Science 10 Unit D - Energy Flow in Global Systems
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Weather
refers to the specific atmosphere condition at a particular location at a specific instant of time.
Climate
is the average weather conditions in a region measured over a period of several years.
Biosphere
is the narrow zone around Earth that can support life.
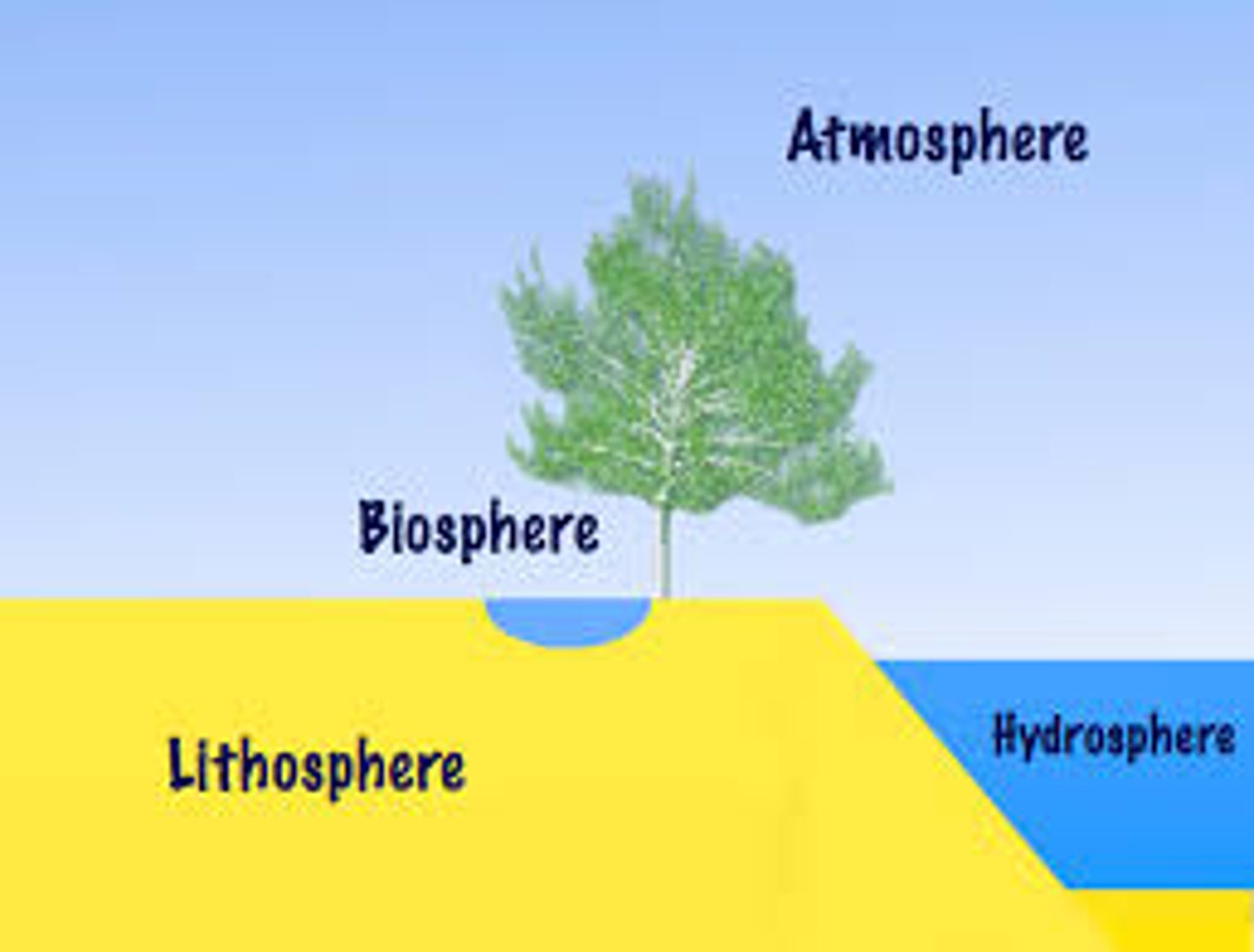
Atmosphere
is the layer of gases that surround Earth
Lithosphere
is the solid portion of Earth

Hydrosphere
is all the water Earth

Atmospheric dust
varying amounts of suspended particulate matter
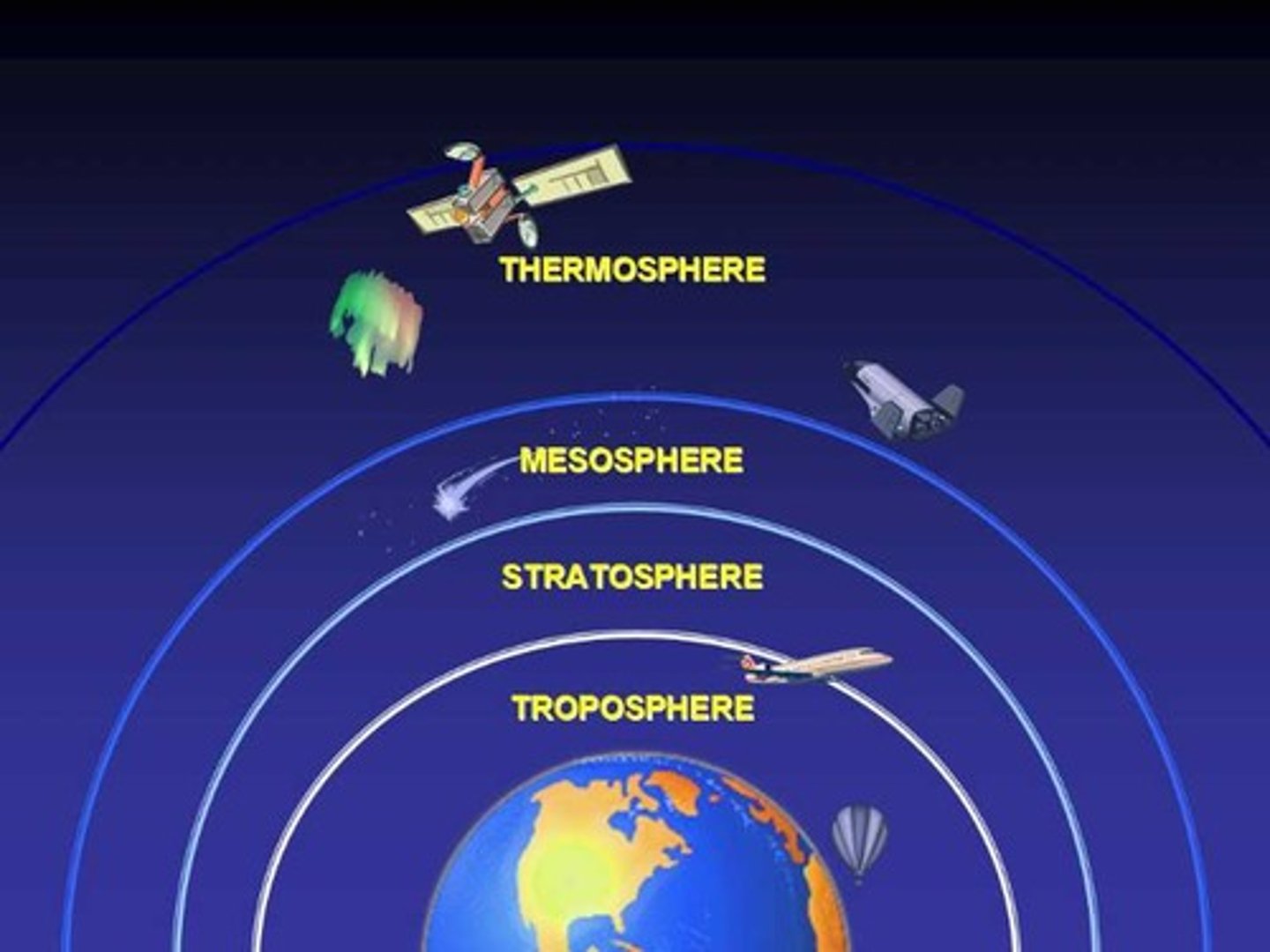
Troposphere
the layer closest to Earth, where almost all weather occurs; the thinnest layer
*10km, 15°C to -60°C
Stratosphere
This is above the troposphere and this is where atmospheric warming takes place with increases in altitude.
*50km (-60°C to 0°C)
Ozone
is a molecule made up of three atoms of oxygen.
Ozone layer
ozone gases forms a layer in the stratosphere called the ozone layer.
Mesosphere
is the third atmospheric layer above Earth's surface.
*80km (0°C to -100°C)
Thermosphere
is the farthest layer from the Earth's surface. 85kn,-100 to +1500
Inversion
is a reversal of normal temperature patterns seen in the troposphere. May trap unusually cold air close to the ground, also less air circulation.
Adaptation
is any change in the structure or functioning of an organism that makes it more suited to its environment.
Climate change
is the change that occurs in the climate of region over time, usually minimum of 30 years.
Anecdotal evidence
relies on reports from people about particular weather events and how they interpret these events changing over time.
Scientific evidence
relies on evidence collected in a manner that, as much as possible, ensures it is unbiased and that reflects general situations.
Thermal energy
is the energy possessed by a substance by virtue of the kinetic energy.
Solar energy
energy from the sun.
Radiant energy
energy transmitted as electromagnetic waves.
Insolation
is the amount of solar energy received by a region of Earth's surface.

