DNA mutations
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
in a natural population, _________ is most common phenotype and some genes have multiple of these alleles prevalent
wild-type
______________ changes wild-type mutation to some new variation (moves away from wild-type)
forward mutation
__________ ________ takes the mutant back to the wild-type phenotype
reverse mutation
_____________ ____________ is an exact fix alteration of of mutated base back to wild-type sequence
true reversion
___________ _________ mutation re-creates original phenotype without correcting mutation itself
second-site reversion
Second-site reversion is also called ___________ __________
suppressor mutation
second-site reversion suppresses the effect of the _______ mutation
first
______________ __________ has the 2nd mutation in same gene as 1st mutation
intragenic suppressor
_____________ __________ mutations are in different gene
intergenic suppressor
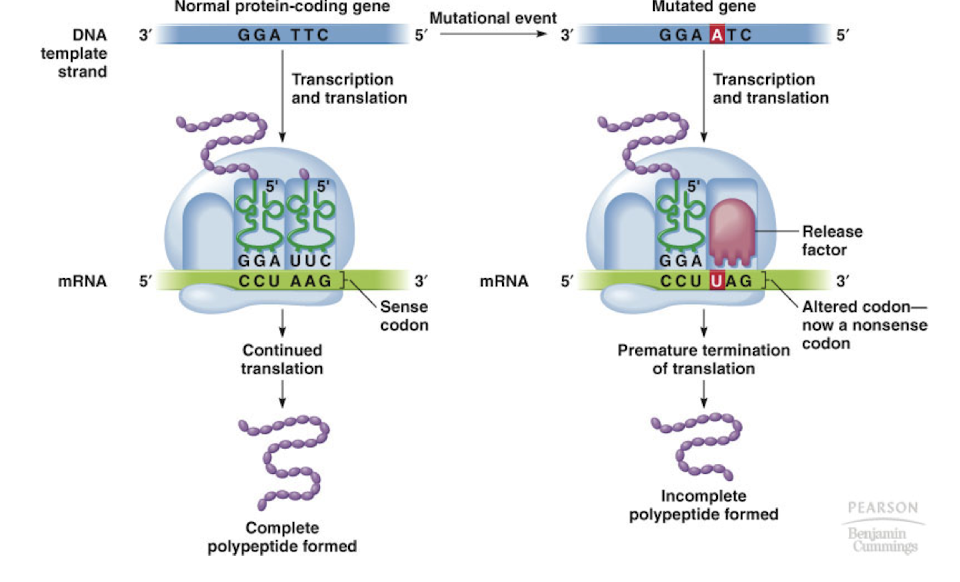
forward mutation example
_________ _______ uses bacterial tester strains to screen for chemical mutagens
Ames test
In Ames test, salmonella cells are histidine _____________
auxotrophs
Salmonella cells are used in ames test because they are ____________ to mutation by chemicals
sensitive
___________ require chemicals because they are unable to synthesize in growth medium
auxotrophs
In Ames test you add suspected mutagen to cells, if it is a mutagen _____________ ____________ will produce his ____________ colonies
revertant mutation, prototrophic
_____________ can synthesize all needed metabolites and are grown on minimal medium
prototrophic
In Ames test you add suspected mutagen to cells, if it is not a mutagen there will be _______ growth meaning it __________ revert back to wild-type
no, cannot
Ames test
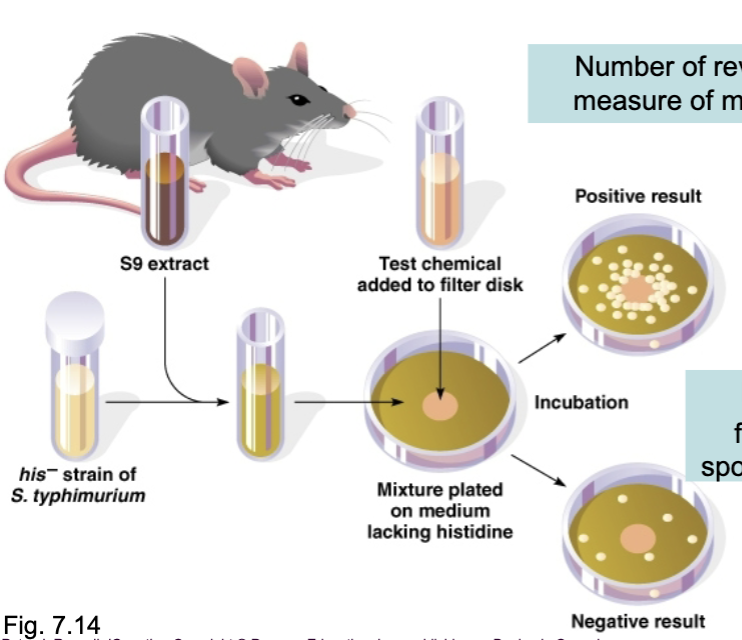
In Ames test, S9 extract is added to the strain and it a ___________ enzyme
liver
In an Ames test, many chemicals are not ___________ themselves
mutagenic
In an Ames test, the strain is converted to mutagens by ______________ _______________ pathways in liver
enzymatic detoxification
In the Ames test, you add the test chemical to ________ of plate
middle
In a Ames test, the mixture is plated on a medium lacking __________
histidine
In a Ames test, you can have negative control which is a plate with _______________ solvent
nonmutagenic
In a Ames test, the number of __________ colonies measure of mutagen potency
revertant
In a Ames test, the ___________ control has few colonies with some spontaneous mutations
negative
______________ _________ ____________ is an unusual form of mutation that can cause several human genetic disorders
trinucleotide repeat expansion
