CHM 2045 Midterm Williams
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Density formula
Density = mass/volume
SI Base Units: Mass
kilogram (kg)
SI Base Units: Time
seconds (s)
SI Base Units: Length
meter (m)
SI Base Units: Temperature
Kelvin (K)
SI Base Units: Amount of substance
mole (mol)
SI base units - electric current
ampere, A
SI Base Units: Luminous intensity
candela (cd)
Metric System - Giga
G 10^9
metric system - mega
M 10^6
metric system- kilo
k 10^3
Metric System Base Units
1
metric system deci
d 10^-1
metric system centi
c 10^-2
metric system milli
m 10^-3
metric system micro
M 10^-6
metric system nano
n 10^-9
Temperature (Kelvin and Celsius)
add 273 for C to K and subtract for K to C
symbolic representation of elements
atomic and mass # switched for periodic table
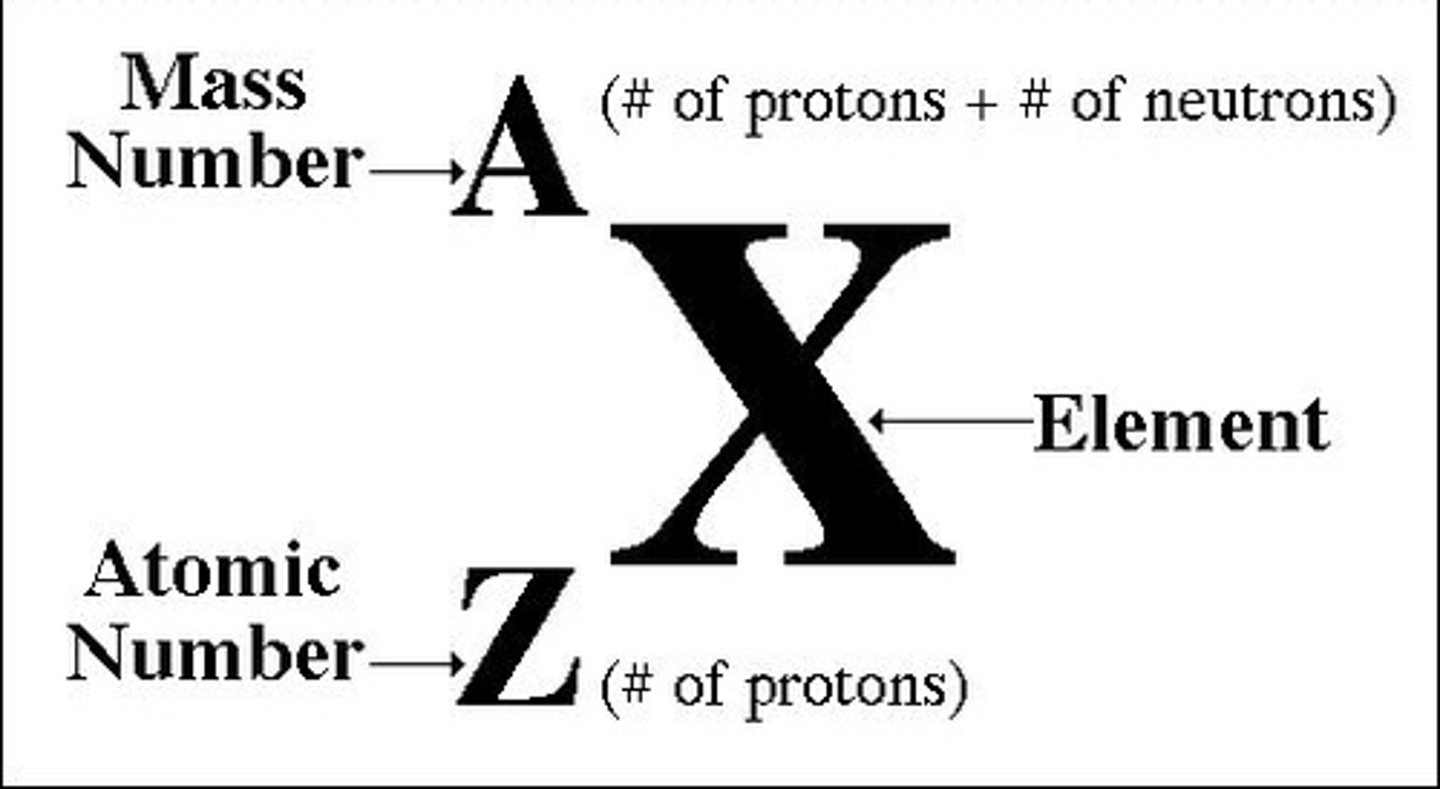
n=
neutrons
Z=
protons
Percent abundance formula
# of atoms of an isotope/ total # of atoms all isotopes of that element*100%
atomic weight formula
% abundance of isotope 1/100 x mass of isotope 1 + % abundance of isotope 2/100 x mass of isotope 2

Binary molecular prefix 1
mono
Binary molecular prefix 2
di
