Unit 1 Ch 14
1/58
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
bedouin
nomadic peoples in arabia
loyal family/clan groups
Muhammad Ibn Abdullah’s early life
born about 570 in Mecca, orphaned, married wealthy widow, worked as merchant
Muhammad’s spiritual transformation
~610 started getting visions from Gabriel about Allah
Muslim beliefs
Allah - 1 and only god
Muhammad is the last prophet so he got the full story
“seal of the prophets” = last prophet
many shared beliefs with Jews + Christians + Zoroastrians
Quran
compiled in early 650s, written versions of Muhammad’s revelations
hadith
saying by Muhammad and accounts of his deeds
conflict in Mecca between Muhammad and the ruling elites
Allah = only god, offensive to polytheistic Arabs
greed = moral wickedness. not taken well by rich elites
idolatry = economic threat
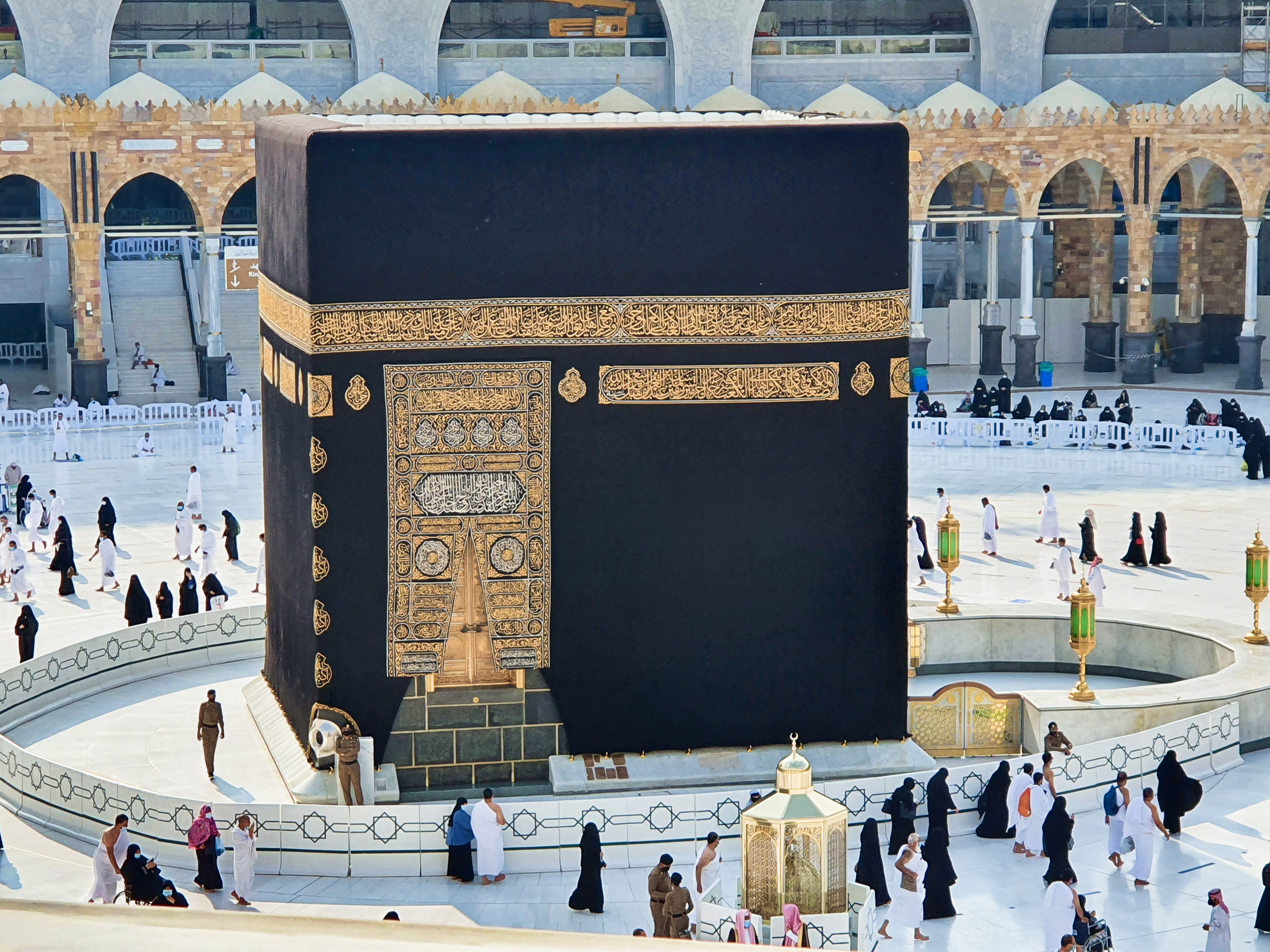
Ka’ba
large black rock, originally dwelling to a polytheistic God
Muhammad said it was a symbols of mecca’s greatness
now islam’s holy site

Hijra “migration” 622 marks beginning of Islamic calendar
Muhammad fleeing Mecca to Medina
Umma
islamic community w/ legal + social code
Muhammad’s return to Mecca 629
629 - visit to mecca (small pilgrimage - umrah)
630 - attacked and conquered mecca
forced elites to adopt Islam, imposed Islamic gov
destroyed pagan shrines, built mosques
first Hajj 632 to Muhammad's death
first Hajj led by muhammad to the ka’ba
Muhammad and followed launched campaigns united most of arabia
Muhammad died in 632
5 pillars of islam
Allah is the only god + Muhammad is his prophet
pray to Allah daily while facing Mecca
fast during Ramadan
almsgiving
hajj
jihad
struggle - combat vice and evil
struggle against ignorance and unbelief and seeking converts
sharia
islamic law, emerged after Muhammad’s lifetime
covers all parts of life
effects of Muhammad's death
towns and Bedouin clans that recently joined went back to their old ways
abu bakr waged war and got these people back
Caliph
“deputy”
no more prophets b/c Muhammad was the “seal of prophets”
head of state for Islamic community, chief judge, religious leader, military commander
Abu Bakr
First caliph
causes of rapid expansion of Islam territory into Byzantine and Sasanid territories
Muslim armies strong b/c doing god’s work = salvation
also byzantine and Sassanid tired from fighting each other and internal uprisings
where did Islamic territory expand to between 633 and 718
muslim forces seized Byzantine Syria, Palestine, and Mesopotamia (from Sasanids)
conquered Egypt + NW Afr
Conquered Hindu Sind (NW India)
crossed Strait of Gibraltar to conquer Iberia
Issues with rapid Islamic expansion
difficulty governing
hard to choose caliph
first four caliphs negotiated between powerful Arab clans
