Volcanoes - Junior Cycle
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is a volcano?
A rupture in the earths crust the allows lava, ash and gases to escape from the magma chamber below the earth's surface
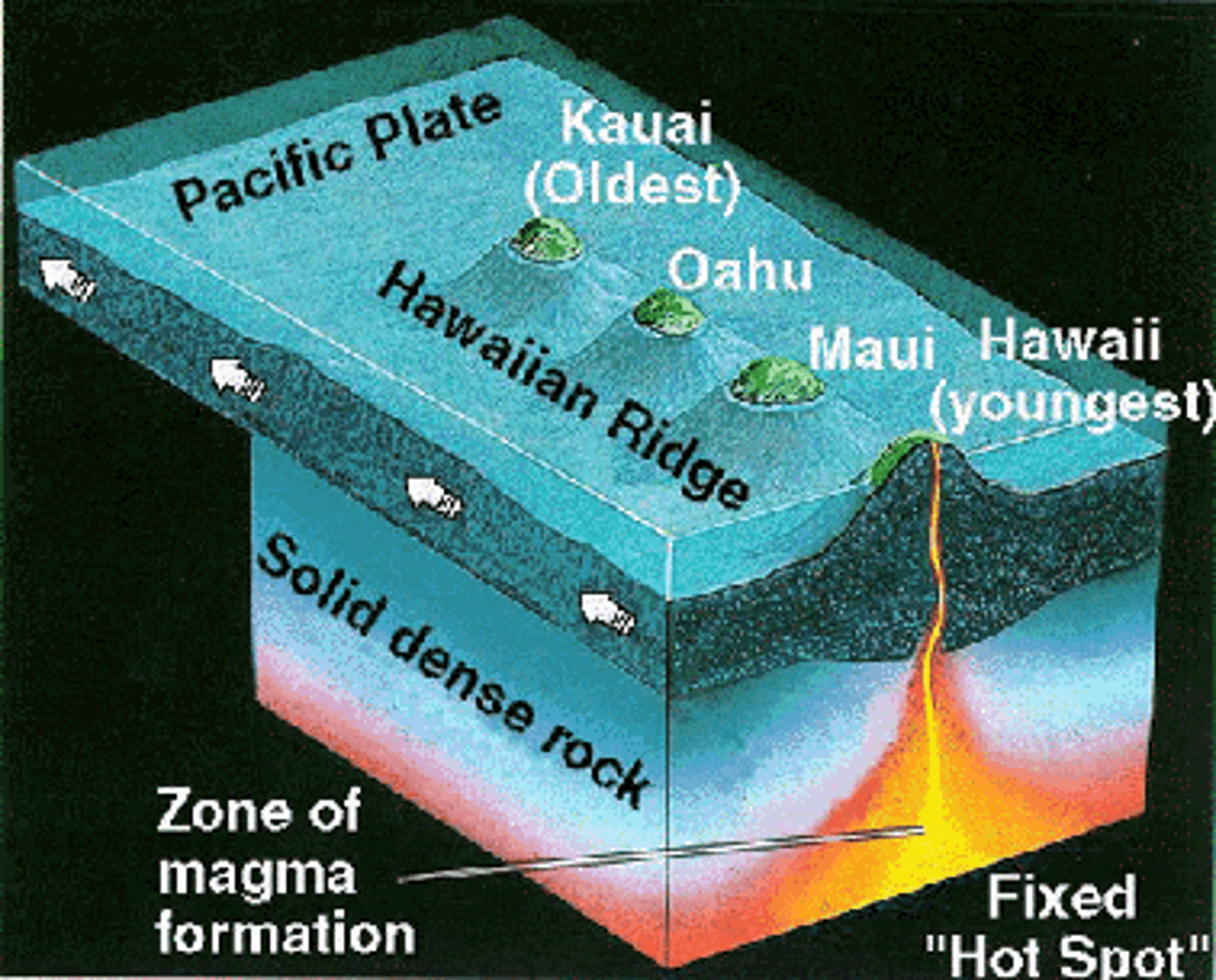
Where do volcanoes happen?
Usually near tectonic plate boundaries but can also be formed near hotspots

What is a hotspot?
Where molten lava is very near the earths crust
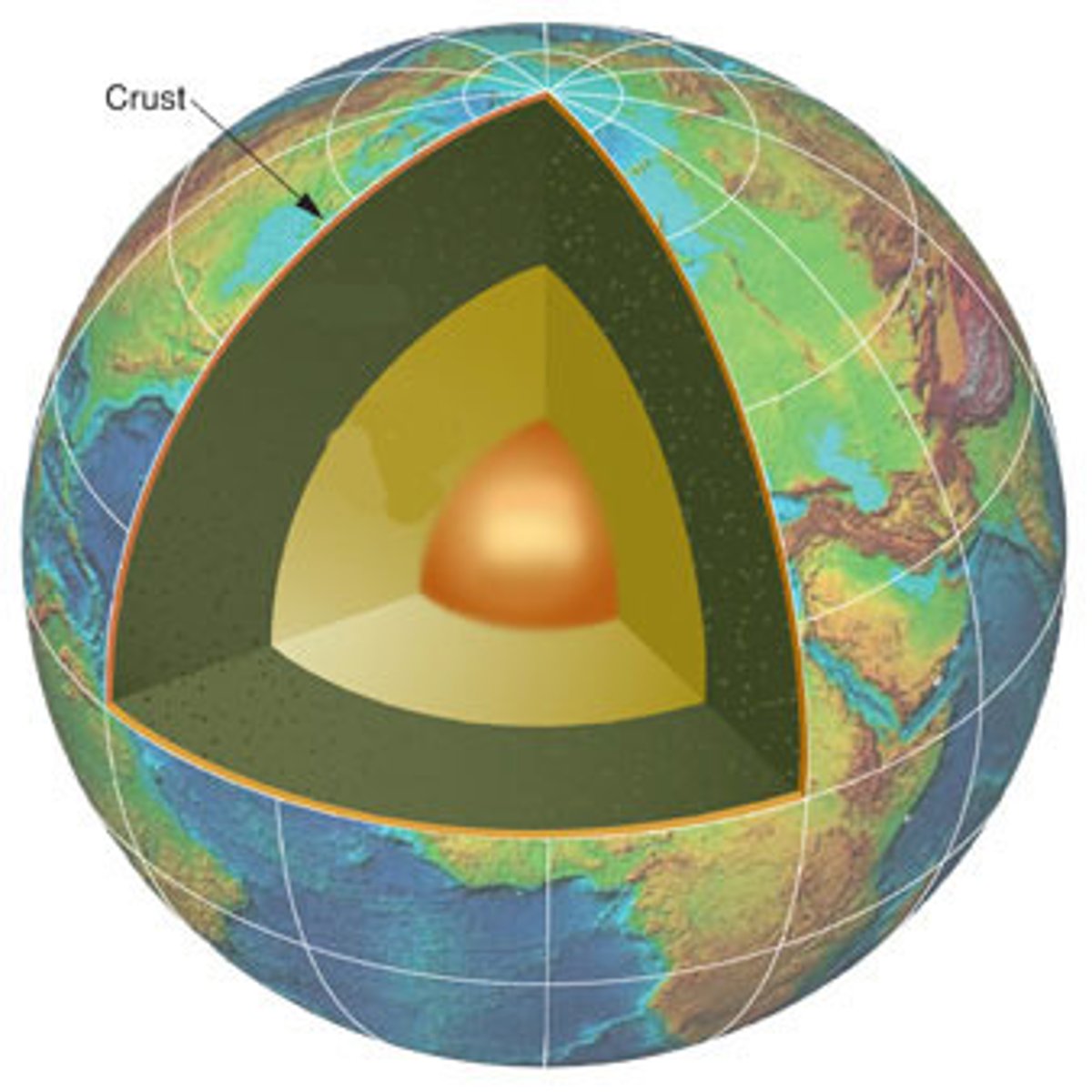
What is the structure of the earth?
Inner core
Outer core
Mantle
Crust

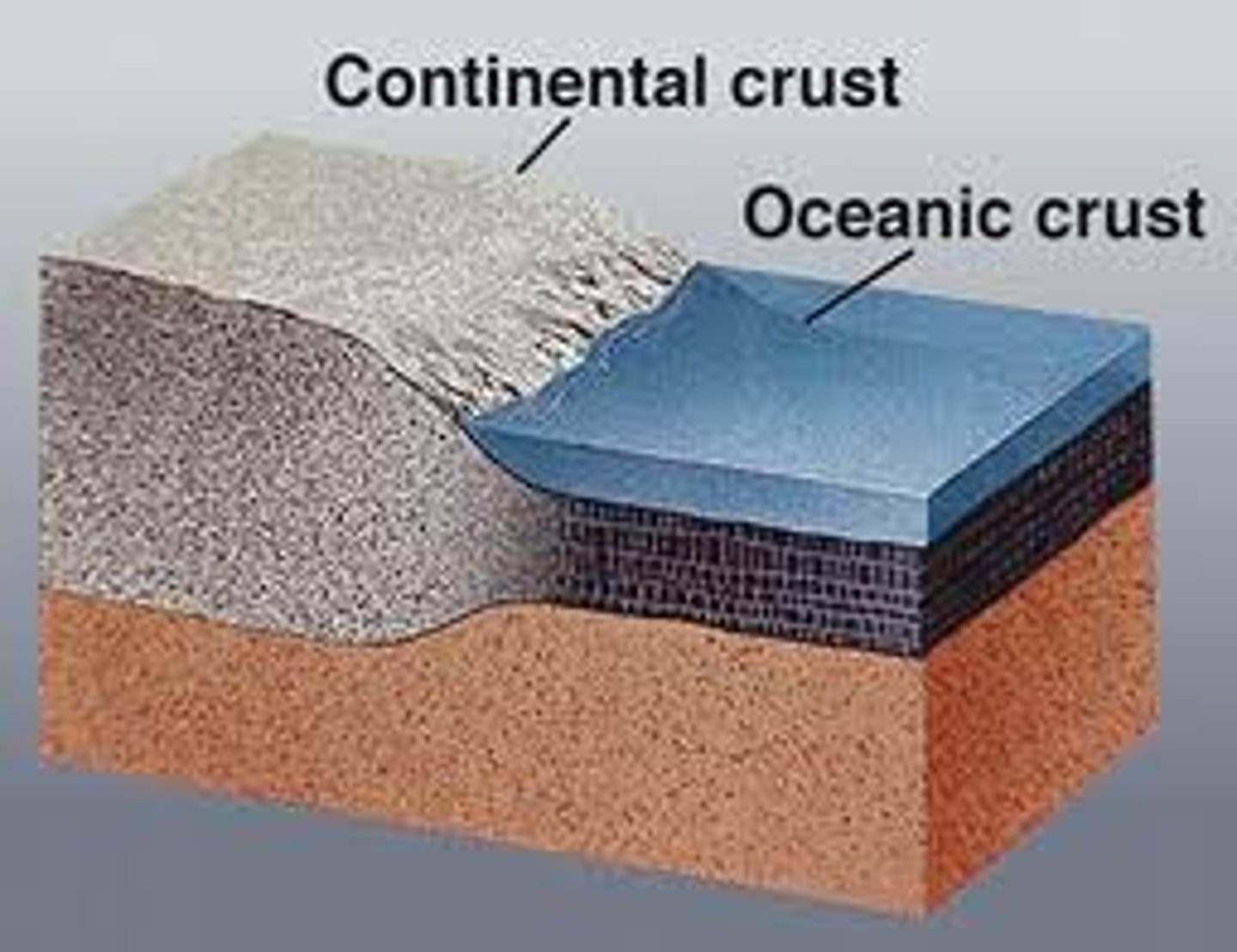
What are the two types of crust?
oceanic and continental
What is an oceanic crust?
