Chem midterm practice
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
What is Ammonia( NH3)
weak base
What is Acetic Acid (HC2H3O2)
a weak acid
ion F-
Fluoride
Ammonium
NH4+
Cyanide
CN -1
Peroxide
O2 2-
Chemical bonds form to _____________ the potential energy of charged particles in atoms
reduce
Molecular formula: exact, actual number of each __________ in the molecule
atom
Empirical formula: simplest ___________________ ratio of the atoms
whole number
Lewis Dot Structure of Neon

Molar mass =
(the number of atoms of each element) × (the molar mass of each element)
ion Cl-
Chloride
ion Br-
Bromide
ion I-
Iodide
O2-
Oxide
S2-
Sulfide
N3-
Nitride
P3-
Phosphide
Acetate
C2H3O2-
Carbonate
CO3 2-
Hydrogen Carbonate
HCO3-
Hydroxide
OH-
Nitrite
NO2-
Nitrate
NO3-
Chromate
CrO4 2-
Dichromate
Cr2O7 2-
Phosphate
PO4 3-
Hydrogen Phosphate
HPO4 2-
Dihydrogen Phosphate
H2PO4 -1
Hypochlorite
ClO-
Chlorite
ClO2 -1
Chlorate
ClO3 -1
Perchlorate
ClO4 -1
Permanganate
MnO4 -1
Sulfite
SO3 2-
Hydrogen sulfite ion
HSO3 -1
Sulfate
SO4 2-
Hydrogen Sulfate
HSO4 -1
Generally, we write the name of the element ___________ first
of the smallest group number
If the two elements lie in the same group, we write the element with ___________ first
the greatest row number
prefix for 1 atom present
mono
prefix for 2 atoms
di
prefix for 3 atoms
tri
prefix for 4 atoms
tetra
prefix for 5 atoms
penta
prefix for 6 atoms
hexa
Prefix for 7 atoms
hepta
prefix for 8 atoms
octa
prefix for 9 atoms
nona
prefix for 10 atoms
deca
If there is only one atom of the first element in the formula
omit mono
Chemical bonds hold ________ together in molecules
atoms
Covalent bonding Electrons are _____________ between nuclei
shared
Covalent bonds form between
nonmetals
The smallest unit of a covalent compound is called a ________________
molecule
Ionic Bonding Electrons are ___________________ from one atom to another
transferred
Ionic bonds form between
metals & nonmetals
Cations and anions are ______ to each other
attracted
The smallest unit of an ionic compound is called a
formula unit
Structural formula: shows
connectivity of atoms and may indicate geometry
A Lewis dot structure is a structural model where each dot is represents a
valence electron
A Lewis dot structure is a structural model where each line represents
bond
Lewis Dot Structure of Lithium
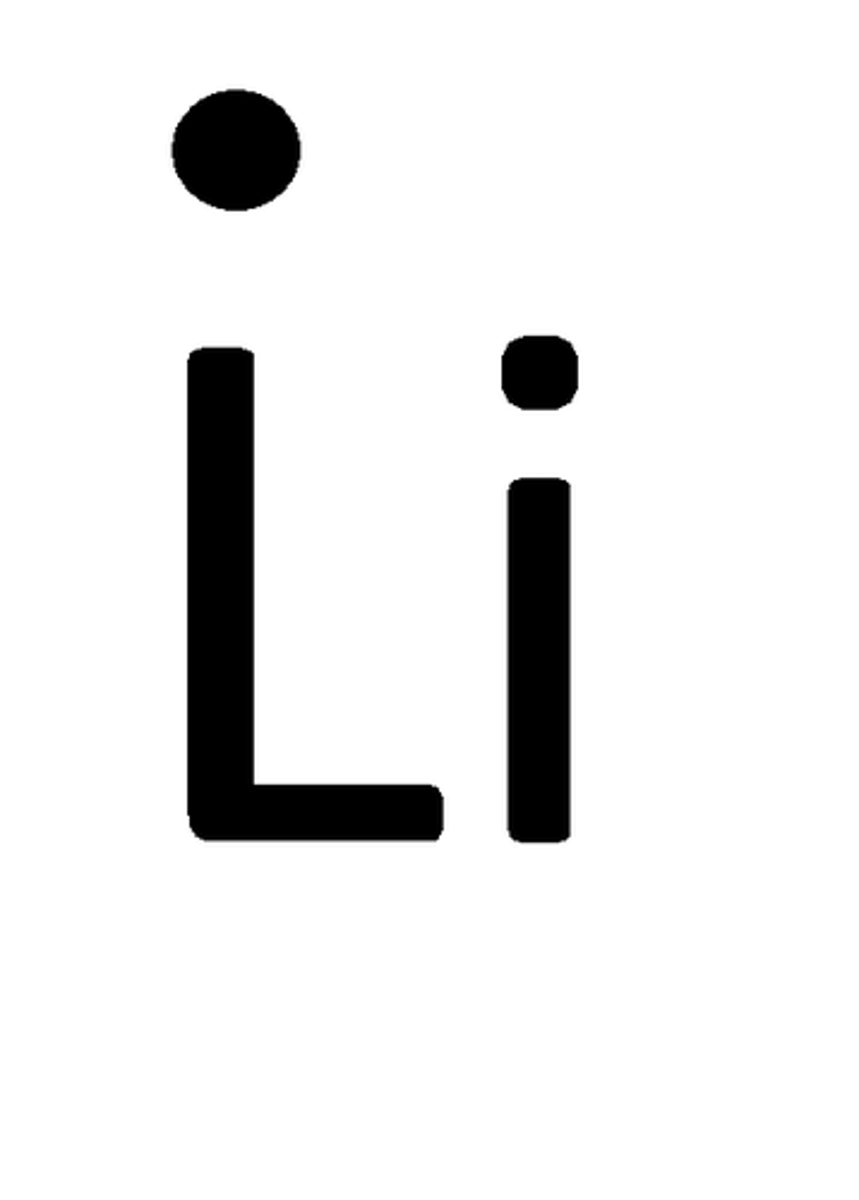
Lewis Dot Structure of beryllium
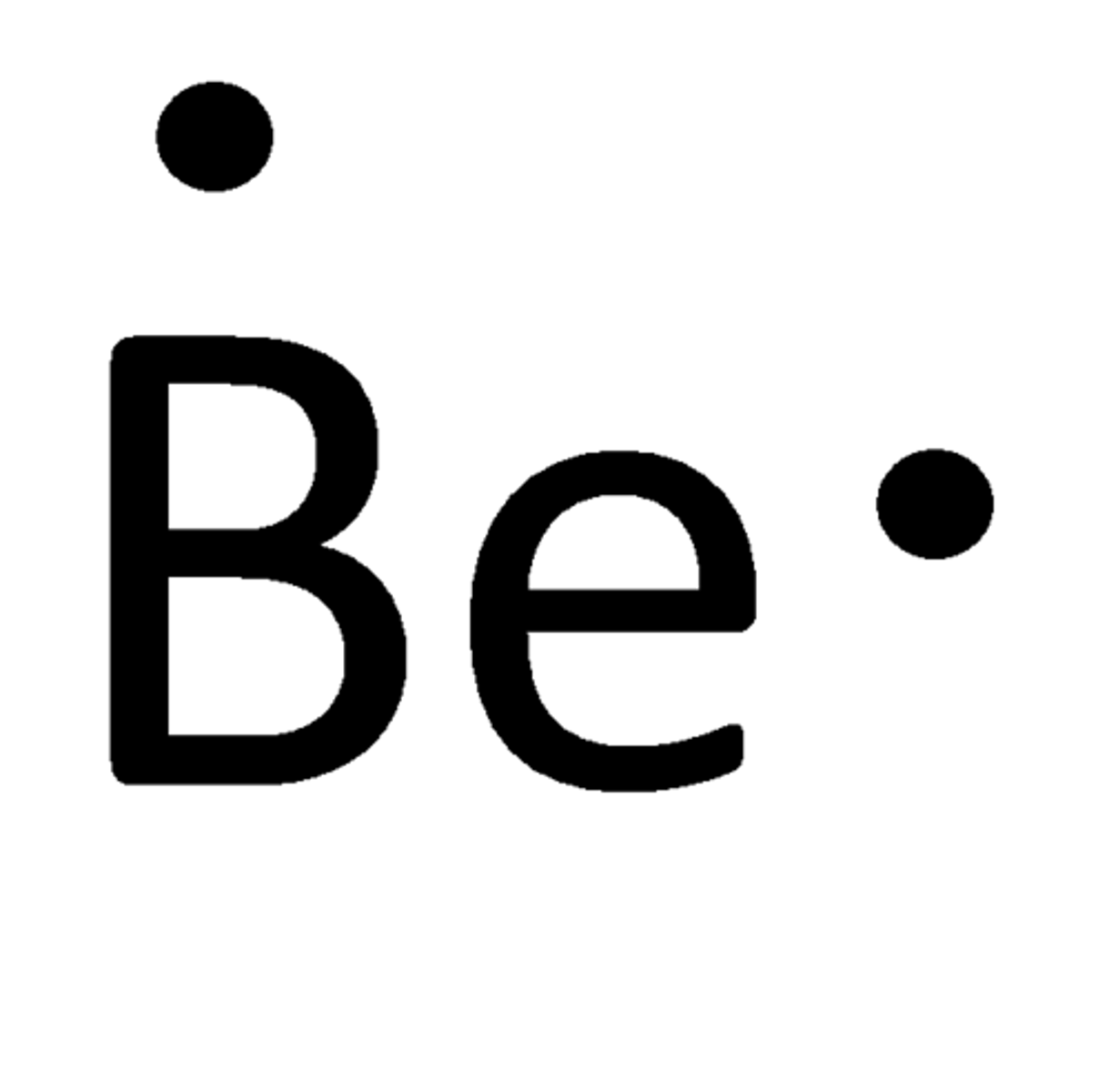
Lewis Dot Structure of Boron
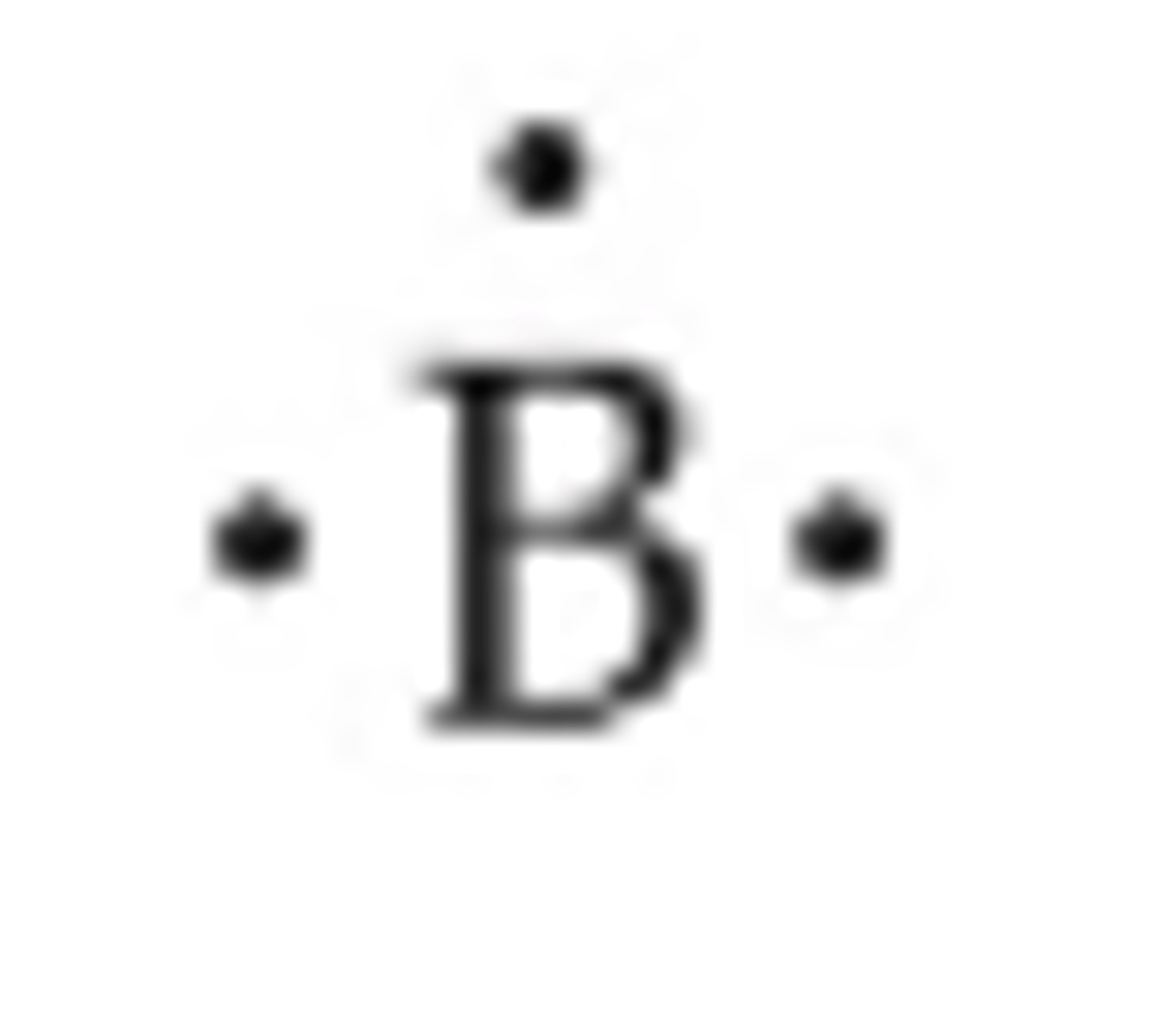
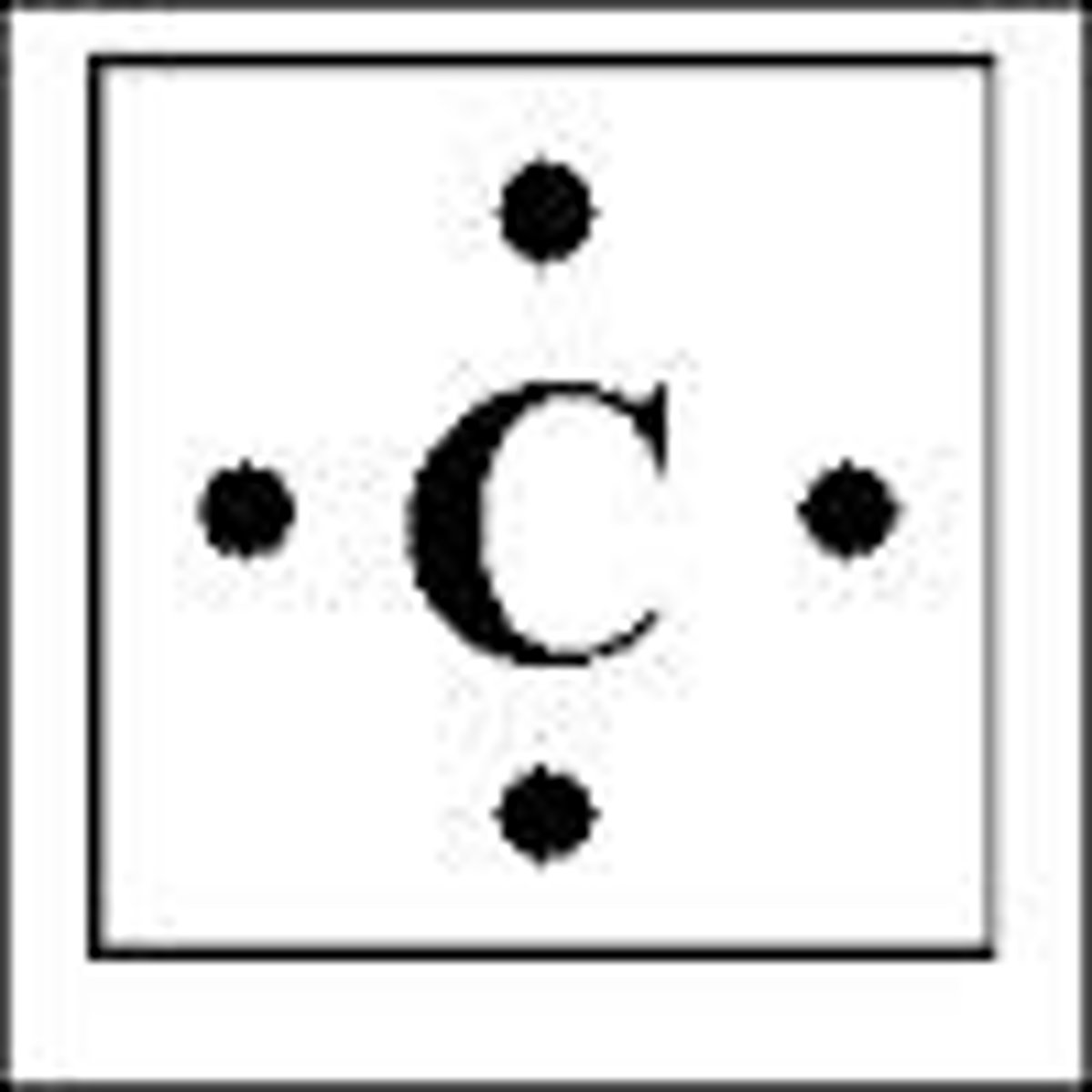
Lewis Dot Structure of Carbon
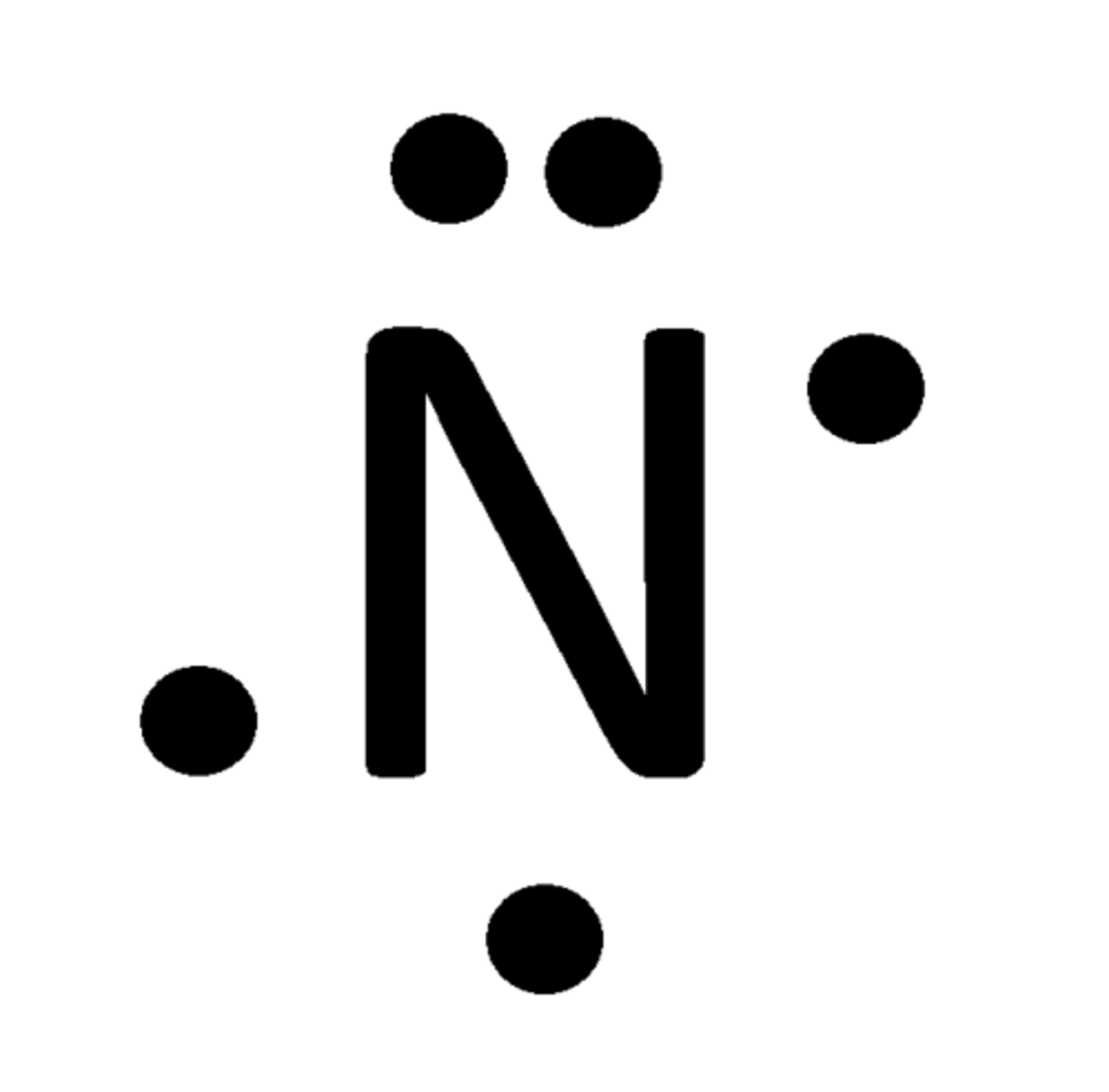
Lewis Dot Structure of Nitrogen
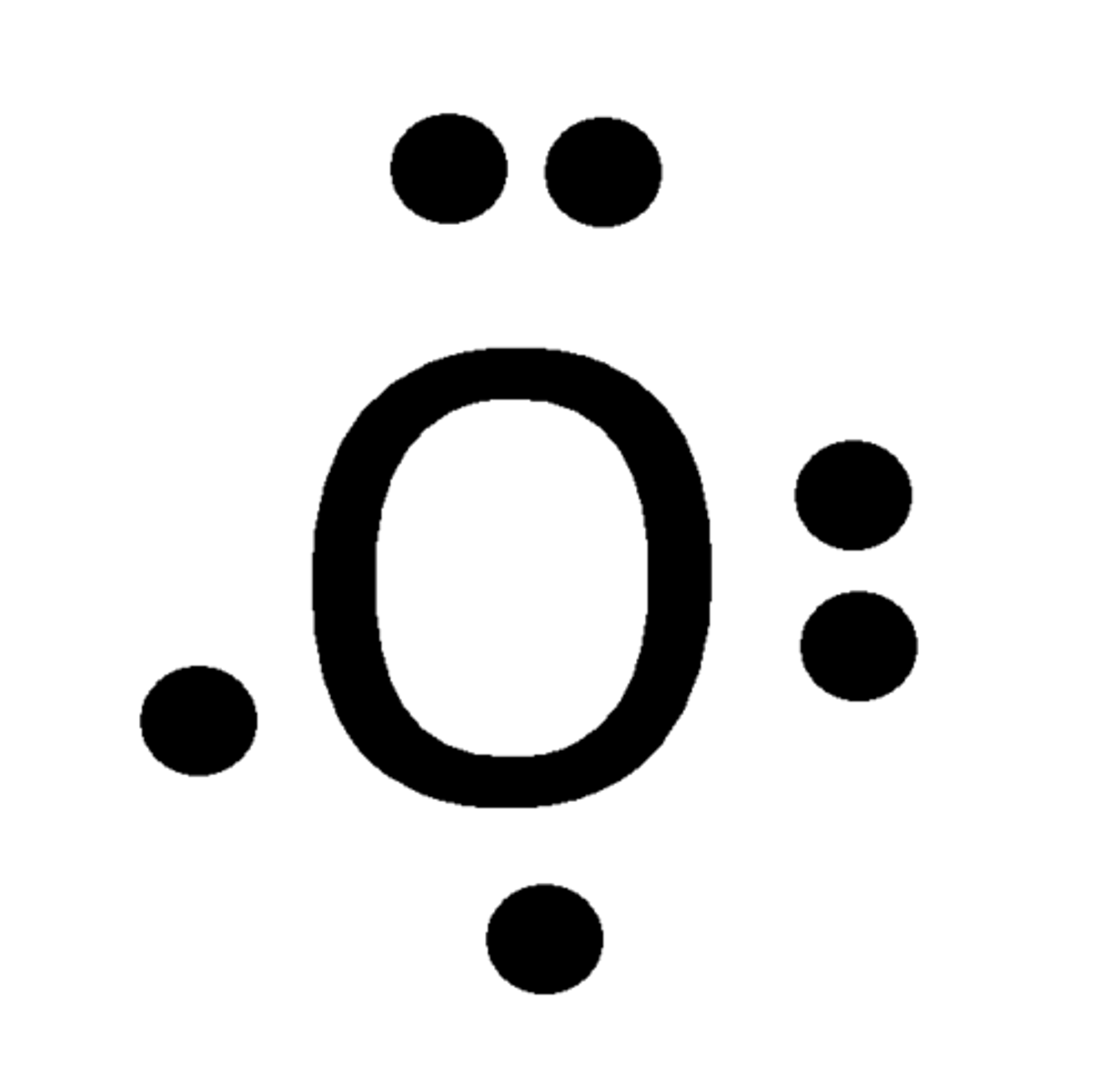
Lewis Dot Structure of Oxygen
Lewis Dot Structure of Florine

covalent single, double, triple bonds lewis structure
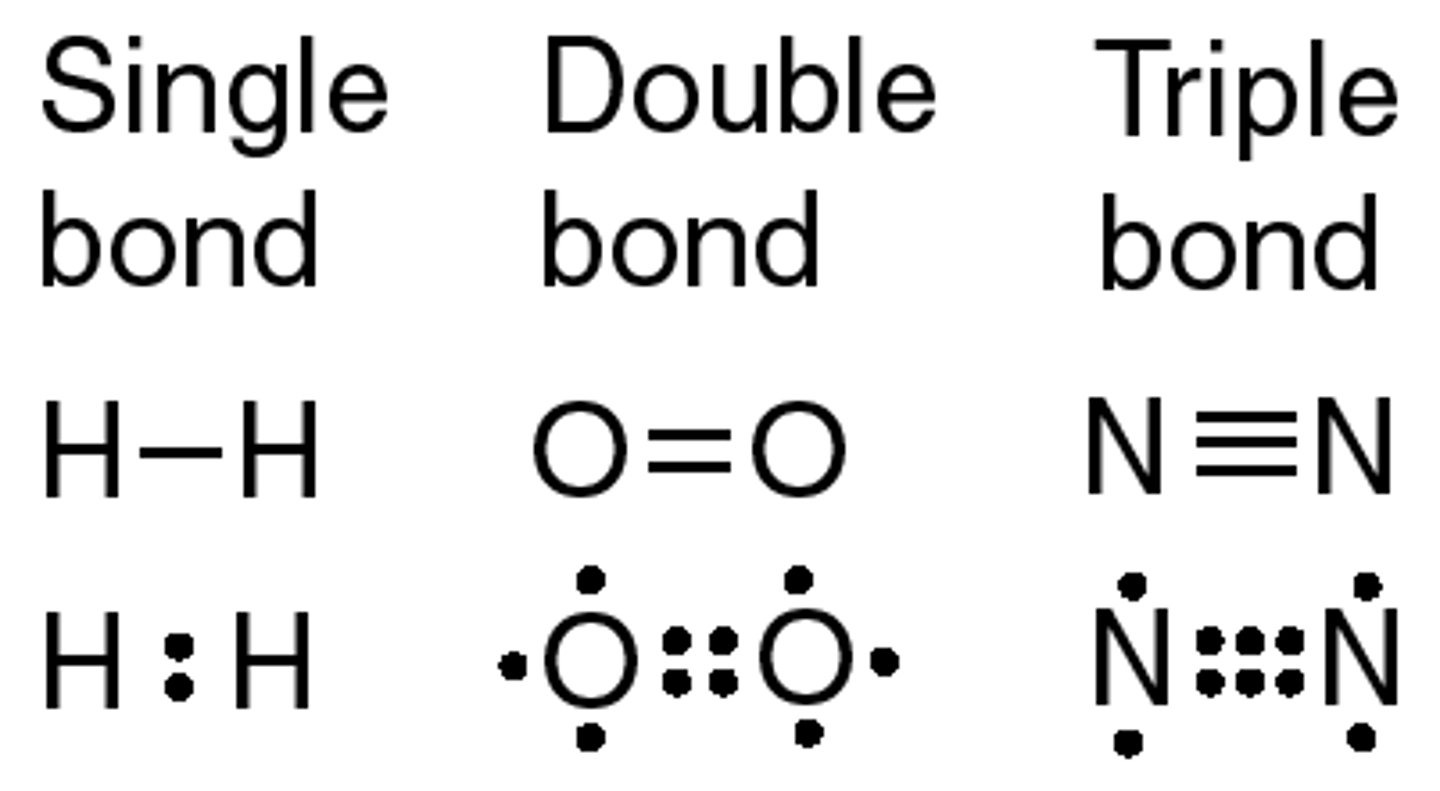
Formula mass: the mass of all of the ______________ in a compound (in atomic mass units)
atoms
Molar mass: the mass of 1 ______________ of a molecule or formula unit (in grams)
mole
1. Formula of compound from percent composition
1. Assume 100 g sample of compound
2. Calculate moles of each element in the 100 g sample
3. Determine the empirical formula (the mole ratio)
4. Determine the molecular formula based on the compound's molar mass and the molar mass of
the empirical formula
2. Formula of compound from decomposition data
1. Convert masses of each element in the sample to moles of each element
2. Use the moles of each element to determine the mole ratio (empirical formula)
3. Determine the molecular formula based on the molar mass of the compound and the molar
mass of the empirical formula
Formula of compound from combustion analysis
1. Determine the moles of carbon in the CO2 product
2. Determine the moles of hydrogen in the H2O
product
3. Convert moles of C and H to grams of C and H in
the product
4. Determine the mass of oxygen using the mass of
C, mass of H, and the total mass of the sample
5. Determine the empirical formula (the mole ratio of
C to H to O
6. Determine the molecular formula using the molar mass of the compound (if provided) and the
molar mass of the empirical formula.
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract _______________ electrons toward itself in a chemical bond
shared
Periodic table trends: Electronegativity(generally) ____________from left to right across a period
increases
Periodic table trends: Electronegativity(generally) ____________ down a group
decreases
the formation of covalent bonds ___________________ energy
releases
Bond energy:
the average energy required to break 1 mole of a bond in the gas phase (units: kJ/mol)
For a pair of atoms, more shared electrons will correspond to a _______________ bond
stronger
Triple bond = largest bond energy = _____________ bond
Single bond = lowest bond energy = _____________ bond
strongest
weakest
Bond Length
average distance between two specific nuclei across many compounds
Depends on elements in the bond and number of shared electrons
Lewis Structures for Molecules
1. Arrange atoms in a skeleton structure
2. Count valence electrons in the molecule
3. Distribute bonding electrons and then nonbonding electrons to complete octets and duets
4. Form double bonds and triple bonds as needed to complete octets
5. Check the electron count
Resonance structures
Two or more Lewis structures
where the same atoms are in the same arrangement but
some electrons are not in the same places.
Formal Charge
the calculated charge an atom in a particular molecule would have if all of its
bonding electrons were equally shared
formal charge calculation
formal charge = (valence electrons in atom alone) - (valence electrons "owned" by atom in lewis structure)
formal charge rules
1. The sum of the formal charges on all atoms in a molecule or polyatomic atom must be equal to
the overall charge of the molecule (0) or ion.
2. The arrangement of atoms in a molecule will minimize the number of non-zero formal charges
and minimizes the magnitude of formal charges.
3. Negative formal charges are generally on the most electronegative atom(s) in a molecule.
exceptions to oclet rule
1. Odd number of electrons
Ex. Nitrogen monoxide, NO
full oxygen, nitrogen 7 valence
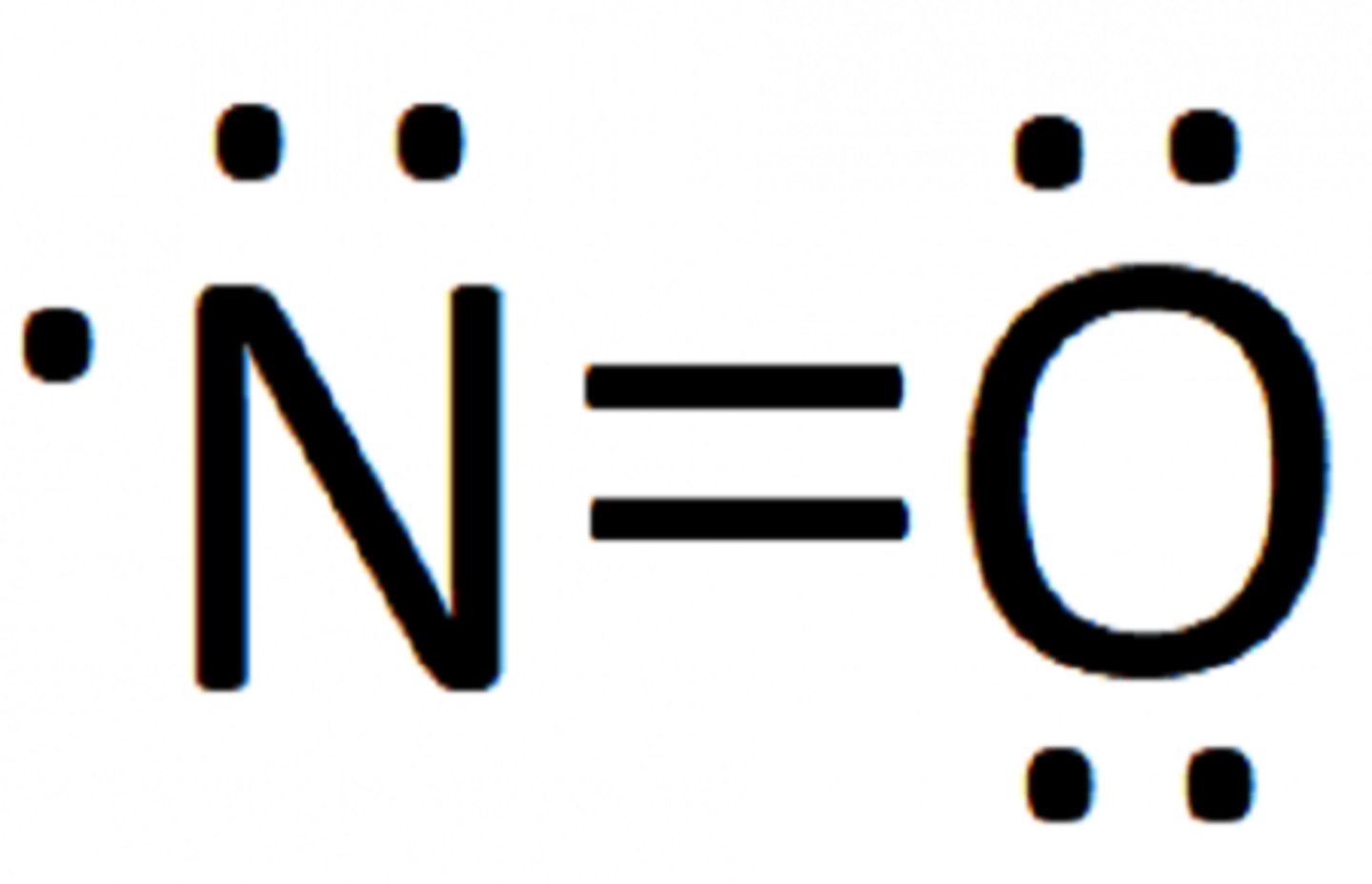
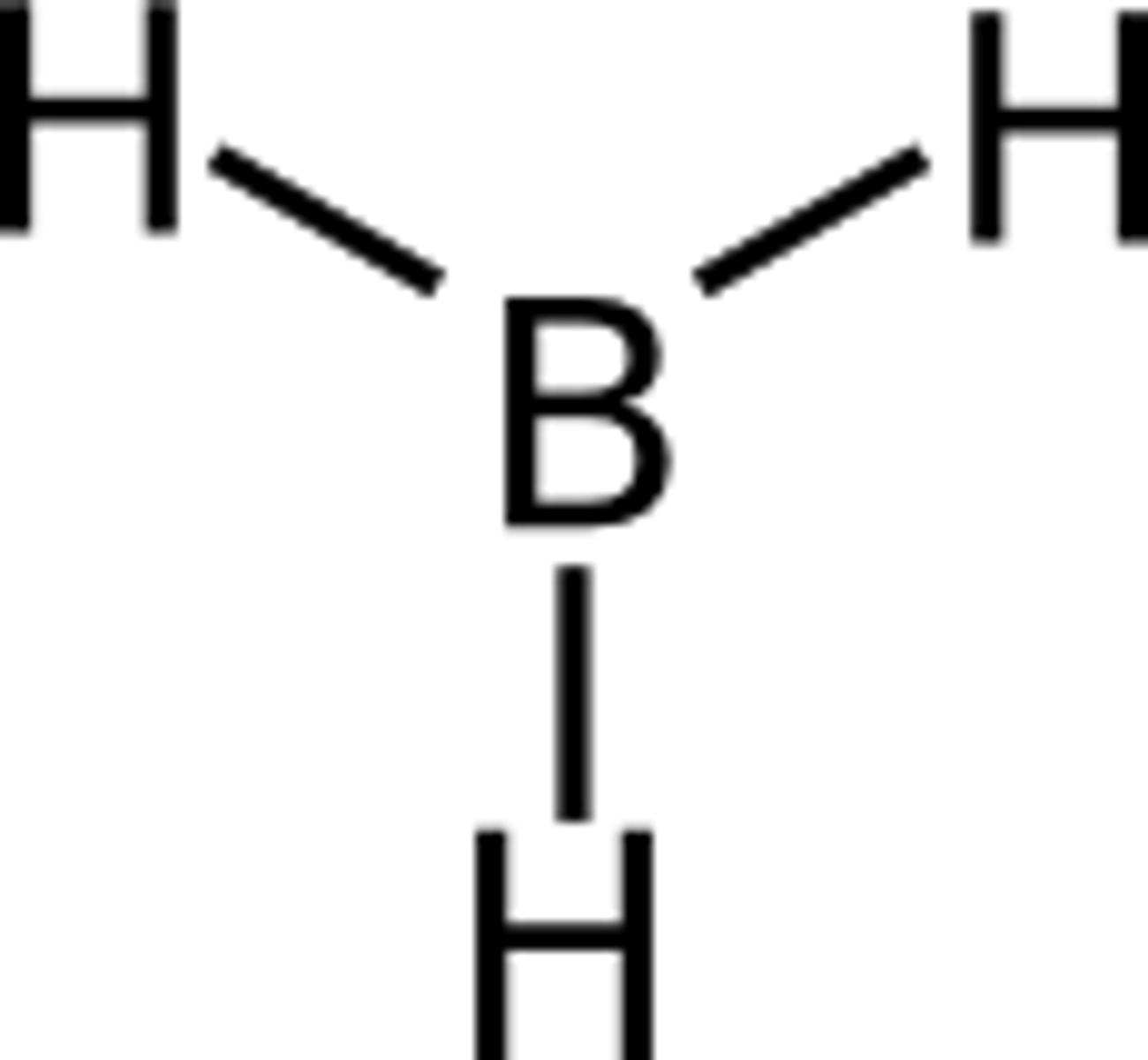
exceptions to oclet rule
2. Incomplete octet (open shell)
Ex. Boron trihydride, BH3
hydrogen full duet, boron 6 valence
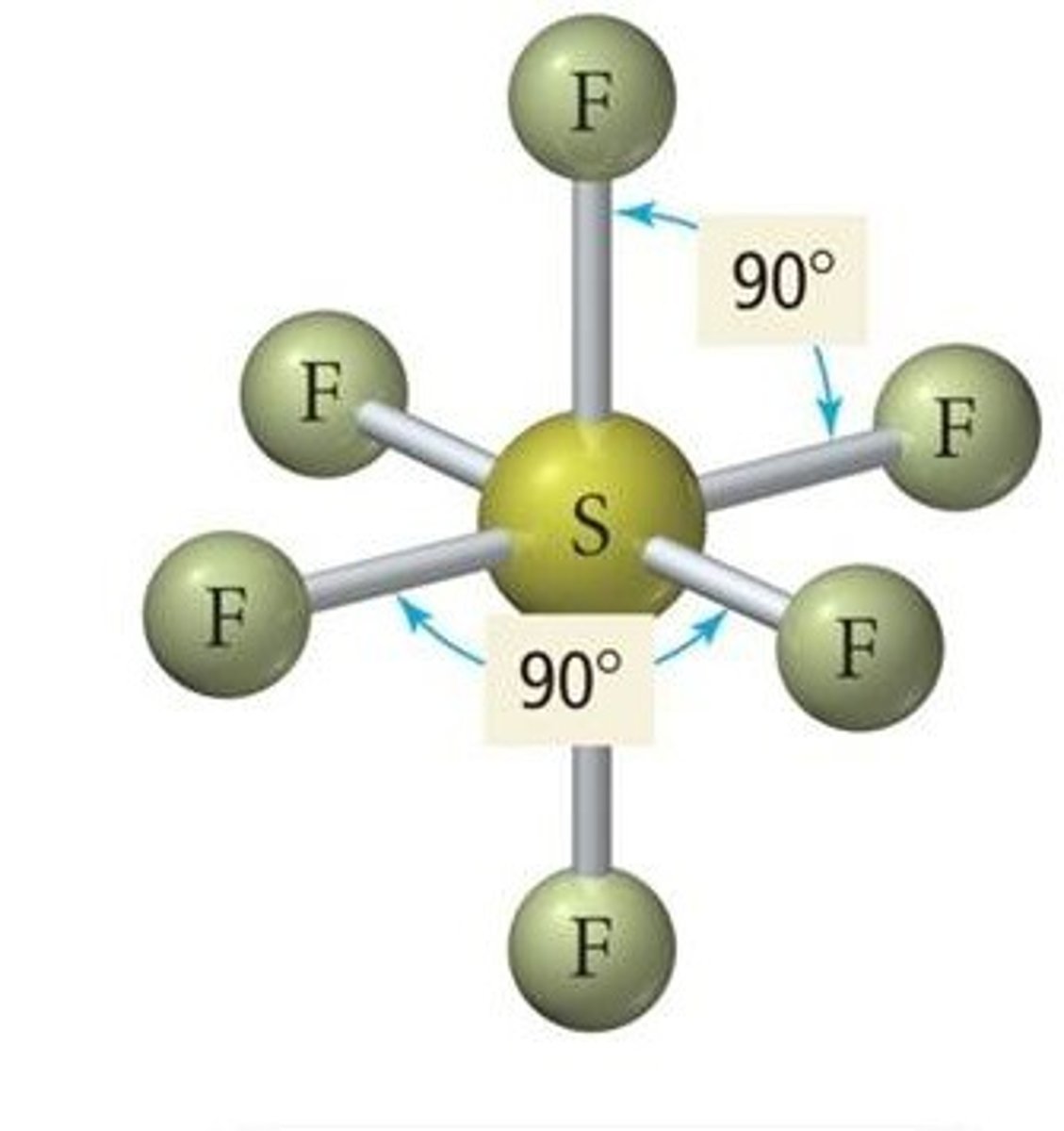
3. Expanded octet
• Only atoms in period 3 or below (valence electrons in n≥3)
• Octet of the central atom is expanded
• Ex. Sulfur hexafluoride, SF6
sextet

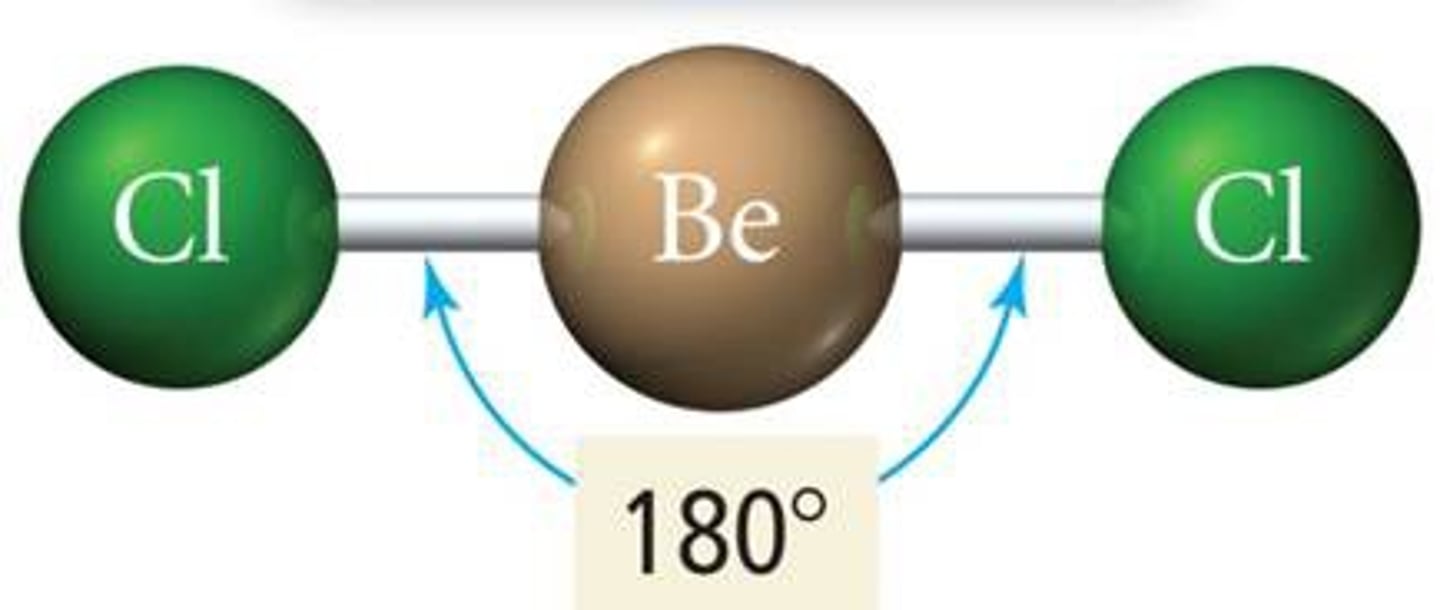
VESPR 2 electron groups (electron geometry)
linear geometry
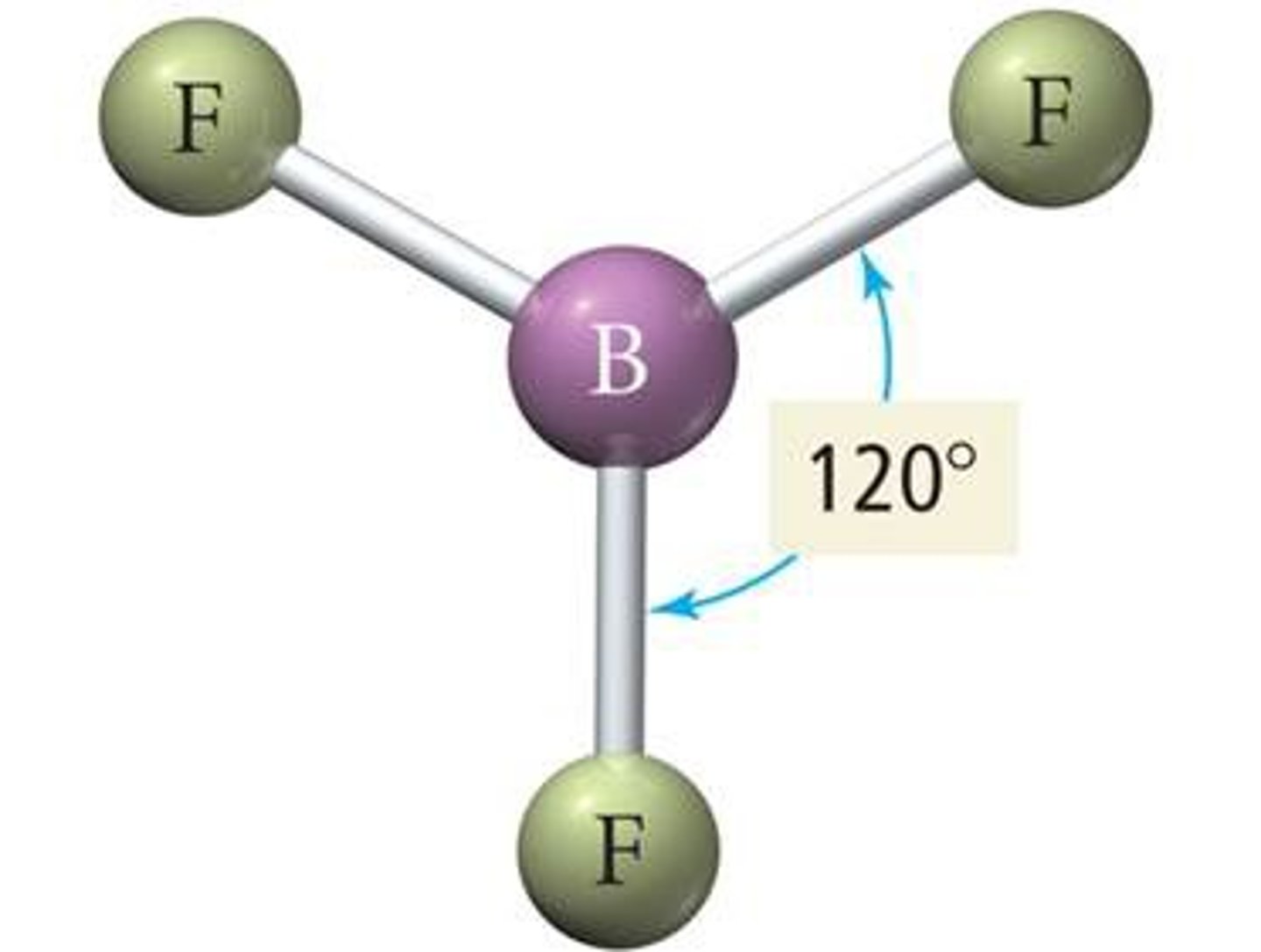
VESPR 3 electron groups (electron geometry)
trigonal planar geometry
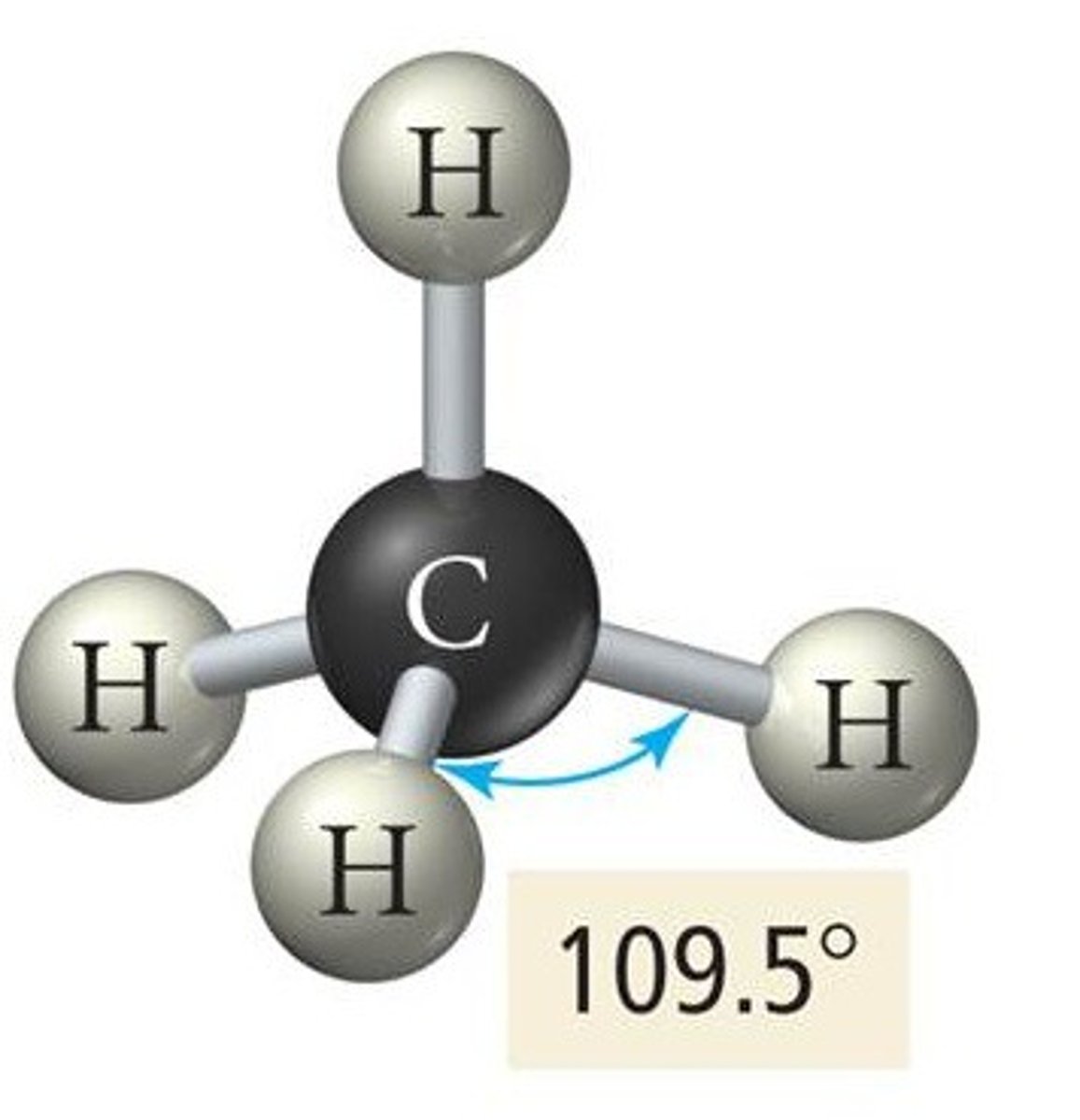
VESPR 4 electron groups (electron geometry)
tetrahedral geometry
VESPR 5 electron groups (electron geometry)
trigonal bipyramidal geometry
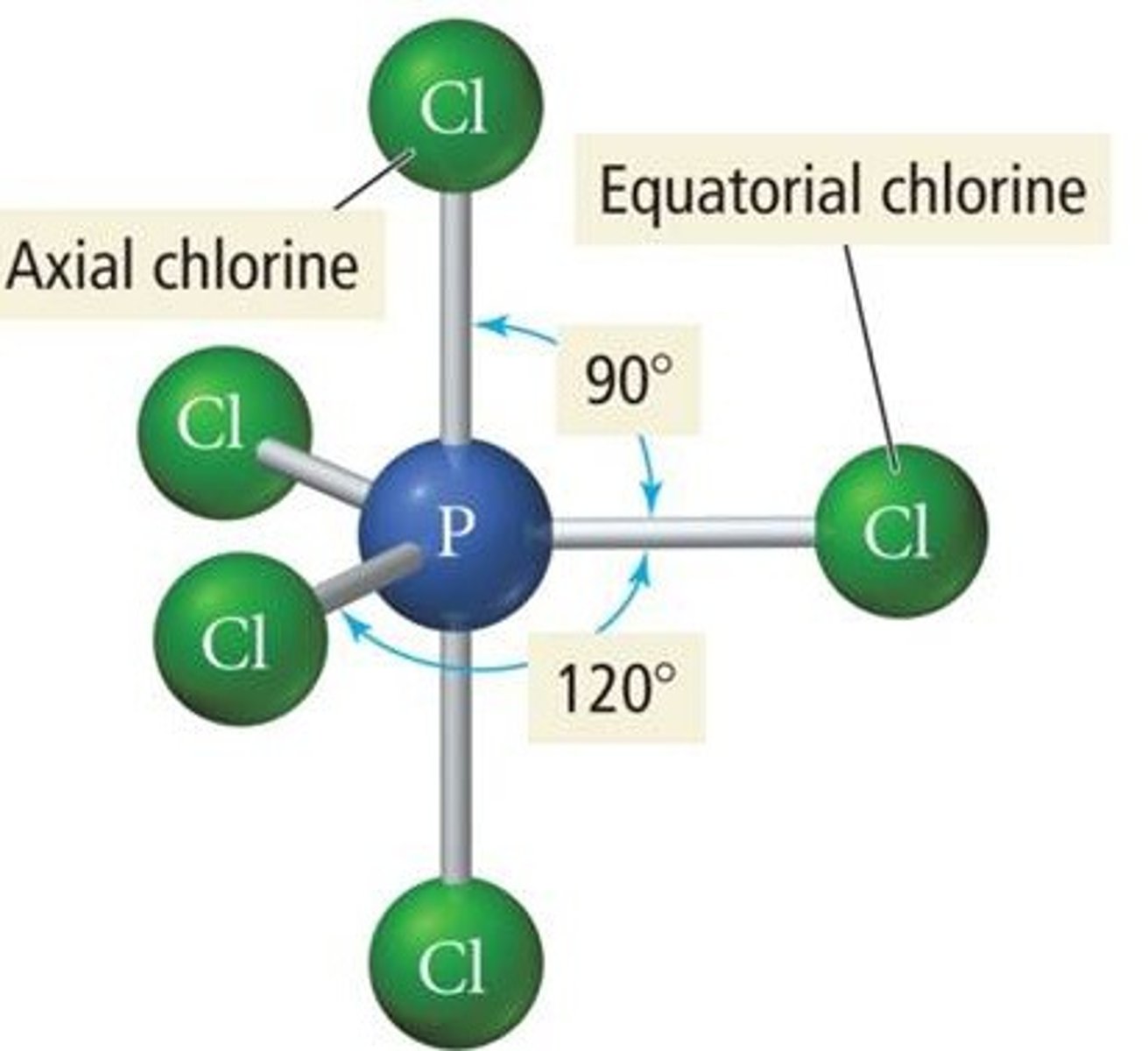
VESPR 6 electron groups (electron geometry)
octahedral geometry
VESPR lone pair effects
Lone pairs occupy more space than bonding pairs and compress bond angles
• The bond angle decreases as the number of lone pairs increases.
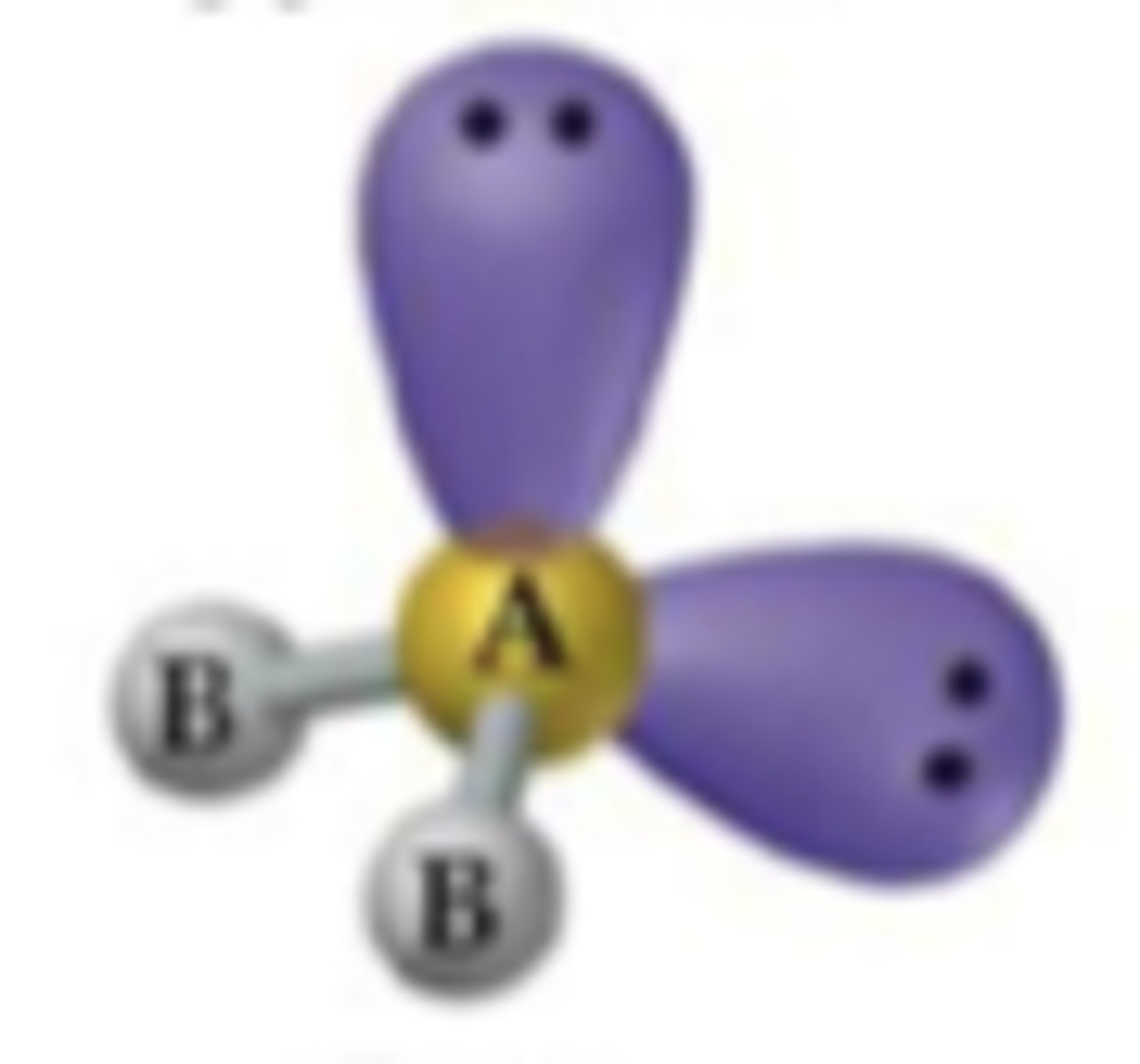
VESPR Tetrahedral electron arrangement with 1 lone pair
electron geometry tetrahedral, molecular trigonal pyramidal
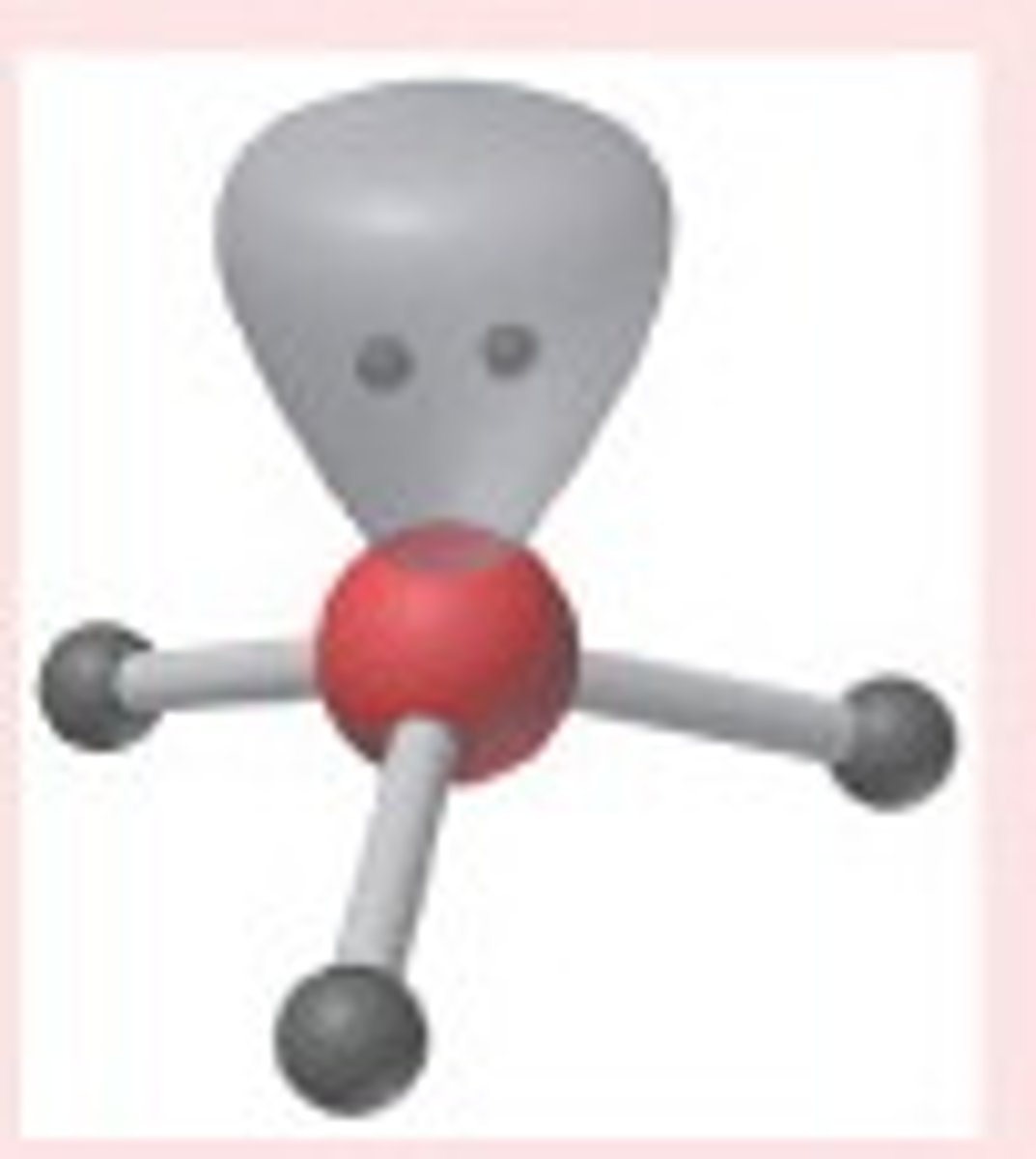
VESPR Tetrahedral electron arrangement with 2 lone pairs
electron geometry tetrahedral, molecular BENT
VSEPR Theory: Predicting molecular geometries
1. Lewis structure
2. Count electron groups around the central atom and determine electron pair geometry (electron
arrangement)
4. Determine number of bonding groups and lone pairs around the central atom
5. Determine molecular geometry and bond angles around central atom