Angle of inclination
refers to the degree by which Earth's poles are tilted from the perpendicular of the plane of its orbit. (23.5°)

Polar regions
regions of Earth surrounding its geographical poles.

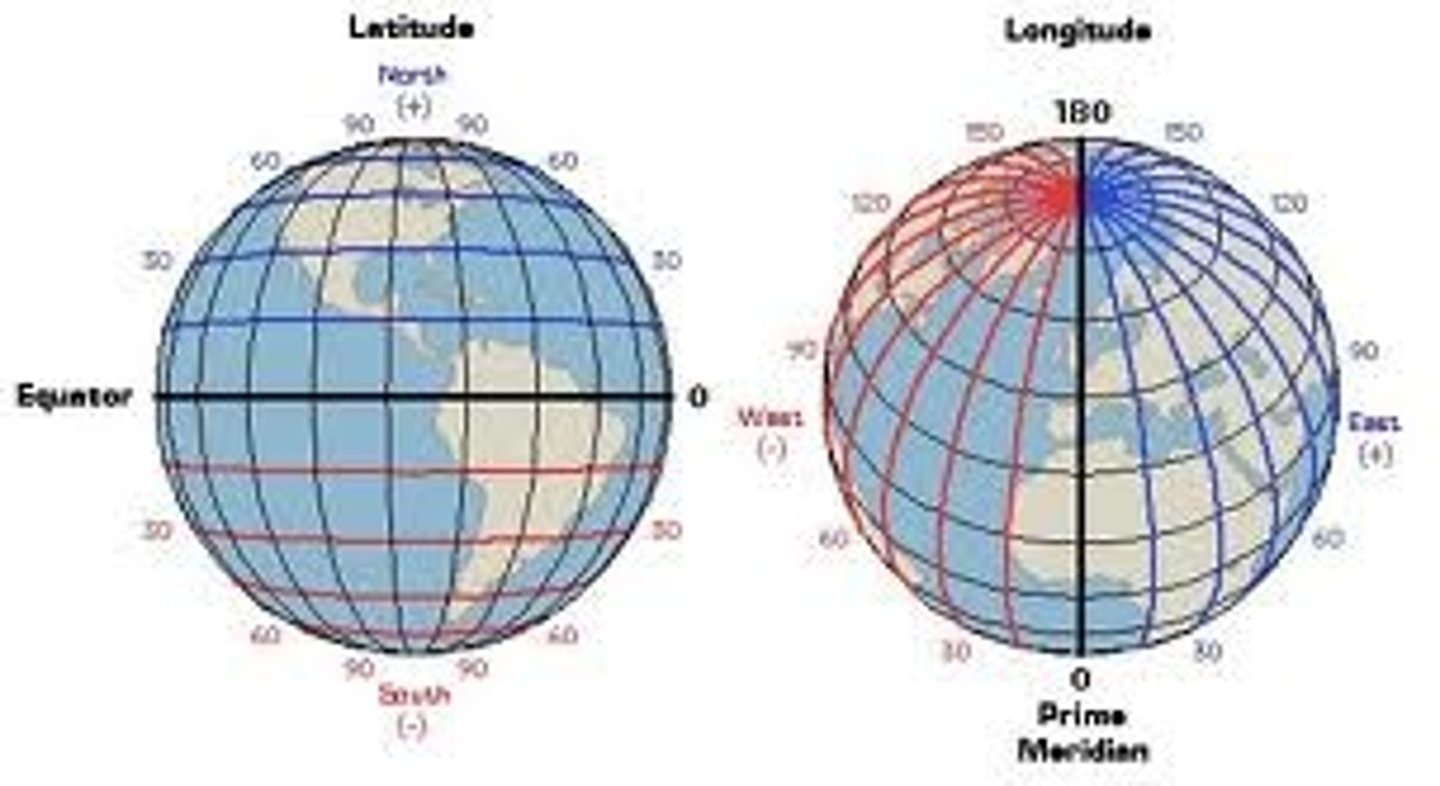
Latitude
are imaginary lines that run parallel to the equator.
