking and pooping AKA SHUKING)
cruise ships, undercooked veggies
Hepatitis A
2-6 weeks post exposure with fecal matter
Liver issues, pale/yellow skin, itchiness
Rotavirus
Foodborne transmission only 1% of cases
By the age of five, nearly every child in the world has been infected with rotavirus at least once. However, with each infection, immunity develops, and subsequent infections are less severe; adults are rarely affected
Shigellosis – “Bacterial Dysentery”
Often from stool on hands, swimming pools; incubation 1-3 days, lasts 5-7 days
Abdominal cramps, fever, often bloody diarrhea 10-30x/day
Salmonella
bacteria attach to GI lining produce toxins and attack the intestinal cells, can survive weeks in frozen water
diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps within 2 hours to 4 days of ingesting bacteria
Cipro treatment
E. Coli
Produce SHIGA toxin STEC. Healthy organism and unhealthy ones in intestine; 24 hours incubation
low fever, nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, bloody diarrhea, hemolytic urea syndrome (HUS), thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura (TTP); “Traveler’s diarrhea” but worse
tx: abx ONLY if septic
Clostridium perfringens
Gram-positive bacterium; normal component of decaying vegetation, marine sediment
Sudden onset (6-24 hr) of colic and diarrhea, maybe nausea; vomiting and fever unusual; rarely fatal; duration 1 day or less
Campylobacter
undercooked poultry or raw milk
vomiting, diarrhea, fever 2-5 days after exposure: rare case leads to Guillain-Barr Syndrome
Increasingly resistant to fluoroquinolones
Staphylococcus Aureas
Food handlers main source of food contamination-especially with foods requiring a bit of handling
sudden onset, 30min-7hr, diarrhea
listeria
Fever, pains, miscarriage, deadly for babies
Especially bad if pregnant
Soft cheeses, Ice creams - contaminated machinery, unpasterized milk, contaminated fruits and vegetables
Toxoplasma gondii
from cats
infection in healthy persons is asymptomatic or mild 'flu-like' sx: headache, muscle aches-can last several weeks; moms can pass on to unborn child leading to death or teratogenic effects
Mushroom toxins
Found in several species of wild mushrooms
Number of cases low
Cases are sporadic
Large outbreaks are rare
Remember SLUDGE from Pharm?
›Muscarinic poisoning: salivation, tearing, bronchospasm, diarrhea, bradycardia, hypotension, CV collapse
atropine treatment
Typical course of foodborne illness
most are self-limiting, supportive care -> rest, rehydration, education
5 Keys to safer food
keep food clean, seperate raw and cooked foods, cook thoroughly, keep food at safe temp, use safe water and materials, wait 24 hours of no s/sx before going to work
keeping water safe
run water for 60 seconds, replace corrosive water systems, clean aerator, replace filters, test wells yearly
Waterborne Disease
›Cholera
›Typhoid.
›Bacterial dysentery
›Giardia lamblia
›Crytosporidiosis
Giardia – Beaver Fever
Diarrhea
Greasy stools that tend to float
Stomach or abdominal cramps
Upset stomach or nausea/vomiting
Dehydration (loss of fluids)
Giardia loves sugar and alcohol
Treated with Flagyl - no alcohol with Flagyl
Stool culture
›Should be requested if diarrhea lasts more than 1 day or if
- Bloody diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Diarrhea leading to dehydration
- Fever
- Prolonged diarrhea (3 or more unformed stools per day for several days)
- Neurologic involvement (parathesias, motor weakness, cranial nerve palsies)
- Sudden onset of nausea, vomiting and/or diarrhea
- Severe abdominal pain
three most common STDs
chlamydia, HPV, trichomoniasis
high risk group for STIs
Have multiple sexual partners
Do not use a condom during sex
Have other STDs
Have a sexual partner who has had an STD
Burden of disease for STIs
chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis all curable but if wait then causes longerm problems
Reportable STDs
Chlamydia, HIV, gonorrhea, syphilis
Expedited Partner Therapy
co treatment for chlamydia or gonorrhoeae (treat both pt and partner)
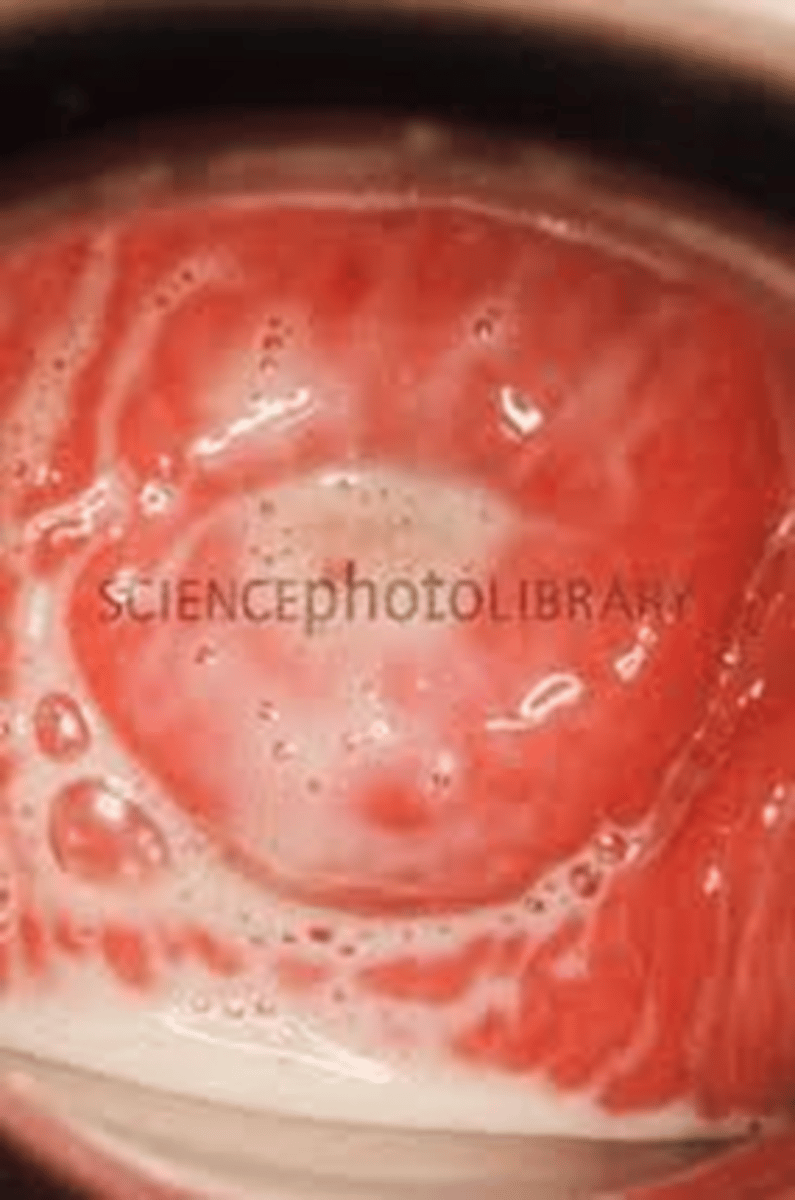
Gonorrhea
bacterial infection, genitals and anus, most people have no s/sx, discharge or burning in urination
Gonococcal pharyngitis
feels like strep throat, purulent discharge
Neonatal gonorrhea of the eye
TX: Oral antibiotics can cure the infection; tx both partners; abstain from sex until gone; test for other STDs; can cause pelvic inflammatory disease in women and infertility. Cephalosporins (Rocephin) + azyrthomicin (macrolide)
Antibiotic resistant gonorrhea
One of the top Seven deadliest superbugs!!!!
