Abdomen Urinary System
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
At 3 weeks gestation the kidneys begin to form columns of mesoderm. By the 5th week of development, three kidneys have developed. These are:
Pronephros
Mesonephros
Metanephros
The Pronephros AKA Forekidney leaves behind a _____ to form the next kidney and has _____ function
duct; no
The mesonephros AKA midkidney provides _______ function while the kidney develops.
partial
Mesonephric duct referred to as the ____________ in males gives rise to the:
Wolffian duct;
epididymis, ductus deferens and ejaculatory duct
Mesonephric duct referred to as the ____________ in females gives rise to the:
Mullerian duct;
uterus, fallopian tubes, proximal vagina
The permanent kidney AKA Metanephros. Within the ____ week of gestation the nephron function begins
8th
What is the function of the two kidneys?
to produce and secrete urine
What are the 2 ureters used for?
They are tubes leading from the kidneys to the urinary bladder
What makes up the upper urinary system?
Two kidneys & two ureters
What makes up the lower bladder?
One urinary bladder and one urethra
True or false: the kidneys are peritoneal
False; they are retroperitoneal
Which kidney sits higher: right or left?
left (makes it harder to see because of gas and rib shadowing)
Right and left kidney measurements should not be more than ____cm of each other in length
1-2
What is the length measurement of a kidney?
9-12cm
What is the (AP) measurement of a kidney?
4-5cm
How thick is the kidney?
2-3cm
Convex lateral borders of the kidney are found on the outside and concave medial borders are found on the _________
inside
The outer & inner portions of the parenchyma are called and they are responsible for?
Cortex - responsible for filtration
Medulla - responsible for absorption
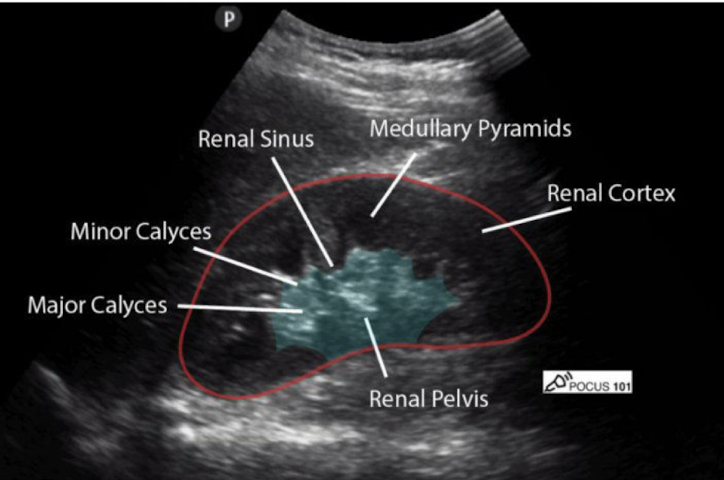
Review this image
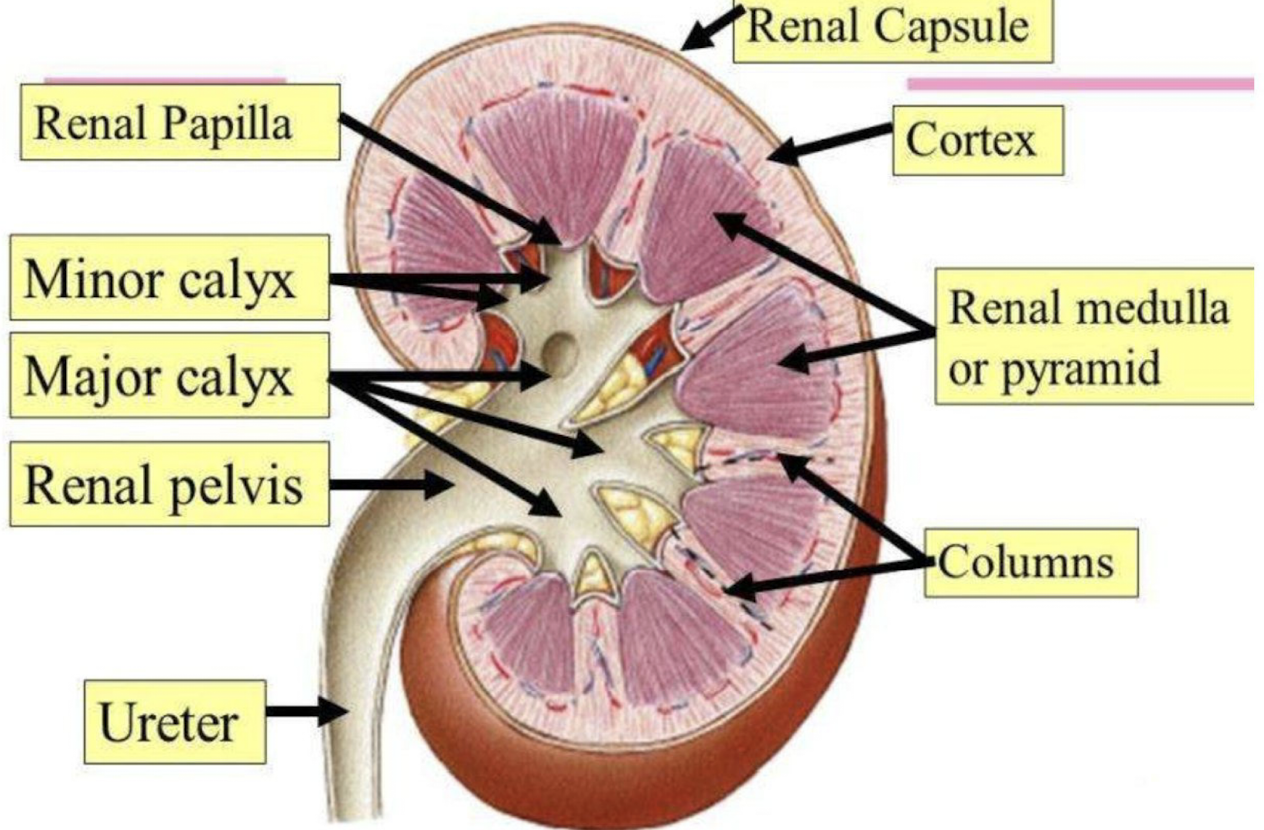
What is the functional unit of the kidney?