In normal individuals, certain genes and chromosomes locations contain regions with _____________ _________
trinucleotide repeats
In normal individuals, sequences are transmitted from parent to offspring _________ mutation
without
trinucleotide repeat expansion results when repeat copy number ___________ above critical size
increases
there are unusual features of trinucleotide repeat expansion disorders, one of which is the severity of disease can worsen in future generations, this is called ______________
anticipation
_____________ is when the repeat range is just above normal to many
premutation
_______________ is when the repeat number expands beyond premutation
full mutation
there are unusual features of trinucleotide repeat expansion disorders, one of which is severity depends on __________ from mother or father
inheritance
there are unusual features of trinucleotide repeat expansion disorders, but the cause is not well understood however increased repeats alter DNA structure (_________ _______ ___________) and can lead to replication error
stem loop formation
Formation of hairpin loop
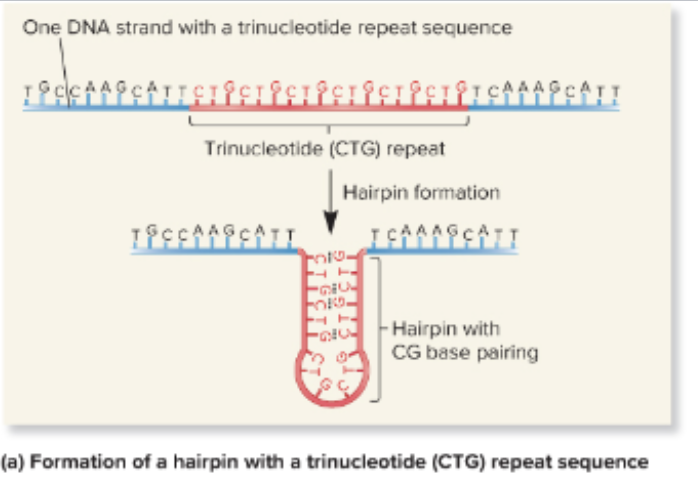
mechanism of trinucleotide repeat expansion
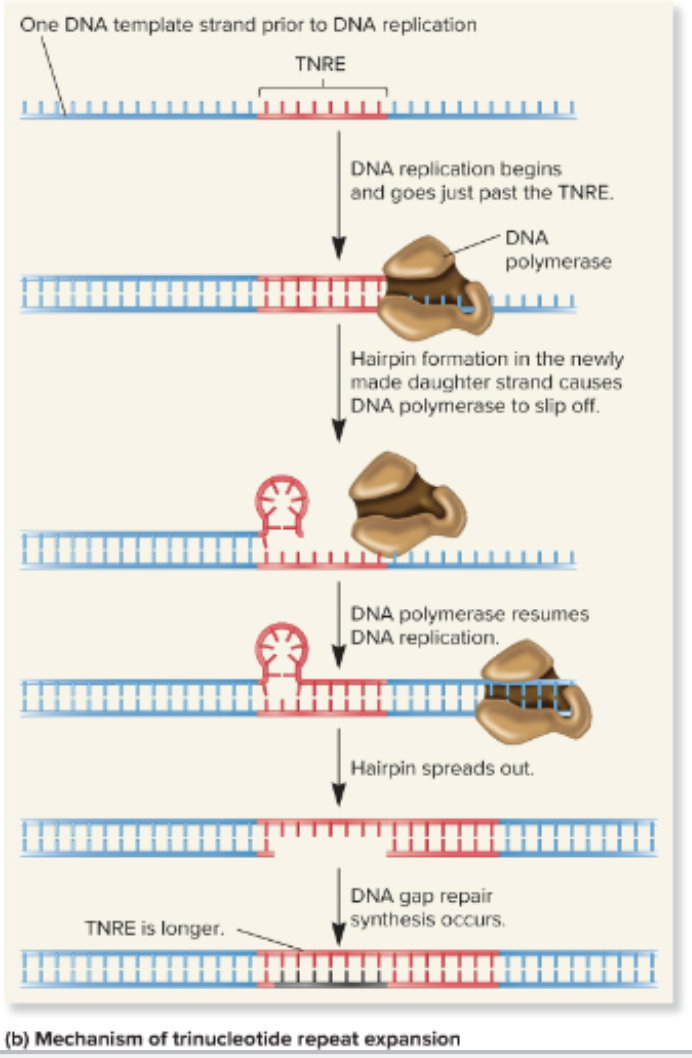
The establishment of a mutation in both DNA strands occur by first, during ___________, DNA polymerase erroneously adds a C instead of a T, creating a mismatch
replication
The establishment of a mutation in both DNA strands occurs by after the mismatch, the mutation is present in ________ strands of one of the DNA molecules following replication
both
The establishment of a mutation in both DNA strands occurs by after the mutations are present in both strands, the ___________ is replicated
mutation
______________ ___________ is changes in DNA structure that result from abnormalities in biological processes
Spontaneous mutations
spontaneous mutations have the following common causes: _________________, _________________, __________________, __________________, _________________
Abberant recombination, Abberant segregation, DNA replication errors, Toxic metabolic products, Transposable elements
____________ ___________ is an abnormal crossing over which may cause deletions, duplications, translocations, inversions
Abberant recombination
_____________ __________ is an abnormal chromosome segregation may cause aneuploidy or polyploidy
Abberant segregation
_________ ____________ ___________ is a mistake by DNA polymerase may cause point mutation
DNA replication errors
____________ ___________ ___________ are products of normal metabolic processes may be chemically reactive agents that can alter DNA structure
Toxic metabolic products
_____________ ____________ can insert themselves into genes
Transposable elements
__________ _________ changes caused by environmental agents
Induced mutation