Found under the sea
Thinner
More dense
Can be destroyed
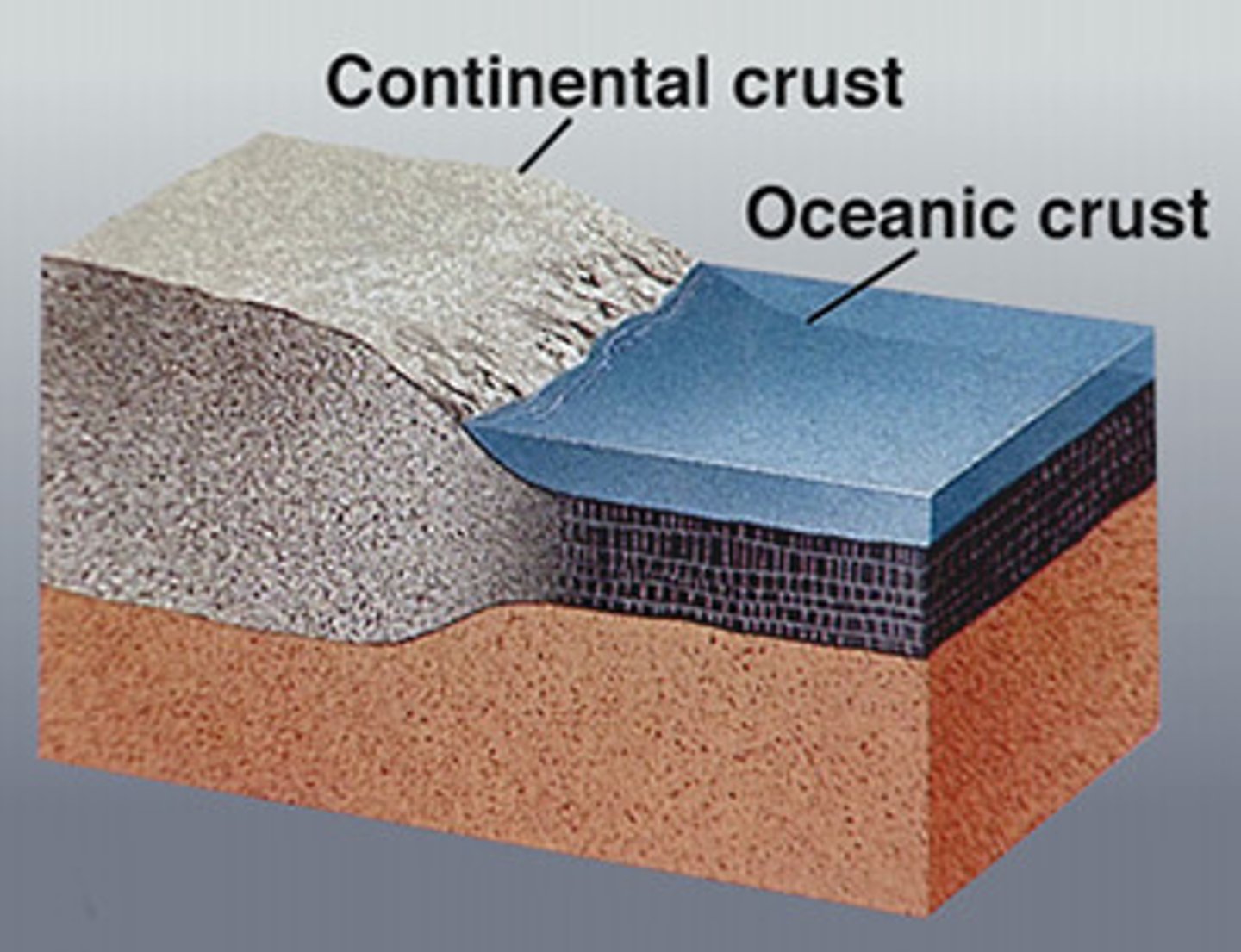
What is a continental crust?
Found on land
Thicker
Less dense
Permanent
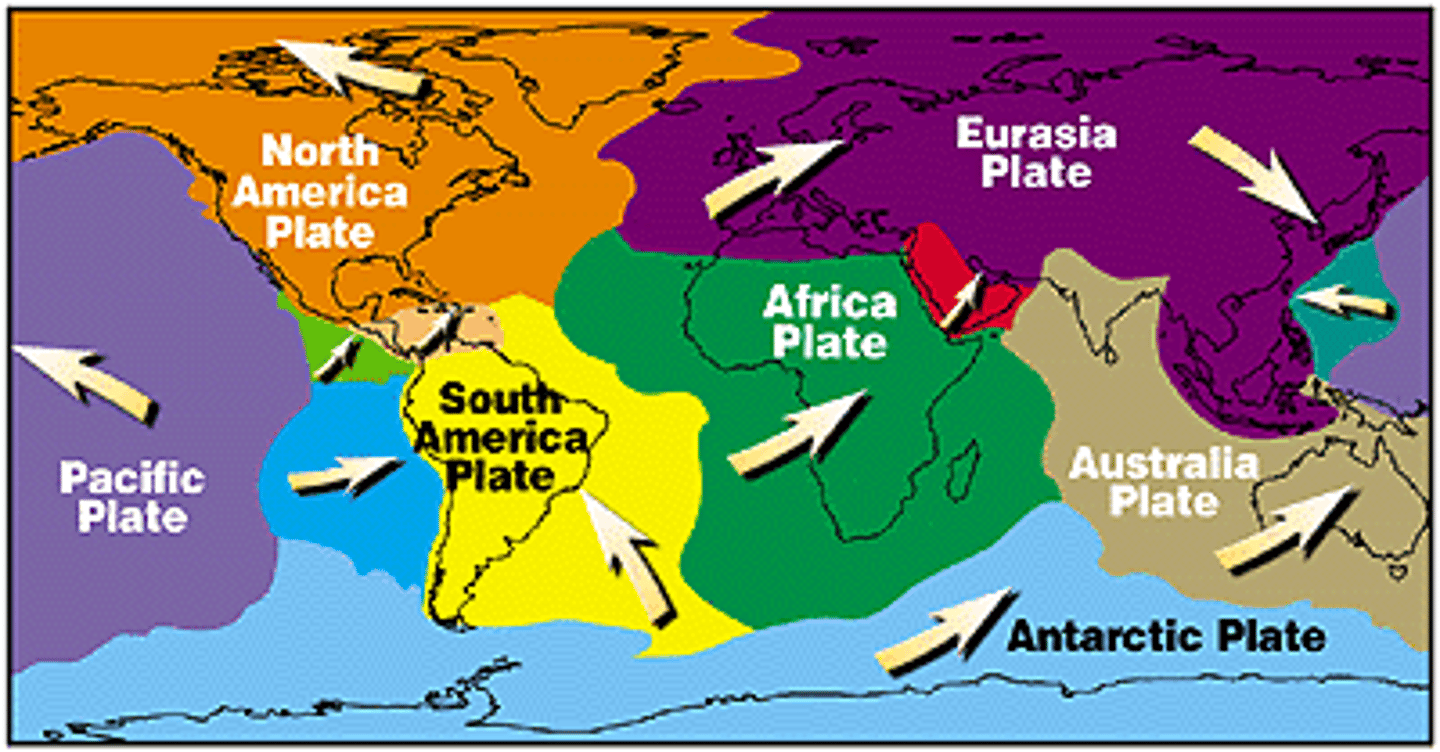
How do the Earth's plates move?
