Anatomy - Special Topics
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
What are the components of the thoracic cage?
12 thoracic vertebrae, 12 pairs of ribs, costal cartilage, and the sternum.
What makes up the floor of the thoracic cage?
diaphragm
What is the location of the sternal angle?
at 2nd rib/costal cartilage or T4-T5
Which of the following is not something the sternal angle marks?
the costochondral junction
The are _____ true ribs and _____ false ribs.
7 (1-7): 5 (8-12 with 11/12 floating)
Normal ratio AP:ML =
1:2
What is the primary function of the thoracic wall?
protects the heart, lungs, and some abdominal organs while providing movement and muscle attachment.
The 1st sternocostal joint is ________ while the 2nd-7th are _________.
cartilaginous; synovial
The sternocostal joints are supported by which ligaments?
sternocostal ligaments
The costochondral joints are bounded by which structure?
periosteum
The costotransverse joints are supported by which ligaments?
costotransverse ligament
The ligaments associated with the costovertebral joint are called:
radiate & intra-articular
Which of the following correctly describes the 1st rib?
Flat, broad, and short with grooves for subclavian vessels and tubercles for anterior and middle scalene
Which of the following correctly describes the 2nd rib?
thinner, less curved, longer
ribs 2-9 have
2 facets (typical)
Ribs 1, 10-12 have
1 facet (atypical)
All ribs have tubercle for articulation with transverse processes of corresponding vertabrae except?
11-12
Match the bony landmark with the correct general location:
spine of scapula = T3
inferior angle = T7
iliac creat = L4
Which of the following muscles acts primarily on the upper extremity but can assist in respiration?
pectoralis major
Which muscle protracts the scapula but also functions as an accessory inspiratory muscle?
Serratus anterior
Which muscle(s) are often hypertrophied in persons with chronic pulmonary disease also assist with accessory respiration?
scalenes
The internal thoracic artery runs inbetween the:
transverse thoracic
external intercostal
11 pairs: run obliquely medial and inferiorly
internal intercostal
11 pairs, run obliquely lateral and inferiorly

A/C =
external intercostal and internal intercostal interchondral part = elevation.
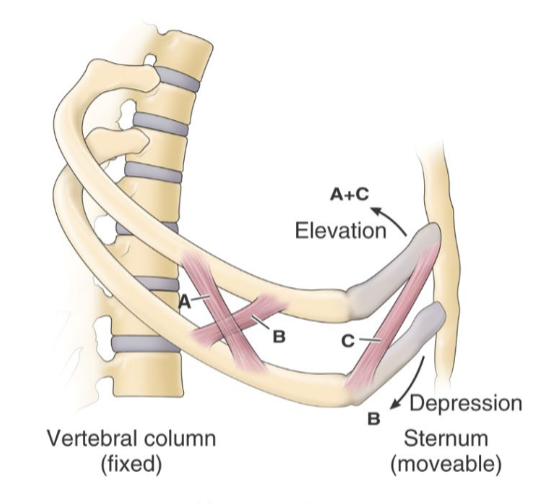
B =
internal intercostal interosseous part = depression
The _______ are located in the intercostal space and they are tucked within _________.
intercostal vein, artery, and nerve; intercostal groove
bucket handle movement invloves
ribs 7-10 extending laterally
pump handle movement involves
ribs 1-6 pushing forward
The endothoracic fascia is firmly attached to which structure?
Thoracic wall
The parietal pleura attaches to ______ and is ________.
endothoracic fascia; highly vascularized
The visceral pleura attaches to _____ and is _______.
lungs; not vascularized
What is the function of the pleural cavity?
serves as space for lung expansion and contains serous fluid to reduce friction
Contraction and descent of the diaphragm in inspiration results in:
increase in thoracic cage volume
inspiration is typically a(n) ______ process and expiration is typically a(n) _______ process.
active; passive
The primary muscles for inspiration are
diaphragm, intercostals, and scalenes
The accessory muscles for inspiration are:
SCM, serratus anterior, pec maj/min, trapezius, erector spinae
During forced expiration, which muscles raise intra-abdominal pressure to expel air?
abdominals
How many pairs of thoracic spinal nerves supply the thoracic wall?
12
The ventral rami of T1–T11 form which nerves?
Intercostal nerves
The ventral ramus of T12 is known as the:
Subcostal nerve
The dorsal rami pass posteriorly to supply
joints, deep back muscles and skin of back in T region
The posterior intercostal arteries arise from which vessel?
the aorta
The anterior intercostal arteries are branches of which artery?