The nephron
Where is the nephron located within the kidney?
almost entirely in the cortex
Where are juxtamedullary nephrons located?
Within the medulla
Another term for a network of capillaries within the corpusle? It is surrounded by:
Glomerulus; Bowmans capsule
Blood is brought into the ______________ via the ___________ arteriole where it is non selectively filtered:
glomerulus; afferent arteriole
Blood exits the glomerulus into Bowman’s capsule via:
the efferent arteriole
The filtered substance that was removed from the blood in the glomerulus is refered to as:
filtrate
At what point is the filtrate considered urine?
Once it enters the collecting duct
True or false: each nephron has its own collecting duct
False; several nephrons will drain into a single collecting duct
What does urine drain through?
Papilla
Write out the correct order of production and pathway of urine
Afferent arteriole → glomerulus → efferent arteriole → Bowmans capsule → proximal convoluted tubule → deceasing loop of henle → loop of henle → ascending loop of henle → distal convoluted tubule → collecting duct → minor papilla → minor calyx → major calyx → renal pelvis → ureter → bladder → urethra
Unfiltered blood enters the corpuscle via the ______________
affarent arteriole
Blood is non selectively filtered in the ___________
glomerulus
Filtered blood exits through the corpuscle via the ______________
efferent (exit) arteriole
Filtrate enters the tubule through an opening in:
Bowman’s capsule
Reabsorbtion occurs along the different sections of the tubule via
Pertubular capillaries & venules
Urine drains from the distal convoluted tubule into a:
collecting duct
After the collecting duct how does urine get to the urethra?
papilla → minor calyx → major calyx → renal pelvis → ureter → bladder → urethra
Renal arteries are ____________ branches of the abdominal aorta just below the SMA
lateral
Which is longer the right renal artery or the left and where is it traveling?
The right is longer and it travels posterior to the IVC
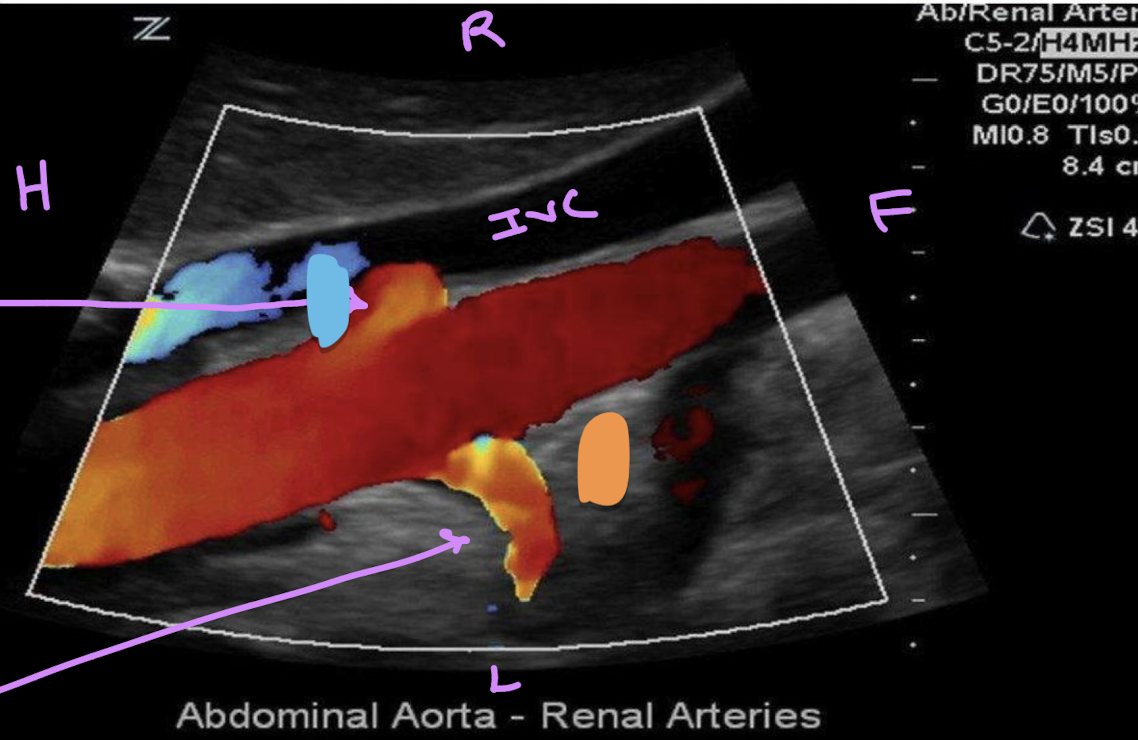
This is right coronal view of the proximal renal arteries. Identify if the right or left arteries are on the orange or blue.