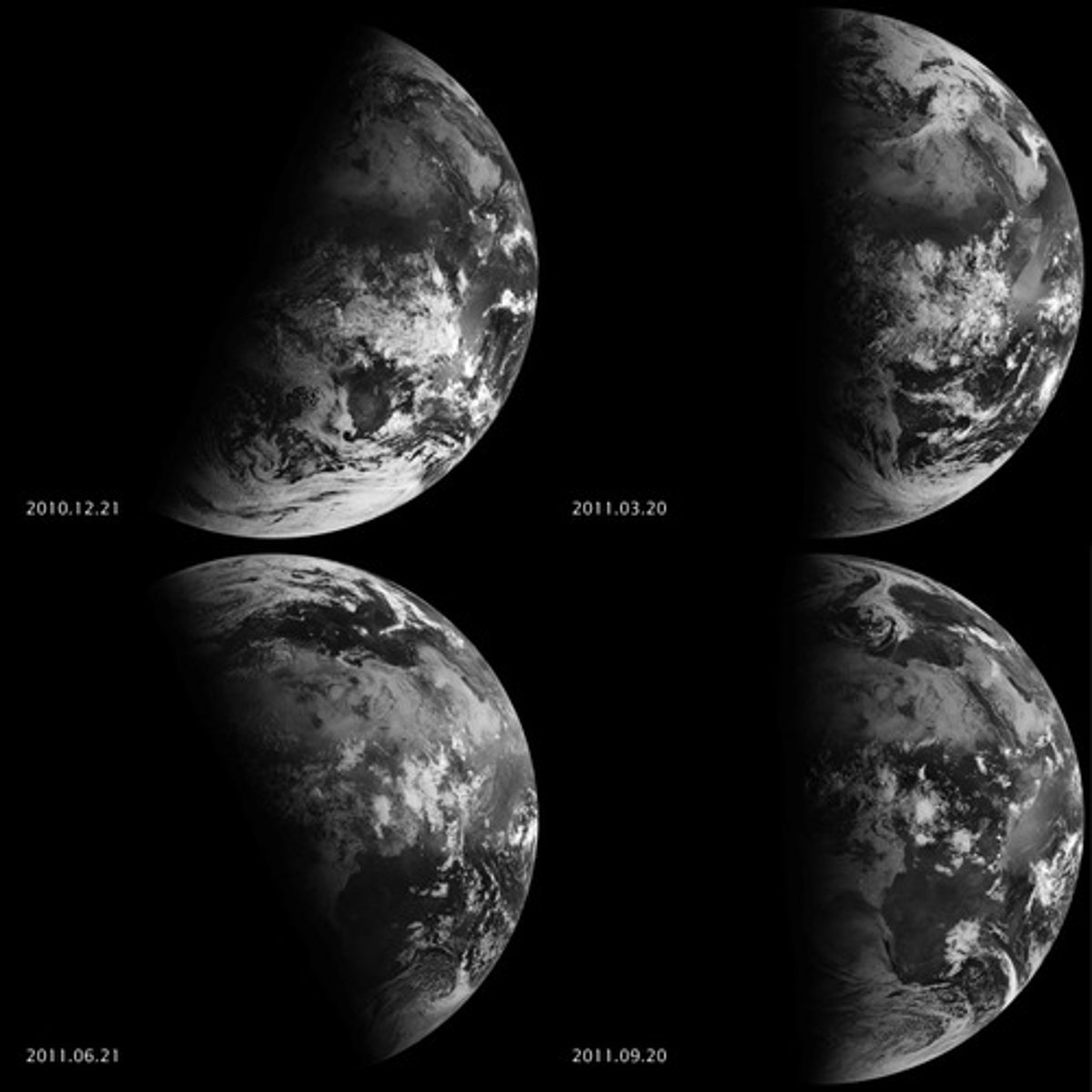
Solstice
is one of two points in Earth's orbit when the poles are more tilted towards or away from the sun.
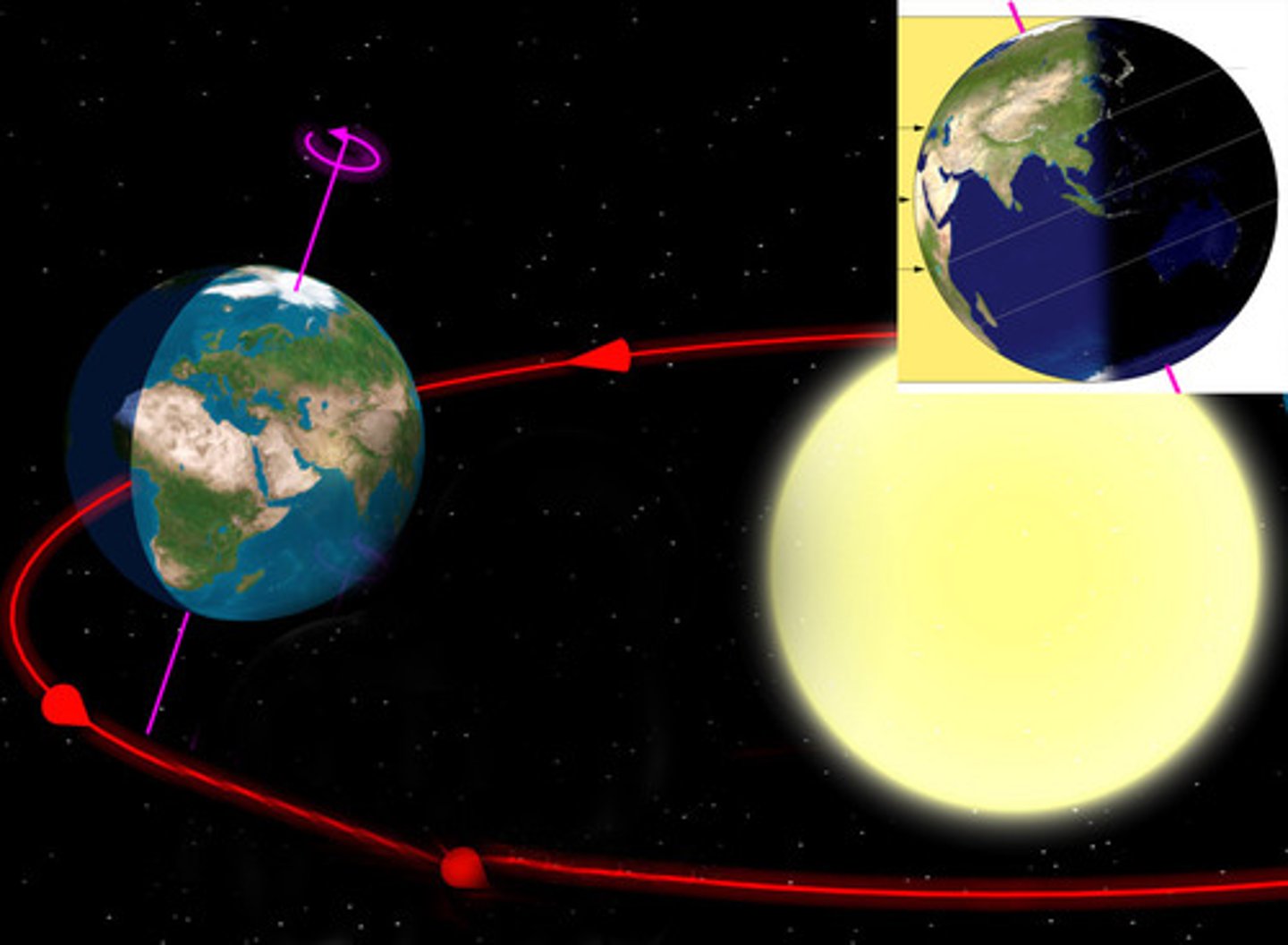
Equinox
is when the number of daylight hours exactly equal to the number of hours of night.

