MGMT 3661 Exam #2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Last updated 4:28 PM on 3/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
1
New cards
planning
setting goals and deciding how to achieve them; coping with uncertainty by formulating future courses of action to achieve specified results
2
New cards
three types of planning
\-strategic
\-operational
\-tactical
\-operational
\-tactical
3
New cards
strategic planning
\-top management
\-determines what the organization’s long-term goals should be for the next 1-5 years with the resources they expect to have available
\-determines what the organization’s long-term goals should be for the next 1-5 years with the resources they expect to have available
4
New cards
tactical planning
\-middle management
\-determining what contributions departments or similar work units can make with their given resources during the next 6 months to 2 years
\-short term goals
\-determining what contributions departments or similar work units can make with their given resources during the next 6 months to 2 years
\-short term goals
5
New cards
operational planning
\-first-line management and team leaders
\-determining how to accomplish specific tasks with available resources within the next 1 week to 1 year period
\-short term goals
\-determining how to accomplish specific tasks with available resources within the next 1 week to 1 year period
\-short term goals
6
New cards
how do the three levels of planning work together?
strategic (passed down)→ tactical (passed down) → operational
7
New cards
SMART goals
a goal that is Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Results-oriented, and has Target dates
8
New cards
SWOT Analysis
Strengths (internal), Weaknesses (internal), Opportunities (external), Threats (external)
9
New cards
forecasting
vision or projection of the future
10
New cards
trend analysis
hypothetical extension of a past series of events into the future
11
New cards
contingency planning
the creation of alternative hypothetical but equally likely future conditions
* look at current trends
* discontinuities
* visualize future possibilities
* look at current trends
* discontinuities
* visualize future possibilities
12
New cards
benchmarking
process by which a company compares its performance with that of high-performing organizations
13
New cards
three levels of organizational culture
1. observable artifacts
2. espoused values
3. basic assumptions
14
New cards
observable artifacts
\-physical manifestations of culture
* most visible level
* manner of dress, awards, myths, and stories about the company, rituals and ceremonies, decorations, as well as visible behavior
* most visible level
* manner of dress, awards, myths, and stories about the company, rituals and ceremonies, decorations, as well as visible behavior
15
New cards
espoused values
\-explicitly stated values and norms
* explicitly stated values and norms preferred by an organization, as may be put forth by the firm’s founder or top managers
* explicitly stated values and norms preferred by an organization, as may be put forth by the firm’s founder or top managers
16
New cards
basic assumptions
\-core values of the organization
* unobservable
* represent the core values of an organization’s culture-- those are taken for granted and, as a result, are difficult to change.
* unobservable
* represent the core values of an organization’s culture-- those are taken for granted and, as a result, are difficult to change.
17
New cards
four types of organizational culture
\-clan
\-hierarchy
\-market
\-adhocracy
\-hierarchy
\-market
\-adhocracy
18
New cards
clan culture
\-internal focus
\-values flexibility over stability
\-collaboration among employees
\-family-like, a strong sense of community
\-values flexibility over stability
\-collaboration among employees
\-family-like, a strong sense of community
19
New cards
adhocracy culture
\-external focus
\-values flexibility
\-adaptable, creative, and quick to respond to changes in the marketplace
\-values flexibility
\-adaptable, creative, and quick to respond to changes in the marketplace
20
New cards
market culture
\-focused on the external environment
\-values stability and control
\-driven by competition and a strong desire to deliver results
\-values stability and control
\-driven by competition and a strong desire to deliver results
21
New cards
hierarchy culture
\-has an internal focus
\-values stability and control over flexibility
\-formalized, structured work environment
\-at extreme: may seem like company values efficiency more than it does its people
\-values stability and control over flexibility
\-formalized, structured work environment
\-at extreme: may seem like company values efficiency more than it does its people
22
New cards
how do employees learn culture in an organization?
