exam 4 psych crying emoji
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Attribution
A conclusion about the cause of an observed behavior/event
attribution theory
situational and dispositional
situational attribution
environmental factors

dispositional attribution
thats the way they are and their traits

fundamental attribution error
overemphasize personality over environmental factors
- dispositional > situational

attitude
Feeling ideas, and beliefs that affects how we approach and reach to other people, objects, and events
- Attitudes affect our actions

central route persuasion
uses logic and evidence
peripheral route persuasion
uses emotion

6 ways to say yes (CCARLS)
- consistency
- consensus
- authroity
- reciprocity
- liking
- scarcity
consistency (CCARLS)
people like being consistent with things they have already done

Consensus (CCARLS)
People look at the actions of
others to determine their
own

Authority (CCARLS)
people trust someone with authority

Reciprocity (CCARLS)
obligation to give when u recieve

Liking (CCARLS)
we say yes to people we like

Scarcity (CCARLS)
we want more of what we cant have

foot in the door phenomenon
we get people to agree by starting small then moving up

role-playing
we adopt the attitudes that go with the role even if it is pretend
cognitive dissonance
when actions aren't matching with attitude, we fix attitudes to match our actions
ex: wanting to be healthy but not exercising regularly

conformity
Adjusting out behavior or thinking to fit in with a group standard (consensus)

