skin, hair and nails
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Largest organ system
the skin
covers 20 square ft or surface area in adults
protectant
skin function
skin is waterproof, protective, and adaptive
protect form environment
bacteria and viruses that are in the area
prevents penetration of microorganisms
keeps electrolytes in the body
prevent electrolyte loss
perception
sensory organ with sensory receptors
feel what’s around us
temp regulation
through sweat glands for heat loss or dilation or cold
Subcutaneous insulation that holds heat
identification
facial features
communication
expression
show emotional state, through blushing or frowning
wound repair
cell replacement
absorption and excretion
excrete things to perspiration
produce vitamin D
layers of the skin
epidermis
dermis
subcutaneous
epidermis
the outer highly differentiated (Has a specific purpose) layer
basal cell layer (inner layer)
forms new skin cells
contains the protein keratin and melanin
keratin: main part and is fibrous and tough
Melanocytes- derivation of skin color
outer horny cell layer of dead keratinized cells (outer layer)
replaced every 4 weeks
Dermis
inner supportive layer
connective tissue (collagen)
thick and fibrous
allows the skin to stretch and by protective
elastic tissue
sebaceous glands, sweat glands, hair follicles
nerves
sensory receptors
blood vessels
lymphatics
richly supplied with blood and vasculature
subcutaneous
adipose tissue
fat cells
stores fat
provides temp control
adds cushioning
normal skin pigments
melanin
gives us brown pigment
genetically determined
color increase with sun exposure
carotene
yellow orange tone
found in the subcutaneous fat
vascular bed
gives us our red and purple tone
oxyhemoglobin
with oxygen
bright red pigmentation
in the arteries and capillaries
increase circulation cause red skin tone
decrease circulation you see pallor (pale)
deoxyhemoglobin
lacking o2
darker or bluer color
Increased concentration make skin look blueish
cyanosis
abnormal skin pigments
jaundice
yellow skin color
see in the sclera and that will extent to the iris, white part of the eye
also seen in the nails palms and soles
best to look in the hard palette of the mouth with a bright light
dark skin patients they might have a yellow sclera as a normal finding which is why you look at the hard palette
cyanosis
blueish skin
lack of oxygen
caused by advanced heart disease, heart disease, genetic disorders
might see in the lips or oral mucosa
also seen in the nails and feet
central lack of oxygen, lack of blood flow to the periphery due to cold or something else you also see cyanosis
hair
threads of keratin
color from melanin production
hair turns white due to lack of melanin
vellus hair
covers most of the body
no pigmented
terminal hair
dark thick hair on the scalp, brows, pubic area, axel area
nails
hard plates of keratin
underlying color = pink, is from the vascular cells
Sebaceous glands
sebum secretion
sebum is a fatty substance secreted through the hair follicles
job: lubricate the skin and hair, prevent water loss from the skin
found everywhere except the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet
Sweat glands
important for fluid balance and thermoregulation
eccrine glands
simple sweat gland
on skin surface
a dilute saline
controls body temp
apocrine glands
a type of sweat gland
most evident during puberty
thick milky secretion that that open up into the hair follicles in the axel and anogenital areas and the nipples
normal bacteria skin flora reacts with the apocrine sweat and that gives the musky odor
Physical examination Equipment needed
Strong direct lighting, gloves, penlight, and small centimeter ruler
Complete physical examination
Skin assessment integrated throughout examination
Separate intertriginous areas (areas with skinfolds) such as under large breasts, obese abdomen, and groin and inspect them thoroughly
These areas are dark, warm, and moist and provide perfect conditions for irritation or infection
Always inspect feet, toenails, and between toes
Regional Examination (focused exam)
Individuals may seek health care for skin problems and assessment focused on skin alone
Assess skin as one entity; getting overall impression helps reveal distribution patterns Inspect lesions carefully
With a rash, check all areas of body as you cannot rely on the history that rash is in only one location
Inspect
Color-Know baseline
General pigmentation, freckles, moles, birthmarks
Widespread color change or localized
Note color change over entire body skin, such as
pallor (pale)
erythema (red)
cyanosis (blue)
jaundice (yellow)
color changes: white (pallor)
Reflects anemia
lack of oxygen
seen in fearful or stressed out people
vasoconstriction
Exposure to cold can also lead to pallor
color changes: red (erythema)
fear, local inflammation, emotional reaction
cannot see inflammation in dark skin
must palpate to confirm inflation
color changes: Blue (cynosis)
due to decreased perfusion
not enough oxygen is getting through the blood.
seen on lips and nose
Dark skin Mediterranean people have natural blueish tone lips
color changes: Yellow/orange (jaundice)
Skin or the white part of the eyes looks yellow.
This happens when there's too much bilirubin (a waste from red blood cells).
It's normal in some newborns, but not in older kids or adults.
color changes: ethnic variations
Brown skin: pale skin (pallor) might look yellow-brown and less red.
Black skin: pale skin (pallor) might look gray or ashy.
Palpating skin
🌡 1. Temperature (Warm or Cold?)
Use the backs of the hands to feel someone’s skin.
Skin should feel warm and about the same on both sides.
Cool hands/feet are okay if the room is cold.
If skin feels cold:
Might mean hypothermia (too cold!)
Could be from ice packs or poor blood flow.
If skin feels hot:
Might mean hyperthermia (too hot!)
Caused by a fever, exercise, or an infection like a sunburn.
💦 2. Moisture (Dry or Sweaty?)
Diaphoresis means sweating a lot — like when you have a fever or you're running.
Dehydration means you're low on water.
Look at the mouth and lips — if they're dry, you might be dehydrated.
✋ 3. Texture (How Does the Skin Feel?)
Skin should be smooth and firm, like a nice clean table.
📏 4. Thickness (Thick or Thin?)
Skin should be thin all over, except it's thicker on the palms and soles of your feet. That’s normal!
🧊 5. Edema (Swelling)
Edema means there’s extra fluid under the skin, making it puffy or swollen.
Press on the skin to see if it leaves a dent. That’s a clue!
🪢 6. Mobility and Turgor (Bouncy or Stuck?)
Mobility is how easily the skin moves when you pinch it.
Turgor is how fast it snaps back when you let go.
If it stays "tented" (doesn’t bounce back), it could mean dehydration.
Edema
when too much fluid builds up in the spaces between your skin and your muscles. It makes the skin look swollen or puffy.
Localized Edema
Happens in just one spot, usually from an injury (like a sprained ankle).
Only one leg or one arm might be swollen.
Systemic Edema
Means the swelling is all over or in more than one place.
It often shows up in lower body parts like:
Feet
Legs
Back or bottom (sacral area) if lying down a lot
Skin can look shiny, feel tight, and feel like it’s full of water.
Pitting Edema
If you press your finger into the skin, it leaves a dent.
This means the fluid is moveable, like water in a water balloon.
Nonpitting Edema (Brawny Edema)
Pressing on the skin doesn’t leave a dent.
This happens because proteins have gotten stuck with the fluid and made it thick and sticky, like jelly.
What is Turgor?
is how quickly your skin bounces back after you pinch it.
It helps nurses see if someone might be dehydrated (missing water in the body).
How to Check Turgor
Pinch the skin just below the collarbone (that’s your clavicle).
The skin should snaps back quickly.
→ That means good turgor and enough water in the body.The skin stays up like a little tent.
→ That’s called tenting and means poor turgor — a sign of dehydration
What is a Lesion?
any spot, bump, sore, or change on the skin that’s not normal.
In a small area
Different from the skin around it
If a nurse sees a lesion, they check:
Pattern or shape
→ Are there a bunch together or just one?Size
→ Measured in centimeters (cm)Location
→ Is it in one place (local) or all over (generalized)?Color, smell, or fluid
→ Is it red, yellow, or has a smell? Is there ooze or pus?
Depth
→ Is it flat, raised, or on a stalk (called pedunculated) like a tiny mushroom?Blanching
→ They press the lesion to see if it turns white, which shows blood flow is moving underneath.
