Glycolysis to ATP synthesis
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Activated Carrier Molecules
Molecules that transport energy from energetically favorable reaction to unfavorable reaction (ATP,NADH, FADH2)
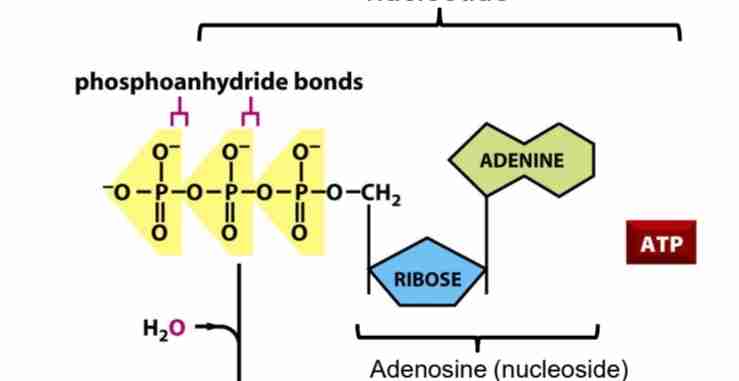
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
Most widely used activated carrier molecule, hydrolisis makes ADP, which liberates phosphate to use as energy
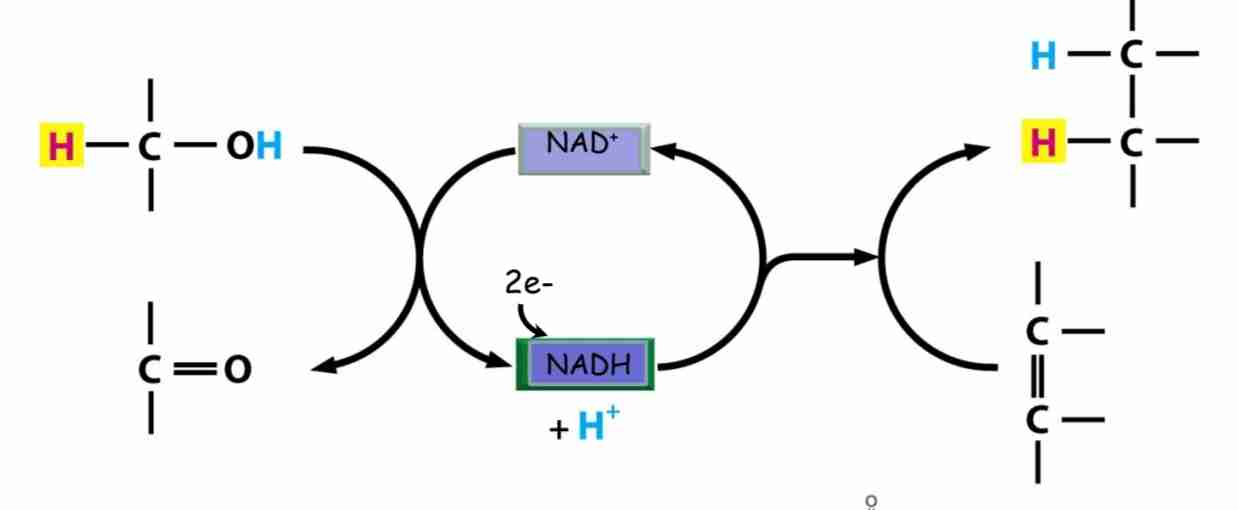
NADH -—> NAD+, FADH2 —> FAD+
Carrier molecule that participates in Oxidation reduction reaction, carries H+ and electrons
Nucleotide Functions
Carry chemical energy, form coenzymes, specific signaling molecules
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Starches are broken down into oligosacharides, which are hydrolyzed into glucose by alpha glucosidase.
