PHYS2212 conceptual flashcards all topics
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
what differentiates a scalar vs a vector?
a scalar does not include direction, a vector has both magnitude and direction

what are some scalar examples?
mass, volume, energy, charge,…
what are some vector examples?
Force, momentum, velocity, displacement, …
how do you calculate a unit vector? (rhat)
divide the direction vector by it’s magnitude
what is the value of the charge of an individual electron (e) ?
1.602×10^-19 Coulombs
What are the 3 experimental facts that Coulomb gave us? (do not need to know Coulomb discovered them, but should know the concepts)
Force is proportional to charge, force is inversely proportional to distance squared, like charges repel and unlike charges attract
is electric field represented with vector or a scalar values?
vector field
which direction does an electric field point near a proton? near an electron?
away from proton (positive charge) and towards electron (negative charge)
Is the magnitude of electric field greater at a point closer to or farther from a point charge?
closer to the point charge
If two dipoles are identical and have the same dipole moment, but dipole 1 is 2x farther from the origin than dipole 2,what will the magnitude of the electric field at the origin be from dipole 1 relative to dipole 2?
e-field from dipole 1 = (1/8)(e-field from dipole 2)
what are the units for electric field?
N/C
Dipole A has a charge of 2q and a separation distance s, dipole B has a charge q and separation distance 2s, which has the larger dipole moment?
they are the same
A dipole has an increase in charge from 2q to 4q, how does this effect the electric field at a point 1 mm away?
the electric field increases by 2x
what are the units for electric charge?
Coulombs
what is the equation for Faraday’s law?
F = qE
what does the superposition principle say?
The electric field at any location in space is the vector sum of electric fields due to any charge not at that location
is electric field stronger 1 cm away from a dipole when the observation point is parallel or perpendicular to the dipole?
parallel
what is the net electric field at the center of a dipole
[(8kq)/s²][rhat]
which direction does the electric field point when the observation point is on the axis (parallel) of the dipole
from negative to positive
which direction does the electric field point when the observation point is perpendicular to the axis of the dipole
positive to negative
what is the net charge of a dipole?
0 C (the positive and negative charges cancel each other out)
what is the formula for the dipole moment and which direction does it point?
p = qs, points from -q to +q
If you have an electric field moving up and to the right and you place a positive point charge into the field, which direction will it accelerate? What if you place a negative point charge?
positive will move with E-field up and right, negative will move opposite so down and left
why does a dipole in a uniform electric field experience no force?
Because the negative charge will pull one direction and the positive in the opposite direction so that they cancel
Which way does a dipole want to align?
with the electric field (axis (dipole moment) parallel to the electric field direction)
what is the relationship between the electric field magnitude of a dipole on axis compared to the magnitude of dipole electric field perpendicular to the axis at the same distance away from the dipole?
on axis is 2x stronger than perpendicular
If a positive charge is placed to the left of a neutrally charged atom, in what direction will the vector p (dipole moment) of the induced dipole point?
to the right (induced dipole will have negative charge on the left and positive on the right)
What happens to an induced dipole when the external electric field is removed?
it ceases to be a dipole and returns to neutral
can 2 neutrally charged objects attract each other?
Yes! but the attraction will be small (this is van der waals forces)
how does the movement of electrons in an insulator differ from that in a conductor?
In an insulator the electrons are still “bound”/localized to the nucleus but in a conductor the electrons can move more freely as a “sea of electrons”
How would you find the net electric field inside a neutral conductor at equilibrium in the presence of an external electric field?
net electric field inside a neutral conductor is ALWAYS 0
How would you find the net electric field inside a neutral insulator at equilibrium in the presence of an external electric field?
Einside = Eexternal + net(Edipole)
How does the E-field inside an insulator compare to the electric field outside the material?
E- field inside is smaller because of Epolarization
what is shielding?
The process that makes it so a hole within a conductor will always have 0 net electric field. Comes from the fact that there is also 0 net e field within a conductor from Epolarization cancelling out with Eexternal
When charges move between two metal blocks is it the protons or the electrons that are doing the transfer?
the electrons move, protons will never be transferred
How would you discharge a conductor?
