DSA20 - Male Reproductive Health and Treatment
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
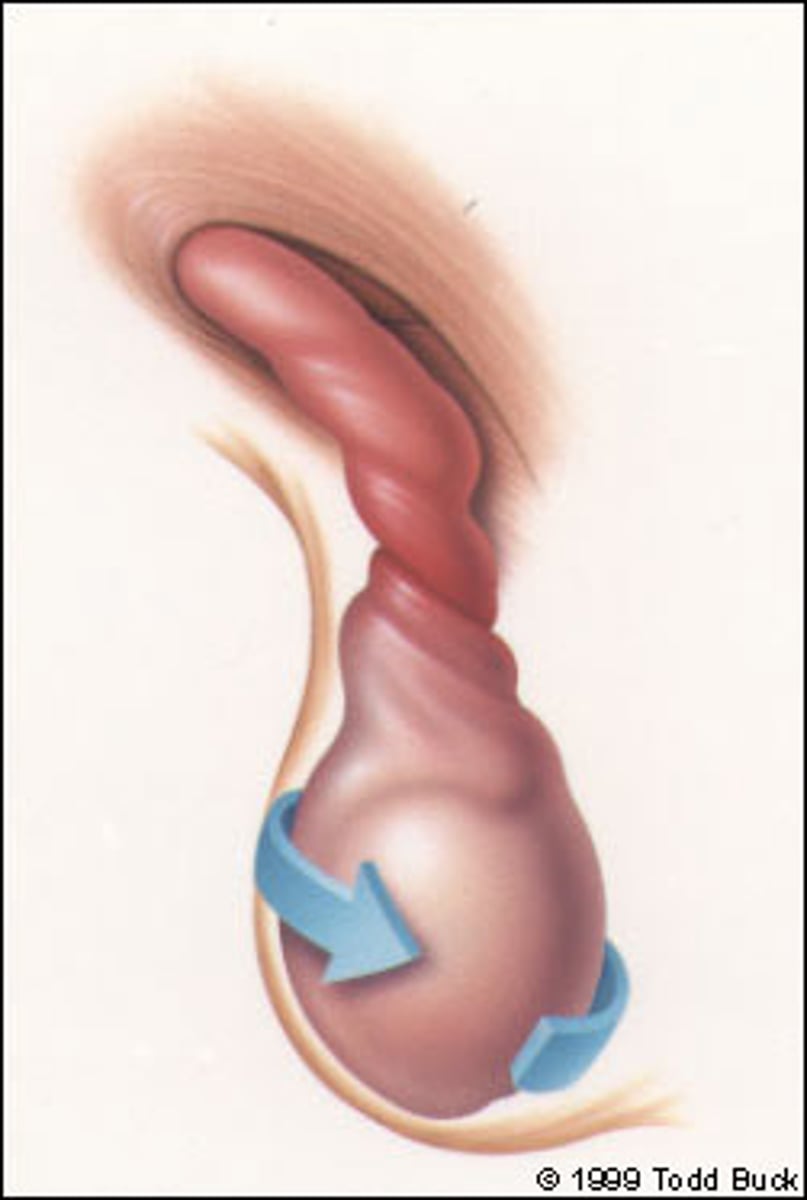
Testicular Torsion
Define Cause of Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
Twisting of testis, spermatic cord and vascular pedicle w/ resultant ischemia
-Hx:
> MC in Neonates & Postpubertal boys
-Path: UROLOGIC EMERGENCY; D/t inadequate fixation of lower pole of testis to tunica vaginalis
-Sx: ACUTE ONSET
> Severe Testicular Pain
> Profound Testicular Swelling
> N/V
> May awaken at night or morning w/ scrotal pain
-PE:
> High riding testis
> Long axis oriented transversely ("Bell-Clapper" Deformity)
> Absent Cremasteric reflex = superficial reflex in males elicited when inner thigh stroked --> cremaster muscle contracts and pulls up ipsilateral testicle toward inguinal canal
> Overlying erythema on scrotum for 12-24 hrs
-Dx: ULTRASOUND
-Tx:
> IMMEDIATE REFERRAL TO UROLOGY
> Manual detorsion (if surgery not available)
-Prog: TIME DEPENDENT - Testis suffer irreversible damage after 8 hours of ischemia (can salvage if Txed w/n 6-8 hrs)
Testicular Appendiceal Torsion
Define Cause of Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
Twisting of testicle appendices; MCC of acute scrotal pain in PREPUBERTAL children
-Hx:
> MC in Neonates & PREpubertal boys
-Path: UROLOGIC EMERGENCY; D/t inadequate fixation of lower pole of testis to tunica vaginalis
-Sx: ACUTE ONSET
> Severe Testicular Pain
> NON-TENDER TESTICLE
> N/V
> May awaken at night or morning w/ scrotal pain
-PE:
> Blue Dot Sign
> Normal Cremasteric reflex = superficial reflex in males elicited when inner thigh stroked --> cremaster muscle contracts and pulls up ipsilateral testicle toward inguinal canal
-Dx: ULTRASOUND (NORMAL DOPPLER Blood Flow)
-Tx: Supportive Mgmt
> Analgesics
> Bed Rest
> Scrotal Support
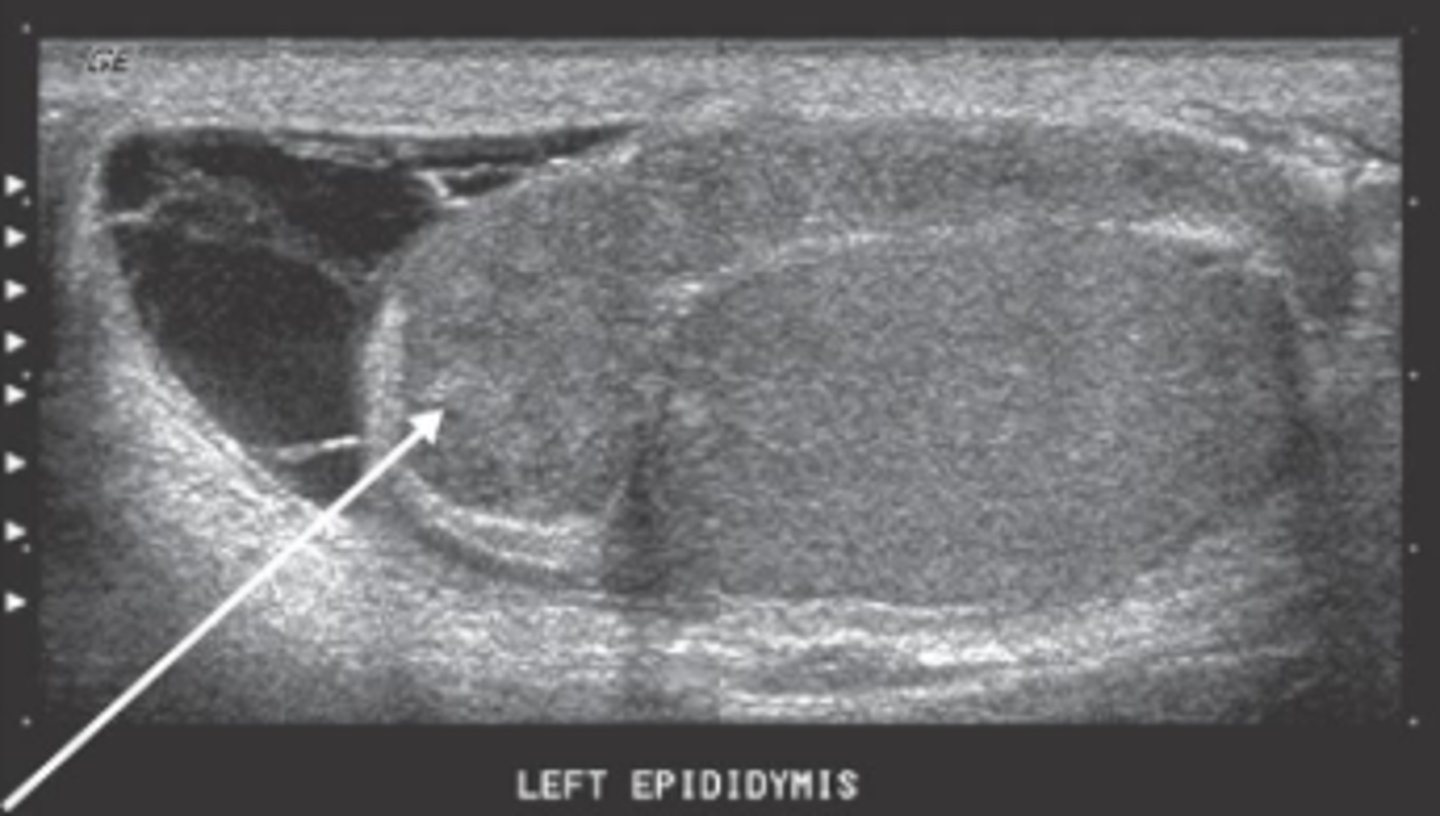
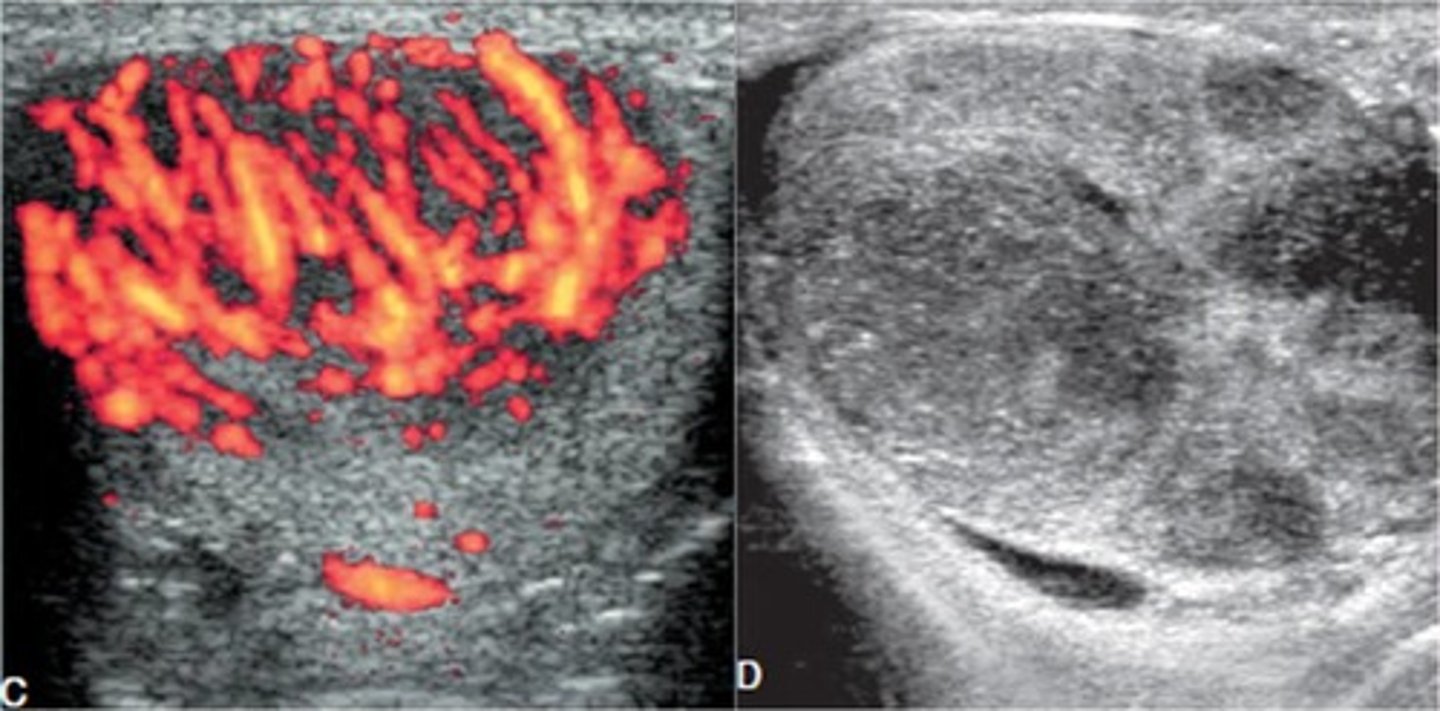
Epididymitis
Define Cause of Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
Inflammation of Epididymis; MCC of Scrotal Pain in Adults
-Hx:
> Young Boys/Late Adolescence
> Sexually Active
> Heavy Physical Exertion
> Direct Trauma
> Structural Anomalies of Urinary Tract
-Sx: ACUTE or SUBACUTE
