Dental Ceramics - Reviewer
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What’s glass infiltrated ceramics/ slip cast ceramics?
specialized ceramics reinforced by an unique glass infiltration process
involves condensation of an aqueous slip on refractory die
In-Ceram was developed by infiltrating glass into a porous ceramic framework, creating a strong and esthetic glass-ceramic used in dentistry.
Types of In-ceram
In-ceram alumina core
In-ceram spinell core
In-ceram zirconia core
In-Ceram Alumina
Made of alumina (Al₂O₃) particles infiltrated with glass
Very strong and fracture-resistant
Opaque appearance (less esthetic)
Best for posterior crowns and short-span bridges
In-Ceram Spinell
Made of magnesium–alumina (MgAl₂O₄), called spinel, infiltrated with glass
Developed to improve translucency compared to alumina
Lower strength than alumina
More esthetic and natural-looking
Best for anterior crowns where appearance matters
In-Ceram Zirconia
Made of alumina + zirconia mixture infiltrated with glass
Highest strength among the three types
Least translucent (more opaque)
Used for posterior crowns and long-span bridges that need extra strength
Differences between in-ceram alumina, spinell, and zirconia
Alumina: Strong but opaque
Spinell: Translucent but weaker
Zirconia: Strongest but most opaque
What are the machinable ceramics?
Digital Systems
Analogous Systems
What are the strengthening methods?
Strengthening brittle materials:
Introduction of residual compressive stresses
Interruption of crack propagation
Methods of designing to:
Minimize tensile stress through design
Avoid stress raisers
Ion exchange mechanism:
This technique is called as chemical tempering and is the most sophisticated and effective way of introducing residual compressive stresses.
This process is best used on the internal surface of the crown, veneer/inlay as the surface is protected from grinding and exposure to acids.
Ion exchange mechanism (Chemical tempering):
It is a chemical process used to strengthen glass-ceramics.
In this technique, the material is heated and placed in a molten salt bath (usually containing potassium nitrate).
Smaller sodium ions (Na⁺) on the glass surface are replaced by larger potassium ions (K⁺) from the salt bath.
Because the larger ions occupy more space, they create compressive stresses on the surface of the material.
These compressive stresses increase the strength and resistance of the ceramic to cracks and fractures.
It is most effective when applied to internal surfaces (like the inside of a crown, veneer, or inlay) because these areas are protected from wear, grinding, or acid exposure, helping preserve the compressive layer.
Thermal tempering
This is the most common method of strengthening glass.
In dentistry silicone oil and other special liquids are used for quenching ceramics instead of water/air
Essentials of cad cam
Scanner/digitizer
Computer
Milling station
Ceramic blanks
Furnace
What’s the CAD-CAM Process?
Optical impression by an intraoral scanner
3d reconstruction of dentitions on the monitor
CAD process
Fabrication of NC data
CAM process
Post treatments
How can CAD-CAM be produced?
by chairside milling units
industrial milling processes
MOST COMMON CAD CAM SYSTEMS
Direct CAD-CAM Systems
Indirect CAD-CAM Systems
Cicero system
Lava system
Cerec scan
Copy milling
Which property best describes the fracture resistance of dental ceramics?
Fracture toughness best describes the fracture resistance of dental ceramics.
It measures a material’s ability to resist crack growth under tensile stress, which is critical since ceramics are brittle.
If tensile strength is not a reliable property of dental ceramics, which property is a better measure of the material’s fracture resistance?
Fracture toughness is a better measure than tensile strength because it reflects a true material property—resistance to crack propagation—
WHILE tensile strength varies with size, shape, and surface conditions.
What roles do oxygen, potassium, and leucite play in the structure and properties of feldspathic veneering (layering) ceramics?
Oxygen forms the basic silicate structure
Potassium acts as a flux that increases thermal expansion
Leucite crystals further raise the thermal expansion coefficient to match the ceramic with metal frameworks.
Which property of bilayer ceramics is used as a measure of the thermal compatibility of ceramic materials?
The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is used to measure thermal compatibility.
Matching the CTE between ceramic layers prevents crack formation due to thermal stress during heating and cooling.
Through what mechanism does transformation toughening increase the fracture resistance of yttria-stabilized zirconia?
Transformation toughening occurs when stress causes zirconia’s tetragonal crystals to transform into the monoclinic phase
= Creating compressive forces that stop crack growth and increase fracture resistance.
Which two inventions dramatically increased the success and survival probability of metal-ceramic restorations?
The development of strong metal-ceramic bonding techniques and the introduction of thermal expansion–matched porcelains greatly improved the durability and success of metal-ceramic restorations.
Which components of ceramics can cause excessive wear of tooth enamel?