Through the process of Grounding. Pulling the charge out of the conductor and into the earth through a grounding wire or some other conducting material. The charge is never destroyed!
If electric potential is calculated around in a circle (you start at one point and end at the same point), how would you find V?
V will be 0 if the total displacement is 0
What is the formula to calaculate dV from A to B?
VB-VA
on an equipotential surface, how do you determine where the strongest E-field is?
Where the equipotential lines are the closest together/ most condensed
What does electric potential inside a conductor at equilibrium look like? What would it look like when there is a charge causing polarization within the conductor?
V is constant (equipotential) but not necessarily 0, it is the same for a polarized conductor inside the conductor.
how does the electric field of a capacitor compare inside and outside of the two plates compared to the electric field from just 1 plate?
Inside the electric field is doubled, outside the electric field is 0
what does it mean that a circuit is a nonequilibrium system?
circuits can’t run forever on their own. Energy will be released as it runs and therefore energy must also be put in for it to run
what does the letter I (capital i) represent in circuits?
current
which way does an electron move relative to the electric field in a circuit wire?
an electron will move opposite of the electric field
What does the node rule say?
At any point in a circuit where the wire is still in series (not split) the current will be the same
which way does current flow in a circuit relative to the charges on the battery?
out of the positive terminal and into the negative terminal
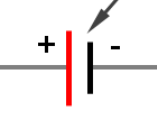
what does this symbol represent?
battery
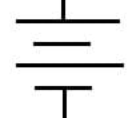
what does this symbol represent?
battery
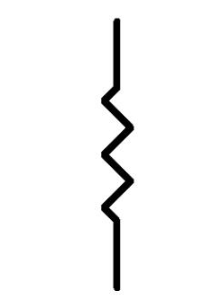
what does this symbol represent?
resistor
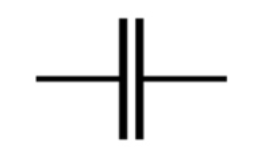
what does this symbol represent?
capacitor
What is Emf most closely related to?
Voltage/ electric potential
What shape is being “added up” to calculate a disk (what shape is dQ coming from)?
ring
if you have two parallel infinite plates, one with charge distribution +sigma and the other -sigma. What is the equation for the Electric field between the two plates?
E = 4(pi)(k)(sigma)
does separation distance matter between two parallel infinite plates of equal and opposite charge?
no, separation does not matter if the plates are infinite
what is a capacitor?
two charges plates of equal and opposite charge that are placed close together so that the field between the plates is twice as strong as for a single plate and the field outside is theoretically 0
Why is the E-field at the center of a uniformly charged spherical shell always 0
The net field at ANY point within the spherical shell will cancel out to 0 (polarization is not involved for a hollow shell)
We know that the electric field within a uniformly charged spherical conducting shell will be 0 at any point. Does this also apply for an insulating spherical shell? Why or why not?
Yes, it will still be 0 inside an insulating shell because polarization is not involved. It is just superposition principle adding up the charges from all directions that will cancel to 0 regardless of the material as long as it is uniformly charged
what is ro? give the equation. Is it a vector or a scalar?
Ro is charge density. ro = charge/volume (ro= dq/dV) in a specific area. It is a scalar value
what is sigma? give the equation
sigma = charge/area
what is lambda? give the equation
lambda = charge/length (use for a line or a very thin rod)
How would you find dq on a piece of a rod length dy when the length of the rod is L and the charge is Q
dq = Q(dy/L)
If you have a vertical rod of charge +Q and an observation point aligned with the center of the rod at some point in the +x direction, which direction will the net electric field point at the observation point?
+x direction, components will all cancel in the y-direction
If the observation point is much much larger than the length of a charged rod, what can the rod be treated as to simplify calculations
a point charge
if you have a ring of charge +Q centered in the xy-plane and an observation location some distance away in the z direction from the center of the ring. Which direction will the net electric field point
in the z-direction away from the ring (x and y components will cancel each other out)
Wjat is the electric field exactly in the center of a ring of charge?