Convection currents in the mantle
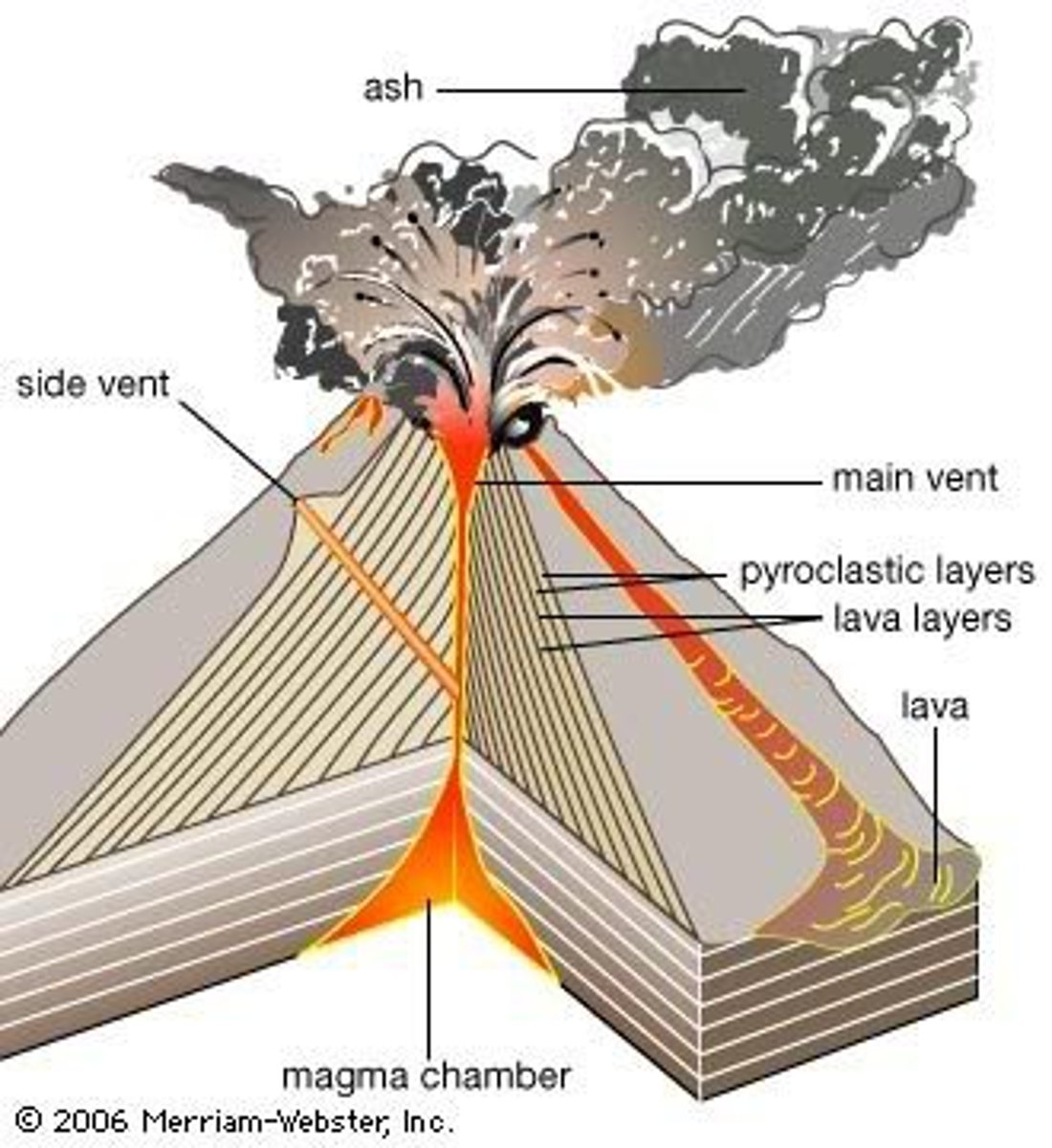
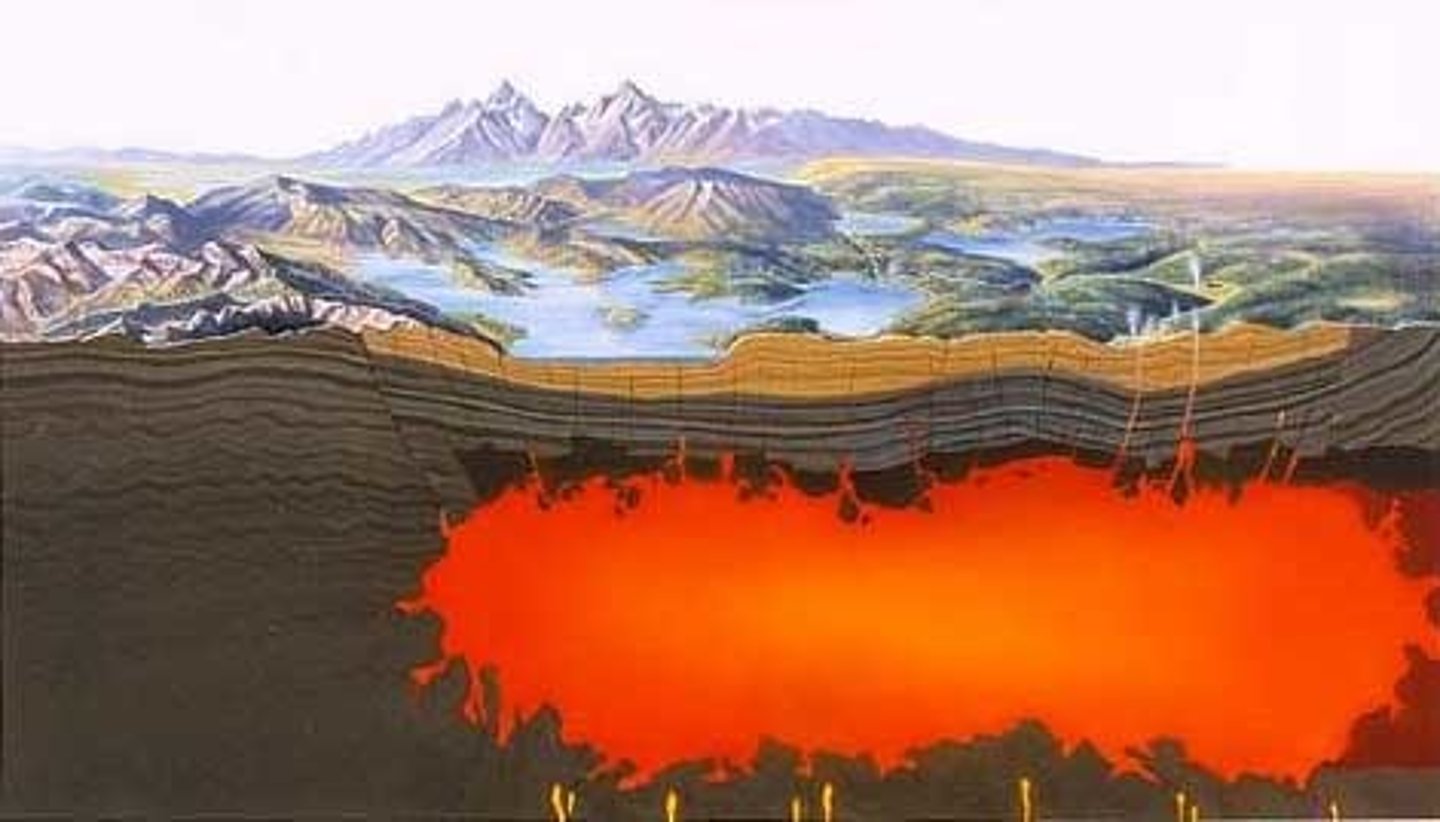
What are the parts of a volcano?
Magma chamber
Main vent
Crater
Ash and cinder cloud
Lava flow
Secondary vent
Layers of lava
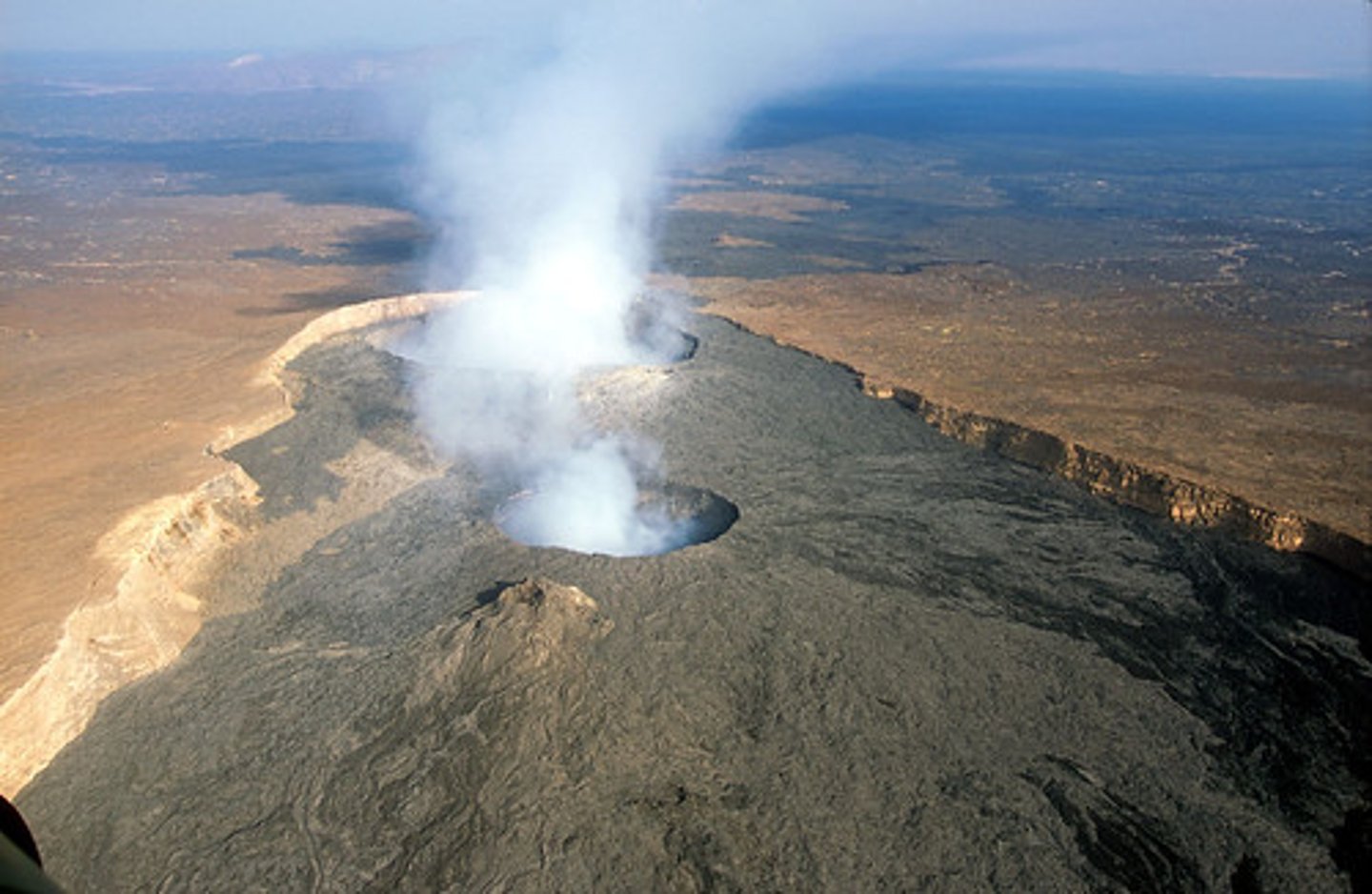

magma chamber
Where molten rock is stored beneath the ground

Vent
A channel through which magma travels to the surface
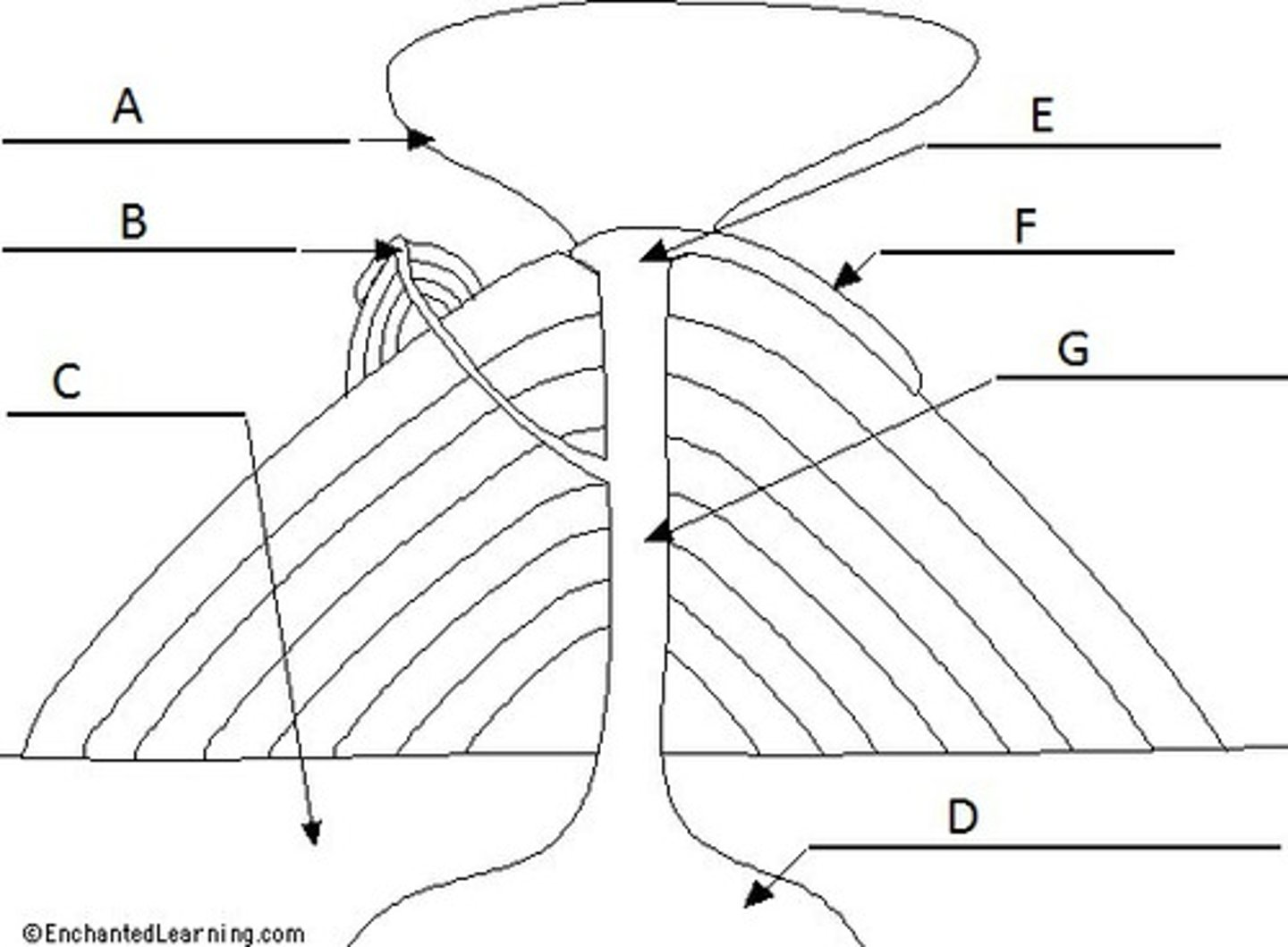
Secondary vent
Some magma may escape through the side of the volcano. Especially if the main vent was blocked.