disagreements led to factions and clan loyalties
Shia vs Sunni (Islam Sects)
Sunni - majority of Muslims “traditionalists”, accepted legitimacy of early caliphs
Shia - most important and enduring alternative
Shia supported supported Ali (and fam) as first caliph instead of Abu Bakr
Ali
Shia “leader”
fourth caliph (served 656-661)
assassinated while praying in mosque 😳😢
Shia specific
observed holy days in honor of their own leaders+martyrs
taught that Ali and his descendants were divinely appointed to rule
slightly diff interpretation of Quran
Umayyad Dynasty (661-750)
est after assassination of Ali
most prominent of Mecca merchant clans
brought stability to Islam world
capt: damascus, syria
Umayyad issues
Favored fellow arabs
mostly allowed people to worship their own religion (esp other abrahamic religions) except also had jizya
Jizya
special head tax on those who weren’t islam
Umayyad Decline
begin in early 8th cent
caliphs devoted to luxury instead of umma
rebellions lead by Abu al-Abbas, won, est Abbasid Empire in 750
Abu al-Abbas
descendant of Muhammad’s uncle, Sunni
Abu al-Abbas taking down the Umayyads
allied with Shia and Muslims who weren’t Arabs esp Persian converts
740s- rejected Umayyad authority seized Persia + Mesopotamia
750- shattered Umayyads in giant battle
killed Umayyads at banquet he hosted
dar al-Islam
house of islam
where the Islamic rulers ruled
Abbasid Dynasty (750-1258) and how they differed from Umayyads
cosmopolitan - didn’t have bias towards Arabs
not a conquering dynasty, ruled what they got from Umayyads
dynasty still grew but mostly from autonomous forces and merchants
Battle of Talas River at Samarkand
(image shows Samarkand)
Abbasids won, ended Tang’s expansion into central Asia
allowed Islam to spread to Turkish
Abbasid Capital
Baghdad (modern Iraq capt)
round protected by walls
Ulama and Qadis
ulama - people w/ religious knowledge, scholars developing laws
qadi - judges
both had formal edu emphasized study of Quran and Sharia
extremely influential
Abbasid Rule
standing army, bureaucracy ran taxes, finance, coinage, postal services
maintained roads from Sasanids
Harun al-Rashid (rule: 786-809)
high point of Abbasid
Baghdad: flush w/ wealth
center of banking, commerce, crafts, industry
metropolis - several hundred thousand people
supported artists+writers, distributed money to poor
elephant to Charlemagne
Abbasid decline
Harun al-Rashid’s sons fought civil war
provincial governors got more power, uprisings, rebellions
Abbasid caliphs became figureheads for long time
945 Persian nobles seized control of Baghdad and held effective power
then Seljuq Turks
Seljuq Sultan had power for 2 centuries
mongols extinguished dynasty in 1258
Umayyad and Abbasid empires and trade in dar al-Islam