Trichomoniasis - trich
smells like fish, copius discharge, bleeding or spotting, tx flagyl
Chlamydia
hand in hand with gonorrhea, silent disease, 5 times more likely to get HIV
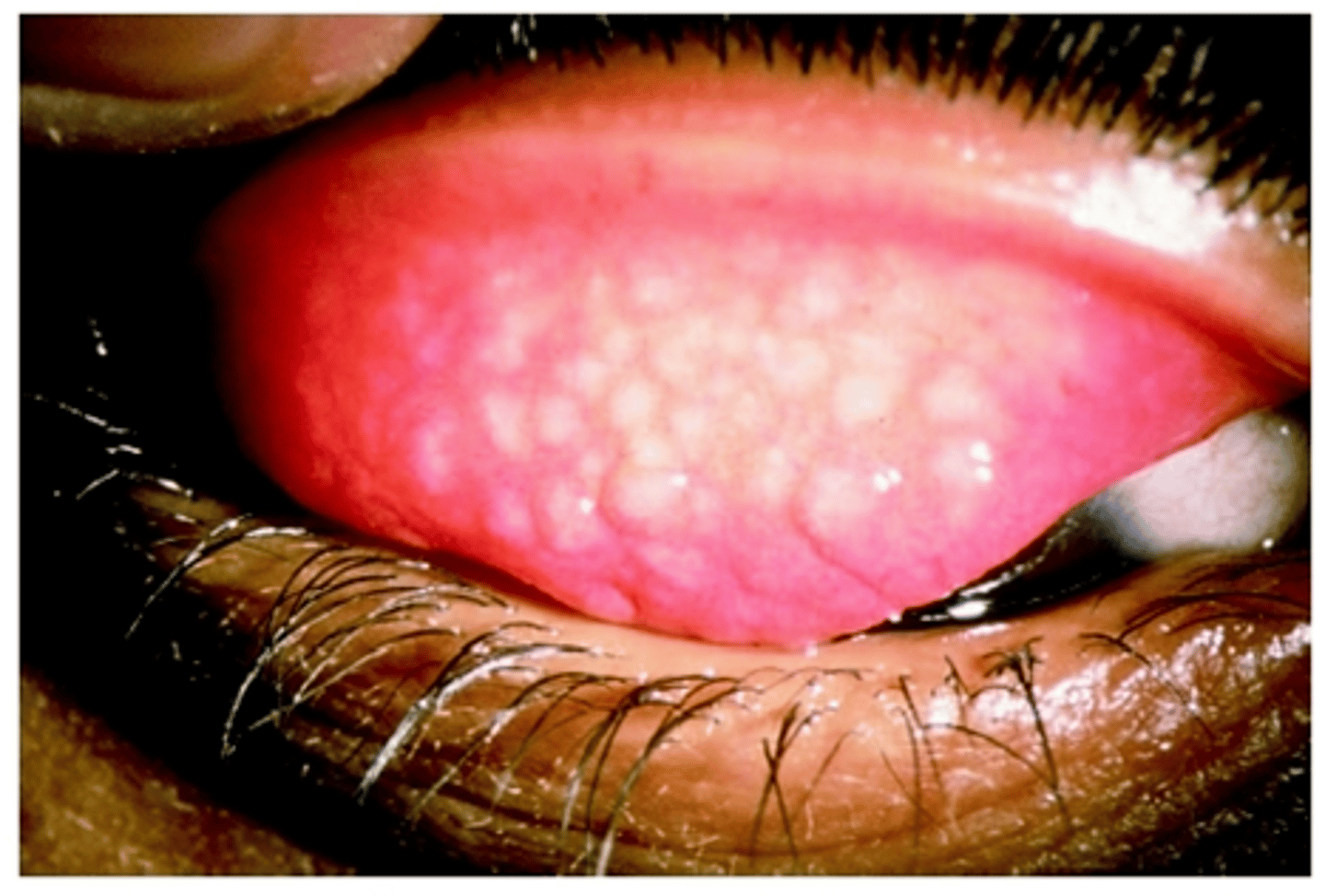
Reiter's Syndrome- "Reactive Arthritis"
Systemic Chlamydia and other
bacteria can cause this reactive