Binary molecular prefix 3
tri
Binary molecular prefix 4
tetra
Binary molecular prefix 5
penta
Binary molecular prefix 6
hexa
Binary molecular prefix 7
hepta
Binary molecular prefix 8
octa
Binary molecular prefix 9
nona
Binary molecular prefix 10
deca
Hydronium
H3O+
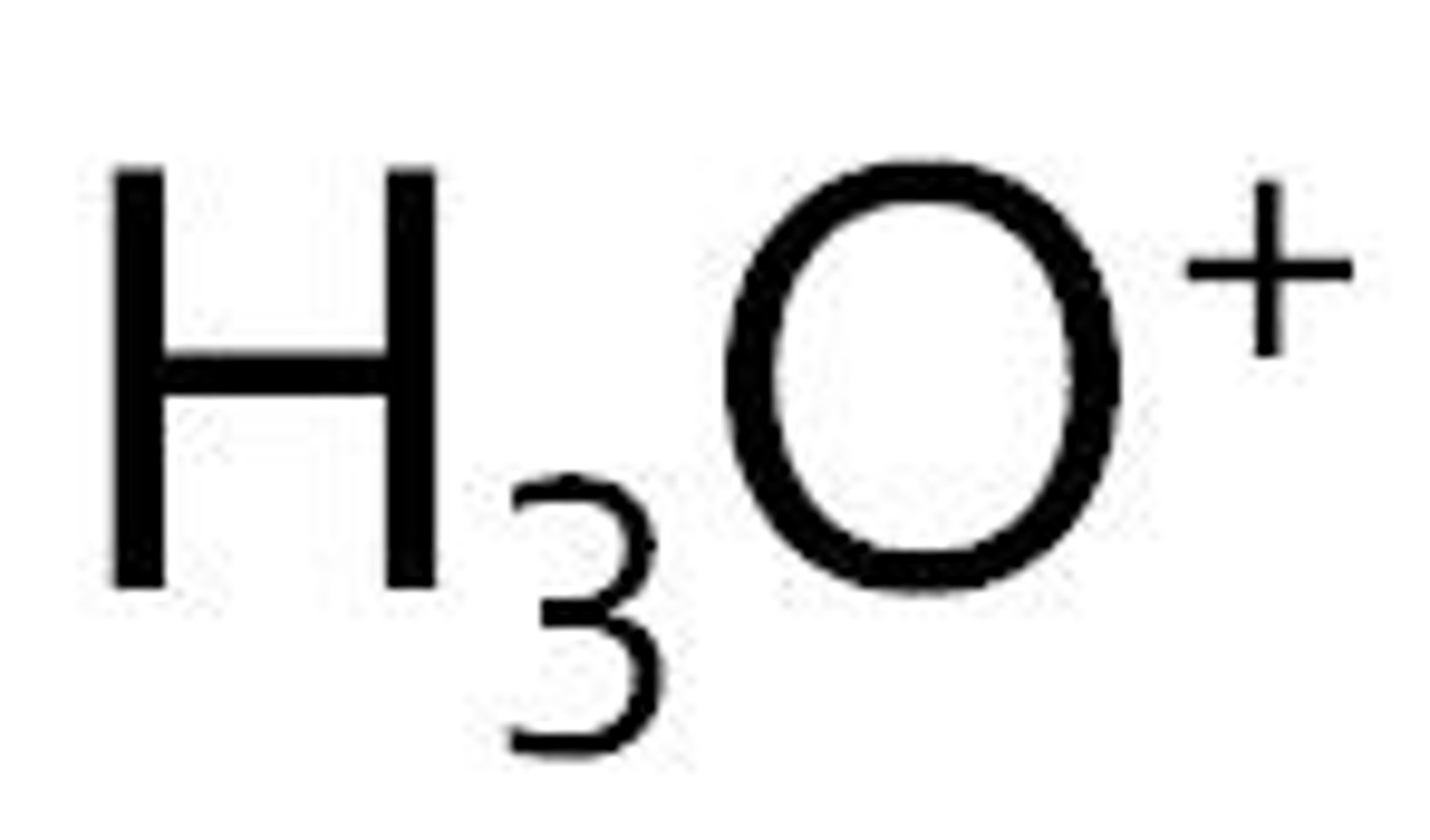
Ammonium
NH4+
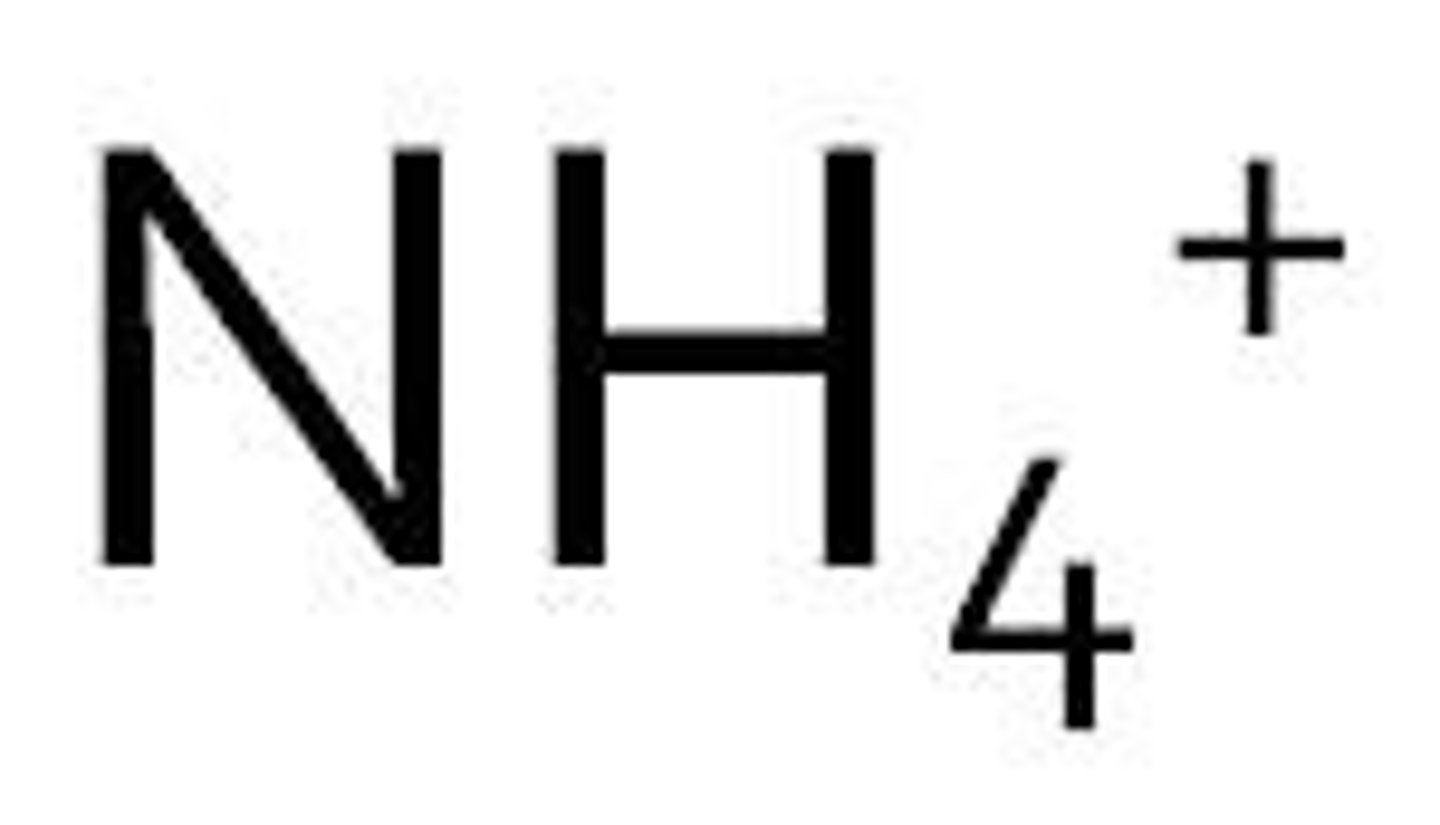
Cyanide
CN-

Acetate
C2H3O2-
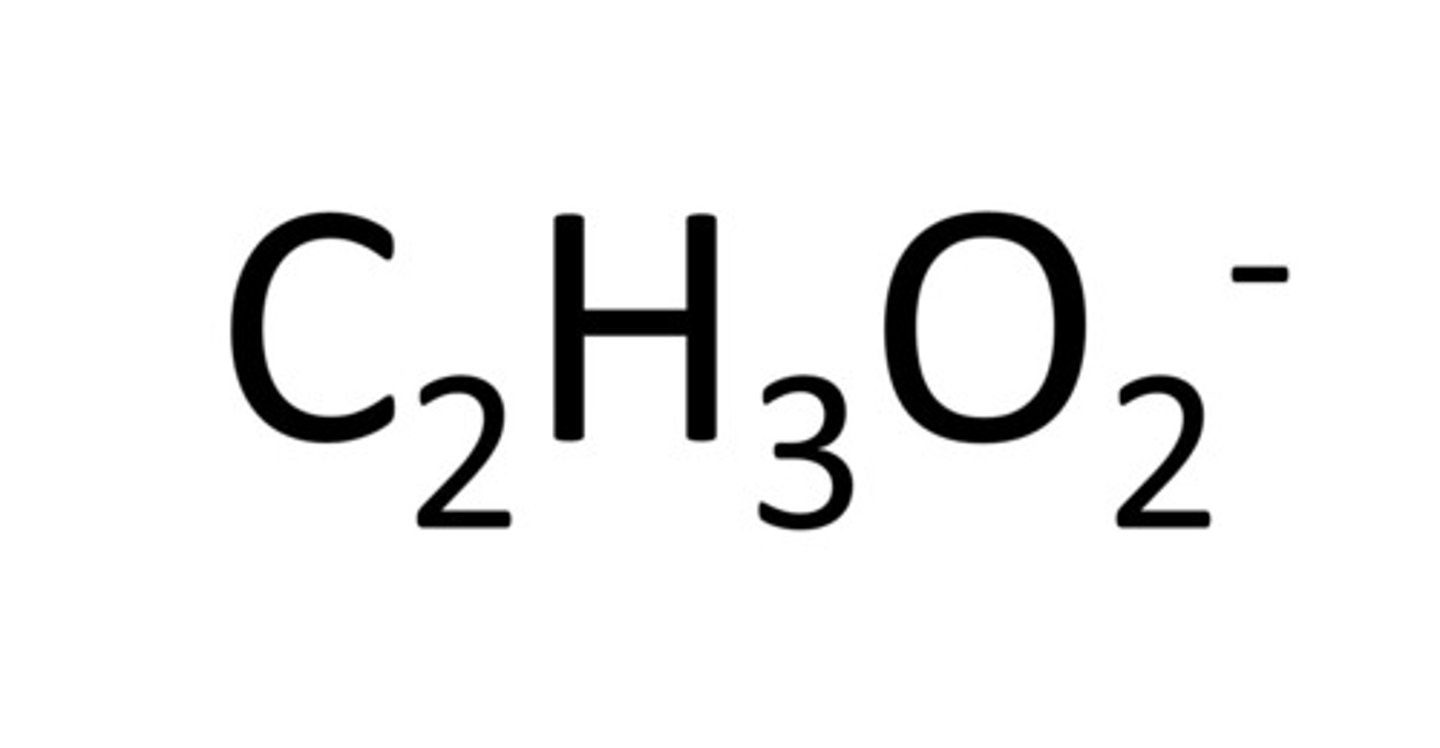
Carbonate
CO3 2-
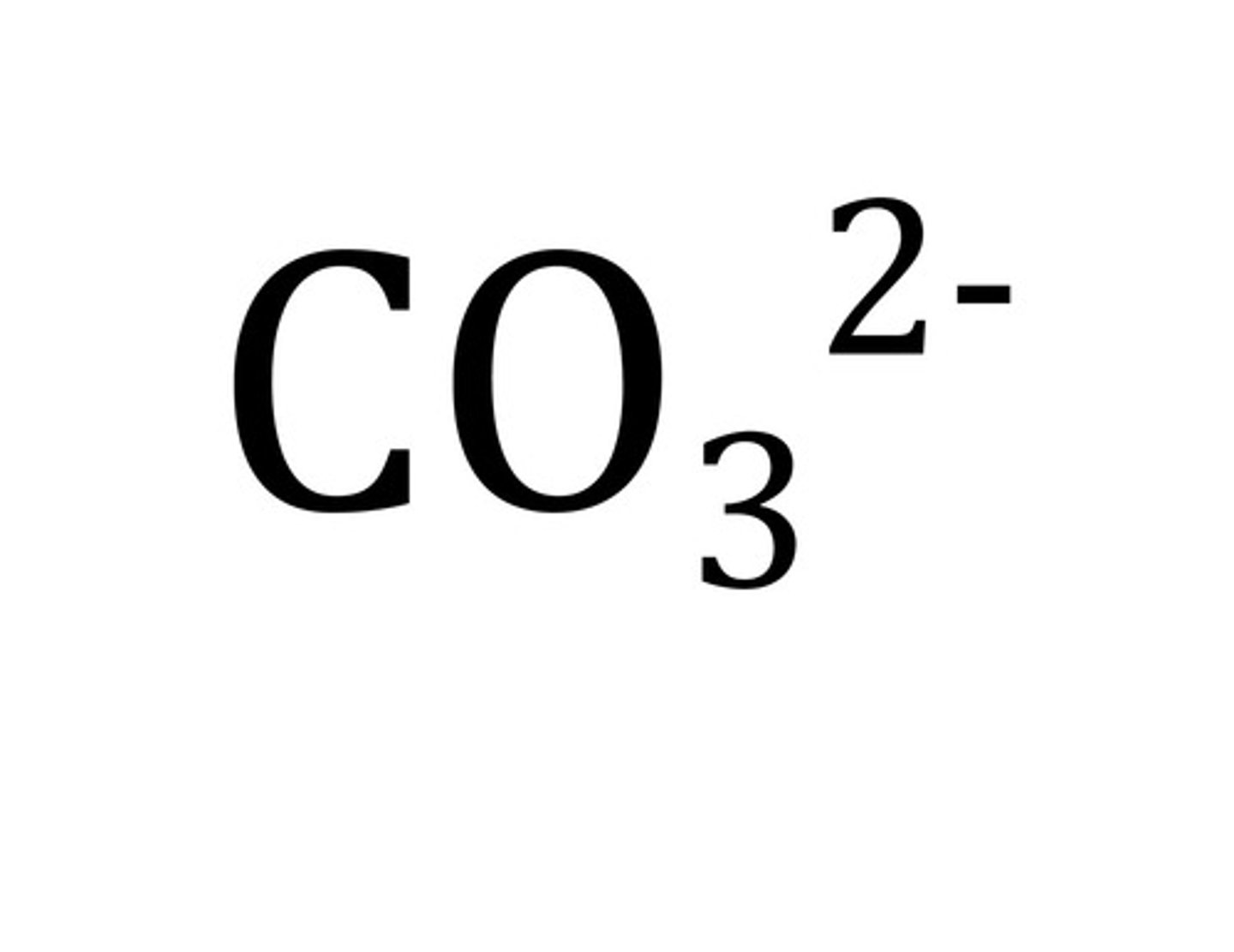
Hydrogen Carbonate
HCO3-
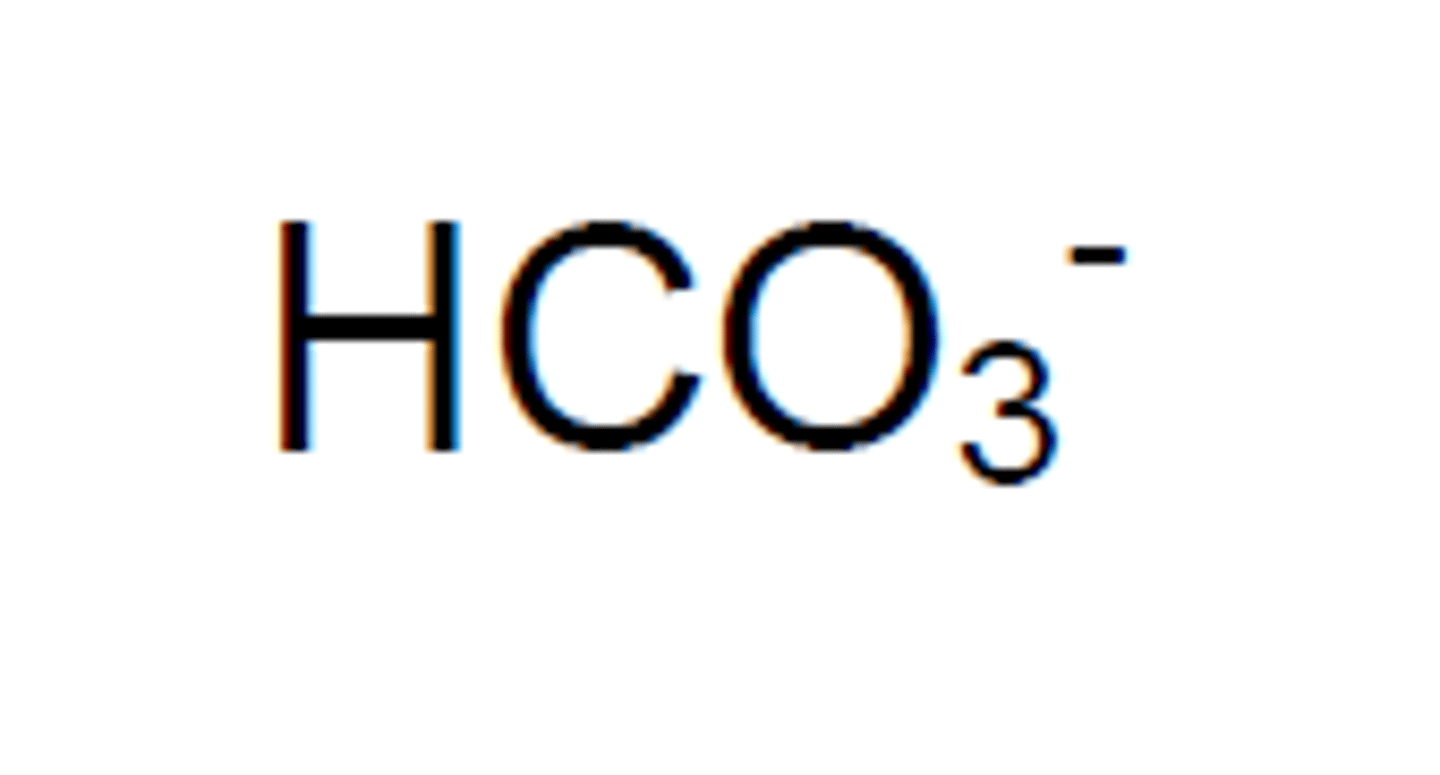
Oxalate
C2O4 2-