sucrose is broken down to glucose and fructose by sucrase
SGLT
sodium glucose co-transporter : gut to intestinal cells
GLUT2 glucose transporter 2
Low affinity, high Km
from intestinal cells into blodd
liver pancreatic beta cells, certain neurons
Enable sense to sense and response to extracellular glucose
GLUT 1/3 glucose transporter
High affinity, low km,’
High Transport
glut1: everywher except neurons
Glut3: neurons
Glut4 glucose transporter
High affinity
Insulin sensitive gluose transporte on skeletal muscle, adipocytes
impaired during diabetes due to insulin resistance
activated during excersice independently of insuline
Glut 5
fructose transporter
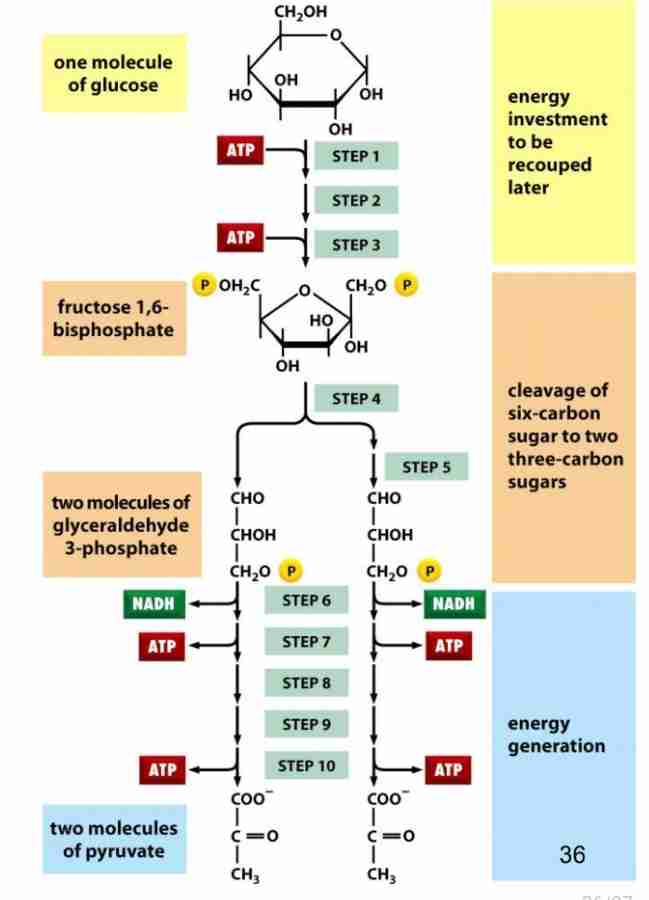
Glycolysis
break down of glucose to pyruvate energy obtain
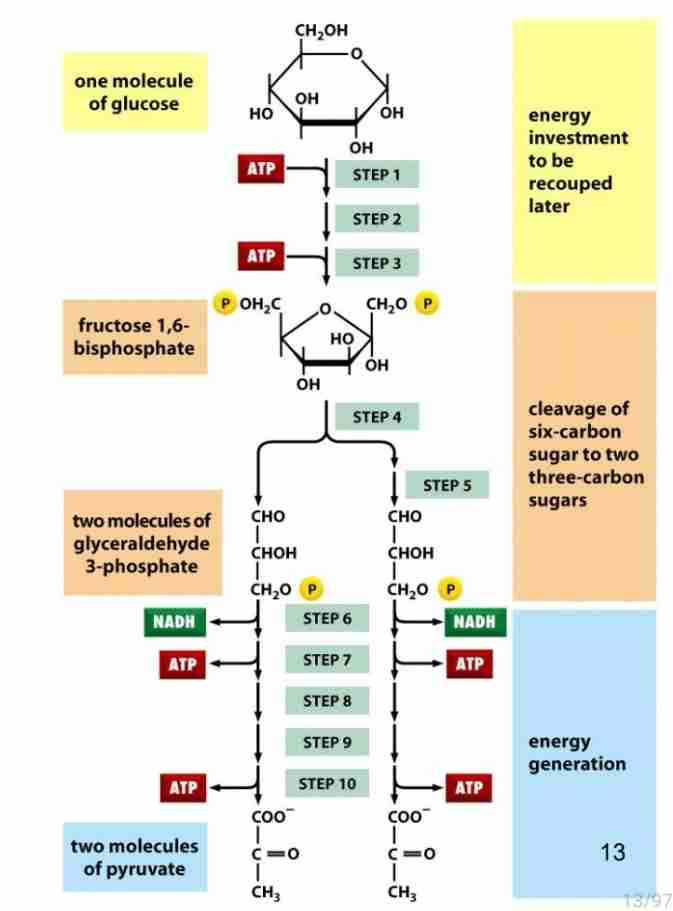
Glycolysis Stage 1
Use of Energy Glucose to F-1,6-BP
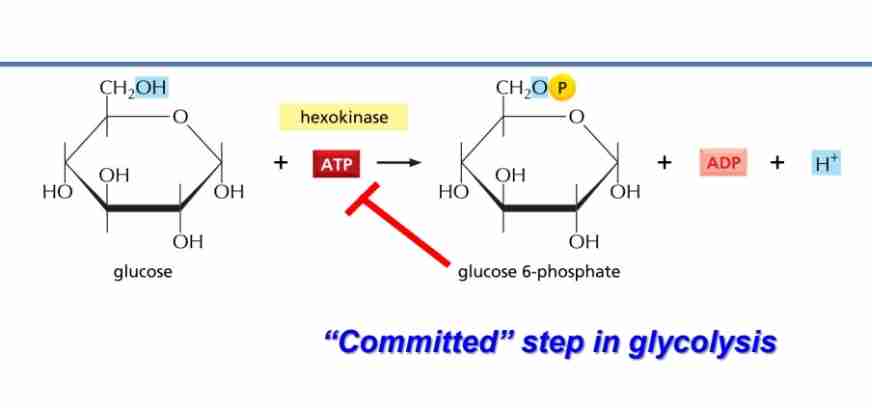
Glucose + ATP → hexokinase → Glucose 6 - Phosphate
Commited step