Orange: left
blue: right (posterior to the IVC)
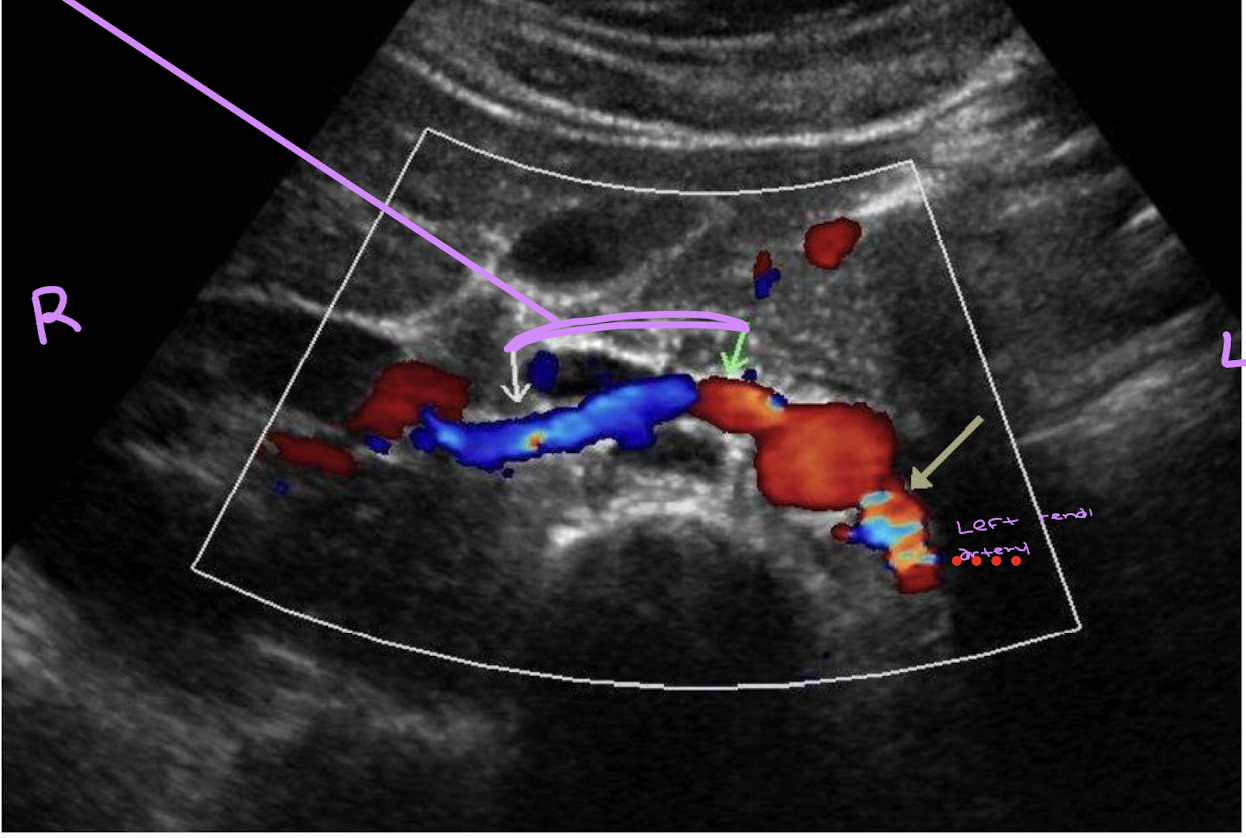
keep in mind the right renal artery is positioned at 10:00 and the left is at 4:00
The right renal vein is ____________- than the left renal vein
shorter
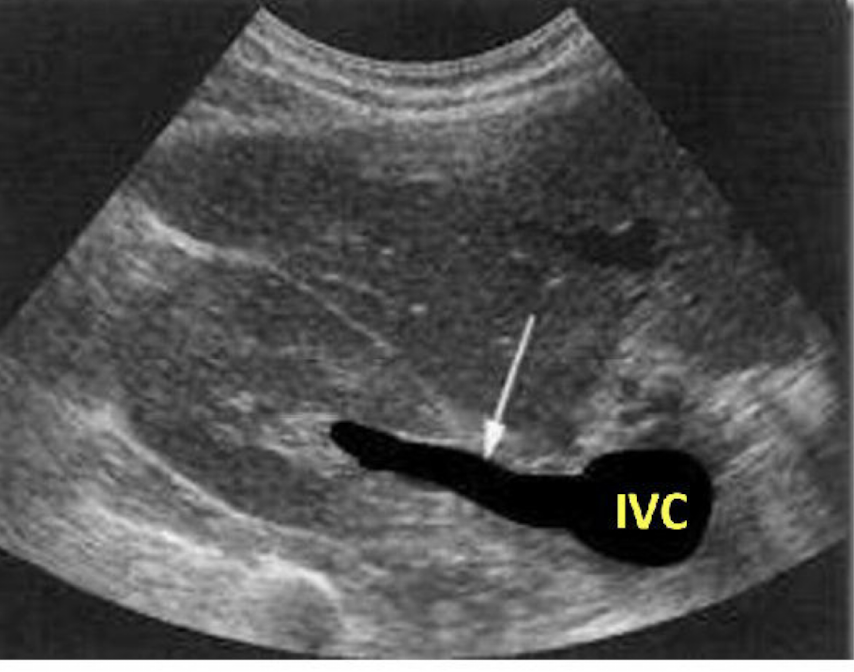
What is this picture showing?
