Prosocial behaviour
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What was the case of Kitty Genovese?
38 people witnessed the murder and didn’t call the police.
What is the bystander effect and who conducted an experiment exploring this?
The idea that people are more likely to help when less people are around, investigated by (Latane & Darley, 1968).
What did their experiment entail^?
They placed individuals in a fake emergency situation, and with different group dynamics. In all the experimental conditions, subjects were asked to complete a survey in a room that slowly filled with smoke.
What were their results^?
When alone, participants were much more likely to report the smoke quicker
When with two confederates (who did not pay attention to the smoke), only 10% of participants reported it
When in a group (of all participants), it took much longer to report the smoke and less people did
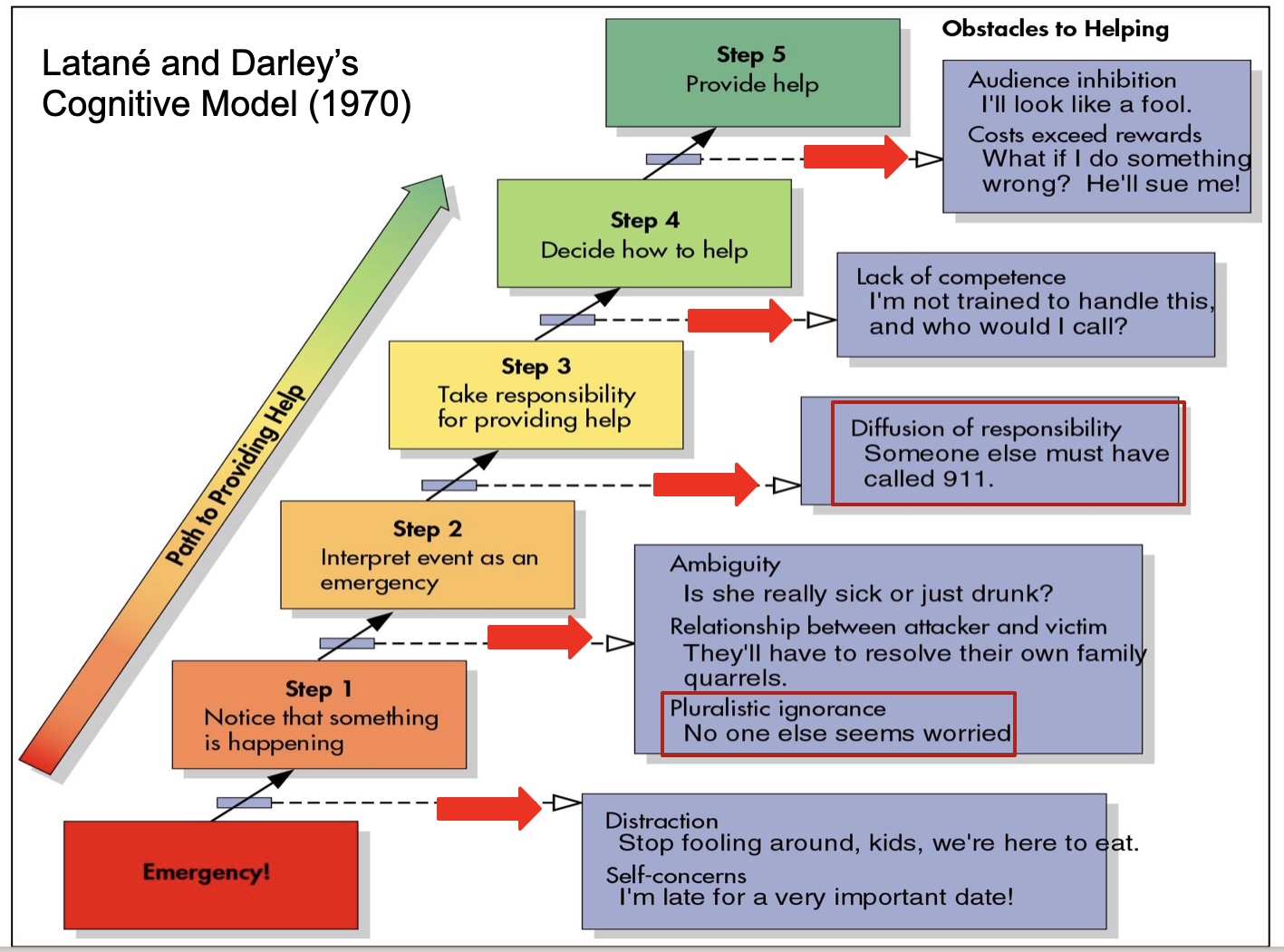
What is Latane and Darley’s cognitive model (1970)?
It suggests that individuals go through a series of cognitive steps— noticing the event, interpreting it as an emergency, assuming responsibility, and deciding how to act—before deciding whether to intervene in a crisis or emergency situation.
What was later found out to be true about Kitty Genovese’s case?
(Manning, 2007)
Later reporting disputes the number of witnesses
People could not see the entire attack
Later reports that people did intervene (yell at attacker, call police)
Does the presence of bystanders inhibit helping?
Yes, but less so in dangerous situations
Why do we help others in need?
Egoism
Altruism
What is the empathy-altruism hypothesis?
It suggests that people are more likely to help others when they feel empathy for them, and this empathy can lead to genuinely selfless, altruistic behavior, rather than helping for selfish reasons.
Who investigated the role of empathy in helping others?
(Batson, 1981)
What did this experiment involve^?
Participants view Elaine receiving a series of painful shocks and are asked if they want to swap places with Elaine.
What were their results?