> Pain & Swelling of Epididymis (dull, persistent ache intensifying w/ time; radiates to spermatic cord and proximal/medial thigh)
> Sx < 6 wks
> Unilateral or Bilateral
> Fever
> Frequency
> Dysuria
> Urethral Discharge
-PE:
> Testis in vertical line
> Normal cremasteric reflex
> (+) Prehn Sign = Pain relief w/ elevation of testis
-Dx:
> Labs:
>> CBC
>> Gram Stain of urethral discharge
>> UA & Culture (+ leukocytes and/or nitrites)
>> STI elevation
> Doppler US/Nuclear Scan (increased flow to affected epididymis)
-Tx:
> Abx
>> Children
>>> 3 WBC/hpf OR (+) Culture OR GU Abn = TMP or Cephalexin
>>> (-) Culture or No Pyuria --> No Abx required
>> Sexually Active (Teens/Adults)
>>> Vaginal Intercourse = Empiric Abx against Chlamydia and GC (Ceftriaxone + Doxycycline OR AZT)
>>> Anal Intercourse = Empiric Abx against Chlamydia, GC, and Coliforms (Ceftriaxone + Doxycycline OR AZT; Coliforms = "-floxacin")
> Supportive
>> Analgesics
>> Scrotal support
>> Elevation
>> Bed rest
-Prog:
> Improvement in days w/ Tx
> Full recovery = 2 wks
> If Tx Delay --> Orchitis, Abscess, Infertility, Chronicity
Orchitis
Define Cause of Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
Inflammation of testis
-Hx/Path:
> Viral
>> Mumps
>> Rubella
>> Coxsackie
>> Echovirus
>> Lymphocytic Choriomengitis Virus
>> Parvovirus
> Bacterial
>> Brucellosis (CHILDREN)
>> N gonorrhoeae & C trachomatis (if UNDER 35)
>> E coli, Pseudomonas, coliforms, Ureaplasma (if OVER 35)
-Sx/PE:
> Unilateral
> Severe Pain & Swelling
-Dx:
> Labs:
>> CBC
>> Gram Stain of urethral discharge
>> UA & Culture (+ leukocytes and/or nitrites)
>> STI elevation
> Doppler US/Nuclear Scan (increased flow)
-Tx:
> Abx
>> Children
>>> 3 WBC/hpf OR (+) Culture OR GU Abn = TMP or Cephalexin
>>> (-) Culture or No Pyuria --> No Abx required
>> Sexually Active (Teens/Adults)
>>> Vaginal Intercourse = Empiric Abx against Chlamydia and GC (Ceftriaxone + Doxycycline OR AZT)
>>> Anal Intercourse = Empiric Abx against Chlamydia, GC, and Coliforms (Ceftriaxone + Doxycycline OR AZT; Coliforms = "-floxacin")
> Supportive
>> Analgesics
>> Scrotal support
>> Elevation
>> Bed rest
Fournier's Gangrene
Define Cause of Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
Necrotizing fasciitis of perineum and scrotum
-Hx/Path:
> Mixed Aerobic/Anaerobic Infex
>> Polymicrobial = C perfinges
>> Group A Strep (GAS)
>> MRSA
> Risks
>> Diabetic
>> Alcohol
>> IVDA
>> Immunocompromised
>> Longstanding indwelling catheters
>> Urethral trauma
-Sx: Severe pain starting on anterior abdominal wall migrates to gluteal muscle, scrotum and penis
-PE:
> Tense edema
> Bullae/Blisters
> Crepitus
> Fever
> Tachycardia
> Hypotension
-Dx: CT
> Air along fascial planes or deep tissue involvement
-Tx:
> EARLY, AGGRESSIVE SURGICAL DEBRIDEMENT!
> Broad spectrum Abx
> Hemodynamic support
-Prog: 25% Mortality Rate
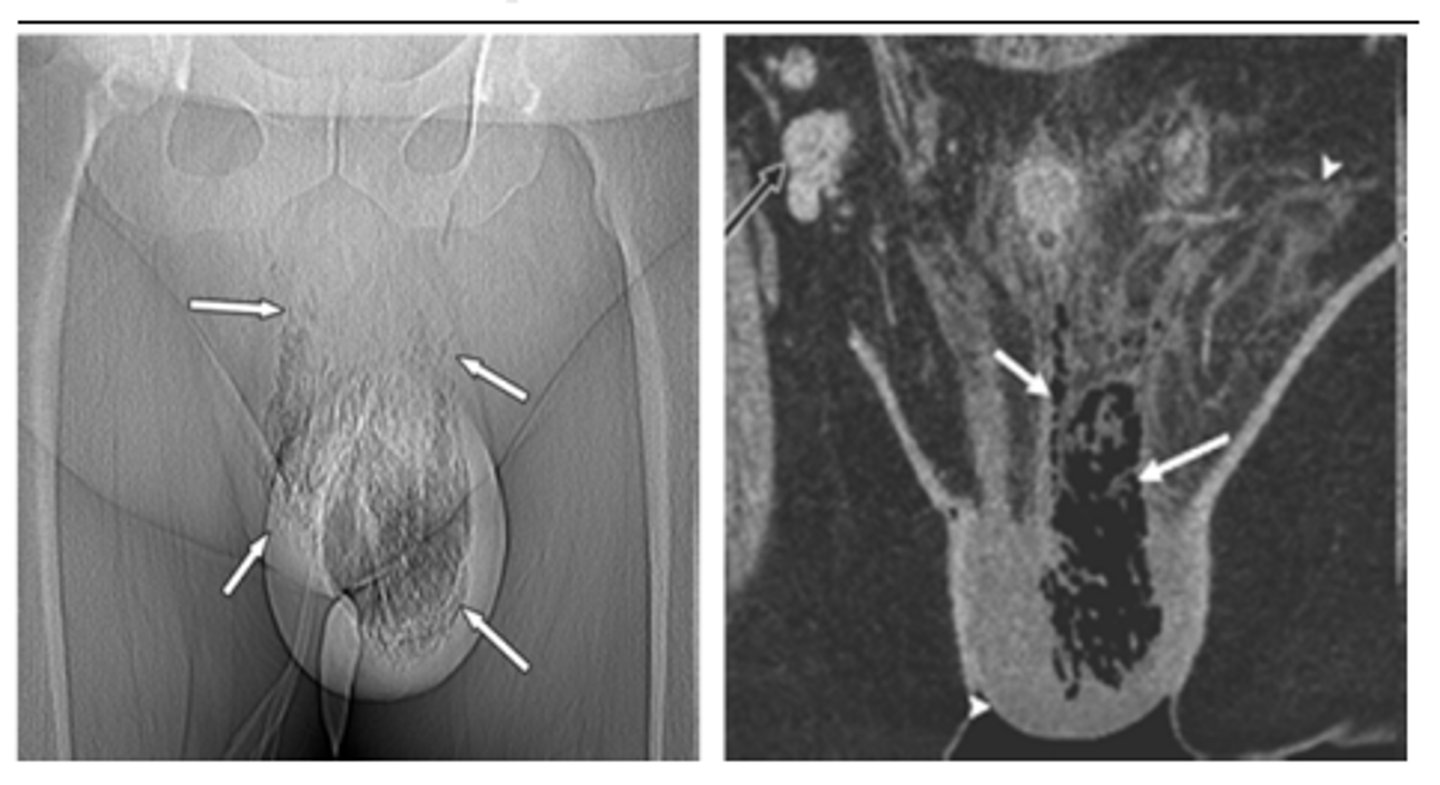
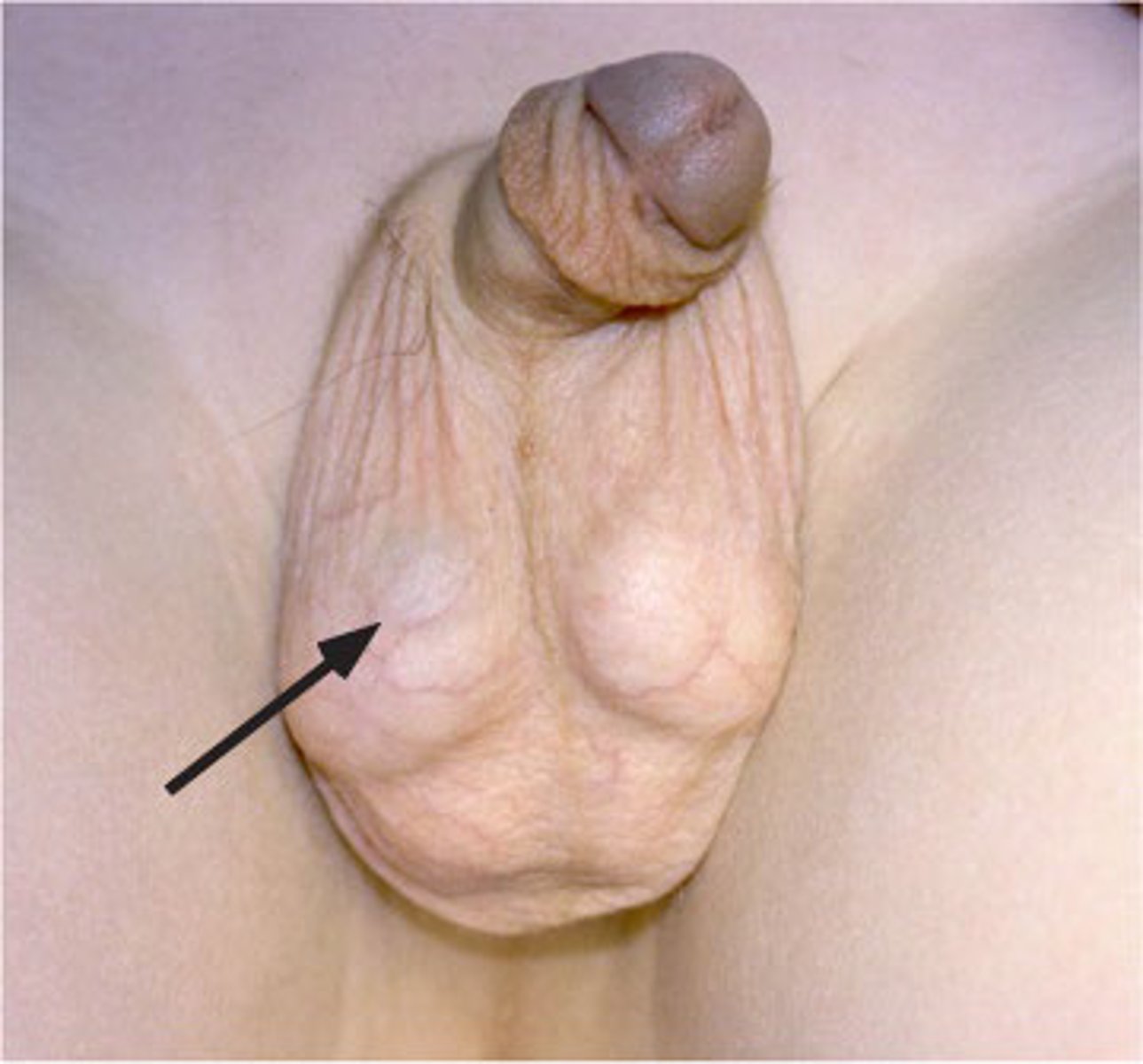
Varicocele
Define Cause of NON-Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
Abnormal dilation of the spermatic venous or pampiniform plexus
-Path: More common on LEFT SIDE (Spermatic vein opens at a sharp angle into the left renal vein)
-Sx:
> Often Asx (part of Infertility workup)
> Pain
> Heavy sensation in scrotum
> Infertility
-PE: "BAG OF WORMS"
-Tx: Surgical Ligation OR none
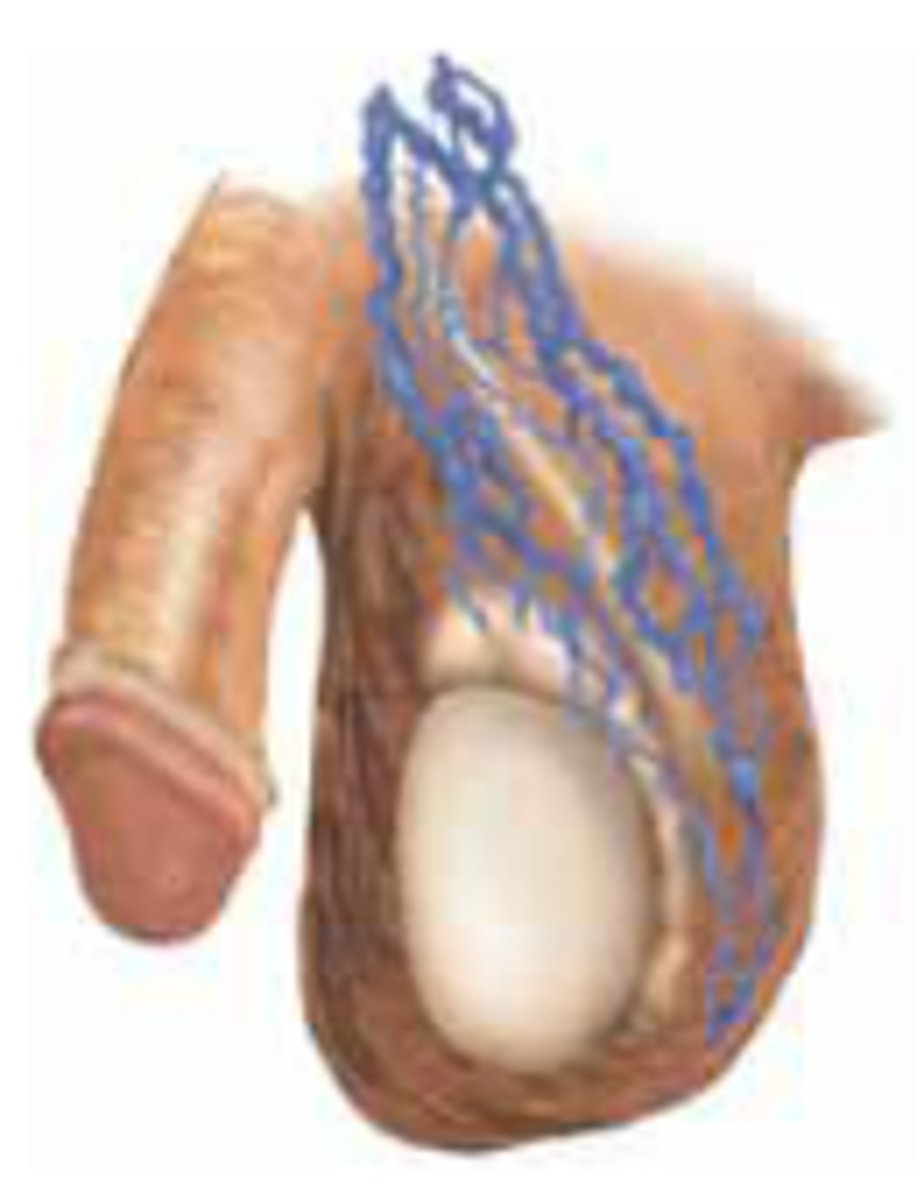
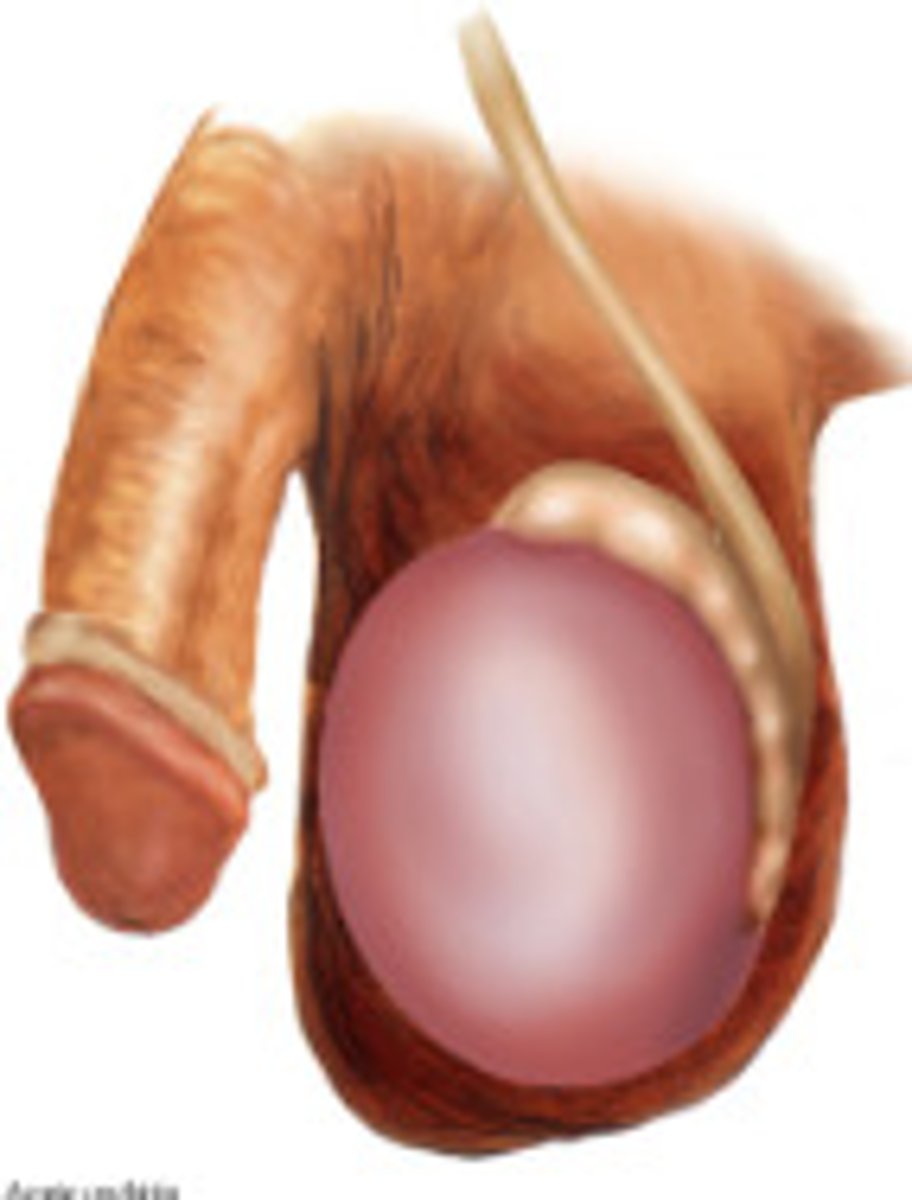
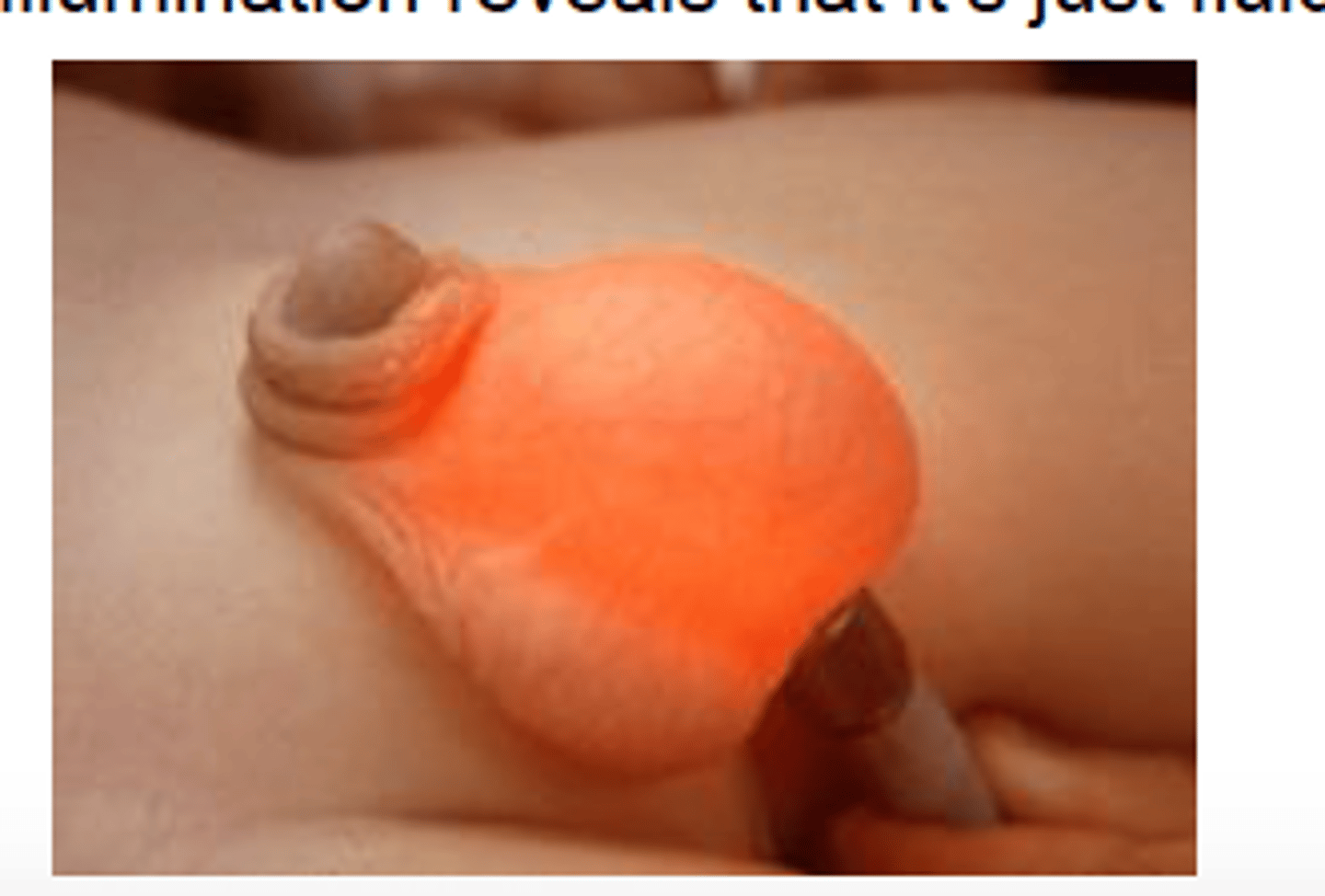
Hydrocele
Define Cause of NON-Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
Abnormal fluid collection in the scrotum between the layers of the tunica vaginalis
-Path: More common on LEFT SIDE (Spermatic vein opens at a sharp angle into the left renal vein)
-Sx/PE: ACUTE OR CHRONIC
> Acute = Mass/Pain
> Chronic = PAINLESS
> Need to R/O torsion or incarcerated hernia
-Dx:
> (+) Transillumination of Scrotum
> Scrotal US
-Tx: SURGERY

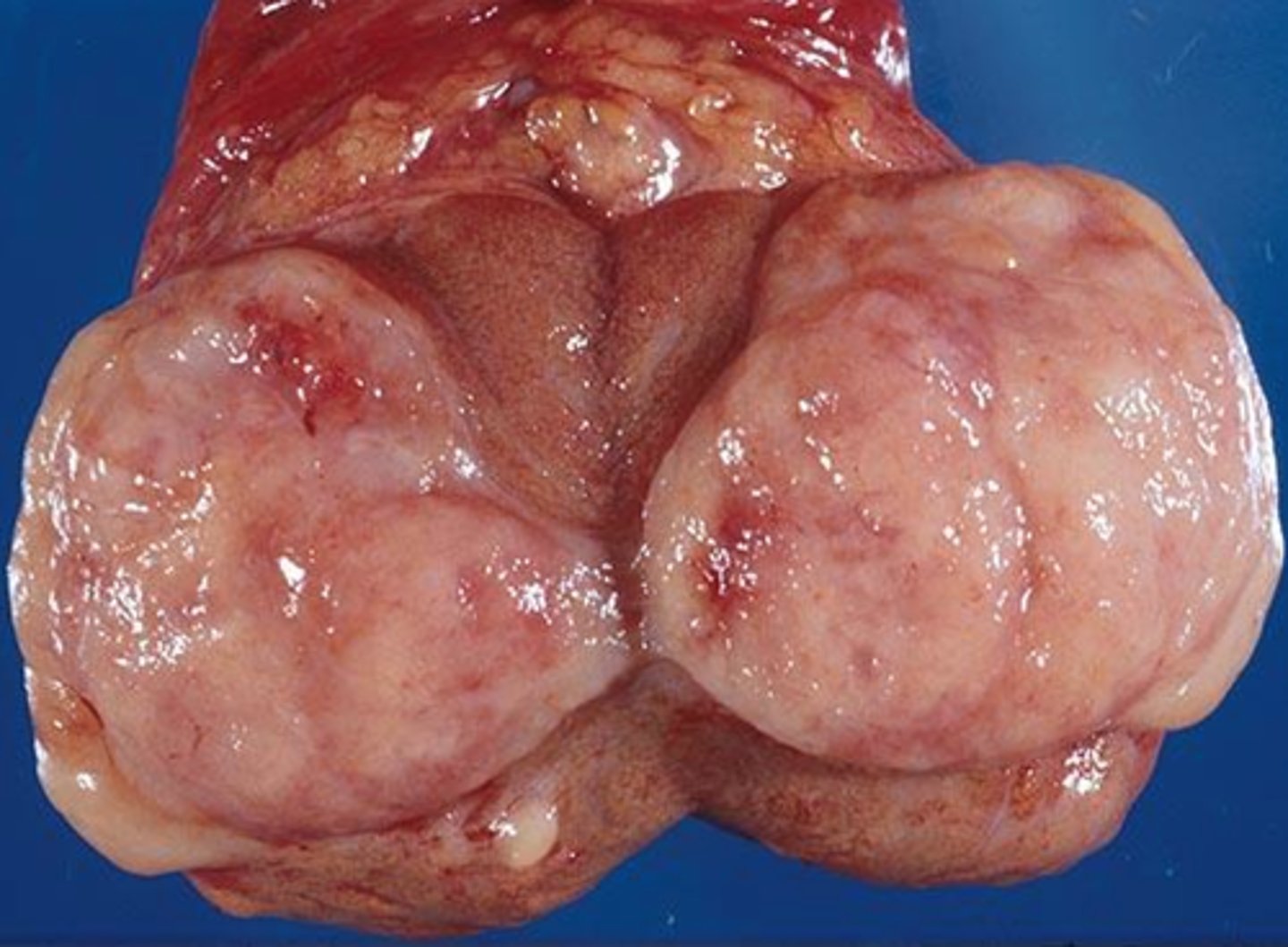
Testicular Cancer
Define Cause of NON-Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
MC Cancer in Young Men
-Hx:
> Cryptorchidism = Descent failure of one or both testes
>> MC in prematurity
>> Bilateral = Decrease in Serum Testosterone
>> Unilateral = Normal Testosterone
>> Becomes Orchoplexy if not spontaneously resolved by 2 y/o
> Klinefelter Syndrome
-Types:
> Mainly GERM CELL Tumors
>> Seminoma
>> Teratoma
>> Embryonal Carcinoma
>> Yolk sac tumor
>> Choriocarcinoma
> NON-GERM CELL Tumors (BENIGN)
>> Sertoli Cell Tumor
>> Leydig Cell Tumor
>> Testicular Lymphoma
-Sx/PE:
> Intra-testicular non-tender mass that doesn’t illuminate
> PAINLESS Mass fixed to underlying tissue (w/n testicle)
> May have acute pain secondary to Torsion or hemorrhage
-Dx:
> (-) Transillumination
> Scrotal Biopsy - NOT tumor itself
-Tx: Radical Orchiectomy
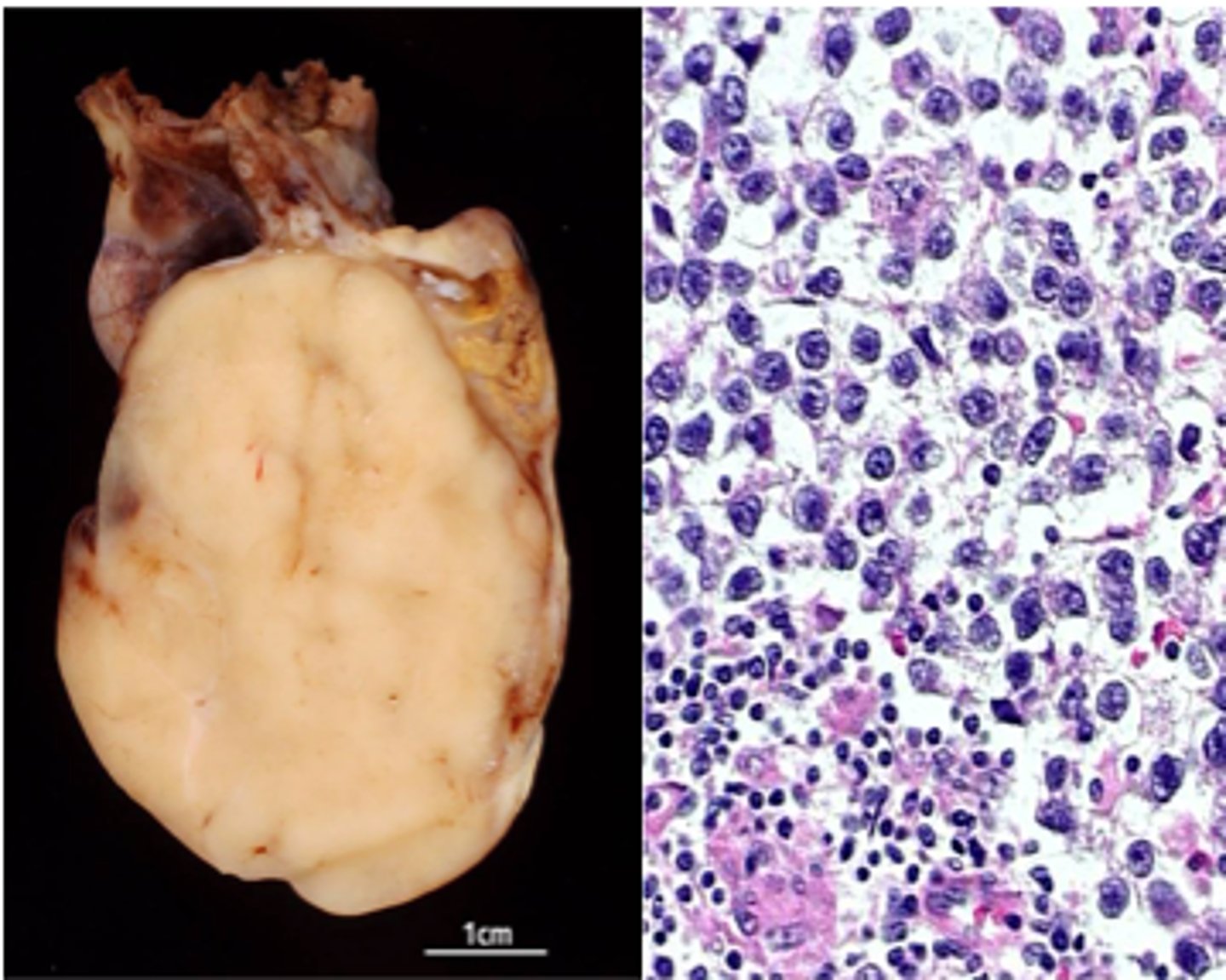
Seminoma
Define Testicular GERM Cancer Type:
•Most common, late metastasis, excellent prognosis
•Not in infancy
•Fried egg appearance on histology
•Increased placental PALP, +/- hCG
•Highly radiosensitive
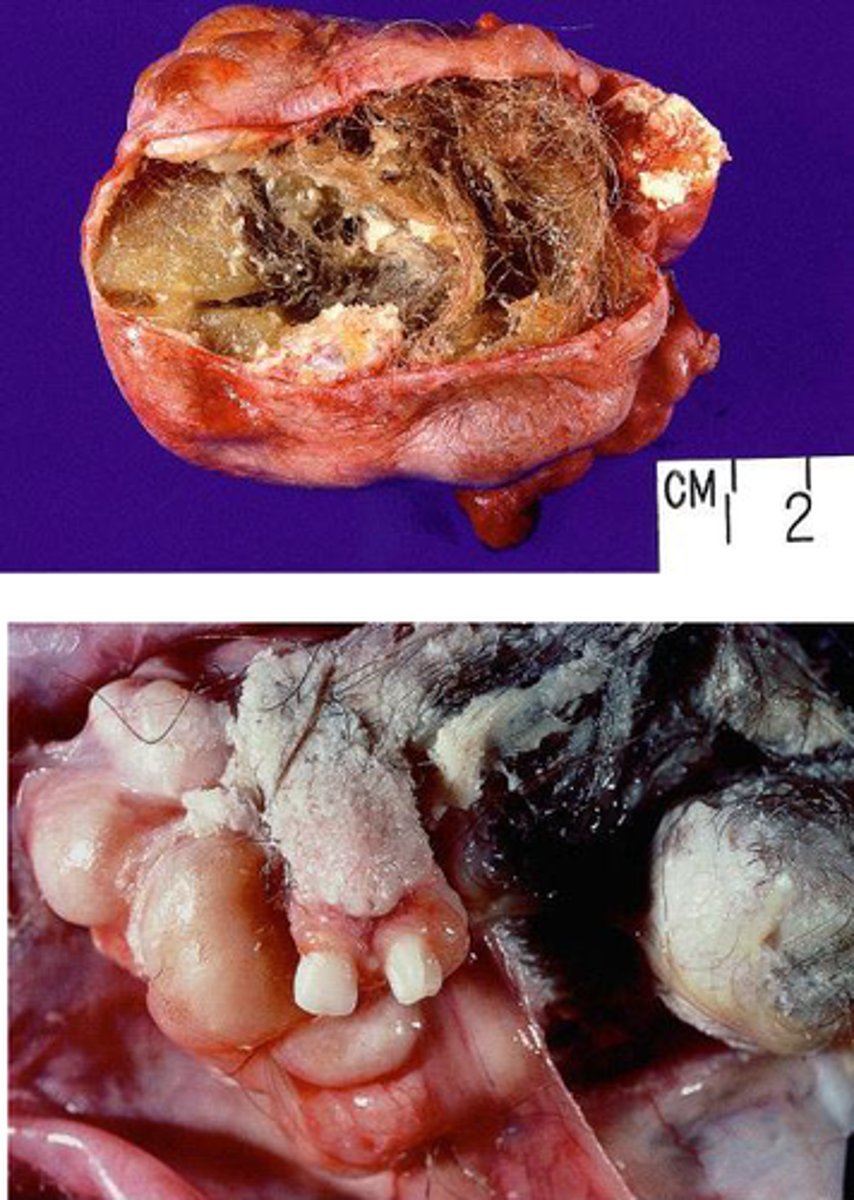
Teratoma
Define Testicular GERM Cancer Type:
•Unlike females, can be malignant in males
•Benign in children
Embryonal Carcinoma
Define Testicular GERM Cancer Type:
•Painful, hemorrhagic mass with necrosis
•‘Pure’ are rare (normal AFP)
•May present with metastasis
•Worse prognosis than seminoma
•Elevated hCG, elevated AFP with mixed
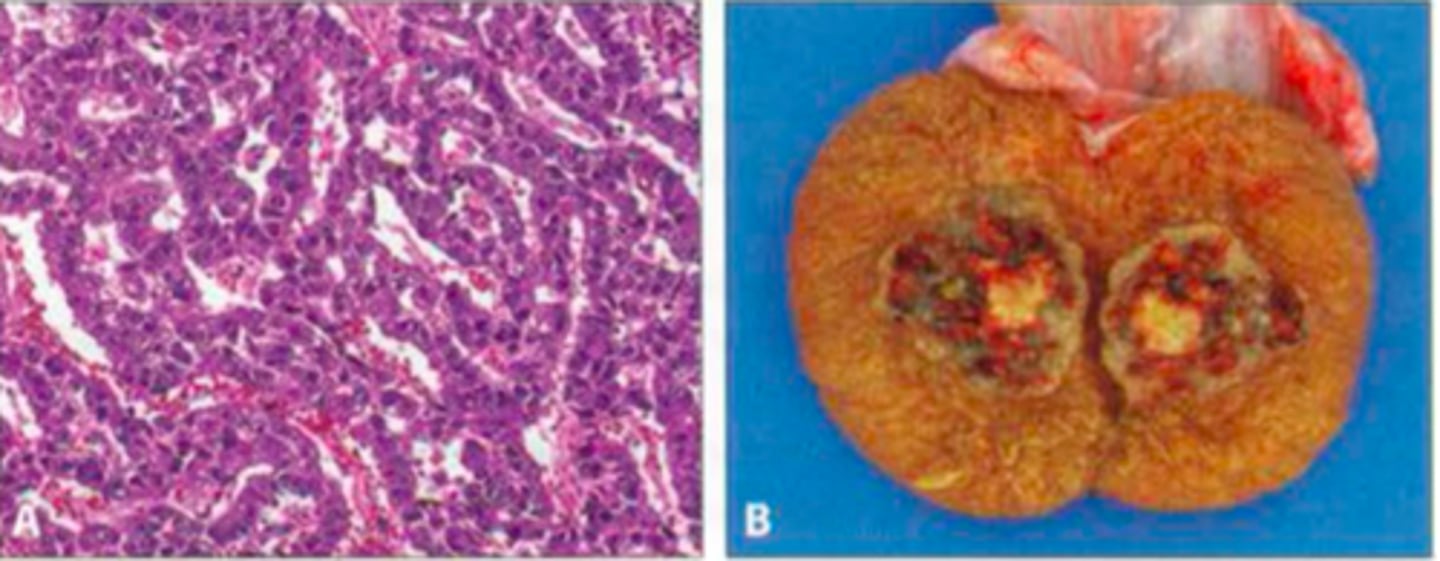
Yolk sac (endodermal sinus) tumor
Define Testicular GERM Cancer Type:
•Schiller-Duval bodies resemble primitive glomeruli
•Yellow, mucinous
•Elevated AFP highly characteristic. +/- hCG
•Most common in boys < 3 years old
•Malignant and aggressive

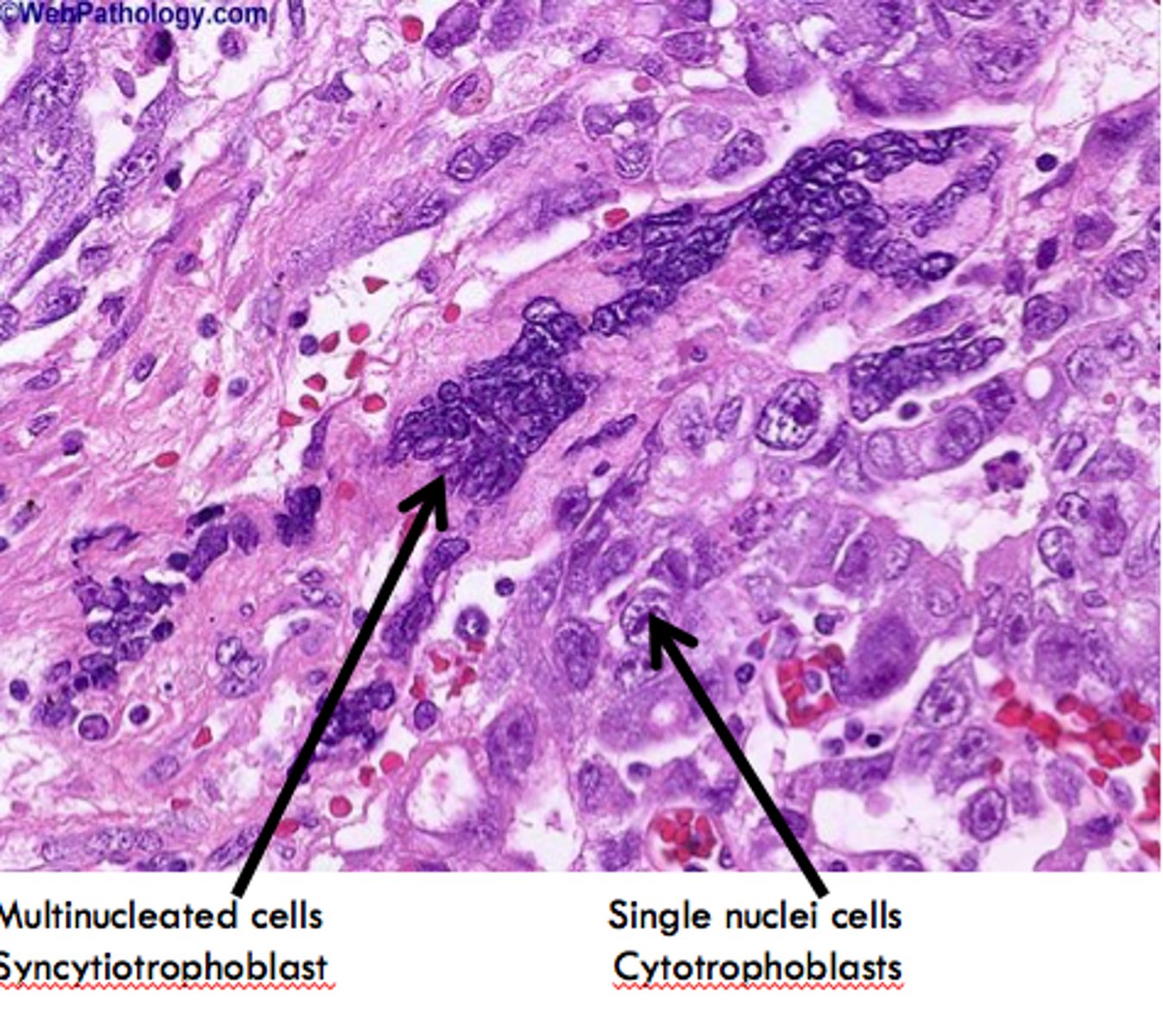
Choriocarcinoma
Define Testicular GERM Cancer Type:
•Very elevated hCG
•Disordered syncytiotrophoblastic and cytotrophoblastic elements
•Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
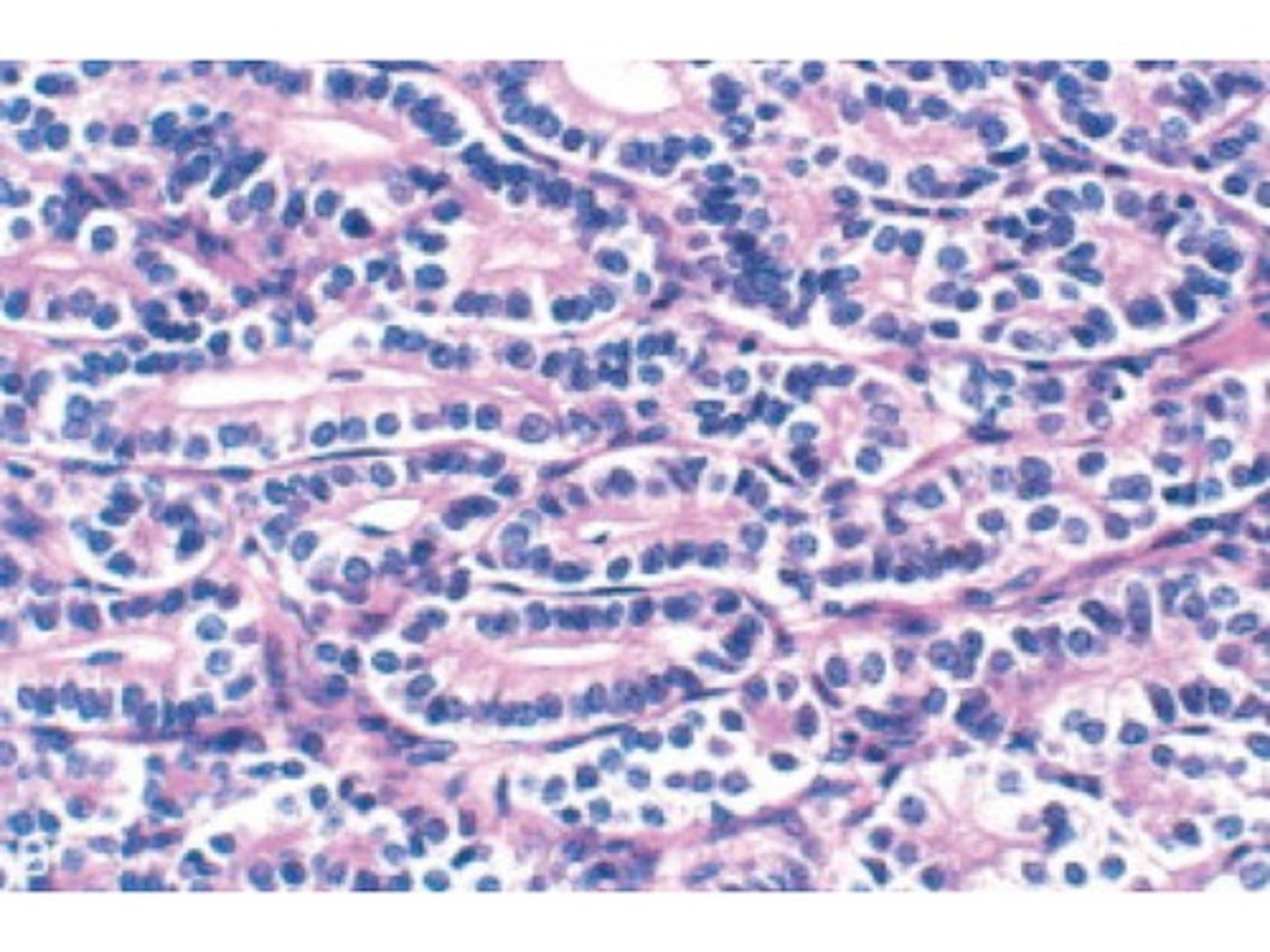
Sertoli Cell Tumor
Define Testicular NON-GERM Cancer Type:
•Mostly benign
•Androblastoma from sex cord stroma
Leydig Cell Tumor
Define Testicular NON-GERM Cancer Type:
•Mostly benign
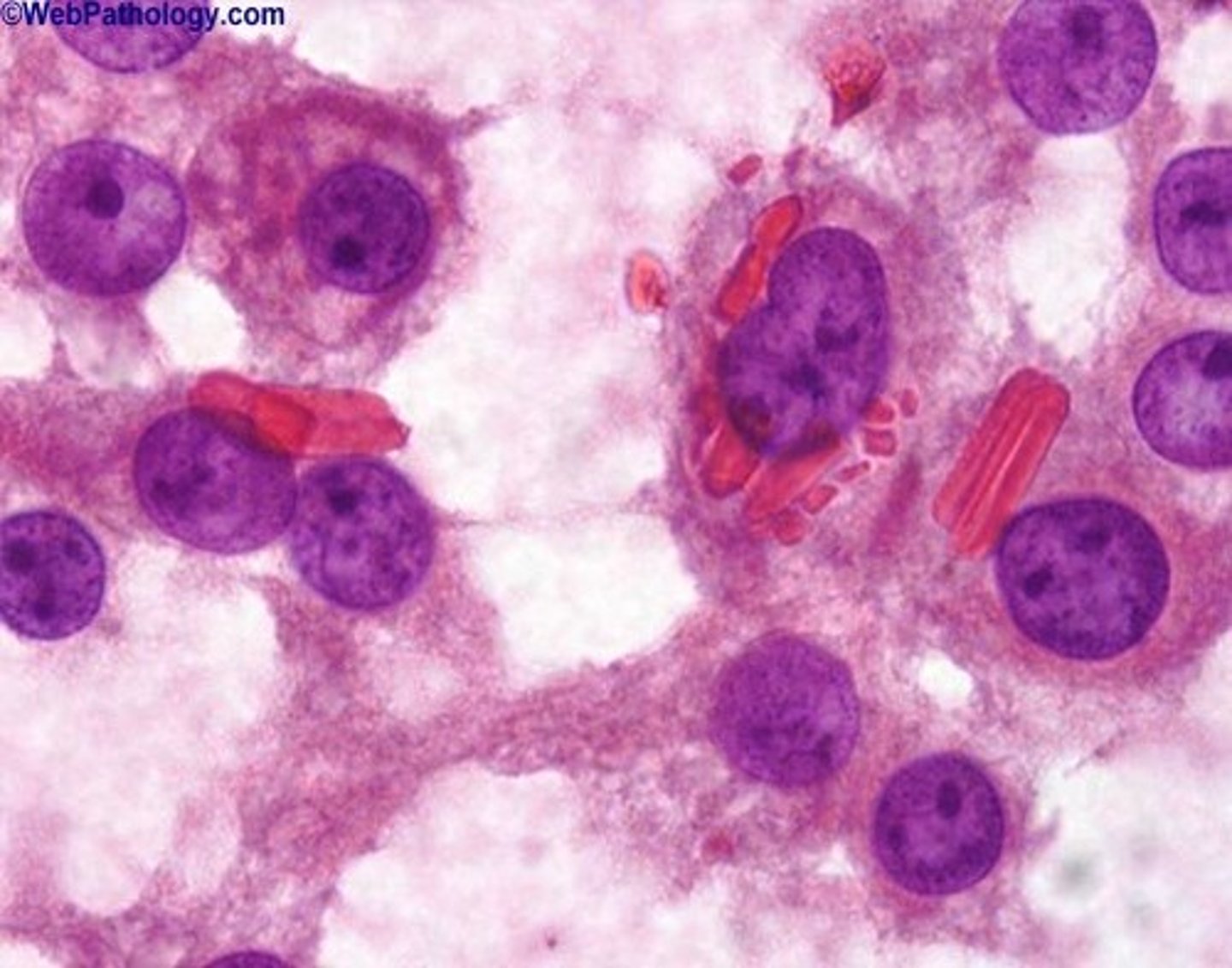
•Golden brown color
•Reinke crystals (eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusions)
•Produces androgens or estrogens:
> Gynecomastia in men
> Precocious puberty in boys
Testicular Lymphoma
Define Testicular NON-GERM Cancer Type:
•Malignant/aggressive
•Most common testicular cancer in older men
•Not primary cancer but metastatic lymphoma to the testes
Prostatitis
Define Cause of NON-Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
Inflammation of prostate
-Hx/Path:
> Acute
>> Bacterial Infex that usually causes UTIs
>>> MC = E coli
>>> Younger Men = C trachomatis, N gonorrhoeae