Induced mutations have the following common causes: _____________ and ______________
chemical agents in DNA structure, Physical agents
___________ ________ ____________ are chemical substances that may cause changes
Chemical agents in DNA structure
___________ _________ are UV lights, X-rays that can damage DNA
Physical agents
Spontaneous mutations are __________ replication
unfaithful
In spontaneous mutations mutant E. coli strains are ___________
mutators
mutators make more mistakes during ______________
DNA replication
____________ rates are higher than wild type
mutation
Genes that are defective in mutator strains: __________ encodes subunit of DNA pol. III and genes encoding proteins for ________ repair mechanisms
mutD, mismatch
mutD is a component needed for 3’ to 5’ __________ _______
exonuclease activity
In spontaneous mutations, DNA bases themselves cause some _________ mistakes
replication
Spontaneous mutation have have DNA bases that normally exist in 1 or 2 possible forms or __________
tautomers
The changing from normal form to rare form is called ____________
tautomerization
In thymine the common form is _______ or _________ form
keto, lactam
In thymine the rare form is when keto switches to __________ or __________ form
enol, lactim
The thymine enol form pairs naturally with ________ instead of adenine
guanine
In thymine, if T in _______ form during replication, then G inserted in place of A
enol
The error in enol thymine if uncorrected, replication will keep going, resulting in a __________
mutation
Guanine also has ________ and ________ forms
keto, enol
In Guanine, the rare enol form of G pairs with normal ______
T
Adenine has _______ and _________ form
amino, imino
The _______ form of adenine pairs with T
amino
The _______ form of adenine pairs with C
Imino
In Adenine, if there is an A in the imino form in DNA, polymerase will insert ______ instead of T
C
Cytosine also has two tautomeric forms: ____________ and ___________
amino, imino
In spontaneous mutations, _______ ____________ also can cause insertion or deletion of 1 or more bases
DNA replication
The changing of of bases, if in a middle of a coding region will change the reading frame from that point on, this is called ___________ _________
frameshift mutation
Frameshift mutations occur when DNA polymerases ______ every now and then
slip
_________ _______ is when a base in 1 strand fails to pair with base in a complementary strand (likely in stretches of DNA with 1 base repeated several times)
looping out
In spontaneous mutations, if a base in template strand loops out, 1 too few bases will be incorporated in progeny strand this would cause a 1 bp ___________
deletion