Angle of incidence
of a ray is the angle between the ray and a line that is drawn perpendicular to the Earth's surface.
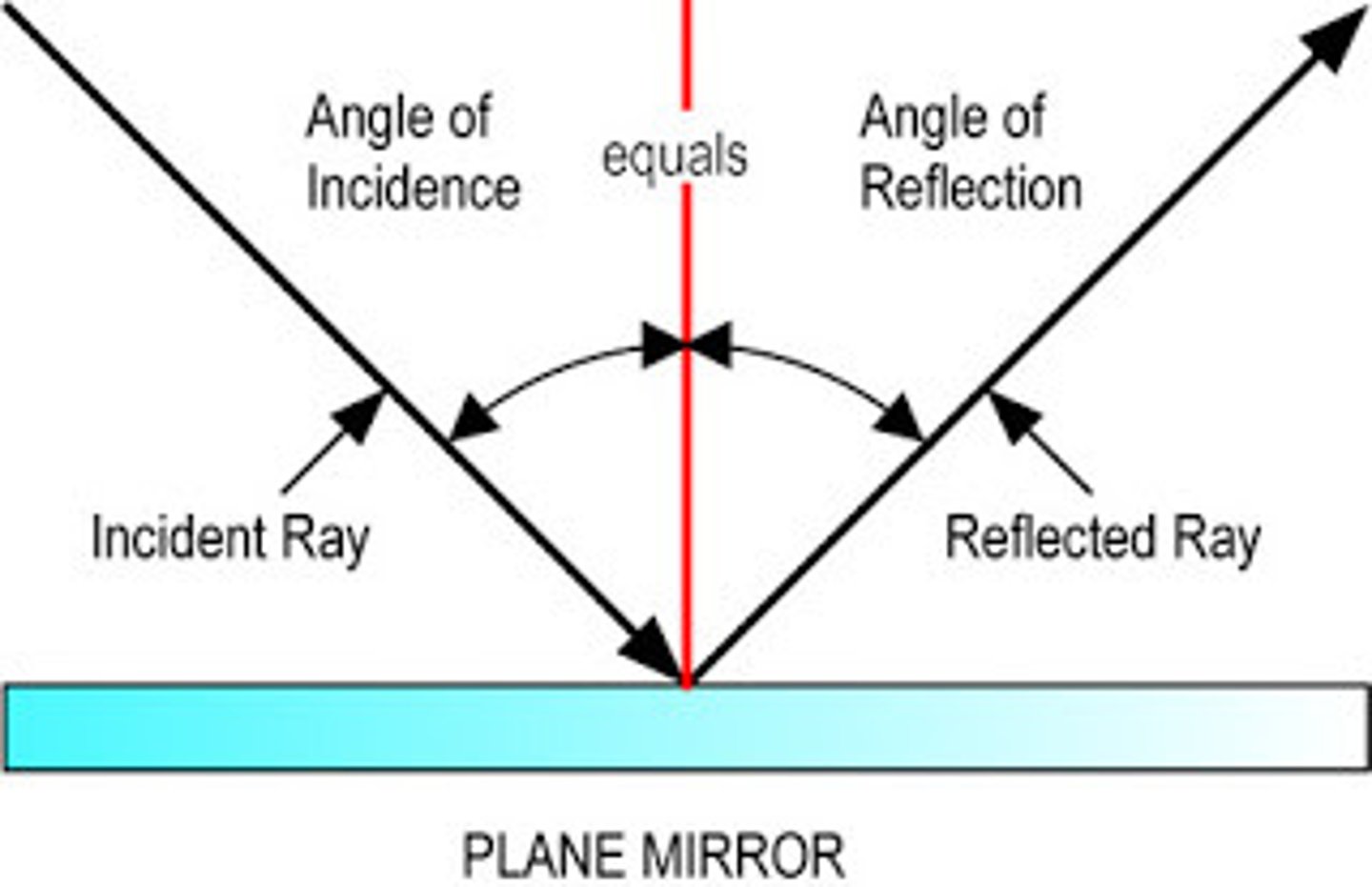
Reflect energy
bounces light off and change the ray's direction.
Absorb energy
takes in light and converts it into another form of energy, such as kinetic energy.
Albedo
of a surface is the percent of solar radiation that it reflects.
*average albedo for the Earth's surface is 30%
Greenhouse effect
the trapping of the sun's warmth in a planet's lower atmosphere due to the greater transparency of the atmosphere to visible radiation from the sun than to infrared radiation emitted from the planet's surface.
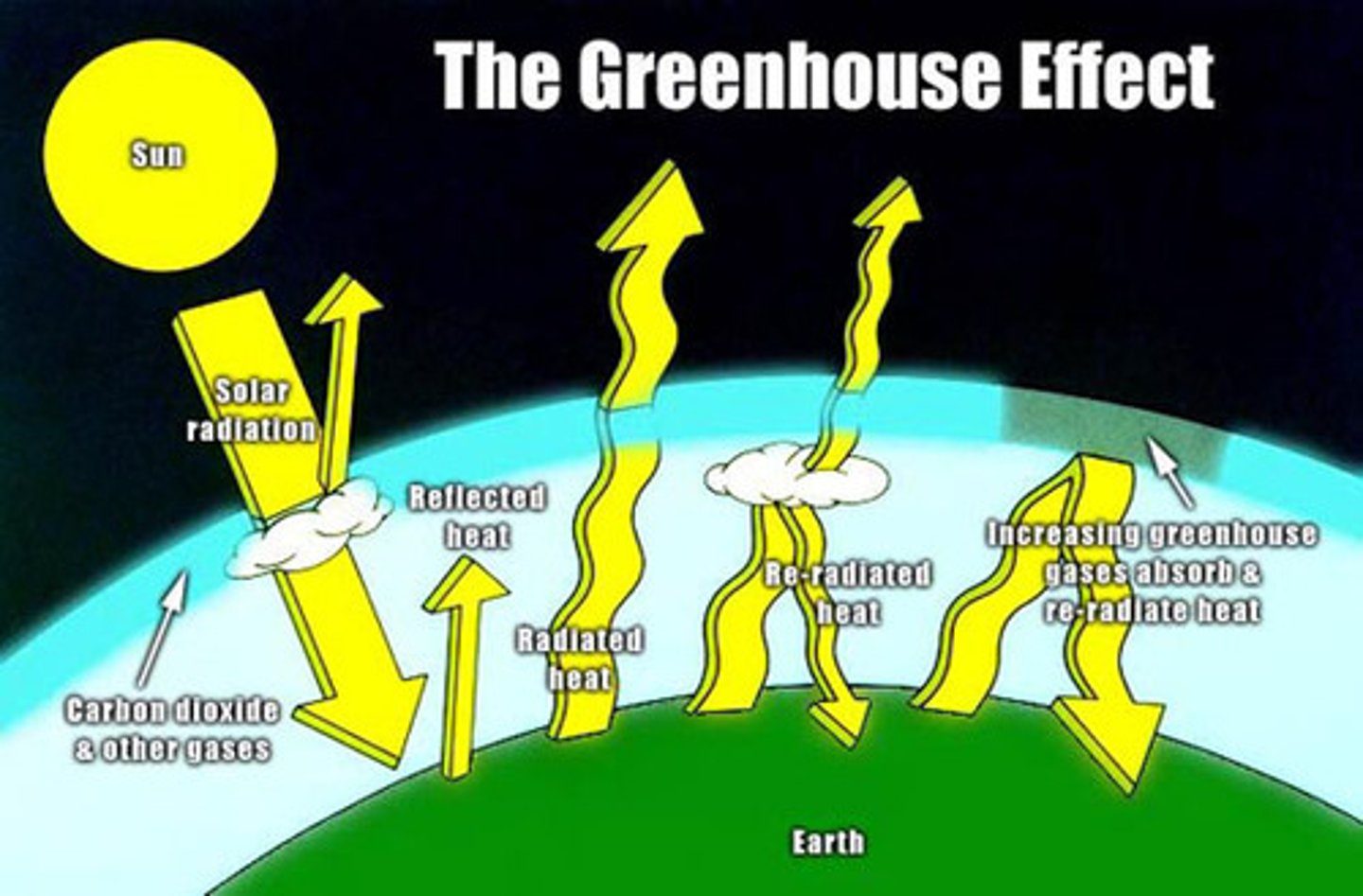
Natural greenhouse effect
the absorption of thermal energy by the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases
are gases that contribute to the artificial greenhouse effect.

