APUSH key terms and concepts Princeton Review
1/411
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
412 Terms
city upon a hill
Said by Winthrop;Puritan idea that New World were part of a special pact with God to create a holy community: a model society to the world/moral commonwealth
encomienda system
A system whereby the Spanish crown granted the conquerors the right to forcibly employ groups of Indians; it was a disguised form of slavery.
headright system
Employed in the tobacco colonies to encourage the importation of indentured servants, the system allowed an individual to acquire fifty acres of land if he paid for a laborer's passage to the colony.
indentured servitude
A worker bound by a voluntary agreement to work for a specified period of years often in return for free passage to an overseas destination. Given right to vote, freedom, and land when finished
joint stock company
a company whose stock is owned jointly by the shareholders.
mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought
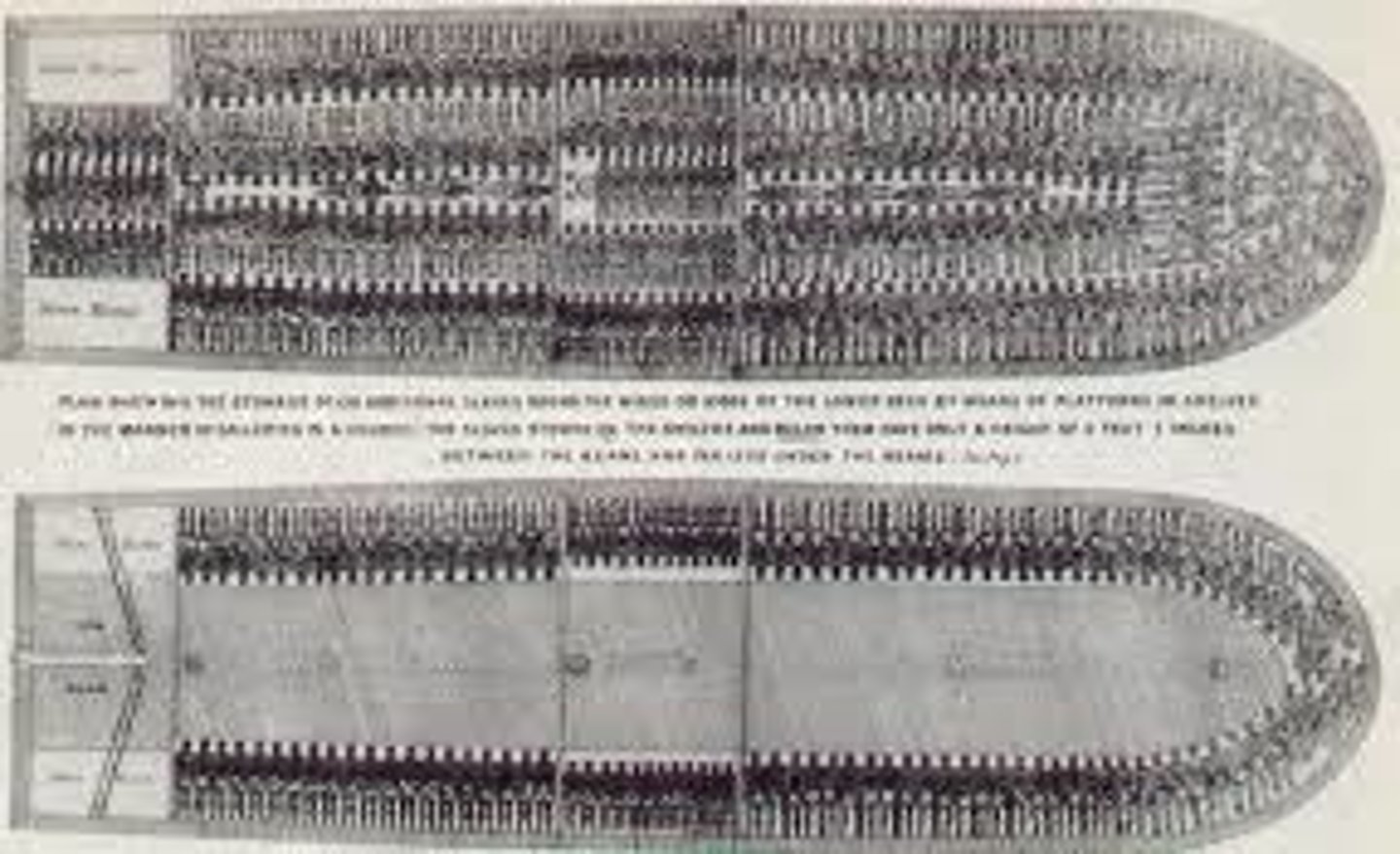
middle passage
A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies
praying towns