arthritis following the bacterial
infection; conjunctivitis, arthritis
(ankles and knees), urination issues
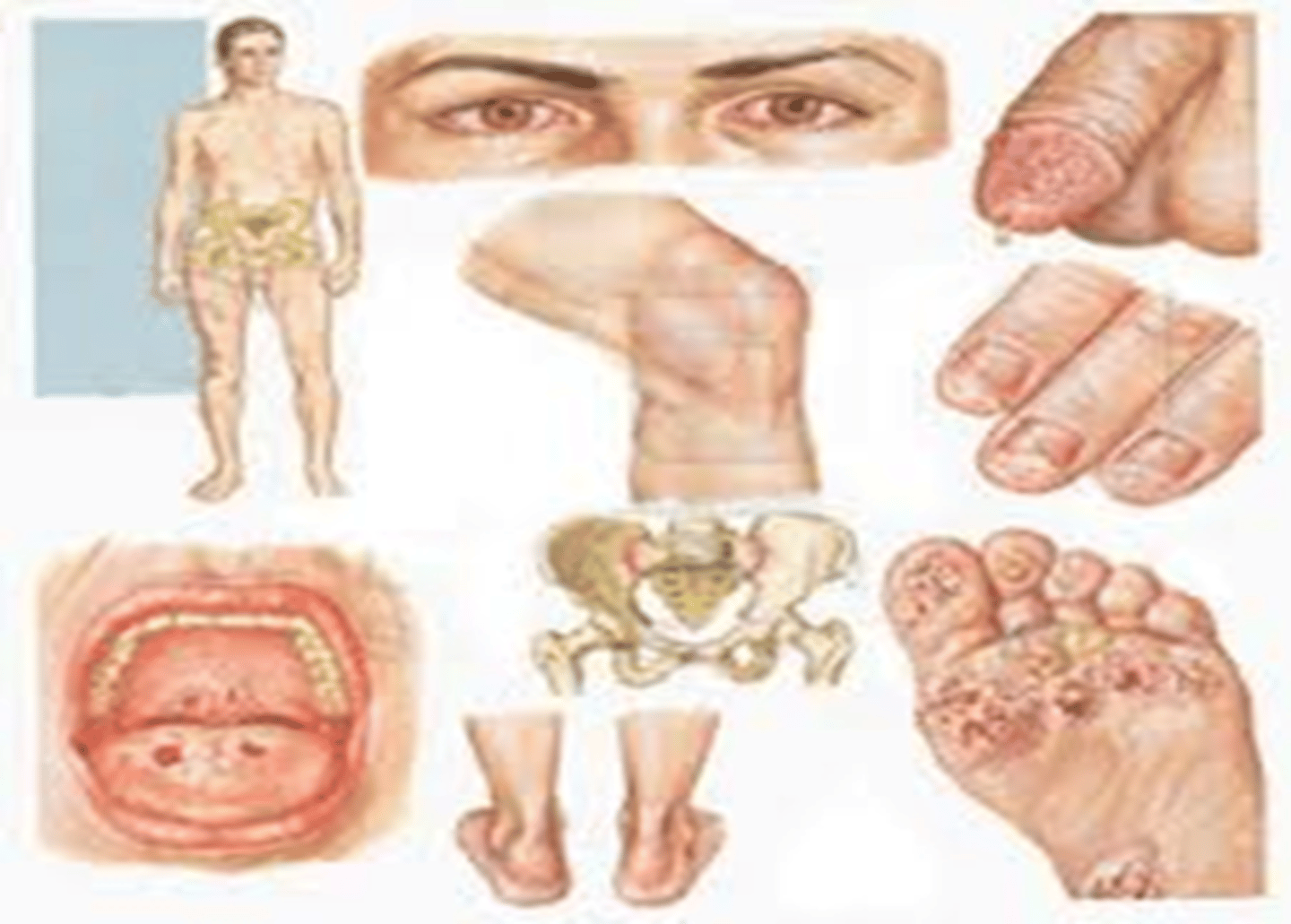
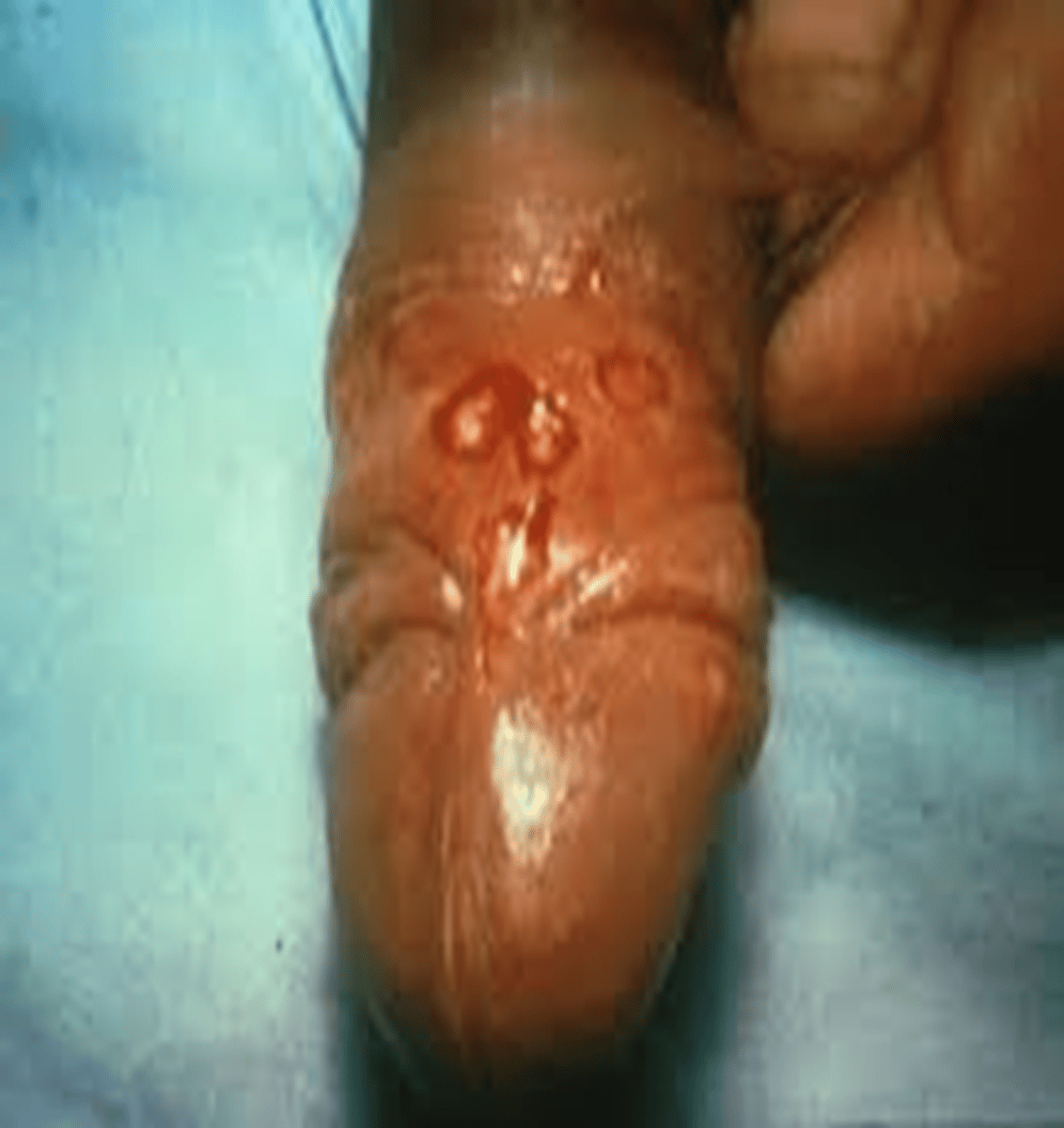
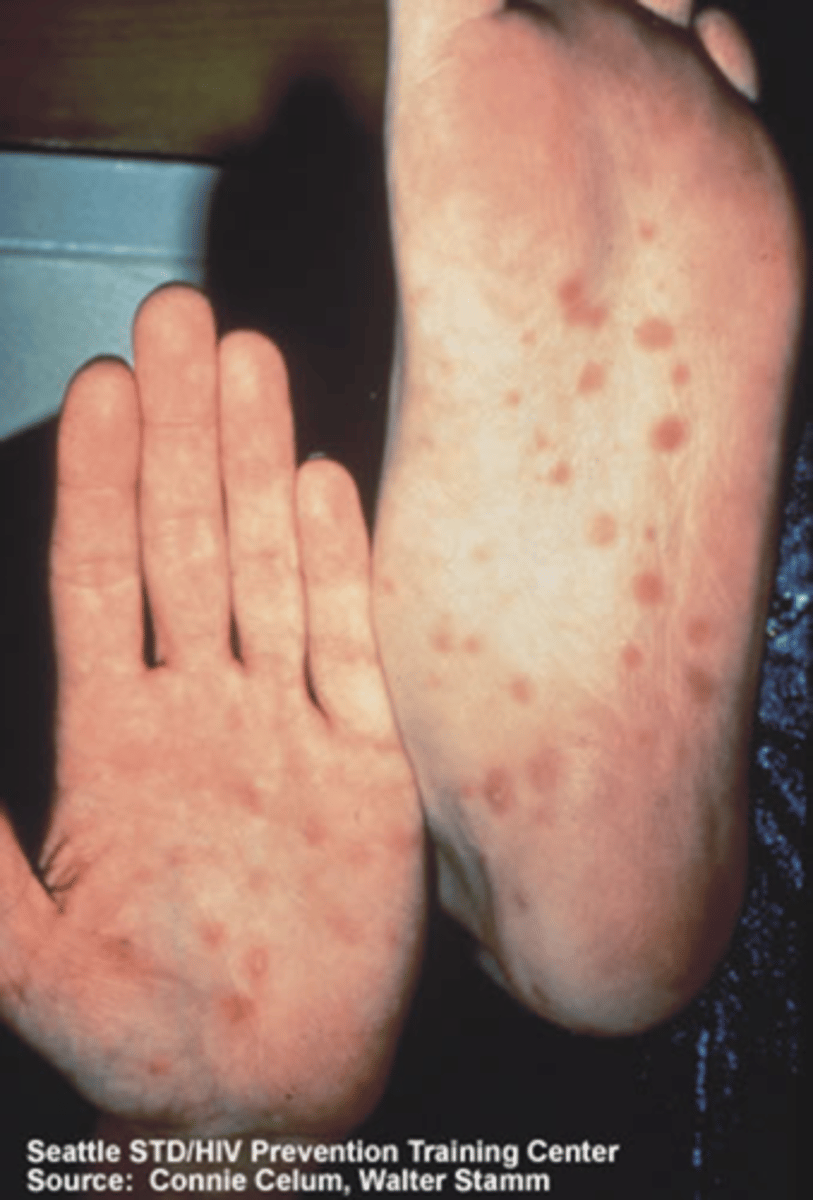
Primary Syphilis
chancre is painless, single, firm; non itchy ulceration/clean base, TX pcn
Secondary syphillis
rash
