APHG Midterm
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Midterm Study Guide
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
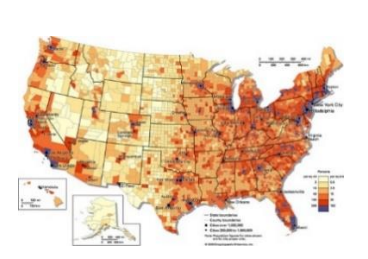
Thematic Map
A map that emphasizes the spatial patterns of geographic statistics or attributes, and sometimes the relationships between them.
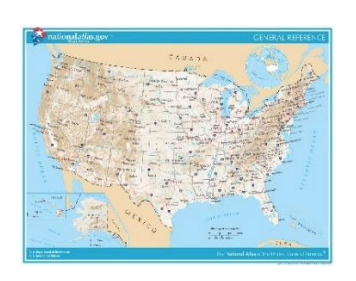
Reference Map
A map that shows geographic locations on Earth's surface, such as the locations of cities or oceans
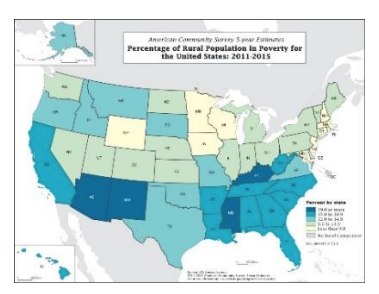
Choropleth Map
A thematic map that shows data aggregated for a specific geographic area, often using different colors to represent different values.
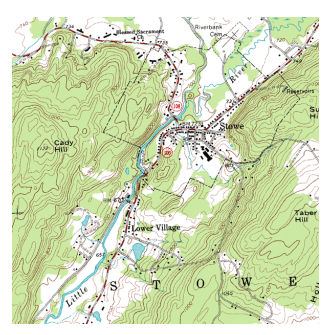
Topographic Map
A graphic representation of the three-dimensional configuration of Earth's surface.
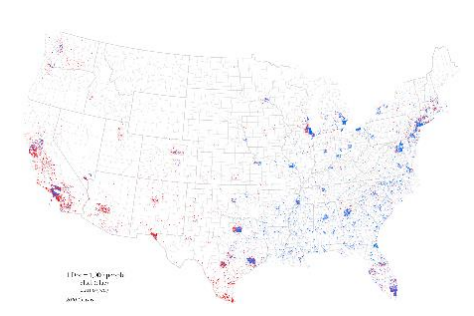
Dot Density/ Dot Distribution Map
A map that uses dots to represent objects or counts.
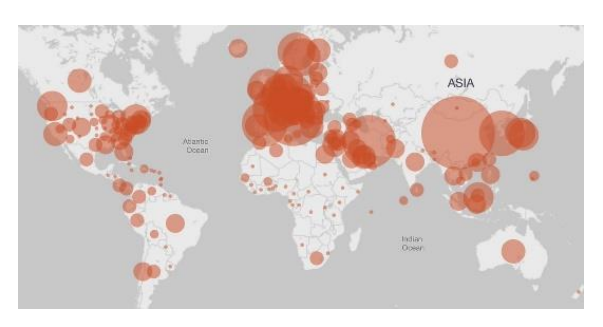
Proportional/Graduated Circle Map
A map that uses symbols of different sizes to represent numerical values.
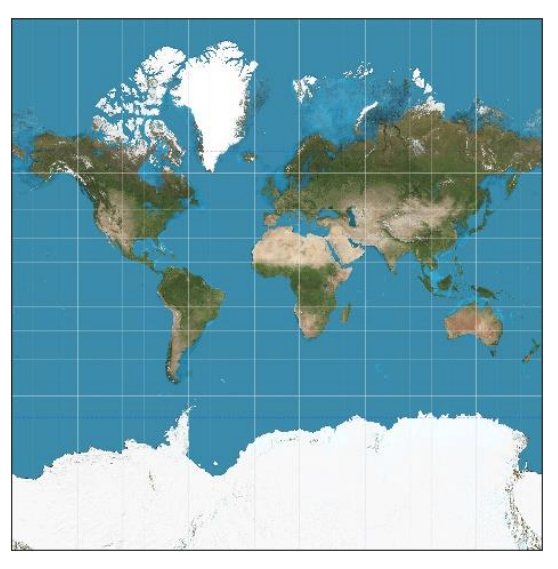
Mercator Projection
A map projection that is useful for navigation because the lines connecting points on the map represent the true compass direction; however, landmasses become increasingly distorted the farther away they are from the equator.