Enhanced greenhouse effect
the change in the earths net radiation budget, caused by the increase in human generated greenhouse gases.
Incoming radiation
solar radiation that reaches the Earth.
*isn't reflected by the atmosphere.
Outgoing radiation
thermal radiation that is re-emitted by Earth's surface into space. IS not absorbed by the greenhouse gases of the atmosphere
Net radiation budget
is the difference between the amount of incoming radiation and of outgoing radiation.
*net radiation budget = incoming radiation - outgoing radiation
Radiation
is the emission of energy as particles or waves.
Conduction
is the transfer of thermal energy through direct contact between the particles of a substance, without moving particles to a new location
Convection
is transfer of thermal energy through the movement of particles from one location to another.
Fluids
substances with no definite shape.
Current
flow from one place to another in one direction.
Density
mass per volume of a substance.
Atmospheric pressure
is pressure exerted by the mass of air above any point on Earth's surface.
Wind
is the movement of cool air from there areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure.
The Coriolis Effect
is the deflection of an object from straight line path by the rotation of Earth.
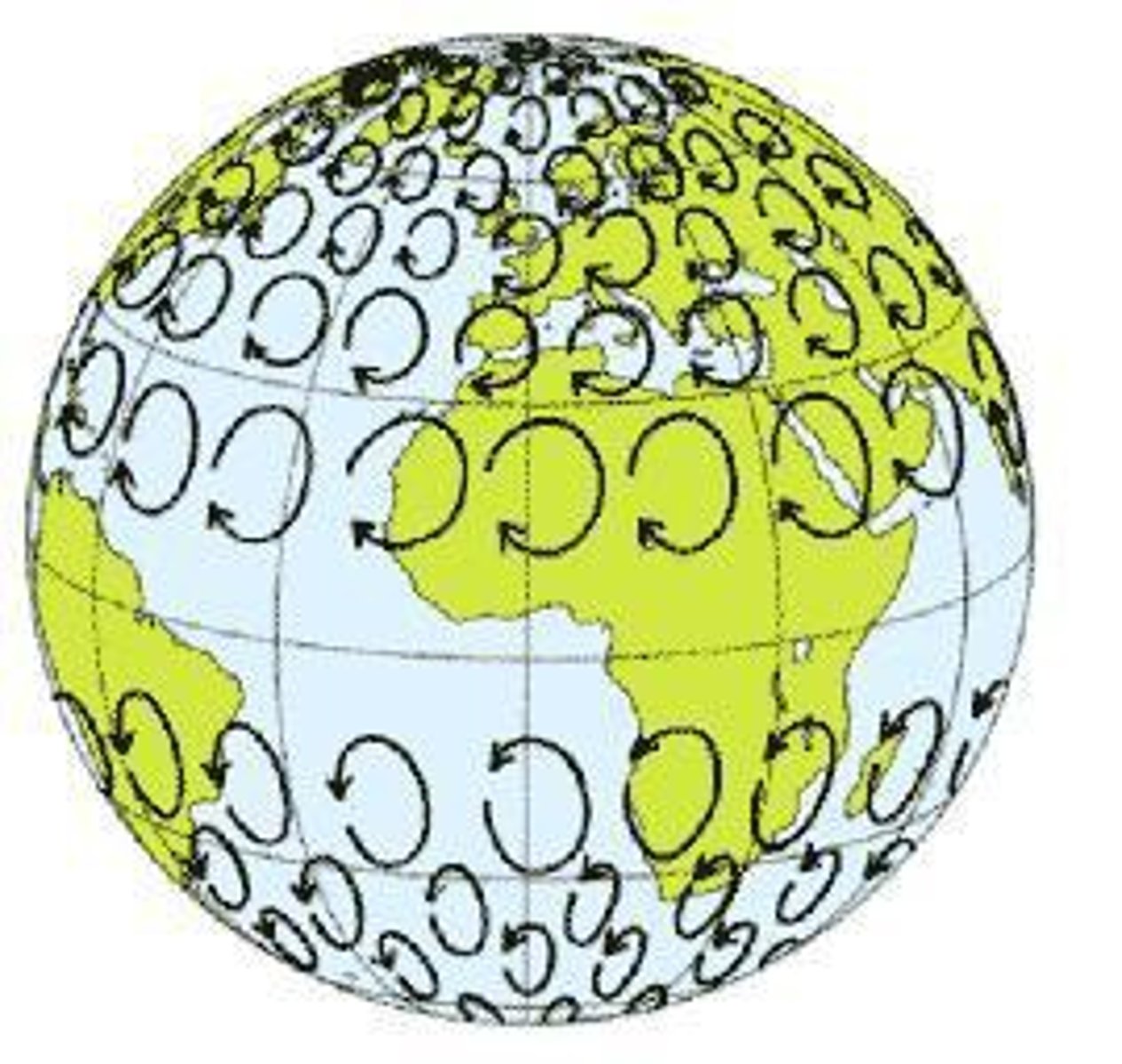
Jet stream
is band of fast-moving air in the stratosphere. important to predicting weather changes
Specific heat capcity
is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of the substance by 1°C.
Quantity of thermal energy
is amount of thermal energy absorbed or released when the temperature of a specific mass substance changes by a certain number of degrees.
*Q = mcΔt
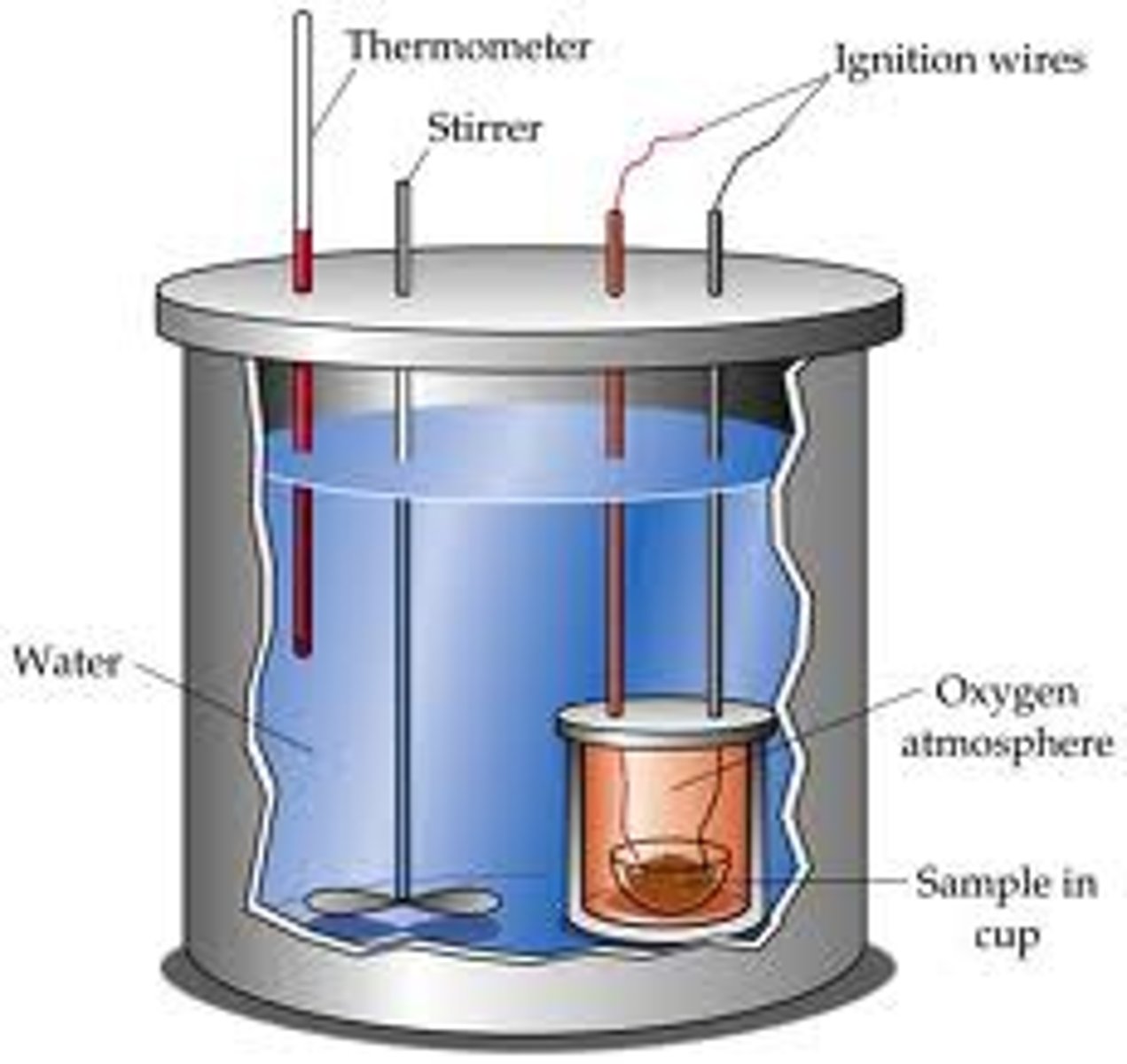
Calorimeter
is any device used to determine the transfer of thermal energy.
Hydrologic cycle (water cycle)
constantly moving water molecules moving among the components of the biosphere.
Heat of fusion