\-symbols
\-stories
\-heroes
\-rites and rituals
\-organizational socialization
\-stories
\-heroes
\-rites and rituals
\-organizational socialization
23
New cards
symbol
an object, act, quality, or event that conveys meaning to others
24
New cards
story
narrative based on true events, which is repeated--and sometimes embellished upon-- to emphasize a particular value
25
New cards
hero
person whose accomplishments embody the values of the organization
26
New cards
rites and rituals
activities and ceremonies, planned and unplanned, that celebrate important occasion and accomplishments in an organization’s life
27
New cards
organizational socialization
the process by which people learn the values, norms, and required behaviors that permit them to participate as members of an organization
28
New cards
division of labor
arrangement of having discrete parts of a task done by different people. the work is divided into particular tasks assigned to particular workers
29
New cards
unity of command
principle that stresses an employee should report to no more than one manager in order to avoid conflicting priorities and demands
30
New cards
span of control
the number of people reporting directly to a given manager
\-wide and narrow
\-wide and narrow
31
New cards
wide span of control
manager has several people reporting
32
New cards
narrow span of control
manager has a limited number of people reporting
33
New cards
authority
the right to perform or command; also, the rights inherent in a managerial position to make decisions, give orders, and utilize resources
* with authority comes: accountability, responsibility, and ability to delegate one’s authority
* with authority comes: accountability, responsibility, and ability to delegate one’s authority
34
New cards
accountability
describes expectation that managers must report and justify work results to the the managers above them
35
New cards
responsibility
the obligation one has to perform the assigned tasks
36
New cards
delegation
process of assigning managerial authority and responsibility to managers and employees lower in the hierarchy
37
New cards
centralization
organizational structure in which important decisions are made by upper managers--power is concentrated at the top
38
New cards
advantages of centralization
\-there is less duplication of work because fewer employees perform the same task; rather, the task is often performed by a department of specialists
39
New cards
decentralization
organizational structure in which important decisions are made by middle-level and supervisory-level managers--power is delegated throughout the organization
40
New cards
advantages of decentralization
\-managers are encouraged to solve their own problems rather than escalate the decision to a higher level of management
\-decisions are made more quickly, which increases the organization’s flexibility and efficiency