>> Direct extension from bladder or urethra
>> Lymphatic/hematogenous spread
> Chronic
>> Common w/ recurrent UTis
>> Bacterial/Non-bacterial
-Sx:
> Asx
> Low back pain
> Urinary Sx
> Fever/Sepsis (if ACUTE)
-PE: Warm, tender, enlarged prostate
-Tx:
> Abx
>> Sexually Active (Teens/Adults)
>>> Vaginal Intercourse = Empiric Abx against Chlamydia and GC (Ceftriaxone + Doxycycline OR AZT)
>>> Anal Intercourse = Empiric Abx against Chlamydia, GC, and Coliforms (Ceftriaxone + Doxycycline OR AZT; Coliforms = "-floxacin")
> Supportive
>> Analgesics
>> Scrotal support
>> Elevation
>> Bed rest
Prostate Cancer
Define Cause of NON-Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
MC Cancer in Men WORLDWIDE
-Hx:
> Men > 50 y/o
> More in African American Men (some in White Men)
-Sx:
> Absent at Dx
> Urinary Sx
-PE:
> Mass on Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) - 30% can't be felt
> Enlarged Prostate = HIGH SUSPICION
-Dx:
> PSA = HIGH (often used for EARLY DETECTION/SCREENING)
> Biopsy = CONFIRM
-Tx:
> Surgery (Orchiectomy)
> Radiation
> Hormonal Modalities (Androgen blockade)
-Prog:
> May have lymphatic/hematogenous spread --> Pelvis & Lower Vertebrae MC sites
> Urinary Incontinence
> Sexual Dysfunction (Impotence)
> Bowel Issues (Diarrhea)
INDIRECT Inguinal Hernias
Define Cause of NON-Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
Protrusion of intra-abdominal contents through a weakness or opening in the abdominal wall
-Hx:
> More in YOUNGER MALES than Females
> Age
> Cigarette smoking
> Systemic disease
> Premature birth/Low birth Wt
> Chronic Steroid Use
-Types:
> Reducible
> Incarcerated
> Strangulated
-Path: Weakened Connective tissue - d/t failure of processus vaginalis to close --> passes through internal inguinal ring (lateral to inferior epigastric artery) into inguinal canal (REMAINS INSIDE CANAL)
-Sx/PE:
> Aching/Discomfort/Burning in groin
> Strangulation/Incarceration:
>> Increase in severity of pain or size of lump
>> Fever, nausea, vomiting
>> Severe constipation or obstipation
-Dx:
> Increase pressure from Valsalva OR Cough
> Ultrasound (good, but rarely needed)
-Tx:
> Asx/Mild = Observe
> Sx = Surgery
> Incarc/Strang = IMMEDIATE Surgery
-Prog: 5% will STRANGULATE
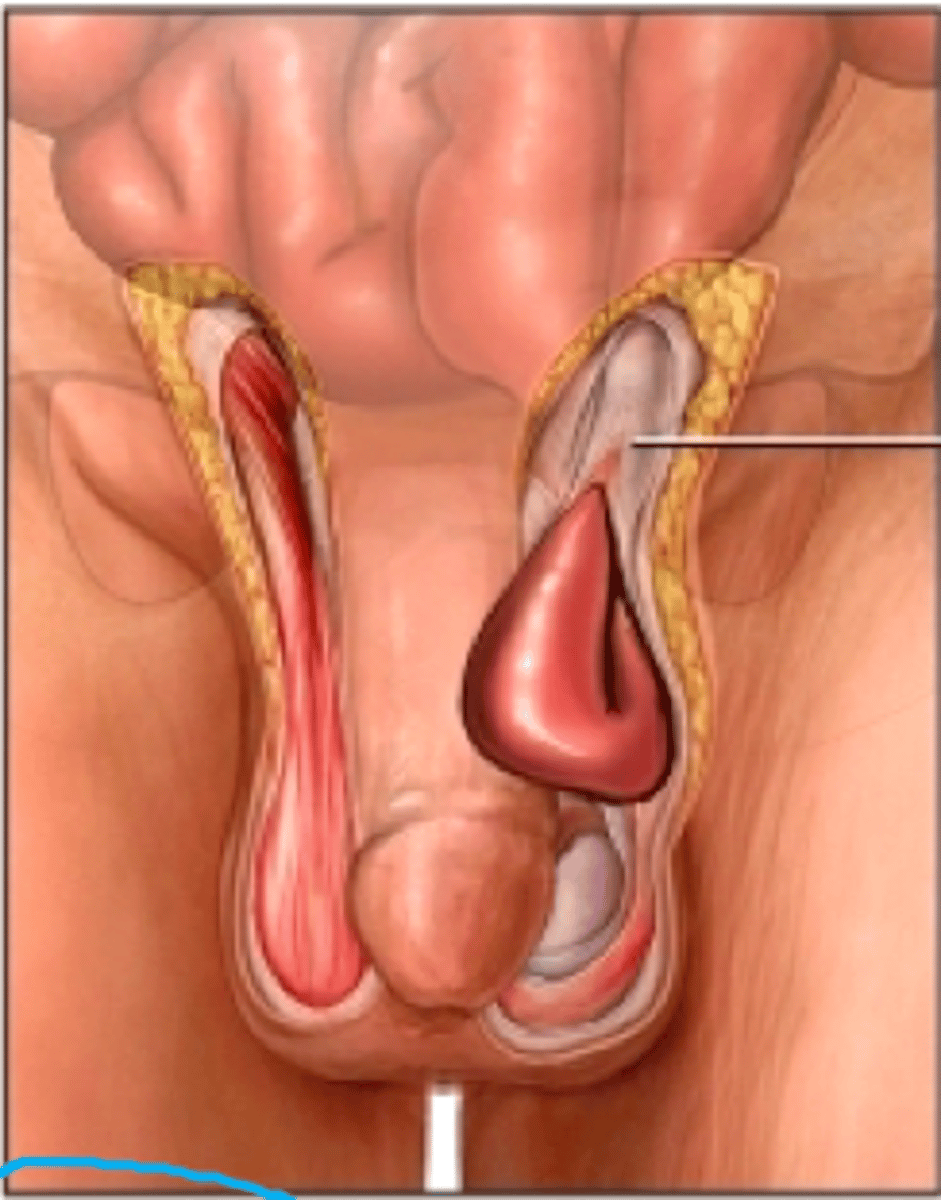