Tertiary Syphilis
Gumma, found in brain, heart, skin, bone, testis "balls of inflammation; grow and damage tissue; when contacting bone very painful leave major scars
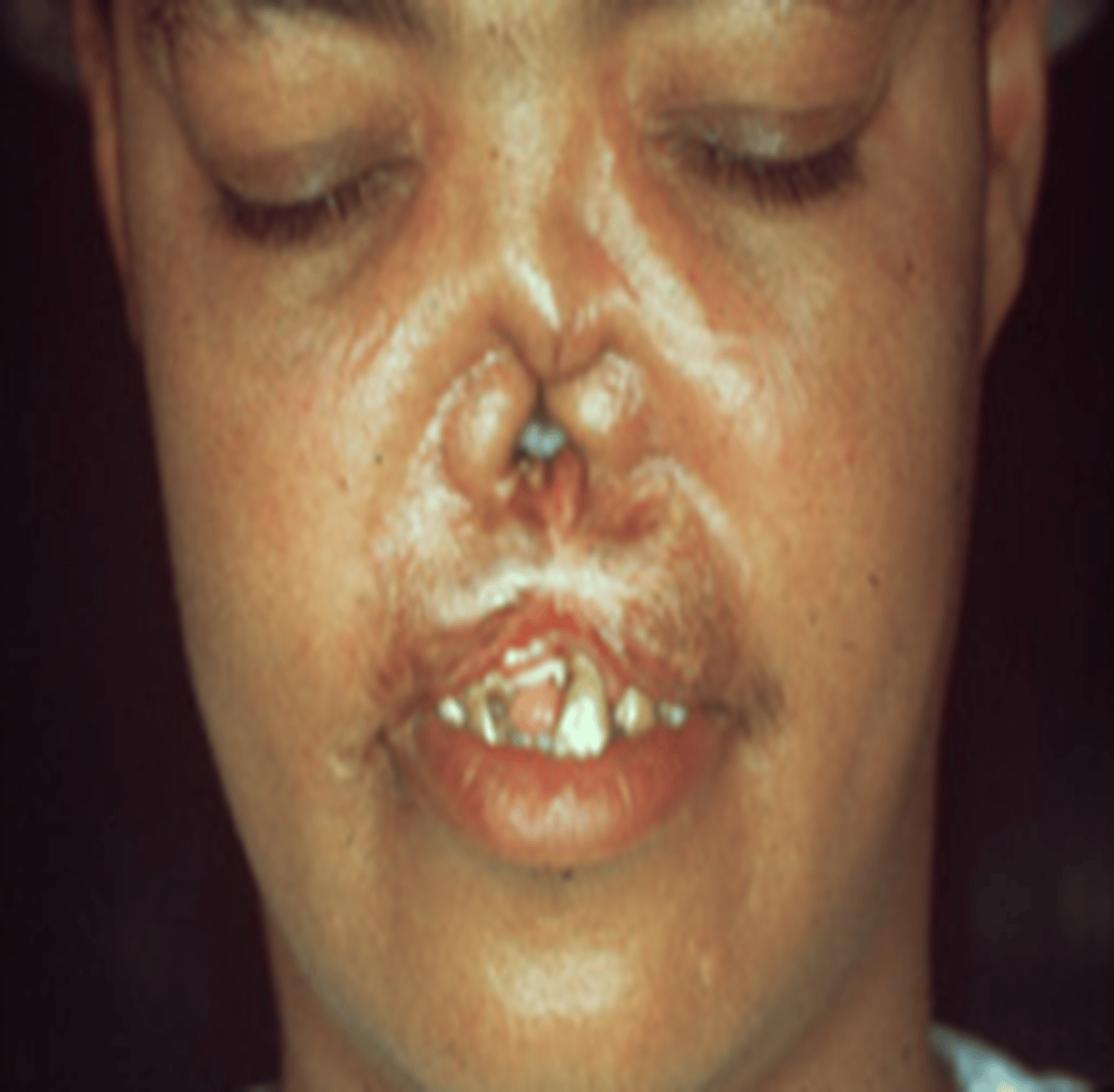
Congenital Syphillis
ÒNearly half of all children infected with syphilis while they are in the womb die shortly before or after birth.