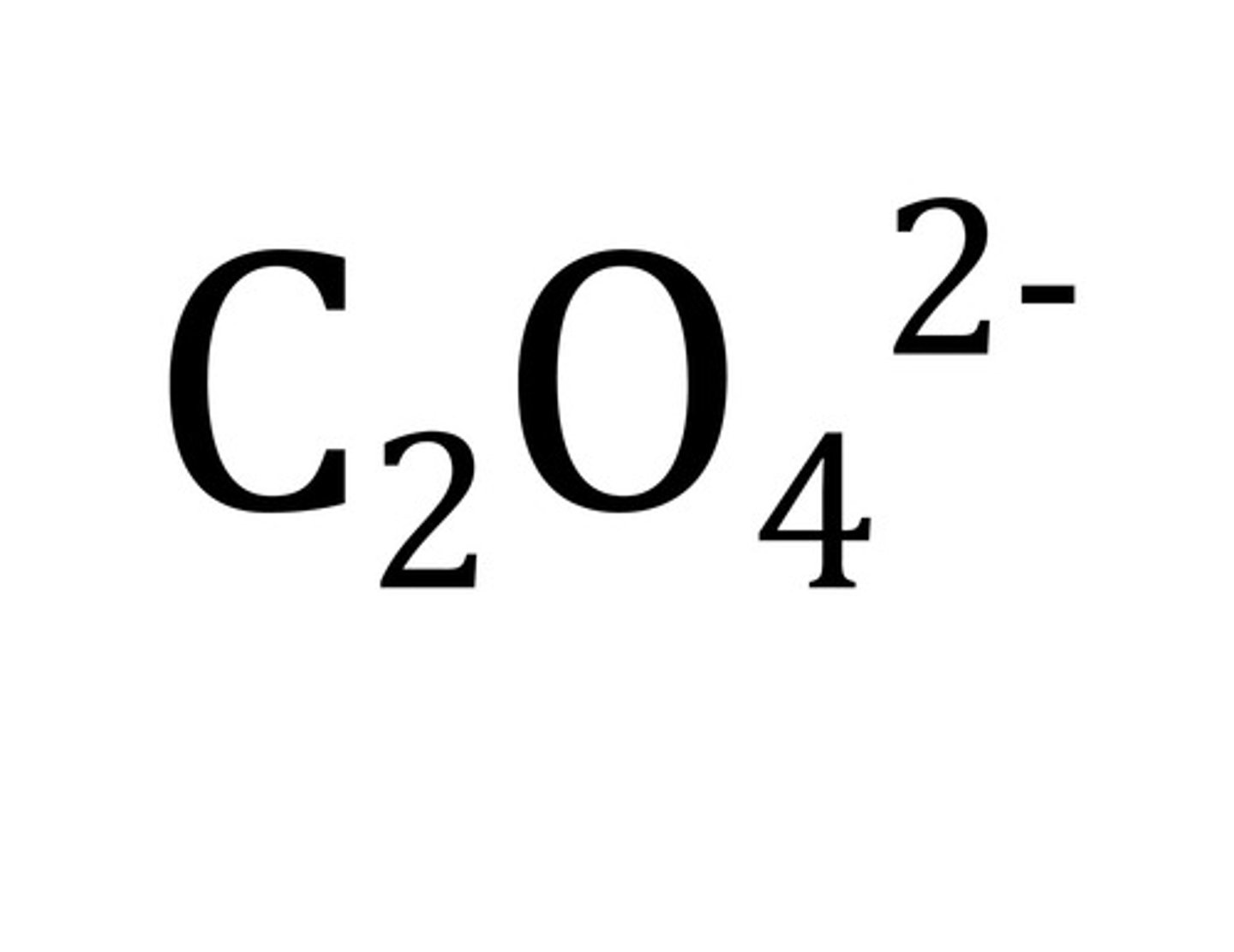
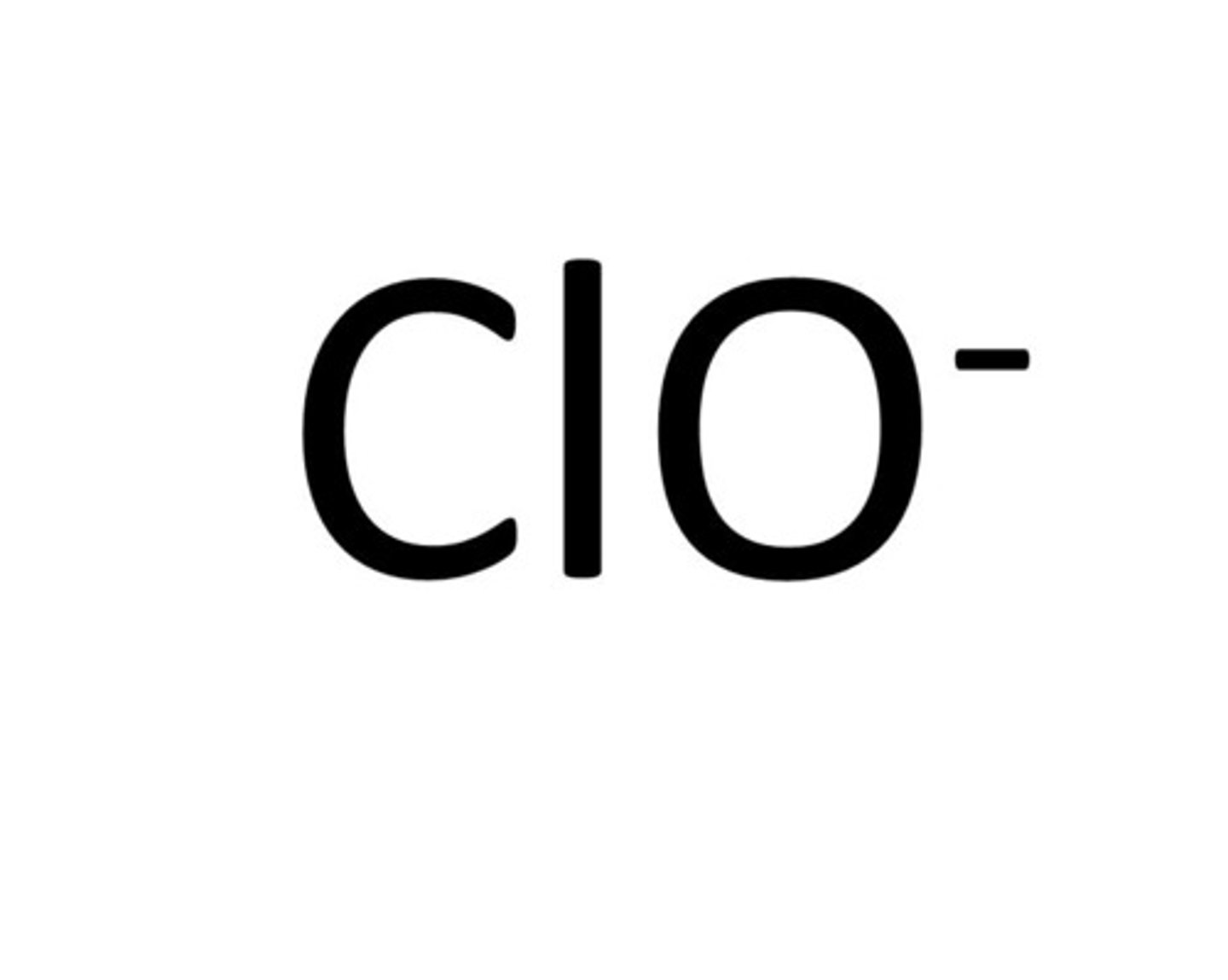
Hypochlorite
ClO-
Chlorite
ClO2-
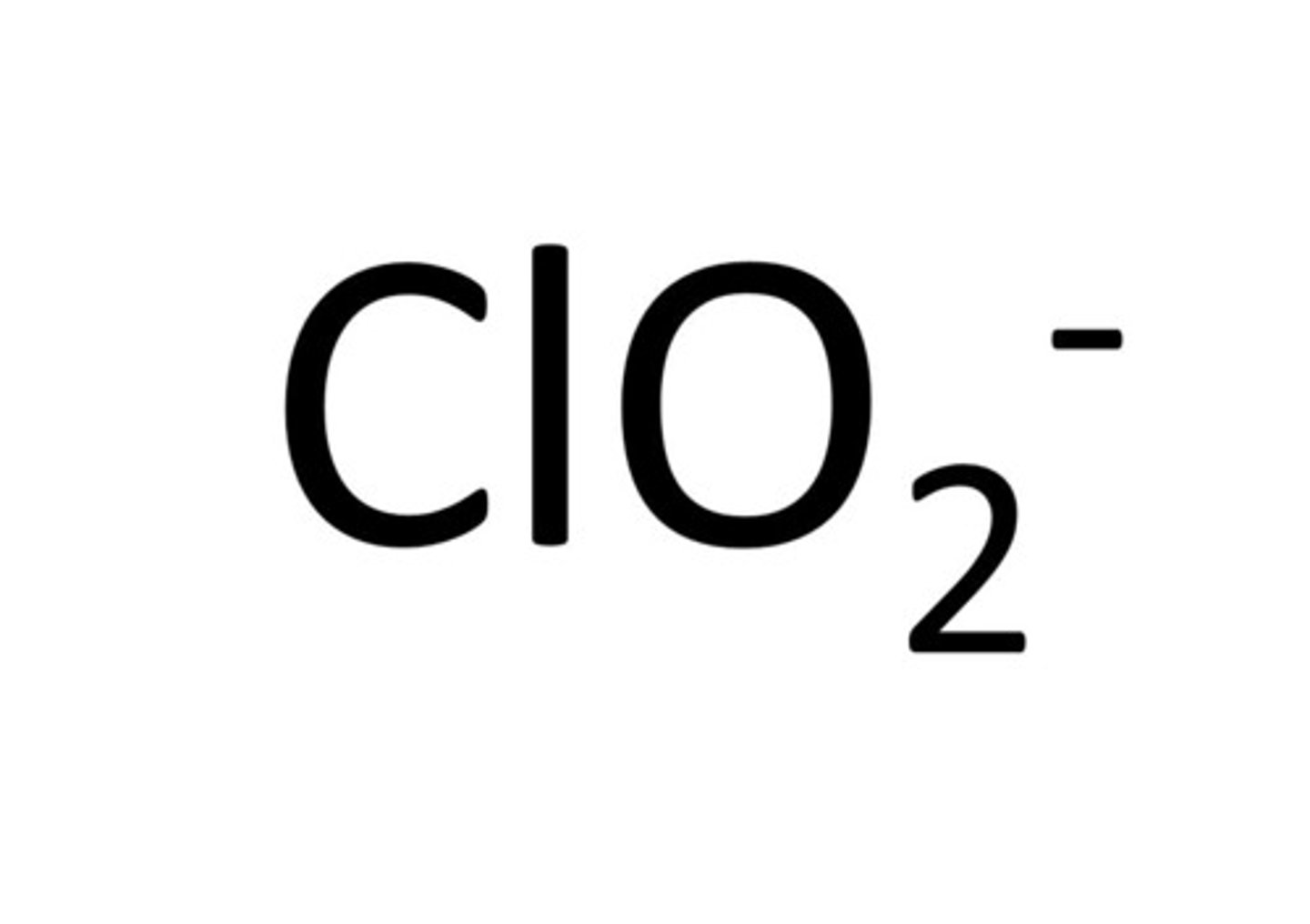
Chlorate
ClO3-
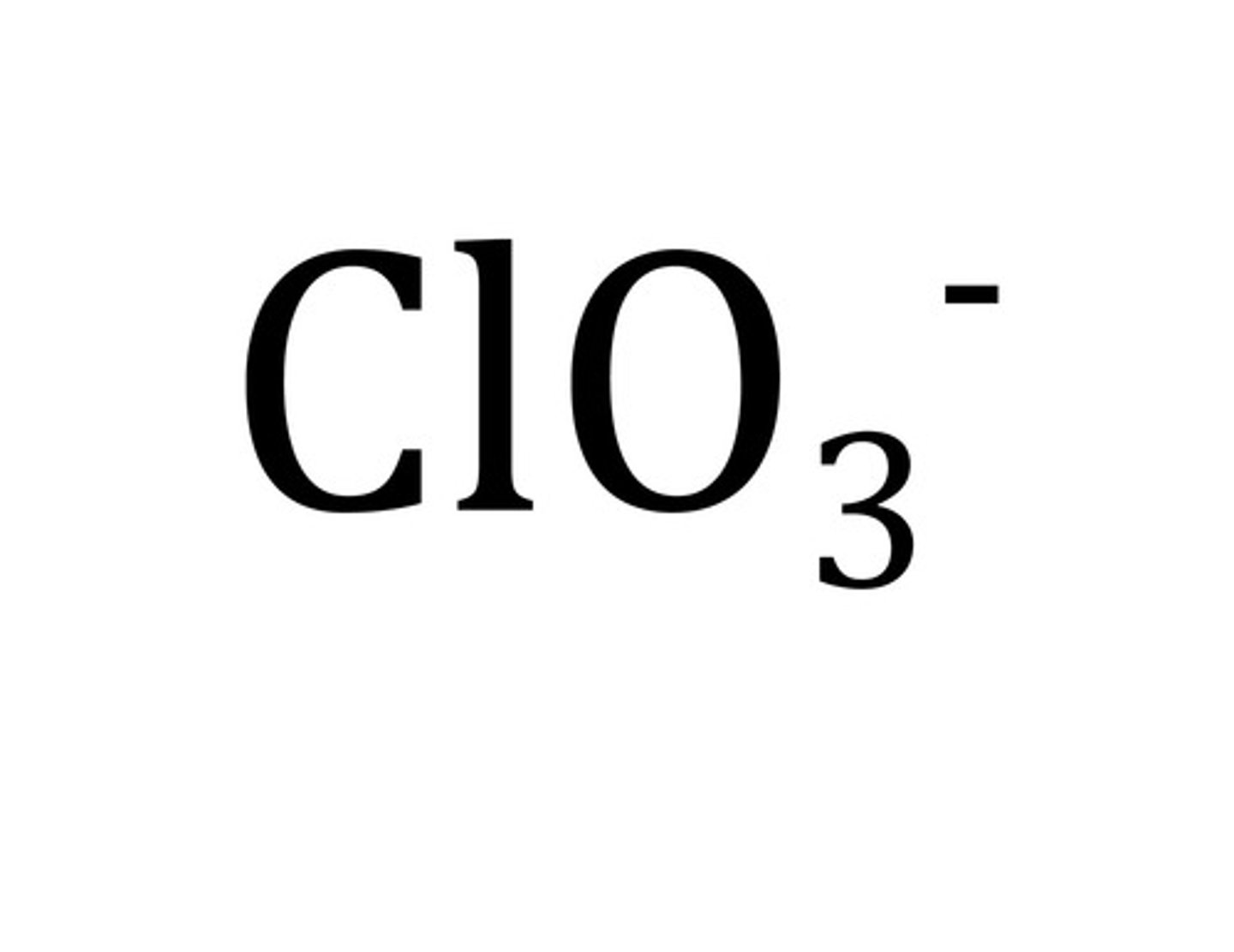
Perchlorate
ClO4-
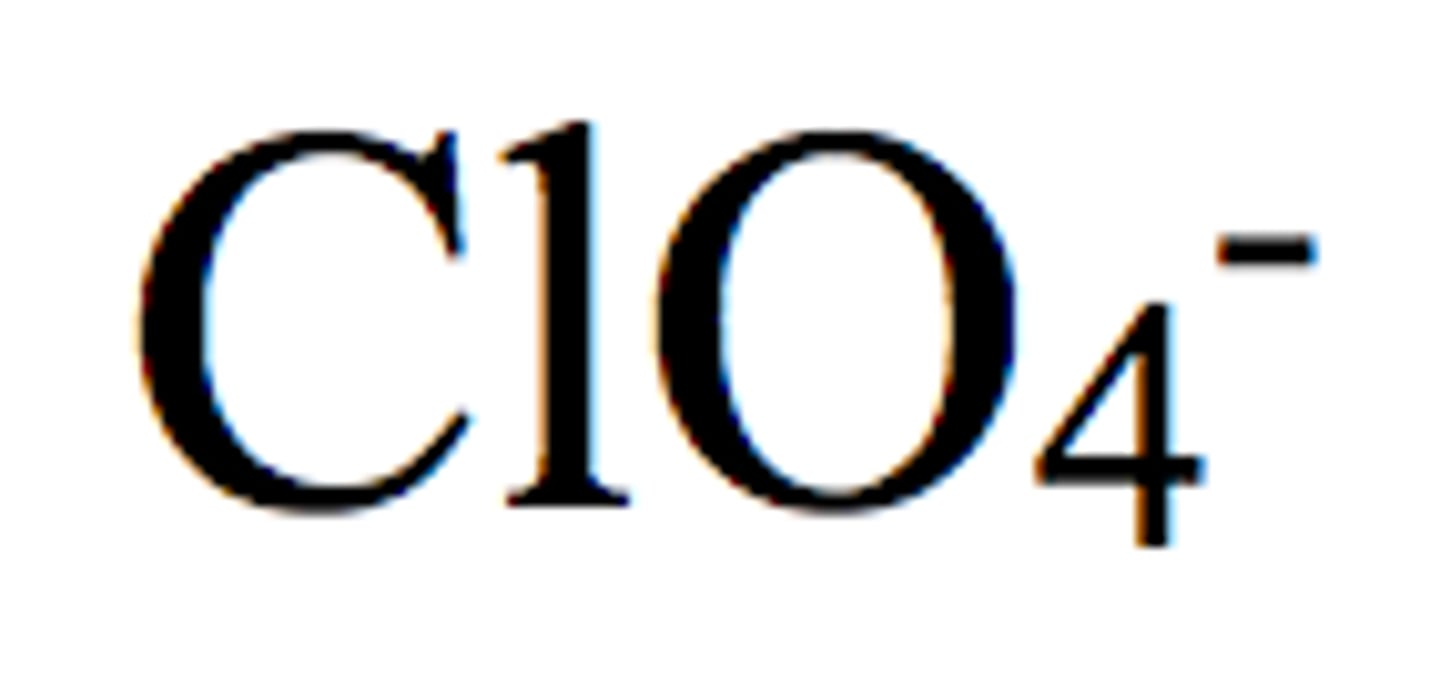
Nitrite
NO2-
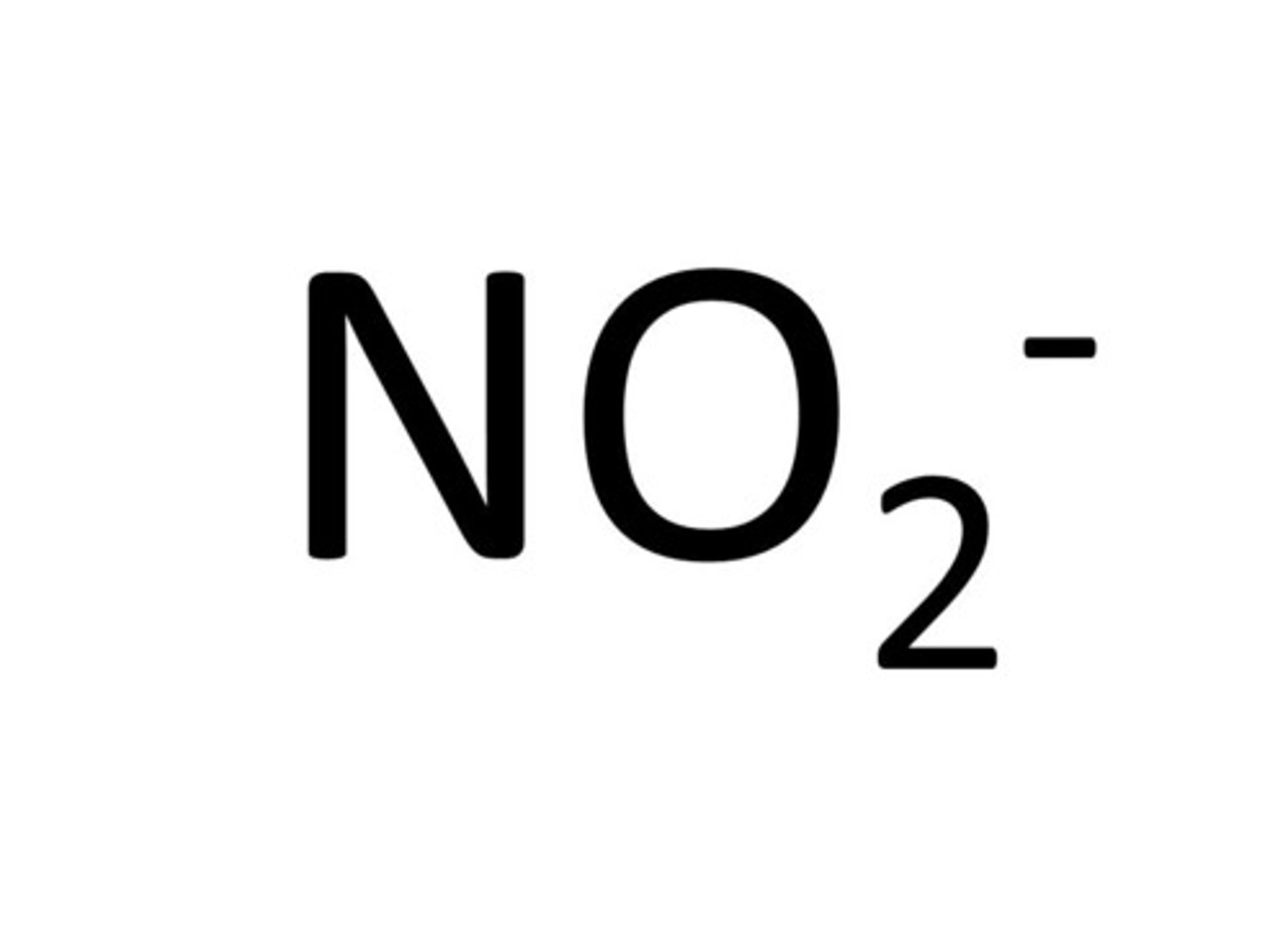
Nitrate
NO3-
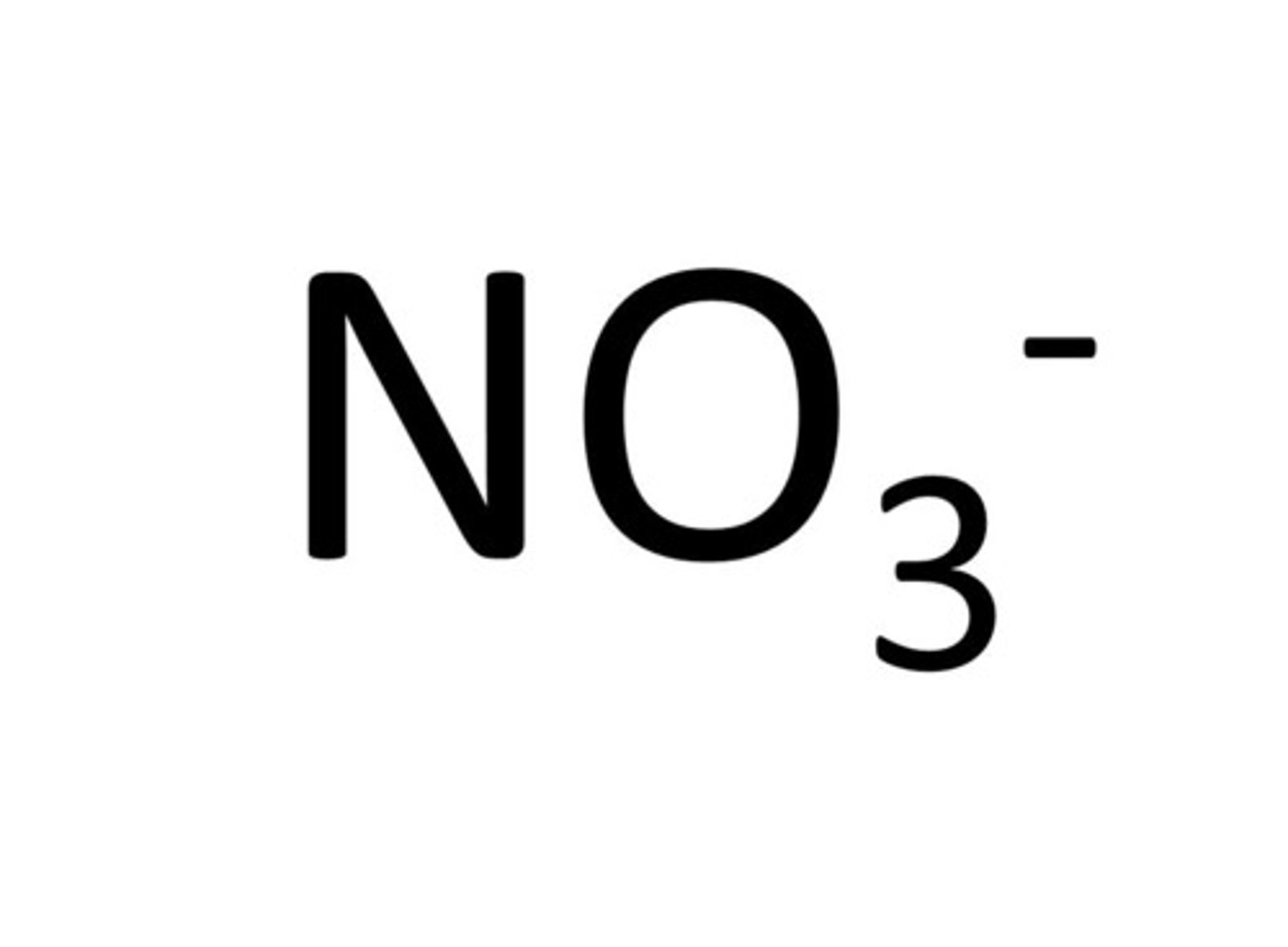
Phosphate
PO4 3-
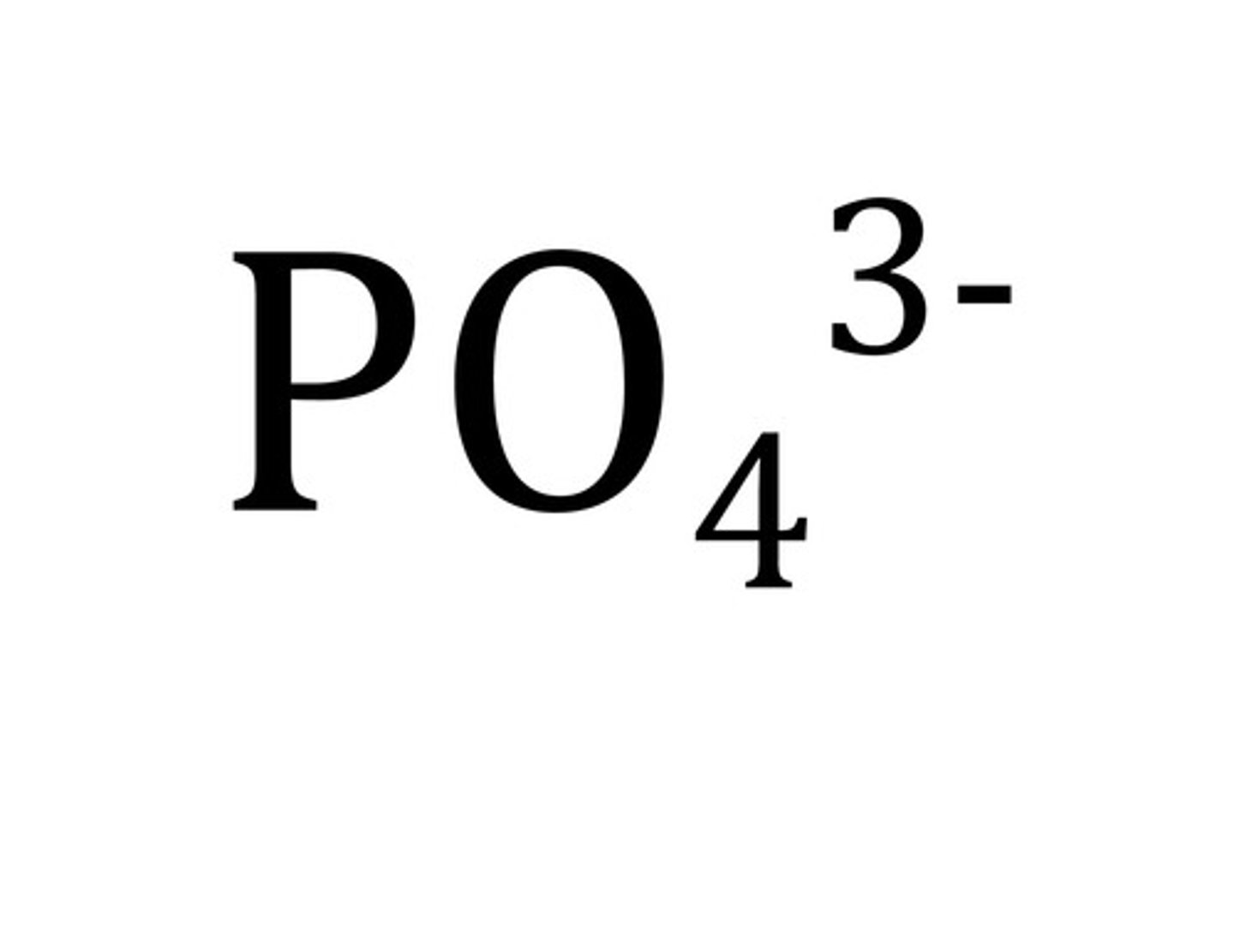
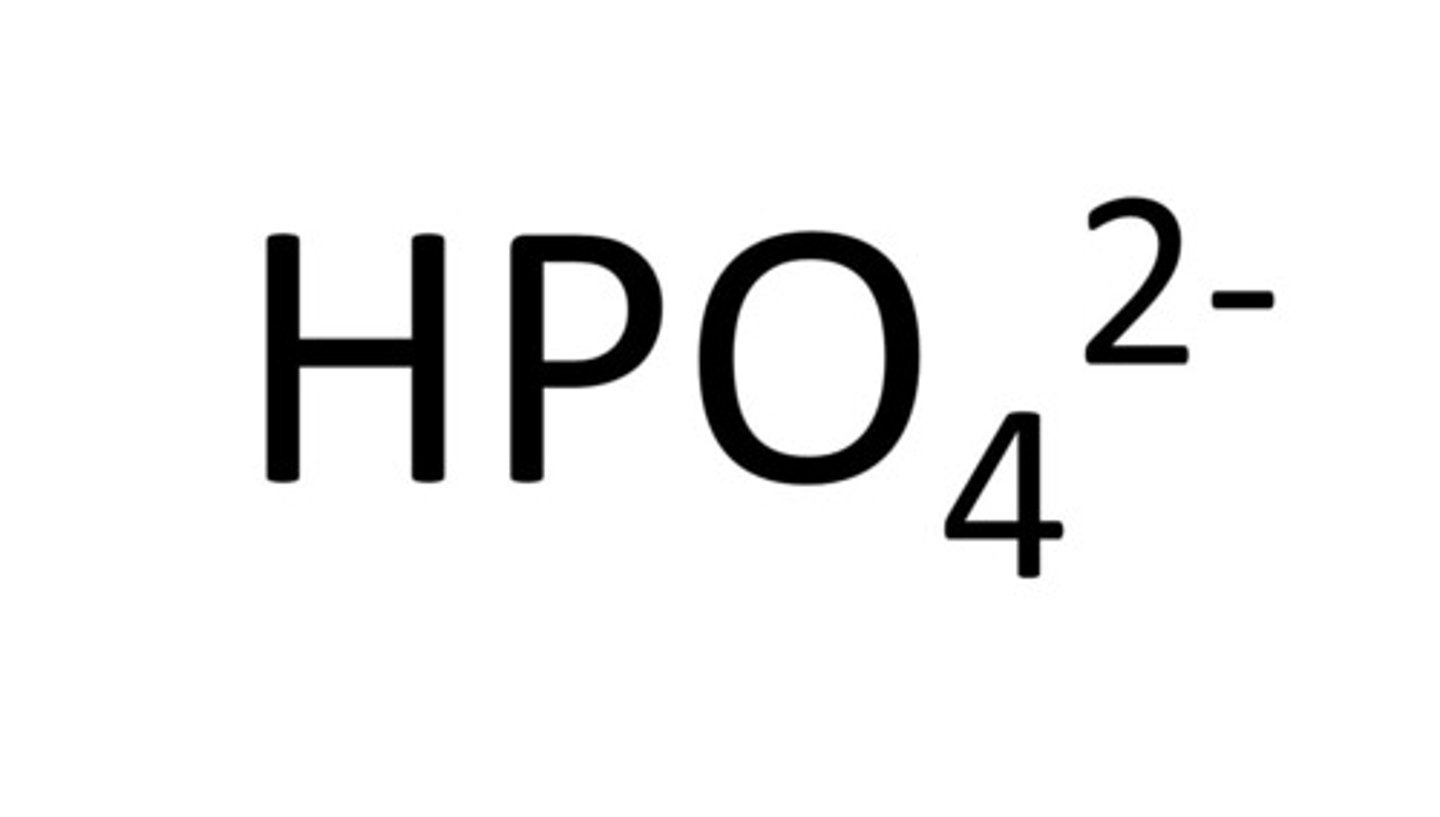
hydrogen phosphate
HPO4 2-
Dihydrogen Phosphate
H2PO4-
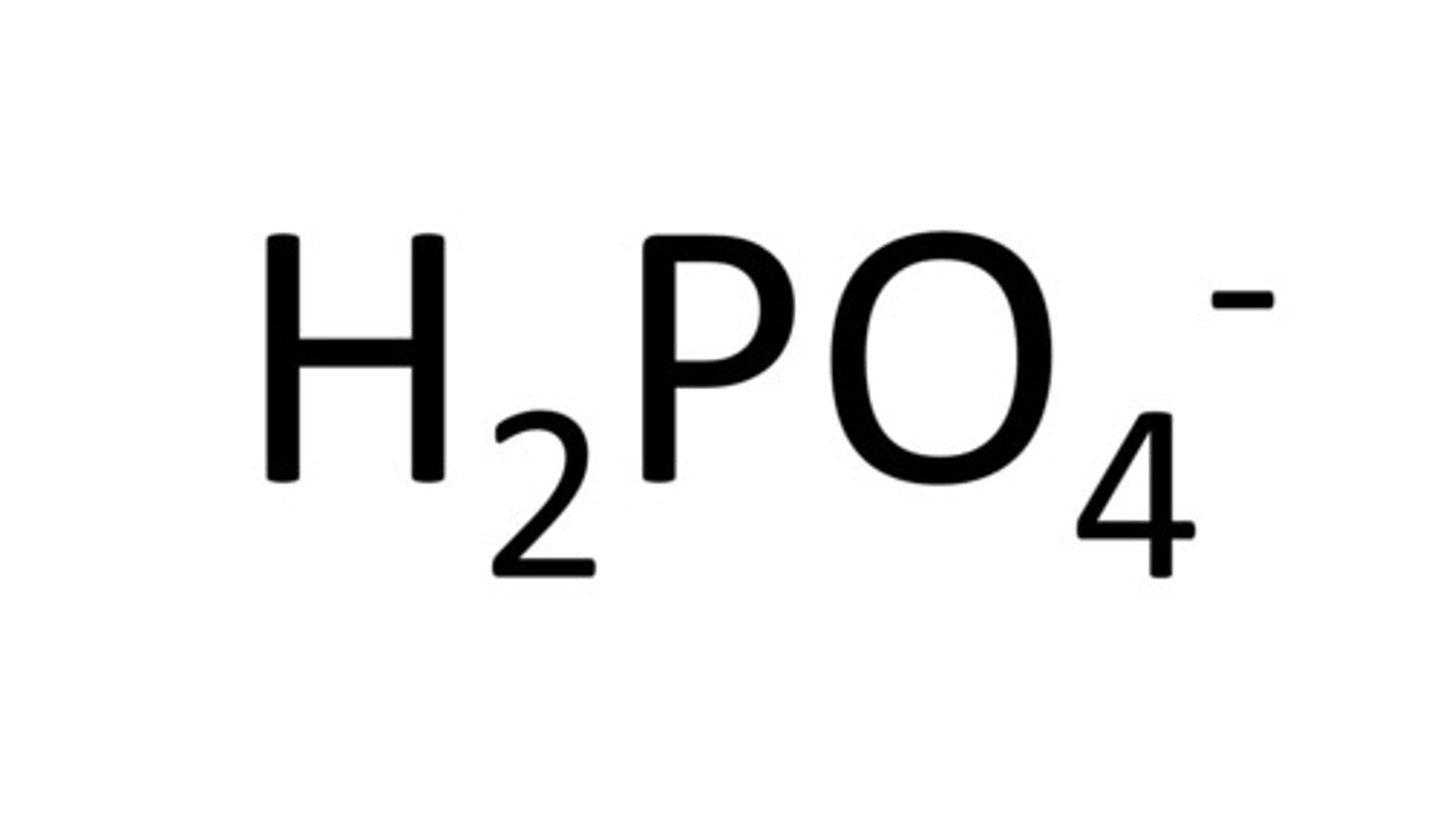