DIRECT Inguinal Hernia
Define Cause of NON-Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
Protrusion of intra-abdominal contents through a weakness or opening in the abdominal wall
-Hx:
> More in ELDERLY MALES than Females
> Age
> Cigarette smoking
> Systemic disease
> Premature birth/Low birth Wt
> Chronic Steroid Use
-Types:
> Reducible
> Incarcerated
> Strangulated
-Path: Weakened Connective tissue - Passes through the abdominal wall medial to the inferior epigastric artery in the area of Hasselbach’s triange
> Medial border = Rectus abdominis
> Lateral border = Inferior Epigastric vessels
> Inferior border = Inguinal ligament
-Sx/PE:
> Aching/Discomfort/Burning in groin
> Strangulation/Incarceration:
>> Increase in severity of pain or size of lump
>> Fever, nausea, vomiting
>> Severe constipation or obstipation
-Dx:
> Increase pressure from Valsalva OR Cough
> Ultrasound (good, but rarely needed)
-Tx:
> Asx/Mild = Observe
> Sx = Surgery
> Incarc/Strang = IMMEDIATE Surgery:
Femoral Hernias
Define Cause of NON-Acute Groin/Scrotal Pain:
Protrusion of intra-abdominal contents through a weakness or opening in the abdominal wall; LEAST common type
-Hx:
> Mainly in FEMALES
> Older Age
> Cigarette smoking
> Systemic disease
> Premature birth/Low birth Wt
> Chronic Steroid Use
-Types: Incarceration and strangulation high (20-30%)
-Path: Weakened Connective tissue
-Sx/PE:
> Bulge in upper medial thigh below inguinal ligament
> Aching/Discomfort/Burning in groin
> Strangulation/Incarceration:
>> Increase in severity of pain or size of lump
>> Fever, nausea, vomiting
>> Severe constipation or obstipation
-Dx:
> Increase pressure from Valsalva OR Cough
> Ultrasound (good, but rarely needed)
-Tx:
> Asx/Mild = Observe
> THIS or Sx = Surgery
> Incarc/Strang = IMMEDIATE Surgery
Erectile Dysfunction
Define Condition:
Consistent/recurrent inability to acquire or sustain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse
-Hx/Path:
> Decreased libido w/ increased age
> CVD
>> DM
>> CKD
>> OSA
> Obesity/Inactivity
> Psychosocial Factors
> Neuro Issues
> Iatrogenic (Surgical scars on abdomen)
> Drugs = Antidepressants (SSRI), Antihypertensives, Chlorthalidone, Spironolactone, clonidine, methyldopa, Alpha blockers ((Doxazosin) help libido), Anti-androgens
