Lab values; O2 transport in blood
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Relevant blood tests
-Complete blood count (CBC): hgb,RBC,Hct
Normal Hgb (females)
12-16 g/dL
Normal hgb males
14-17.4 g/dL
Increased Hgb may be _________ or ___________
-pathological or normal
-expected in smokers, high altitude, CHF, polycythemia
Decreased Hgb limits the ___________ and _________ of O2 to tissue
-availability and transport
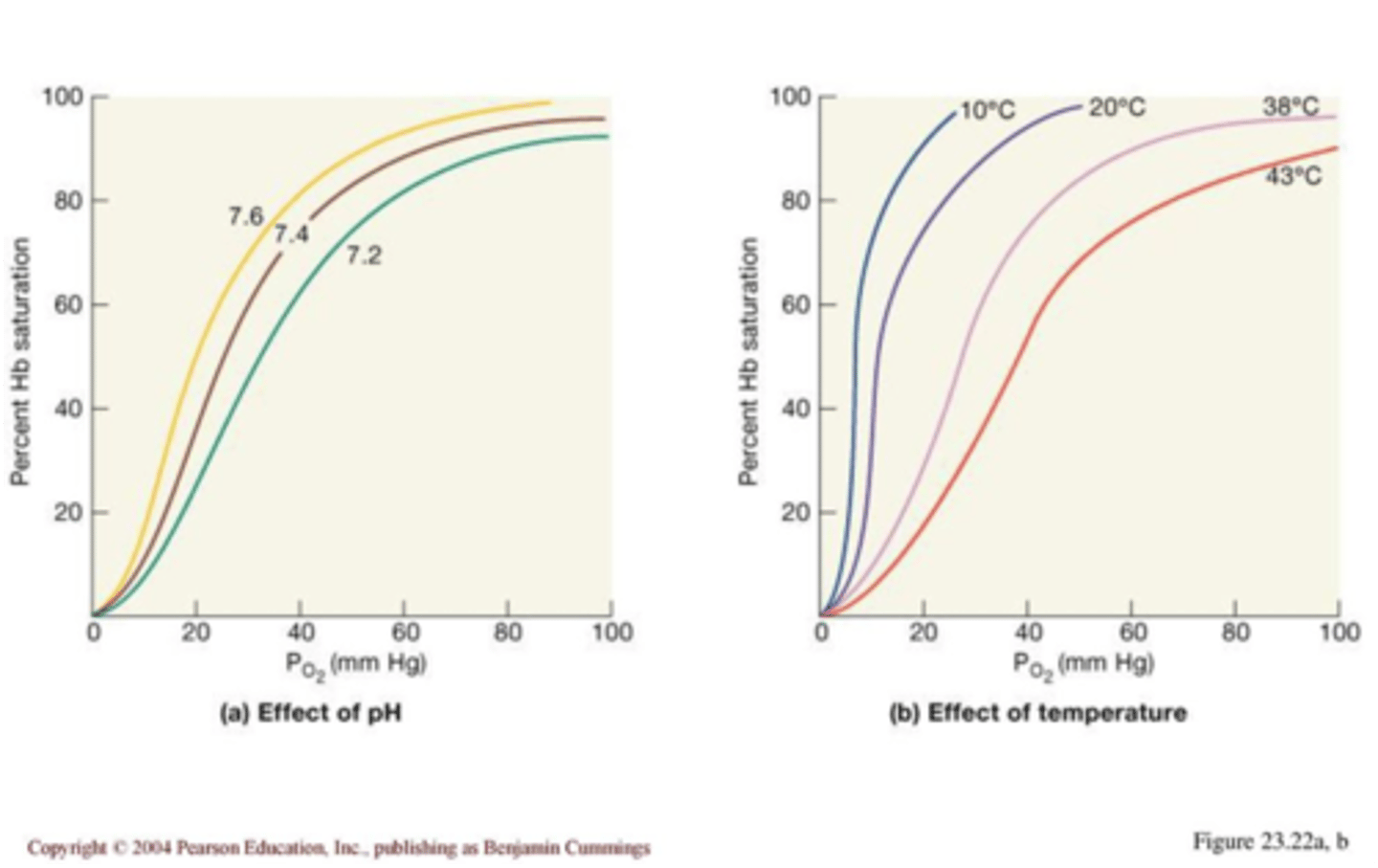
Effect of pH and temp on Hgb
-less binding in acidic and hotter environments
-more binding in alkaline and cooler environment
RBC normal range female
-3.6-5 cell/ mcL
RBC normal range male
-4.2-5.4 cells/mcL
increases RBC increases
-viscosity of blood
-risk for thrombus formation, stroke, MI
decreased RBC
-reduces O2 carrying capacity
Hematocrit
-Packed RBCs as a percentage of total volume of whole blood
Normal Hct females
-36-48%
Normal Hct males
-42-55%
Increased Hct increases
-viscosity of blood
-risk for thrombus formation, stroke, MI
Decreased Hct
-reduces O2 carrying capacity of blood
MCV
-mean cell volume
-avg vol of RBC
-hct/RBC
McHgb
-avg amt
-(hgb/rbc) x 10
McHc
-mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
-(hgb/hct) X100
RDW
-red cell distribution width
-not used frequently