Core ceramics or opaque porcelains that have large or hard crystalline particles and rough, unglazed surfaces.
The particle type and crystal size make the ceramic surface more abrasive.
Proper glazing or polishing of veneering ceramics reduces this wear against natural tooth enamel.
How does the leucite content of veneering porcelain for metal-ceramic prostheses control the cracking resistance of the porcelain?
How is the degree of sintering controlled and what parameter defines complete sintering?
The degree of sintering is controlled by the
firing time and
temperature used during the heating process.
Complete sintering is defined when the porcelain reaches its theoretical density = porosity has been minimized and the particles are fully bonded.
What condition is required of cast metals to achieve ionic and/or covalent bonding to veneering porcelain?
Why should a metal coping or framework have a higher expansion coefficient than its veneering porcelain?
What is dental ceramics?
Inorganic, non-metallic materials composed primarily of oxygen and one or more metallic or semi-metallic elements, formulated to be used as the structural or esthetic component of dental prostheses.
ONE LINER:
Inorganic, non-metallic materials composed of oxygen and metallic or semi-metallic elements, used for esthetic and structural dental restorations.
Ceramic is derived from the word? Which means?
Keramos - burnt stuff
The only true crystalline ceramic used in restorative dentistry is? Which is one of the hard and probably the strongest oxides known.
ALUMINA
Ceramics are reinforced with crystalline inclusions such as ____ & ___ into the glass matrix to strengthen the material and improve its fracture resistance.
ALUMINA & LEUCITE
This process of forming a glass is called _.
VITRIFICATION
Why dental ceramics?
LICCAR
Refractory nature
Long term colour stability
Insulator
Can be formed into precise shapes
aesthetics
Chemically inert
How are dental ceramics classified?
UCPPFMTFA
Uses/Indications
Composition
Firing temperature
Processing methods
Principal crystal phase
Microstructure
Translucency
Abrasiveness
FRACTURE RESISTANCE
Dental ceramics are mainly composed with?
CRYSTALLINE MINERALS
GLASS MATRIX
Classifications of Metal-Ceramic System?
Cast metal ceramic restorations
Swaged metal ceramic restorations
What is metal-ceramic system?
Consist of cast metallic framework (CORE) on which at least 2 layers of ceramics baked.
What are the benefits of condensation?
Lower fining shrinkage
Less porosity in the fired porcelain
What are the methods of condensation?
Vibration
Spatulation
Brush technique
What is condensation?
Process of packing the particles and removing the liquid.
Steps of condensation?
Build up of cervical porcelain
Build up body porcelain
Cut back
Build up enamel porcelain
What is sintering?
The glass particles soften at their contact areas and fuse together.
What are the stages of maturity?
Low bisque
Medium bisque
High bisque
What’s glazing?
Porcelains are glazed to give a smooth and glossy surface.
The glazing should be done only on a slightly roughened surface and never should be applied on glazed surfaces.
What’s the difference between overglaze and self glaze?
Over glaze is a separate glaze layer applied to the restoration and fired at a lower temperature than body porcelain.
Self glaze has no separate layer; the surface of the porcelain is melted to form a vitreous layer.
Over glaze has lower chemical durability due to its high flux content.
Self glaze is more chemically durable but requires complete stripping if unsatisfactory.
What is swaged metal-ceramic system?
Designed to fabricate the metal coping of a metal-ceramic crown without the use of a melting and casting process
What are the bonding mechanisms?
Chemical adhesion
Mechanical entrapment
Compression bonding
Advantages of metal-ceramic system: BMLLL
More fracture resistant and durable than most all-ceramic
Low fracture rate
Less removal of tooth structure
Better marginal fit
Long term clinical durability
Disadvantages of metal-ceramic system:
Potential for metal allergy
Poor esthetics(Can not be used when a relatively high degree of translucency is desired.)
Abrasive damage to opposing dentition
Potential for fracture
Metal framework sometimes shows through gingiva resulting in dark margins
What’s all-ceramic sytem?
Any restorative material composed exclusively of ceramic such as:
feldspathic porcelain
glass ceramic
alumina core systems
and certain combination of these materials.
What are the classifications of dental ceramic?
