neuro usmle
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
astrocytes
CNS
Physical support, repair, removal of excess neurotransmitters, component of blood-brain barrier, glycogen fuel reserve buffer. GFAP ⊕.
reactive gliosis in response to injury
oligodendrocytes
Myelinate axons in CNS (including CN II). “Fried egg” appearance histologically
Injured in multiple sclerosis, leukodystrophies, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
ependymal cells
cns
Ciliated simple columnar glial cells lining ventricles and central canal of spinal cord. Apical surfaces are covered with cilia (which circulate CSF) and microvilli (which help with CSF absorption).
choroid plexus
produce csf
microglia
cns
Activation in response to tissue damage p release of inflammatory mediators (eg, nitric oxide, glutamate). Not readily discernible by Nissl stain.
Phagocytic scavenger cells of CNS. HIV-infected microglia fuse to form multinucleated giant cells in CNS in HIVassociated dementia.
satellite cells
pns
Surround neuronal cell bodies in ganglia
equivalent of astrocytes
schwann cells
Myelinate axons in PNS (including CN III-XII). S100 ⊕.
injured in GBS
free nerve endings sensation
pain, temperature
meissner corpuscules
light touch
low frequency vibration
pacinian corpuscules sensation
high frequency vibrations and pressure
merkel disc sensation
pressure, deep static touch
ruffini corpuscules sensations
stretch, joint angle change
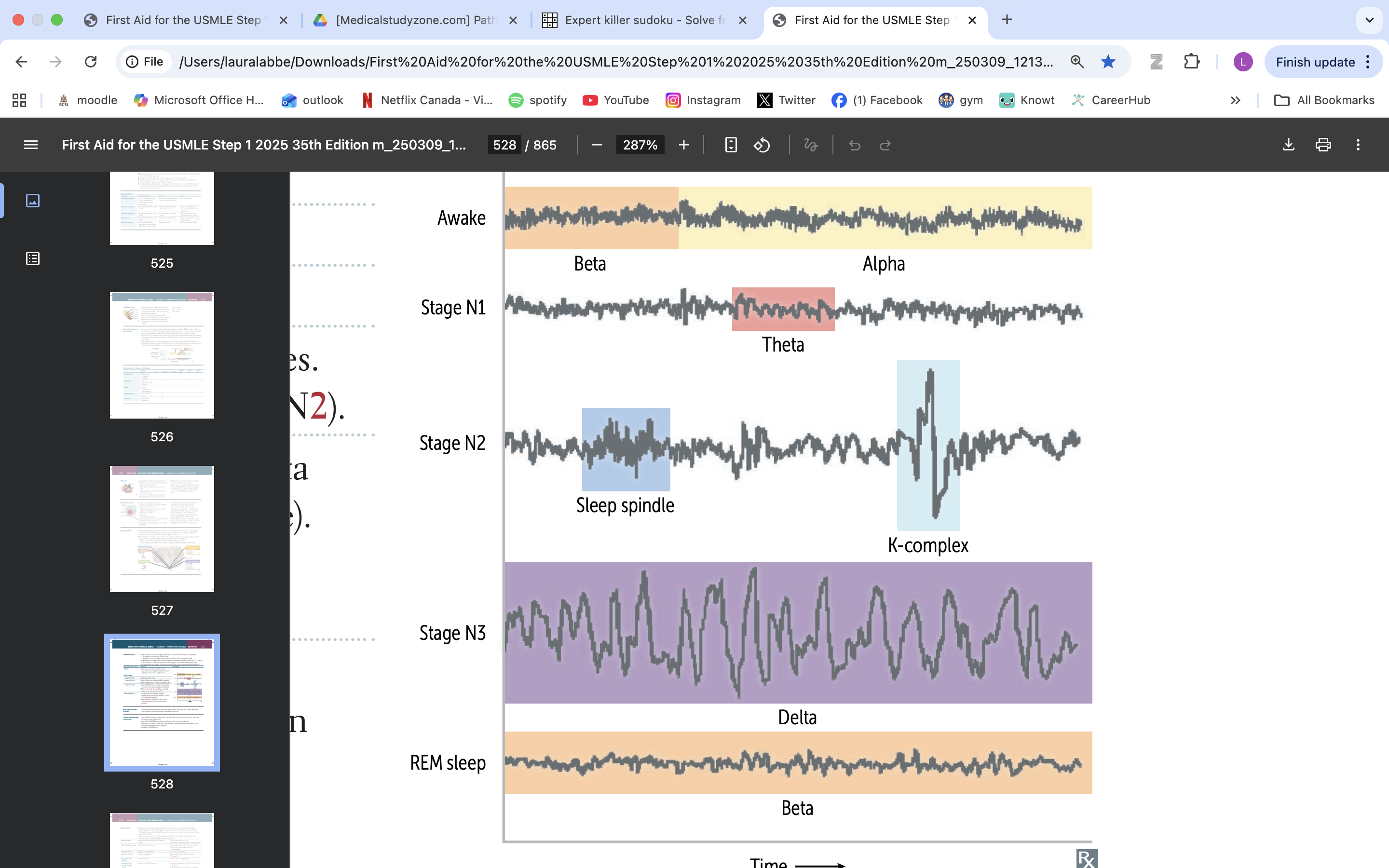
stage n1 of sleep
light sleep
theta waves
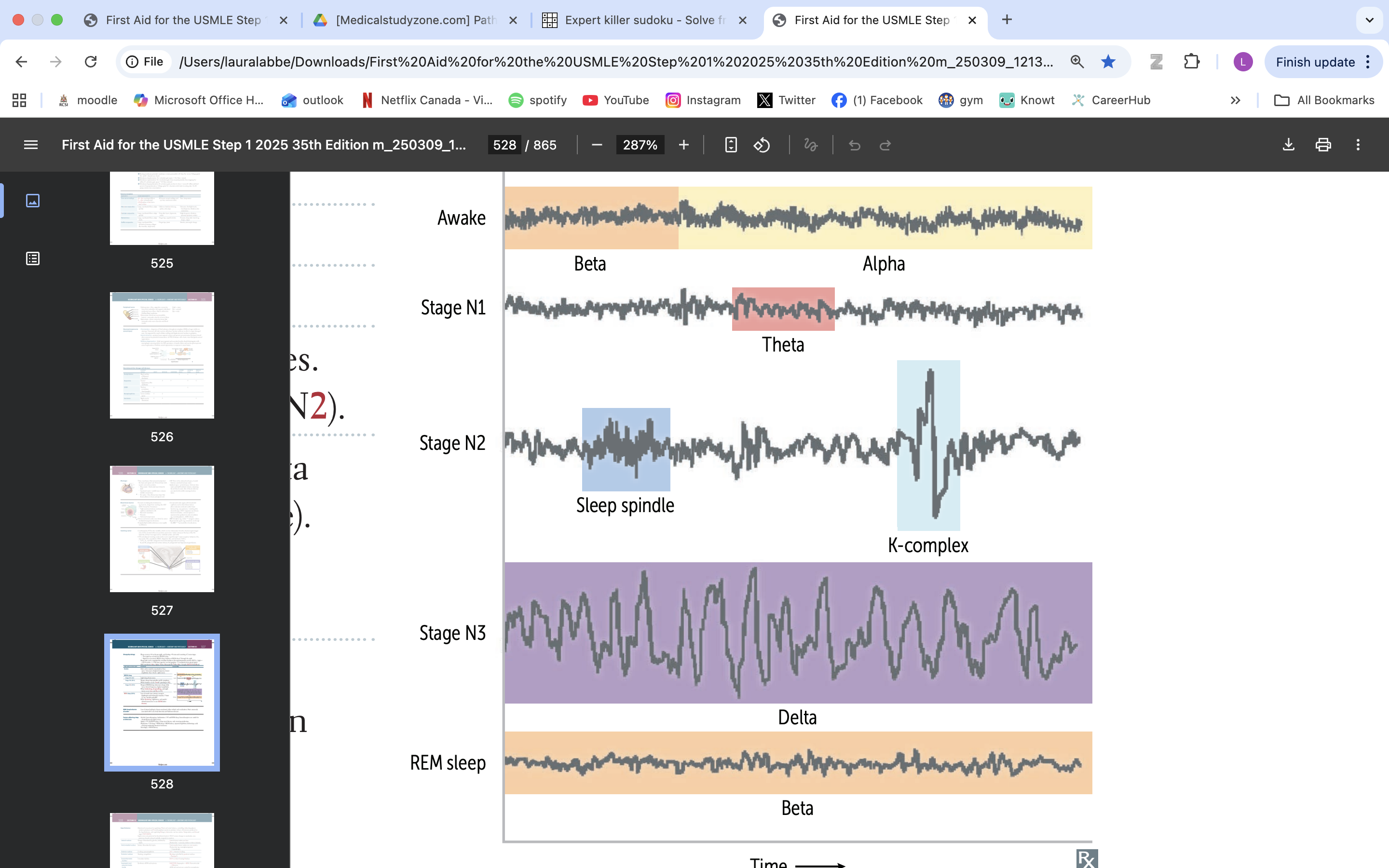
stag n2 sleep
sleep spindles and k complexes
when bruxism occurs
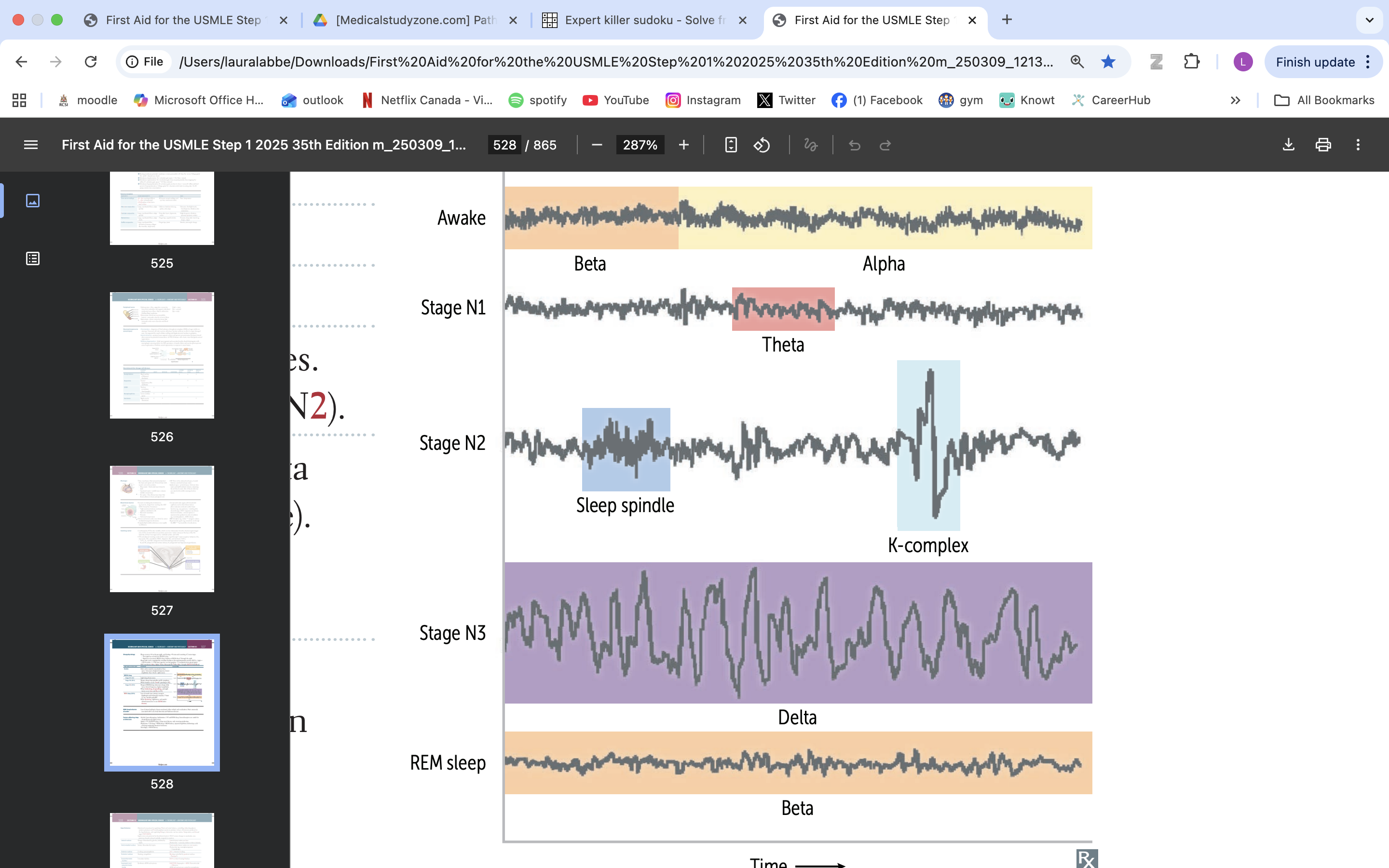
stage n3 sleep
delta waves
sleep walking, bedwetting, night terrors
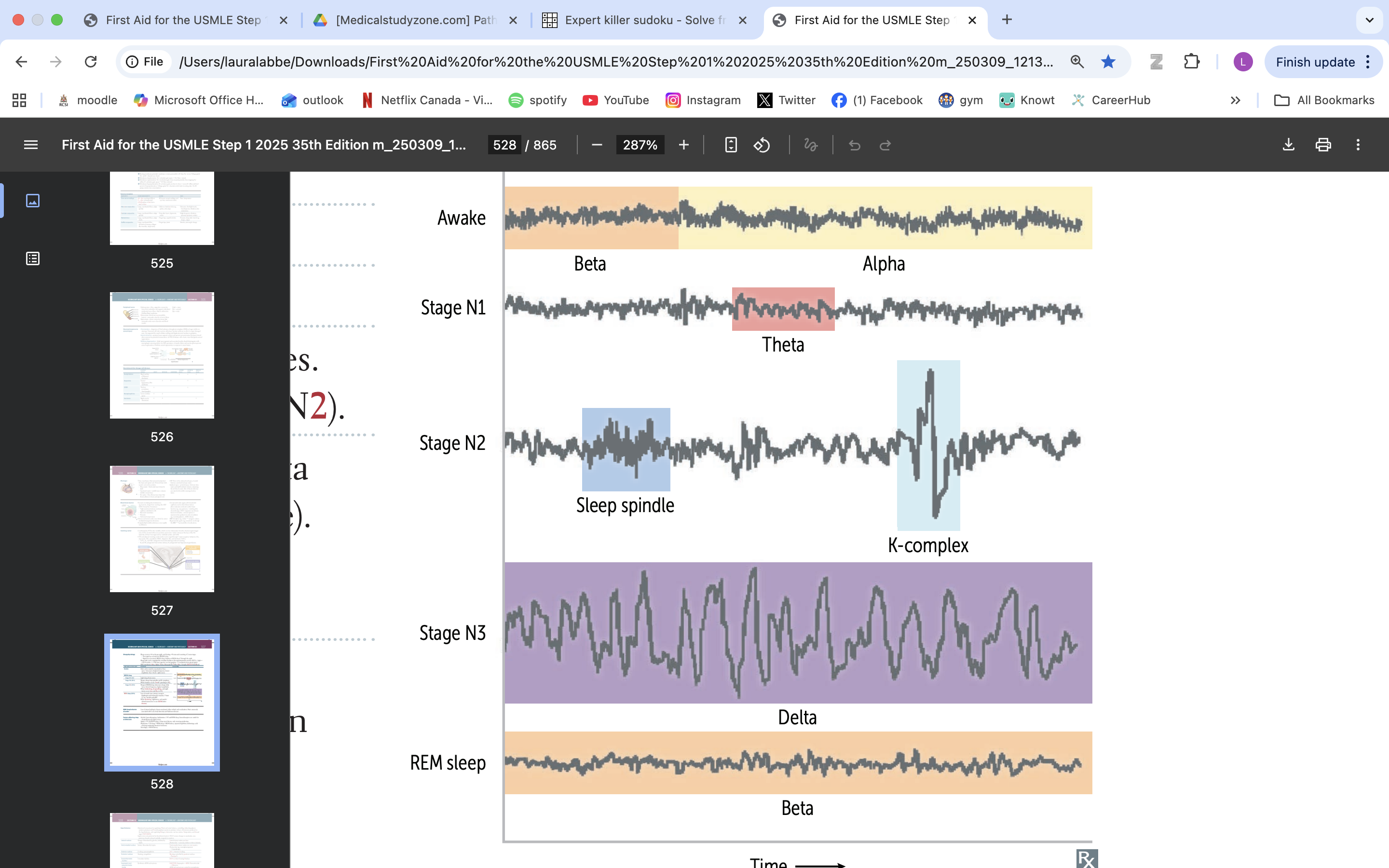
rem sleep
when brain most active/ dreams
atonia
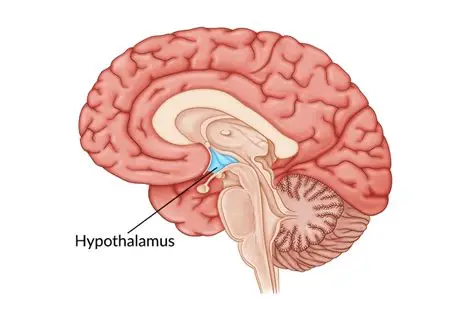
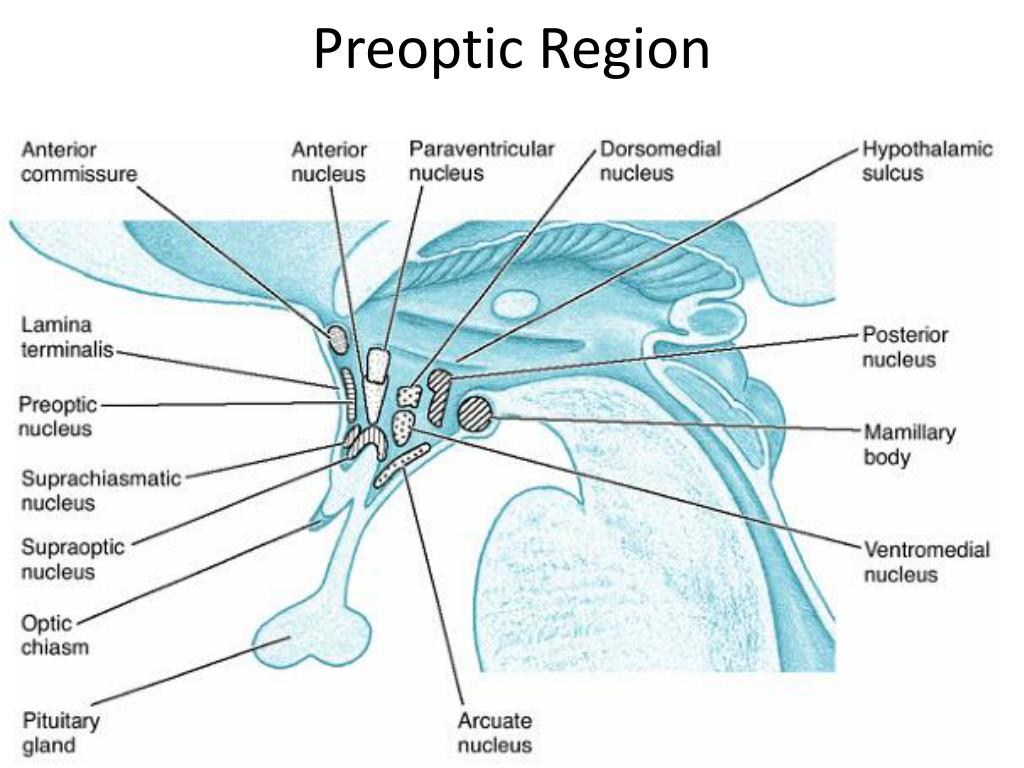
hypothalamus
Maintains homeostasis by regulating Thirst and water balance, controlling Adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary) and Neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary) release of hormones produced in the hypothalamus, and regulating Hunger, Autonomic nervous system, Temperature, and Sexual urges
lateral nucleus
hypothalamus
Hunger. Stimulated by ghrelin, inhibited by leptin
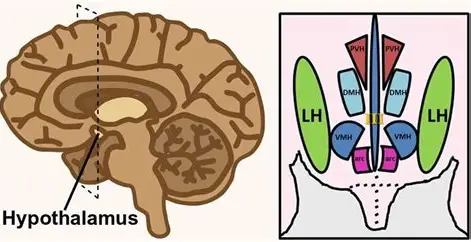
ventromedial nucleus
hypothalamus
Satiety. Stimulated by leptin
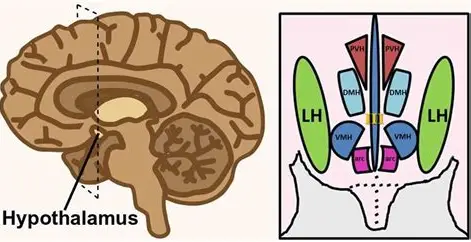
anterior nucleus
hypothalamus
Cooling, parasympathetic.
posterior nucleus
hypothalamus
Heating, sympathetic.
suprachiasmatic nucleus
hypothalamus
Circadian rhythm.
supraoptic/ paraventricular nucleus
hypothalamus
Synthesize ADH and oxytocin.
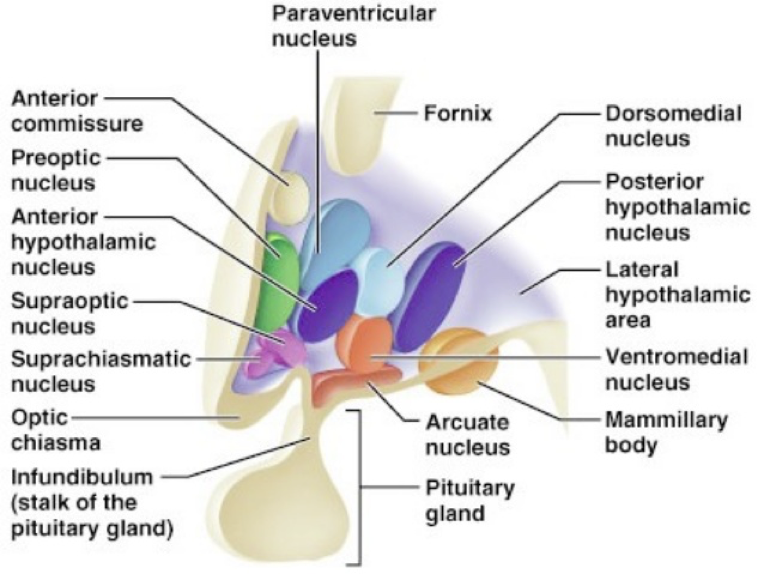
preoptic nucleus
hypothalamus
Thermoregulation, sexual behavior. Releases GnRH
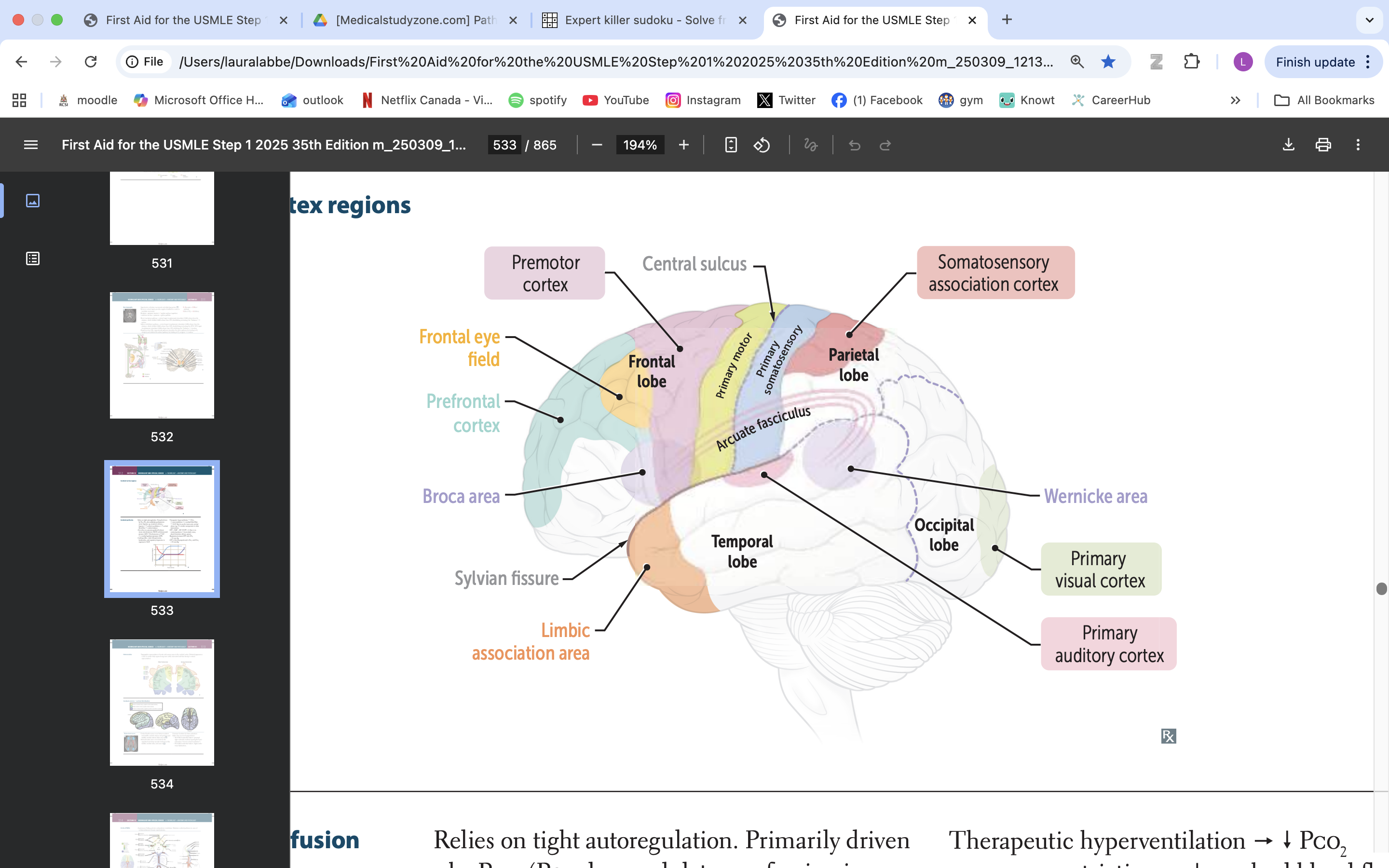
limbic association area
emotional processing
memory formation
behaviour regulation
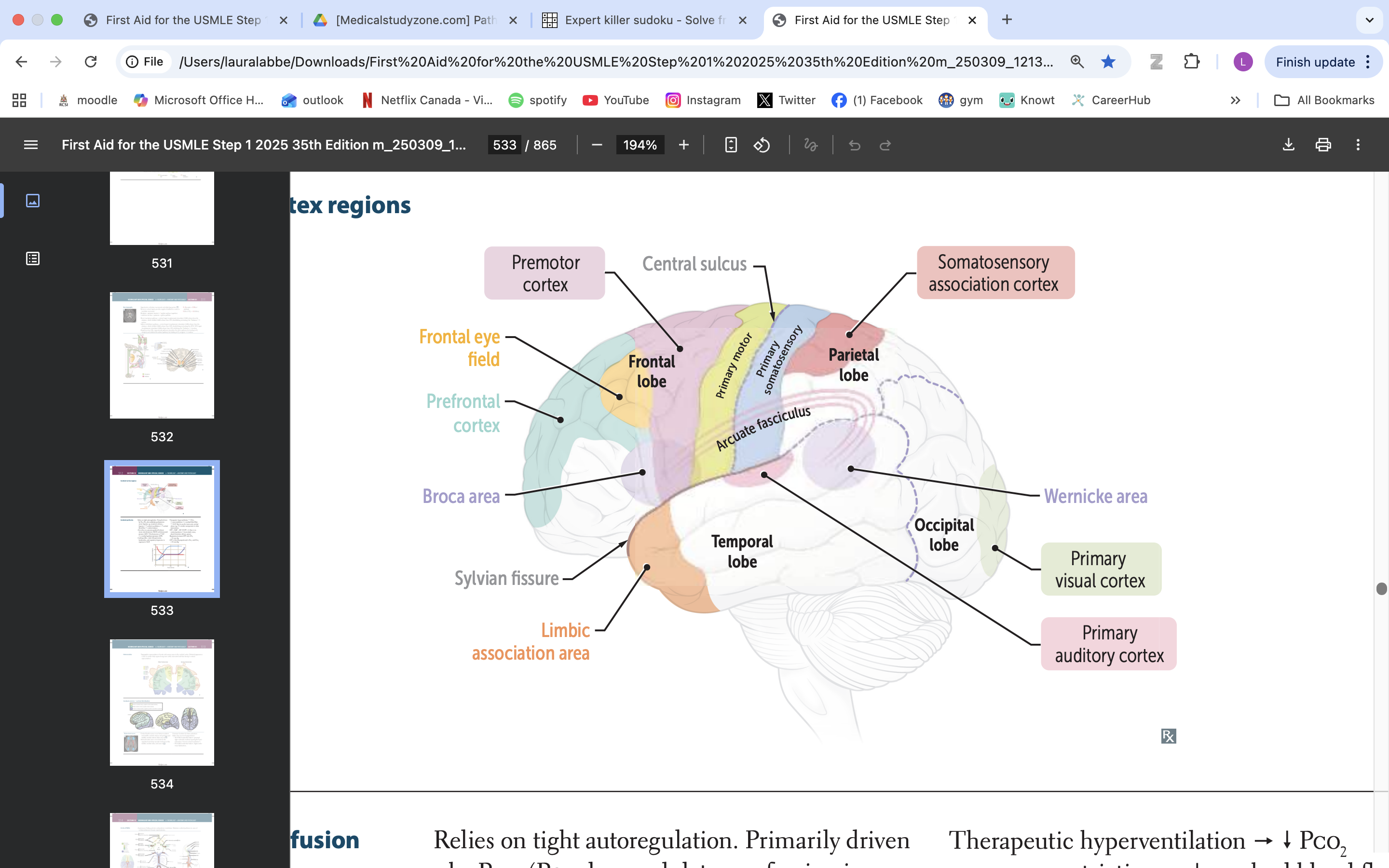
broca area
speech production, language processing
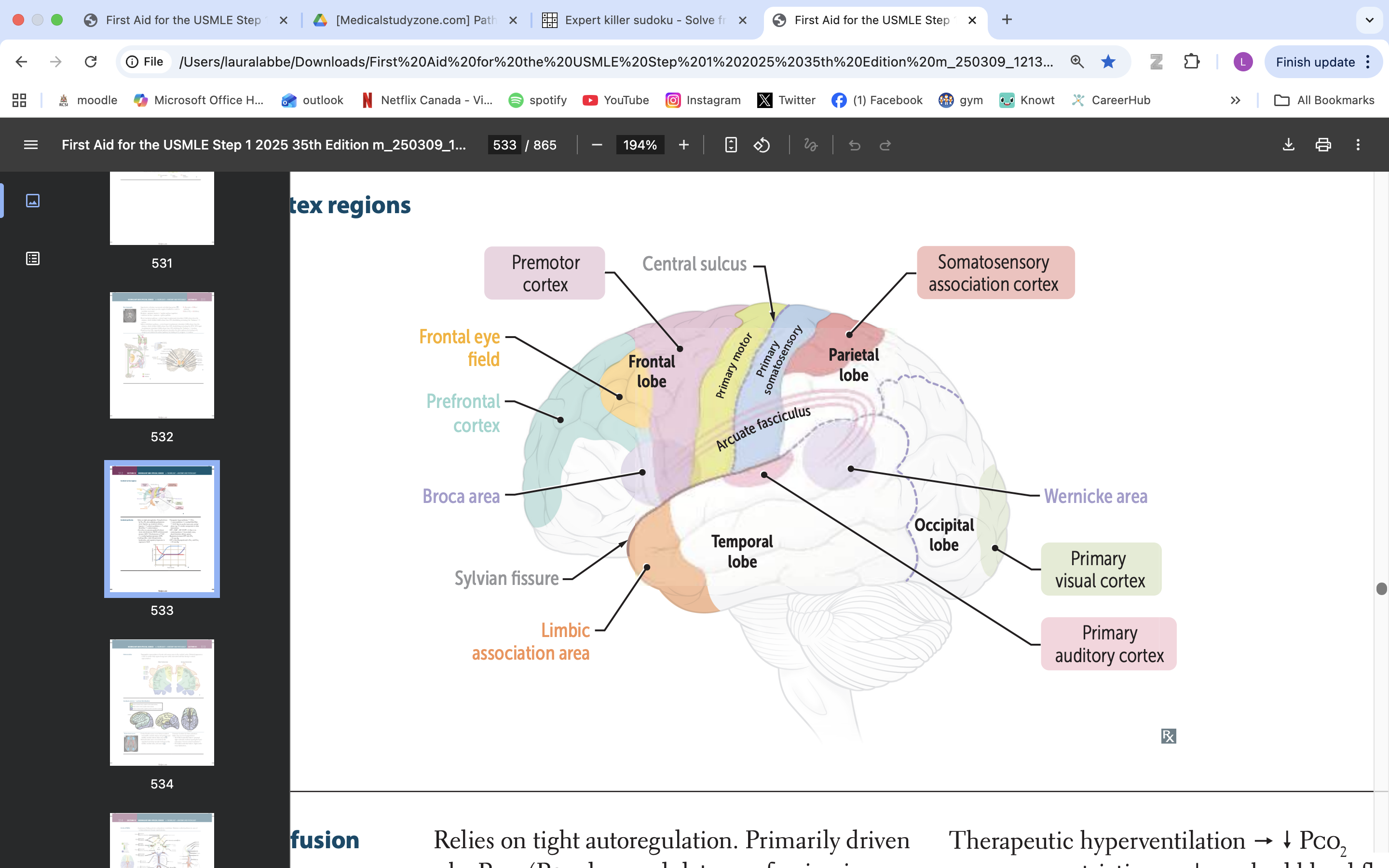
prefrontal cortex
manage thinking, emotions and behavior by using executive functions. These are skills you rely on to plan, make decisions, solve problems, stay focused and adjust to new situations.
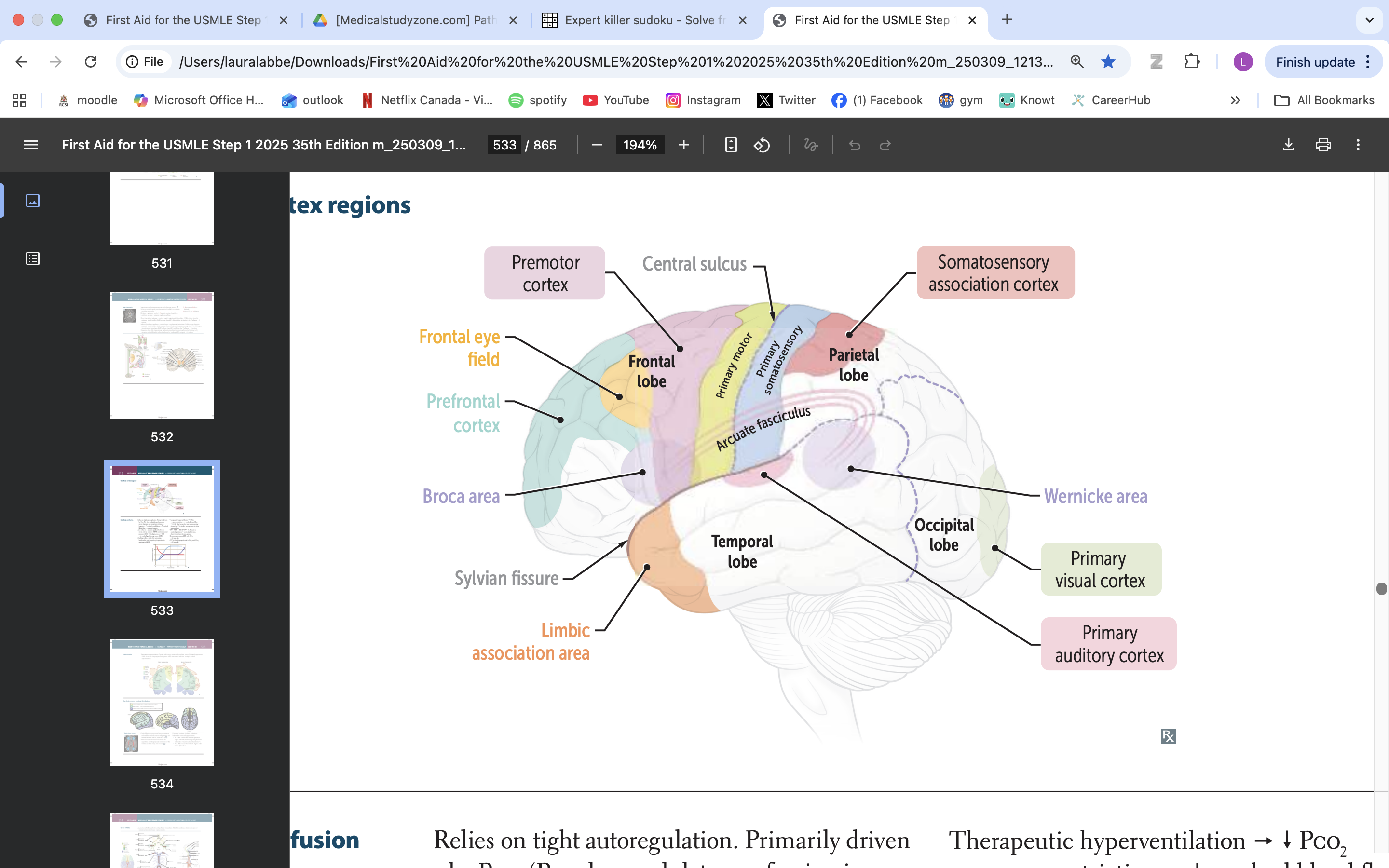
frontal eye field
responsible for controlling eye movements and visual attention, playing a key role in saccadic eye movements and the coordination of visual stimuli
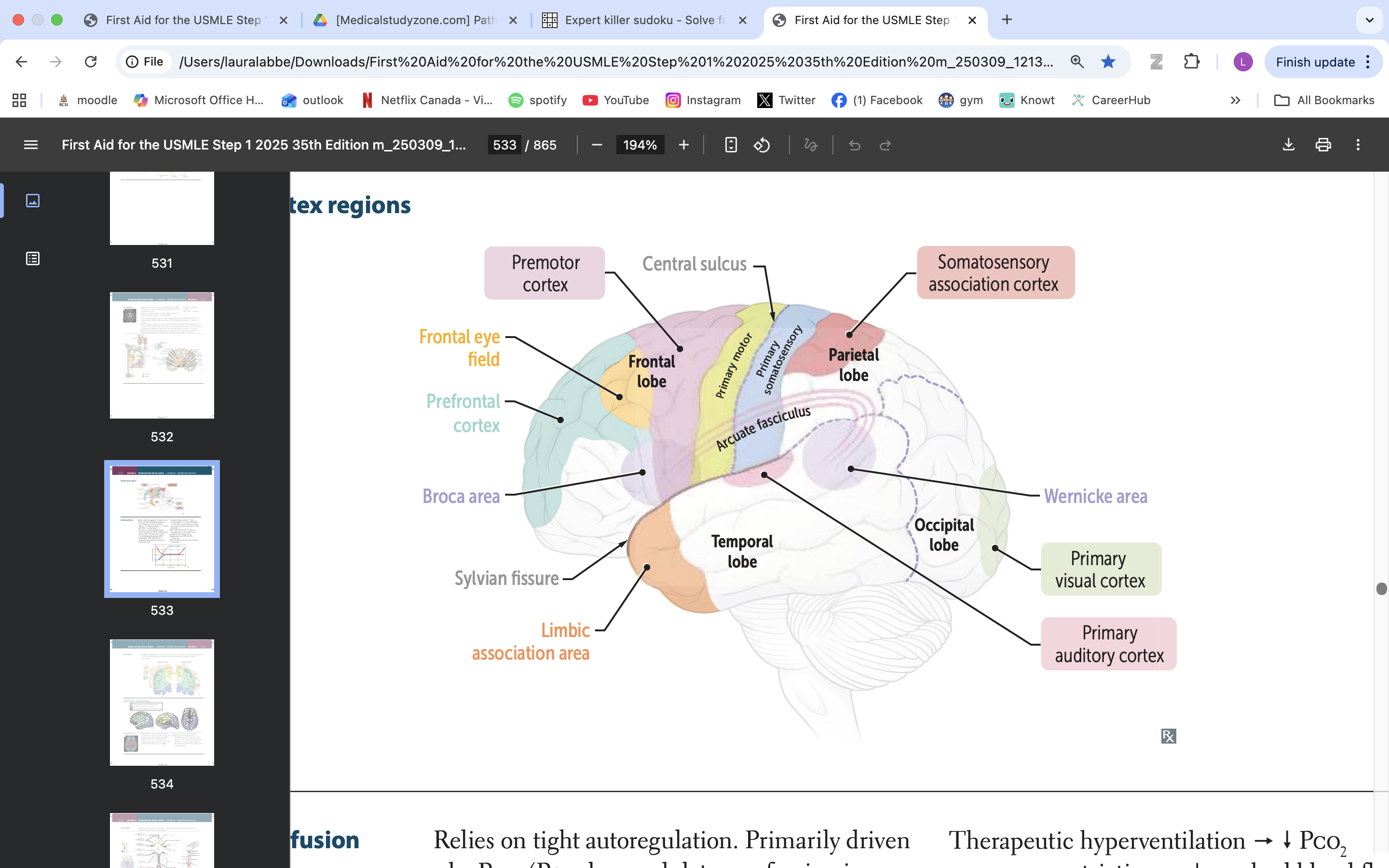
premotor cortex
planning, executing, and coordinating voluntary movements
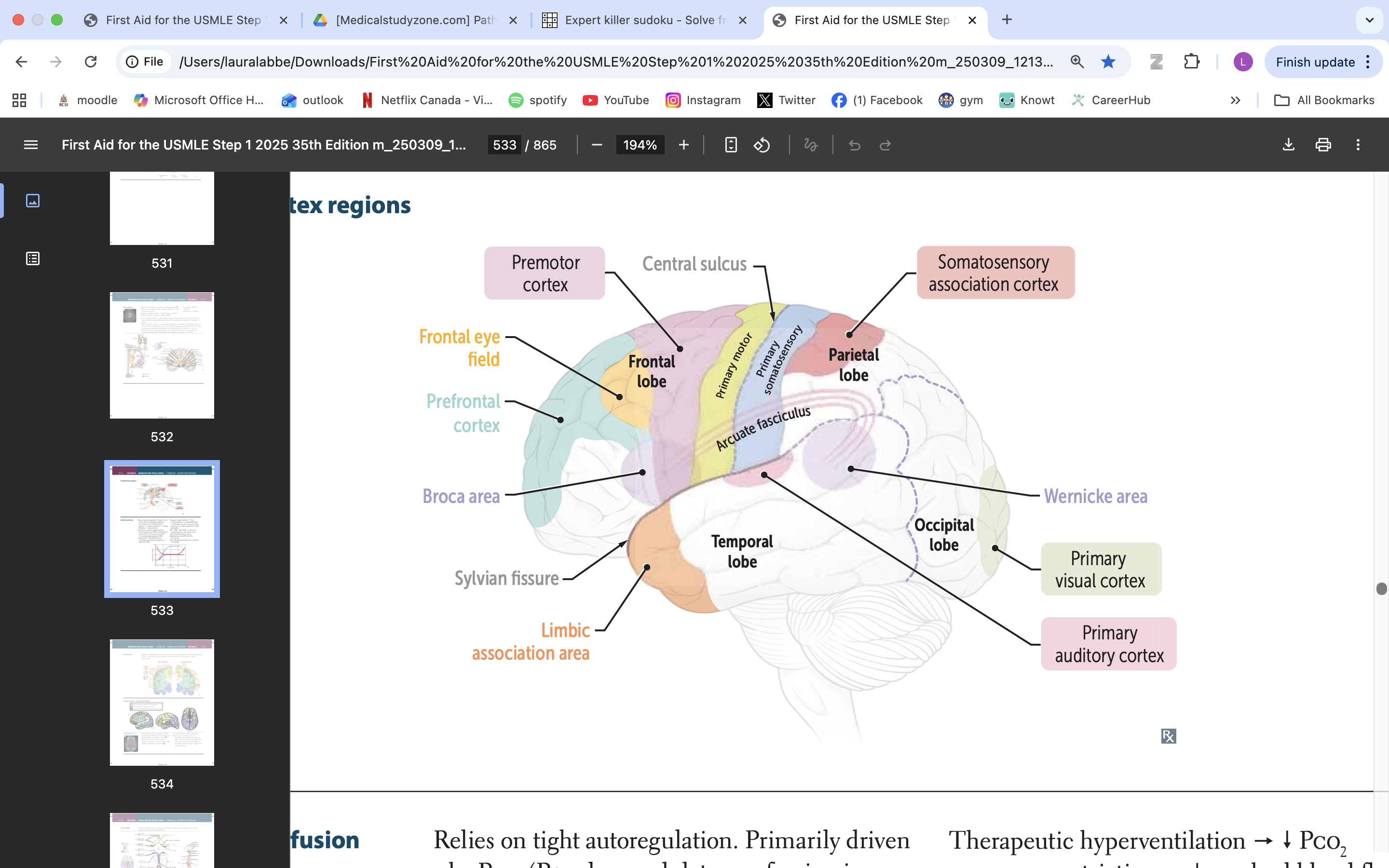
primary motor cortex
voluntary movement
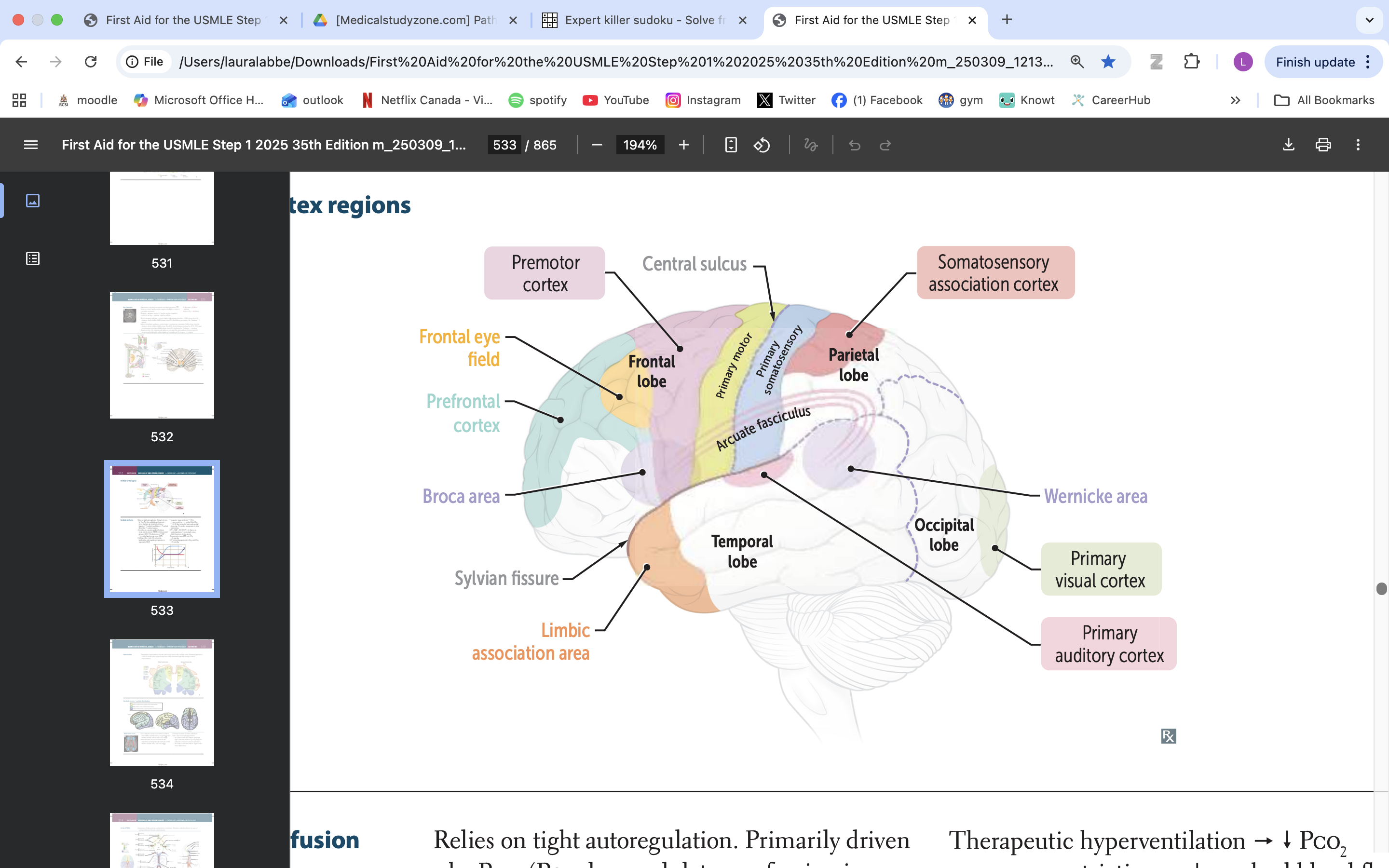
primary somatosensory cortex
somatic information processing
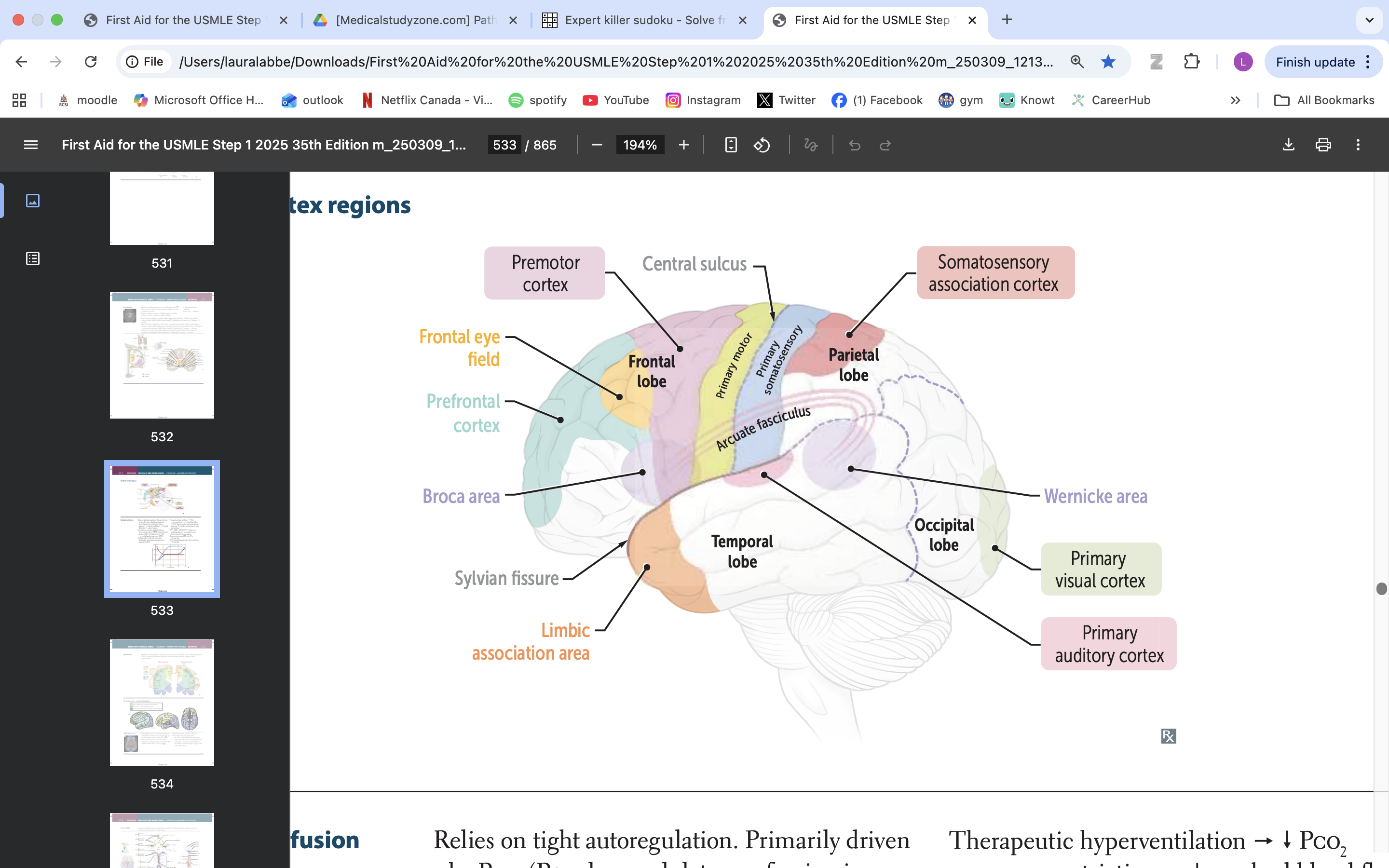
somatosensory association cortex
processes and integrates sensory information related to touch, proprioception, and spatial awareness
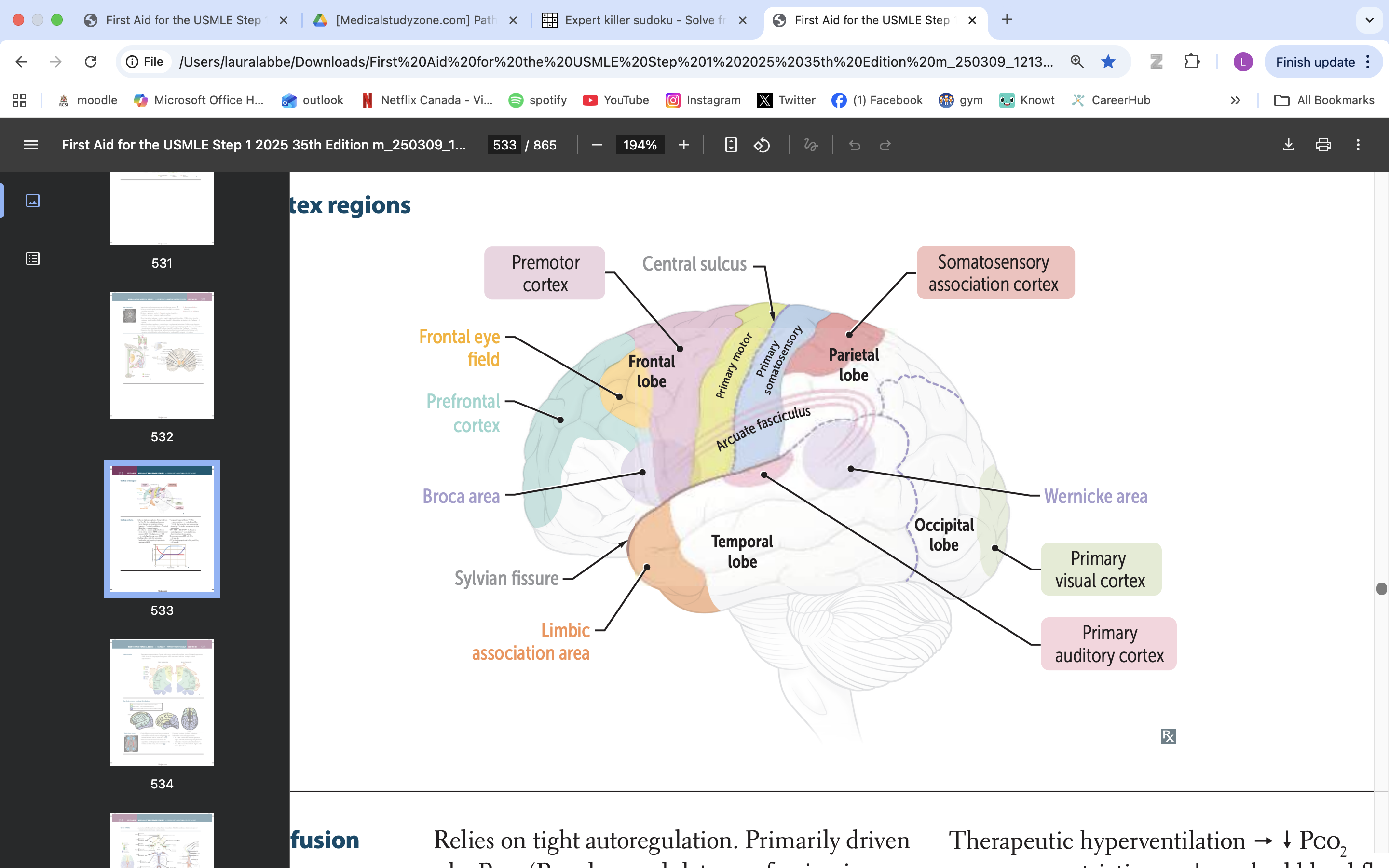
arcuate fasciculus
connects Broca's area and Wernicke's area, playing a vital role in language processing and communication
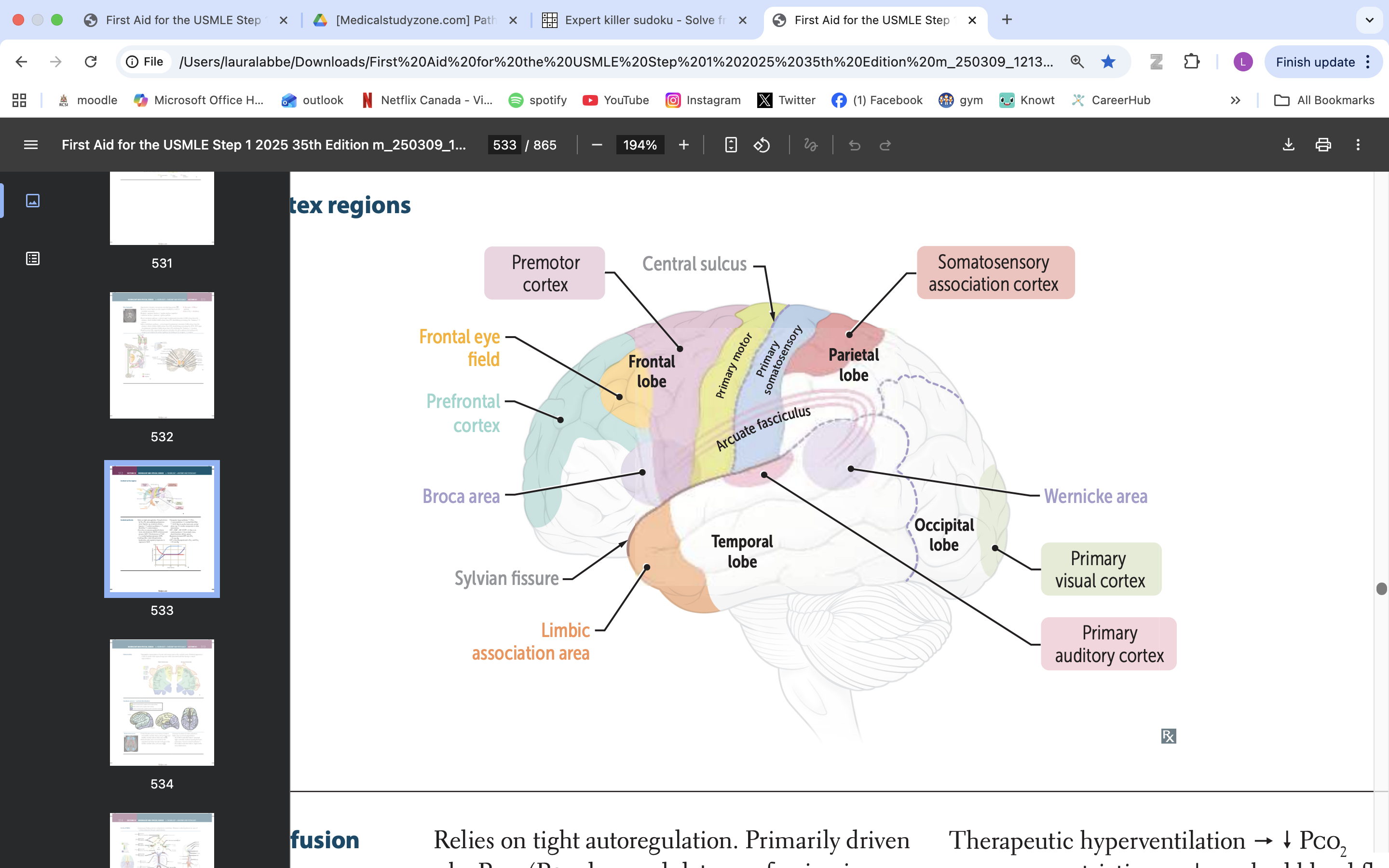
wernicke area
language comprehension, typically located in the left temporal lobe
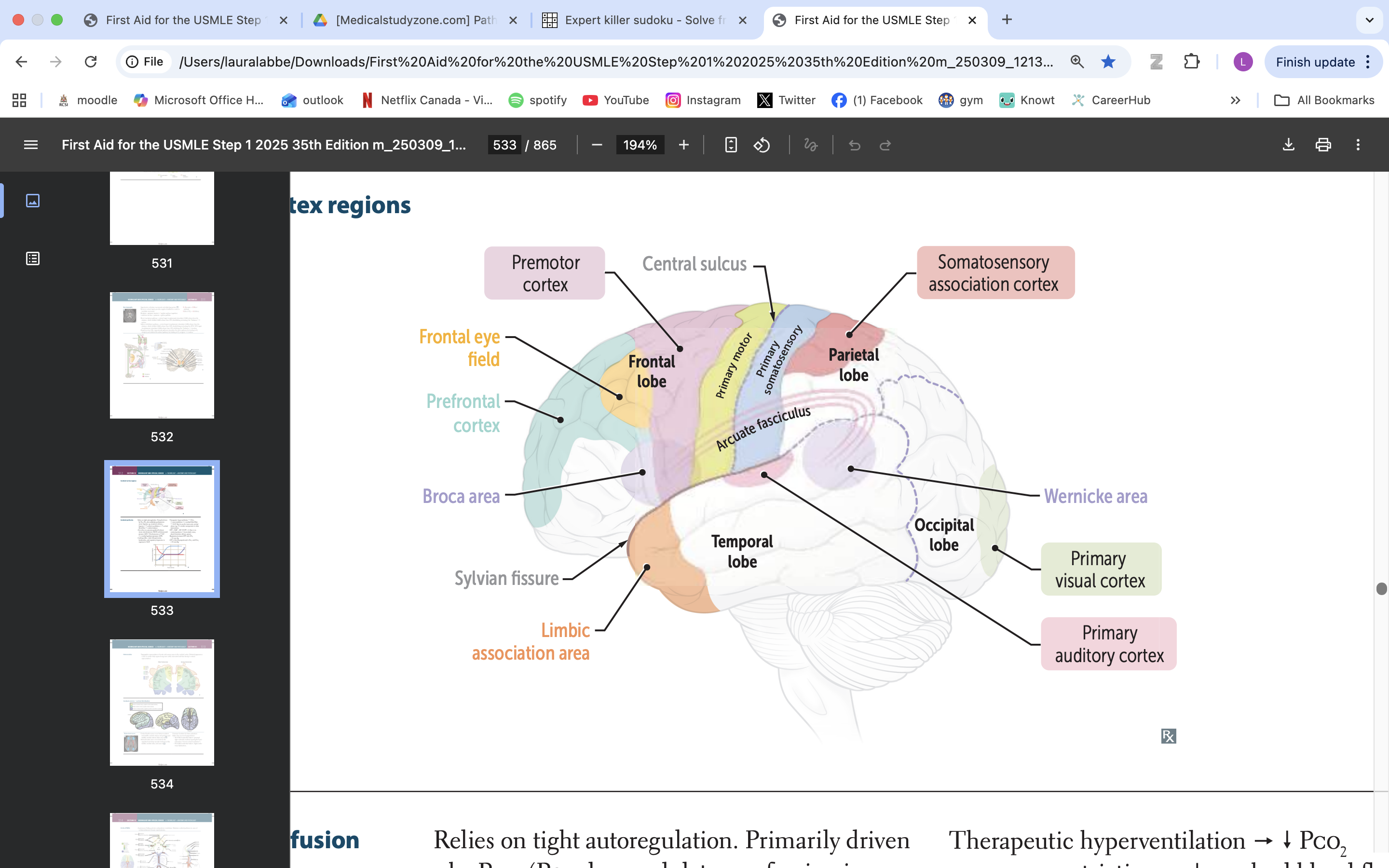
primary visual cortex
process visual info
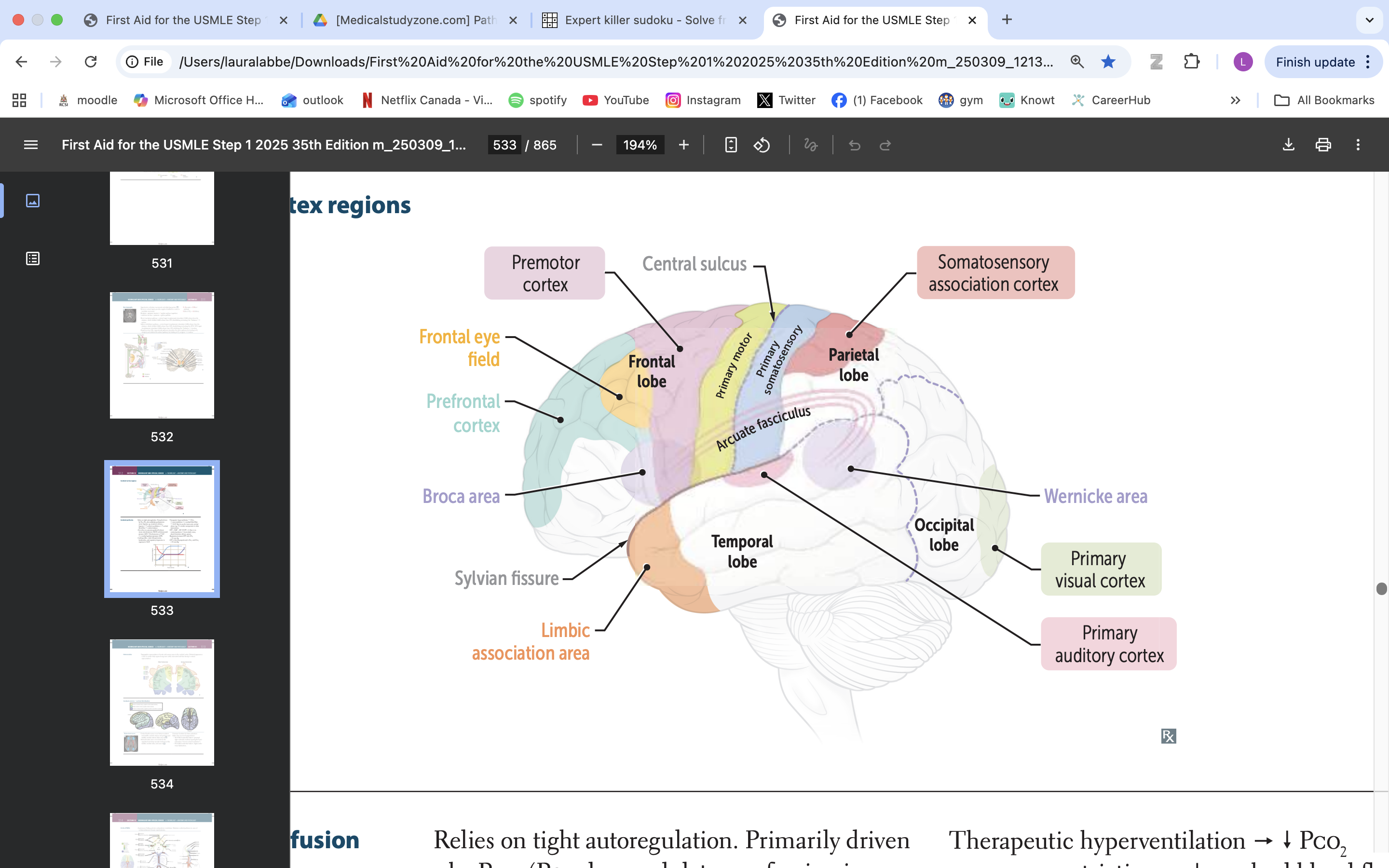
primary auditory cortex
process auditory info
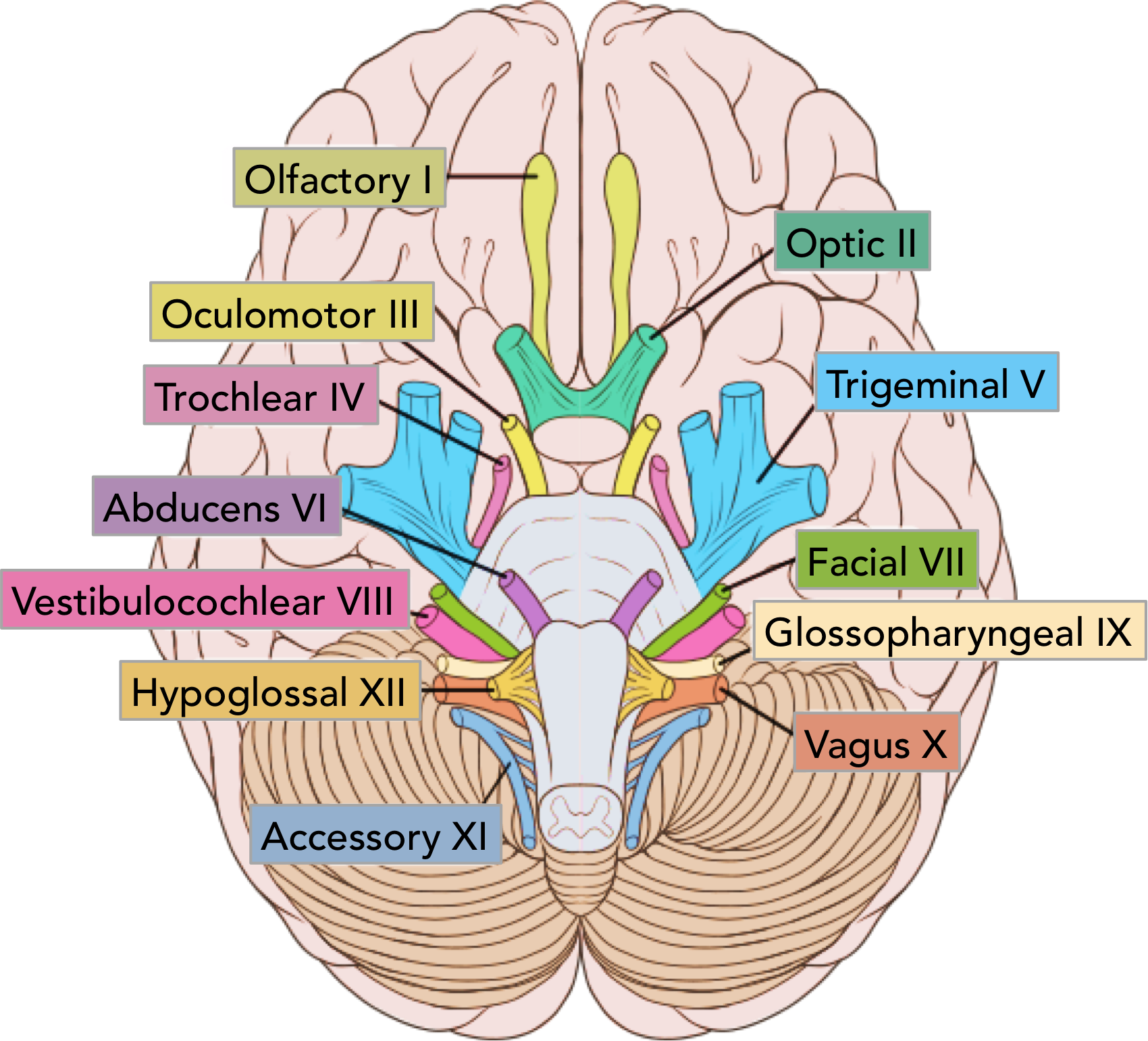
CNI
olfactory
cribiform plate
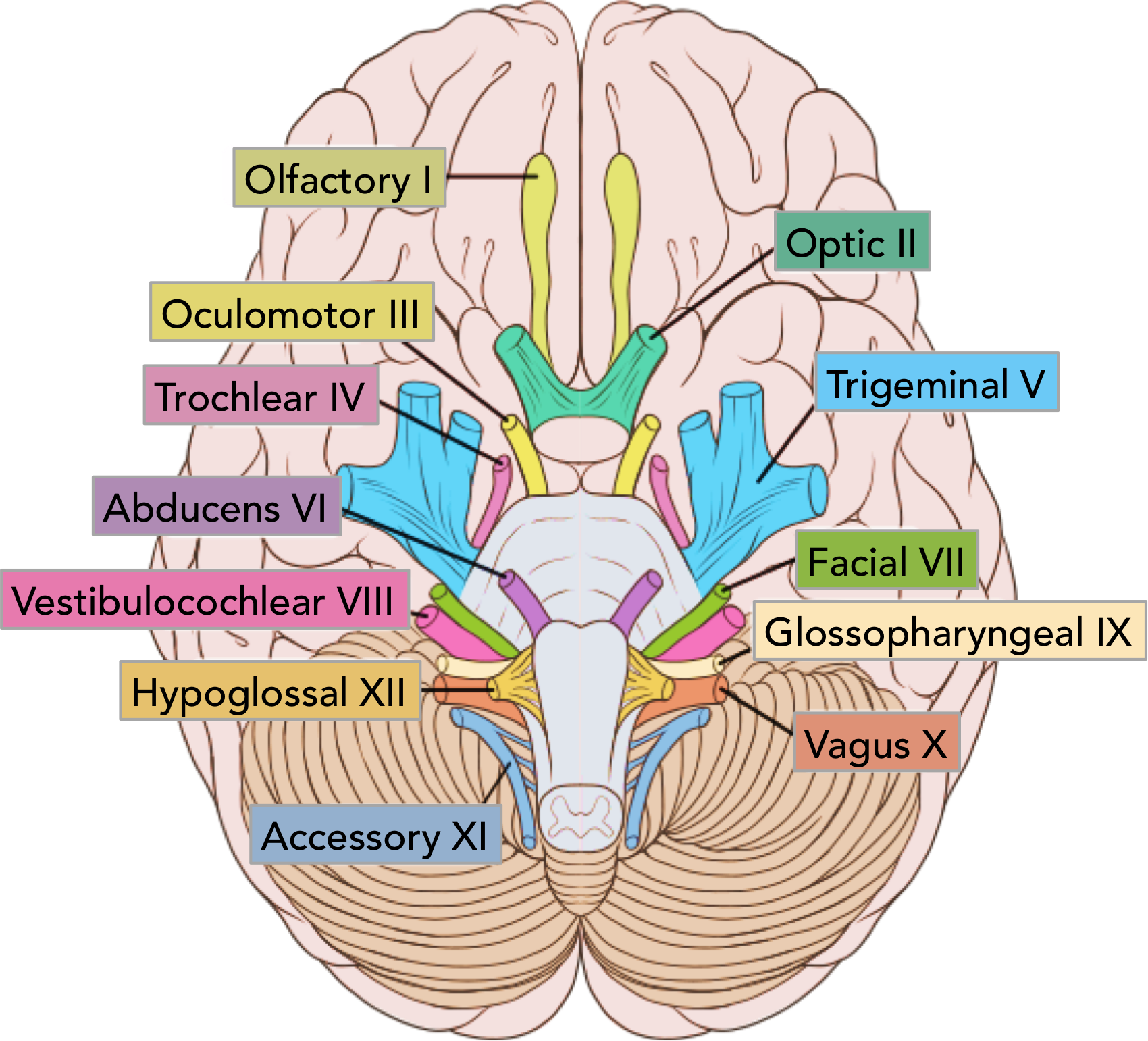
CNII
optic
via optic canal
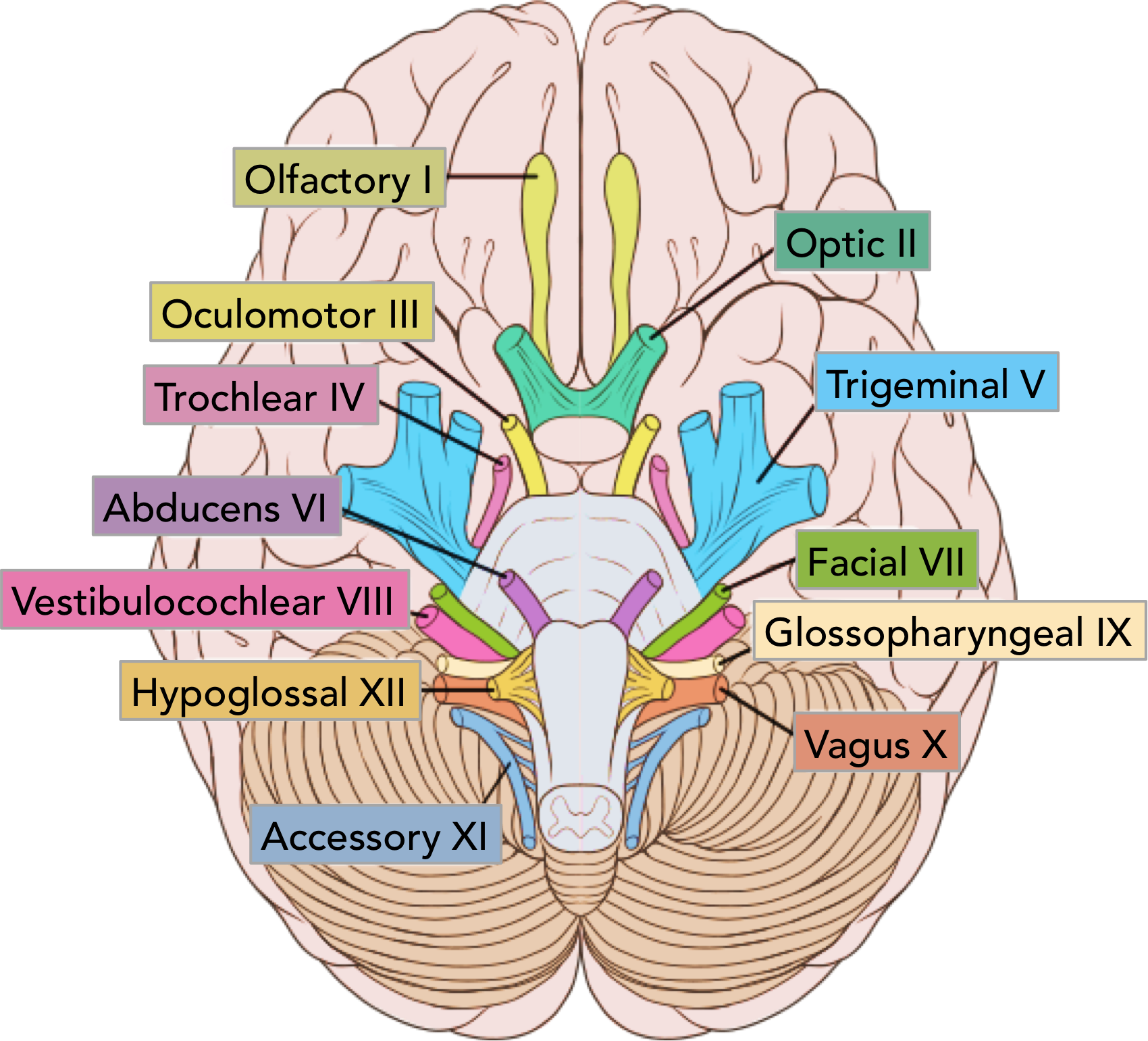
CNIII
oculomotor
superioir orbital fissure
pupillary sphincter and 4 extrinsinc eye muscles
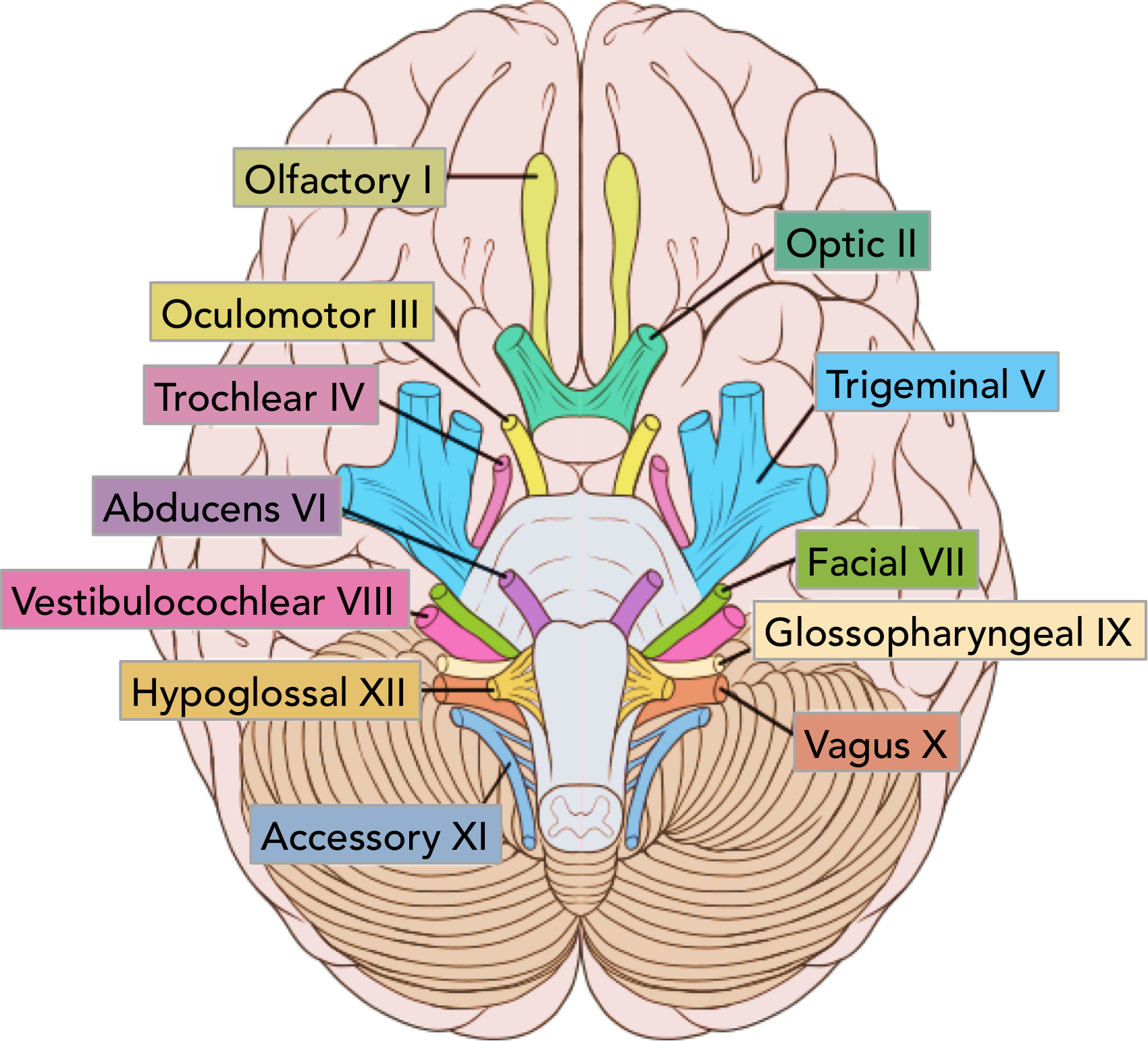
CNIV
trochlear
superioir orital fissure
superioir oblique
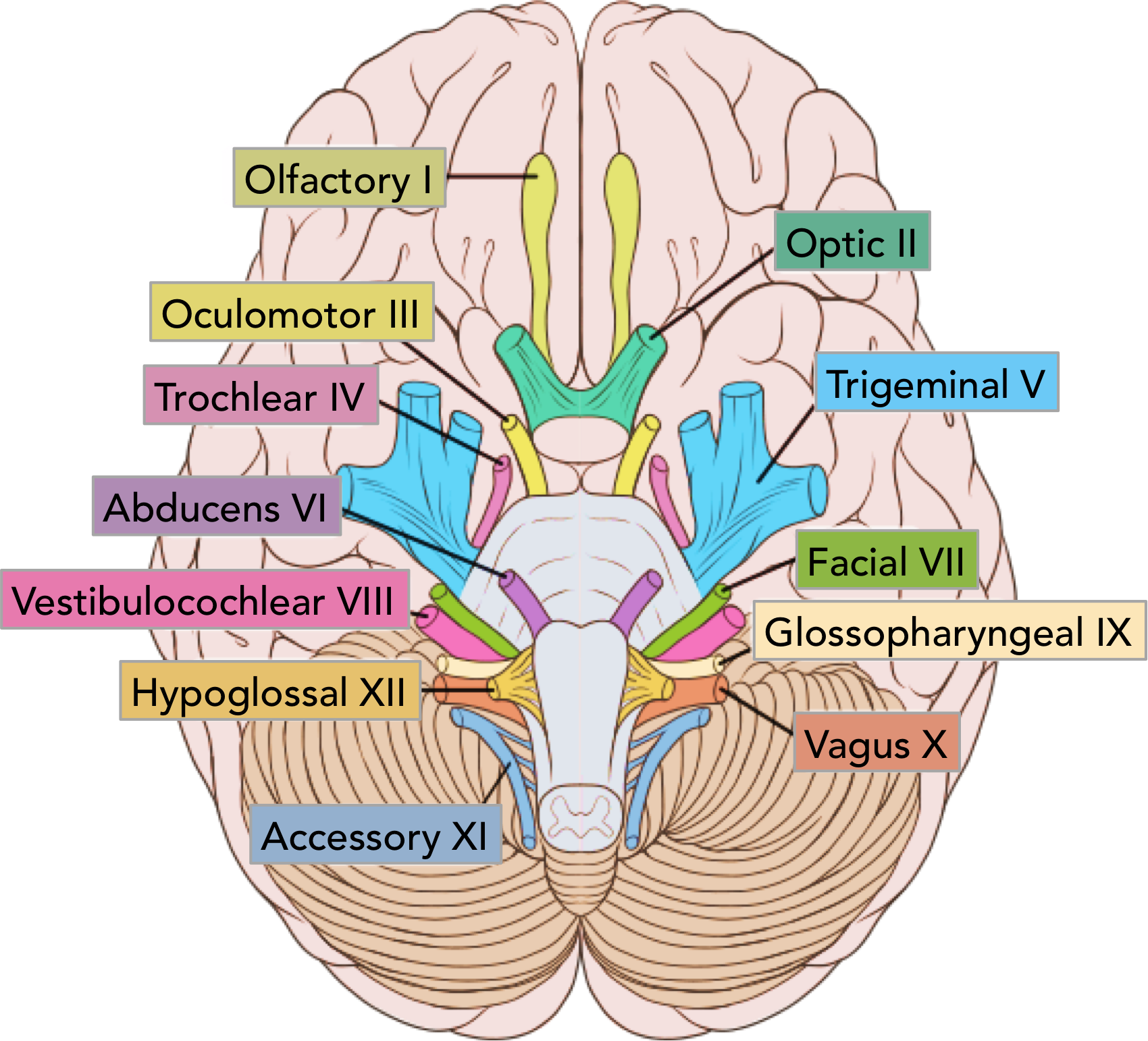
CNV
trigeminal
ophtalmic- superioir orbital fissure, sensory forehea
maxillary- foramen rotundum, sensory mid face
mandibular- foramen ovale, senspry lower face/ anetrioir 2/3 tongue + movement (muscles of mastication)
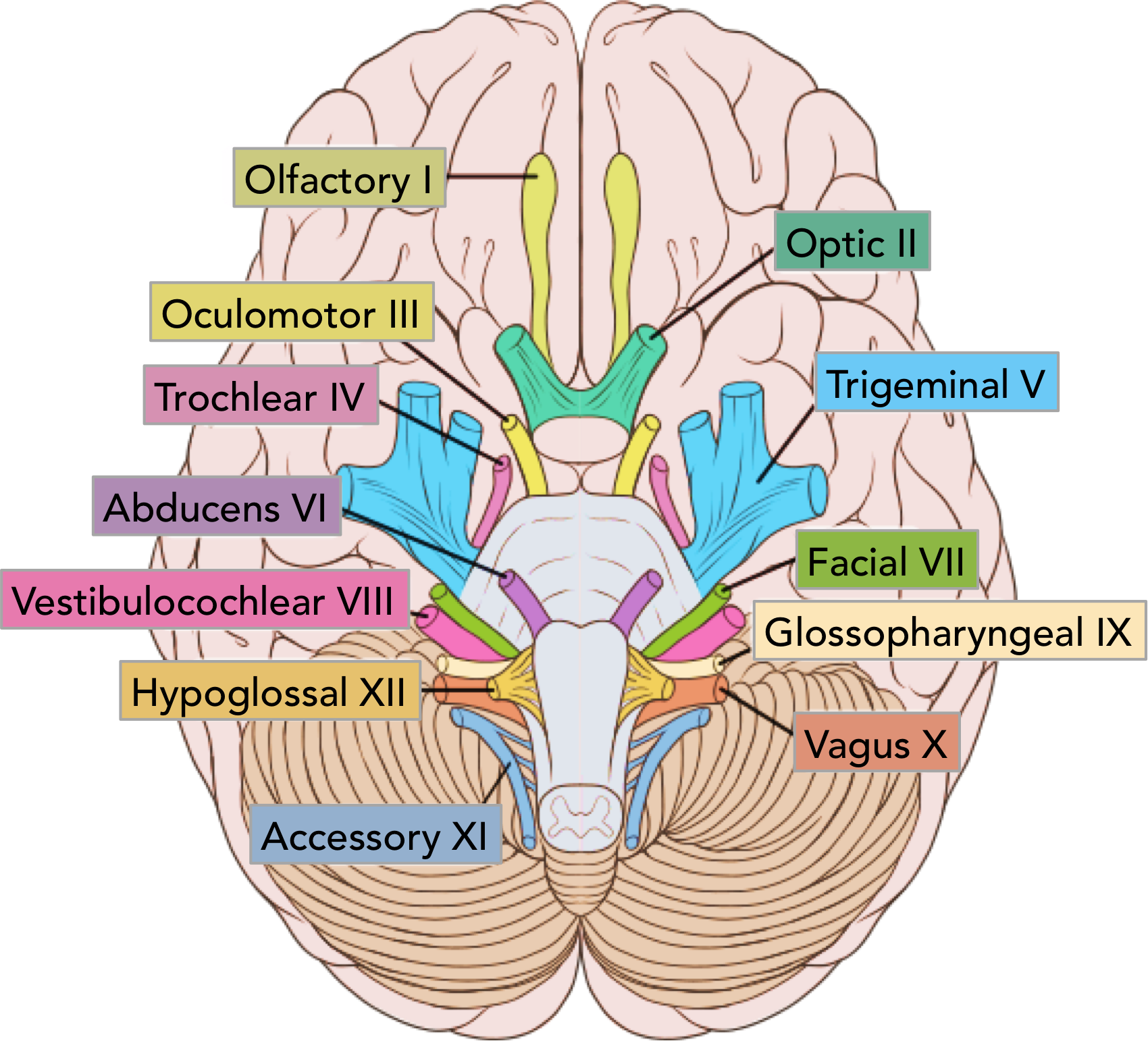
CNVI
abducens
superioir orbital fissure
lateral rectus
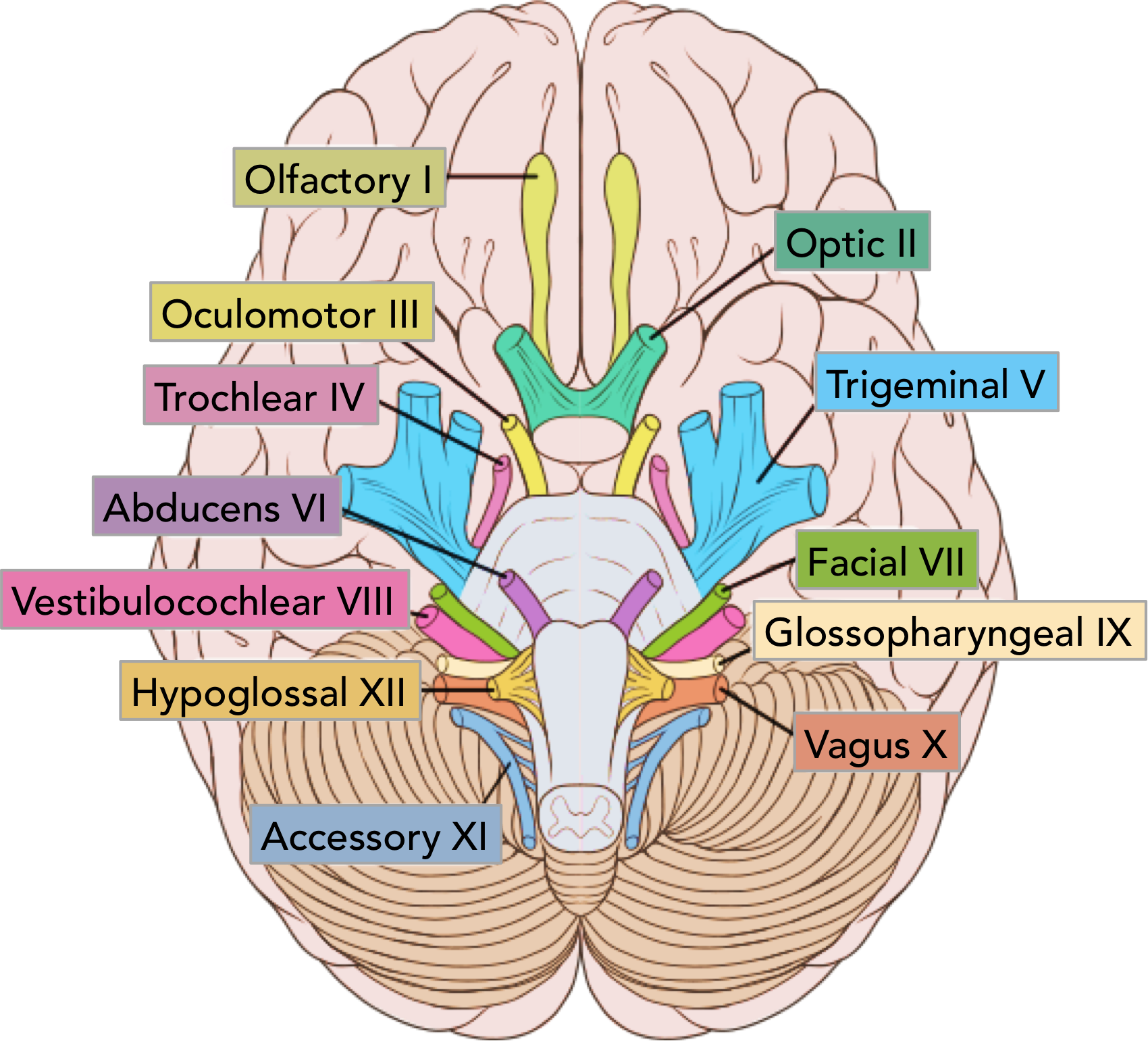
CNVII
facial
internal acoustic meatus
sensation part external ear
taste anterioir 2/3 mouth + hard palate
muscles facial expression
mucous glands mouth and nose
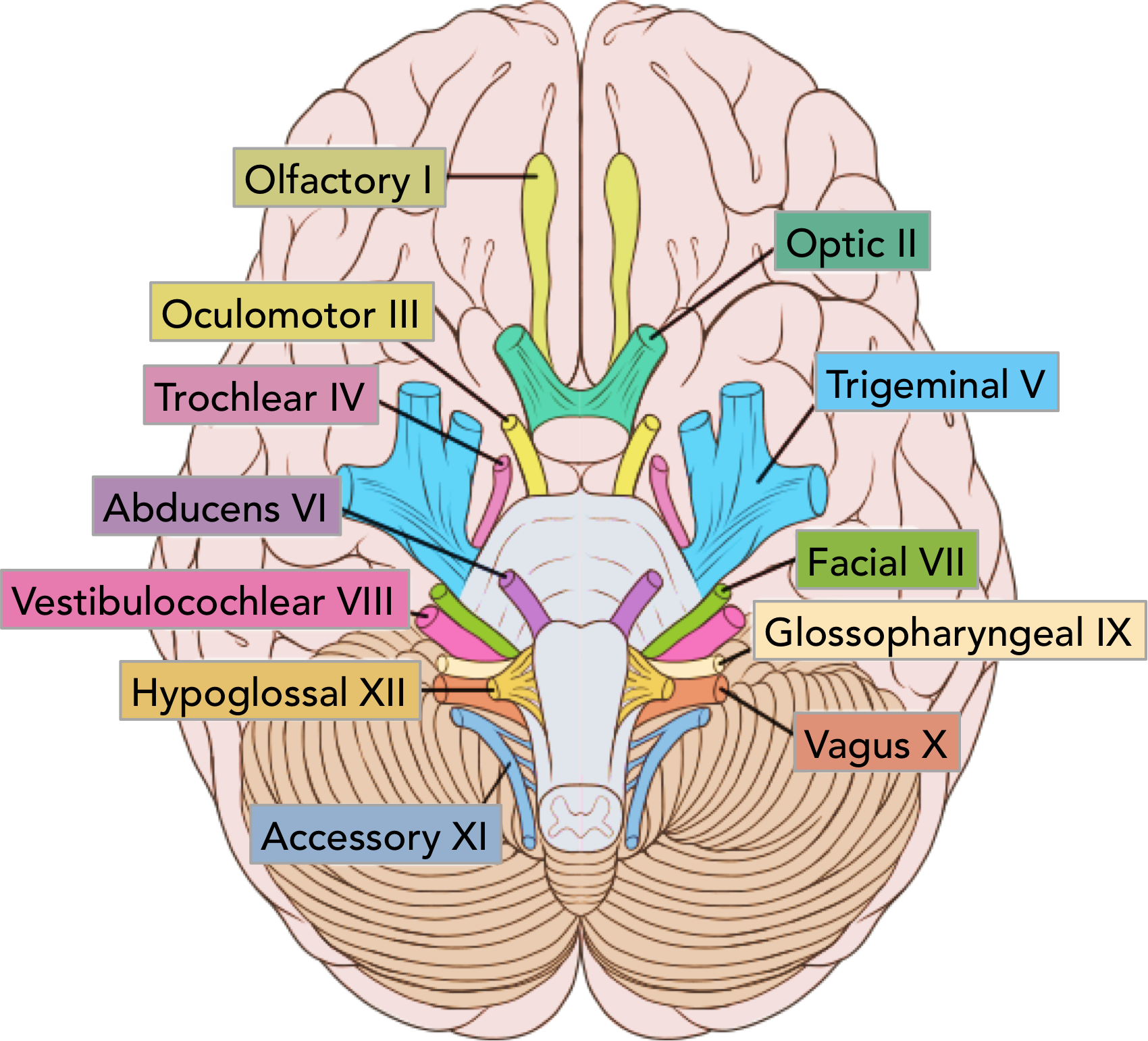
CNVIII
vestibulocochlear
internal acoustic meatus
hearing and balance
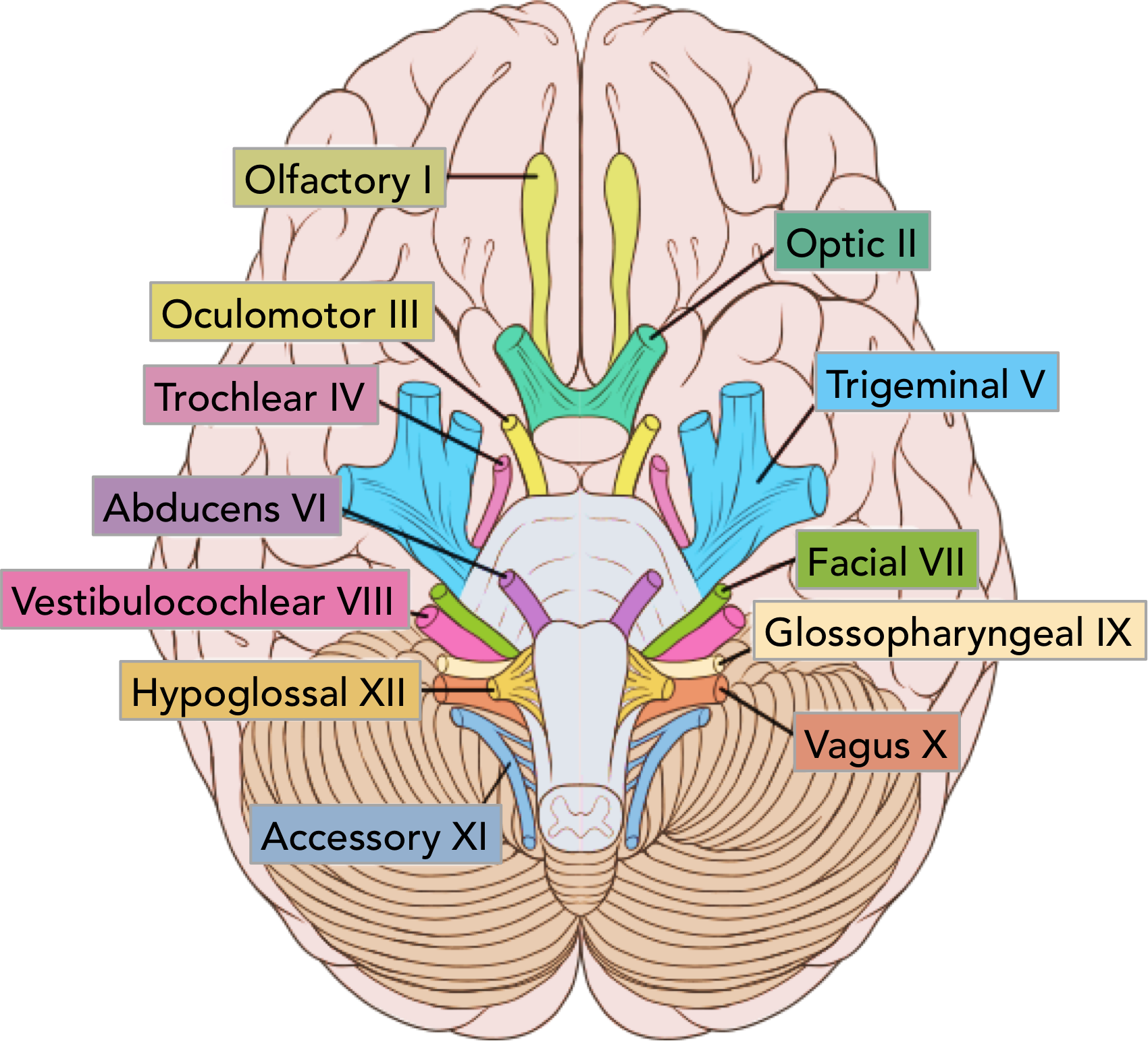
CNIX
glossopharyngeal
jugular foramen
taste/ sensory posterioir 1/3
parotid gland
stylopharyngeous
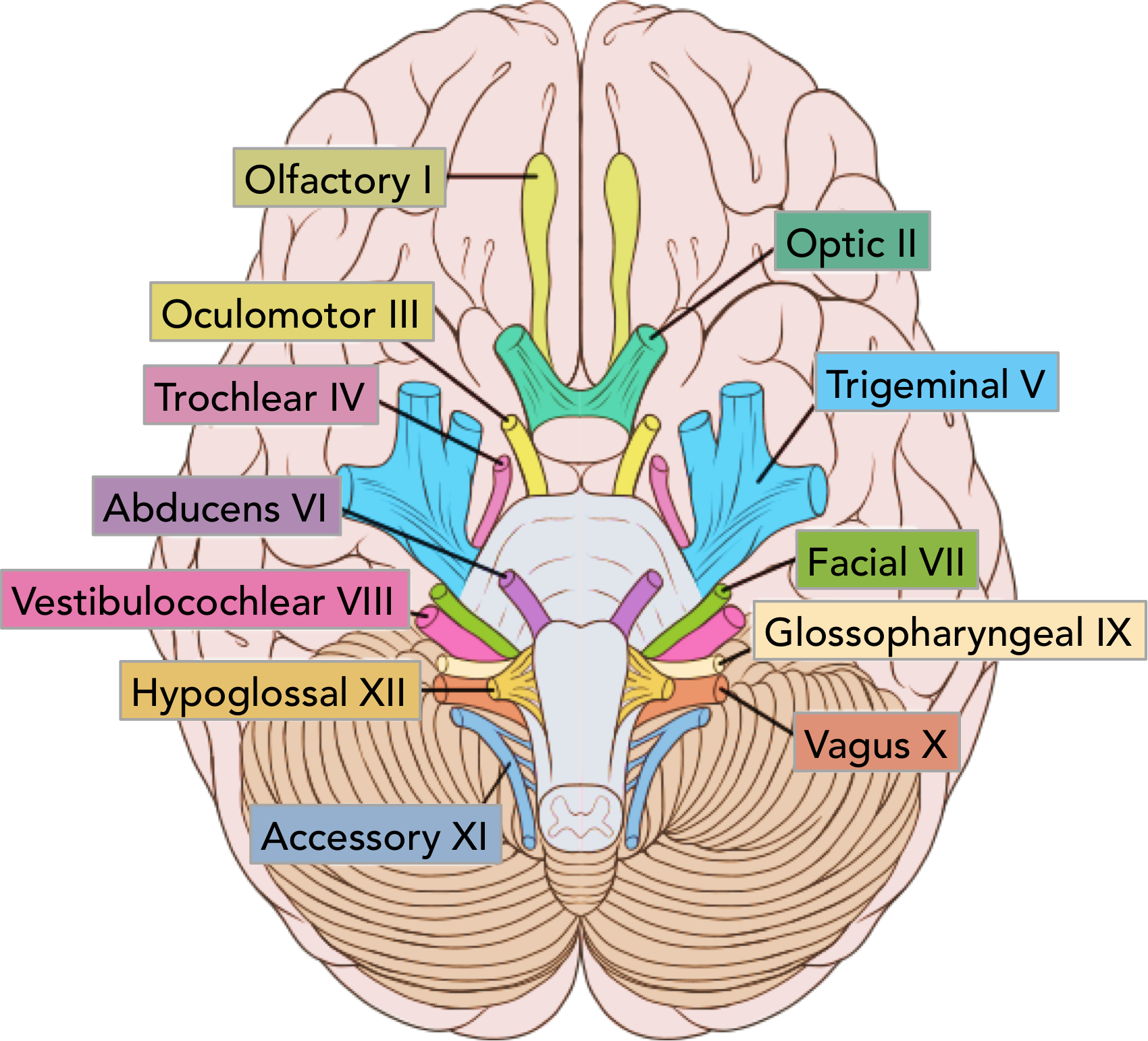
CNX
vagus
jugular foramen
sensory external ear and larynx
taste epiglottis
muscles pharynx and larynx
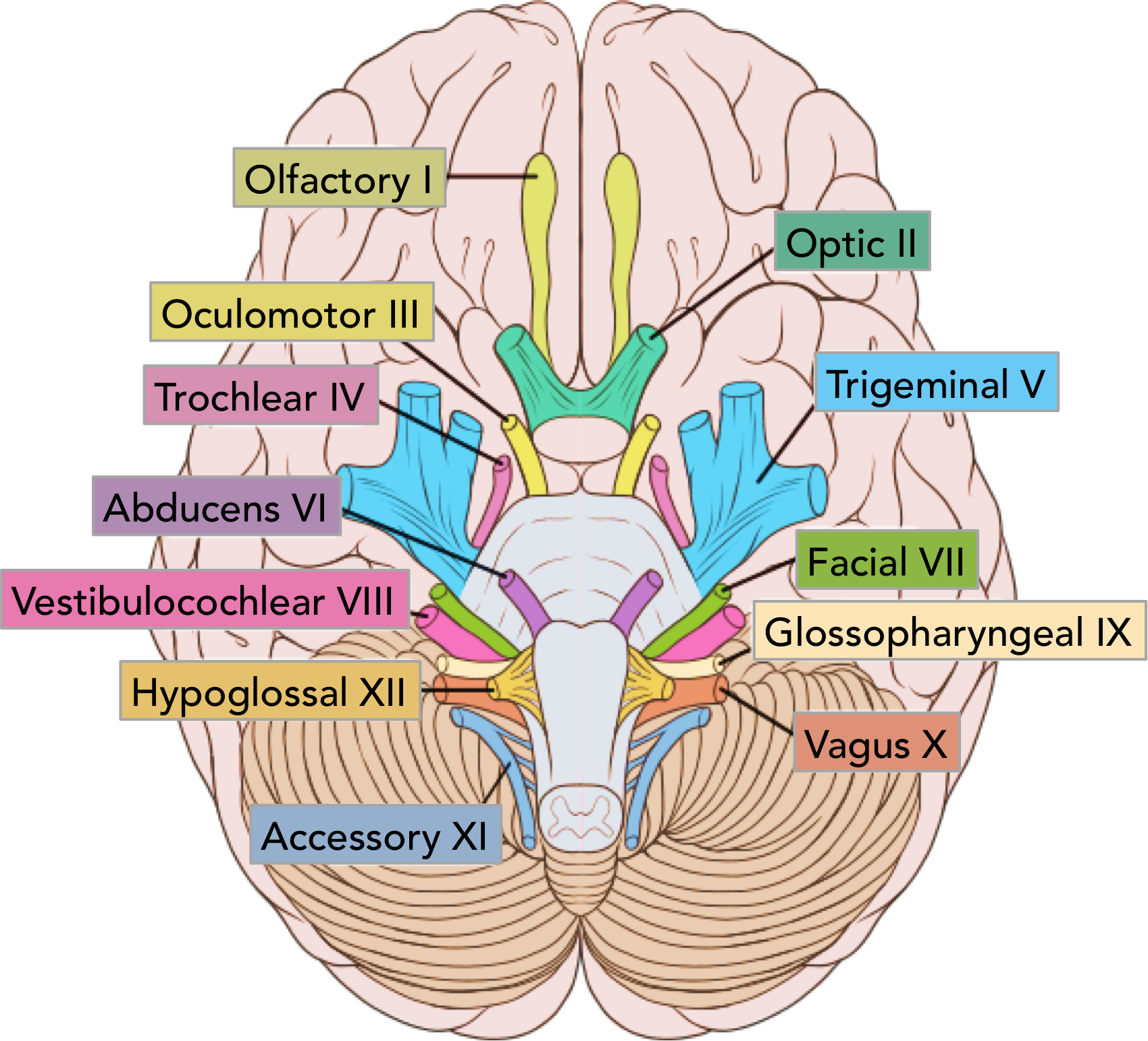
CNXI
accessory
jugular foramen
trapezius/ sternocleidomastoid
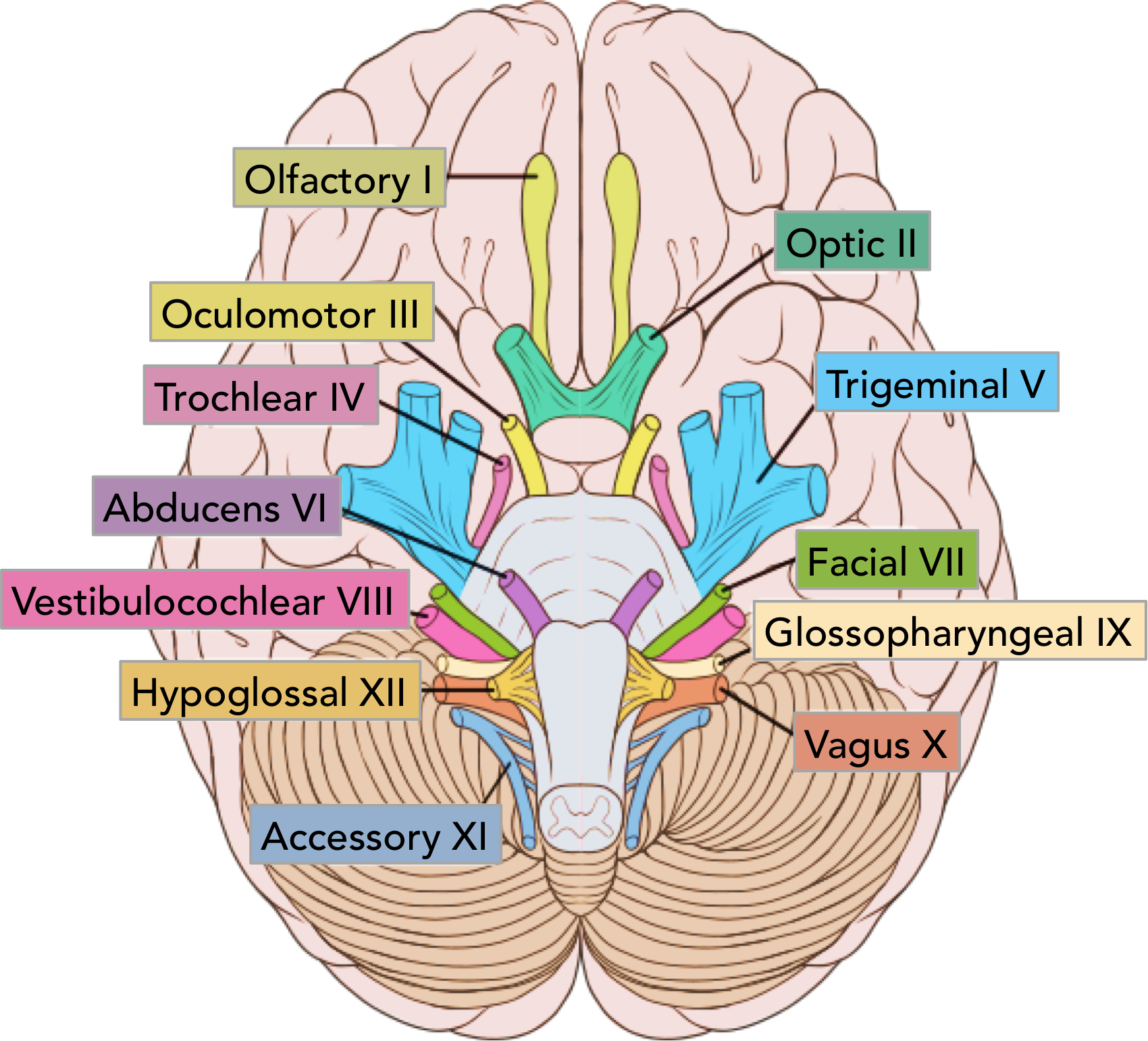
CNXII
hypoglossal
hypoglossal conal
tongue muscles