mimicry, chameleon effect
natural tendency to mimic others

social norms
A "correct" or "normal" way to behave or think in a group

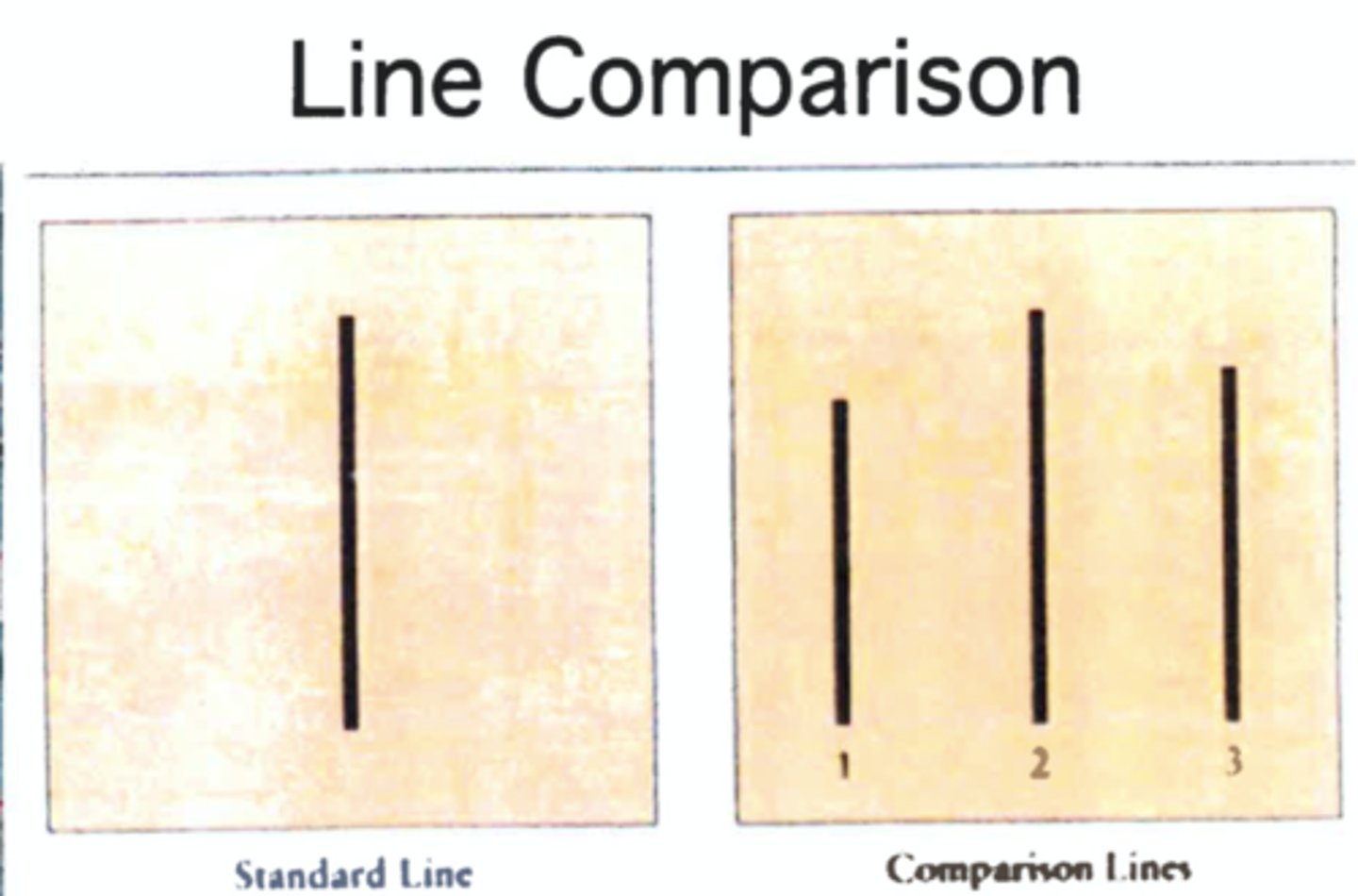
Solomon Asch Conformity Studies
1/3 of people will agree with obvious mistruths because the group said so
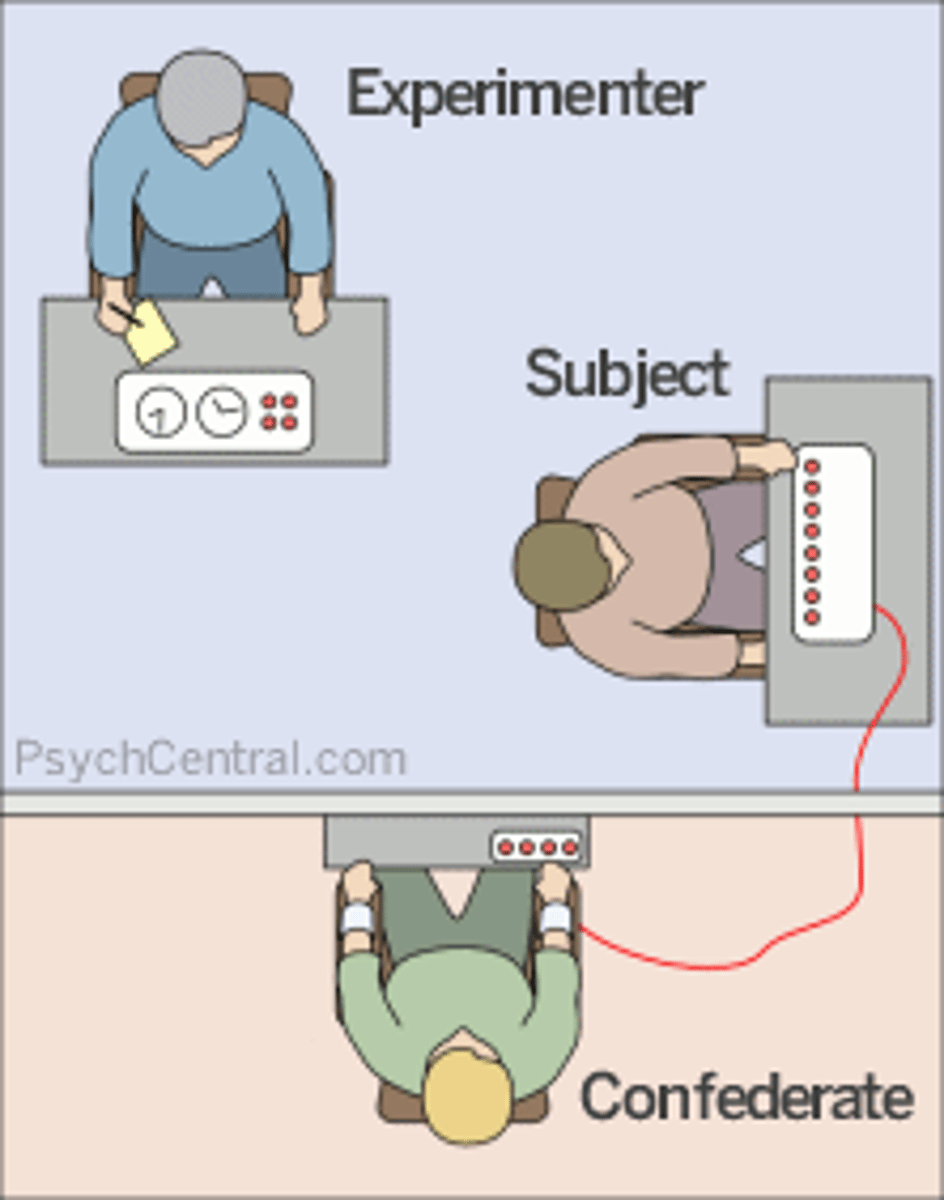
obedience
Response to commands by one in authority
group behaviors (SSDGG)
- social loafing
- social facilitation
- Deindividuation
- group polarization
- groupthink