Chromate
CrO4 2-
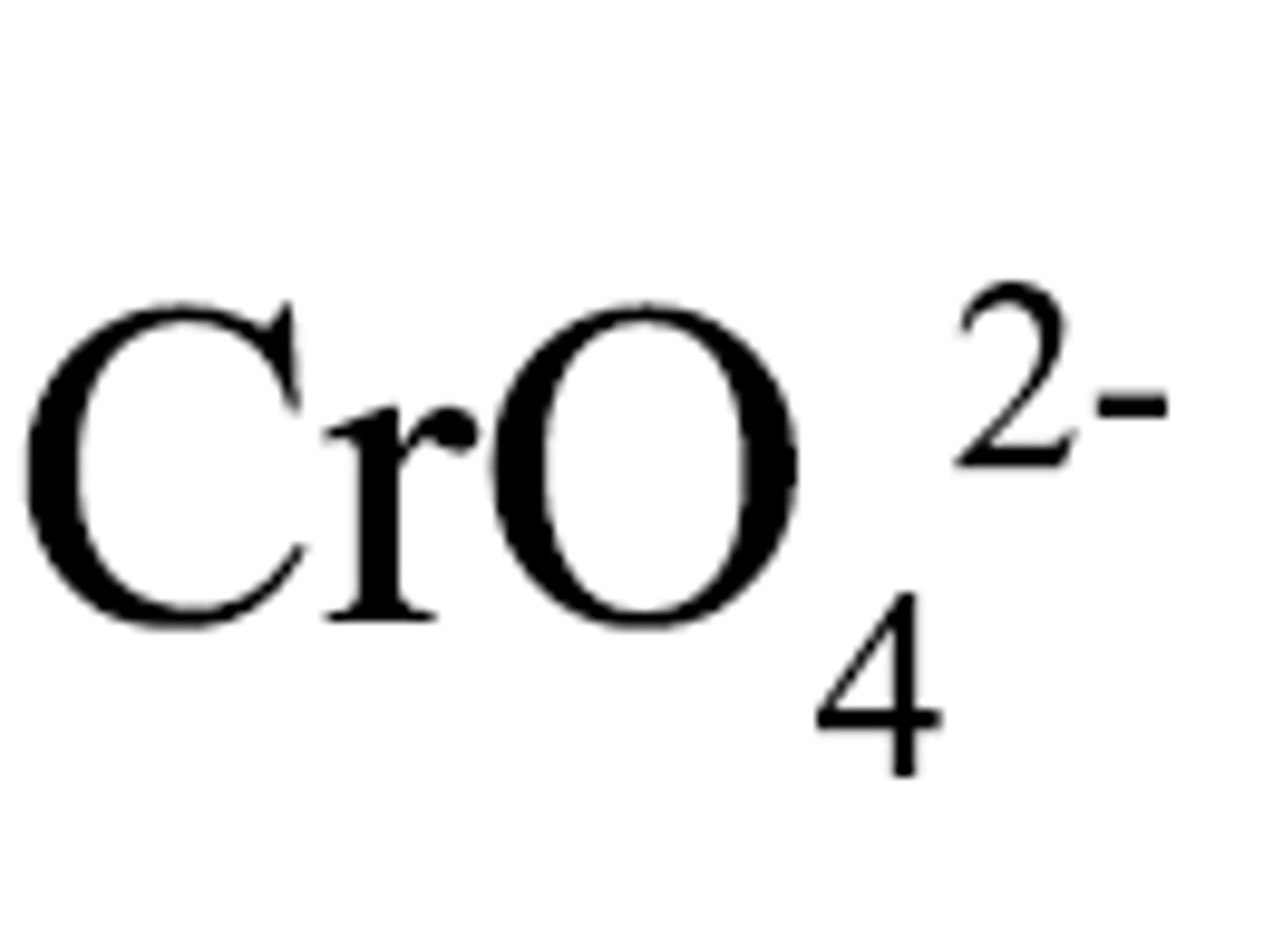
Dichromate
Cr2O7 2-
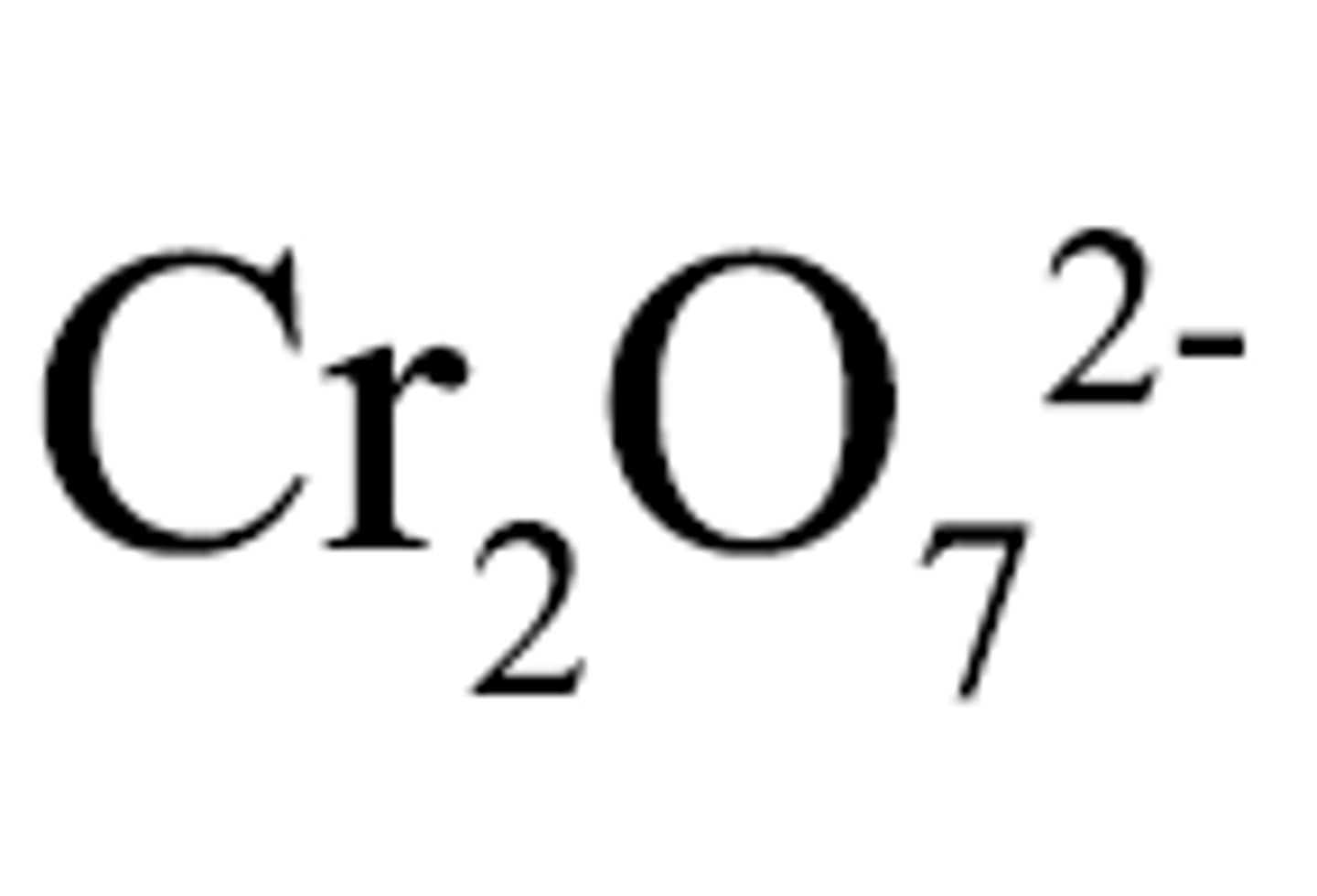
permanganate
MnO4-
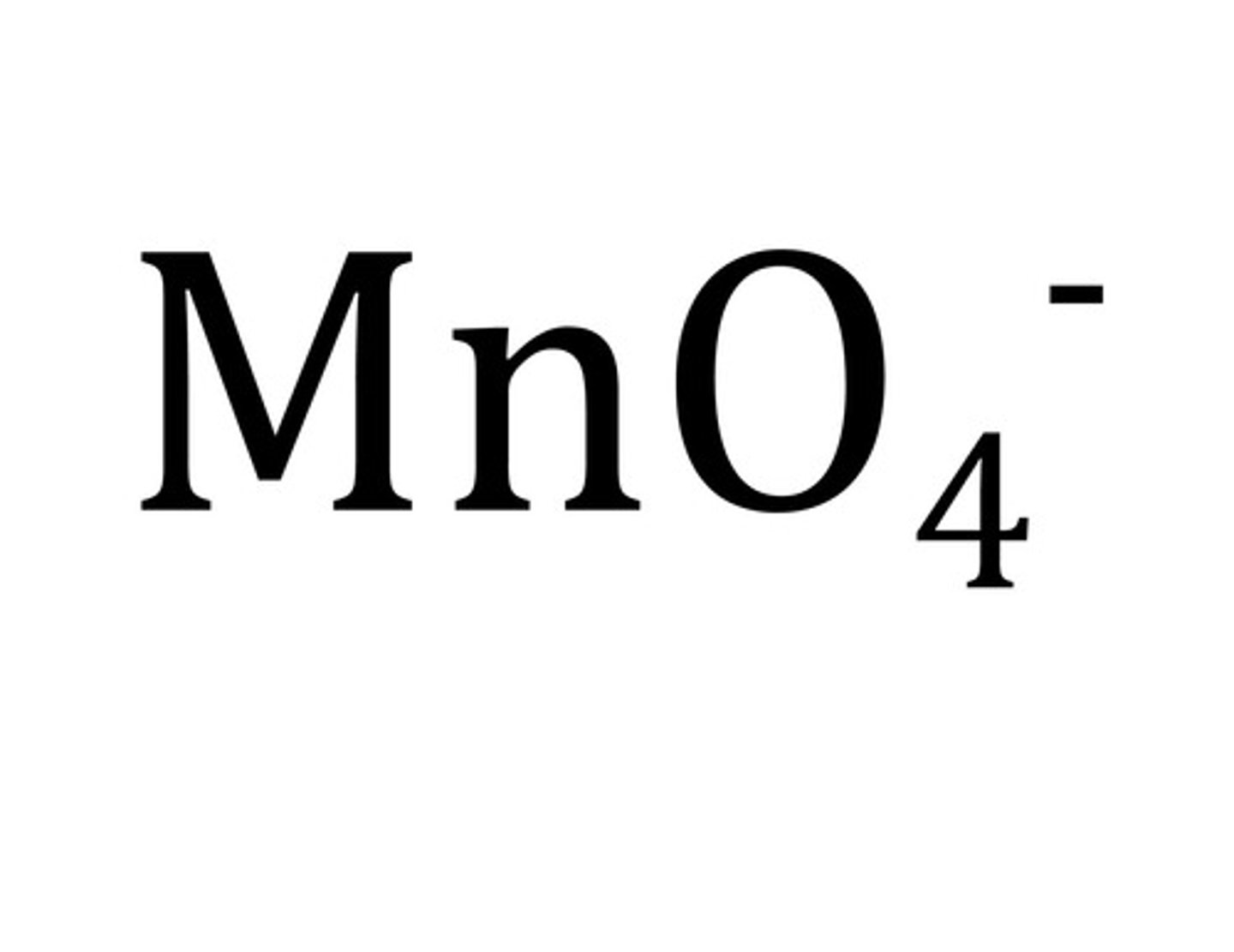
hydroxide
OH-
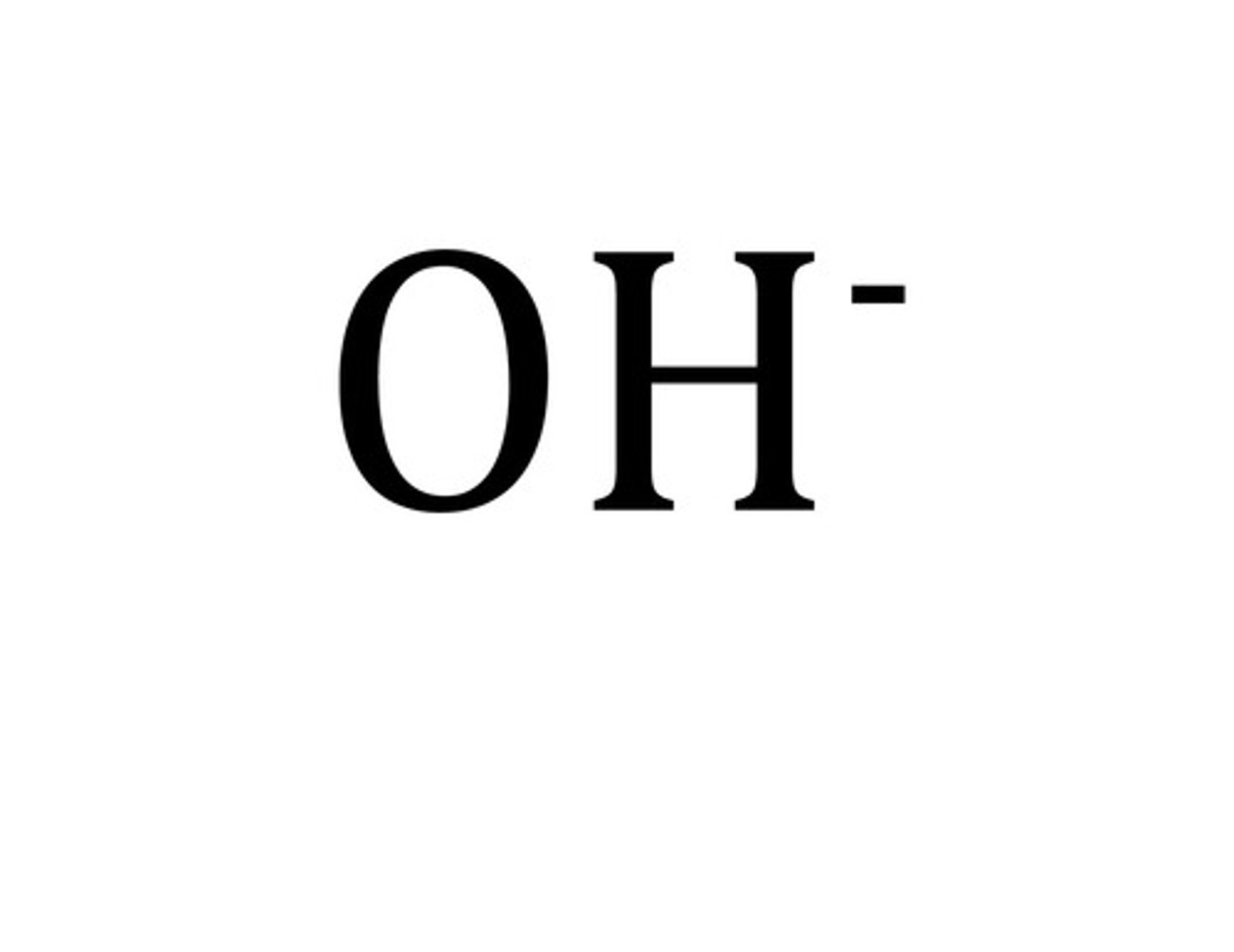
Sulfite
SO3 2-
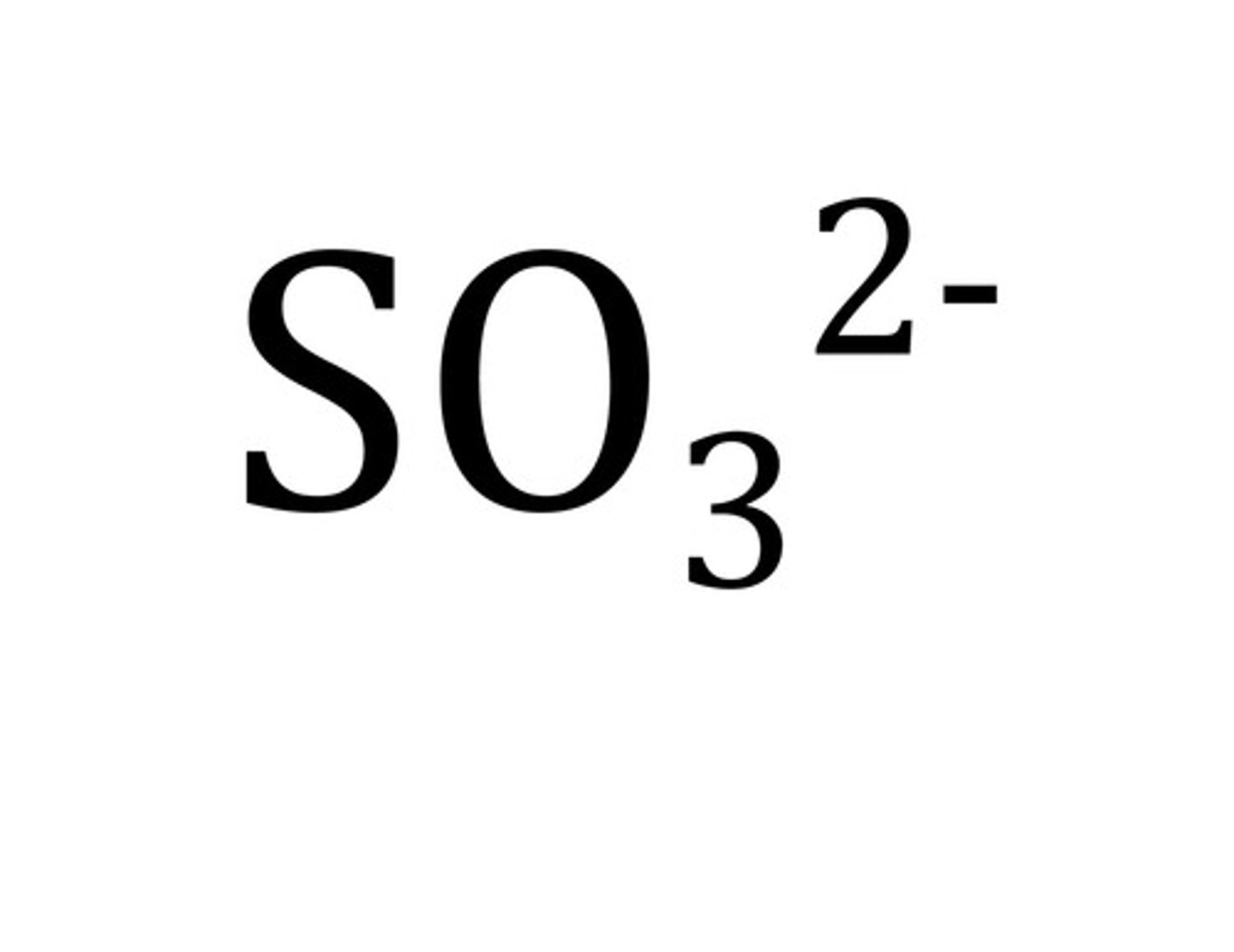
Sulfate
SO4 2-
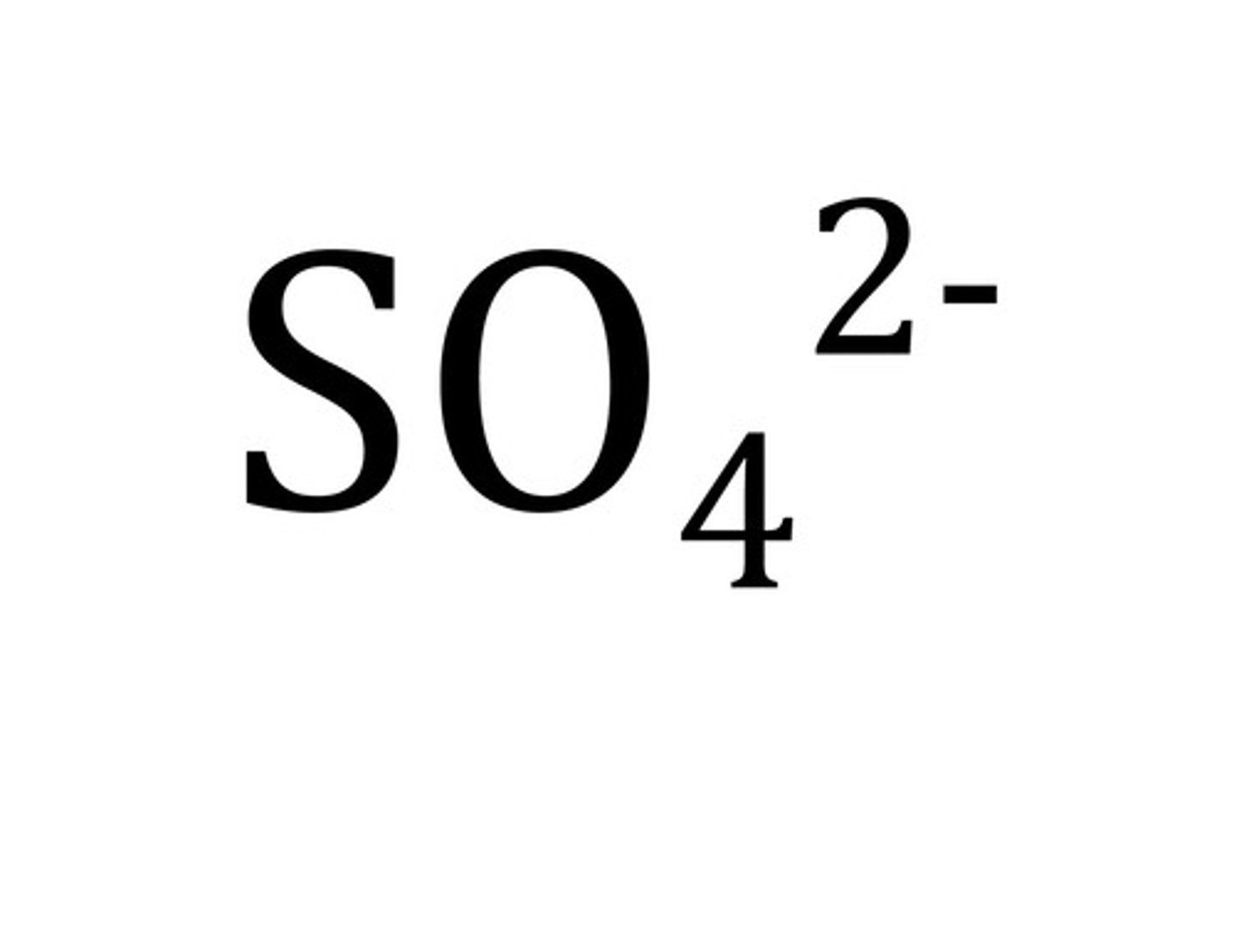
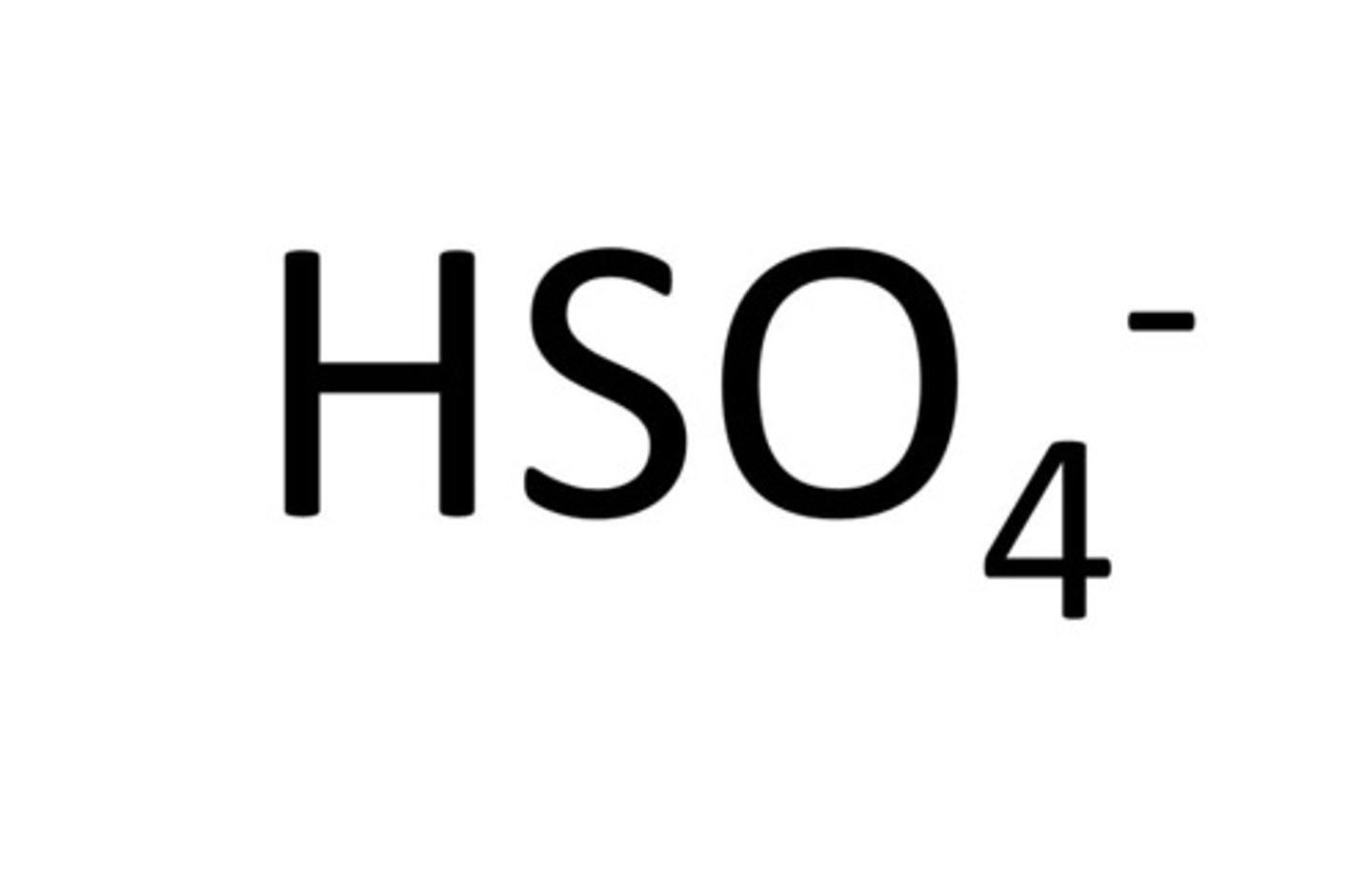
Hydrogen Sulfate
HSO4-
Polyatomic cations end in
ium
monoatomic anions end in
-ide
(cations/anions) go before (cations/anions) when forming equations
cations then anions
Ionic compouds are?