When empathy was high, participants were equally likely to help regardless of how easy it was to escape, indicating altruistic motivation. However, when empathy was low, participants were more likely to help when escape was difficult, suggesting egoistic motivation.
What is moral elevation?
A warm, uplifting feeling that people experience when they see unexpected acts of human goodness, kindness, courage, or compassion.
Who conducted a study exploring the idea of moral elevation?
(Schnall, 2010)
What did their study include^?
In two experiments, participants in an elevation-inducing condition were compared with those in control conditions.
What were their results^?
In Experiment 1, participants feeling elevated were more likely to volunteer for an unpaid study than those in a neutral state. In Experiment 2, elevated participants spent roughly twice as long helping the experimenter with a tedious task compared to those experiencing mirth or neutrality.
What are some theories of aggression?
Social learning theory (Bandura, 1970)
General aggression model (Anderson & Bushman, 2002)
What is social learning theory?
It suggests that people learn behaviors through observing and imitating others, particularly those who are seen as role models, and through the rewards or punishments that follow these behaviors.
Whose experiment explored this theory^?
(Bandura, 1963)
What did this experiment entail^?
This study tested whether exposure to aggressive models in films increases children's aggression after frustration.
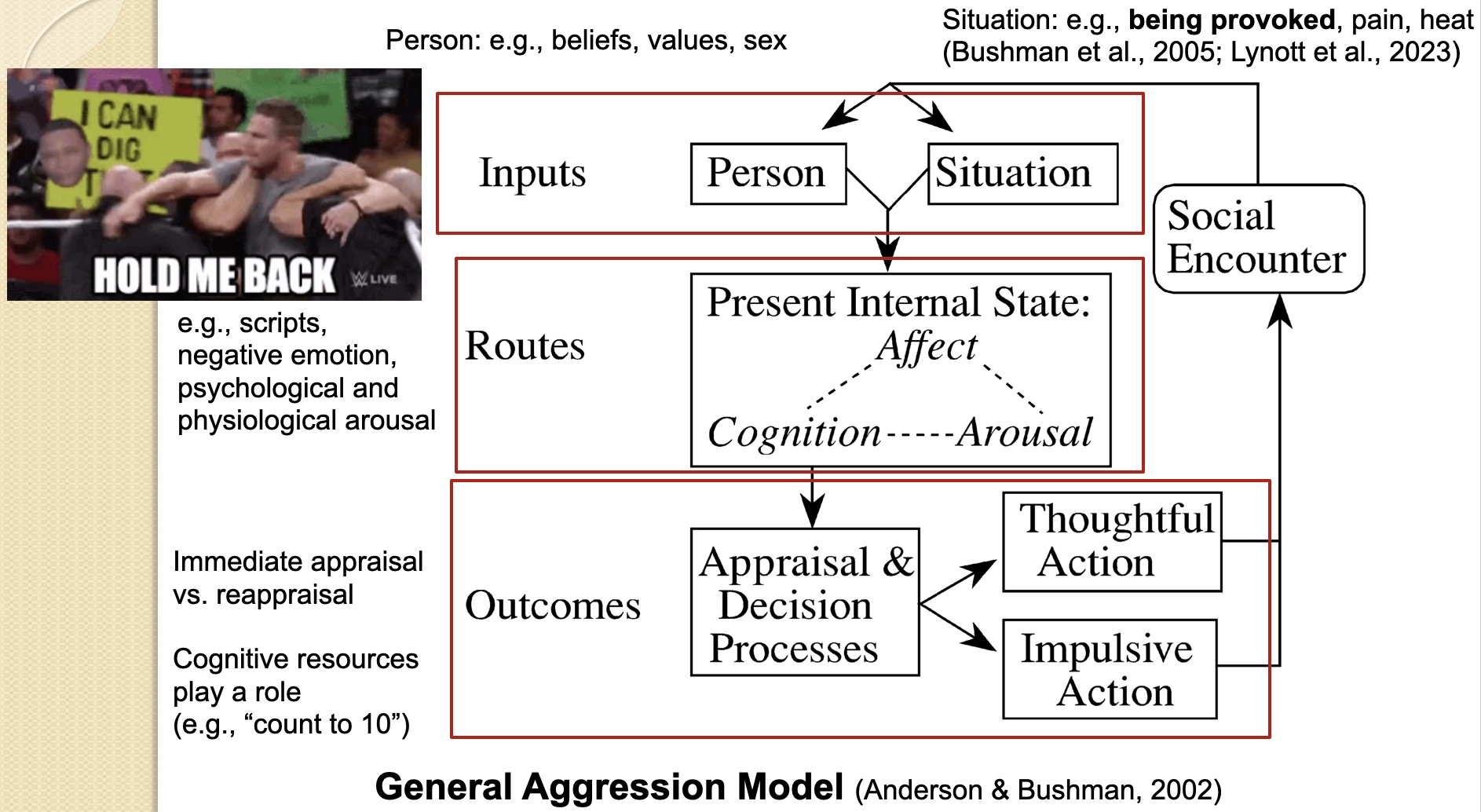
What is the general aggression model?
It suggests that aggression is the result of both personal and situational factors that interact with an individual's internal states (such as thoughts, emotions, and arousal), which influence the likelihood of aggressive behavior in a given context.
What is catharsis?
The idea that observing violence (or ‘ventilating’ it) gets rid of hostilities.
Who investigated this^?
(Anderson & Bushman, 2010) - Meta-analysis that showed that playing violent video games resulted in increased aggression, decreased helping, increased aggressive thoughts, increased anger, and increased arousal (with the same effects for male/female and different ages).