The right renal vein draining into the IVC
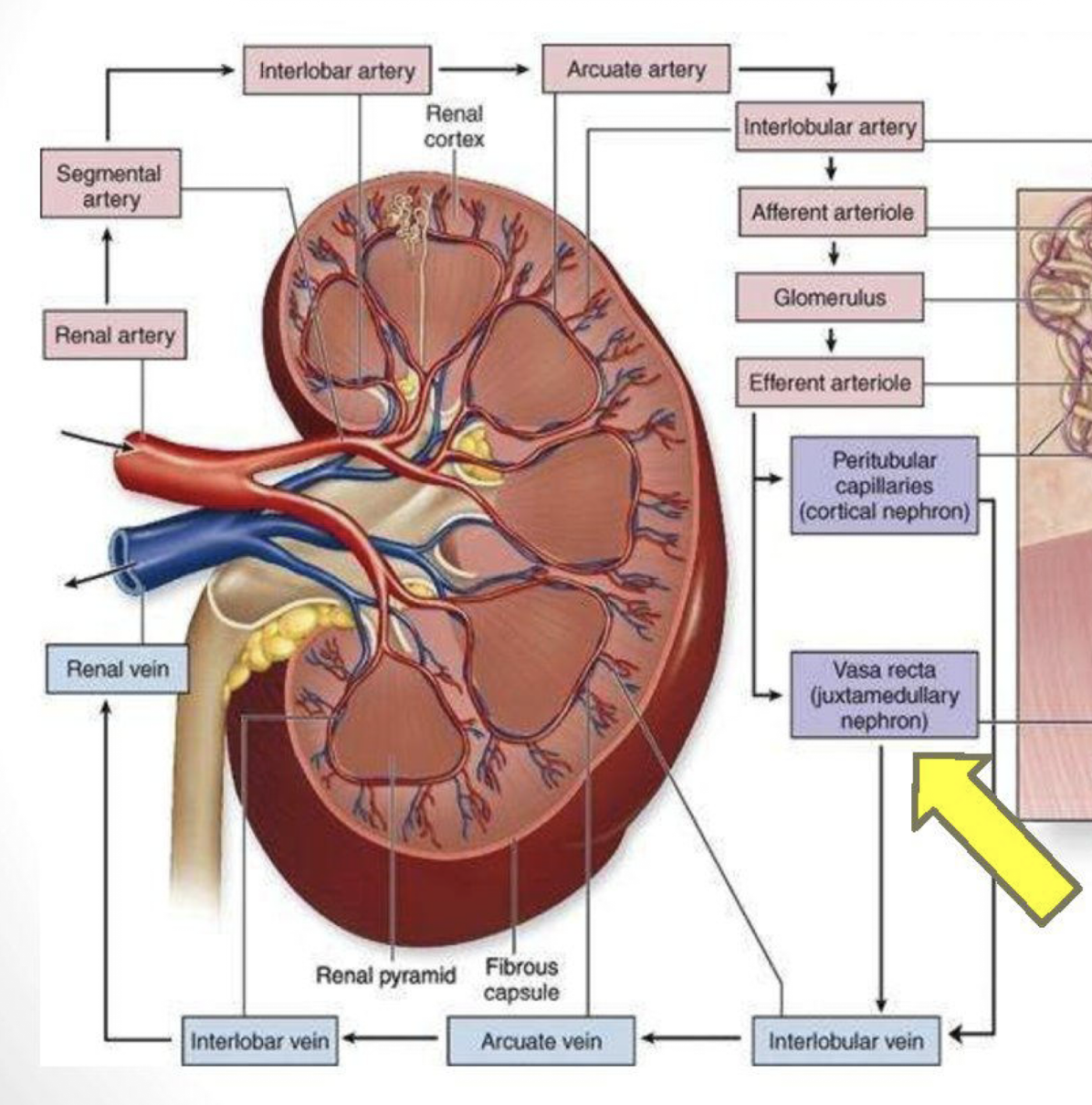
What is the order of blood flow through the kidney?
Renal artery → segmental arteries → interlobar arteries → arcuate arteries → interlobular arteries → arrerent arterioles → glomerular capillaries → efferent arterioles → peritubular capillaries → vasa recta → interlobular veins → arcuate veins → interlobar veins → renal vein
Ureters undergo ______________ in order to facillitate the flow of urine from the renal pelvis towards the bladder
peristalsis
Can we see normal ureters on ultrasound?
Not well
Is the urinary bladder a retroperitoneal organ?
yes
The bladder wall consists of four layers. List from superficial to deep
Serosa → muscular → submucosa → mucosa
What makes up the trigone of the bladder?
two posterior ureters & one inferior urethra
The _________ muscle controls the UB contractions
detrusor muscle
Which wall of the bladder do we measure?
anterior wall of a full bladder
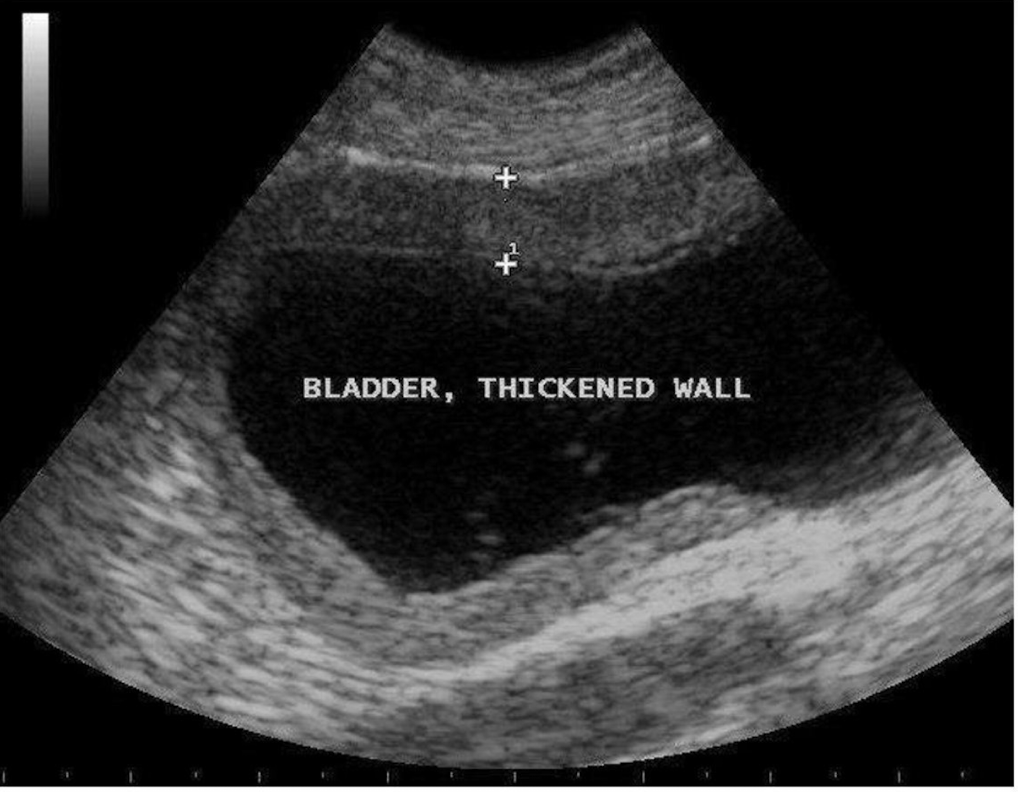
What is being measured here?