metals or NH4
Molecular compounds are?
nonmetals (2 or more)
moles equals
6.02 X 10^23 molecules/atoms
Mol to mass conversion
moles times grams/1 mol
mass to mol conversion
grams times mol/1 gram
percent composition formula
mass of element/mass of compound x 100
empirical formula
percent g times mol. molar mass in grams equals _____ mol, once all formulas composition is used then divide all by smallest amount of mols. These will be the lower subscript for the formula.
Molecular formula
molar mass g/mol divided by emperical formula mass=n. n is then multiplied by the original coefficents from the empirical formula
Solubility
if a substance is not soluble on the solubility chart, the product will form a solid)
Complete Ionic Equation (CIE)
every element written out besides the solids
net ionic equation (NIE)
formula left after spectator ions are removed from complete ionic equation
strong acids and bases __________ dissolve
completely
1 multiple choice option
weak acids and bases________ dissolve
do not completely
1 multiple choice option
Strong acids: Hydrochloric acid
HCl
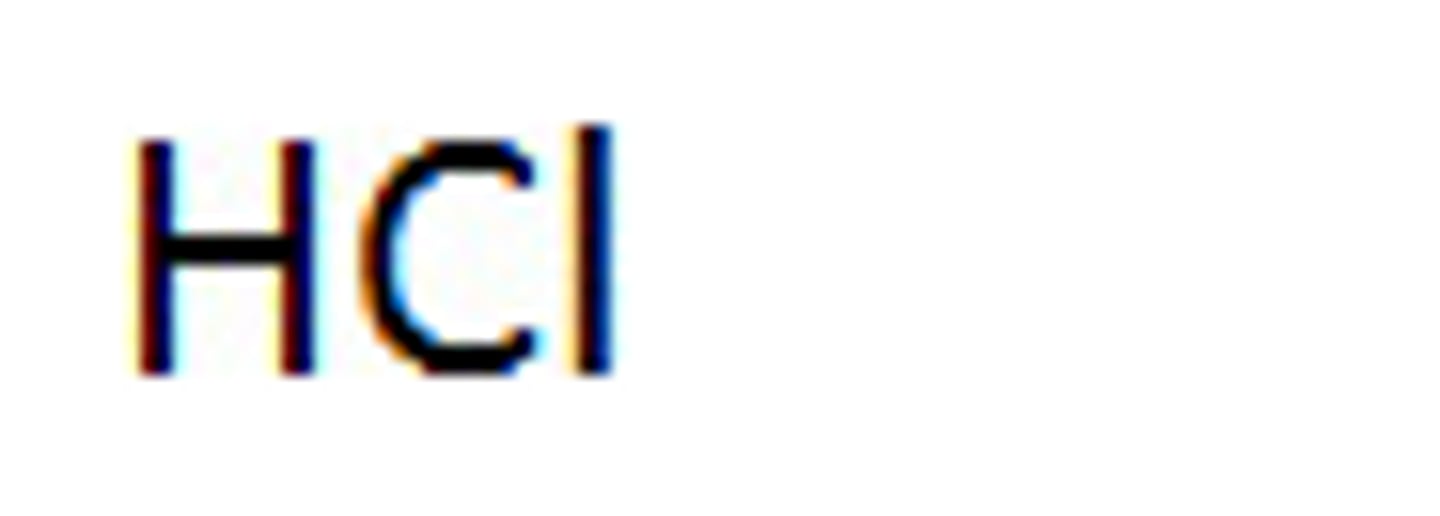
strong acids- hydrobromic acid
HBr
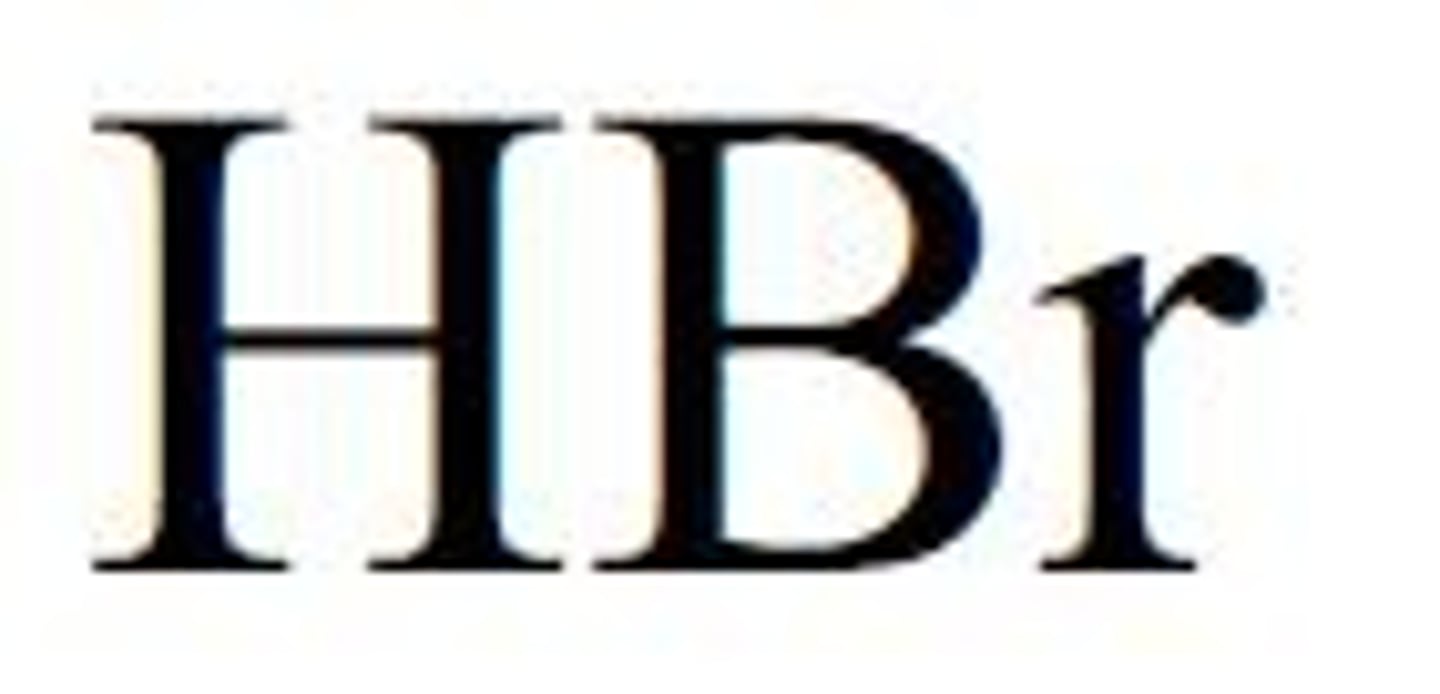
strong acids- Hydroiodic Acid
HI
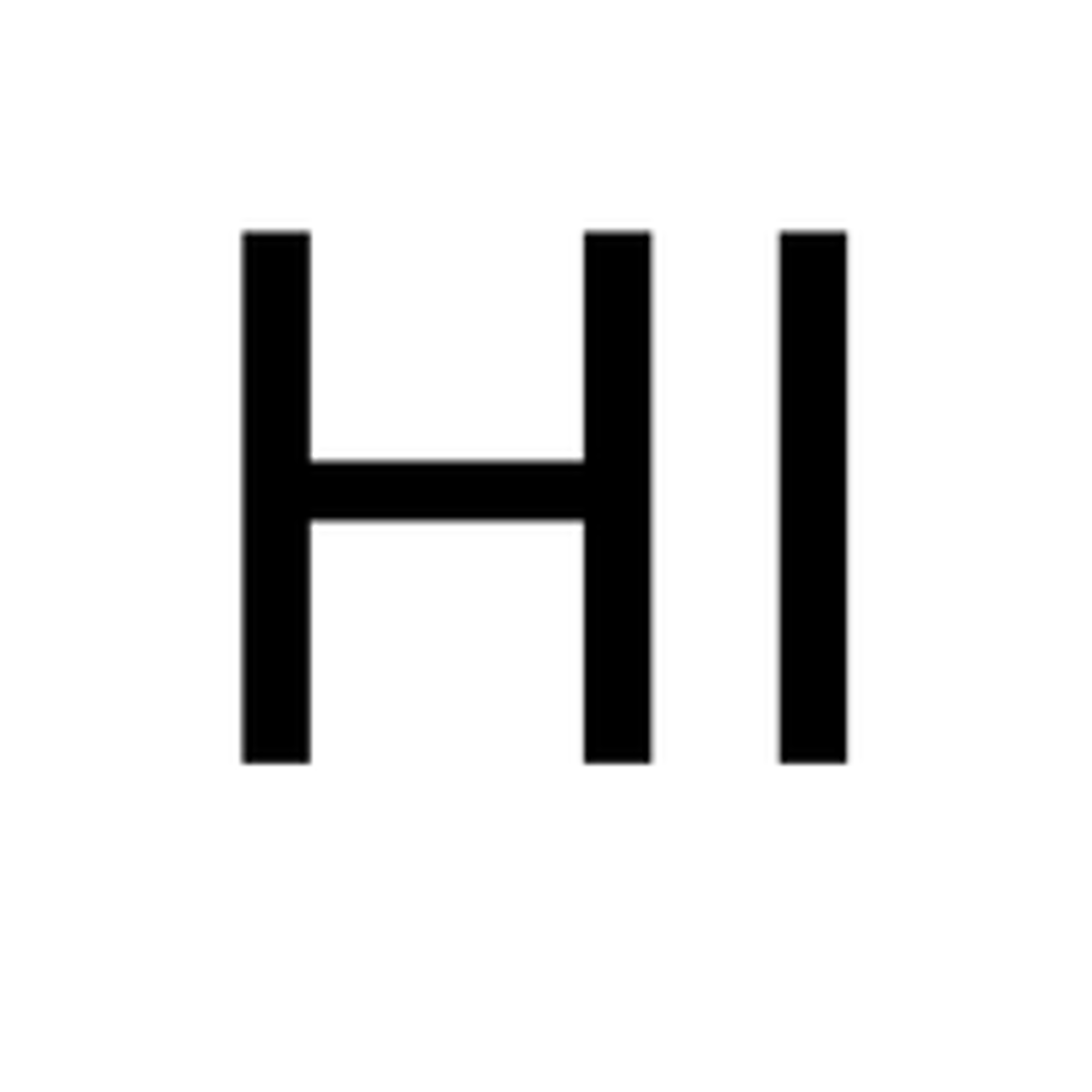
Strong acids: Nitric acid
HNO3
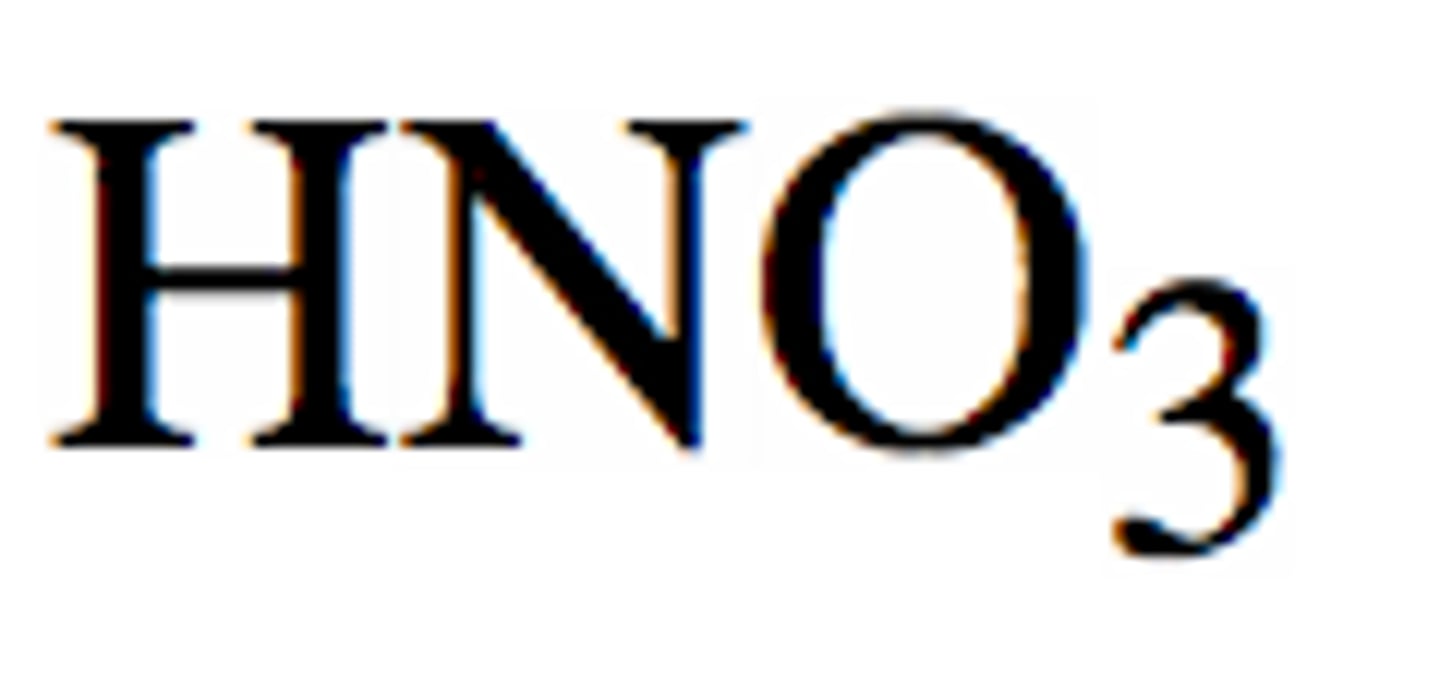
Strong Acids chloric acid
HClO3
Strong acids: Perchloric acid
HClO4
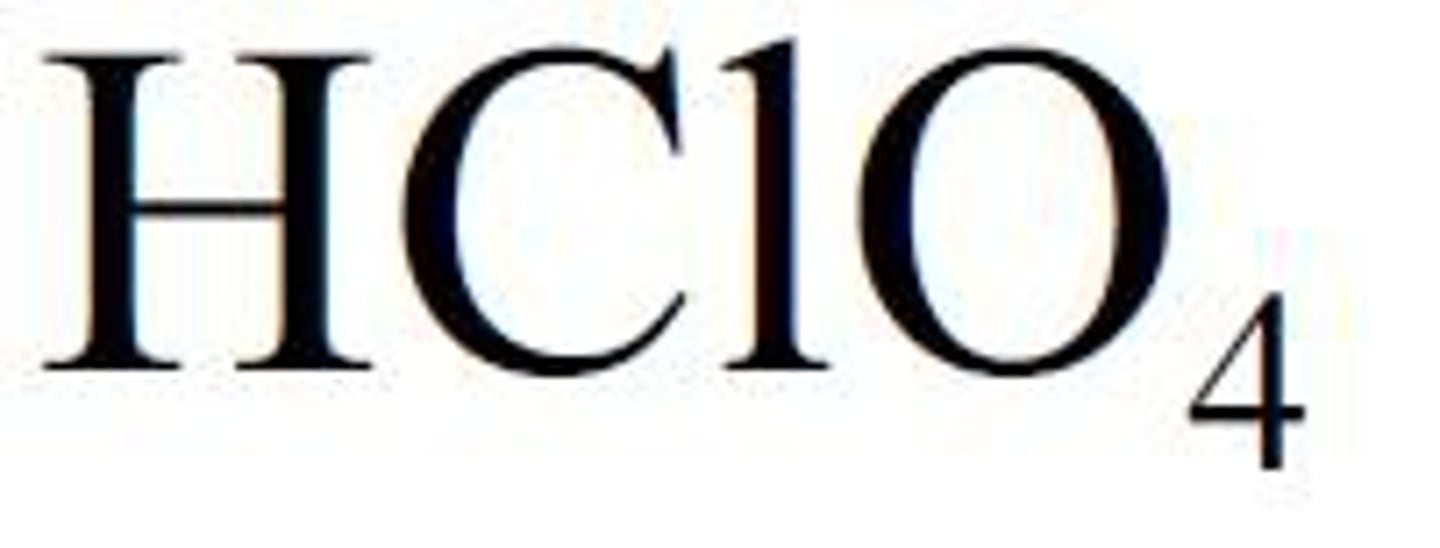
Strong acids: Sulfuric acid
H2SO4
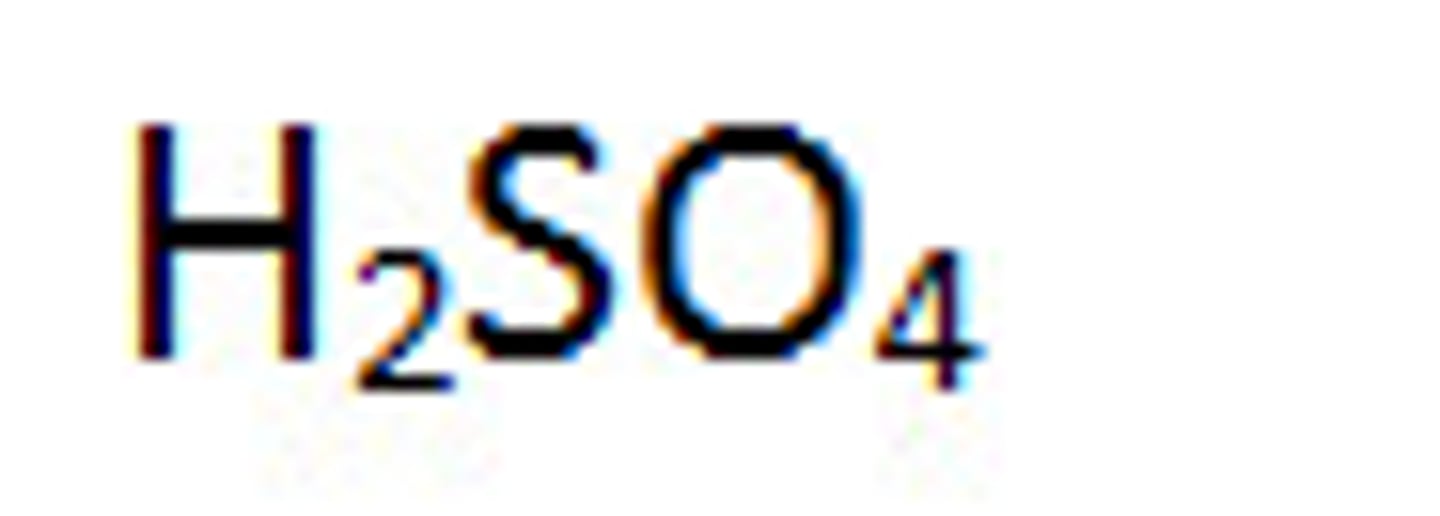
Weak Acid- Hydrofluoric
HF
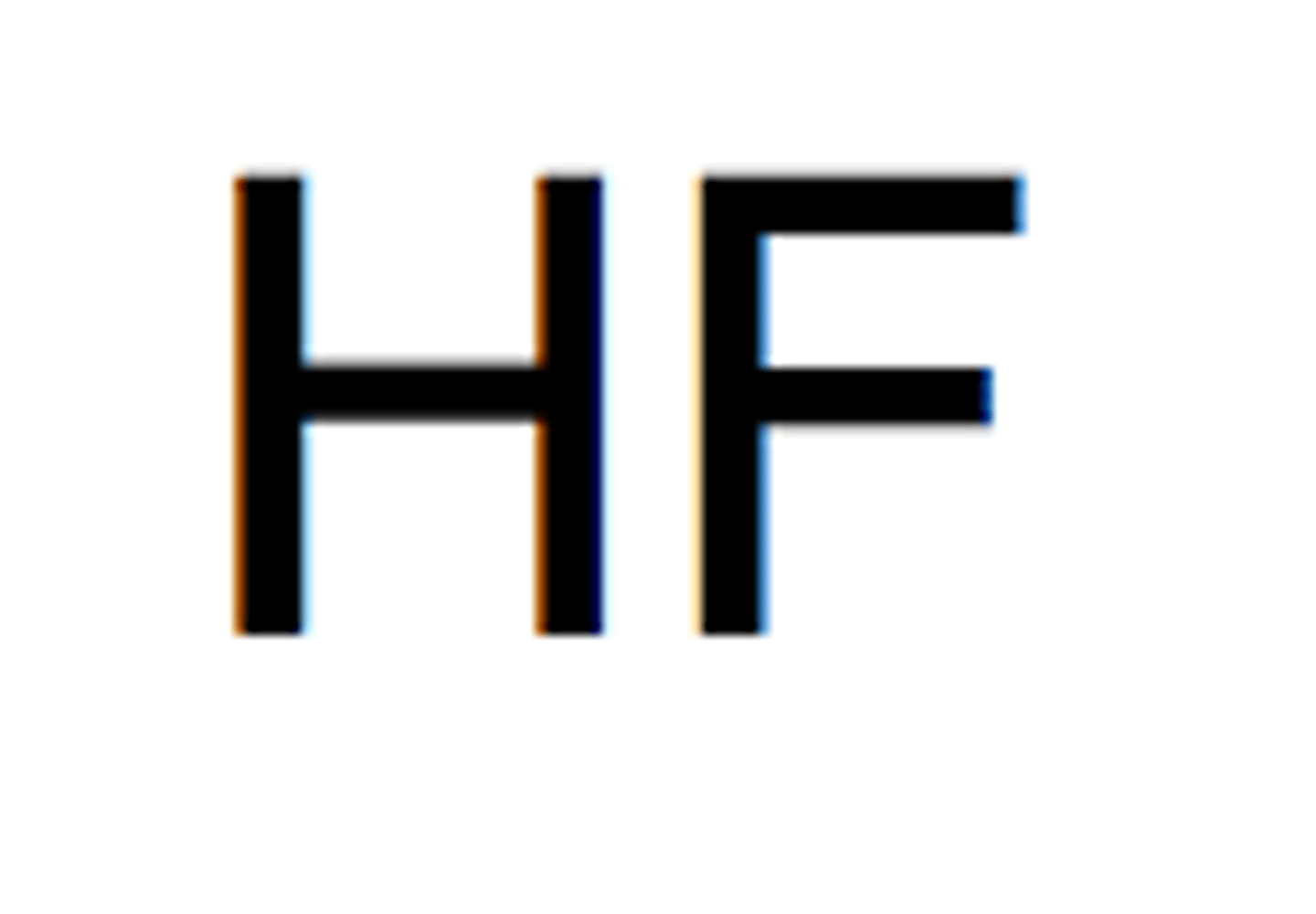
Weak Acid: Phosphoric Acid
H3PO4
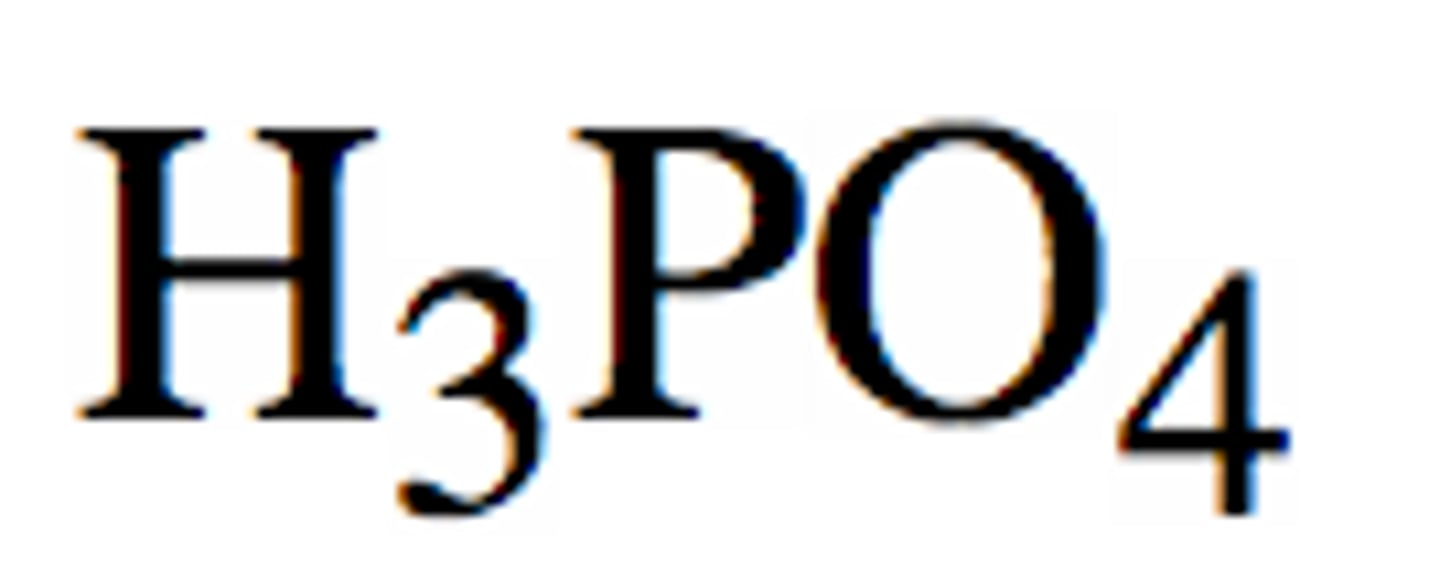
Weak Acid: Carbonic Acid
H2CO3
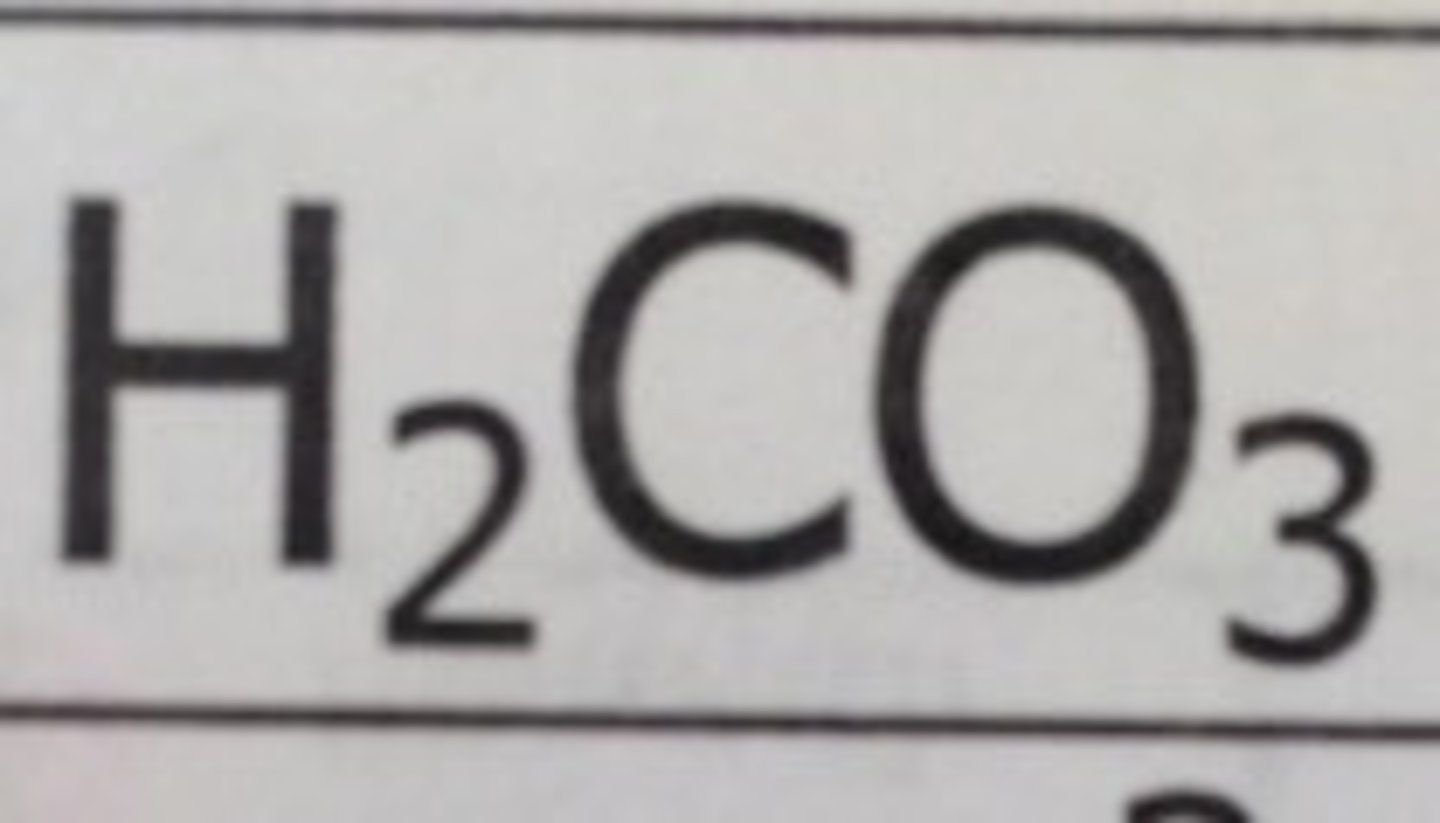
strong base lithium hydroxide
LiOH
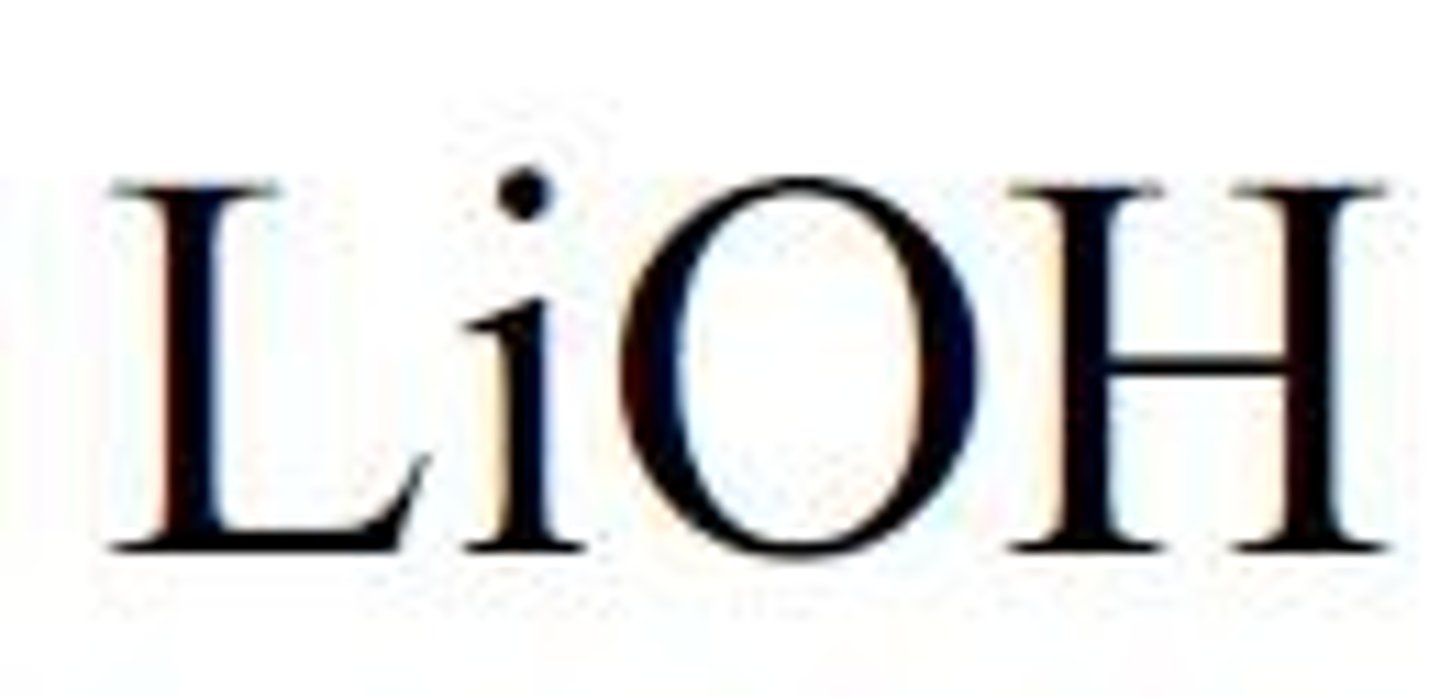
Strong Base: Sodium Hydroxide
NaOH
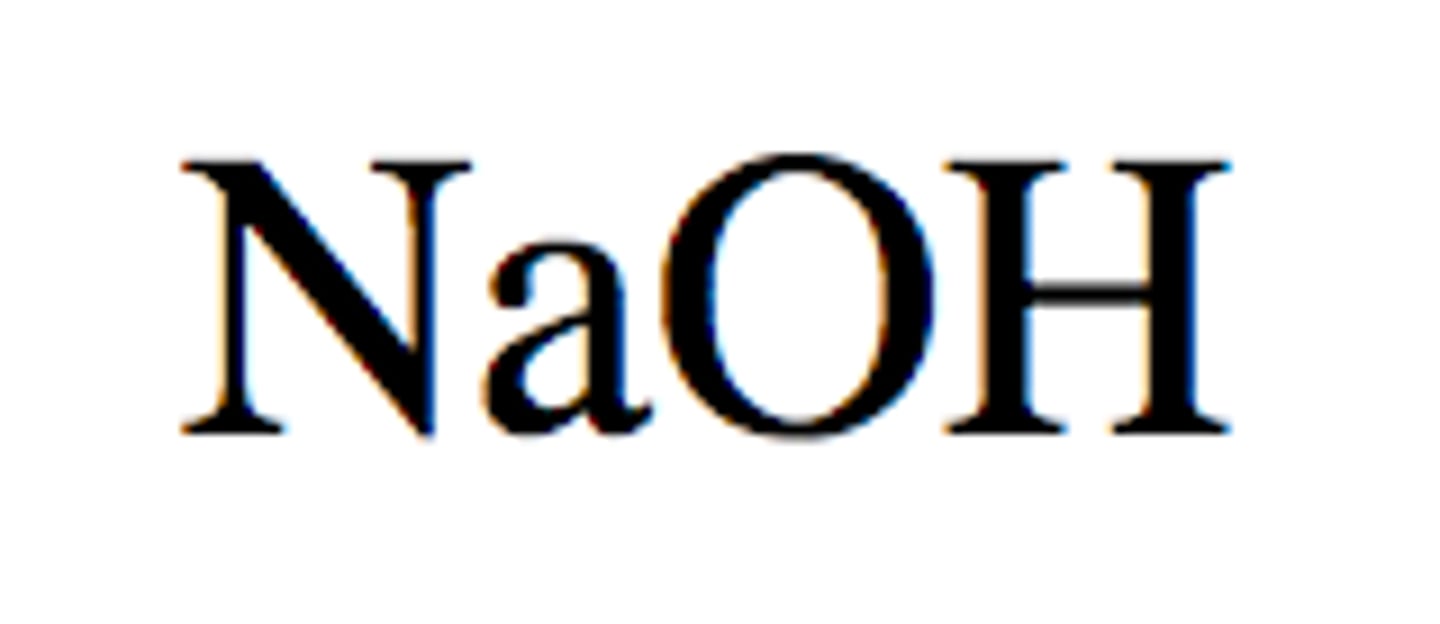