Social Facilitation
We do better when were being watched

social loafing
uneven work load and over-reliant in a group seeing

Deindividuation
Losing self-awareness or restraint when theres high emotion or anonymity

group polarization
When people of similar views enhance their views

groupthink
In pursiut of social harmony, groups will make decisions without realistic appraisal of alternatives
- people would rather get along than find a solution

prejudice
Unjustified ATTITUDE
discrimination
Unjustified BEHAVIOR
stereotype
A generalized BELIEF

roots of prejudice
social, emotional, cognitive
social (ingroup bias)
favoring ones own group

emotional (scapegoat theory)
offers an outlet for anger by finding someone else to blame

cognitive
other race effect, just world fallacy
other race effect
tendency to see uniformity in appearance in other groups and assume other similarities
- all asian people look the same

just world fallacy
people get what they deserve

Aggression
Behavior whose purpose is to harm another; does not always involve violence

premeditated aggression
concious decision to acheive goals

impulsive aggression
spontaneous withtout premeditation

aggression in men
- impulsive
- status competitions
- more likely to cause physical harm

aggression in women
- Premeditated
- focused on attaining/protecting resources
- more likely to cause psychological or social harm

aggression roots
biological and psychological

frustration agreesion principle
people get mad when their goal is stopped by an obstacle

social script
Cultural directions on how to act
- earing out food is by ordering eating then paying

proximity and exposure
we are attracted to people we see more

similarity and reciprocity
we like people similar to us and people who show interest in us

ideal partner for men
- shorter
- younger
- very attractive
- healthy

ideal partner for women
- taller
- older
- mature
- moderately attractive

evolutionary explanation to male and female partners
- women have higher reproductive costs
- reproductive success is higher when chosing a loyal man
- men have higher reproductive rates with young mates

passionate love
feelings of euphoria, intimacy, and intense sexual attraction

compassionate love
Involves affections, trust, and concern for a partner's well-being

social exchange
people remain in relationships only as long as they have a good ratio of costs to benefits

key to a lasting love relationship (ESSP)
- Equity
- self-disclosure
- support
- positive interactions

altruism
Any behavior that benefits someone else without benefiting you

reciprocal altruism
expectation that those benefits will be returned in the future

bystander effect
We don't help someone in need because we think someone else will take care of it

social traps
Situations in which pursuing self-interest makes things worse for everyone

mirror image perception
Both sides assume the worst of the other

factors that reduce conflict (CCCC)
- contact
- communication
- conciliation
- cooperation
contact (CCCC)
exposure and interaction → familiarity → acceptance → connection
conciliation (CCCC)
(smile, apologize, gesture)

cooperation (CCCC)
behavior by two or more individuals that leads to mutual benefit

Psychological disorders
Patterns of thoughts, feelings, or actions that are:
- Deviant
- Distressful
- Dysfunctional