the anterior wall of the bladder
Which sphincter of the urethra is voluntary and involuntary?
Internal sphincter - involuntary sphincter
External Sphincter - voluntary control
What is the main function of the kidneys?
filter wastes from the blood and produce and excrete urine
Urine is primarily made up of _________
96% water
What helps control the following:
Blood pressure
Ions
pH
Osmolarity (protein balance going back and fourth)
The Kidney
When BP is elevated, the kidneys help lower it by:
excreting excess salt and water
When blood pressure is too low how do the kidneys help make it rise?
They reduce the amount of salt and water removed from the blood and the enzyme renin aids in constriction of blood vessels causing BP to rise
When ion levels are too high, the kidneys will:
increase their levels of excretion
When ion levels are low, the kidneys will:
allow ion reabsorption into the blood
Kidneys monitor and regulate levels of _____________ and ____________ in the blood to control PH
hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions)
Laboratory data: kidney function can be evaluated by testing:
Blood & Urine
A patient with a urinary tract infection (UTI) may present with an increase in
WBC
In addition to being able to detect a UTI urinalysis also tests for specific gravity which is:
the kidneys ability to concentrate urine. Meaning if you drink more fluid specific gravity will decrease and vice versa
Increased levels of BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen), Creatinine and Uric acid all indicate:
renal function impairment
The three steps involved in the production of urine:
1) glomeruluar filtration
2) tubular reabsorbtion
3) tubular secretion
What enzyme is released by the kidneys to help lower BP?
Renin
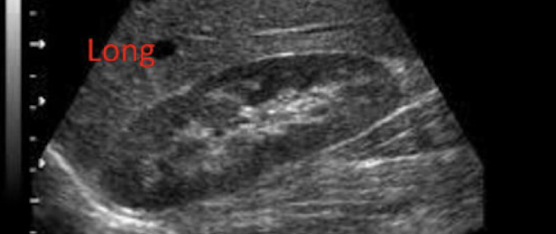
Which type of kidney image is this?
longtudinal
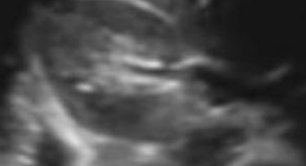
What section of the kidney is this and which scan plane?
Transverse midpole (has a horseshoe shape)
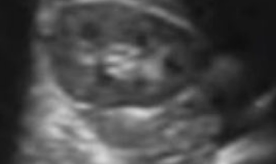
What portion of the kidney is this that looks like a donut
upper & lower poles in transverse
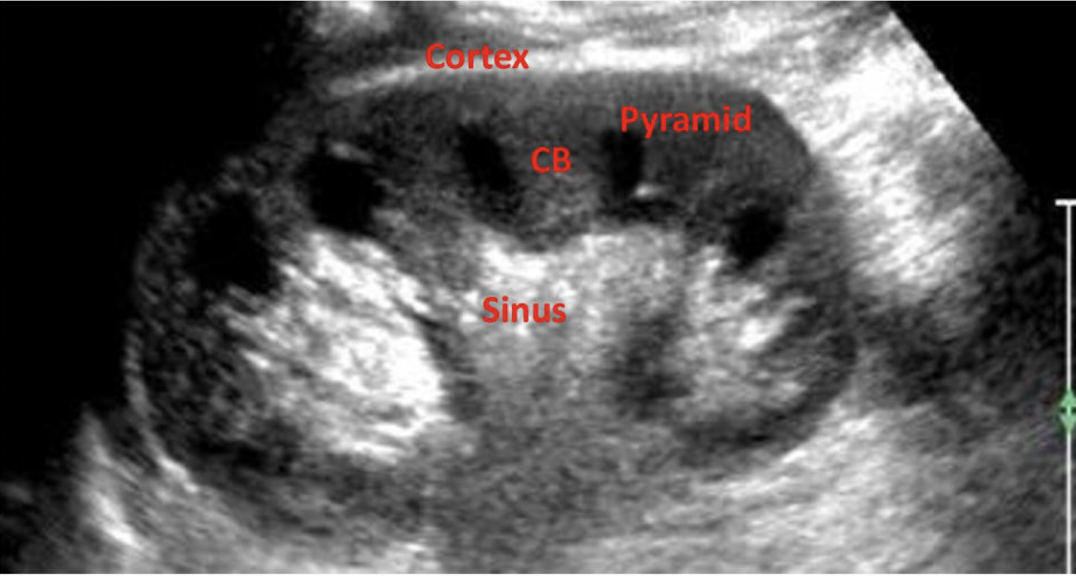
What does CB stand for in this image?