Strong Base: Potassium Hydroxide
KOH
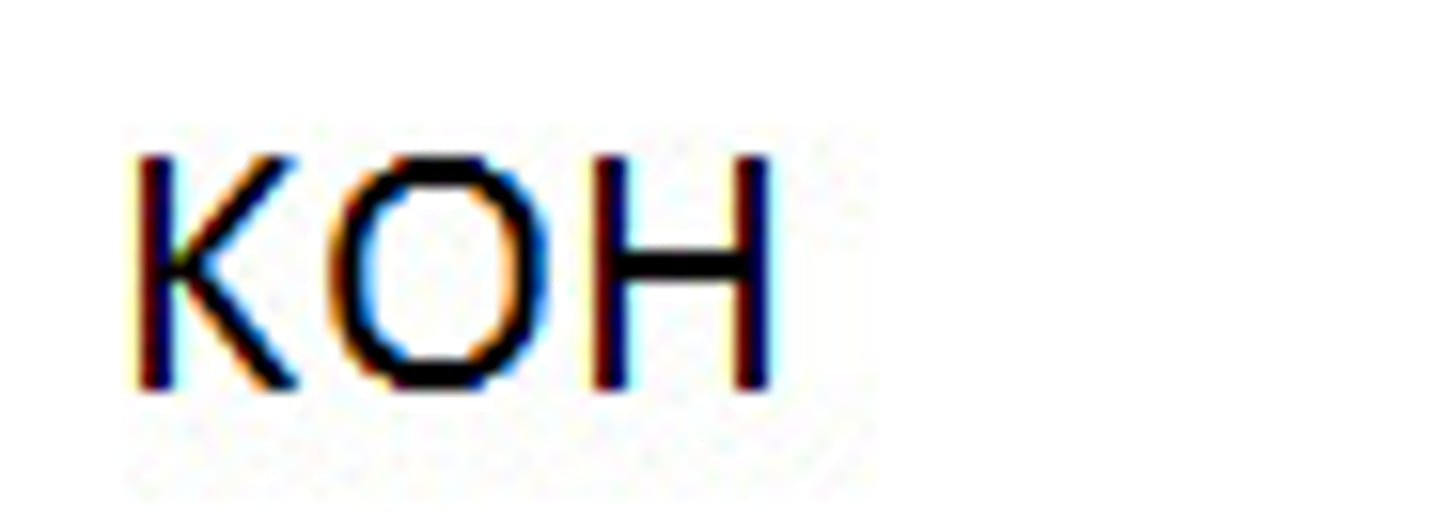
strong base barium hydroxide
Ba(OH)2
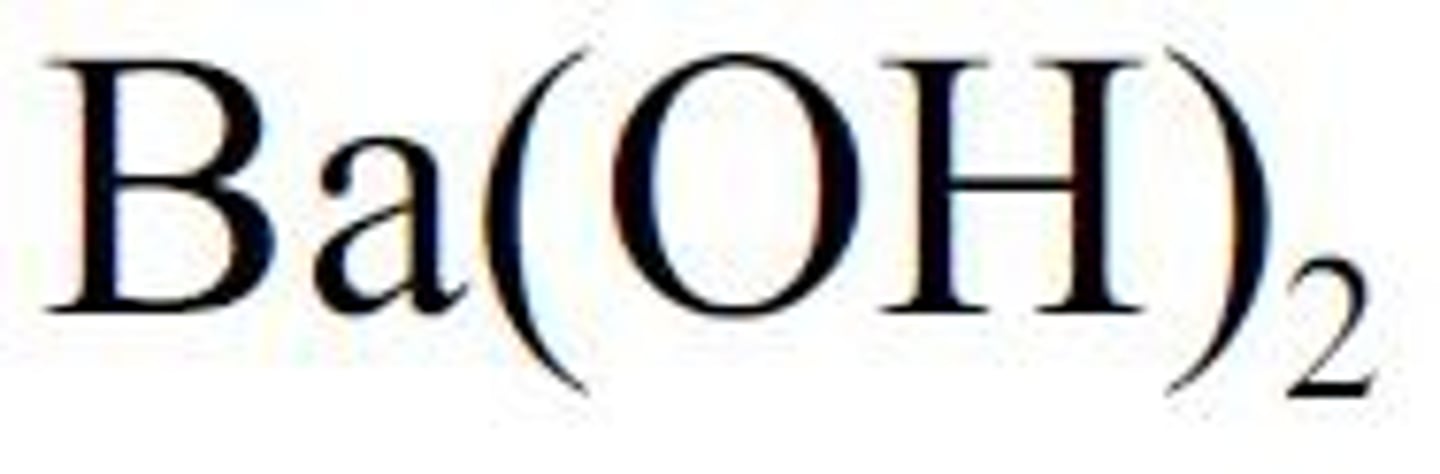
strong base strontium hydroxide
Sr(OH)2
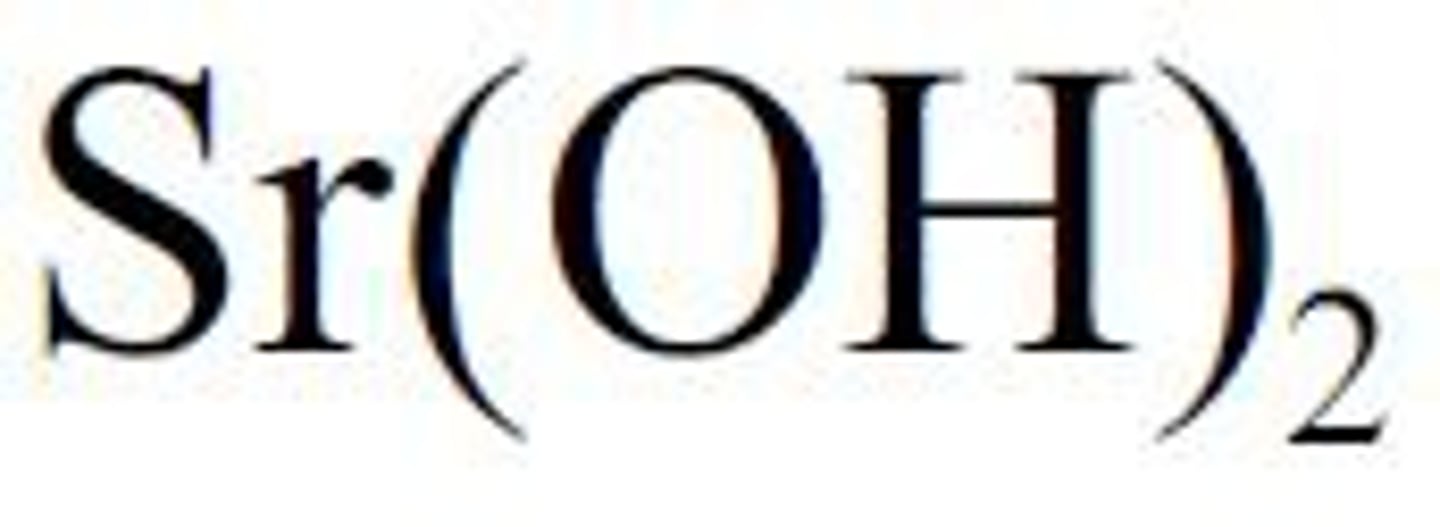
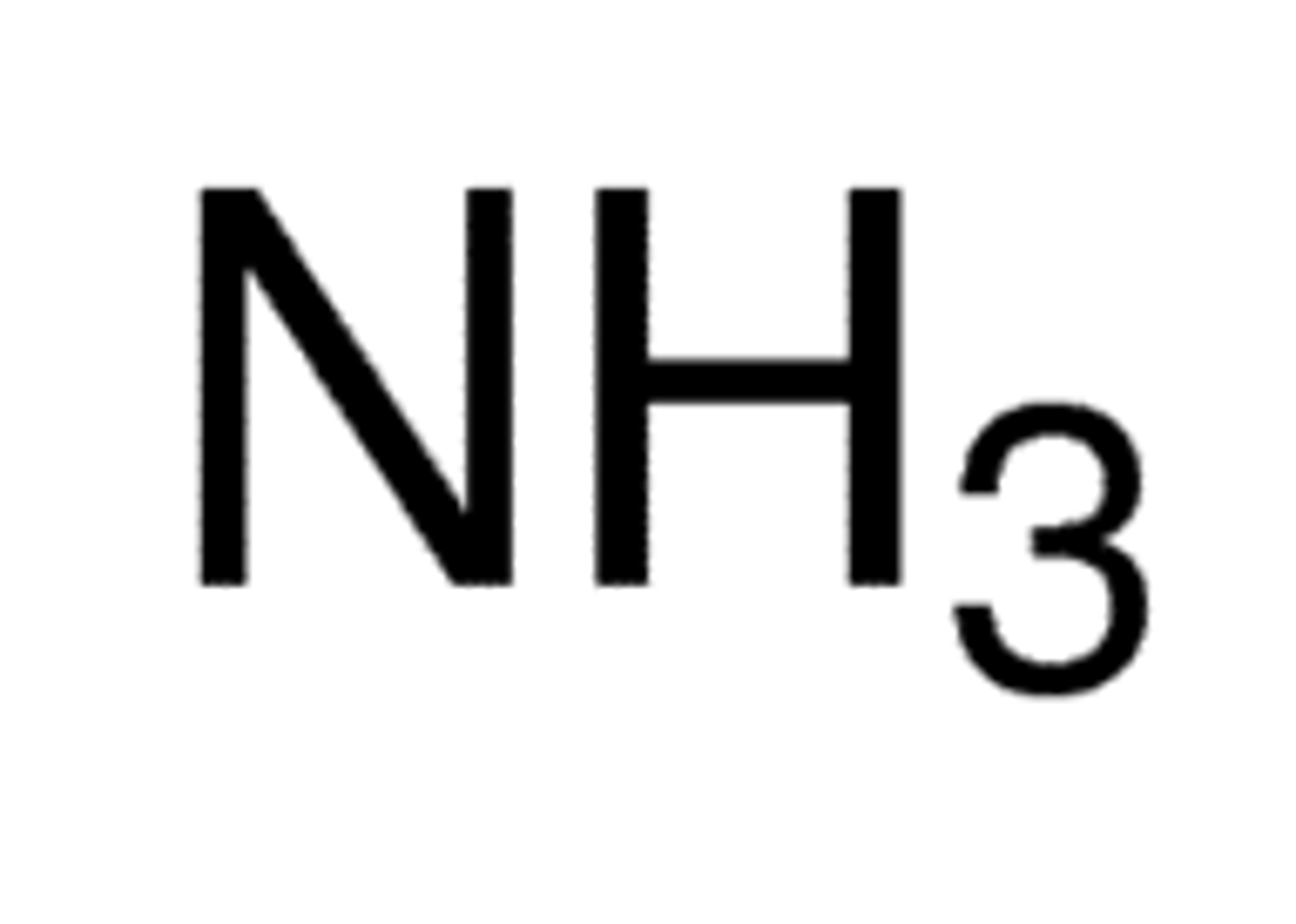
Weak Base: Ammonia
NH3
A acid_____ h+ ions
donates
a base ____ H+ ions
accepts
1 multiple choice option
a strong base/acid
dissociate completely
a weak base/acid
partial dissociates
OIL RIG stands for
Oxidation is loss of electrons
Reduction is gain of electrons
oxidizing agent
gains electrons (reduction)
reduction agent
loses electrons (oxidization)
Oxidation rules: Each atom in a pure substance has a ON of
0
Oxidation rules: monoatomic ions have a ON of
their individual charge
Oxidation rules: F is always
-1 except when other elements are involved
Oxidation rules: oxygen is often
-2
Oxidation rules: halogens have a ON of
-1 unless paired with F or O