the amount of energy absorbed when 1 mol of the substance changes from solid phase to liquid phase.
Heat of solidification
energy released during the reverse phase change, when 1 mol of a solid forms.
Heat of vaporization
the amount of energy absorbed when 1 mol of substance changes from liquid phase to vapor phase.
Heat of condensation
the energy released during reverse phase change, when 1 mol of vapor condenses to a liquid.
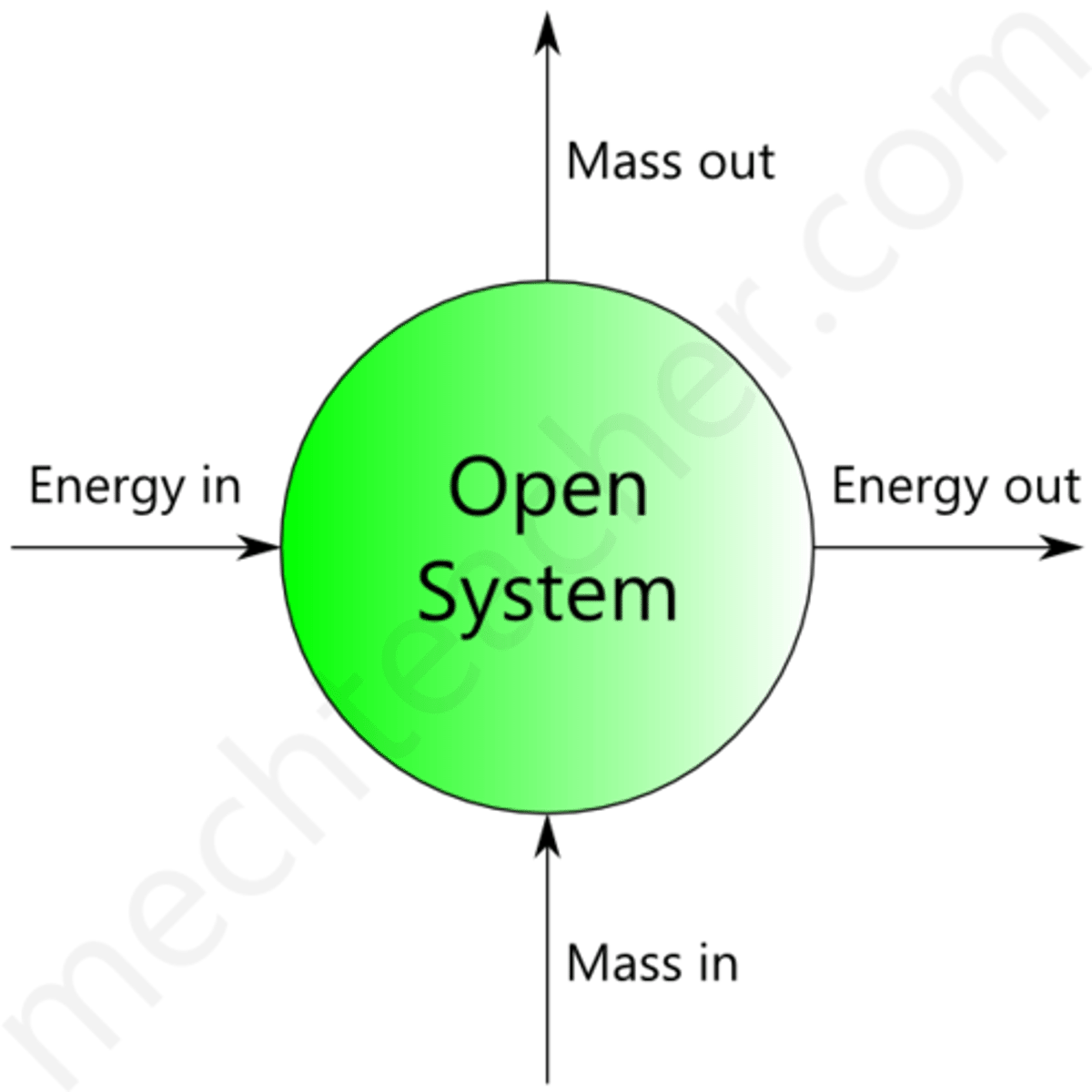
Open system
a system that exchanges both matter and energy with its surroundings.
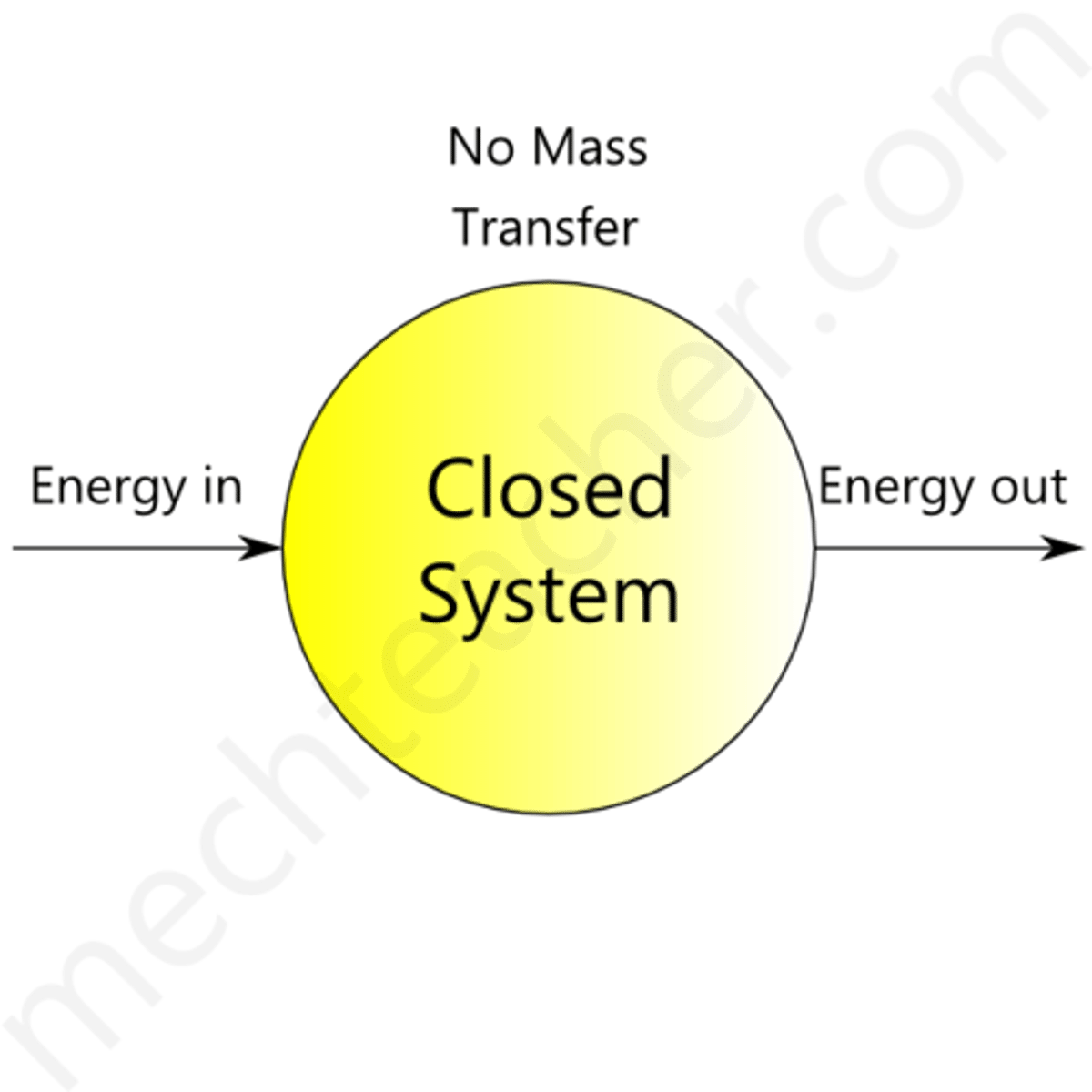
Closed system
any system that exchanged energy with it's surroundings but does not exchange matter.
Biome
is a large geographical region with a specific climate that the plants and animals that inhabit are adapted to.
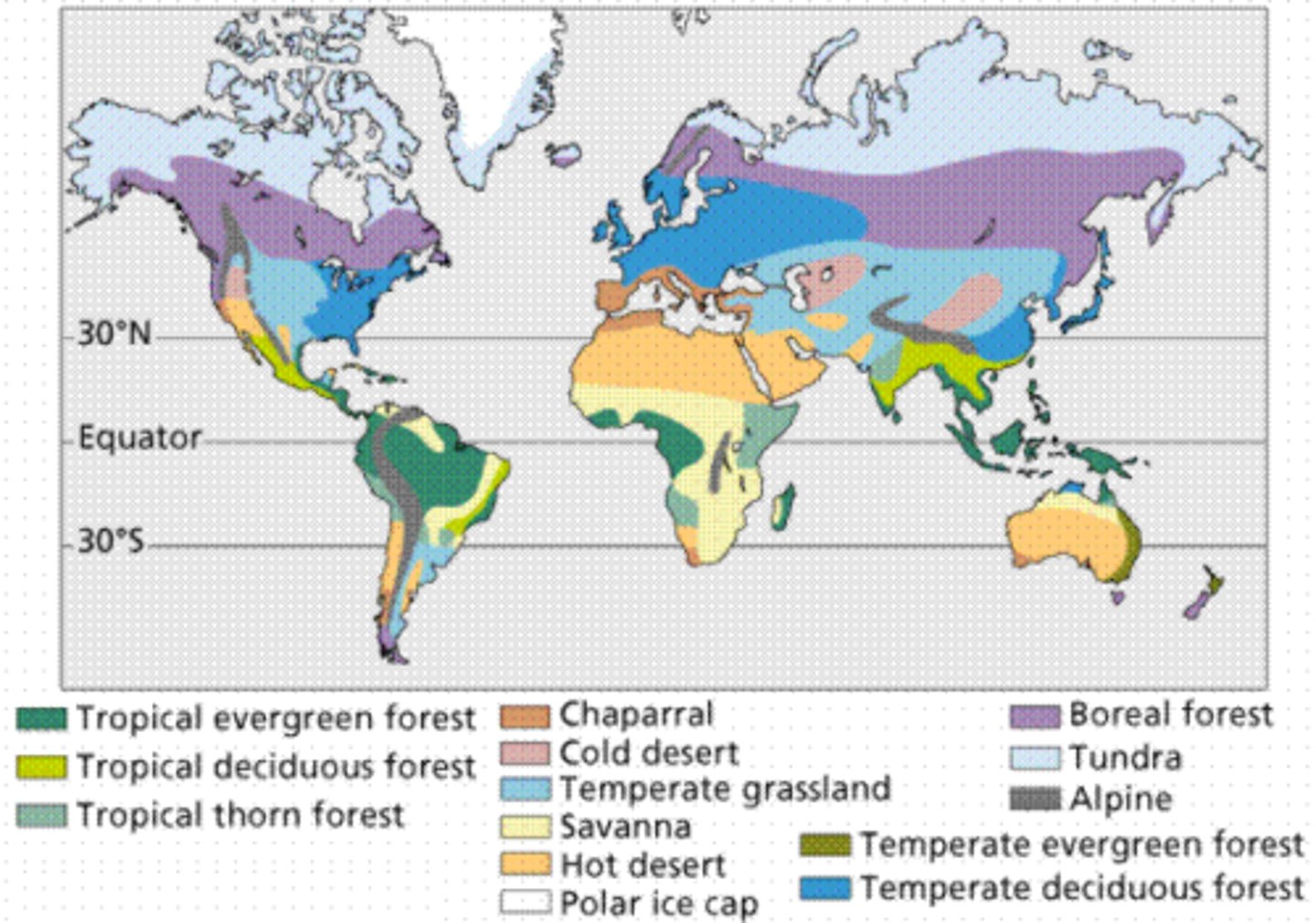
Tundra
-Perma forest, bitter cold, and high winds means no trees or tall plants. Little rainfall but accumulation on top of perma forest.
-Mountaintops around the world can be alpine tundra.