-Tx: Depends on pathophysiology
> Testosterone supplement
> Control chronic disease
> Improve lifestyle
> Meds = Selective PDE-5 Inhibitors
Peyronie's Disease
Define Condition:
Abnormal curvature of the erect penis
-Hx:
> Erectile Dysfunction
> Scleroderma
> Trauma
> HTN
> DM2
-Path: Curvature secondary to fibrosis of tunica vaginalis
-Sx/PE: Marked, abnormal curvature of the penis
-Tx:
> Surgical Repair: Penile Pilocation
> Intralesional injections/Oral Meds:
>> Verapamil
>> Collagenases
>> Interferon
> Topical Med: Verapamil Cream
-Prog:
> Stomach Cancer (43%)
> Testicular Cancer (39%)
> Melanoma (19%)
Priapism
Define Condition:
Painful, persistent erection of penis
-Hx/Path:
> MC = ISCHEMIC
>> D/t impaired relaxation and paraylsis of cavernosal smooth muscle (Compartment Syndrome)
>> Bimodal Age (5-10, 20-50)
>> Causes
>>> Meds (MCC OVERALL) =
>>>> ED Meds = Alprostadil (Caverject, Edex, others), Papaverine, phentolamine (Oraverse)
>>>> Antidepressants = fluoxetine (Prozac), bupropion (Wellbutrin XL, Wellbutrin SR), trazodone and sertraline (Zoloft)
>>>> Alpha blockers = prazosin (Minipress), terazosin, doxazosin (Cardura) and tamsulosin (Flomax)
>>>> Anti-anxiety/psychotic = hydroxyzine (Vistaril), risperidone (Risperdal), olanzapine (Zyprexa), lithium (Lithobid), clozapine (Clozaril), chlorpromazine and thioridazine
>>>> Blood thinners = warfarin (Jantoven), heparin
>>>> Hormones = testosterone, GnRH
>>>> ADHD Meds = Methylphenidate (Concerta, Ritalin, others) and atomoxetine (Strattera)
>>> Sickle Cell Disease (children)
>>> Neuro-spinal shock
> NON-ISCHEMIC (HIGH FLOW) - secondary to trauma
-Sx/PE:
> Prolonged, painful erection > 4 hrs (unrelated to sex or stimulation)
> Rigid shaft, soft glands
-Dx: Cavernosal Blood gas (Ischemic vs Non-Ischemic)
-Tx:
> Aspiration
> Intracavernosal Injection of Sympathomimetic (Phenylephrine)
Male hypogonadism
Define Condition:
Decrease in sperm production and/or testosterone production
-Types/Path:
> Primary (Hypergonadotropic) = Disease of Testes
>> Klinefelter Syndrome (47, XXY)
>> Cryptorchidism
>> Anorchia
>> Acquired
> Secondary (Hypogonadotropic) = Disease of hypothalamus/pituitary
>> Kallmann
>> Prader-Willi Syndrome
