GGR112 - Physical Geography Test 2 prep
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
3 states of water
solid, liuid, vapour
2
New cards
6 phases changes
- liquid to vapour (vaporization)
- vapour to liquid (condensation)
- liquid to solid (freezing)
- solid to liquid (melting)
- solid to vapour (sublimation)
- vapour to solid (deposition)
- vapour to liquid (condensation)
- liquid to solid (freezing)
- solid to liquid (melting)
- solid to vapour (sublimation)
- vapour to solid (deposition)
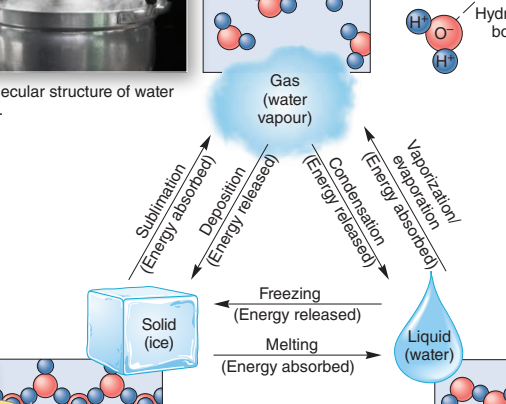
3
New cards
Sensible heat
Transfer of energy that results in a change in temperature.
4
New cards
Latent heat
A transfer of energy that causes a phase change without a change in temperature. (e.g., liquid water to vapour)
5
New cards
Unique properties of water
1. Hydrogen Bonding
2. Surface Tension
3. Density
2. Surface Tension
3. Density
6
New cards
1. Hydrogen Bonding
- The 'bent' geometry of hydrogen and oxygen atoms in the water molecule (O having negative charge and 2 H atoms with positive charge) causes strong forces of attraction between water molecules
- This property is also the reason why so much energy is needed to evaporate water
- The latent heat of vaporization is 540 calories!
- This property is also the reason why so much energy is needed to evaporate water
- The latent heat of vaporization is 540 calories!
7
New cards
2. Surface Tension
- Hydrogen bonding is the reason water strider rest on water
- Downward force exerted by their body is less than force of hydrogen bonds holding the water molecules together
- Downward force exerted by their body is less than force of hydrogen bonds holding the water molecules together
8
New cards
3. Density
- Solid phase of water (ice) is less dense than liquid phase
- Density of liquid water = 1.00 g/cm^3
- Density of ice = 0.91 g/cm^3
- Density of water vapor = 0.0006 g/cm^3
- Density of liquid water = 1.00 g/cm^3
- Density of ice = 0.91 g/cm^3
- Density of water vapor = 0.0006 g/cm^3
9
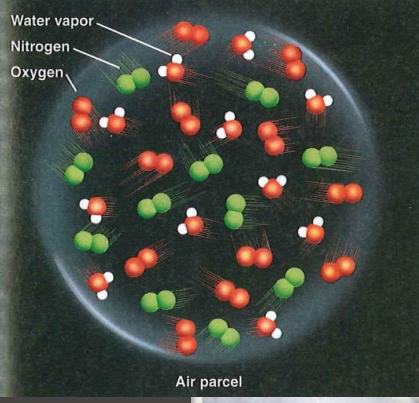
New cards
Humidity
- How much water vapour in the atmosphere
- Air parcel = bodies of water defined by its humidity characteristics and temperature (Consists of Nitrogen, oxygen, and Argon)
- More water vapour occurs at sea level and areas of high evaporation
- To measure/quantify humidity:
1. Absolute humidity
2. Specific humidity
3. Vapour pressure
4. Relative humidity
5. Dew point temperature
- Air parcel = bodies of water defined by its humidity characteristics and temperature (Consists of Nitrogen, oxygen, and Argon)
- More water vapour occurs at sea level and areas of high evaporation
- To measure/quantify humidity:
1. Absolute humidity
2. Specific humidity
3. Vapour pressure
4. Relative humidity
5. Dew point temperature
10
New cards
1. Absolute humidity
Mass of water vapor (H2O) per volume of air (the parcel size)
11
New cards
2. Specific humidity
Mass of water vapor (H2O) per mass of air (parcel mass)
12
New cards
3. Vapour Pressure
- Total vapour pressure = total pressure/force exerted by all gas molecules pushing against the 'outer wall' of a parcel of air
- Vapour pressure = the Partial Pressure exerted by vapour in a parcel of air
- Vapour pressure = the Partial Pressure exerted by vapour in a parcel of air
13
New cards
4. RELATIVE HUMIDITY
- Ratio of actual vapour pressure to saturation vapour pressure
14
New cards
Orographic lifting
\- to form precipitation, air masses lift and rise in altitude to reach dew point temp, condense, and form clouds - Oro means mountain- occurs when air is forced to ascend up-slope as it is pushed against a mountain
15
New cards
Frontal lifting
- to form percipitation, air masses lift and rise in altitude to reach dewpoint temp, condense, and form clouds