created zone of trade from India to Iberia
econ stimulus thru out dar al-Islam
new crops spread thru dar al-Islam
soldiers, admins, diplomats, and merchants traveled thru out dar al-Islam and introduced new crops
few ex: sugarcane, rice, new types of wheat + sorghum
assorted veggies and fruits
industrial crops: cotton, henna, and indigo
effects of new crops
richer, varied diet
new crops = growing season longer (new crops good with heat) = more food = more people
agri improvements
irrigation, fertilization, crop rotation recorded in agri manuals
= more productive agri = econ growth
urbanization
food up = people up = urbanization
big cities emerge with flourishing arts + crafts people
new industry emerged = paper knowledge came from china
led to records, books, treatises
formation of hemispheric trade
revived silk roads from China to Med sea
used good inherited roads for trade + poli + mili + pilgrimages
camels 🐫
great for desert travel, carry heavy loads
maritime trade
Chinese magnetic compass!!
lateen sail - triangular
astrolabe
Islamic / Abbasid Banks
conducted lots of business, lent money, brokers, exchanged currencies, sakk
sakk
checks basically
why were group investments used
less risk, easier to absorb losses
abbasid empire traded all over the hemisphere
north to Russia, W & E Afr, SE Asia, Med Basin etc.
maintained thru good banking, transportation, banking, and business
Al-Andalus (place not person)
Islamic Spain
Muslim Berber conquerors from N Afr
Umayyads who refused to recognize Abbasid dynasty, had their own caliphs
Capt: Cordoba thriving
women’s status
arab women originally had decent rights
could own property, divorce, business
early Quran provided some freedom to women, later Quran became harsher on women’s rights 🫤
men = 4 wives
when Islam got to Byzantine and Sasanid they adopted their patriarchal traditions like veiling
Arabic Quran
only definitive and reliable scripture, translations not as powerful
very very important
madrasas
higher edu Islamic schools
SUFIS !!!!!!!!
pious, ascetic, mystical, spiritual emphasis
very, very popular - kind, tolerant
not very popular with traditional Muslim theologians
emphasized devotion over doctrine
allowed people to keep aspects of traditional religions
Al -Ghazali (1056-1111)
early Sufi, Persian
human reason couldn’t understand Allah, you just needed to be devoted
persian influence on Islam
took persian admin, lit, poetry, history, and poli
Rubaiyat - book of Persian poems by Omar Khayyam
Indian influence
math, science, and medicine
Hindi numerals became “arabic” numerals to Euros
greek influence
appreciated plato + aristotle
Ibn Rushd (1126-1198) qadi in Seville
liked Aristotle, used it to shape Islamic philosophy
heavy influence on natural reason