Conventional ceramics
Castable glass ceramics
Injection moulded glass ceramics
Glass infiltrated core ceramics
Machinable ceramics
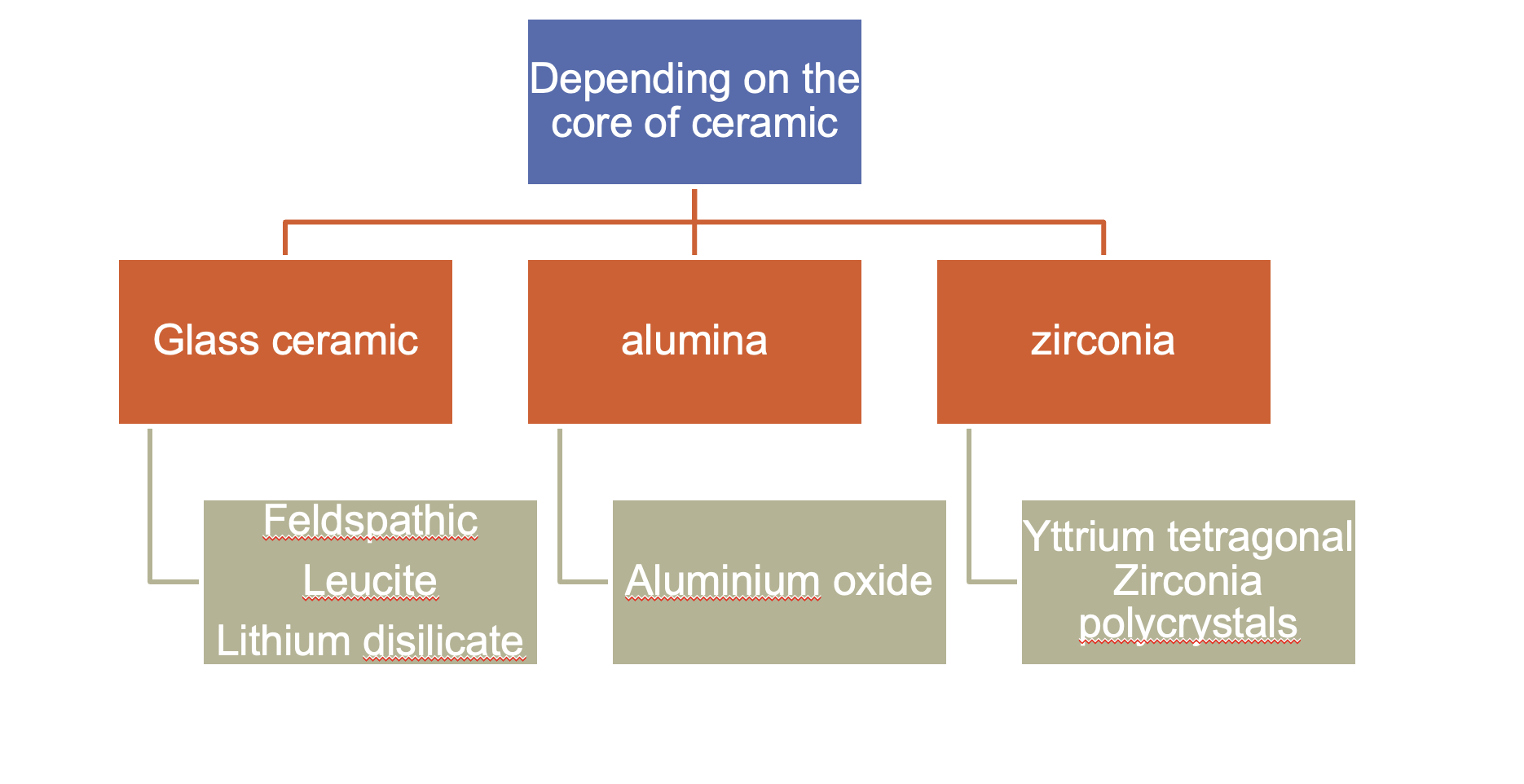
Conrad et al. (2007) JPD; 85: 5 classified all ceramic materials under three categories
glass ceramic
alumina
zirconia
What’s Castable Glass Ceramics?
Are polycrystalline materials developed for application by casting procedures using the lost wax technique
hence - castable ceramic
polycrystalline materials developed for application by casting procedures using the lost wax technique”, it means:
These materials are made to be used as dental restorations (like crowns, bridges, inlays, etc.)
And the method to shape them for that use is casting with the lost wax technique.
In simpler terms: “application” = where and how the material will actually be used in dentistry.
Castable glass ceramics classifications:
fluormicas
apatite glass ceramics
other glass ceramics
What’s the first commercially available castable glass-ceramics?
DICOR
Cast glass ceramic is composed of:
a. Tetrasilicic flouromica crystals (crystalline) - 55% by volume.
b. Glass matrix (non-crystalline) - 45% by volume.
What’s chameleon effect of dicor glass-ceramic?
Chameleon Effect
Refers to a material’s ability to blend with surrounding tooth structure, making restorations look natural.
In Dicor glass-ceramic, this effect is particularly strong because of its optical properties.
Pressable ceramics classifications:
Shrink free ceramic
Leucite reinforced
Lithia reinforced
Drawbacks of dental ceramics:
Low fracture toughness
Brittleness
High wear resistance