\-decisions are made more quickly, which increases the organization’s flexibility and efficiency
41
New cards
traditional organizational designs:
\-simple
\-functional
\-division
\-matrix
\-functional
\-division
\-matrix
42
New cards
simple structure
authority is centralized to a single person
\-found in very early stages of an organization
\-found in very early stages of an organization
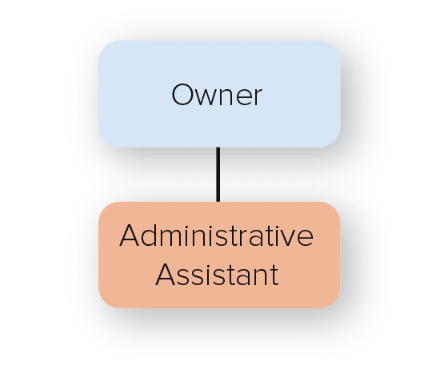
43
New cards
functional structure
people with similar occupational specialties are put together in formal groups
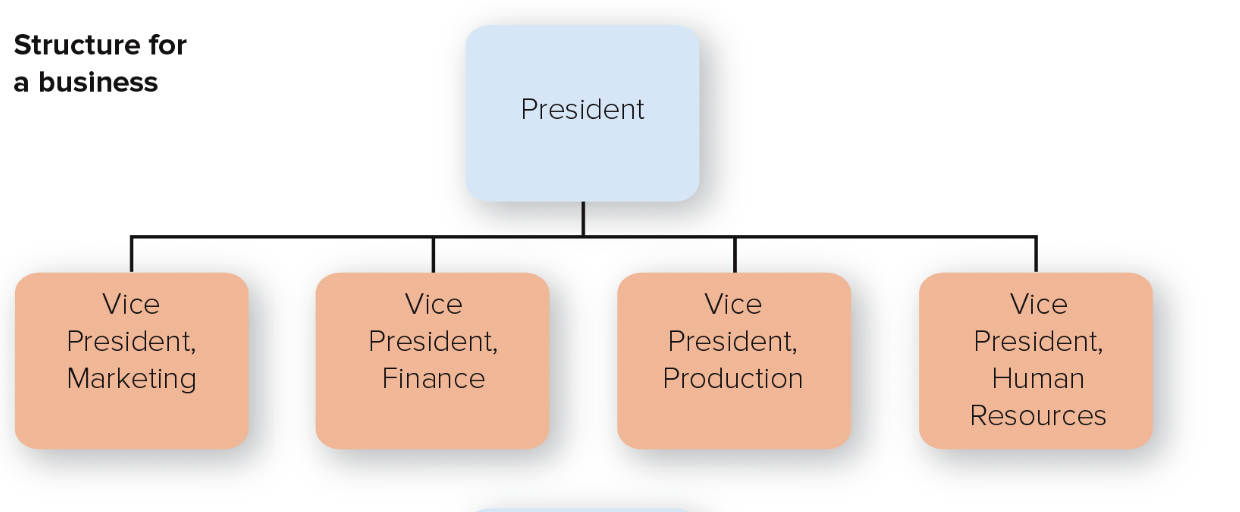
44
New cards
divisional structure
people with diverse occupational specialties are put together in formal groups according to products and/or services, customers and/or clients, or geographic regions
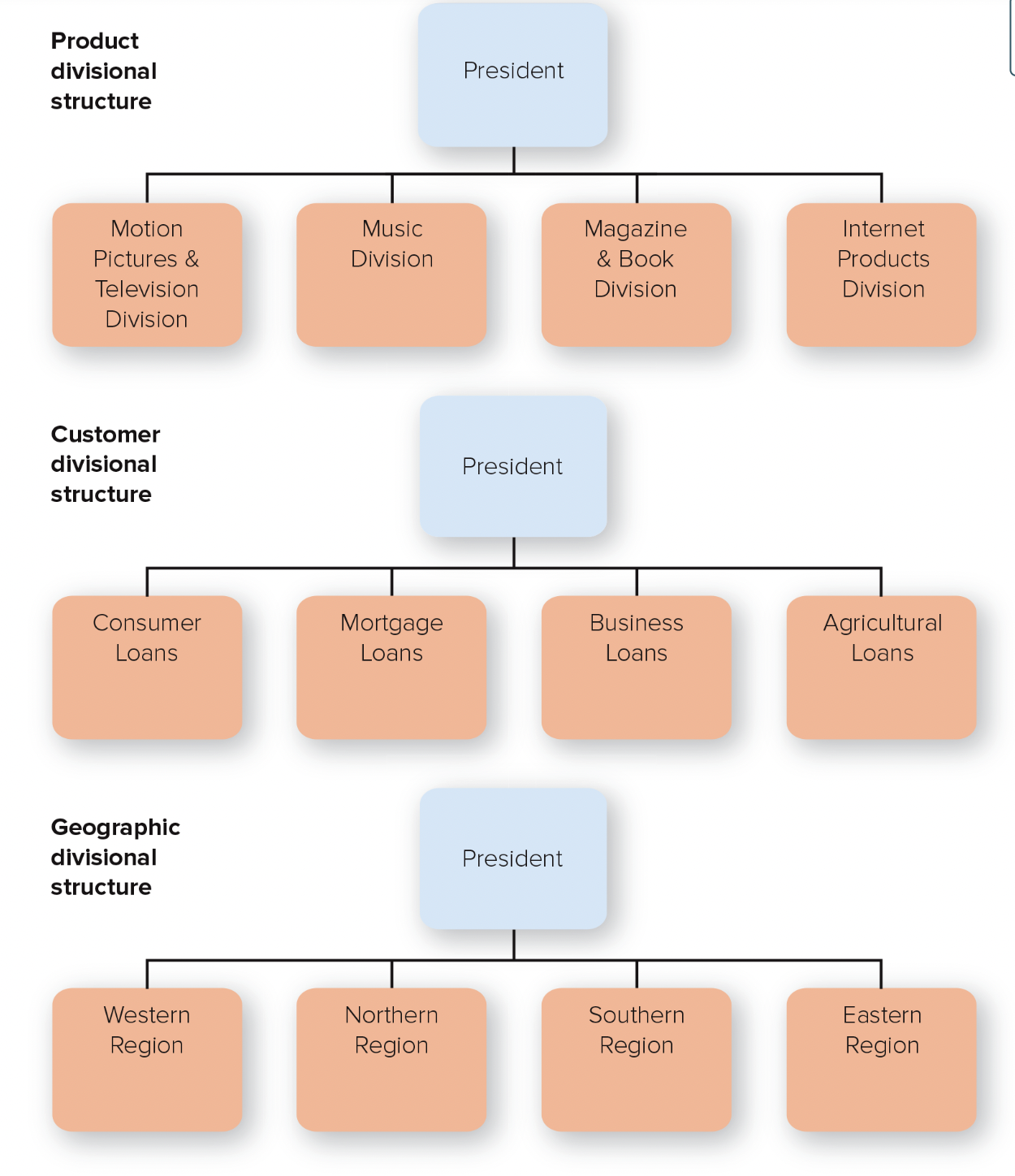
45
New cards
matrix structure
combines functional and divisional chains of command in a grid so that there are two command structures--vertical and horizontal
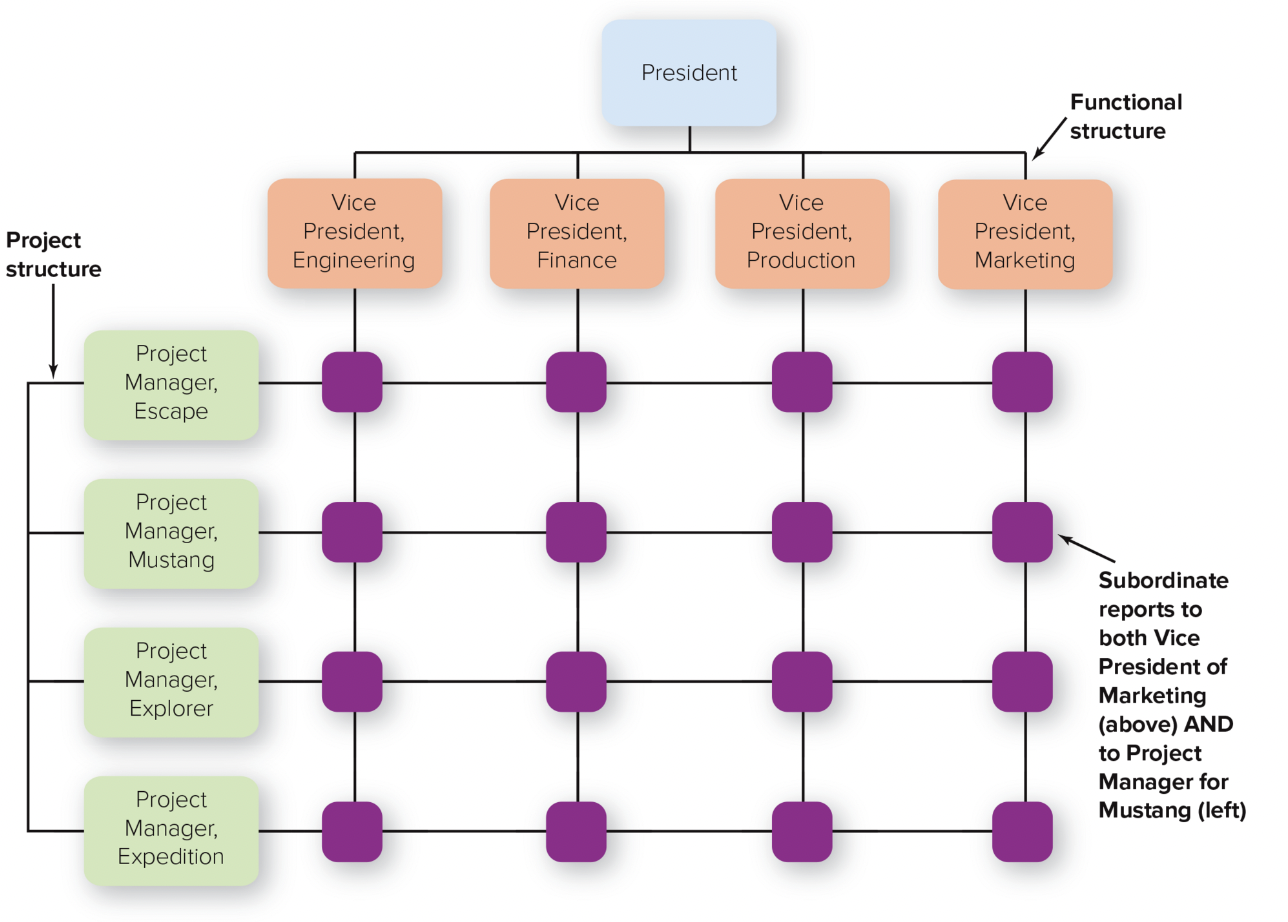
46
New cards
horizontal structure
teams or workgroups, either temporary or permanent, are used to improve collaboration and work on shared tasks by breaking down internal boundaries
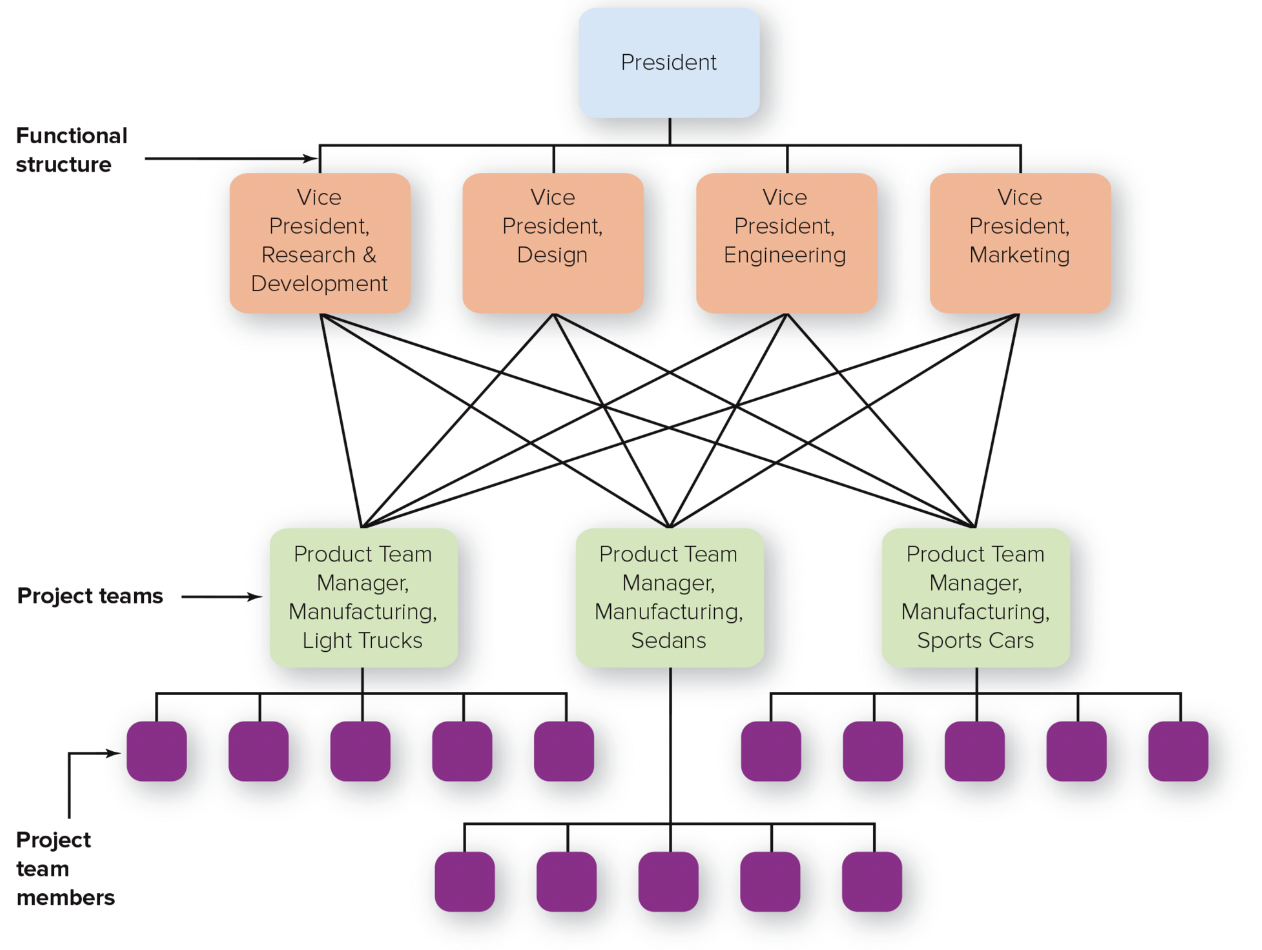
47
New cards
open boundary organizational designs:
\-hollow structure
\-modular structure
\-virtual structure
\-modular structure
\-virtual structure
48
New cards
hollow structure