Internal thoracic artery
The diaphragm is innervated by the:
phrenic nerve (C3-C5)
The diaphragm’s central tendon fuses with the:
fibrous pericardium
superior mediastinum
above sternal angle
inferior mediastinum
below sternal angle
The inferior mediatinum is divided into
anterior, middle, and posterior parts.
The ________ lung has 3 lobes divided by a horizontal and oblique fissure and _______ lung has 2 lobes divided by an oblique fissure.
right; left
upper respiratory track:
nose → larynx
lower respiratory track:
trachea → alveoli
What are the two parts of the lower respiratory tract?
tracheobronchial tree and termial repiratory units
Which of the following best describes the tracheobronchial tree?
conducting airways not involved in gas exchange, including the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
What are bonchopulmonary segments?
unit of lung that is structurally separate and functionally independent (supplied by one segmental bronchus, and its own artery, vein and nerve)
parasympathetic stimulation of the lungs results in
bronchoCONSTRICTION and increased mucus secretion.
sympathetic stimulation of the lungs results in
bronchoRELAXATION and decreased mucus secretion.
What is the function of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)?
It is a mixed nerve responsible for sensory and motor functions, particularly mastication.
What are the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve?
V1 (Ophthalmic), V2 (Maxillary), V3 (Mandibular).
Which branch of the trigeminal is the only one to include sensory AND motor?
V3 (Mandibular)
The V3 Mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve provides motor to which mastication muscles:
Masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid, and lateral pterygoid.
What is the role of the masseter muscle?
It closes the jaw and elevates the mandible.
Which nerve innervates the muscles of mastication?
Mandibular nerve (V3) from the trigeminal nerve.
What is the function of the masseter?
closes jar and elevates mandlible
What is the function of the temporalis?
closes jaw and elevates mandible
What are the primary actions of the medial pterygoid muscle?
elevates mandible
What are the primary actions of the lateral pterygoid muscle?
Protrudes and depresses the jaw
swings jaw to CONTRA side
How is the facial cranial nerve (CN VII) classified?
It is a mixed nerve with sensory and motor functions.
The sensory part of the of the facial (CN VII) supplies
taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue
Which nerve of supplies taste to posterior 1/3 of tongue?
glossopharygneal CN IX
What nerve is supplies taste to epiglottis?
vagus nerve (CN X)
The motor part of the of the facial CN VII supples
muscles of facial expression
What are the muscle groups controlled by the facial nerve?
Muscles of facial expression, including the orbicularis oculi and zygomaticus.
What does Bell's palsy affect?
It involves a lesion of the facial cranial nerve, affecting facial muscles.
What lesion of motor neuron if Bell’s Palsy considered?
lower motor neuron lesion
Name two key facial expression muscles.
Orbicularis oris and zygomaticus.
Which cranial nerve is responsible for taste in the anterior two-thirds of the tongue?
Facial nerve (CN VII).
What are the muscles responsible for mouth movement?
Zygomaticus major, zygomaticus minor, and risorius.
What is the orientation of muscle fibers in facial expression muscles?
They are oriented perpendicular to the skin, causing wrinkles.
Describe the temporalis muscle's main function.
It closes the jaw and elevates the mandible, being a primary retractor.
What connections does the platysma have?
It stretches from the mandible to the skin and fascia in the neck.