Villages where New England Indians who converted to Christianity were gathered
Pre-Columbian era
The period before Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World
proprietary colony
English colony in which the king gave land to proprietors in exchange for a yearly payment
royal colony
A colony under the direct control of a monarch
salutary neglect
An English policy of not strictly enforcing laws in its colonies
tariffs
Taxes on imported goods
Bacon's rebellion
A rebellion lead by Nathaniel Bacon with backcountry farmers to attack Native Americans in an attempt to gain more land; burnt down Jamestown. Bacon was the leader of the army, rebellion ended when Bacon died
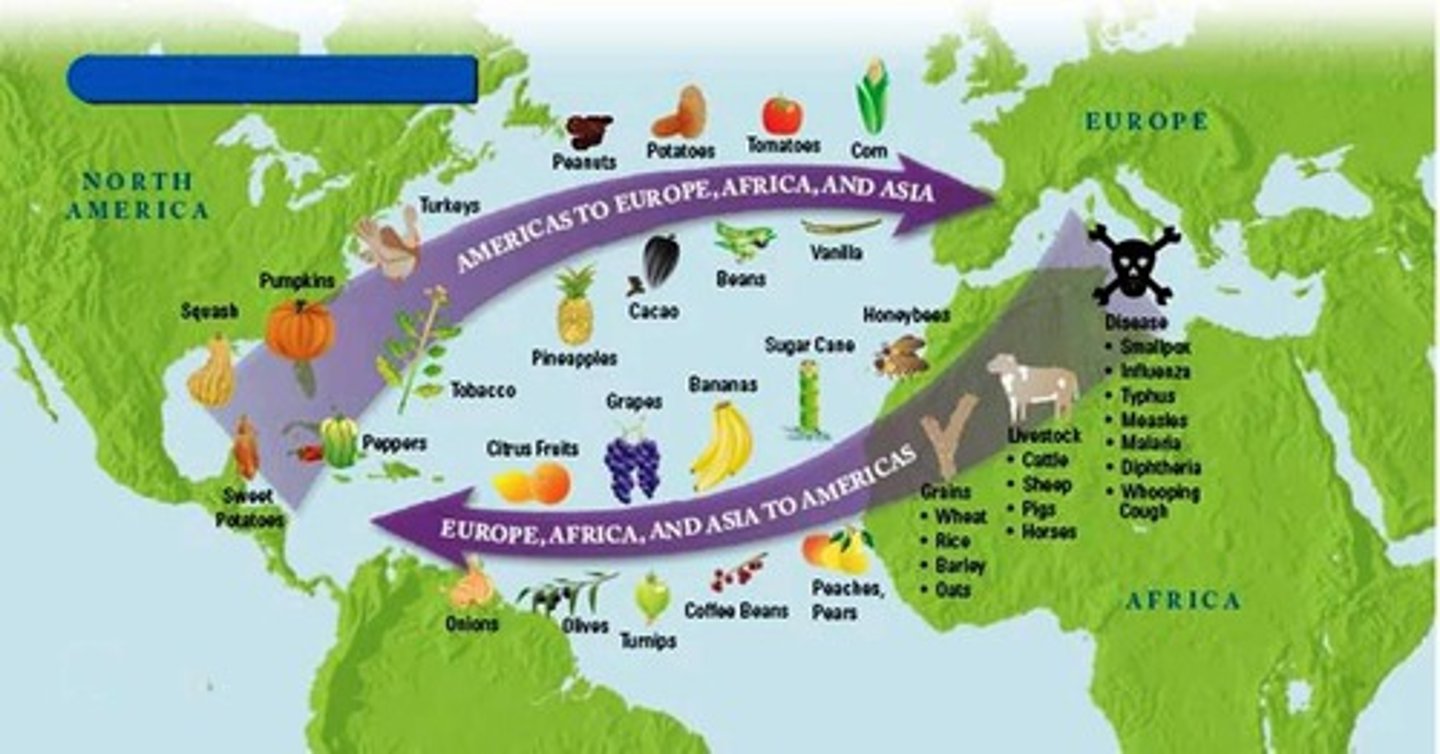
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, ideas, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
first great awakening
Religious revival in the colonies in 1730s and 1740s; George Whitefield and Jonathan Edwards preached. Religious splits in the colonies became deeper. Motivation by fear; "go to church or go to hell"
huron confederacy
A group of Indians similar to the Iroquois. French joined them in the fight against the Iroquois.