irriversible reaction
allosterically inhibited by glucose -6 phosphate
traps glucos in the cells
Hexokinase (HK)
4 major iso form of mammalian HK
HK 1-3 km « 1mM (high Affinity)
HK 4 = glucokinase low affinity. Hk 4 found in liver
HK 4 or glucokinase is not subject to end product inhibition, mutation is linked to diabetes
glucose-6-phosphate → phosphoglucose isomerase <--- Fructose 6 phosphate
Reversible
formation of fructose 6 phosphate
rearrangement of chemical to by isomerase to form another
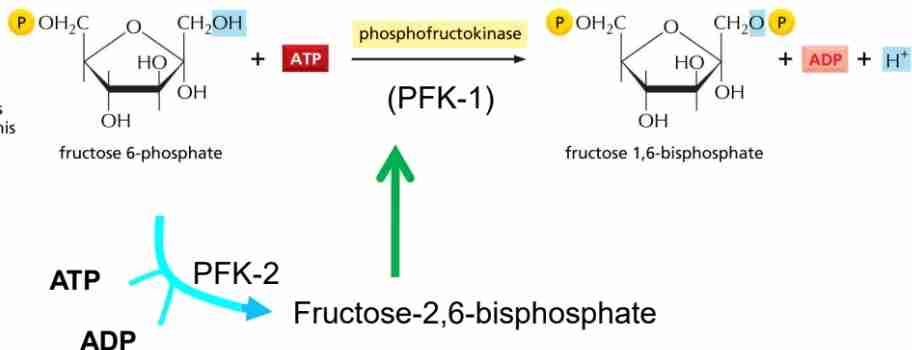
Phosphofructokinase reaction (PFK-1) (rate limiting Enzyme)
Fructose 6-phosphate + ATP →
→ fructose 1,6 biphosphate
Irreversible
Energy consumptio
PFK1: allosteric enzyme that regulates the pace of glycoslisis principal rate limiting enzyme
Inhibited by ATP activated bt AMP
Allosterically activated by fructose 26 biphosphate
Glycolysis: Stage 2
No energy used or extracted
two 3-carbon fragments are produced from one 6 carbon sugar