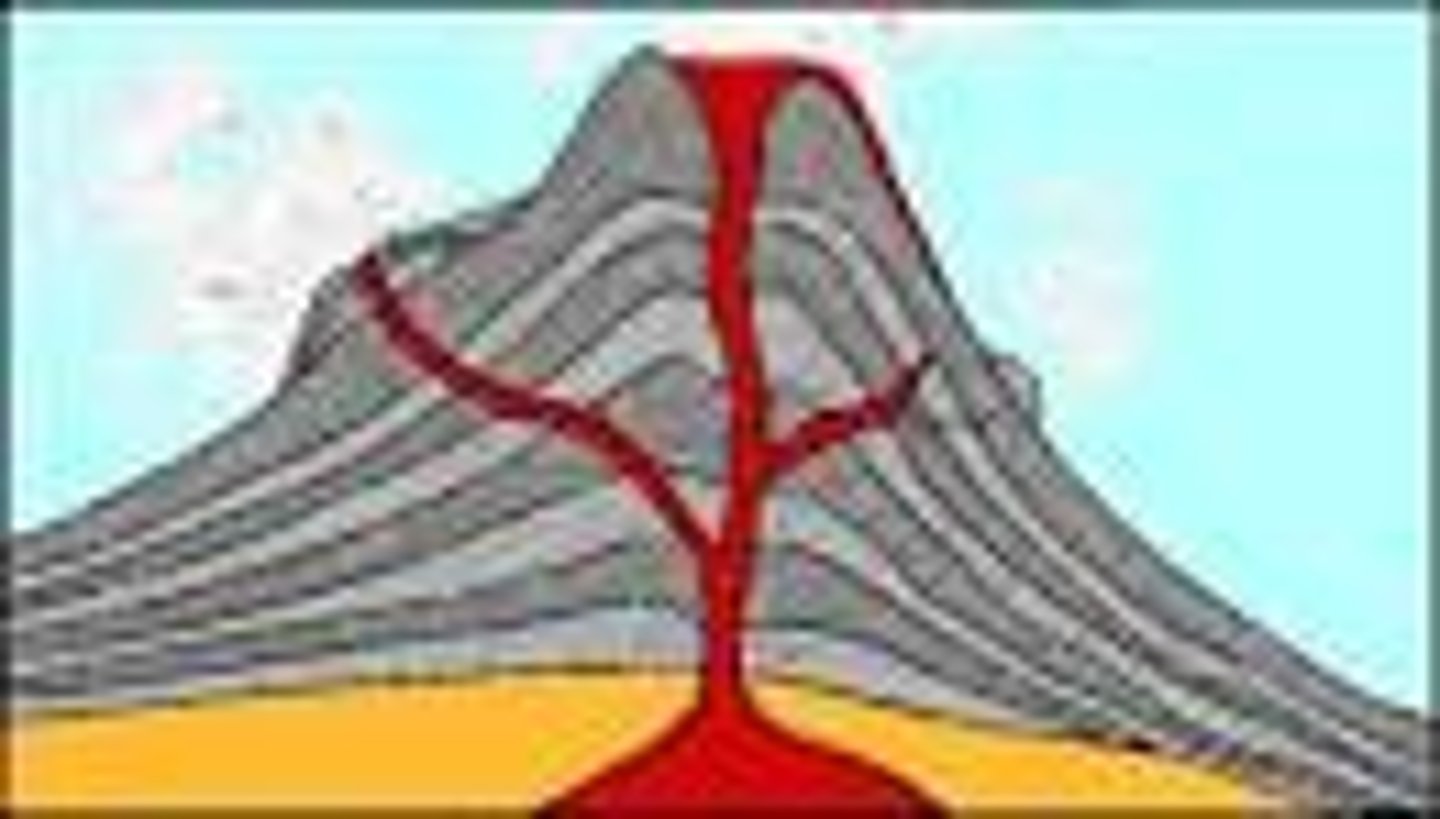
crater
A bowl shaped area that may form at the top of a volcano around the vent.
What are the advantages of why people live near volcanoes?
Rich fertile soil.
Geothermal energy.
Tourism.
Precious metals and minerals.
What are the disadvantages for living near a volcano?
Risk.
Takes time for soil to develop.
High installation cost for geothermal energy.
Tourism can change places.
Economic activity can suffer.
Lava can damage landscapes.