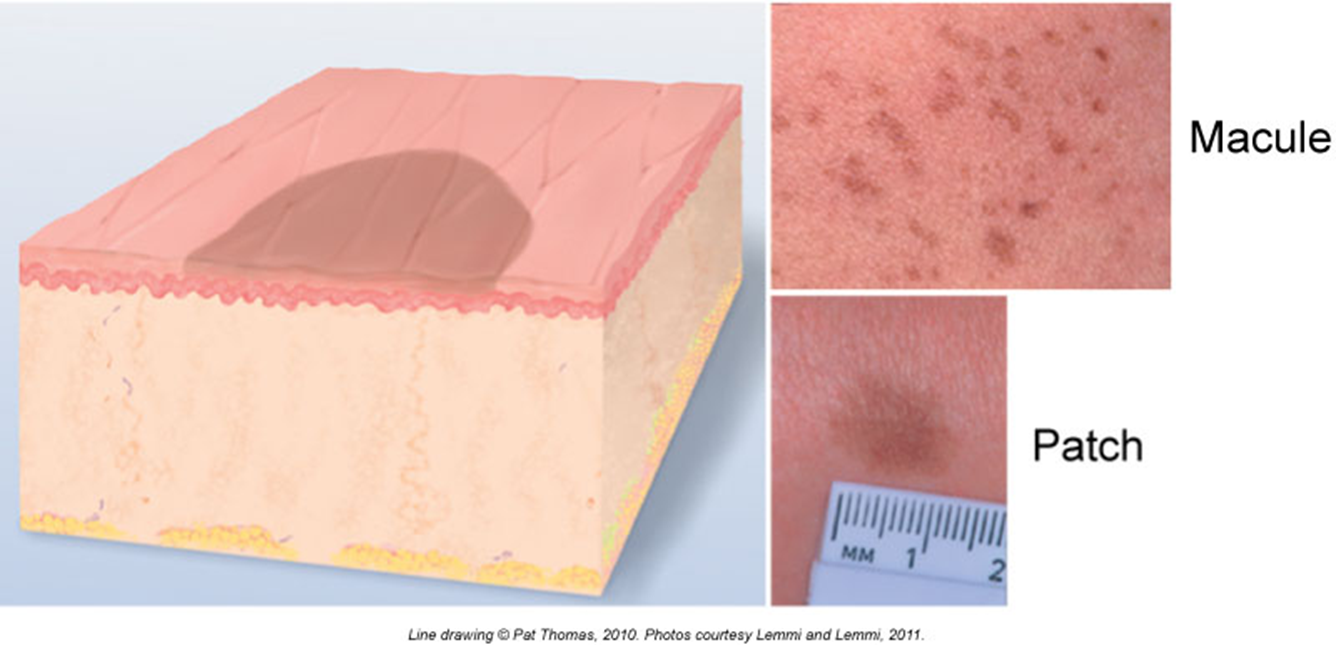
Macules & Patches
Macule = small, less than 1 cm
Examples: freckles, tiny red dots (petechiae)
Patch = bigger than 1 cm
Example: big flat birthmarks
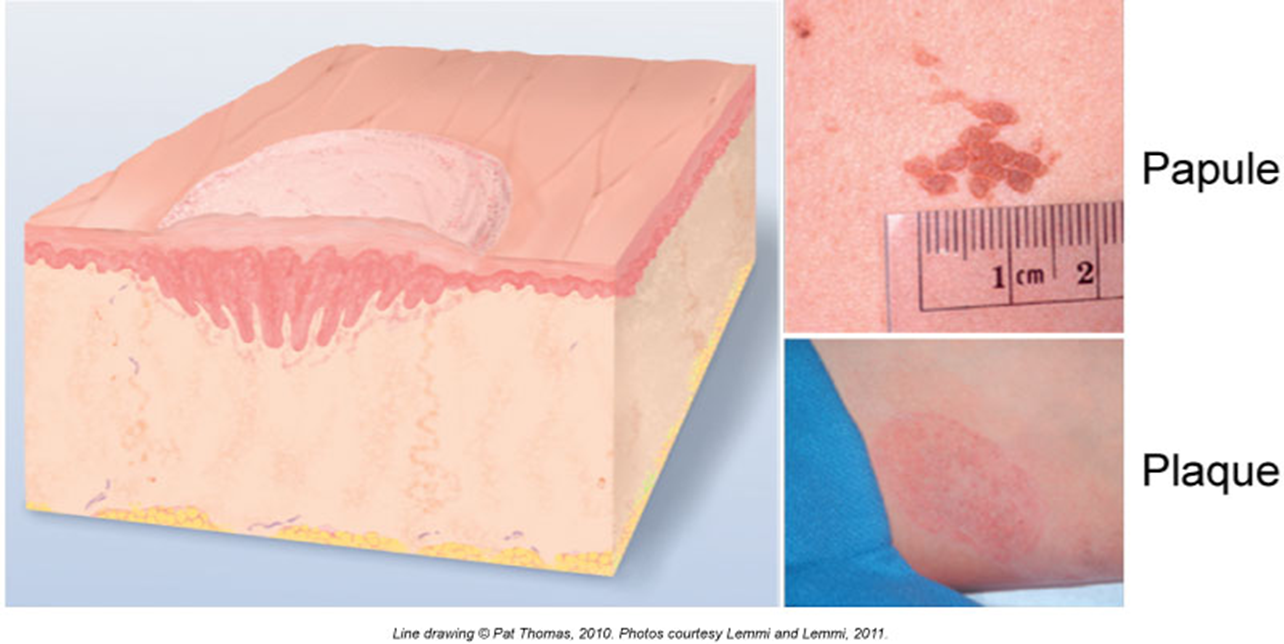
Papules & Plaques
You can feel these—raised spots!
Papule = small bump, under 1 cm
Example: wart, mole you can feel
Plaque = big flat bump, more than 1 cm
Example: psoriasis
Pustules
These are raised, filled with pus
Example: acne or pimples
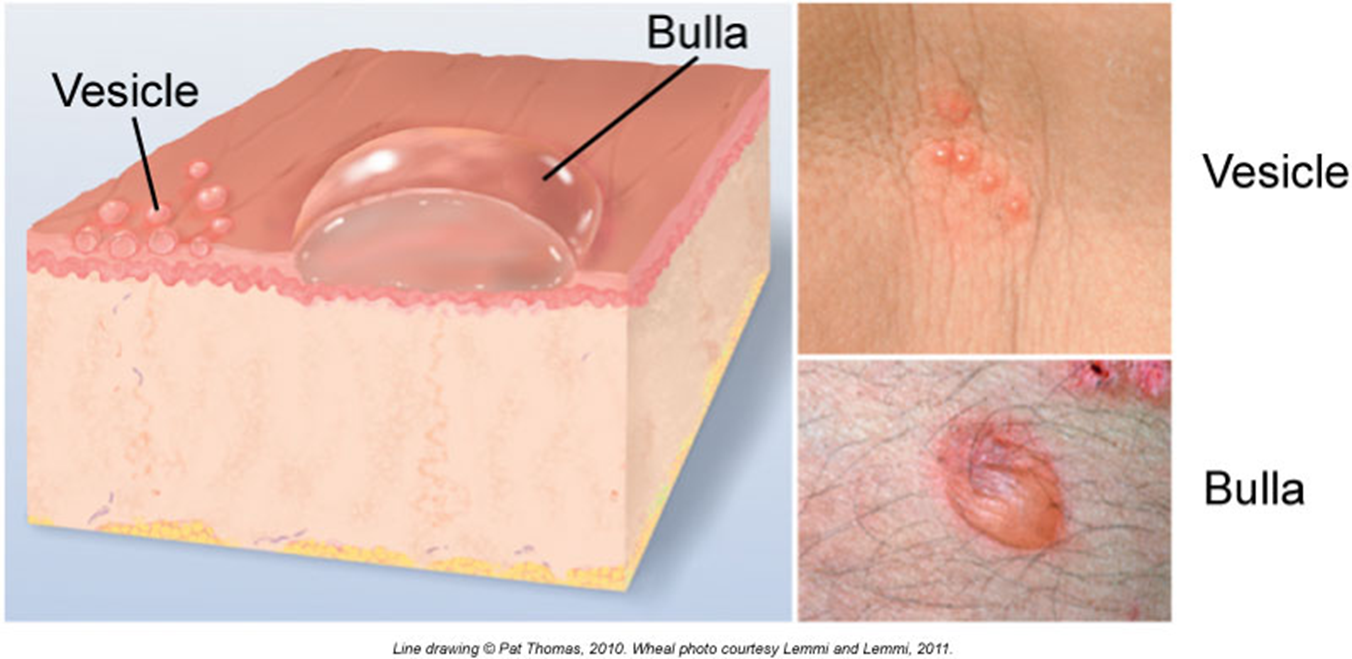
Vesicles & Bullae
These are bubbles filled with clear fluid (serous fluid)!