The heart is located in the
middle mediastinum below the sternal angle
The base of the heart is located near
the 3rd rib
The apex of the heart is located near
the 5th rib
The anterior portion of the heart is mostly made up of the
right ventricle and right atrium
The diaphragmatic portion is made up of
the left and right ventricles
The lateral portion is made up of
the left ventricle
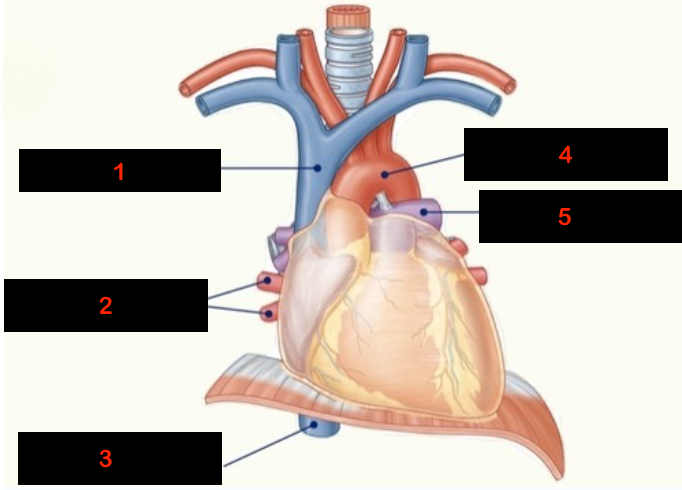
1
superior vena cava

2
pulmonary veins
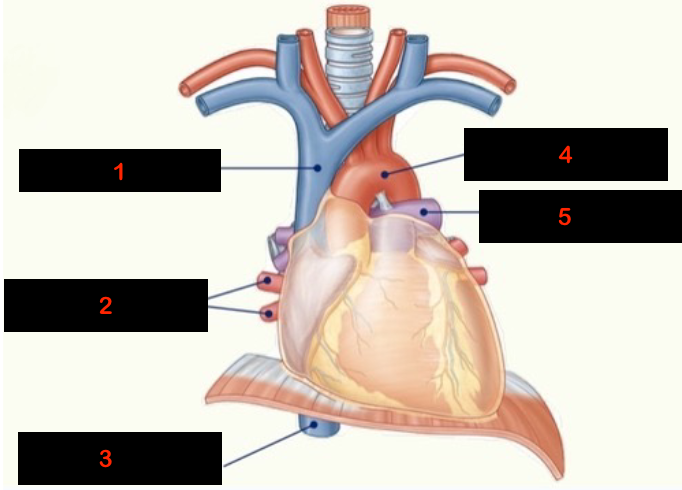
3
inferior vena cava
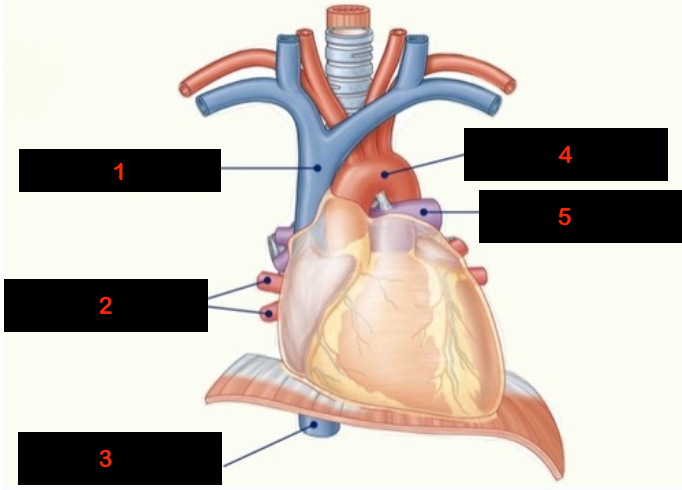
4
aorta
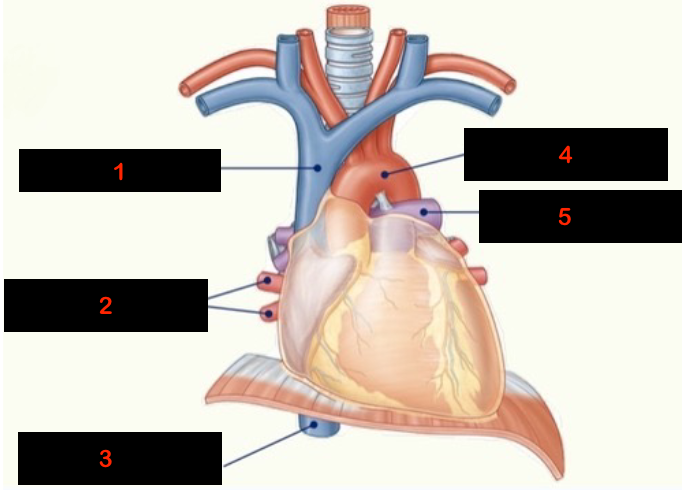
5
pulmonary arteries
The phrenic travels in close proximity to
the fibrous pericardium
The vagus nerve runs ________ to ___________,
posterior; middle mediastinum
Whhich ligament is the site of continuity between fibrous pericardium of heart and central portion of diaphragm?
pericardiacophrenic ligament
What are the components of the pericardial layers?
fibrous pericardium (outermost)
serous pericardium (parietal and visceral layers)
All the following are true about the fibrous pericardium except?
it is divided into two layers (parietal/visceral)
The parietal is the ______ layer of the serous pericardium and is attached to the ________.
outer; inside of fibrous pericardium
The visceral is the ______ layer of the serous pericardium and is attached to________.
inner; the heart muscles (myocardium)
What are the tissue layers of the heart?
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium.