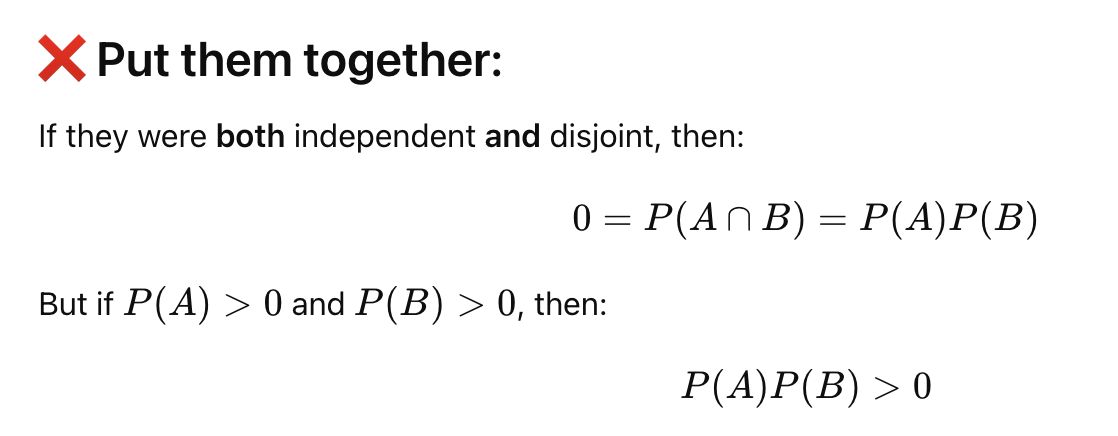AP Stats unit 6
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Imitation of chance behavior based on a model that accurately reflects the phenomenon
simulation
List the steps when setting up a simulation:
state the ____ or describe a ____
state the ____
assign ____ to represent ____
describe a ___ and what you’ll ____
simulate many _____ (use randint)
state ur _____
problem, random phenomenon
assumptions
digits, outcomes
trial, measure
repetitions
conclusions
randomness: Short run events are _____, but in _____ we expect reg distribution
unpredictable, long run
probability of random phenomenon is the ____ of times the outcome is _____ to occur in the long run
proportion, expected
law of large numbers
The more you ____ an event, the more that your experimental probability tends toward ____
Every future event has ____ influence on overall prob, so u see fewer fluctuations
Next n events are expected to be ___ to actual prob, so ____ is expected to tend toward actual prob
does NOT mean that if I flip heads 5 times, tails is more likely next time
tells you about ____ averages, NOT what the next flip will be (next flip is still independent of past ones)
repeat, actual prob
smaller
close, graph
long-run
a probability model: ____ S (all possible outcomes) with _____ assigned to each event
sample space { }, probabilities
probability models
infinite, continuous sample space: use a _____
finite, discrete sample space: ___ or ____
density curve
table, equally likely outcomes

Probability rules
probability P(A) of any event A satisfies ___ ≤ P(A) ≤ ___
If S is sample space, P(S) = __
Complement rule: P(A^c) = ____
0, 1
1
1-P(A)
2 events are _____ if the occurence of one doesn’t affect the probability of the other
independent
sampling ____ replacement: randint
sampling ____ replacement: randIntNoRep
with, without
If A and B are independent P(A ∩ B) =
P(A) * P(B)
only reason why this works or doesn’t work is that its ind or not ind
If A and B are disjoint/mutually exclusive (can never occur simultaneously), P(A ∪ B) = ______ and P(A∩B) =_____
write these two relationships down!
P(A) + P(B), 0
General addition rule: P(A ∪ B) = ______
P(A) + P(B) - P(A ∩ B)
Strategies for solving probability problems:
Draw a picture of the situation
overlapping groups and unions/intersections
categorical counts or percentages in two variables
multi-stage processes or changing probabilities
normal distributions, z-scores, percentiles
venn diagram
two-way table
tree diagram
normal curve
Conditional Probability: P(A|B) =
Does P(A|B) always equal P(B|A)
P(A ∩ B) / P(B)
No, if P(A) and P(B) are diff
If events are independent, _____ and _____ Write these two relationships down!
If they’re not equal/independent, they’re ____
P(B|A) = P(B), P(AnB)=P(A)*P(B)
associated
General multiplication rule: P(A∩B)
P(A) * P(B|A)
P(at least one) =
1-P(none)
mean formula stats probability
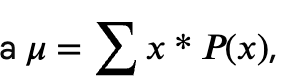
below what probability level would we start questioning whether the claim is true?
0.05
Probability Density Curve
only requirements: must be positive (always above x axis) and area under it must be __
does NOT have to be continuous curve, can be piecewise
1
can two events with nonzero probability be both ind and disjoint at same time?
No