Vesicle = small (under 1 cm)
Example: chickenpox, cold sore
Bulla = big bubble
Example: blister from a burn
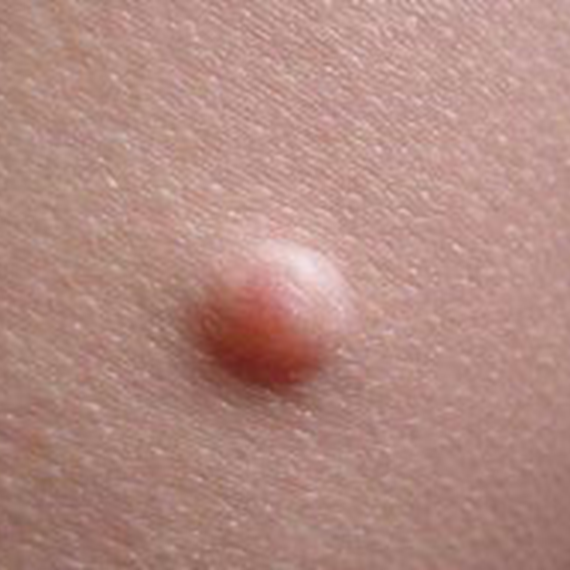
Nodules
These are solid, deep lumps
Bigger than 1 cm
Grow in the dermis or deeper
Example: deep wart, big mole
Urticaria/Wheal (Hives)
Raised, itchy bumps that come and go
From allergies, bug bites, or stress
Look like welts on the skin
Burrows
Tiny tunnels under the skin
Caused by mites, like in scabies
Might see tiny lines, papules, or pustules
Known as the “7-year itch” — because it itches a lot
Crusts
Dried-up blood, pus, or fluid
Like a scab after a scrape
May be yellow, brown, or red depending on what leaked out
Scales
Flaky skin pieces
Can be dry (like dandruff) or greasy
Look white or tan, and happen when skin is shedding keratin too fast
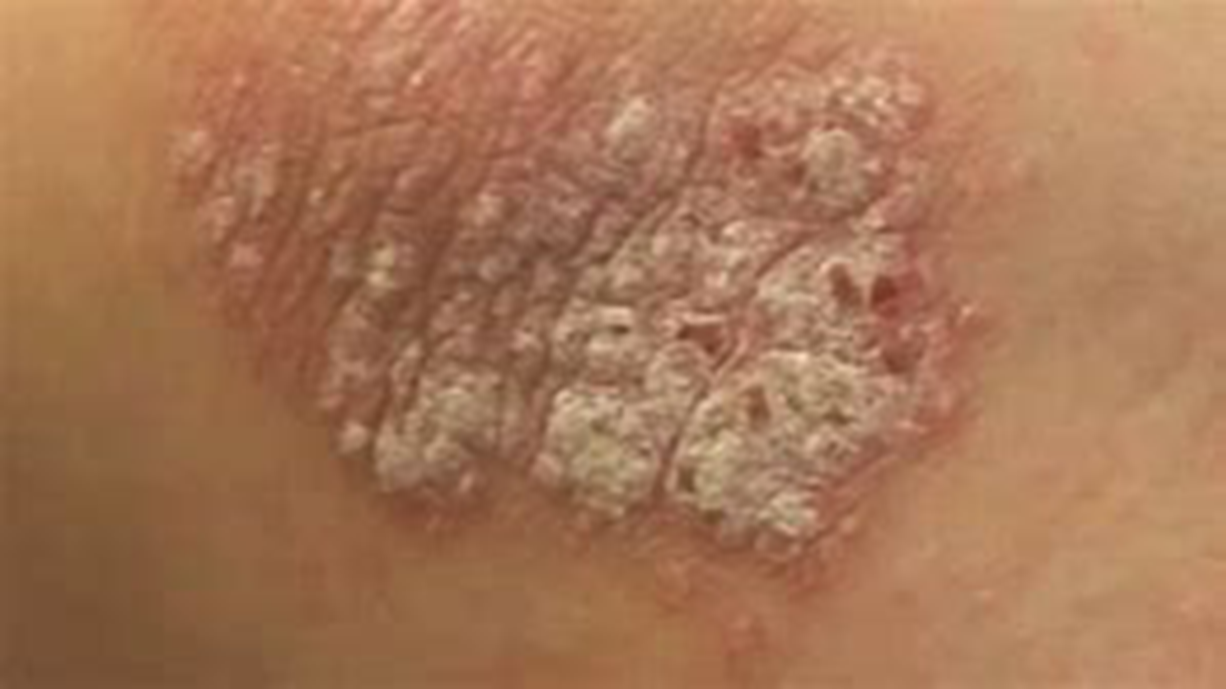
Lichenification
Skin becomes thick and rough
Happens when you scratch a lot
Feels like tree bark
eczema
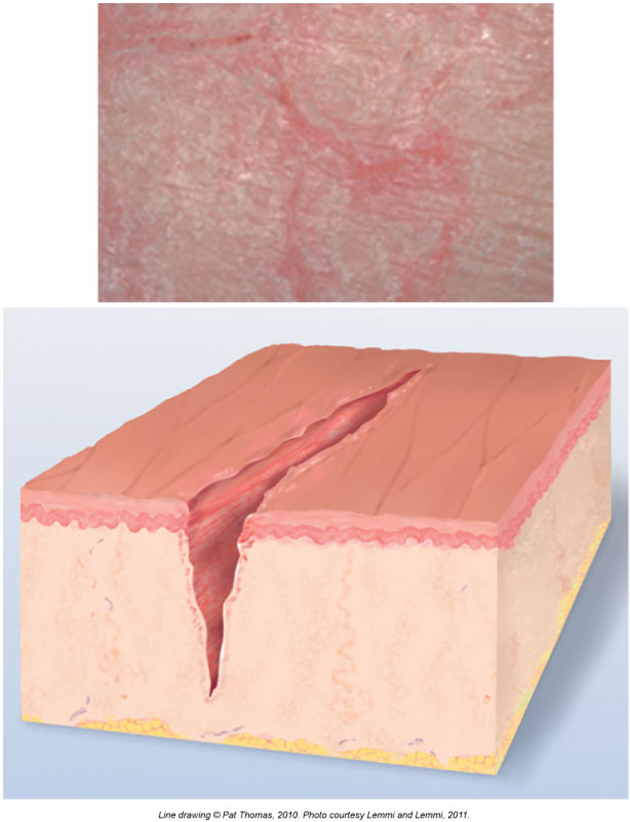