structure in which the organization has a central core of key functions and outsources other functions who can do them cheaper or faster
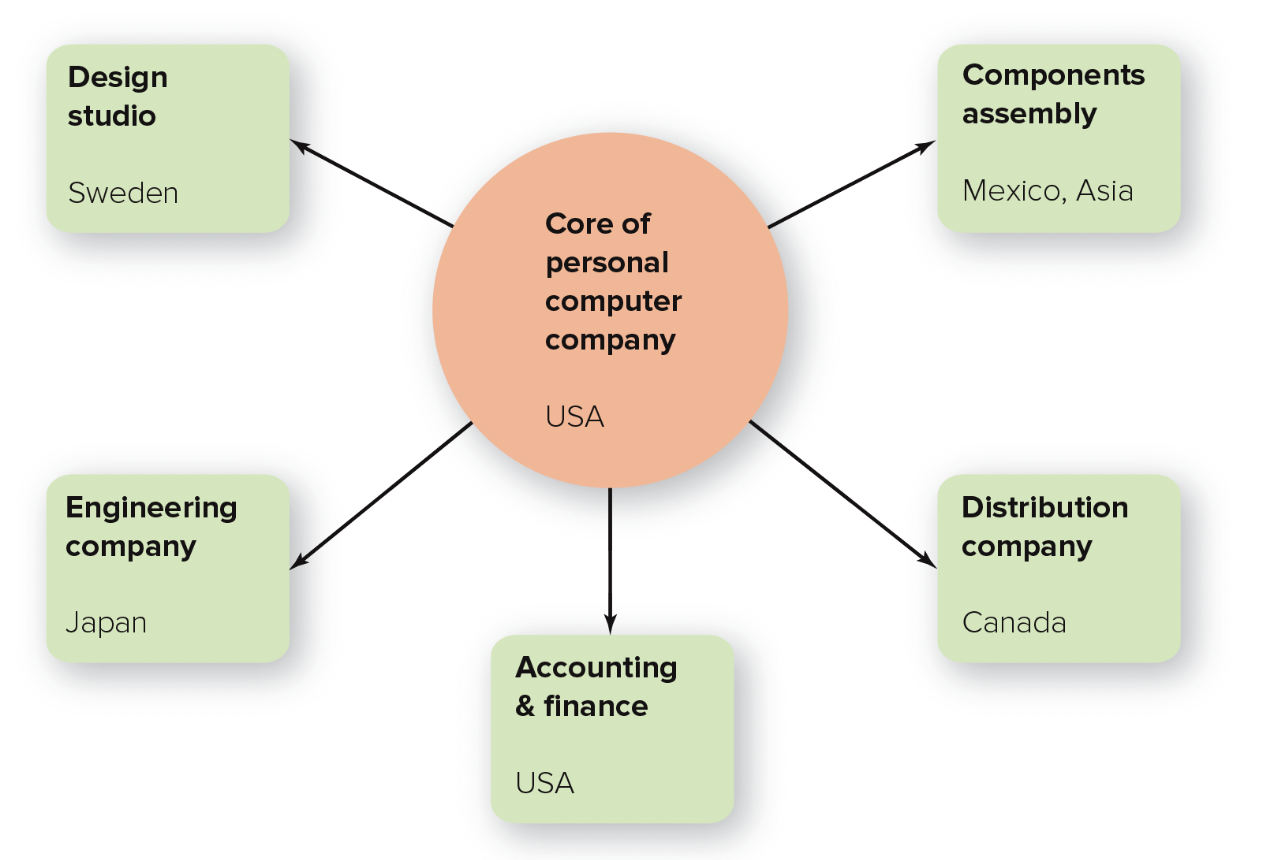
49
New cards
modular structure
a firm assembles product chunks, or modules, provided by outside contractors
50
New cards
virtual structure
an organization whose members are geographically apart, usually working with e-mail, collaborative computing, and other computer connections
51
New cards
6 sources of power
\-legitimate
\-reward
\-coercive
\-expert
\-referent
\-informational
\-reward
\-coercive
\-expert
\-referent
\-informational
52
New cards
legitimate power
power that results from managers’ formal positions within the organization
\-power given; can be taken away
\-power given; can be taken away
53
New cards
reward power
power that results from a manager’s authority to reward their subordinates
\-power given; can be taken away
\-power given; can be taken away
54
New cards
coercive power
results from manager’s authority to punish their subordinates
\-power given; can be taken away
\-power given; can be taken away
55
New cards
expert power
power resulting from one’s specialized information or expertises
\-power comes from person; cannot be taken away
\-power comes from person; cannot be taken away
56
New cards
referent power
power deriving from one’s personal attraction (strong, visionary)
\-power comes from person; cannot be taken away