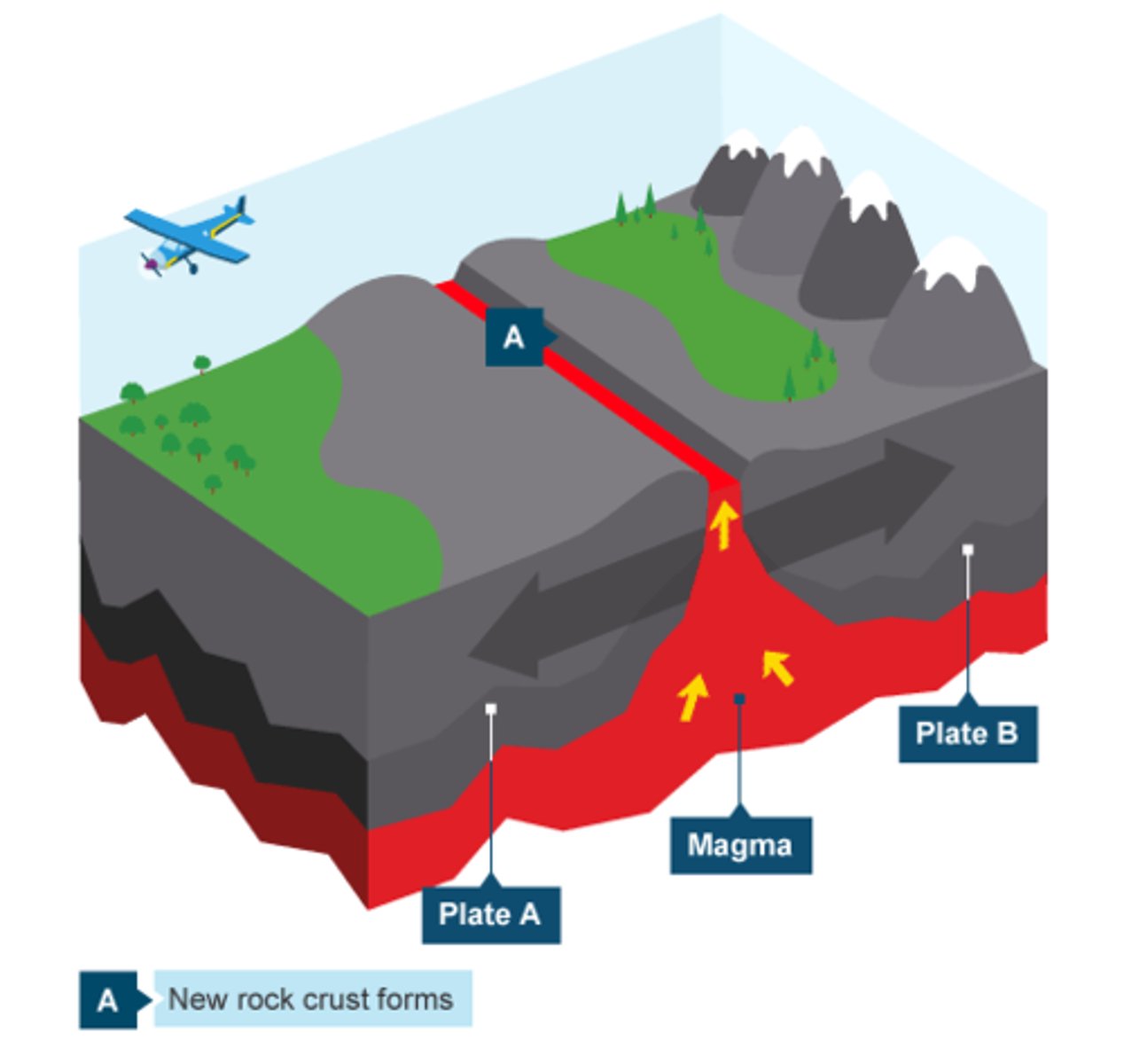
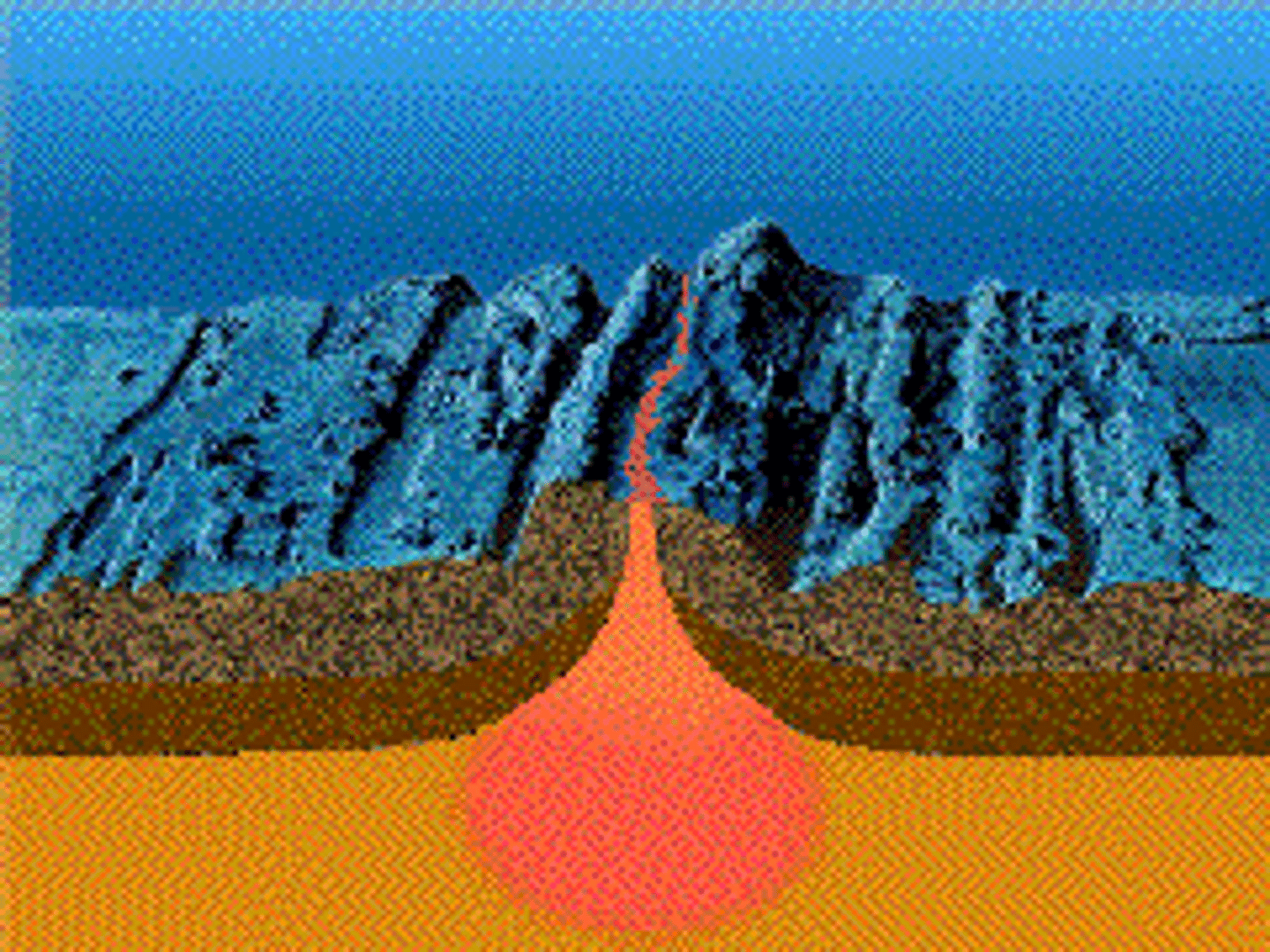
Constructive plate boundary
It happens where two plates are pulled apart by convection currents. Molten magma comes to the surface through a crack called a fissure. This creates new land.
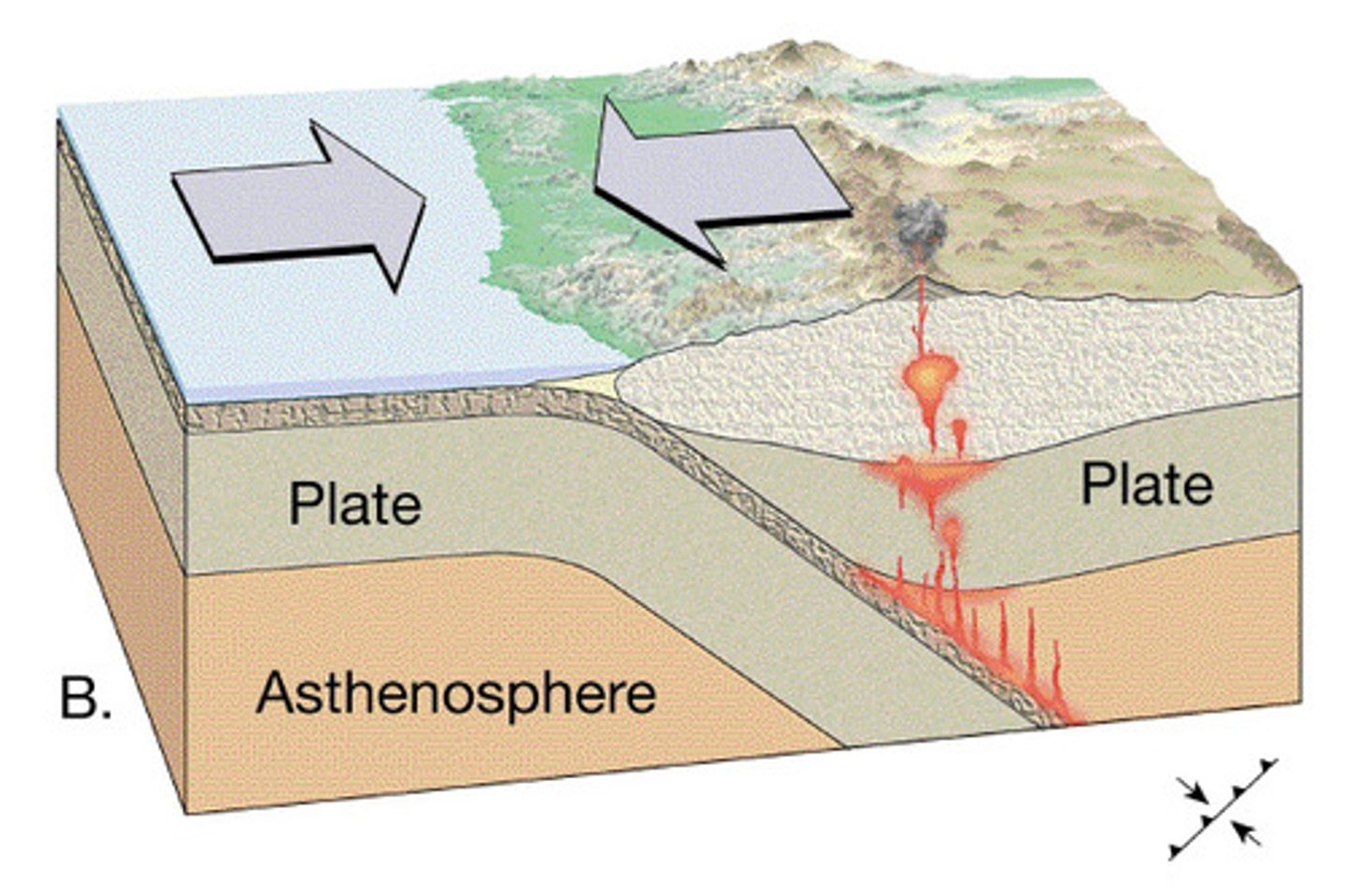
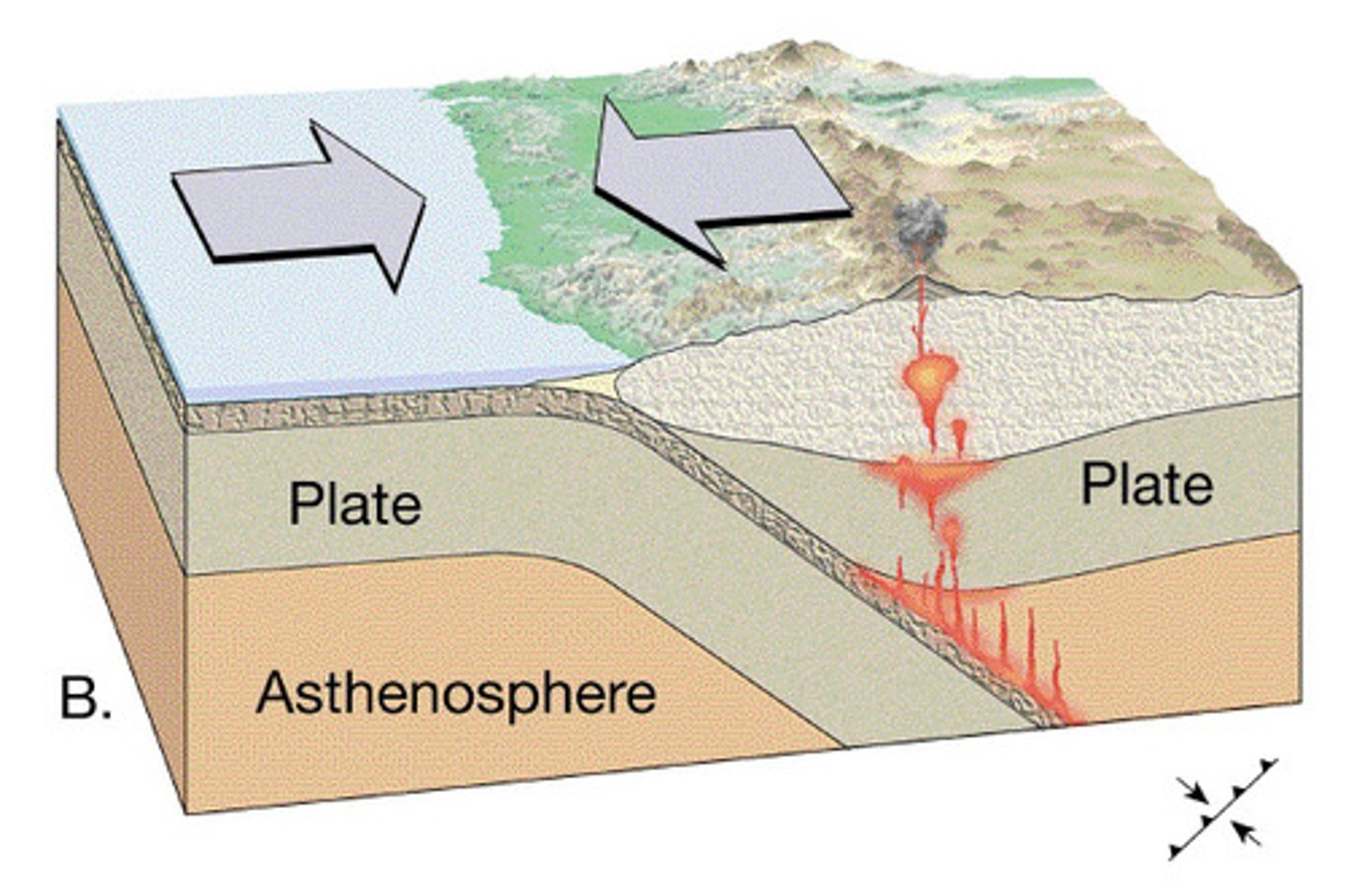
Destructive plate boundary
Convection currents cause two plates to collide. The heavier plate sinks into the mantle and is destroyed. The lighter plate buckles upwards, creating fold mountains and sometimes volcanoes.