Fissures
A deep crack in the skin
Can be painful
Common in the corners of your mouth or heels
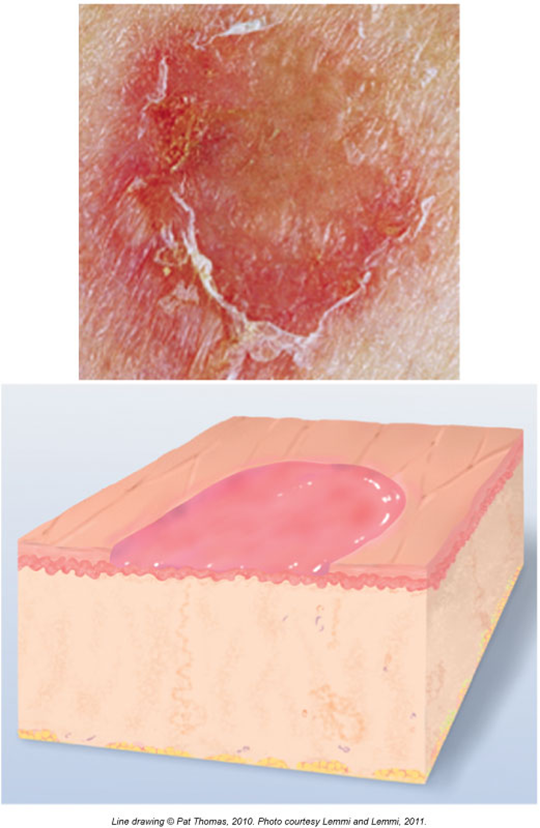
Erosions
A shallow scoop out of the top layer of skin
No scar left behind
Looks wet and shiny
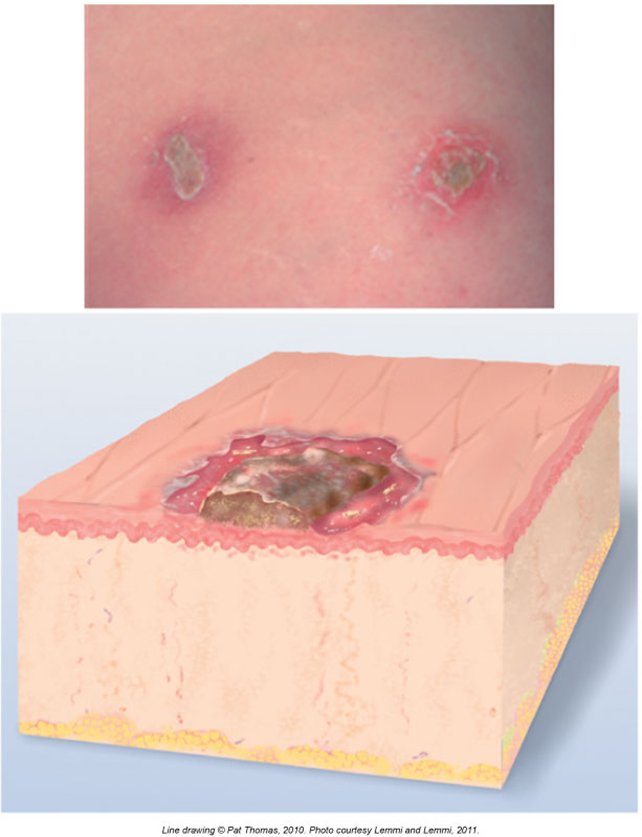
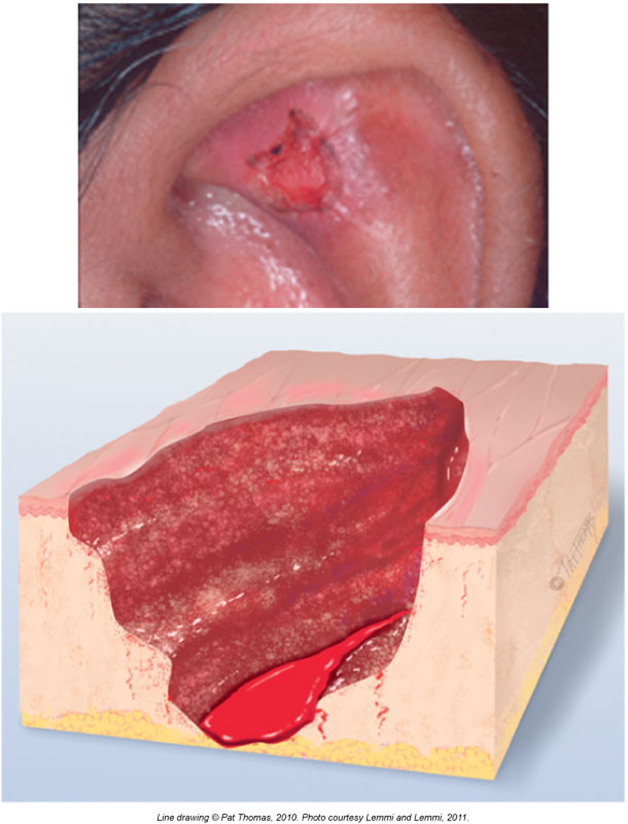
Ulcers
Deeper wound than an erosion
Goes down into the dermis (middle skin layer)
Leaves a scar
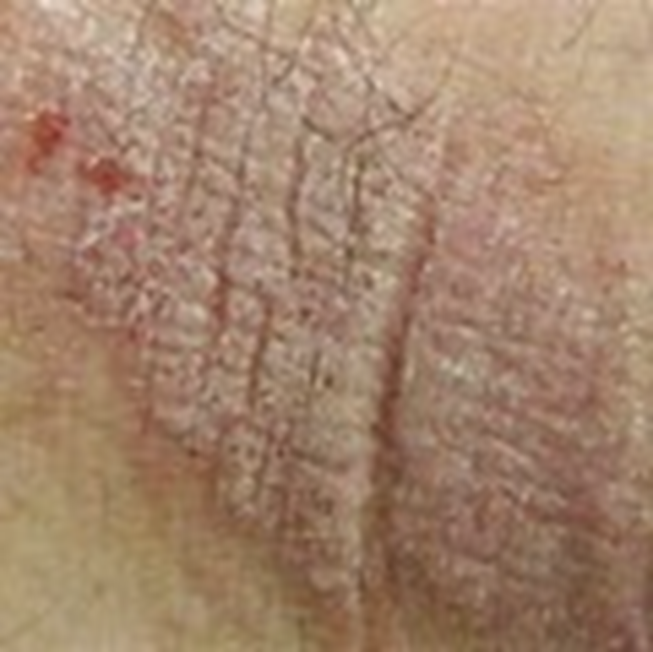
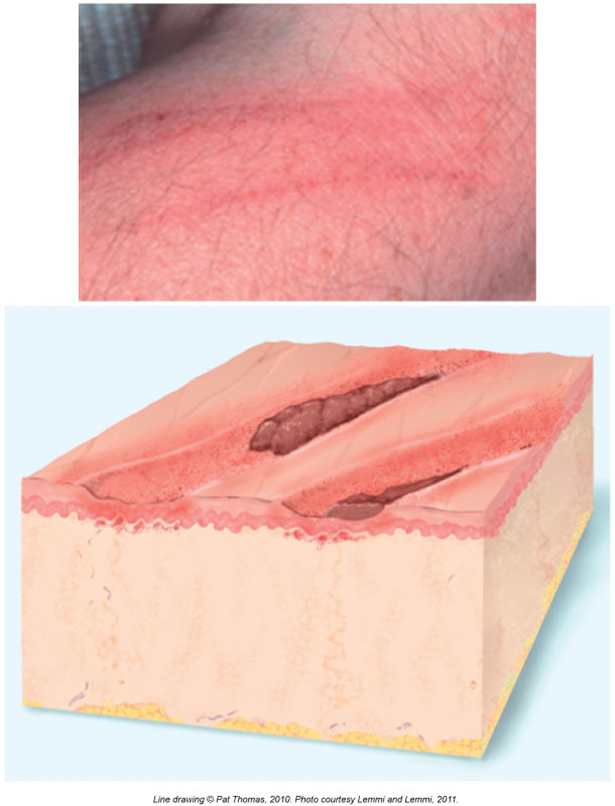
Excoriations
Scratches from fingernails or rubbing
Usually superficial (top layer only)
Can have some crust from dried fluid
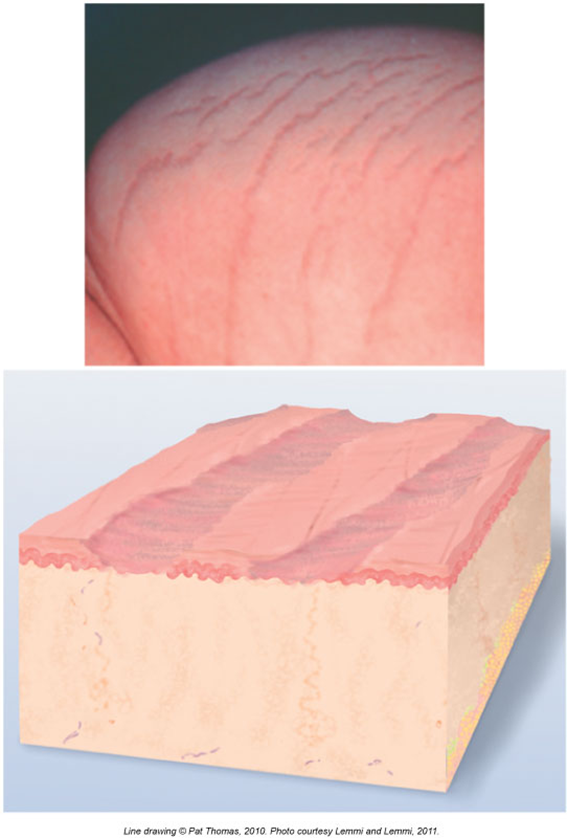
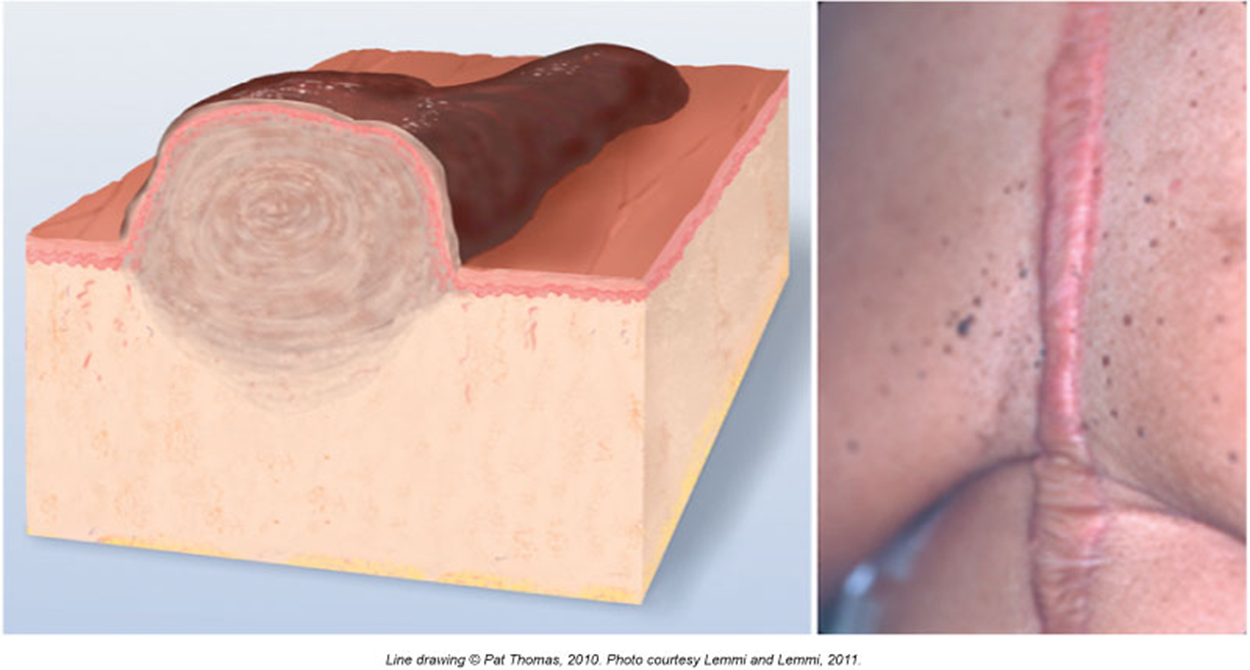
Atrophic Scar
Skin looks sunken or stretched, like in stretch marks (striae)
Happens when your body doesn’t make enough collagen (the stuff that heals skin)
Keloid
A big, puffy scar
Grows past the original injury
Looks smooth and shiny
Happens when the body makes too much scar tissue