-Sx/PE:
> Pre-Pubertal = Don't develop secondary characteristics
>> Small genitalia
>> Decreased muscle mass
>> Lack of facial hair
>> Failure of voice deepening
> Post-Pubertal
>> Low energy
>> Depressed Mood
>> Decreased libido
>> Erectile dysfunction
>> Infertility
-Dx:
> Labs
>> Morning serum TOTAL Testosterone --> Repeat next Morning for confirmation
>>> Test = LOW --> FSH/LH = HIGH ==> PRIMARY
>>> Test = LOW --> FSH/LH = LOW ==> SECONDARY
> Semen Analysis
> Testicular U/S + Biopsy
> Karyotype Analysis
> Pituitary MRI
-Tx: Testosterone Supplementation w/ Caution (if etiology not correctable)
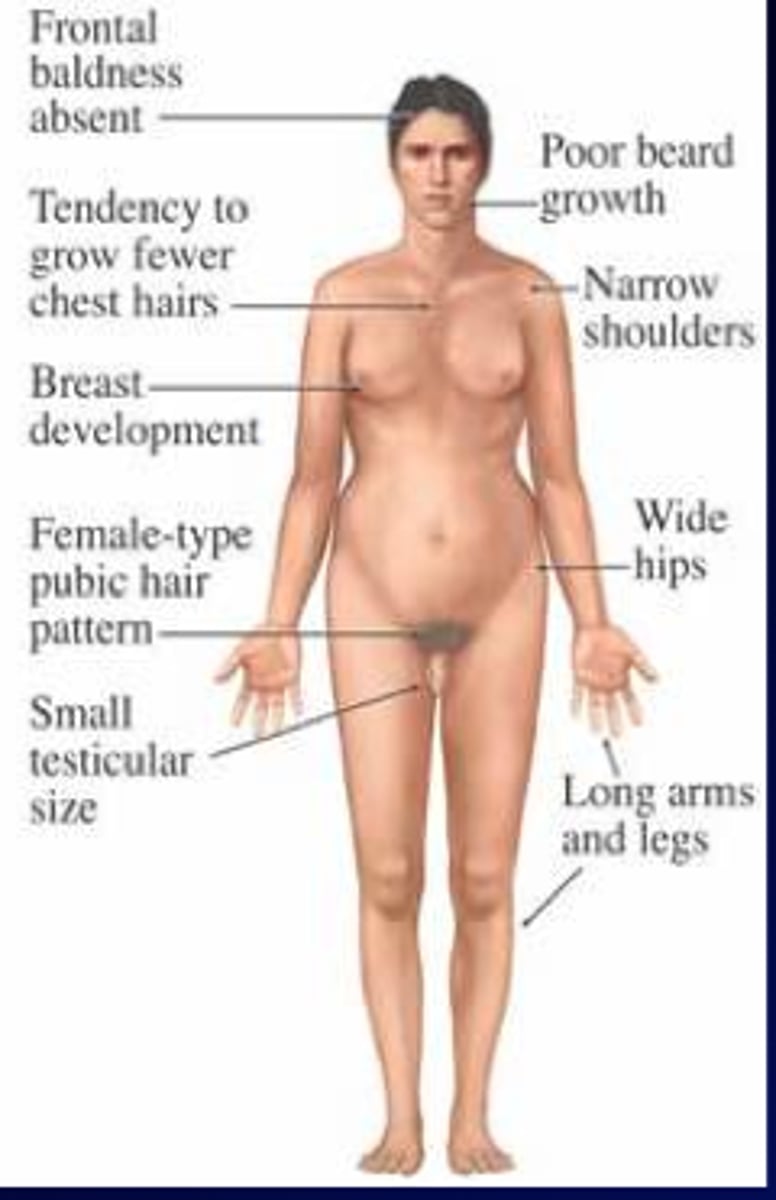
Klinefelter Syndrome (47, XXY)
Define Cause of CONGENITAL PRIMARY Hypogonadism:
-Hx:
> Most common cause with prepubertal onset
> Often not diagnosed until adulthood
-PE:
> Increased lower/upper body segment ratio
> Gynecomastia
> Small penis
> Sparse body hair with female pubic hair pattern
Cryptorchidism
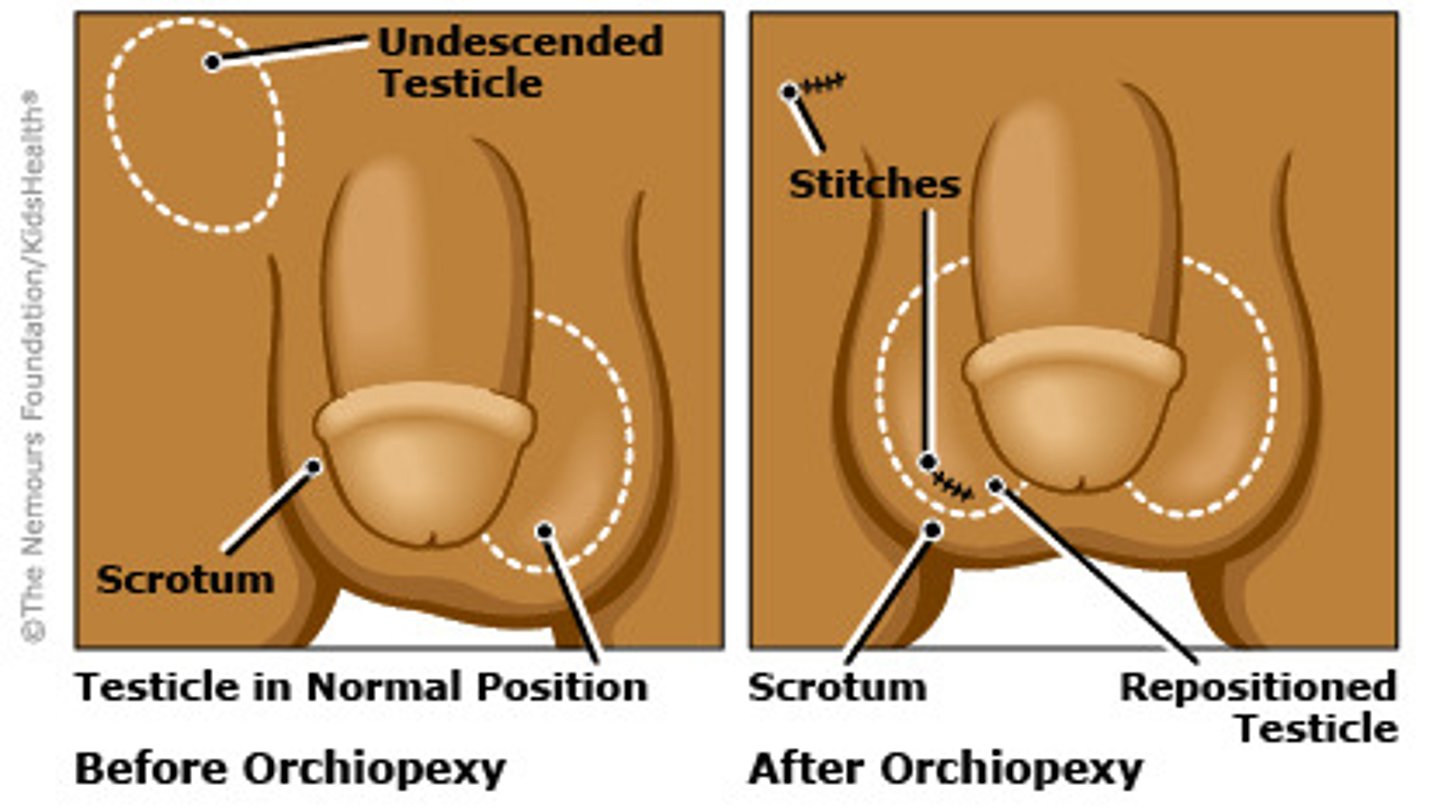
Define Cause of CONGENITAL PRIMARY Hypogonadism:
Undescended or maldescended testes
-Path: Reduced sperm production + Increased risk of testicular cancer
-Tx: Orchioplexy
-Mumps orchitis
-Autoimmune orchitis
-Testicular trauma, irradiation
-Alcohol, ketoconazole, anticancer agents
-Hemochromatosis
-Increase in testicular temperature
Name Causes of ACQUIRED PRIMARY Hypogonadism
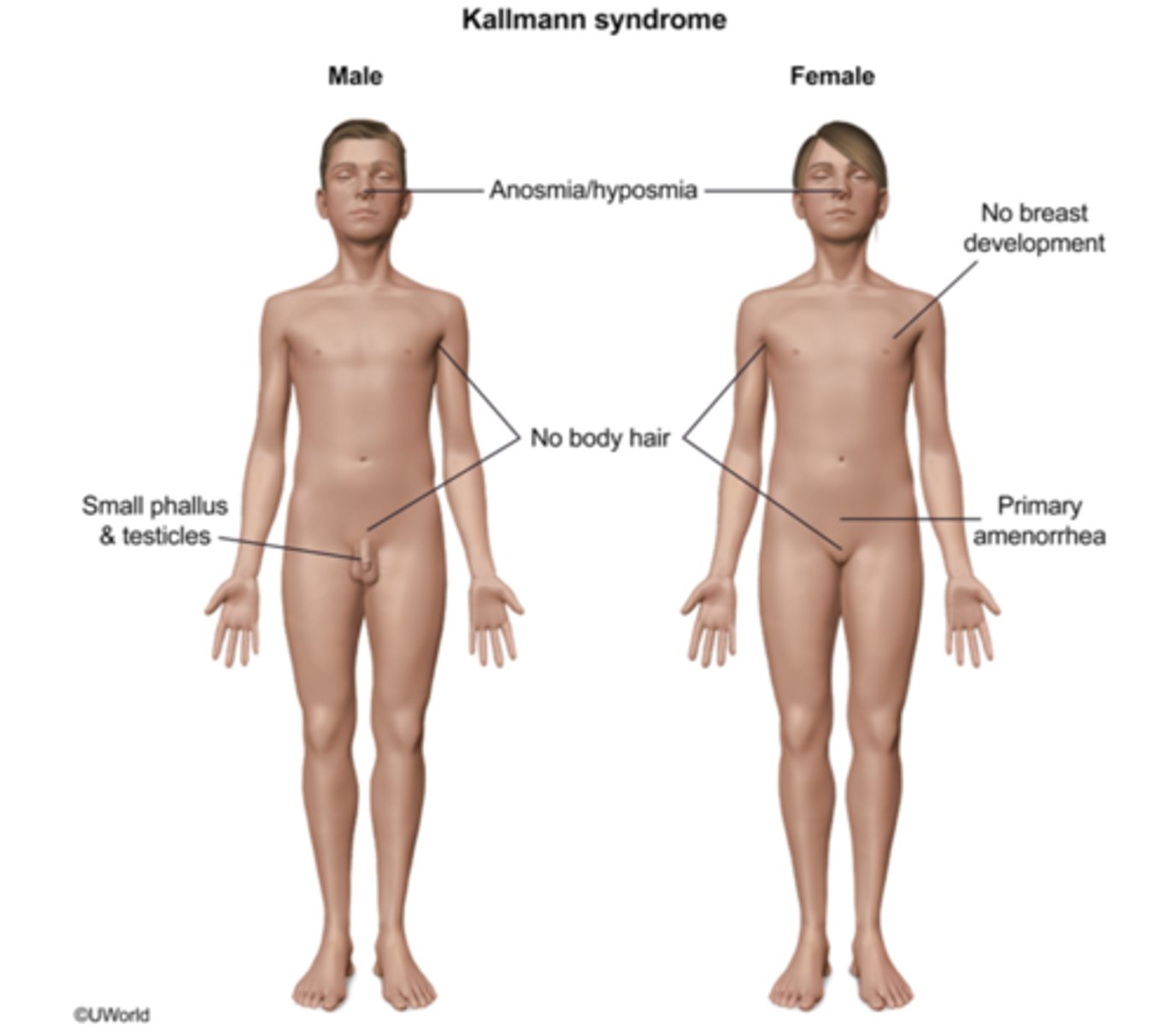
Kallmann Syndrome
Define Cause of CONGENITAL SECONDARY Hypogonadism:
-Delayed or absent puberty
-Infertile
-Impaired sense of smell (anosmia)
-Cleft lip with/without cleft palate
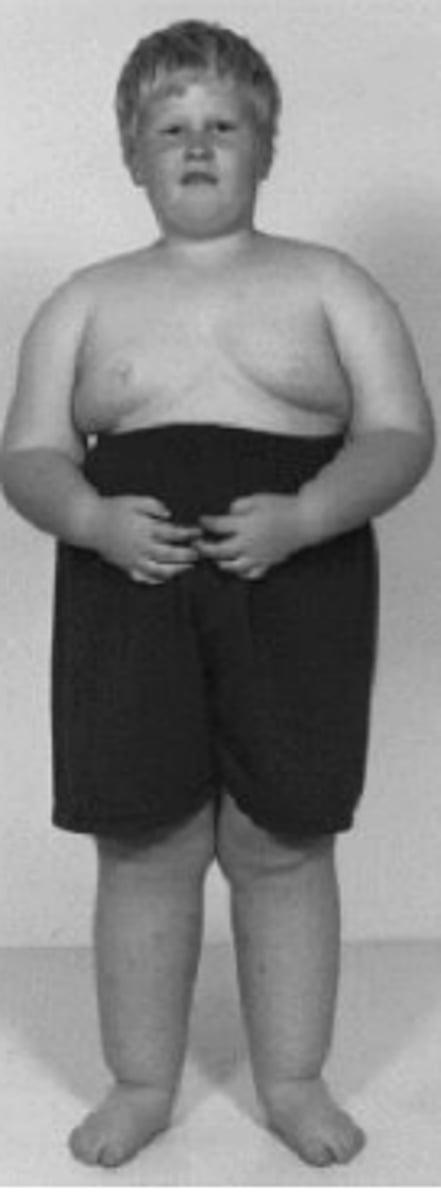
Prader-Willi Syndrome (partial deletion of chromosome 15)
Define Cause of CONGENITAL SECONDARY Hypogonadism:
•Food cravings and weight gain
•Small testes
•Poor growth and physical development
•Cognitive impairment
•Delayed motor development
•Sleep disorder
Gonadotroph Damage
Define Cause of ACQUIRED SECONDARY Hypogonadism:
-Hx:
> Pituitary and hypothalamic lesions
> Trauma, ischemia, hemorrhage
> Radiation
> Infection
Gonadotroph suppression
Define Cause of ACQUIRED SECONDARY Hypogonadism:
-Hx:
> Hyperprolactinemia (prolactinoma, dopamine antagonists)
> Obesity
> Sleep Apnea
> Alcohol
> Severe primary hypothyroidism