ÒNo bridge to nose (saddle nose)
Herpes
Type 1 Cold sores/fever blisters
Type 2 genital
no cure
Acyclovir may reduce symptoms
Can self-inoculate
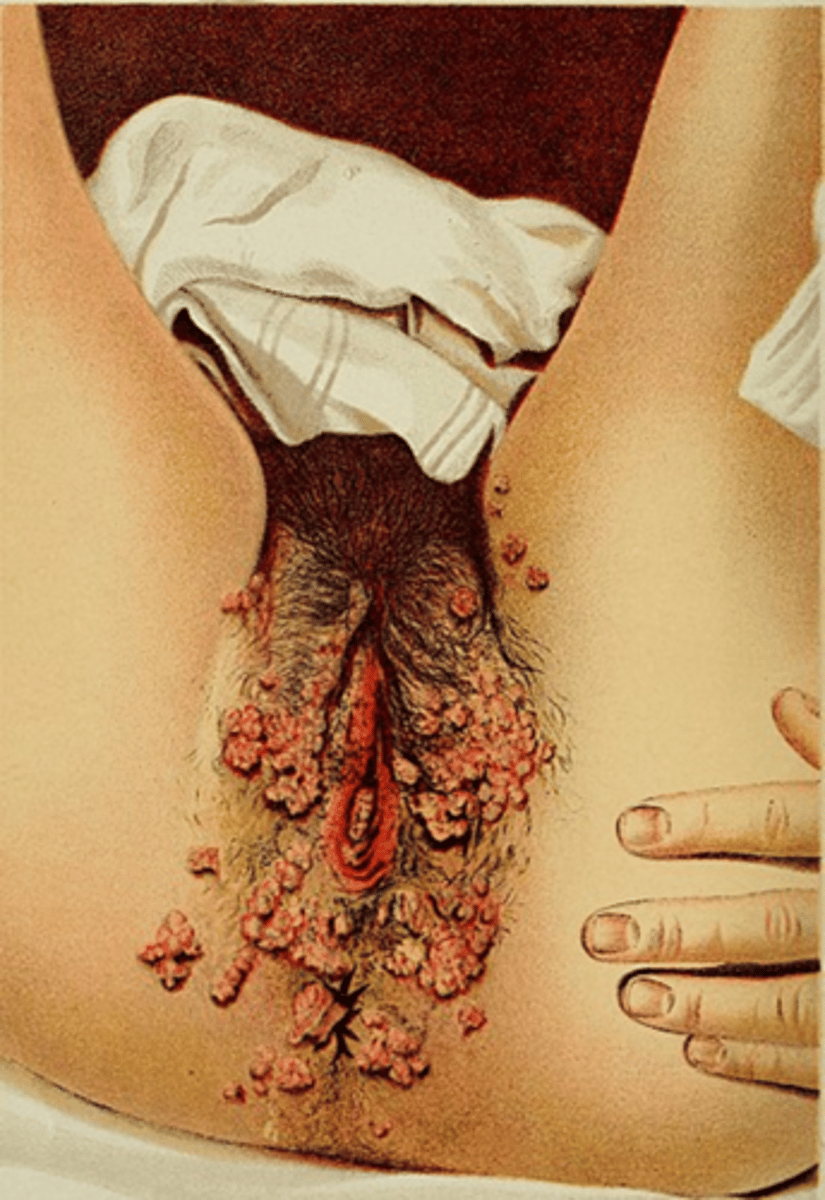
Genital warts
Warts form around cervix, vulva, urethra, glans penis, and anus and anal canal
ÒMajority caused by Viruses HPV-6 and HPV-11
crotherapy
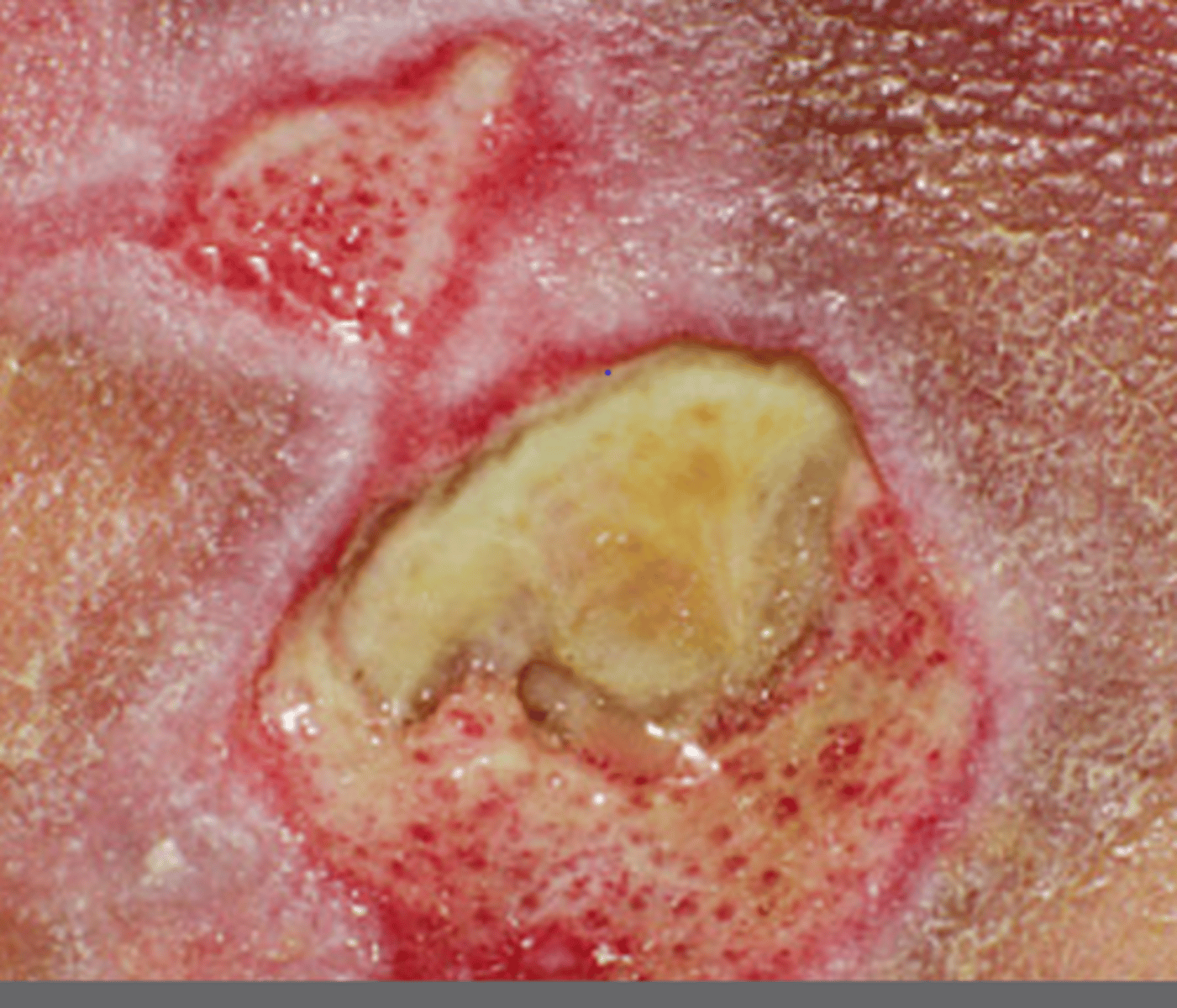
granuloma inguinale
new overseas sti
North Korea is pretty dark
We need to nuke it so that it glows toxic green at night

Pan American Health Organization
Quasi-independent branch of WHO
25 member countries in Western Hemisphere
United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF)
Concentrates its efforts in maternal and child health
Agency of the UN
Focus:
•Communicable diseases
•Primary prevention
•Fresh water
•Safe food supplies
•Health education for mothers of children
•Education for girls
•Immunization programs
World Bank
35-40 year repayment period on loans
Major resource for developing countries to provide safe environment for people
•Safe water
•Adequate housing
•Proper agricultural techniques
•Improved sanitation
Agency for International Development (USAID)
Arm of the US State Department
“USAID's work advances U.S. national security and economic prosperity, demonstrates American generosity, and promotes a path to recipient self-reliance and resilience.”