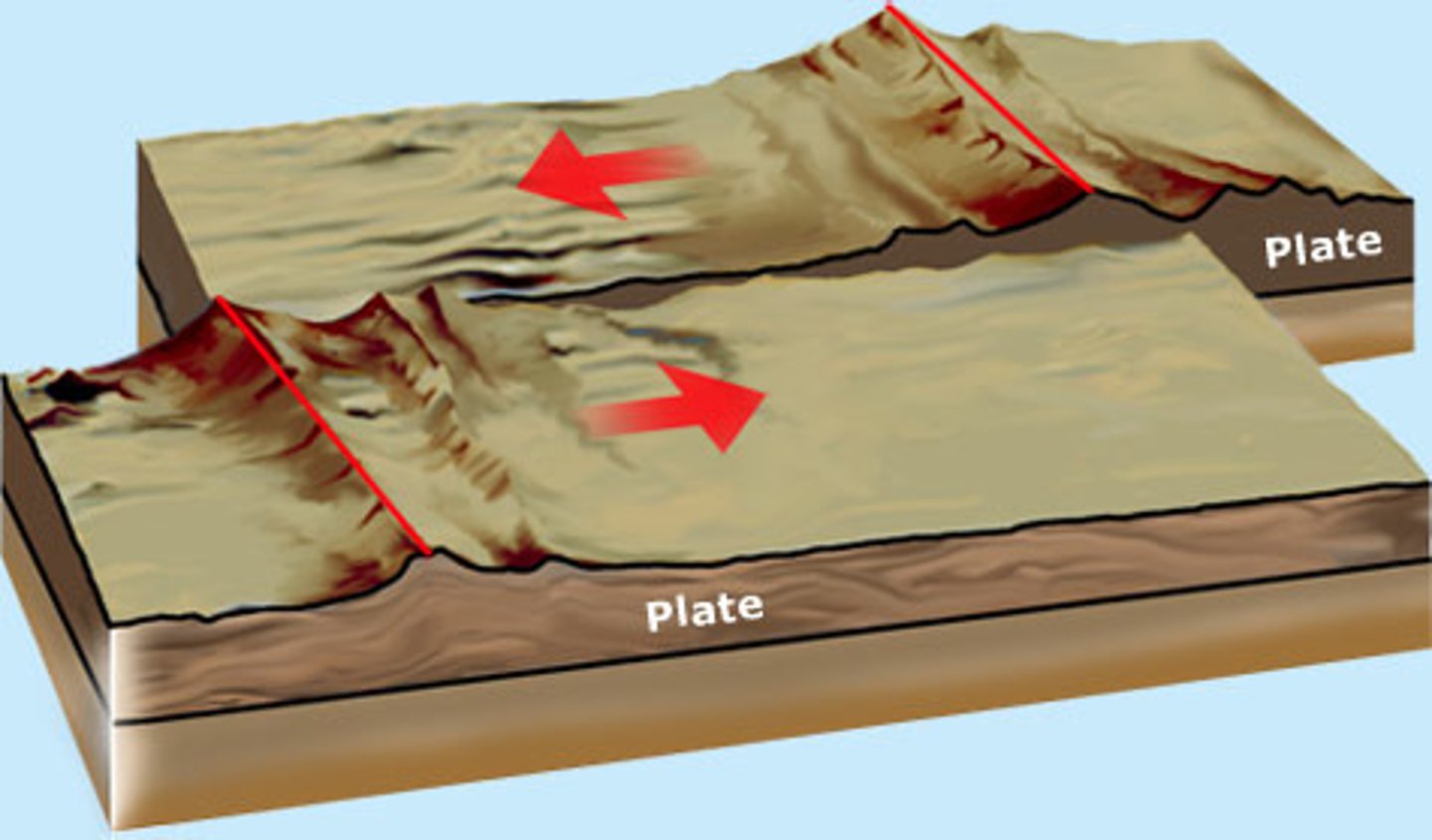
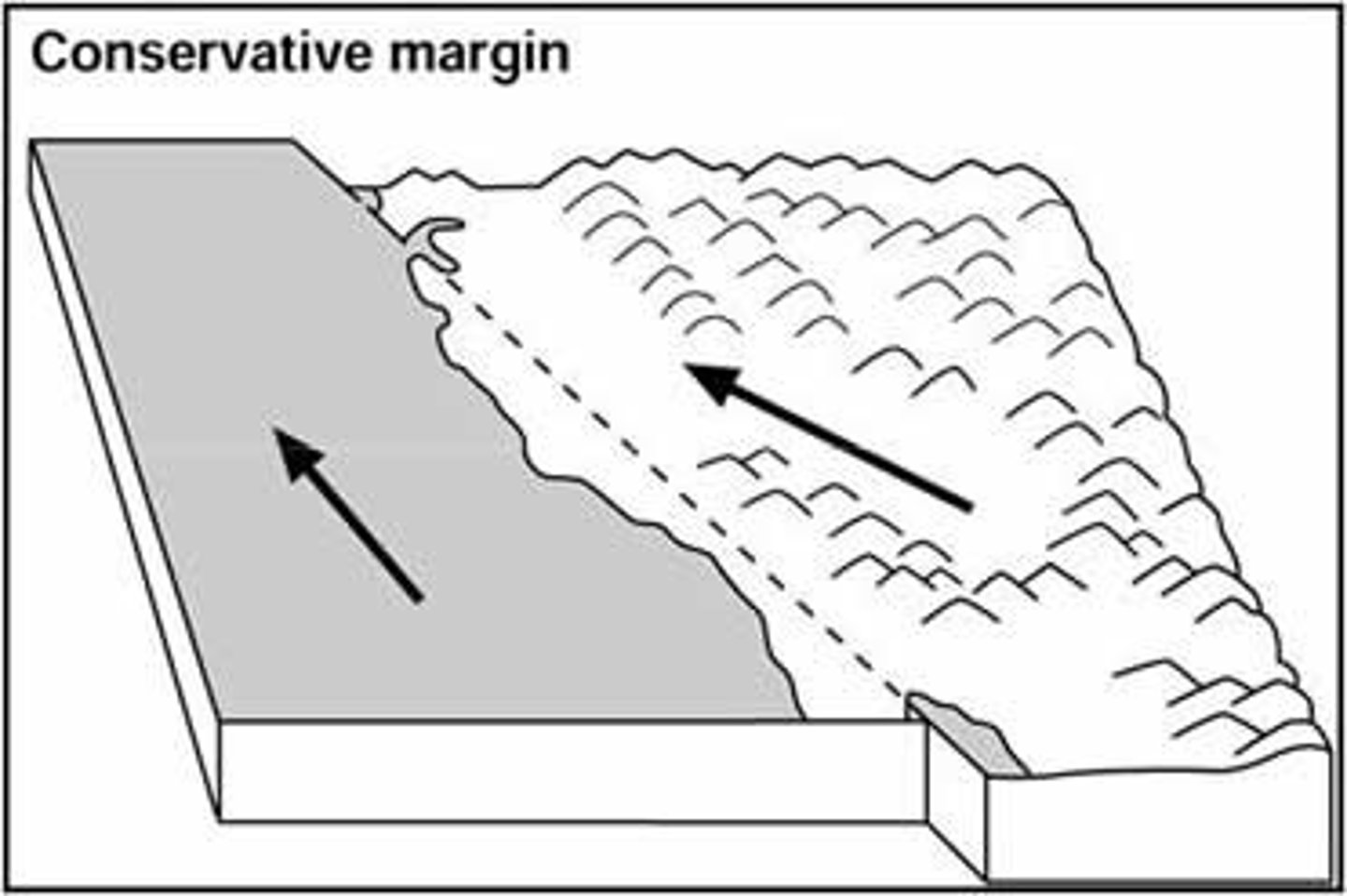
Conservative plate boundary
Two plates are moving alongside each other, either in opposite directions or in the same direction but at different speeds. This causes friction and the energy released creates an earthquake.