The medical model
mental illnesses viewed more seriously and could have genuine causes and treatments like a physical illness
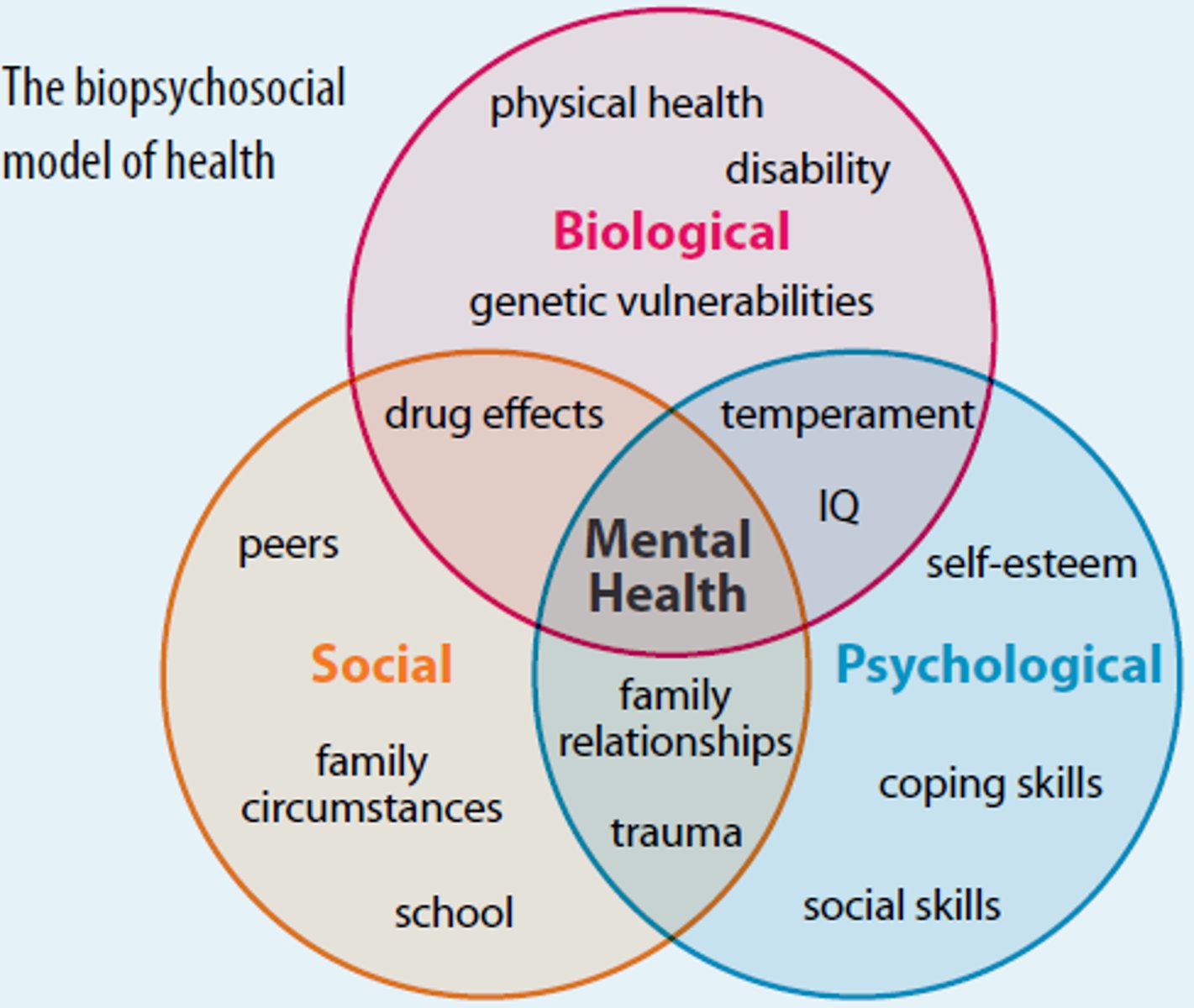
biopsychosocial model
mental illness is viewed with a broad spectrum of factors including biological, psychological, and social
etiology
specific patterns of causes

