AP BIOLOGY -- MASTER FLASHCARDS
1/221
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
222 Terms
Properties of water
adhesion (sticks to other things), cohesion (sticks to itself, polar, high specific heat, less dense as a solid, surface tension,
What part of a water molecule is negatively charged
Oxygen
What part of a water molecule is positively charged
Hydrogen
What is the structure of an amino acid? (its functional groups)
Amino group (NHH), R group (differs), carboxyl group (COOH)
How an amino acid interacts with other amino acids is dependent on….
If it is hydrophilic/polar, hydrophobic/nonpolar, or special/charged
Elements of a carbohydrate
CHO (Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen)
Elements of a protein
CHON (Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen) + sometimes Sulfur in the R group
Elements of a nucleic acid
CHONP
Elements of a lipid
CHO
What are the functions of lipids in living organisms?
Energy storage, cell membranes, messenger molecules (hormones (steroids))
How does the R group affect the folding of a protein?
If the R group is polar, it will be on the outside of the folded protein. If the R group is nonpolar, it will be on the inside of the folded protein.
Dehydration synthesis
Water is REMOVED when two substances are synthesized
Hydrolysis
Water is ADDED to separate two substances (breaks the bond)
Bond between carbohydrates
Glycosidic, between monosaccharides
Bond between amino acids (protein monomers)
Peptide bond, between the carbon in the carboxyl group and the nitrogen in the amino group
Bond between nucleic acid monomers
Phosphodiester between the phosphates, hydrogen between nucleotides
How does an enzyme affect the rate of biological processes?
Speeds it up
What is the difference between a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid?
Unsaturated fatty acid has a bend in one of the chains and has at least 1 double bond.
How does the level of saturation affect the function of the lipid?
Saturated FA are solid at room temperature (butter), unsaturated are liquid (oil)
What kind of bonds are found in each level of folding of a protein?
Primary: Covalent/peptide
Secondary: Hydrogen
Tertiary: Many specific kinds of bonds
Quaternary: Hydrogen
How many bonds are found between adenine and thymine?
2 hydrogen bonds
How many bonds are found between guanine and cytosine?
3 hydrogen bonds
Purines
Adenine and guanine — DOUBLE ring
Pyrimidines
Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil — SINGLE ring
Osmosis
The net movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of HIGH water concentration to LOW water concentration
Hypertonic
If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will flow OUT of the cell. If a solute concentration is higher outside the cell than inside the cell, the solution is hypertonic.
Hypotonic
If a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water will flow INTO the cell because the solute concentration is higher INSIDE the cell than it is out of the cell.
Isotonic
No net flow of water into/out of the cell in an isotonic solution
Structure of a ribosome
rRNA and proteins
Function of a ribosome
Translation of mRNA to protein
Rough ER
Contains ribosomes, protein production
More surface area = more ribosomes = more efficient protein production
Smooth ER
Carbohydrate and lipid synthesis, detoxification
Golgi Bodies/Apparatus/Complex
Transports, sorts, and modifies proteins/lipids
Contains Golgi vesicles which transport products
Mitochondria
ATP production - folded inner matrix and double membrane
*Introduced to eukaryotic cells through endosymbiosis - evidence of how eukaryotic cells originated from prokaryotic cells
*All mitochondrial DNA is inherited from the mother
*Matrix folds increase surface area for ATP production
Lysosome
Has a different PH inside of it, contains enzymes, controls apoptosis or programmed cell death
Vacuole
Holds materials and waste — more important in plant cells because it provides turgor pressure which gives plants structure
*Contractile vacuole: pumps water out of the cell
*Food vacuole: ingests food through phagocytosis
Chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis, consists of stroma and thylakoid stacks (grana), THREE membranes
*Also supports endosymbiosis theory of eukaryotic origin
Where do the light dependent (ETC) and independent (calvin cycle) reactions take place?
Light dependent: Thylakoid
Light independent: Stroma
Where does the citric acid cycle take place?
Mitochondrial matrix
Where does the cellular respiration ETC take place?