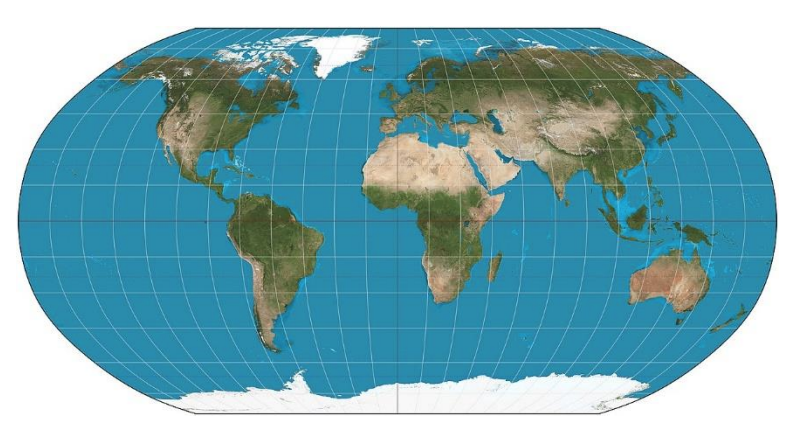
Robinson Projection
A map projection that attempts to create the most visually appealing representation of Earth by keeping all types of distortion relatively low over most of the map.
GPS
A system of 24 satellites that orbit the Earth twice daily and transmit radio signals Earthward.
GIS
A software application for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying, data related to positions on Earth’s surface.
Expansion Diffusion
Occurs when ideas or practices spread throughout a population, from area to area, in a snowballing process, so that the total number of knowers or users and the areas of occurrence increase.
Hierarchical Diffusion
Occurs when ideas leapfrog from one important person, community, or city to another, bypassing other persons, communities, or rural areas.
Reverse Hierarchical Diffusion
Occurs when ideas leapfrog from a lower level of a hierarchy to a higher level.
Contagious Diffusion
The wavelike spread of ideas in the manner of a contagious disease or forest fire, moving throughout space without regard for hierarchy.
Stimulus Diffusion
Occurs when a specific trait is rejected, but the underlying idea is accepted.
Relocation Diffusion
Occurs when individuals or groups with a particular idea or practice migrate from one location to another, thereby bringing the idea or practice to their new homeland.
Environmental Determinism
The belief that the physical environment is the dominant force shaping cultures and that humanity is a passive product of its physical surroundings.
Environmental Possibilism
The belief that any physical environment offers a number of possible ways for a society to develop and that humans can find ways to overcome environmental challenges.
Global Scale
The world at one level of data, no boundary lines.
Regional Scale
Data by continents or world regions, regional boundary lines shown.
National Scale
Data for one or more countries, shows political boundary lines.
Local Scale
Data at a subregional level, shows subregional boundary lines.
Formal Region
A geographical area inhabited by people who have one or more traits in common.
Functional Region
A geographic area that has been organized to function politically, socially, culturally, or economically as one unit.
Perceptual/Vernacular Region
A geographic area that is perceived to exist by its inhabitants, based on the widespread acceptance and use of a unique regional name.
Arithmetic/Crude Density
Population density, persons per square mile.
Physiological Density
Only looks at the arable land so it removes places where people typically don’t/won’t live so it’s more accurate, but the number will be higher.
Agricultural Density
Measures the number of farmers per unit of arable land.
Carrying Compacity
Number of people an area (or Earth) can support on a sustainable basis.
High Stationary Stage (DTM)
Birth rates and death rates are both high before the demographic transition starts. Substantial fluctuation in total population may be common.
Early Expansion Stage (DTM)
Death rates drop rapidly, and rates of population growth increase quickly.
Late Expansion Stage (DTM)
Birth rates decline and as a result the RNI decreases.
Low Stationary Stage (DTM)
Birth rates and death rates are similar again, but at much lower levels than before.
Natural Decrease Stage (DTM)
The total fertility rate drops below replacement level and birth rates are persistently below death rates, causing a natural decrease in population over time.
Dependency Ratio
The number of dependents in a population, that each 100 working-age people (ages 15 to 64 years) must support.
Challenges of Having a Young Population
Less people who are working and more people who need care and education as in daycares and schools.
Challenges of having an Aging Population
Less people working, less children being born, and higher need for care/retirement homes.
Population Pyramids
Graphic device for comparing age and sex structure.
4 Types of Population Pyramids
Rapid growth, slow growth, stability, and decline.
Push Factors
Factors that cause people to be dissatisfied with their present locales and want to move somewhere else.
Ex of Push Factors
Low wages, high unemployment rate, and religious persecution.
Pull Factors
The attributes of other places that make them appealing to potential migrant.
Ex of Pull Factors
High wages, economic opportunities, good climate, and higher standards of living.
Intervening Opportunities
A nearby attractive locale where migrants may decide to settle instead of going to the intended destination father away.
Intervening Obstacles
The complications that potential migrants will need to overcome to reach their destination.
Crude Birth Rate
Average number of births per 1000 people; the traditional way of measuring birth rates.