In spontaneous mutations, if a base in progeny strand loops out, 1 too few bases will be incorporated in progeny strand this would cause a 1 bp ___________
insertion
In spontaneous mutations, mutations can occur by mechanisms other than in ________ ____________
DNA replication
Spontaneous mutation bases, especially cytosine, have slight tendency to lose amino groups is called ______________
deamination
In spontaneous mutation, when C is deaminated, it receives carbonyl oxygen in place of its amino group and it converts to ________ which means it now pairs with ______ instead of G
uracil, A
In spontaneous mutations, Adenine also can be deaminated, it yields base termed ____________ and it now pairs with ________ instead of T
hypoxanthine, C
In spontaneous mutations, deamination can potentially cause mutation because new ________ with new ________ properties is created
base, pairing
The most common deamination is ______ converting to ______, although this does NOT usually lead to mutation
C, U
In spontaneous mutations, cells have a mechanism for removing uracil from DNA, this is seen as a __________ and uses the enzyme ________________
mistake, uracil-DNA-glycosylase
uracil-DNA-glycosylase cuts bond between _______ and ___________, it then removes _______ leaving behind DNA nucleotide without base and another enzyme will replace base by pairing with opposite strand
U, deoxyribose, U
In spontaneous mutations, certain mutations are recognized by _______ ____________
DNA glycosylase
DNA glycosylase breaks glycosidic bond between damaged base and sugar and it leaves an ________ or __________ site (______ ________)
apurinic, apyrimidic, AP site
In spontaneous mutations, AP site recognized by _________ _____________
5’ AP endonuclease
5’ AP endonuclease _________ DNA strand on 5’ side of AP site
cuts
The cut termed _________, creates free end within DNA strand
incision
The cutting of the DNA strand signals other enzymes to complete _________ process
excision
After the excision process, _______ _________ adds in new nucleotides
DNA polymerase 1
after the new nucleotides are added, __________ ________ repairs nick (forms phosphodiester bond)
DNA ligase
Spontaneous mutations - repairing damaged bases
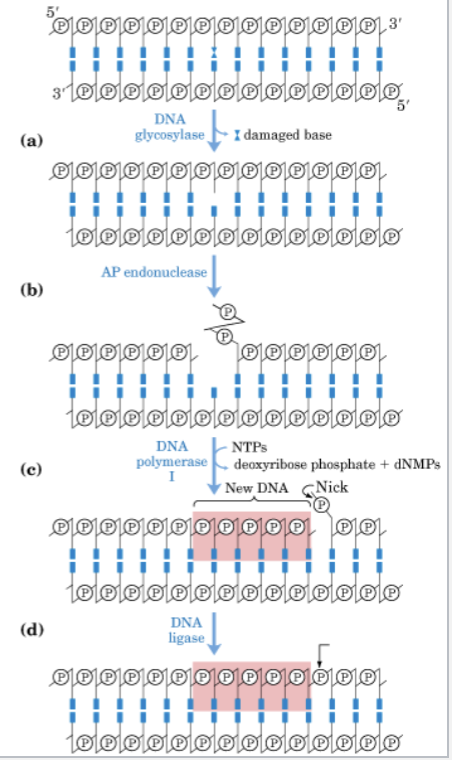
Spontaneous mutations to our DNA happens _______ in every human cell
daily
In spontaneous mutations, DNA of many organisms contains a small number of modified bases, the most common is _____________ (which also pairs with G)
5-methylcytosine
5-methylcytosine is not exactly like C, the sites with __________ can be hot spots for spontaneous mutation via deamination
5mC
Deamination of C results in U which is easily ___________ and ___________ but this is not so with 5mC deamination
recognized, removed
Since T is normal base in DNA it is not ____________ as mutation
recognized