Provides expertise and funding to countries needing economic development
Doctors Without Borders (MSF)
Non govermental
•Founded in France in 1971
•Provides medical care to people in more than 80 countries
•Provides both health personnel & supplies to people caught in wars, refugees, displaced persons, & victims of natural disasters
•Provides long-term assistance in countries with little or no health care delivery systems such as Sudan and Ethiopia
•Staff is composed primarily of volunteers: doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals
The Carter Center
established by President Jimmy Carter
neglected diseases
Committed to
promoting human rights
and
improving health
Improving food production
Promotes peace
Carter center diseases
•Elimination of guinea worm disease,
lymphatic filariasis,
river blindness,
schistosomiasis
The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation
•Endowed initially by $220 million donated by Bill & Melinda Gates
•In 2006 Warren Buffett donated $34.7 billion worth of shares
•Annual budget for global health alone is $800 million – same as WHO
WHO ungraded
an event that is being assessed, tracked or monitored by WHO but that requires no WHO response at the time
WHO grade 1
a single or multiple country event with minimal public health consequences that requires a minimal WCO response or a minimal international WHO response.
WHO Grade 2
a single or multiple country event with moderate public health consequences that requires a moderate WCO response and/ or moderate international WHO response.
WHO Grade 3
a single or multiple country event with substantial public health consequences that requires a substantial WHO response and/ or substantial international WHO response.
lobal goals (for essay)

Poor nutrition leads lifetime issues with
•Stunting
• Susceptibility to disease
• Susceptibility to intestinal parasites
•Anemia
•Lethargy and apathy
Globesity
1 billion overweight or obese worldwide
Costs us $147 billion a year in the U.S.
A crisis of "epidemic" proportions (WHO)
Major threats in war
Fatal injuries
Antibiotic resistance
Infectious diseases (Ebola in Congo)
Disruptions in food supply
Lack of sanitation and water supply
Rebuilding health care services
Health issues in war regions
Mass immunization needs
Long-term malnutrition and dehydration
Uranium exposure
Landmines
Child soldiers
Displaced persons
Mental health issues
Rape
Mental illness and disability
Accounts for 30% of disability worldwide
Replacing Millennium Goals: Global Goals (for essay)
https://sdgs.un.org/goals pick a few headlines and say youre working towards it
Neglected Tropical Diseases
diverse group of communicable diseases in tropical and subtropical conditions in 149 countries
Rabies, Chagas Disease, Dengue, Hanson's, Guinea
Guinea Worm success
Being wiped out through filtering water, and changing people's behavior
Hanson's Disease- Mycobacterium Leprae (leprosy)
95% of humans immune, common with people who work/eat armadillos, wil take millennia to get rid of, reprograms liver of armadillo and causes liver to regrow
is a treatment
Polio
goal to eradicate it, for every 200 wpv1 only results in 1 symptomatic polio, aka hard to get rid of
Malaria
4 different types, 1 million annual deaths, vaccine pilot, spread by mosquitos,
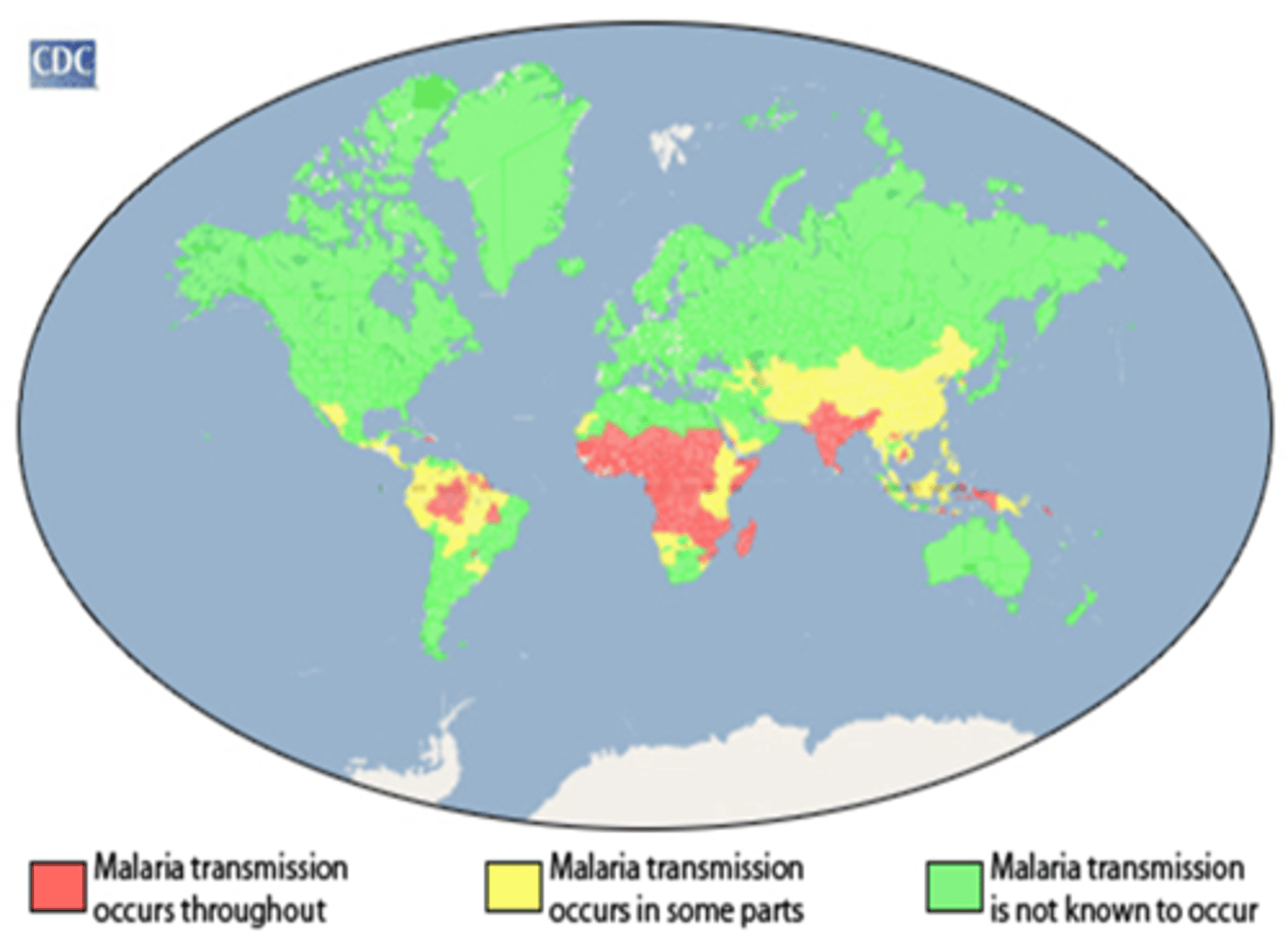
mosquitos
carry 35 diseases
Quinine
used in tx of malaria, can be used to cut heroine
Symptoms of malaria
3 stages
10-16 days after bite, Symptoms coincide with RBC cell rupture at known time pattern - fever
With P. vivax malaria, the person may feel fine between attacks. Even without treatment, the paroxysms subside in a few weeks
with P. falciparum malaria, however, is likely to feel miserable even between attacks and, without treatment, may die
Malaria stages
First stage: chills, HA, fatigue, N and V, diarrhea - all lasts 1-2 hours
Second stage: fever, skin feels hot and dry.