Vascular Lesions
spider angioma
telangiectasia (spider viens)
cherry angioma
Spider Angioma
Looks like a red dot in the middle with thin red lines coming out—like a spider!
May appear on the face, neck, or arms
Common in pregnancy or with high estrogen
Blanches (turns white) when you press on it
Rarely found below the waist
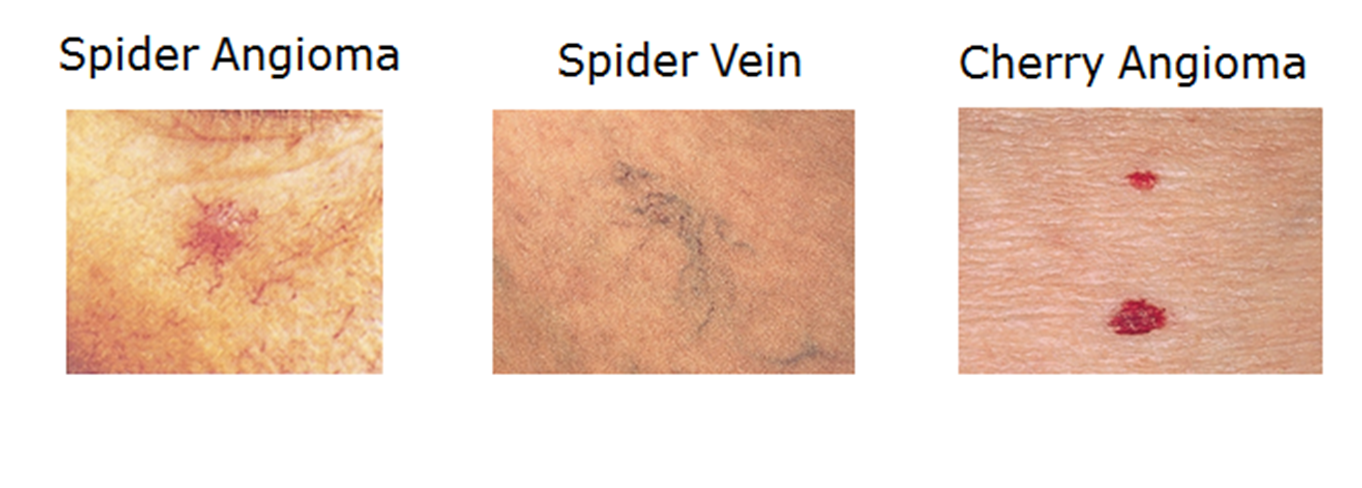
Telangiectasia (Spider Veins)
Looks like blue or purple squiggly lines
Found on the legs or chest
Does not pulse and does not blanch
Common with aging or vein issues

Cherry Angioma
Bright red or dark red bump
Can be flat or raised
Tiny! (About 1–3 mm)
Found mostly on the trunk (chest, back, belly)
May blanch when pressed
More common with age, and they grow over time

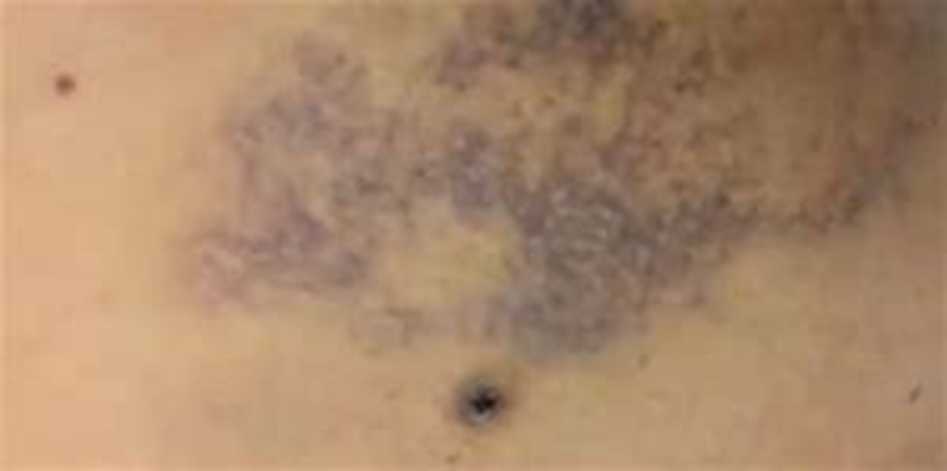
Purpuric Lesions
petechaie
purpura
🚫 Blanching Reminder
Neither petechiae nor purpura turn white when pressed — this helps nurses tell them apart from other red spots like spider angiomas!