King Phillip's War
Series of assaults by Metacom, King Philip, on English settlements in New England. The attacks slowed the westward migration of New England settlers for several decades.
Pequot War
The Bay colonists wanted to claim Connecticut for themselves but it belonged to the Pequot. The colonists burned down their village and 400 were killed.
Pueblo revolt
Native American revolt against the Spanish in late 17th century; expelled the Spanish for over 10 years; Spain began to take an accommodating approach to Natives after the revolt
starving time (1609-1610)
Period of starvation endured by the Jamestown colonists. Colonists depended upon trade with the local Native Americans for their food supplies caused series of conflicts between the colonists and the Native Americans. Large number of colonists died and others tried to flee to England; boats arrived with supplies from England and forced colonists to return to Jamestown
stono uprising
The first and most successful slave rebellion. It took place 70 years after slavery began in America. Stole guns and ammunition, they killed storekeepers, planters, and liberated a number of slaves. All captured and executed. Passed restrictive laws on slaves behavior
Anne Huntchinson
Held unorthodox views against the Puritan experiment. She was an outcast and thought if you are saved by God you don't need to follow the law
bartolome de las Casas
Spaniard who fought for Native American rights.
calvinists
Doctrine was similar to that of Lutherans' except Calvinists also believed in predestination and the insignificance of humanity. John Calvin
Christopher Columbus
He mistakenly discovered the Americas in 1492 while searching for a faster route to India funded by Spain.
congregationalists
Puritans who wanted to reform the Anglican church from within
George Whitefield
Christian preacher and he sparked the First Great Awakening.
John Rolfe
English settlers at Jamestown and married Pocahontas. Successfully grew tobacco in Virginia and made Virginia an economically successful colony.
John Smith
English explorer who helped found the colony at Jamestown, Virginia
Jonathan Edwards
Preacher during the First Great Awakening; "Sinners in the hands of angry god"
Juan de Onate
Spanish explorer and conquistador. He claimed New Mexico for Spain and took control of the Rio Grande region
maroons
Runaway slaves who gathered in mountainous, forested, or swampy areas and formed their own self-governing communities. raided plantations for supplies, had military skills from Africa.
mestizos
A person of mixed Native American and European ancestory
metacomet
Native American also known as Prince Phillip who fought against European settlers
Pilgrims
English Puritans who founded Plymouth colony in 1620
Plain tribes
Native American group located between the Mississippi River and the Rocky Mountains. Lived in teepee hunted buffalo
Pocahontas
A native Indian of America, daughter of Chief Powahatan, who was one of the first to marry an Englishman, John Rolfe, and return to England with him. Pocahontas' brave actions in saving an Englishman paved the way for many positive English and Native relations.
Powhatan Confederacy
A group of seven Indian tribes that controlled Virginia. It was led by Powhatan and was an agricultural group. They allowed the original English Settlers to survive
Pueblo people
These Indians lived in the Southwestern United States. They built extensive irrigation systems to water their primary crop, which was corn; also lived in stone cities
Puritans
A religious group who wanted to purify the Church of England. They came to America for religious freedom and settled Massachusetts Bay.