Column of Bertin
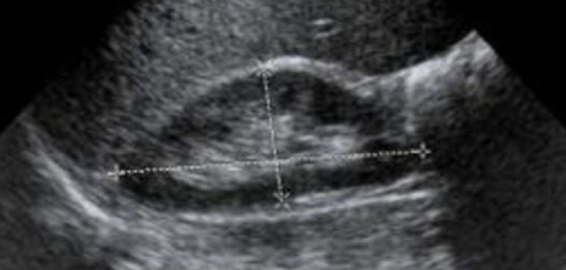
What is this image showing?
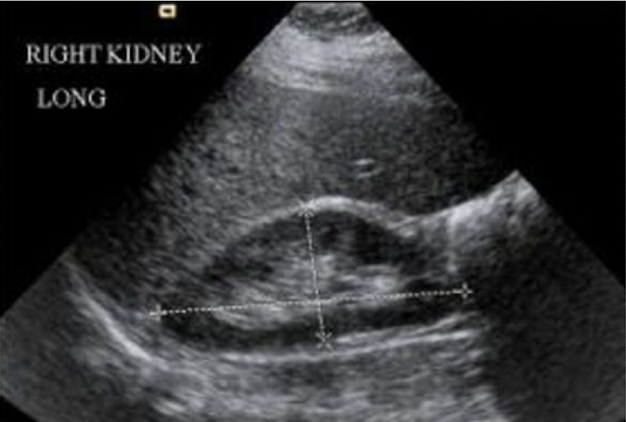
More of the liver is shown in this image so it is the ________ kidney
Right kidney is shown
Prominent Columns of Bertin can be mistaken for:
a renal mass
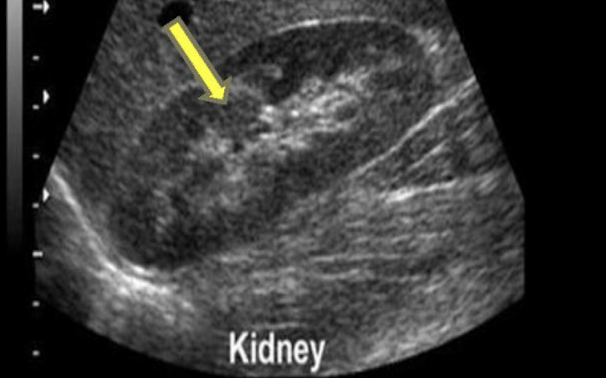
Congenital variants: Compensatory hypertrophy
enlargement of the healthy or unaffected kidney
Found in cases of unilateral renal agenesis or compromised renal function of one kidney
Compensatory Hypertrophy
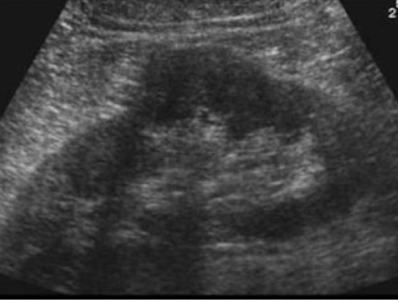
What anatomic variant is this and which kidney is it most commonly found in:
Dromedary hump: Most commonly found in the left kidney
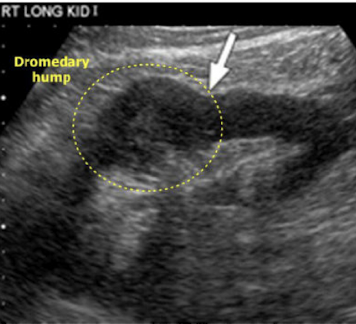
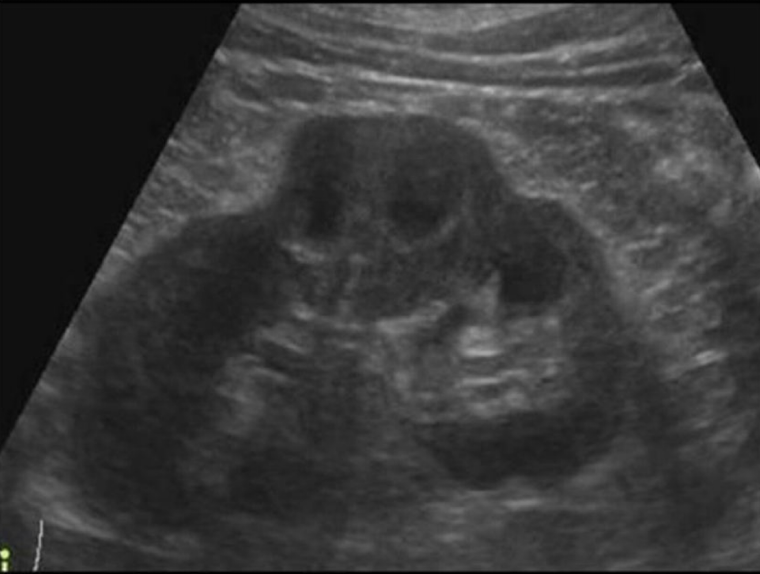
What is this image showing:
Dromendary hump
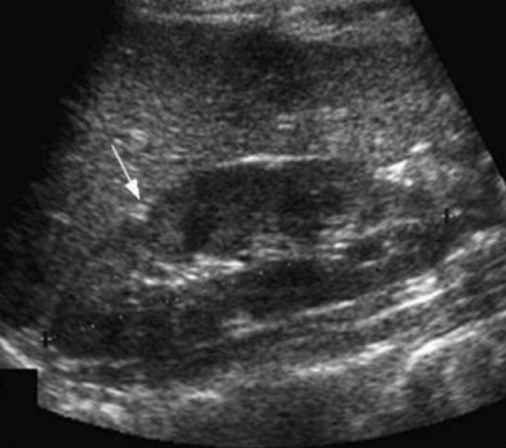
What is the arrow pointing to? A small hyperechoic triangle
Junctional Parenchymal defect
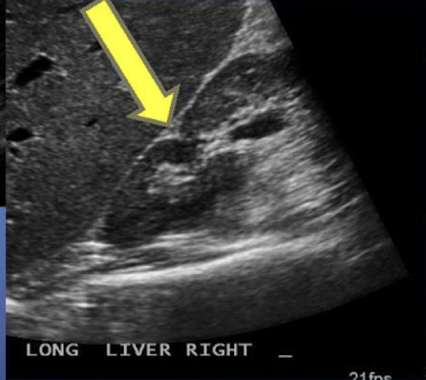
What is the arrow pointing to:
Junctional Parenchymal defect
This type of congenital variant occurs when there is fusion of the kidneys.typically the fusion is of the lower poles
Horseshoe kidney
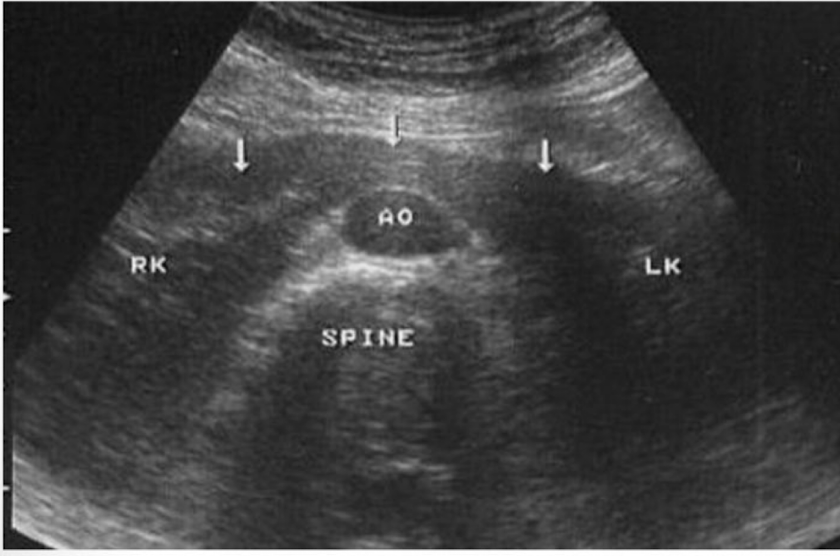
Which type of analomy is shown in this image→ ?
Horseshoe kidney
When the renal pelvis is located outside the renal hilum what congenetal varient is that?
Extrarenal pelvis
Duplicated collecting system has two subcategories:
complete duplication
incomplete duplication: more common
Complete duplication consists of:
two collecting systems and two ureters
Incomplete duplication consists of:
consists of two collecting systems and two ureters. The ureters will join and only one will drain into the urinary bladder
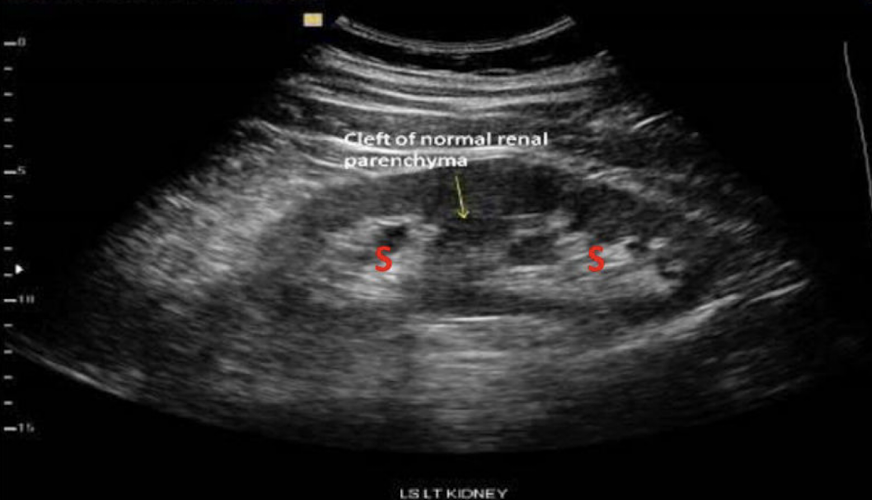
Which congenital varient is this showing?
The renal sinus is two echogenic regions seperated by tissue. it is a duplicated collecting system
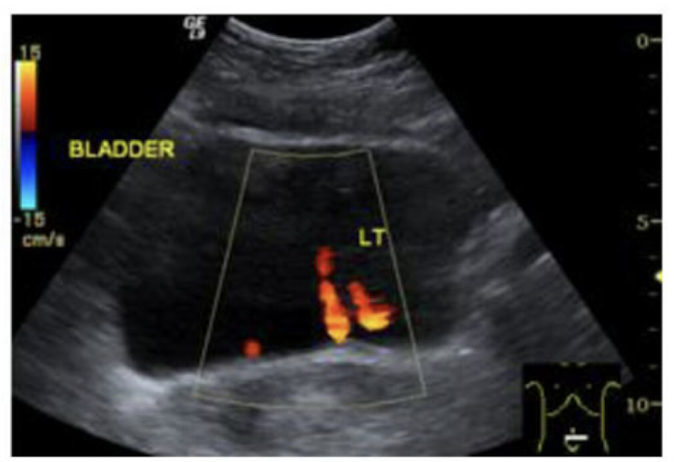
How can we differentiate between an incomplete and complete duplicating system?