Inner mitochondrial membrane
Where is ATP synthesized in PHOTOSYNTHESIS?
Chloroplast (thylakoid membrane)
How does surface area to volume ratio affect the size of the cell?
The larger the cell is, the more the SA to volume ratio decreases.
What type of surface area to volume ratio is most favorable?
HIGH surface area to volume ratio because this allows for more effective and efficient exchange of materials and heat
How can a cell increase surface area without increasing the volume?
By dividing into smaller sections
How do organisms obtain nutrients and eliminate waste?
Endocytosis, exocytosis, diffusion
What are the components of the cell membrane?
Phospholipid bilayer, transport proteins, carbohydrates, cholesterol
Do enzymes affect the Gibbs Free Energy of a chemical reaction?
No. They lower the activation energy but not the amount of reactants/products that are formed.
What is Gibbs Free Energy?
The amount of energy in a system that is available to do work
What happens when a substrate binds to an enzyme?
The substrate is either synthesized with another substance or broken apart
Conditions that affect enzyme structure
PH, Temperature
What happens to the PH when the concentration of hydrogen ions increases?
Becomes more acidic
What happens to the PH when the concentration of hydrogen ions decreases?
Becomes more basic
What happens to enzymes when the PH increases?
Speed up until optimal PH, then denature
What happens to enzymes when PH decreases?
Slows down (depends on optimal PH)
A competitive inhibitor is
An inhibitor that binds to the active site
How can researchers overcome competitive inhibitors?
They can make something that binds to the inhibitor, preventing it from fitting in the allosteric site
What is an allosteric inhibitor?
An inhibitor that binds to an allosteric site which changes the shape of the active site
All enzyme inhibitors ___
Block the active site to slow down the chemical process
First law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted/transferred
Second law of thermodynamics
The entropy of the universe only increases
How is order (entropy) maintained in a system?
Chemical reactions transfer energy to make it more ordered
How are cellular processes powered
ATP
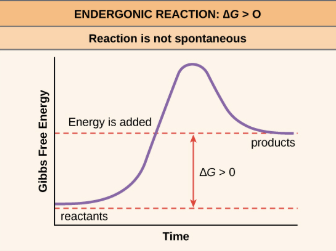
Endergonic reaction
Energy ENTERS the reaction, +DeltaG to products
Requires energy to occur
Anabolic
Non--spontaneous
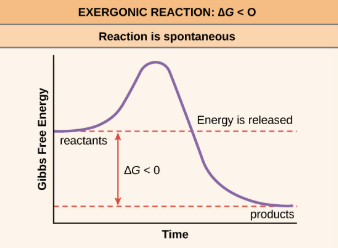
Exergonic reaction
Energy exits the reaction, —DeltaG to products
Catabolic
Spontaneous
What is energy coupling?
When energy from an exergonic reaction powers an endergonic reaction
What organism first evolved photosynthesis
Cyanobacteria
What/Where are the light dependent reactions?
Electron transport chain, occurs in the grana (stacks of thylakoids)
What/Where are the light independent reactions?
Calvin cycle, occurs in the stroma
Calvin cycle
Carbon Fixation, Reduction, Regeneration
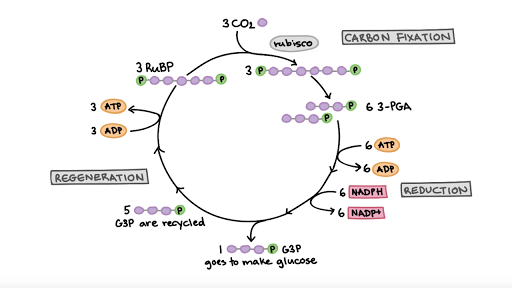
What is reduced in the photosynthetic electron transport chain?
NADP+ to NADPH
How is ATP synthesized in the photosynthetic electron transport chain?
The electrons create a proton gradient that powers ATP synthase
Reduction
+electron, Increases energy of the compound that is reduced
Oxidation
Takes away an electron, releases energy
Redox reactions
Chemical processes like photosynthesis that consist of both oxidation and reduction taking place
What happens to the electrons after light is absorbed?