0
If you are tracing around a circuit in the direction that flows out of the positive node of a battery, will the current flow through a resistor from positive to negative or negative to positive?
positive to negative, represented in the loop rule were deltaV resistor = -IR. (so that the deltaV of the entire circuit is 0)
How do you find total resistance for resistors in series?
Just add their resistances (R1 + R2 + … )
How do you find the total resistance for resistors in parallel?
(1/R1 + 1/R2 + … )-1
what is the difference in appearance of resistors in series vs parallel?
Resistors in series are along the same wire and would have the same current running through them, resistors in parallel come from a split in the wire/current and do not have the same current running through them. (Be careful, parallel resistors will not always be visually parallel)
How might you set up an equation to represent the node rule at a junction where current I1 splits into two directions I2 and I3?
I1 - I2 - I3= 0 or I1= I2 + I3. (This represents that at any junction the current in will be equal to the current out)
What happens in a circuit once a capacitor is fully charged?
Current will no longer flow through the capacitor
in a loop rule, if the battery Emf is positive, generally should the sign for Emf from a capacitor be written as positive or negative
negative, from loop rule
If the conventional current is running clockwise, which direction is the electron current running?
counterclockwise (remember that conventional current accounts for the negative charge from electron current so it flows in the opposite direction)
If current runs clockwise when a capacitor is charging in a circuit, which way will it run when the capacitor is discharging?
counterclockwise
How is power different for a small R vs a large R
small R is larger power to start and short decay, large R is small power to start and long decay (this relates to how it should be graphed
What are the equations for power?
P= IV, P = V2/R, P = I2R
what is the equation for kinetic energy?
K = ½ mv²
what is the definition of work?
a force acting over some distance
is work a vector or a scalar?
scalar
what is the relationship between work and change in potential energy?
Work = - change in potential energy
how are electric potential and electric potential energy related?
U = qV
what is the relationship between electric potential (V) and electric field (E)?
dV = -E(dL) where dL is change in position
what are the units for electric potential?
Volts
Does electric potential increase or decrease as you move against the electric field?
it increases along a path against the electric field because dV= - E(dl)
What happens to electric potential on a path directly perpendicular to the E-field?
change in electric potential difference is 0
If electric potential decreases, what is happening to potential energy
potential energy also decreases (they can be related with U=qV)
Is electric potential a vector or a scalar?
scalar (do not include direction)
Formula relating magnetic field and charge and velocity of a point charge to magnetic force
FB= qv x B
how do you determine total force on a particle that has both electric and magnetic force acting on it
Just add them (Ftotal = FE + FB) (Lorentz force law)
When is magnetic force going to be 0 if magnetic field at point charge velocity is not 0?
When B is parallel to v
what is special about Force and velocity? (remember from physics 1)
force and velocity are always 90 degrees to each other
what is the most common trajectory for a charged partible in a constant magnetic field?
a helix
Can current carrying wires exert force on each other?
yes, if they exert a B field in the same direction (or the current is running in opposite directions) then they will repel, if B is opposite (current runs in same direction) then the attract. (use RHR to figure this out)
if you have two rings of charge side by side and the magnetic field running through the center of them is in the same direction, will they attract or repel?
they will repel, currents will be in opposite directions and B in the same, RHR they will repel
if you have two current carrying rings stacked on top of each other with some space in between. When will they repel and attract in regards to current direction
attract when currents in the same direction, repel when currents in opposite direction
how would you calculate net magnetic force on a closed current carrying loop in a uniform magnetic field?
there is no net magnetic force in this situation (net magnetic force = 0) (only true if B is uniform)
what are the 2 poles of a magnetic dipole called?
North and South poles
which pole of a magnet does the magnetic field flow out of
the north pole
what tool can be used to measure the direction of magnetic fields
a compass (just remember that what we call Earth’s North pole is actually the magnetic South pole)
Describe how to use the right hand rule (what parts of the hand represent what)
Start with fingers facing towards v, curl towards rhat direction, thumb is B directi