Total Fertility Rate
Average number of children born per woman during her reproductive lifetime.
Woman Reproductive Lifetime
15 to 49 years of age.
Replacement Fertility Rate
The average number of children needed to replace both parents and stabilize the population over time.
Replacement Level
2.1
Global Fertility Rate
2.4
Centripetal Forces
A force that brings people together and unifies a neighborhood, society, or country.
Centrifugal Landscape
A place with many layers of history that evolves through design and use over time.
Physical Landscape
All the physical surroundings that create and shape the places we are living in or examining. (not built by humans)
Economic Landscape
A the land around that has been affected by economic activities like, mining or farming.
Agricultural Landscape
The dominant feature of the rural landscape that can powerfully evoke a sense of place.

Modernist Architectural Landscape
The most fundamental and economic land use is agriculture, which is the dominant feature of the rural landscape.

Postmodern Architectural Landscape
A design style that is a reaction against modernist architecture; it has a flair for the dramatic , creating a spectacle while serving a variety of functions.
Material Culture
Physical, visible objects made and used by member of a cultural group.
Nonmaterial Culture
Intangible elements of culture including a wide range of beliefs, values, myths, and symbolic meanings passed from generations within a given society.
Indigenous Culture
A local culture that is no longer the dominant ethnic group within its traditional home-land because of migration, colonization, or political marginalization.
Popular Culture
Heterogeneous culture that is more influenced by key urban areas and quick to adopt new technologies.
Homogenous
Consisting of parts or elements that are all the same.
Heterogenous
Consisting of parts or elements that are different.
Political Geography
A branch of human geography concerned with the spatial analysis of political systems.
Political Map
A map that shows the spatial organization of the countries and territories on the entire globe at a given point in time.
State or Country
An independent political unit with a centralized authority that makes claim to sole legal, political, and economic jurisdiction over a region with defined boundaries.
Independent State
A state that rules itself and is not subject to the authority of another state.
Sovereign State
A state that possesses the sole authority over the land and people within its boundaries.
Nation
A community of people bound to a homeland and possessing a common identity based on shared cultural traits such as language, ethnicity, and religion.
Nation-State
The nation’s geographic boundaries (a people and its culture) exactly match the state’s territorial boundaries.
Nation-State Ideal
The idea that political authorities govern in the name of all a country’s citizens, modern mass communications link all residents, and state-based citizenship rights reinforce the idea of a national identity.
Nationalism
Sense of belonging to and self-identifying with a national culture.
Stateless Nation
An ethnic group or nation that does not possess its own state and is not the majority population in any nation-state.
Multinational State
A country containing multiple national, ethnic, and religious groups within its boundaries.
Multistate Nation
Ethnic groups territorially divided by one or more international boundaries.
Autonomous Region
A subdivision or dependent territory or country that has a degree of self-government, or autonomy, in its decision making.
Semiautonomous Region
A subdivision or dependent territory of a country that has some degree of, but not complete, self-government.
Self-determination
A nation’s ability to determine its own statehood and form its own allegiances and government.
Core Area
A small territorial nucleus from which a country grows in area and over time.
Escarpments
Aslopes that break up the general continuity of the terrain.
Devolution
The movement of power from the central government to regional governments within the state.
Ethnonationalism
A form of nationalism in which the nation is defined in terms of ethnic identity.
Neocolonialism
The set of economic and political strategies by which wealthy and powerful countries indirectly maintain or extend their influence over less wealthy areas.
Peripheral States
States that have relatively little industrial development, simple production systems focused mostly on agriculture and raw materials, and low levels of consumption of manufactured goods.
Core States
States that have the most advanced industrial and military technologies, complex manufacturing systems, external political power, and the highest levels of wealth and mass consumption.
Shatter-belt Region
Region of continuing and persistent fragmentation due to devolution and centrifugal forces.
Choke Point
A narrow passage that restricts traffic to another region.
Main Strategic Choke Points
Strait of Gibraltar, Strait of Magellan, Strait of Hormuz, Strait of Malacca, and Suez Canal.
Strait
A narrow body of water connecting two larger bodies of water.
Boundary
A clearly demarcated line that marks both the limits of a territory and divisions between territories; often called a border at the global scale.
Median Line Principal
An approach to dividing and creating boundaries at the midpoint between two places.
Borderland
A region straddling both sides of an international boundary where national cultures overlap and blend to varying degrees.
Frontier
A region in the margins of state control and settlement.
Enclave
A territory surrounded by a country but not ruled by it.
Exclave
Part of a national territory separated from the main body of the country to which it belongs.
Delimited
Describing how boundaries are fixed or defined to identify their limits.
Demarcated
Describing how boundaries are set apart to distinguish their limits.
Relic Boundary
A boundary that no longer functions as an international border.
Superimposed Boundary
A boundary that is placed on an area without regard to existing boundaries.