- a Front is the boundary between 2 air masses of diff densities
- fronts usually seperate air masses with contrasting temperatures
- a Front is the boundary between 2 air masses of diff densities
- fronts usually seperate air masses with contrasting temperatures
16
New cards
Cold front
the front/leading edge of an advancing mass of colder air
- cold air forces, warm air aloft
- zone of active precipitation is 400 km wide
- sharp line of cumulonimbus clouds marks the front and its a blunt front edge
- cold air forces, warm air aloft
- zone of active precipitation is 400 km wide
- sharp line of cumulonimbus clouds marks the front and its a blunt front edge
17
New cards
Warm front
the front/leading edge of an advancing mass of warmer air
- warm air moves up and over cold air
- 1000 km wide
- precipitation ahead of the warm front
- creates a wedge, slanted shape
- warm air moves up and over cold air
- 1000 km wide
- precipitation ahead of the warm front
- creates a wedge, slanted shape
18
New cards
Water out-gassing from the Crust
Earths hydrosphere owes primarily to out-gassing from volcanoes - gases such as H2O, CO2, CO, SO2 are expelled
19
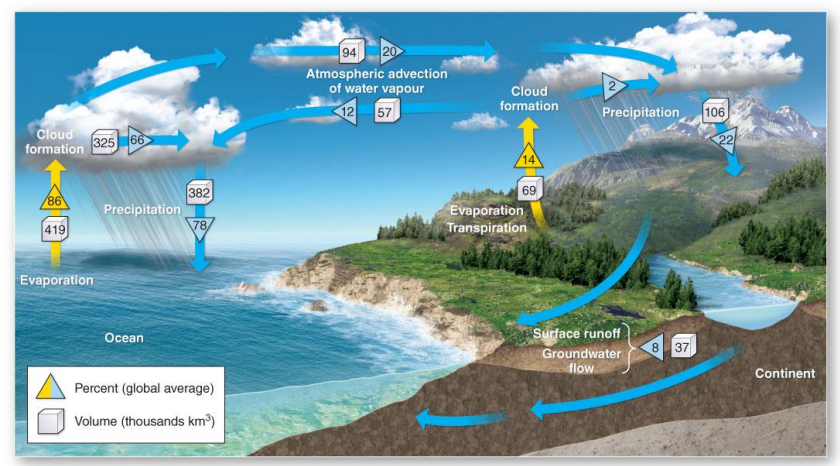
New cards
Hydrlogic Cycle
Evaporation - water loss from the surface
Transpiration - water loss from plant leaves
Evapotranspiration - all processes by which water in solid/liquid phase near land surface becomes water vapour
Transpiration - water loss from plant leaves
Evapotranspiration - all processes by which water in solid/liquid phase near land surface becomes water vapour
20
New cards
Earth water distribution
\- Ocean 97.22 %- Freshwater 2.78% -> Surface water 77.78 -> Ice and glaciers 99.3 -> Groundwater 11.02 -> Deep groundwater 11.02 -> Soil moisture 0.18 in order ocean, fresh, ice and glaciers, groundwater, deep groundwater, soil moisture
21
New cards
Soil water balance equation
moisture supply (P) - Actual moisture (AE) + moisture oversupply (S) + moisture savings
AE - Moisture demans (PE) - Deficit (D)
PET - Potential evapotranspiration
PET > AE - deficit, sever moisture shortage
PET = AE or AE > PET - surplus, excess moisture
AE - Moisture demans (PE) - Deficit (D)
PET - Potential evapotranspiration
PET > AE - deficit, sever moisture shortage
PET = AE or AE > PET - surplus, excess moisture
22
New cards
types of soil water
\- Gravitational: excess water within pore space (too much water) - Capillary is best: loosely attracted to soil, available to plants (some water) - Hygroscopic: strong electrostatic forces between soil and h2o molecules Unavailable to plants (no water)
23
New cards
Groundwater
- groundwater flow is dictated by gravity
- moves from high to low pressure elevation
- moves from high to low pressure elevation
24
New cards
Drainage basin
surface and groundwater from a topographically defined area known as a drainage basin, collect in streams rivers and drain from a common point (KEY!)
25
New cards
Drainage patterns (7/8)
Dendritic: resembles tree root
-like or vein
structure
• Trellis: constrained by tilted/folded bedrock strata
• Radial: steep slope, central peak required, e.g., volcano
• Parallel: similar to dendritic, elongated due to steep slope
• Rectangular: right angle drainage due to faulting
• Annular: similar to radial, requires dome-like rock
• Deranged: a young drainage pattern typical of northern regions, influenced by till deposits from the last glaciation
• Trellis: constrained by tilted/folded bedrock strata
• Radial: steep slope, central peak required, e.g., volcano
• Parallel: similar to dendritic, elongated due to steep slope
• Rectangular: right angle drainage due to faulting
• Annular: similar to radial, requires dome-like rock
• Deranged: a young drainage pattern typical of northern regions, influenced by till deposits from the last glaciation