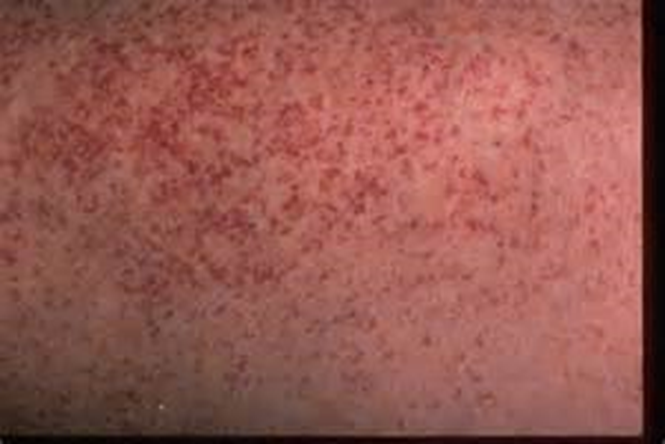
Petechiae (say: peh-tee-kee-eye)
Tiny red, purple, or brown dots
About the size of a pinhead (1–3 mm)
Happen when tiny blood vessels break under the skin
Causes:
Hard coughing or vomiting
Injections (shots)
Some medications
Found on arms, legs, chest, or belly
Can be hard to see on dark skin, so nurses check the abdomen
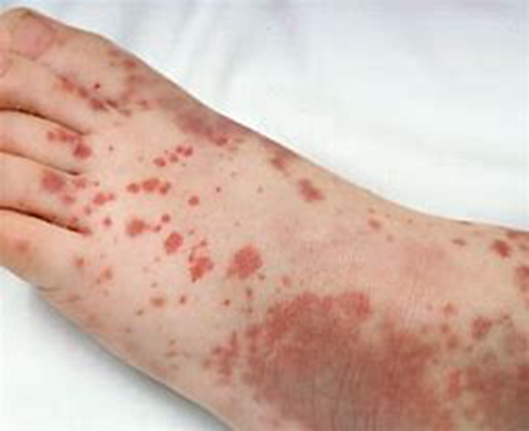
Purpura (say: per-pyoo-rah)
Bigger patches of bleeding under the skin — larger than 3 mm
Can look like a big bruise or like lots of petechiae stuck together
Can be a sign of a serious bleeding problem
Found anywhere on the body
Ecchymosis (say: ek-i-mo-sis)
Bigger than 3 mm
Flat on the skin
Color can change over time:
Starts red or purple
Then turns blue, green, yellow, and finally brown before fading
Usually takes 1 to 3 weeks to go away
Cause: Blood leaks under the skin after:
Bumping into something
Injury
Medical conditions or blood thinners
❌ Important Clue:
Does not blanch (turn white) when you press on it
That’s because the blood is trapped under the skin, not flowing
Lesions from Trauma or Abuse
📏 1. Pattern Injury
A mark that matches the shape of the object that caused it
Example: belt marks, burns from a cigarette, or handprints
These patterns help health workers figure out how someone got hurt
May be a sign of abuse
🩸 2. Hematoma
A swollen lump under the skin filled with trapped blood
Feels like a raised bruise
Often happens from a hit or fall
May feel tender or painful
🟣 3. Contusion (Bruise)
Flat, discolored spot caused by bleeding under the skin
Changes color over time (like ecchymosis)
You can have a contusion even without breaking the skin
Can be caused by accidental bumps or intentional harm
How Nurses Check Lesions (Skin Spots or Bumps)
🎨 1. Color
What color is it?
Red that turns white when pressed = inflammation (like swelling or irritation)
📍 2. Location
Where is it on the body?
Is it on open skin or in a skin fold (like under the arm or breast)?
📏 3. Size
Measured using a ruler in millimeters (mm) or centimeters (cm)
🔼 4. Elevation
Is it flat, raised, or bumpy?
🔢 5. Number
How many are there?
Just one, a few, or lots?
🤲 6. Texture
Does it feel smooth, rough, or scaly?
🧴 7. Type of Lesion
Is it a pustule, macule, vesicle, ulcer, etc.?
(Nurses figure out what kind it is using everything above!)
🔷 8. Shape & Pattern
Is it round, star-shaped, line-shaped, or in a group?
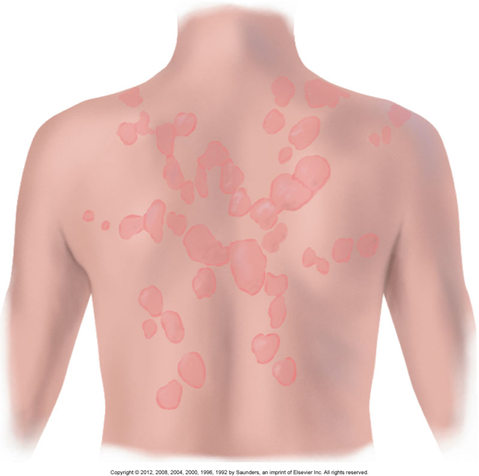
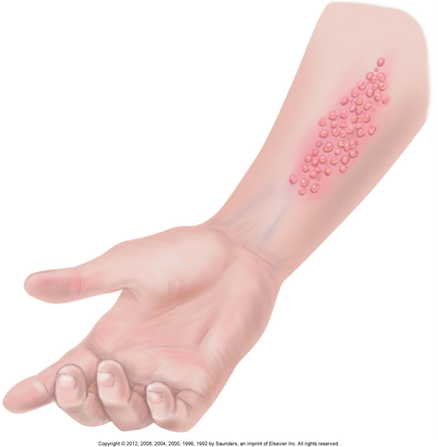
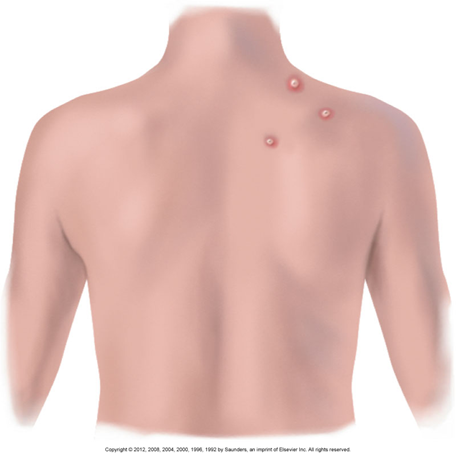
Lesion Shapes & Patterns
confluent
clustered
discrete
linear
zosteriform
target
circular
Confluent
Spots run (connected) together into one big area
Like a bunch of blobs melting into each other
Clustered
Grouped together in one area
Think of it like grapes on a stem or chickenpox
Discrete
Each lesion is separate and alone
Like polka dots — spaced out and not touching
Linear
Arranged in a line, like a scratch, cut, or streak
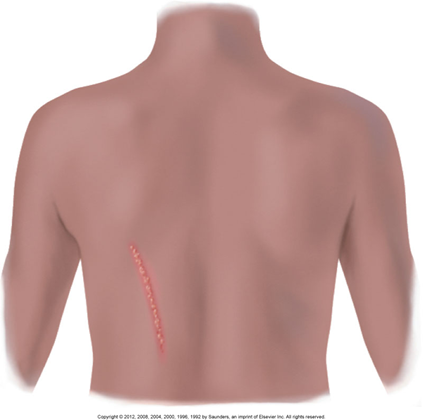
Zosteriform
Follows a nerve line, often on one side of the body
Common in shingles
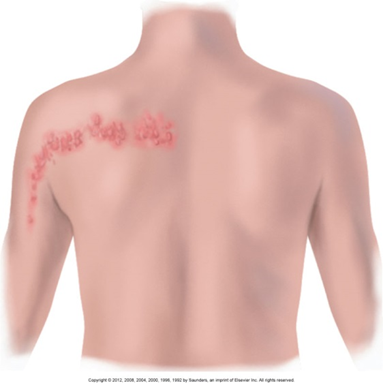
Target (or Bull’s Eye)
Looks like a circle with a dot in the middle
Seen in things like Lyme disease

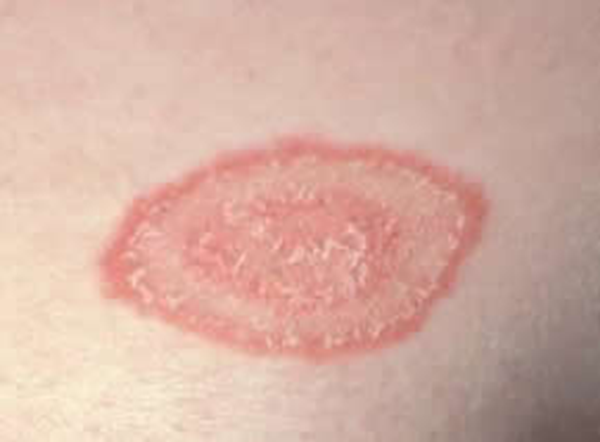
Circular
Round spot that starts in the middle and spreads out
Example: ringworm
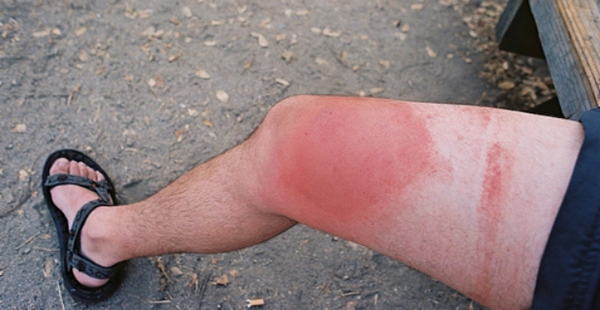
Bee Sting
Usually causes a red, swollen bump
It may be raised, warm, and itchy or painful
Often shows a central puncture mark (where the stinger went in)
Skin around it might look tight or shiny
🩹 This is a local reaction — your body is reacting to the bee venom!
Poison Ivy
Causes an itchy, red rash that often looks linear (in lines or streaks)
May have blisters or fluid-filled bumps
Usually appears where the plant touched the skin
🧪 The rash is caused by urushiol oil from the plant — it’s an allergic reaction!
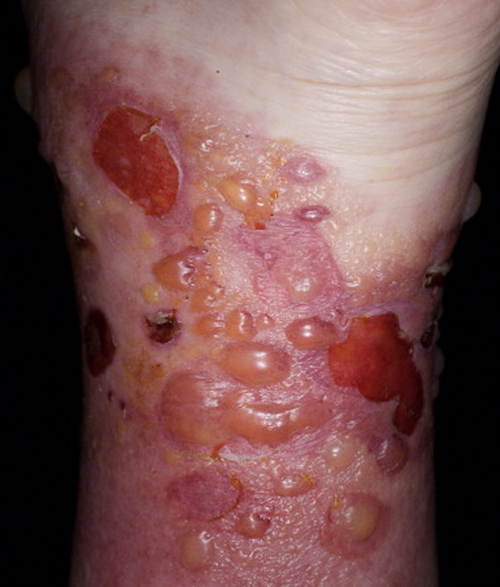
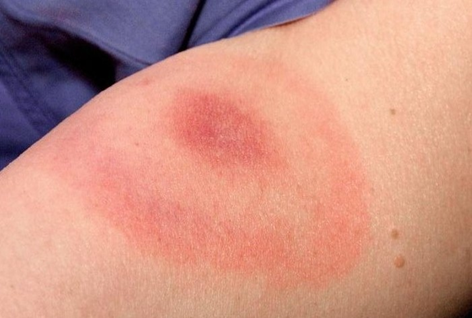
Lyme Disease
Early sign: a bull's-eye rash (called a target lesion)
Red outer ring with clearer center and maybe a dot in the middle
Caused by a tick bite
Rash can get larger over days (not usually itchy or painful)
🦠 This rash shows a possible infection from the bacteria that causes Lyme disease — it needs medical attention!
Inspection Hair
Color
Is the hair natural, dyed, or patchy in color?
Texture
Is the hair:
Fine (thin) or thick
Straight, curly, or kinky (tight coils)
Does it look shiny and healthy or dry and dull?
Distribution
Is the hair growing evenly or are there bald spots?
Is there hair in places where it normally should be, like on the head, eyebrows, arms?
Lesions (Problems on the scalp)
Are there any lice (tiny bugs)?
Is there dandruff (flaky skin)?
Any sores or bumps?
Abnormal Hair & Scalp Conditions
tinea capitis
alopecia areata
trichotillomania
pediculosis capitis
pseudofolliculitis
hirsutism
Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm)
A fungal infection (not a real worm!)
Causes scaly, round patches and hair loss
Very contagious — can spread from person to person
Looks like ring-shaped bald spots
Alopecia Areata
A condition where hair suddenly falls out
Leaves round bald spots
The scalp looks healthy — just no hair in those areas
Trichotillomania
Hair loss from pulling it out
Usually done by the person themselves (a habit or stress reaction)
The bald spots often look uneven or broken
Pediculosis Capitis (Head Lice)
Tiny bugs (lice) live in the hair and lay eggs (nits)
Cause itching and red bumps on the scalp
You might see tiny white nits stuck to hair strands
Pseudofolliculitis
Also called razor bumps
Happens when hairs curl back into the skin after shaving
Can cause red bumps and ingrown hairs
Hirsutism
When females grow too much body or facial hair (like a beard or chest hair)
Often caused by a hormone or metabolic problem
Nail Assessment
👀 1. Shape & Contour
Look at your index finger from the side (this is called the profile sign)
The angle between your nail and finger should be about 160 degrees (like a smooth hill)
If it’s curved too much or rounded, it could be a sign of health problems (like clubbing)
✨ 2. Consistency
Healthy nails should feel smooth and firm
Not brittle, split, or peeling
Problems here could mean issues like nutrient deficiency or fungal infections
🎨 3. Color
Nails should be pink underneath (that’s your nail bed)
If they look blue, white, or yellow, something might be wrong
Could be a problem with oxygen, liver, or blood flow
💓 4. Capillary Refill Test
This checks how well blood flows to your fingers:
Press on the nail until it turns white
Let go
The pink color should come back right away (within 1–2 seconds)
If it takes longer, it might mean poor circulation (blood isn't flowing well)
Paronychia
The most common nail infection
Happens when germs (like staph or strep bacteria) get into the skin around the nail
Caused by:
Nail biting
Rough manicures
Picking at your nails
The skin near the nail gets:
Red
Swollen
Tender or painful
Sometimes filled with pus
🧴 This needs to be kept clean and may need treatment if it gets worse!