Third stage: fever breaks with drenching sweat, weakness and may actually sleep.
Severe cases: anemia, jaundice, seizures, confusion,
kidney failure, ARDS, coma, death
Dengue Fever Virus
breakbone fever, spread by mosquitos, type of flavovirus, dengue likes urban environments,
Dengue Fever Virus s/sx
breakbone fever, high fever, rash, fatigue, headache, muscle aches, nausea, swollen lymph nodes
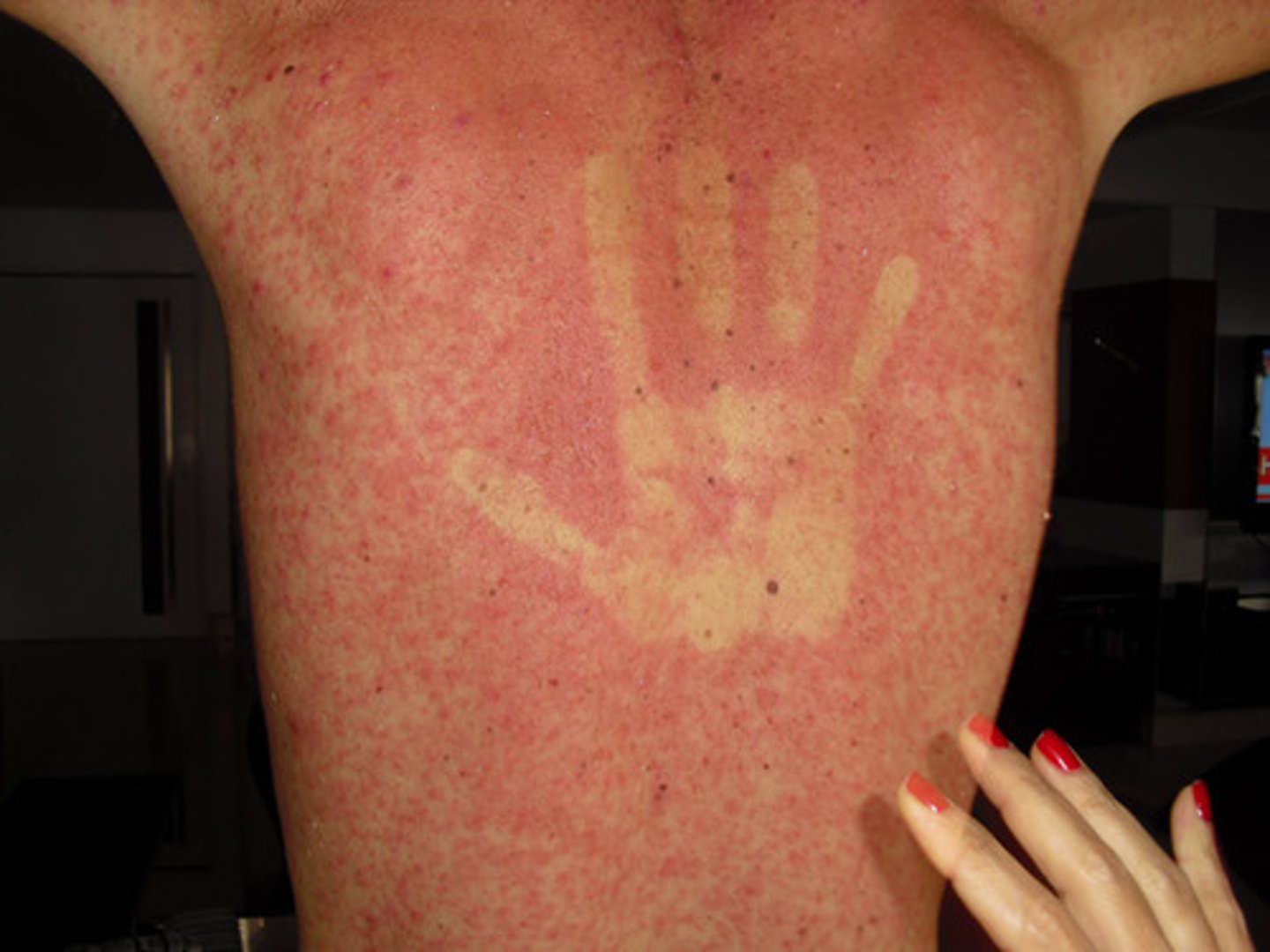
Hermans sign
no ibuprofen or asprin
Hermans sign
dengue fever, hand print stays on rash
treatment for dengue
tylenol, prevent dehydration, watch for hemorrhagic form akak blood in paces it shouldn't
Chikungunya Virus
hard to distinguish from dengue, tylenol only
Zika virus
also found in semen, spread by mosquitos, problems with pregnant people
Cholera
fecal-oral route, shit out your own intestines villi, disease of the poor
>1L poop a hour
vaccine available
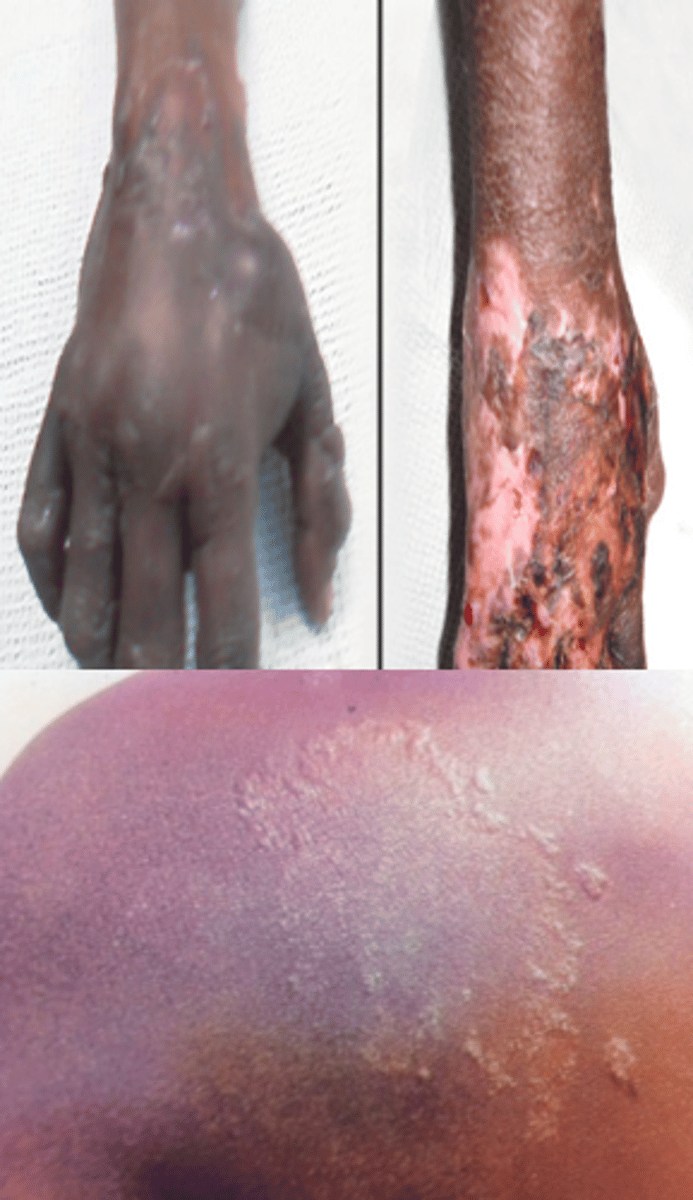
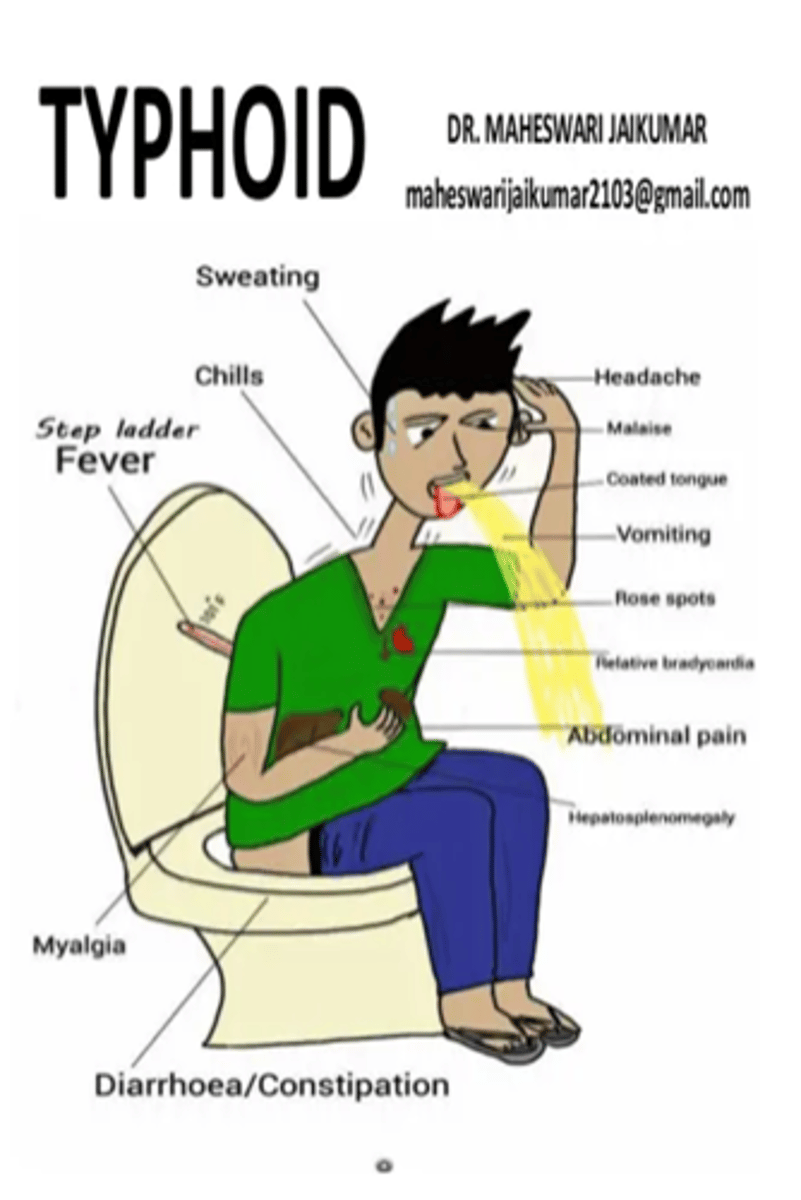
Typhoid fever
can be deadly, highest risk in southern asia, fecal oral route
treat with abx
typhoid fever s/sx
fever, diarrhea, rose spots, spontaneously resolves 2-5 days, blanching rash
non blanching rash - remember for life not on exam
meningitis
Advice for Travelers to stay Healthy
Boil it, cook it, peel it, or forget it
TB and abx
not easily treated with simple antibiotic
2/3 of all TB case countries