\-power comes from person; cannot be taken away
57
New cards
informational power
power deriving from one’s access to information
58
New cards
transactional leadership
leadership style that focuses on clarifying employees’ roles and task requirements and providing rewards and punishments contingent on performance
59
New cards
transformational leadership
leadership style that transforms employees to pursue organizational goals over self-interests
\-influenced by 2 factors: individual characteristics and organizational culture
\-influenced by 2 factors: individual characteristics and organizational culture
60
New cards
servant leadership
focuses on providing increased service to others--meeting the goals of both followers and the organization--rather than to yourself
61
New cards
four steps of the control process
1. establish standards
2. measure performance
3. compare performance to standards
4. take corrective action
62
New cards
three types of control
1. feedforward
2. concurrent
3. feedback
63
New cards
feedforward control
\-focuses on preventing future problems
\-collects information about past performance in order to establish new standards→ plans then made to avoid pitfalls prior to starting a task
\-collects information about past performance in order to establish new standards→ plans then made to avoid pitfalls prior to starting a task
64
New cards
concurrent control
\-entails collecting performance information in real-time
\-enables managers to measure performance and determine if employee behavior and organizational processes conform to regulations and standards
\-technology is typically used
\-enables managers to measure performance and determine if employee behavior and organizational processes conform to regulations and standards
\-technology is typically used
65
New cards
feedback control
\-collecting performance information after a task or project is done
\-this information is used to correct or improve future performance
\-this information is used to correct or improve future performance
66
New cards
what are the 2 core principals of total quality management (TQM)
1. people orientation
2. improvement orientation
67
New cards
people orientation (TQM)
everyone involved with the organization should focus on delivering value to customers
68
New cards
improvement orientation (TQM)
everyone should work on continuously improving the work processes
69
New cards
budget
\-formal financial projection
\-states an organization’s planned activities for a given period of time in quantitative terms
\-states an organization’s planned activities for a given period of time in quantitative terms
70
New cards
balance sheet
a summary of an organization’s overall financial worth--assets and liabilities--at a specific point in time
71
New cards
income statement
summary of an organization’s financial results--revenue and expenses--over a specified period of time