Paranasal Sinuses and Maxillary Sinus Fractures
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering anatomy, fractures, and pathologies of the paranasal sinuses.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What are the four paired airfield spaces that constitute the paranasal sinuses?
Maxillary, sphenoid, ethmoid, and frontal sinuses
What are the main functions of the paranasal sinuses?
Reduce the weight of the head, humidify air, and act as a cushion against facial blows.
Which sinuses get drained through the osteomeatal complex under the middle coana in the middle meatus?
Frontal sinus, anterior ethmoid sinus, and maxillary sinus.
What gets drained into the inferior meatus?
The nasolacrimal gland.
What are the two radiographic views used to study the paranasal sinuses?
Occipitomeatal (Water's) view and Caldwell view.These views help visualize sinus pathology and anatomy.
What are the clinical signs of paranasal sinus fractures?
Facial pain, swelling, deformity, and possibly other fractures in the body.
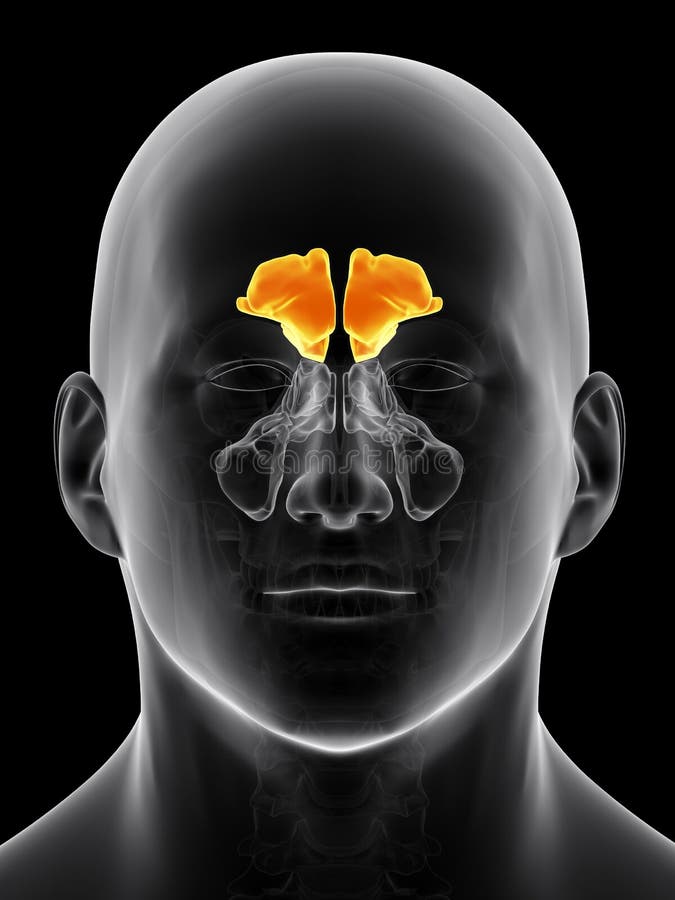
What are the potential complications of a fracture of the posterior wall of the frontal sinus?
CSF leak and potential meningitis.
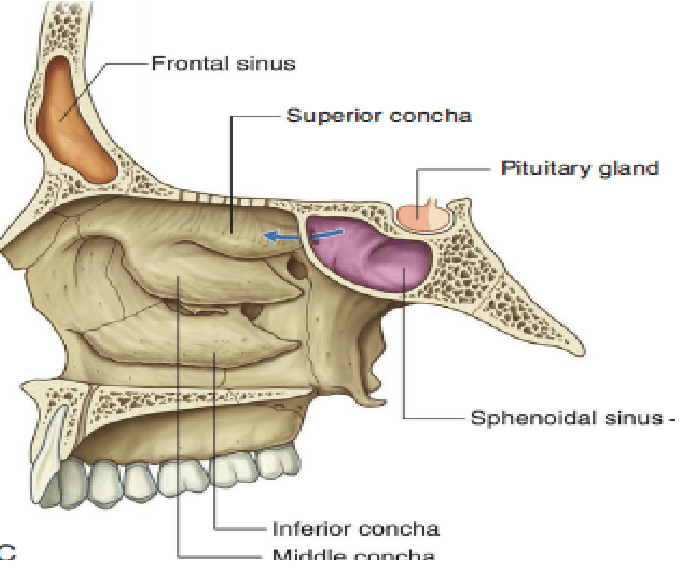
What are the implications of a sphenoid sinus fracture?
Poor prognosis due to the central location in the cranial vault and potential damage to oculomotor nerves and the internal carotid artery.
What does the LeFort classification of complex fractures of the face describe?
Lefort I: Floating palate; Lefort II: Floating maxilla; Lefort III: Floating face.
What are the symptoms of acute sinusitis?
Fever, headache, nasal discharge, and abnormal sense of smell.
What are the typical radiographic findings in sinusitis?
Thickening of the mucosa or a gas-fluid level.
What can cause obstruction of the frontal, maxillary, and ethmoid sinuses on one side?
Obstruction of the osteomeatal complex.
What is a paranasal retention cyst?
Mucous accumulation in a submucosal mucinous gland, usually asymptomatic.