Roger Williams
A dissenter who clashed with the Massachusetts Puritans over separation of church and state and was banished in 1636, after which he founded the colony of Rhode Island to the south
Separatists
People who wanted to have a separate, or different church. Also known as Pilgrims.
Virginia Company
The first joint-stock company in the colonies; founded Jamestown; promised gold, conversion of Indian to Christianity, and passage to the Indies
Sir Walter Raleigh
An English adventurer and writer. Raleigh sponsored the first English colony in America on Roanoke Island in present-day North Carolina. It failed and is known as " The Lost Colony."
Wampanoags
tribe whose chief, Metacom, known to the colonies as King Phillip, united many tribes in southern New England against the English settlers
Zambos
People of mixed Native American and African descent. Lowest tier of social class, with no rights whatsoever.
Bering Strait
Narrow body of water that separates Russia from Alaska
Jamestown (1607)
First permanent English settlement in North America
Massachusetts Bay Colony
Colony founded in 1630 by John Winthrop, part of the Great Puritan Migration, founded by puritans. Had a theocratic republic. "City upon a hill"
Middle colonies
New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware
New England colonies
Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut
The Lower South colonies
Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, Florida, Georgia, and South Carolina
Act of Toler
a 1649 Maryland law that provided religious freedom for all Christians
Dominion of New England
administrative body created by King James II that oversaw British colonies in the New England region. Implement the Navigation Acts; An administrative union of English colonies in the New England region of North America.
Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
Set up a unified government for the towns of the Connecticut area (Windsor, Hartford, and Wethersfield). First constitution written in America.
Halfway Covenant
In the 1660s, people could now take part in church services and activities without making a formal commitment to Christ. It was created because the next generation of colonists were less committed to religious faith, but churches still needed members.
Maryland Toleratio
Act that was passed in Maryland that guaranteed toleration to all Christians. Granted religious freedom to all.
Mayflower compact
1620 - The first agreement for self-government in America. It was signed by the 41 men on the Mayflower and set up a government for the Plymouth colony. A legal contract in which they agreed to have fair laws to protect the general good
Navigation Acts
Laws passed by the British to control colonial trade
Common Sense by Thomas Paine
powerful pamphlet telling the colonists to break free. British were trying to destroy colonies' natural rights. Government is there to protect life liberty and property. Power came from people, not kings. Colonies don't benefit from British Empire.
Hamilton's Financial Plan
Pay off all war debts, raise government revenues, create a national bank
Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions
Written by Jefferson and Madison in response to the Alien and Sedition Acts, they declared that states could nullify federal laws that the states considered unconstitutional.
Loose constructionism
Courts should read the Constitution expansively and should not limit themselves to what is explicitly stated
Nullification
A state's refusal to recognize an act of Congress that it considers unconstitutional
Republican Motherhood
Expectation that women would teach Republican values to children; helped increase education for women. The idea that American women had a special responsibility to teach their kids how to be citizens. Educational opportunities for women expanded due to this.
strict constructionism
a person who interprets the Constitution in a way that allows the federal government to take only those actions the Constitution specifically says it can take; read literally
virtual representation
British governmental theory that Parliament spoke for all British subjects, including Americans, even if they did not vote for its members
Washington's Farewell Address
Warned Americans not to get involved in European affairs, not to make permanent alliances, warned not to form political parties and to avoid sectionalism. Said he wasn't running for president again and set a tradition
Battle of Concord
The British leave Lexington and head to Concord to take the weapons and gunpowder from the colonists. The British were burning the town when the colonists began firing on soldiers. Colonists win this battle.
Battle of Lexington
First battle of the American Revolution
Battle of Fallen Timbers
The U.S. Army defeated the Native Americans and ended Native American hopes of keeping their land
Battle of Saratoga
Turning point of the American Revolution. Convinced the French to give the U.S. military support and showed the French that the Americans had the potential to beat their enemy, Great Britain.
Battle of Yorktown
the last major battle of the American Revolution
Boston Massacre 1770
The first bloodshed of the American Revolution where British soldiers fired into a crowd of colonists who were teasing and taunting them; five colonists were killed. Boston's radicals used to incident to wage an Anti-British propaganda war.