Turn on color doppler and if two jets enter the bladder on the same side it is a complete duplication
Congenital varients: Supernumery Kidney is a third kidney that will appear __________. This is very rare
smaller
Congenital variants:
absence of a kidney
True or false: you need to have at least one kidney to live
true; Bilateral renal agenesis is incompatable with life
When looking for an ectopic kidney you shouldn’t automatically assume one kidney is missing you instead should:
check the pelvic region first to see if the kidney is there since this is the most common location for ectopic kidney
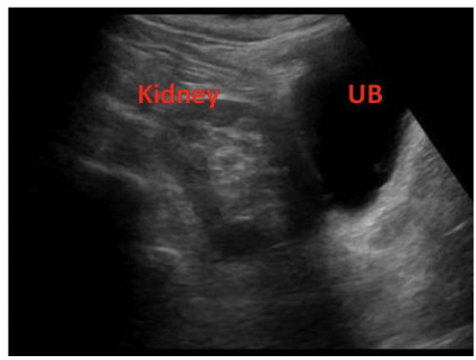
You can rule an ectopic kidney if:
1) demonstrates an empty renal fossa
2) a single pelvic kidney was found in left lower quadrant
Ectopic Kidney: intrathoracic
results when the kidney continues to ascend. Diaphragm closes below the kidney
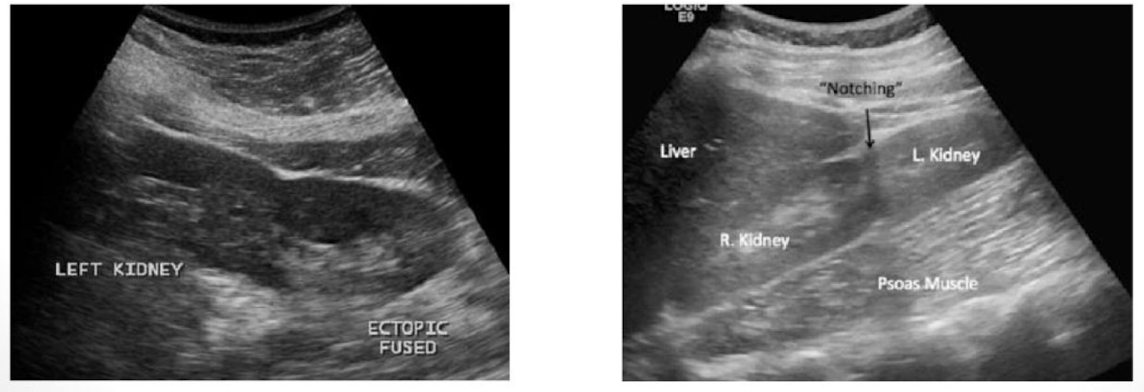
both kidneys are located on one side of the body. What type of ectopic kidney is this:
Ectopic kidney: cross fused
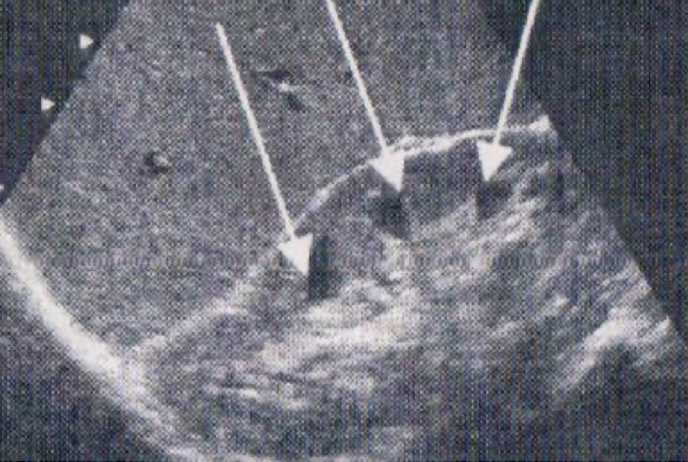
What are the arrows pointing to?
The pyramids of the kidney
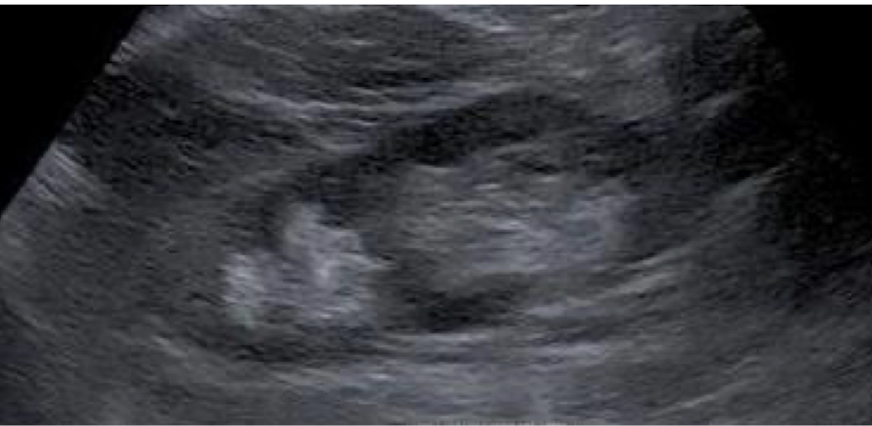
What anatomical variant is shown below?
duplicated collecting system
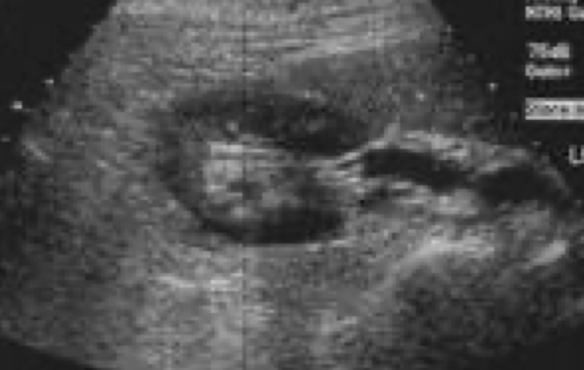
Is this the right or left kidney? trans or long? upper, mid or lower pole
Right (the C is the correct direction), trans, mid pole
Majority of the nephron is found in:
the cortex