What causes a paranasal sinus mucocele?
Obstruction of the ostium, leading to mucus accumulation and potential expansion of the sinus.
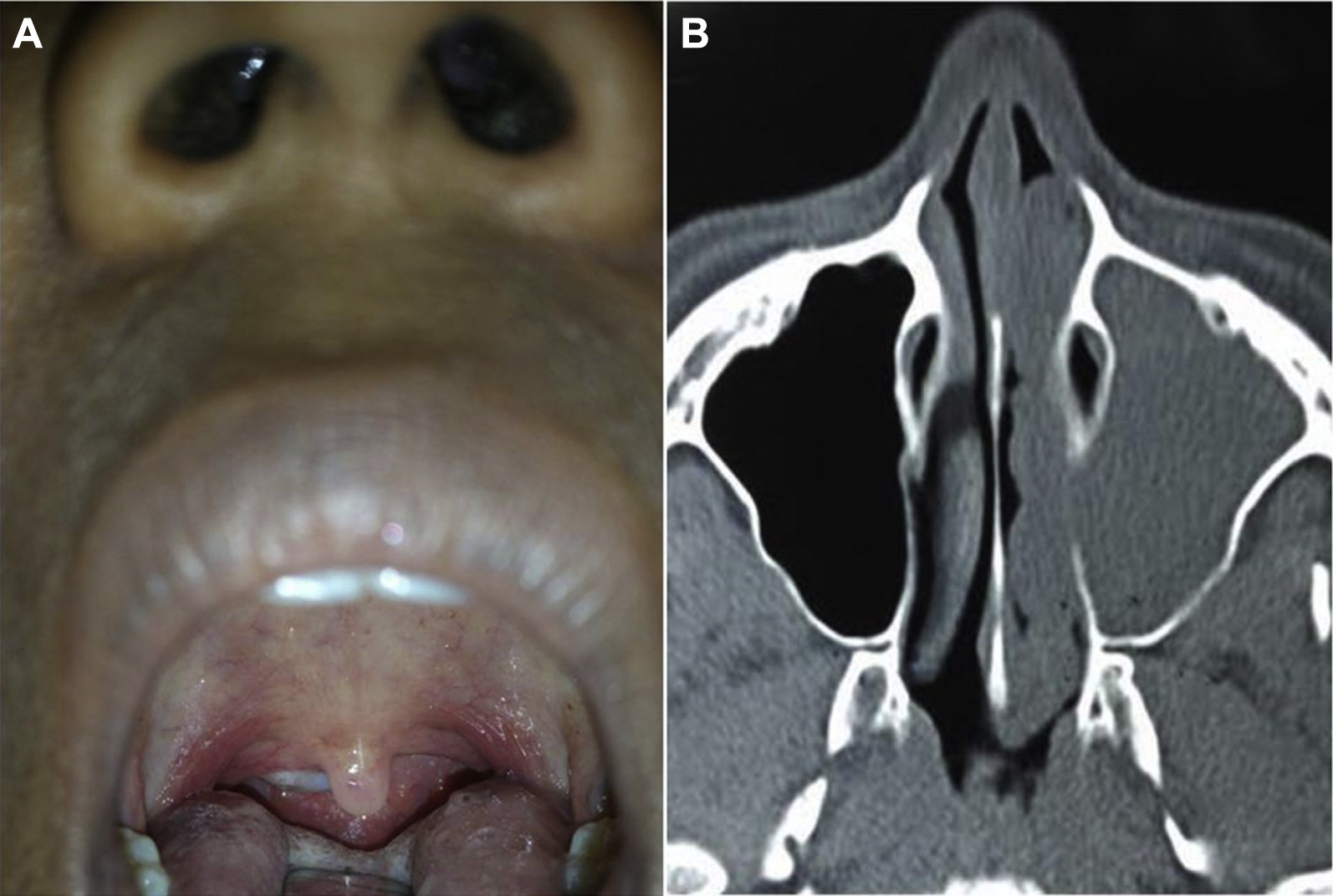
What is an antrochoanal polyp?
Polyp arising in the maxillary sinus, protruding into the nasal cavity and nasopharynx.
What is a paranasal sinus osteoma?
Benign tumor of the bone, usually in the frontal sinus, often asymptomatic.
What is the most common type of carcinoma in the paranasal sinuses?
Squamous cell carcinoma.
What is a juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma?
Benign, highly vascular tumor in young male adolescents, starting in the sphenopalatine fossa.
How can juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas be treated to reduce bleeding during surgical removal?
Embolization of feeding vessels by interventional neuroradiologists.
What lab tests do we prefer to use for paranasal sinus pathologies
We prefer using computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for assessing paranasal sinus pathologies, as they provide detailed images of sinus structures and any potential abnormalities.
When do we favour MRI over CT
in evaluating soft tissue details or when radiation exposure must be minimized, such as in pediatric patients.
When do we favour CT over MRI
when quick assessment of bony structures or when evaluating acute sinus disease is needed.
T1 and T2 weighted MRI differences
T1-weighted MRI provides anatomical detail and highlights fat while T2-weighted MRI emphasizes fluid and edema, making it useful for identifying abnormalities.