Boston Tea Party
protest against increased tea prices in which colonists dumped british tea into boston harbor dressed up as native americans. Intolerable Acts were passed in reaction to the tea being dumped.
French Revolution
The French wanted America to join their revolution since they helped Americans in their revolution. Some Americans thought they should help, but some Americans wanted to stay loyal to their ally Britain. George Washington passed the Neutrality Proclamation
Pontiac's Rebellion 1763
An Indian uprising after the French and Indian War, led by Ottawa chief Pontiac. They opposed British expansion into the western Ohio Valley and began destroying British forts in the area. The attacks ended when Pontiac was killed.
Seven Years War
War fought in the colonies from 1754 to 1763 between the English and the French for possession of the Ohio River Valley area. The English won the war and the Peace of Paris was negotiated in 1763
Shay's Rebellion
Armed uprising led by Daniel Shay seeking lower taxes and an end to property foreclosures. Caused criticism of the Articles of Confederation for weak government and led to creation of Constitution.
Whiskey Rebellion 1794
Farmers in Pennsylvania rebelled against Hamilton's excise tax on whiskey, several federal officers were killed in the riots. Washington put down the rebellion and shows that the Constitution was working unlike Shays Rebellion
XYZ Affair 1798
A commission had been sent to France in 1797 to discuss the disputes that had arisen out of the U.S.'s refusal to honor the Franco-American Treaty of 1778. President Adams had also criticized the French Revolution, so France began to break off relations with the U.S. Adams sent delegates to meet with French foreign minister Talleyrand in the hopes of working things out. Talleyrand's three agents told the American delegates that they could meet with Talleyrand only in exchange for a very large bribe. The Americans did not pay the bribe, and in 1798 Adams made the incident public, substituting the letters "X, Y and Z" for the names of the three French agents in his report to Congress.
Abigail Adams
wife of John Adams, wrote him many letters regarding women's rights and her dislike for slavery. John Adams frequently sought the advice of his wife.
Alexander Hamilton
First Secretary of the Treasury. He advocated creation of a national bank, assumption of state debts by the federal government, and a tariff system to pay off the national debt. Federalist.
Anti-Federalists
people who opposed the Constitution
Ben Franklin
American patriot, writer, printer, and inventor. During the Revolutionary War he persuaded the French to help the colonists. A delegate from Pennsylvania and proposed the "Albany Plan of the Union" as a way to strengthen colonies. Member of the Continental Congress
Committees of Corree
Organization founded by Samuel Adams consisting of a system of communication between patriot leaders in New England and throughout the colonies
Democratic-Republican Party
Led by Thomas Jefferson, believed people should have political power, favored strong STATE governments, emphasized agriculture, strict interpretation of the Constitution, pro-French, opposed National Bank
East India Tea Company
The company that shipped the tea to America for the Boston Tea Party
Federalists
supporters of the Constitution in favor of strong central government
George the third
King of England during the American Revolution
James Madison
"Father of the Constitution," Federalist leader, and fourth President of the United States.
John Adams
America's first Vice-President and second President. Sponsor of the American Revolution in Massachusetts, and wrote the Massachusetts guarantee that freedom of press "ought not to be restrained."
John Jay
1st Chief Justice of the Supreme Court, negotiated with British for Washington
Loyalists
American colonists who remained loyal to Britain and opposed the war for independence
Mercy Otis W
She became a Patriot writer and first woman historian of the American Revolution. She wrote plays, poems and more that supported independence. She convinced many people in Massachusetts to become Patriots.
Minutemen
Member of a militia during the American Revolution who could be ready to fight in sixty seconds
Patrick Henry
Speech in the Virginia Convention; a leader of the American Revolution and a famous orator who spoke out against British rule of the colonies
Paxton boys
They were a group of Scots-Irish men living in the Appalachian hills that wanted protection from Indian attacks. made an armed march and protested
Sons of Liberty 1765
A radical political organization for colonial independence after the passage of the Stamp Act. They incited many riots and included Samuel Adams and Paul Revere.