Name a real world example of a constructive plate boundary
Mid-Atlantic Ridge runs through Iceland
Name a real world example of a destructive plate boundary
Andes Mountains in South America
Name a real world example of a conservative plate boundary
San Andreas Fault, USA
Features found at constructive plate boundaries
New land
Volcanoes
Mid-ocean ridges
Volcanic islands
Earthquakes
geyser
A fountain of hot water and steam that erupts from the ground

Features found at destructive plate boundaries
Fold mountains
Volcanoes
Earthquakes
Features found at conservative plate boundaries
Earthquakes
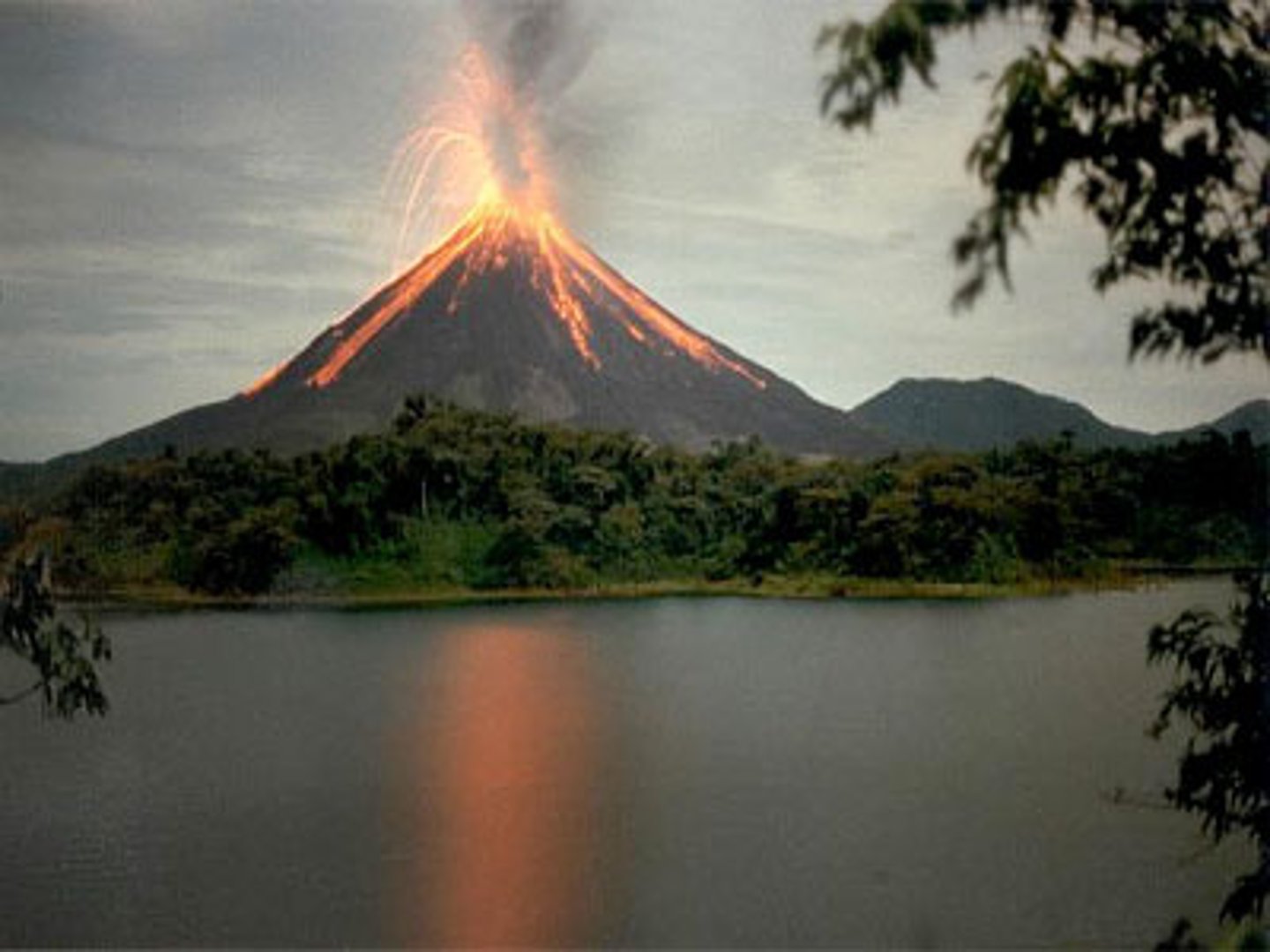
active volcano
a volcano that is erupting or has shown signs that it may erupt in the near future

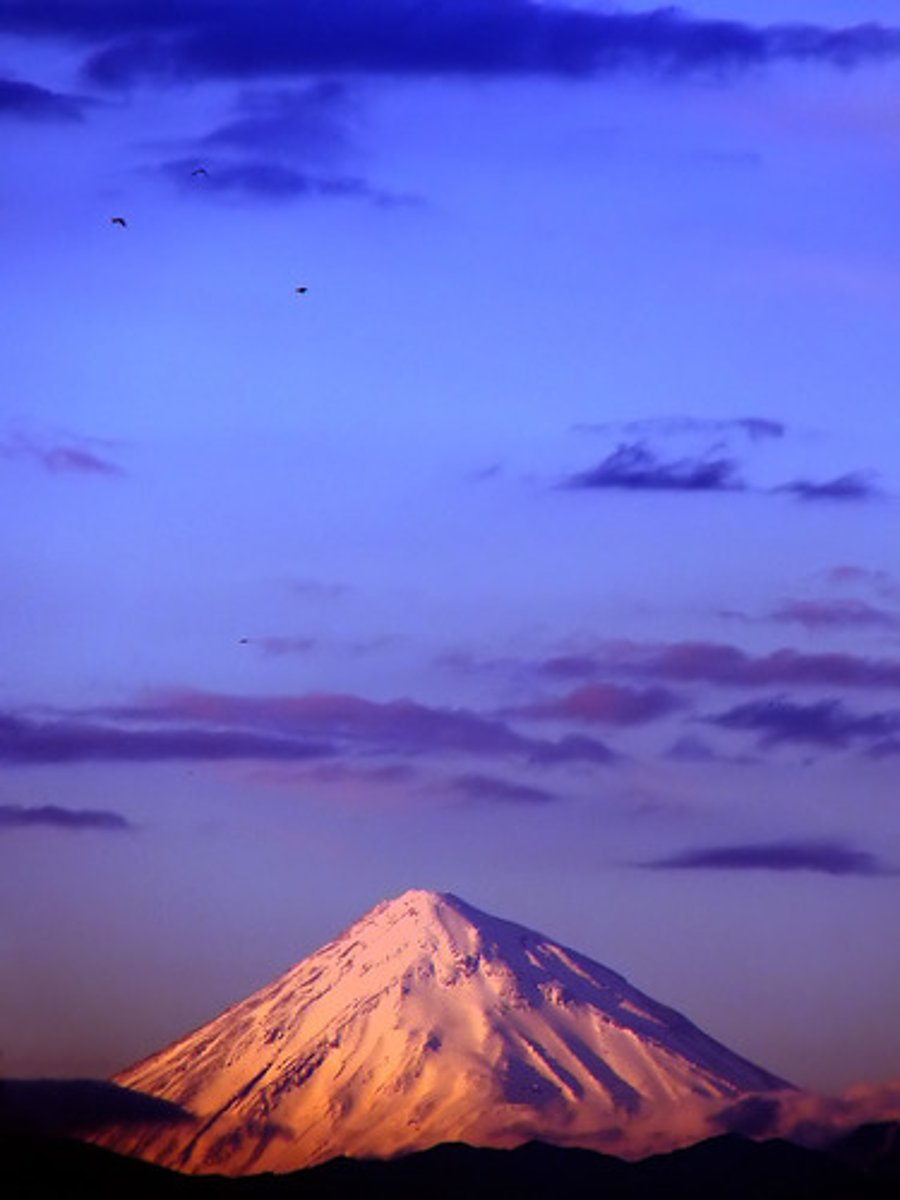
dormant volcano
A volcano that has not erupted for a long time, but may erupt again one day.

extinct volcano
A volcano that has not erupted for thousands of years and probably will not erupt again.