India (highest rate), china, indonesia, russia, philippines, pakistan, nigeria, bangladesh, south africa
Rnot TB
3.5
s/sx of active TB
Fever, night sweats, weight loss
Who should get tested for TB?

Slides 7-9 of TB/HIV slides will be on exam
yup
Who really needs to get tested? High Risk for Exposure
•Close contacts of a person who has active TB
•Employees of correctional facilities and nursing homes
•Health care workers working with certain populations
•Medically Underserved & Low Income
–Native Americans, African Americans, Migrant workers, Homeless
•Immigrants
– From countries with high incidence rates
India (lead), China, Indonesia, Philippines, Pakistan, Nigeria, Bangladesh, South Africa, Russia
Latent TB
no s/sx, does not feel sick, cannot spread, can tst positive, normal chest xray and negative smear, needs treatment to prevent active TB
Active TB
has s/sx, feels sick, may spread TB to others, tsts positive, positive xray and smear, needs treatment
Who is at risk of developing Active Disease once Infected?
•Immunosuppressed
-HIV infection
-Prolonged steroid
tx or other
immunosuppressive drug
•Chronic Disease
-Diabetes
-Cancer
-COPD
•Poor Nutrition
-alcoholics
What is the risk of developing TB disease over a lifetime
no risk factors have 5% risk in first 2 years and 10% risk over lifetime
30% with diabetes
TB treatment
use multiple drugs:
Isoniazid
rifampin - (causes orange pee)
pyrazinamide
ethambutol