Taiga (boreal forest)
-large terrestrial biome
-mostly evergreen trees (coniferous)
-adapted to heavy snowfall

Deciduous forest
-mid latitudes,with enough moisture to support trees.
-deciduous trees drop their leaves in the winter

Grassland
-deep, rich topsoil, great for agriculture.
-seasonal drought, fire, grazing large mammals who prevent shrubs and trees establishment.

Rain forest
-great diversity of plants and animals.
-closed tree canopy.
-pronounced vertical stratification (layering)

Desert
-little to no rainfall.
-extreme temperature (hot and cold).
-organisms adapted to conserve water.
-many protective adaptation of plants to deter herbivory.

Climatograph
is a summary of the average temperature and precipitation for each month of the year.
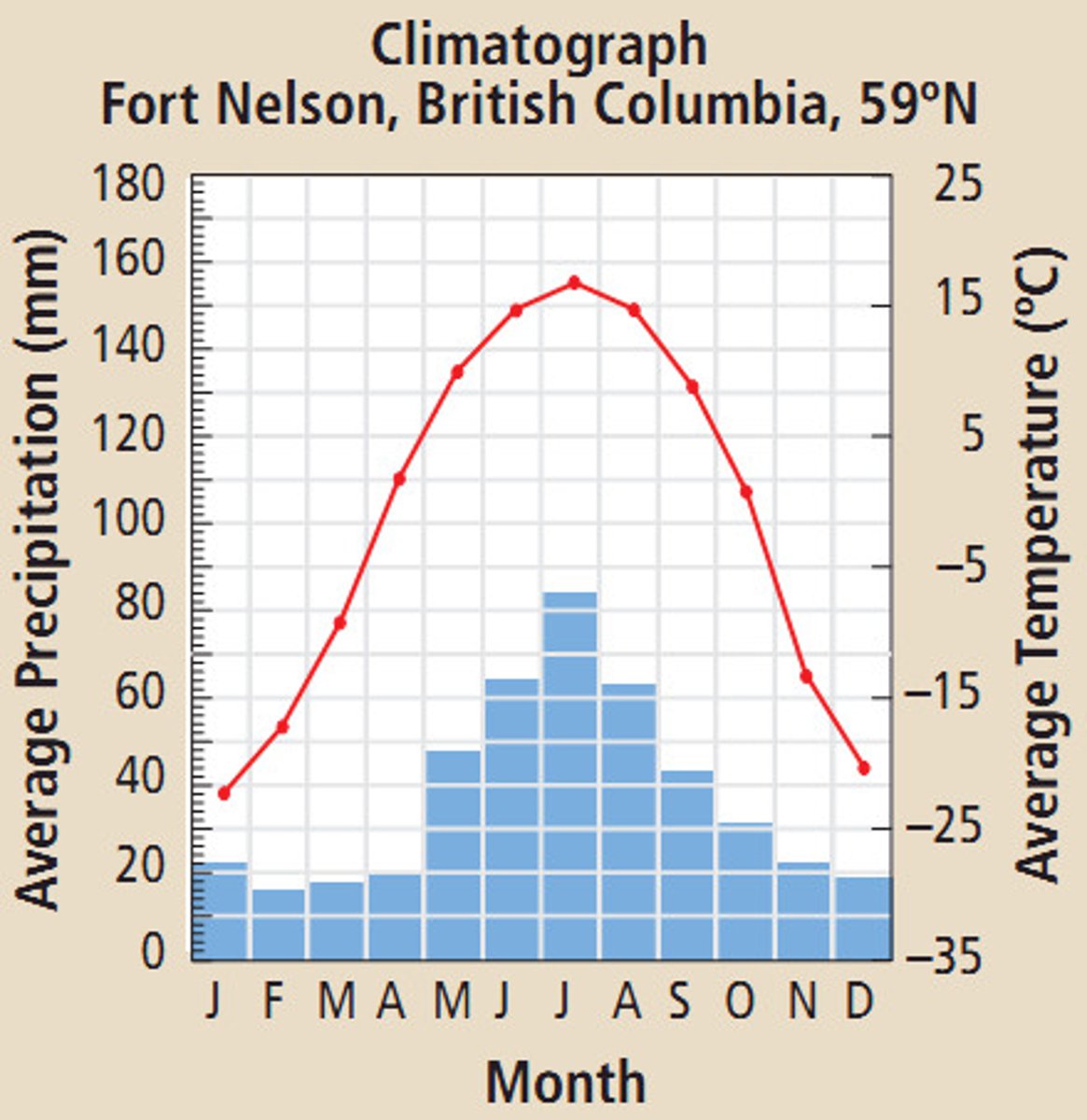
Average precipitation
is always plotted as a bar graph.
Average temperature
is always plotted as a line graph.
Carbon source
any process that releases carbon into the atmosphere.

Fossil fuels
are fuels that contain large amounts of carbon.
Carbon sink
forests' are called this because photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.

Halocarbons
human-made chemicals that can absorb significant amount of thermal energy.
Global warning
refers to the observed increase in Earth's average temperature.
Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs)
any of a class of inert compounds of carbon, hydrogen, hydrocarbons, chlorine, and fluorine, used in place of chlorofluorocarbons as being somewhat less destructive to the ozone layer.
Sustainable development
is the use of the world's resources in ways that maintain these resources for future generation.
Carbon dioxide sequestering
process where carbon dioxide gas is pumped into the ground to help extract underground oil reserves.
Global warning potential (GWP)
of an atmosphere gas is a measure of thy relative ability to trap thermal energy in the atmosphere.
Persistence
is how many years a gas will remain in the atmosphere.
Evidence of global warming
1. flowers in the northern hemisphere have begun to bloom earlier and earlier over the past century.
2. the incidence of extreme weather events such as ice storm and flood have been on a rise.
3. snow in some polar regions has decreased
4. the average level and temperature of the Earth'd ocean have been increasing.
The atmosphere rises over ____ from earths surface
500km
The atmosphere is mainly composed of a mixture of different gases that include.
78.0% nitrogen. 20.95% Oxygen. 0.97% other gases.
The Atmosphere is divided into 4 parts
Troposhere,Stratosphere,MesopheremThermosphere
Net radiation budget and latitude
Latitude is an important factor in predicting whether the net ration budget of a region will be out of balance
Thermal energy transfer
the movement if thermal energy from an area of high temperature to an area of low temperature, Can occur by conduction or convection