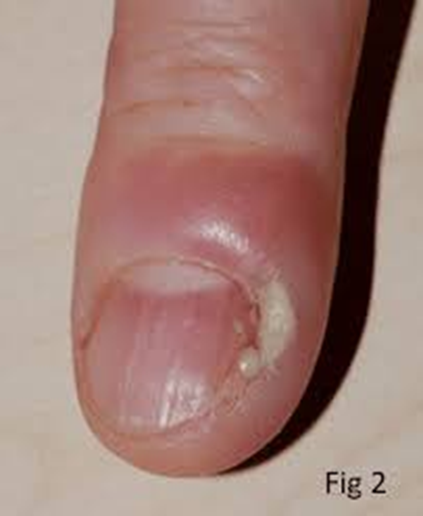
Leukonychia
Just a white spot on your nail
Caused by minor trauma, like:
Hitting your nail
Biting your nails
It’s not dangerous and goes away as your nail grows out
Clubbing (of the Nails and Fingers)
The angle where your nail meets your skin becomes more than 180°
(Normal is around 160°)Fingertips look rounder, bulging, or like they are floating
The nails curve downward and feel soft or spongy
How Nurses Check It:
Put both index fingers together like in the bottom right image.
If you can see a little diamond-shaped window, it’s normal.
If the window is gone (no gap), that’s a sign of clubbing.
What Causes Clubbing?
Low oxygen in the blood over a long time
Diseases like:
Lung disease (like COPD or cancer)
Heart disease
Liver or digestive disorders
Sometimes even aging
Abnormal Nail Signs Nurses Look For
📉 Beau’s Lines
🕳 Pitting
📉 Beau’s Lines
These are white, deep grooves or lines that go side to side across the nail
They look like someone pressed a dent into the nail
Caused by big body stress like:
Severe illness
Malnutrition (not enough healthy food)
Heart problems
Injury or trauma
They show that nail growth stopped for a while while the body was healing
📅 They can help tell when the illness happened — the further out the line, the longer ago it was
Pitting
Looks like tiny holes or dots in the nail surface
Like someone poked the nail with a pin
Most often caused by psoriasis, a skin condition
Can also happen with other autoimmune or skin diseases
Pressure Injuries (Bedsores) Happen because…
The pressure blocks blood flow, and the skin and tissue underneath start to break down.
It’s kind of like when you sit on your leg too long and it "falls asleep" — but if you never move, the skin can get hurt.
common areas for pressure injuries
Mostly on bony areas — places with very little fat or cushion, like:
Sacrum (lower back/tailbone)
Ischial tuberosities (bottom bones you sit on)
Greater trochanters (sides of your hips)
Heels (back of your feet)
Tubes, oxygen masks, or braces can press on the skin if they’re tight or left too long
These can cause pressure damage on the soft tissue or mucous membranes (like inside the mouth or nose)
What Causes a Pressure Injury?
Pressure
This is the main reason.
When you lie too long on one spot, it squeezes blood vessels shut, so the skin and tissue don’t get enough blood.
This causes damage or even death of the skin and tissue.
Friction
Happens when two surfaces rub together — like your skin rubbing against bedsheets.
This can make the skin red, raw, or scratched.
Shearing
This is a pulling force where the skin moves, but the bone stays still.
For example, if someone slides down in bed, the skin may stretch and tear underneath — even if it looks okay on top.
This can injure deep tissues near the bones.
Moisture (Complication)
Doesn’t cause pressure injuries by itself, but it makes everything worse.
Wet skin from sweat, pee, or wound drainage becomes soft and more likely to break down.
What Makes Pressure Injuries More Likely?
🚶♂ 1. Decreased Mobility
If a person can’t move much, pressure stays in one spot too long
More risk when there’s friction (rubbing) or shearing (sliding skin)
🧠 2. Decreased Sensation
Some people can’t feel pain or pressure
Happens with:
Spinal cord injuries
Brain problems (like coma or confusion)
Nerve diseases
They don’t feel the need to move, so skin gets hurt
❤ 3. Decreased Blood Flow
Blood carries oxygen, and skin needs that to stay healthy
Less blood flow = higher risk
Caused by:
Low blood pressure (hypotension)
Diabetes
Atherosclerosis (clogged arteries)
🚽 4. Fecal or Urinary Incontinence
Poop or pee on the skin makes it wet and weak
Leads to faster skin breakdown
🦴 5. Fractures or Contractures
Broken bones or tight muscles (contractures) can stop someone from moving
Less movement = more pressure
🥣 6. Poor Nutrition or Low Albumin
If someone isn’t eating well, the skin doesn’t get the nutrients it needs
Albumin is a protein that helps heal wounds — low levels = slow healing
stage 1 pressure injury
Skin is not broken, but it looks red or discolored
Might feel warmer or cooler, softer or firmer than the skin around it
Person might say it hurts or burns
In dark skin tones, it may not look red—so you check for firmness, pain, and warmth instead
stage 2 pressure injury
Top layers of skin are broken (epidermis and maybe part of the dermis)
Looks like a blister or a shallow open sore
Skin barrier is partially broken
Like a peeled sunburn or popped blister
stage 3 pressure injury
Skin is fully broken — now it’s all the way down to the fat tissue
May have dead tissue (necrosis)
Does not go into muscle, but it's close
Looks like a deep hole or crater
stage 4 pressure injury
Goes through all skin layers and into muscle, bone, or nearby structures (like tendons)
Very serious and can take months or years to heal
May see tendons, muscle, or bone at the bottom
Unstageable Pressure Injury
The skin is so covered with dead tissue (slough or eschar) that the nurse can’t tell how deep it goes
Once the dead tissue is removed, it usually turns out to be a Stage 3 or Stage 4
If the eschar is dry, stable, and not infected, it’s usually left alone to protect the area
Skin Cancer Risk Factors
☀ High UV Exposure
From the sun or tanning beds
More time in the sun = higher risk
👨👩👧 Family History
If someone in your family had melanoma, your risk is higher
🔴 Atypical or Lots of Moles
If you have weird-looking moles or more than 50 moles, your risk goes up
🔥 Burns Easily
People who burn instead of tan have higher risk
Especially those with natural blond or red hair
Who Has Some Natural Sun Protection?
People with darker skin have more melanin (skin pigment), which helps block UV rays
This means they have a lower risk for skin cancer
White people have less melanin, so they’re more likely to get skin cancer
Black and Hispanic people still can get skin cancer — it’s just less common
Skin Tumors
☀ 1. Actinic Keratosis
Caused by too much sun exposure over time
Looks rough, scaly, and crusty — like a dry patch
Can be pink, red, or skin-colored
Often found on faces, ears, hands, or arms (sunny spots)
Considered a precancerous lesion
→ If untreated, it can turn into skin cancer
📍 Think of it like a "sun warning" spot on your skin
🧓 2. Seborrheic Keratosis
Looks like a waxy, raised, and sometimes bumpy mole
Can be tan, brown, or black
Often looks like it’s been "stuck on" the skin
Not dangerous — not cancer
More common as people get older
📍 Think of it like a harmless "age spot" that just hangs out on the skin
Basal Cell Carcinoma
✅ Most common skin cancer
🐢 Grows very slowly
☀ Found on sun-exposed areas (like face, neck, ears)
👩 Fair-skinned adults, often under 40 years old
😣 Can become painful
🔴 Starts as a pink or red bump
🧬 Rarely spreads (metastasizes) or causes death
📍 Grows from the base layer (bottom) of the skin
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
⚠ Less common, but more aggressive
🐰 Grows faster than BCC
☀ Happens on sun-damaged skin — like hands, scalp, ears
🔥 Can be:
Painful
Crusty
Bleeding
Inflamed
Can form an ulcer
🧬 Can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body if untreated
📍 Comes from the upper layer of the skin (epidermis)