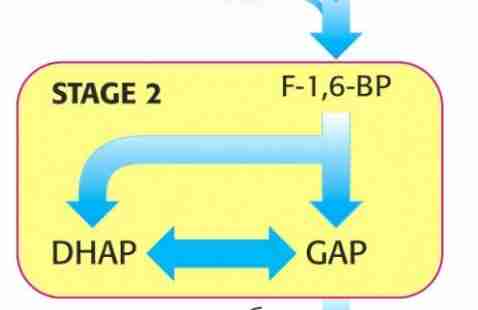
Cleavage of 6 carbon sugar
fructose 1,6 biphosphate → aldolase A <- dihidroxyacetone + glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate
fructose → fructokinase → fructose 1-p → aldolase B <- DHAP + glyceraldehyde
depending on sugar the reaction is different
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate → triose phosphate isomerase <- glyceraldehyde 3 - phosphate
salvage of three carbon fragment
Glycolysis stage 3
Energy extracted
2× 2 atp / molecule of glucose
the oxidation of three carbon fragments yields atp
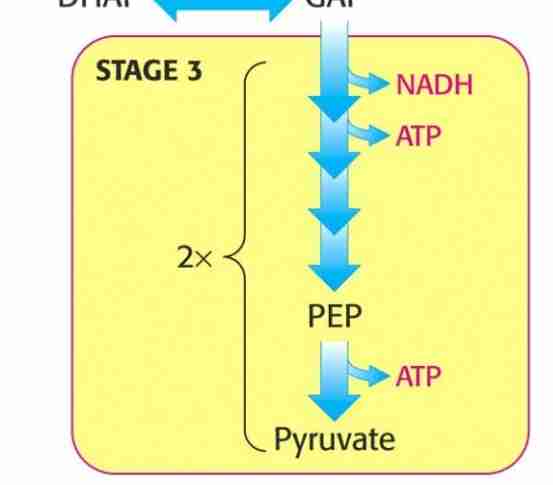
How enzymes couple oxidation to energy storage
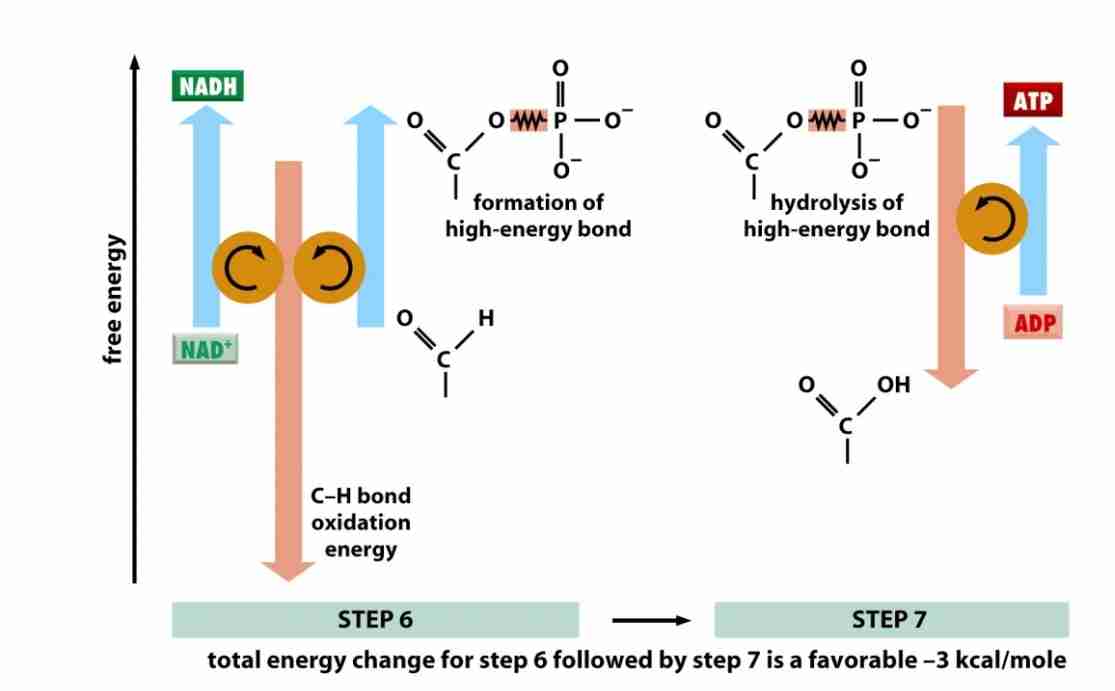
Glyceraldehyde -3 phosphate dehydrogenase, and phosphoglycerate kynase
oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate, the reaction gives a NADH and 1,3 biphosphoglycerate
the kynase removes the phosphate group from 1,3 biphosphoglycerate and generates 1 atp and 3 - phosphoglycerate