They become excited
What direction are the protons pumped during light dependent reactions to generate the photon gradient?
INTO the thylakoid
Photosynthetic electron transport chain
Consists of photosystem ll and photosystem l, produces oxygen by splitting water and ATP through chemiosmosis, also produces NADPH
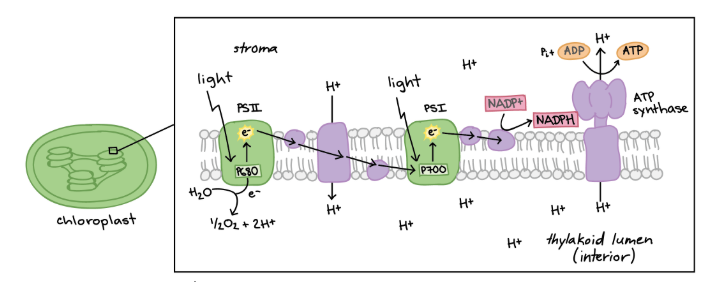
Chemiosmosis
movement of ions across a semipermeable membrane to form a gradient
What is fermentation?
anaerobic respiration
Products of fermentation
Ethol Alcohol (yeast fermentation), Lactic acid (muscles)
Where are electron transport chains located in cells?
Membranes (cell membrane, mitochondrial membrane)
Oxidative phosphorylation
Electron Transport chain AND Chemiosmosis produce ATP
Photophosphorylation
Using light energy from photosynthesis to convert ADP into ATP
How does the proton concentration affect the PH?
Intermembrane space is more acidic
Glycolysis
Splitting glucose into pyruvate acid
Occurs in the cytoplasm
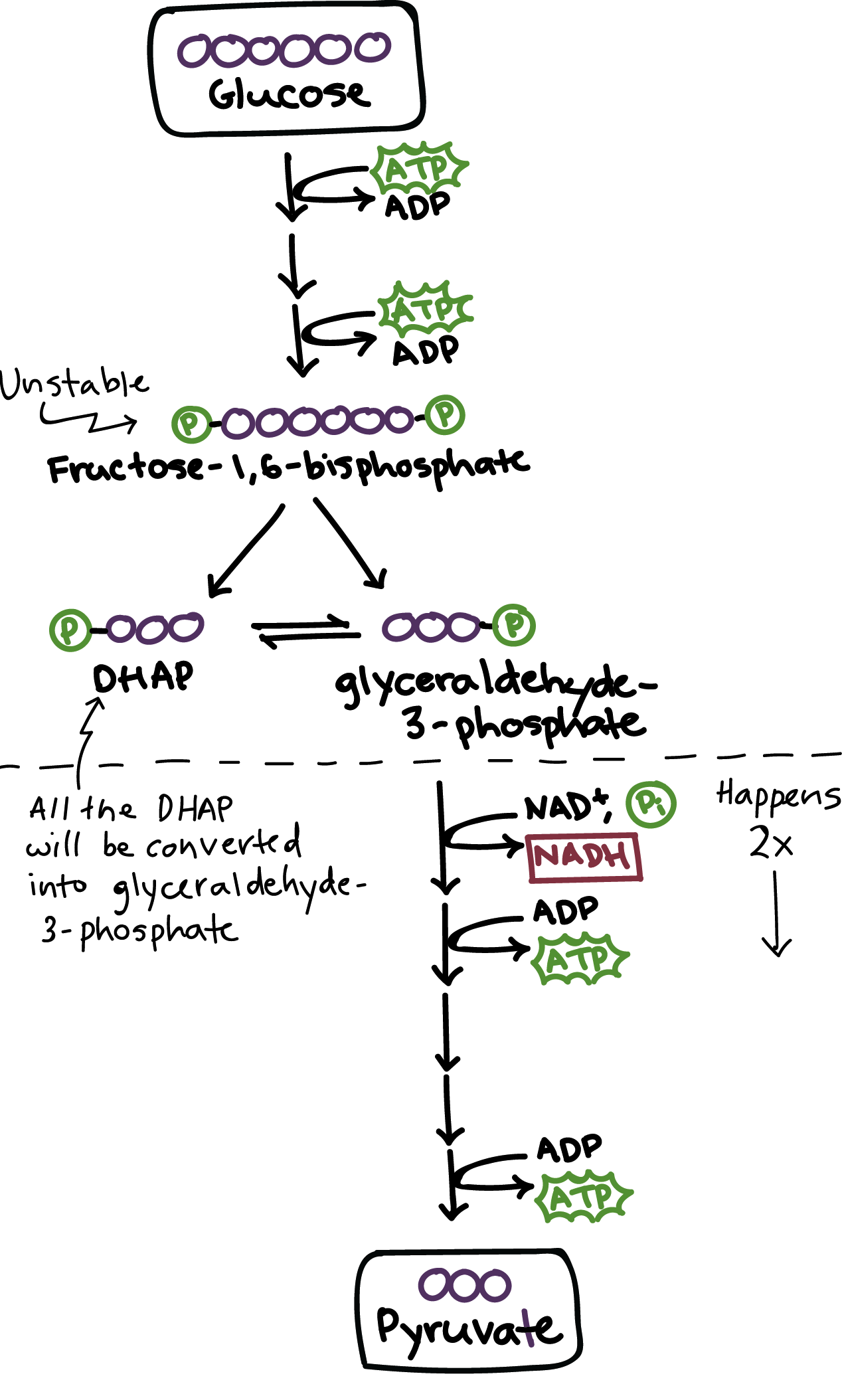
Starting materials of glycolysis
6 carbon glucose