fissure
a narrow opening or large crack in the ground
mid-ocean ridge
An underwater mountain range that forms under the ocean as a result of volcanic activity
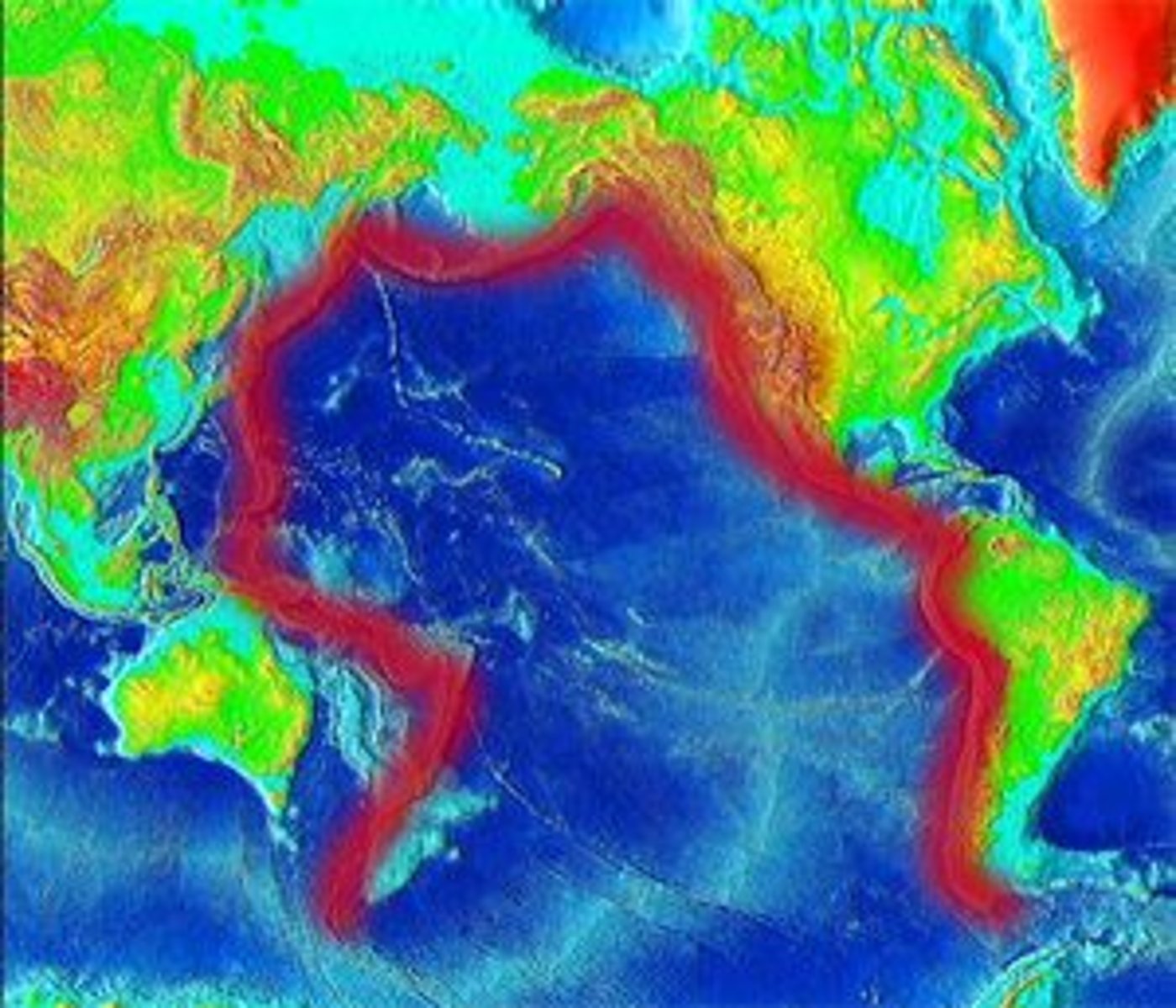
Pacific Ring of Fire
region around the Pacific Ocean where most of the volcanoes and earthquakes on Earth occur regularly
continental drift
the gradual movement of the continents across the earth's surface through geological time.
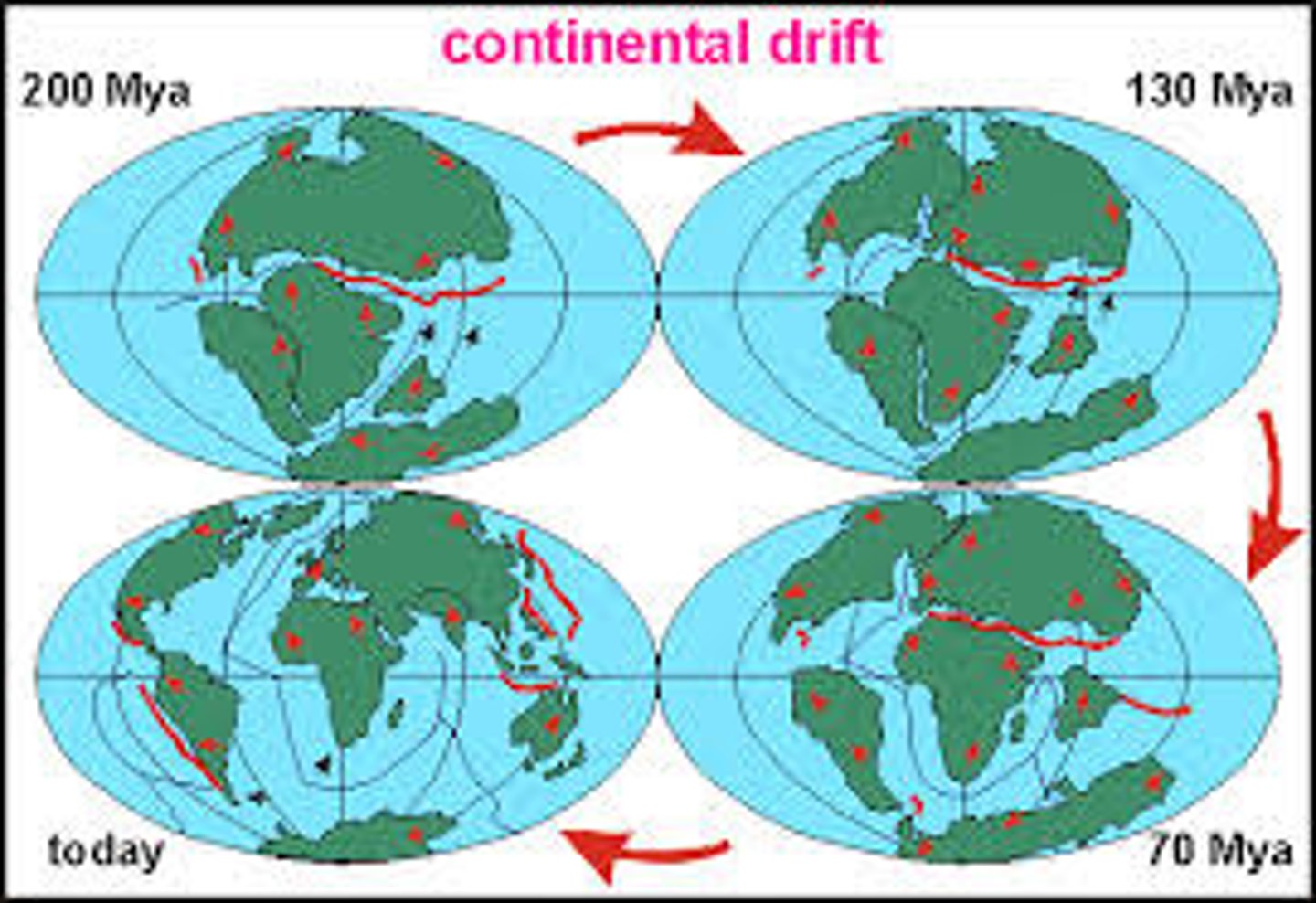
Pangaea
The name of the single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago and gave rise to today's continents
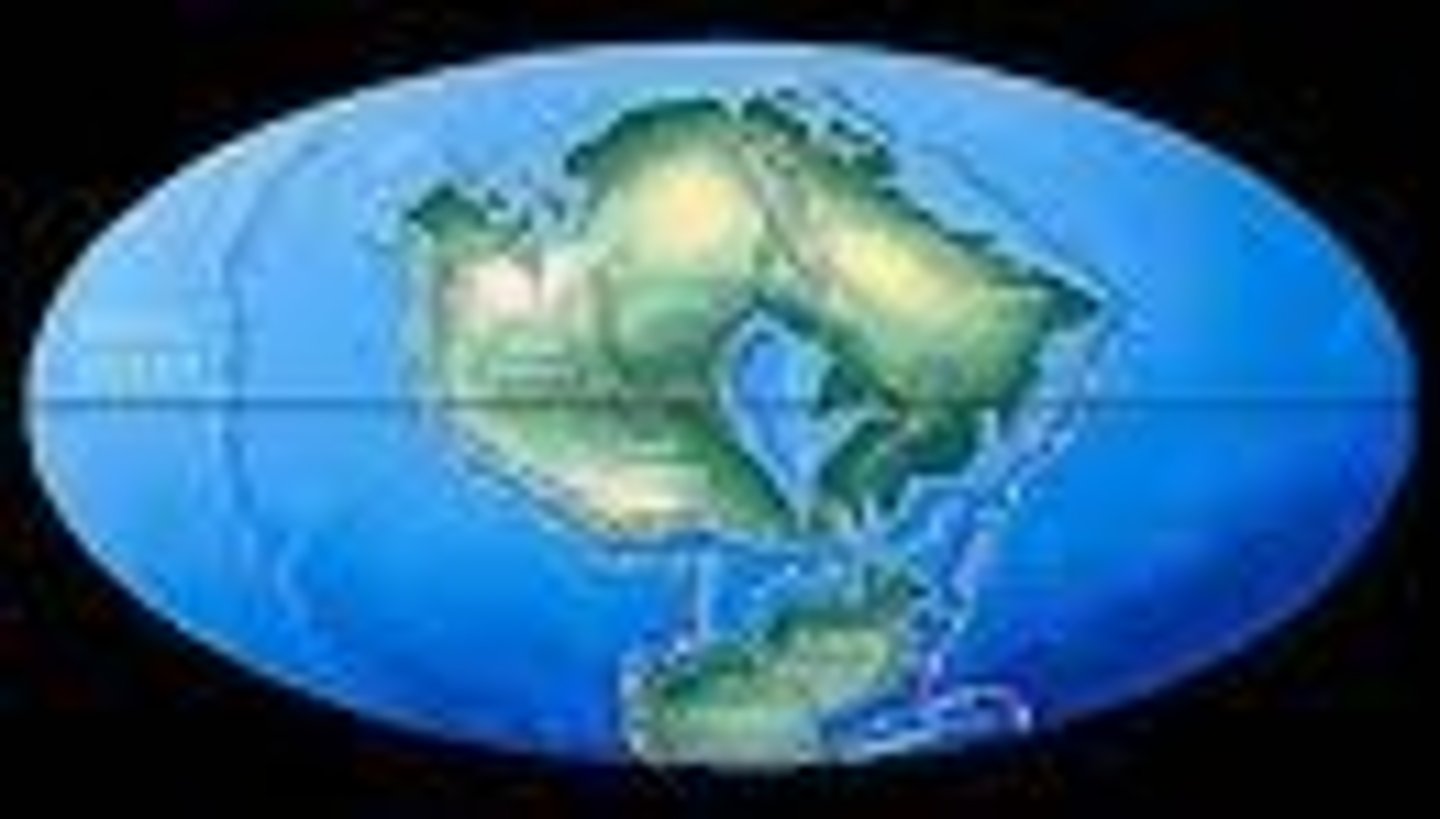
Plate Tectonic Theory
A theory stating that the earth's surface is broken into plates that move.

Example of dormant volcano
Mount St Helens
Example of a Active volcano
Mount Etna
Example of an extinct volcano
Slemish, Co. Antrim
Eyjafjallajokull
Eruption of this Icelandic volcano caused the cancellation of thousands of trans-Atlantic and European airline flights

The 3 P's responding to volcanoes
Prediction
Planning
Preparation
Volcanologist
a scientist who studies volcanoes

Country known as the Land of Ice and Fire
Iceland