3 -phosphoglycerate → phosphoglycerate mutase <- 2 -phosphoglycerate
reversible rearrangfe phosophate group
2 -phosphoglycerate -—> enolase <- phosphoenolpyruvate
enol is oh bonded to c=c, the removal of H2O creates a high energy enol phosphate linkage
phosphoenol pyruvate + ADP + H → pyruvate kinase → pyruvate + ATP
irreversible
ATP formation
Pk is inhibited by ATP
Glycolysis Energy generation
4 ATP generated - 2 ATP use: total 2 ATP / Glucose
2NADH molecules generated
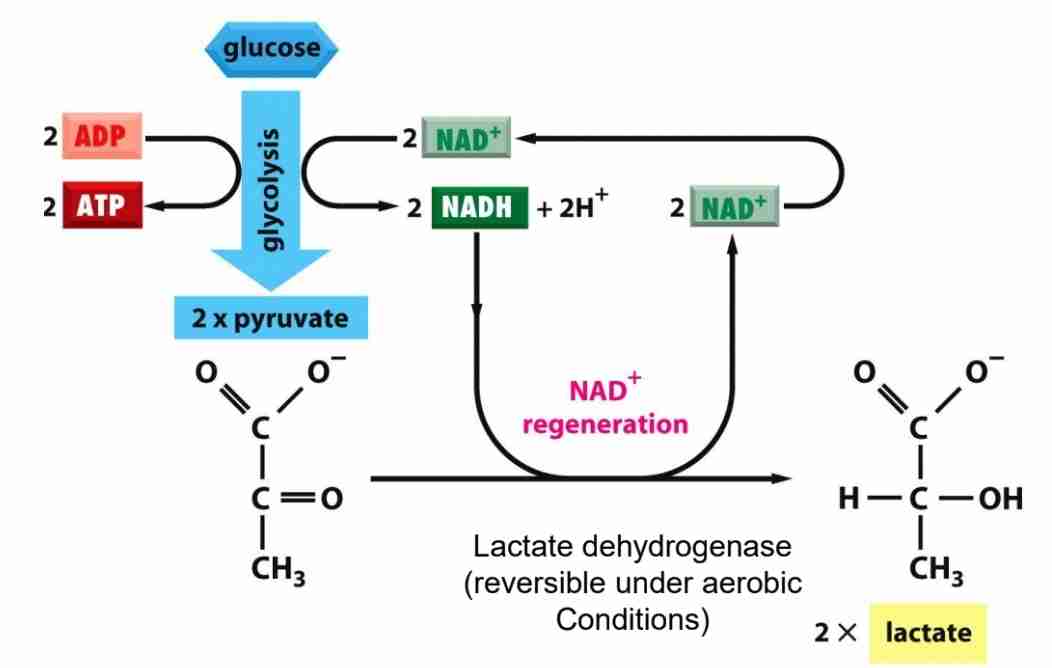
NAD regeneration in anaerobic conditions
Fermentation leads to excretion of lactate,which is self limiting
Glycolysis overview
6-c sugar to two pyruvate molecules
2ATP net production
2NADH
Rate of glycolysis is adjusted to meet the cells need for ATP
3 allosteric controlled enzymes: hexokinase, PFK-1, Pyruvate Kinase
These 3 enzymes catalyze reaction with large negative dG regulate the entire pathway