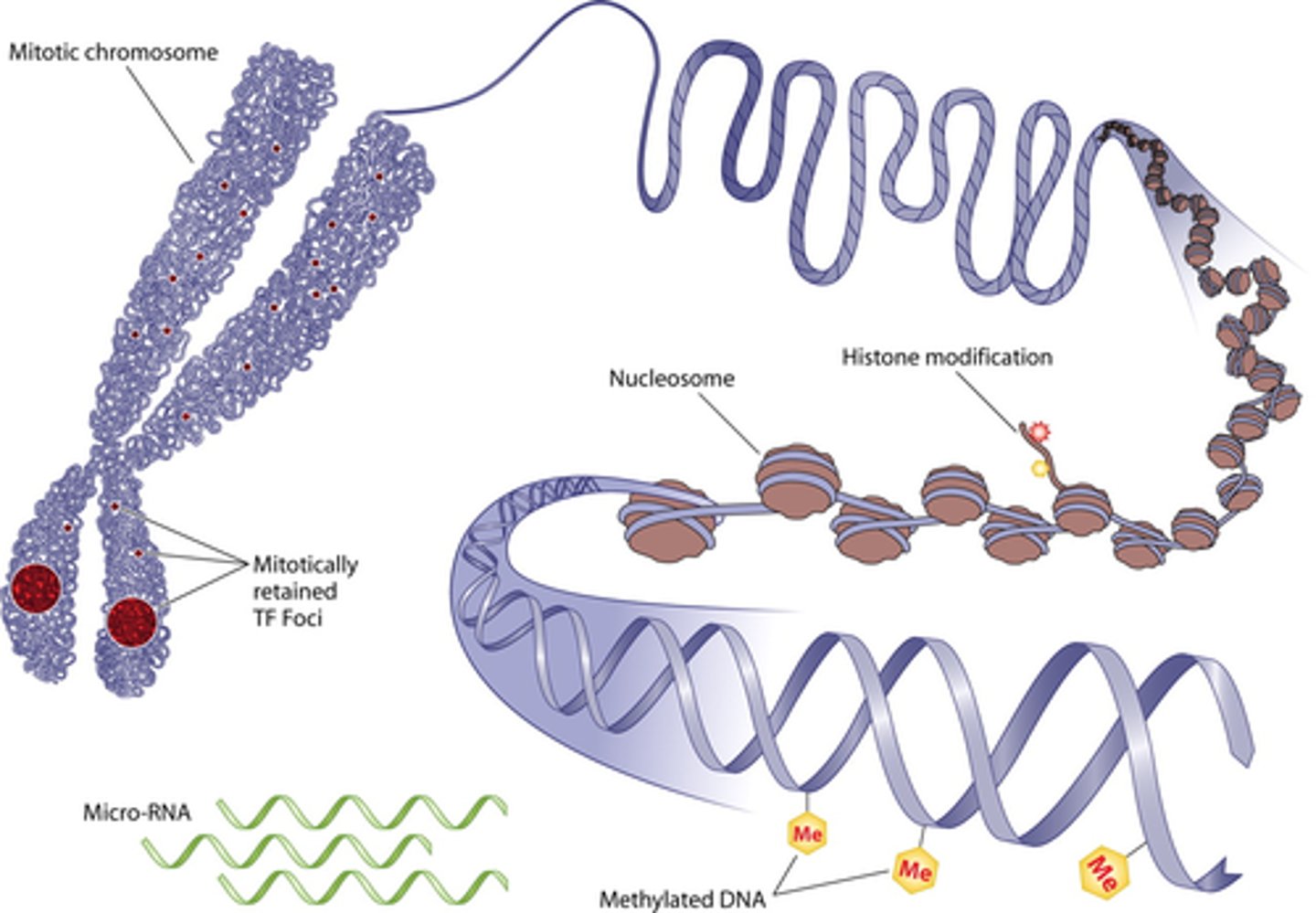
epigenetics
Genetics may predispose a person to a disorder
- But symptoms aren't expressed until the environmental trigger switches the gene on
DSM-V
a big book of all the disorders bruh

what was wrong w the DSM 5
- Turning any type of behavior into a disorder (Boys are overdiagnosed with ADHD)
- Some new or altered diagnoses are controversial

comorbidity
Co-occurrence of 2 or more disorders at the same time

Labeling pros and cons
leads to stereotypes, but makes it easier for doctors