Products of glycolysis
2 ATP, 2 Pyruvate, 2 NADH
How are electrons transported to the electron transport chain?
NADH and FADH2
What are the starting materials of the Krebs cycle?
Acetyl-CoA, oxlacoacetate
Pyruvate oxidation
In aerobic respiration, Pyruvate is converted into acetyl-coA
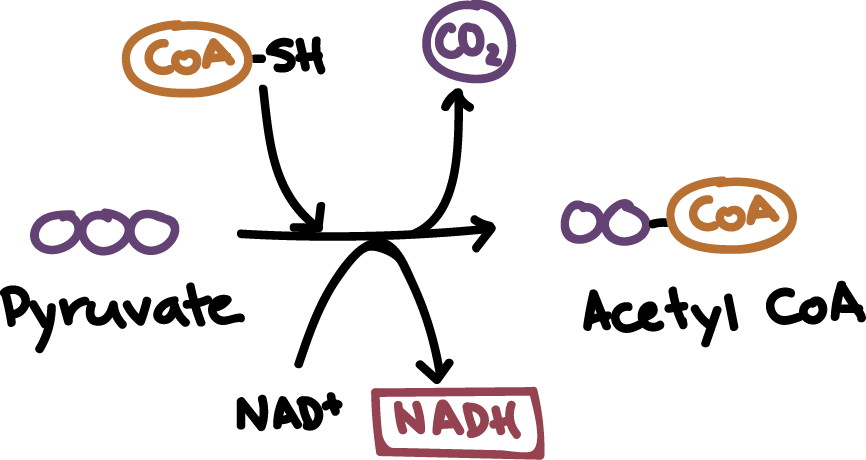
What is the role of pyruvate oxidation in anaerobic respiration?
Pyruvate converts to lactate or ethanol
What is the function of ATP hydrolysis?
Releases energy
Message communicated by direct cell-to-cell contact
Juxtacrine (used by immune cells)
Message communicated during chemical signaling
Endocrine (Hormones)
How cells communicate over a short distance
Paracrine (neurotransmitters at synapses)
Example of endocrine signaling
Hormones traveling through the bloodstream
What process releases a chemical signal from a cell?
Exocytosis
Where are chemical signals synthesized and processed?
Synthesized: ER, Golgi
Processed: Golgi
What occurs during reception
Ligan binds to receptor on target cell
Where is the receptor for a steroid hormone?
Inside the cell