Genetics Multiple Choice (from Lectures)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Which of the following is not a model genetic organism?
a.) budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae
b.) fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster
c.) Human beings, Homo sapiens
d.) worm, Caenorhabditis elegans
e.) weed, Arabidopsis thaliana
c.) Human beings, Homo sapiens
Which of the following are traits a model genetic organism should have?
a.) Long generation time
b.) Easily defined characteristics
c.) Small number of progeny
d.) Require highly technical equipment
e.) Easy to study outdoors
b.) Easily defined characteristics
Which of the following is NOT a major division of genetics?
a.) Transmission genetics
b.) Molecular genetics
c.) Agricultural genetics
d.) Population genetics
c.) Agricultural genetics
Recent discoveries in genetic engineering allowed humans to genetically manipulate agriculture for the first time.
a.) True
b.) False
b.) False
By cutting the tails of mice in 22 consecutive generations, August Weismann demonstrated that the final progeny had:
a.) no tail at all
b.) tails that were shorter than any previous generation
c.) longer tails than any previous generation
d.) tails the same length as the first and subsequent generations
e.) a mixture of tail lengths
d.) tails the same length as the first and subsequent generations
Why did the progeny in August Weismann’s experiment continue to have tails, even though their parent’s tails had been removed?
a.) All necessary genetic material is present in sex chromosomes
b.) The mice procreated prior to having their tails removed
c.) Mice tails can regenerate
d.) Tails don’t have genetic material
e.) This is still a mystery and we don’t understand
According to Chargaff’s rules, if a genome is 30% Adenine, then what percentage of the genome should be Guanine?
a.) 30%
b.) 35%
c.) 40%
d.) 20%
e.) 70%
d.) 20%
All organisms use DNA as their genetic material.
a.) True
b.) False
b.) False
DNA consists of repeating units of nucleotides. Which is NOT a component of those nucleotides?
a.) a ribose sugar
b.) purine or pyrimidine nitrogen-containing bases
c.) a deoxyribose sugar
d.) phosphate
e.) DNA contains all of the above
a.) a ribose sugar
Which is true of the secondary structure of DNA?
a.) Nucleotide bases are on the outside of the DNA molecule
b.) Sugar-phosphate groups are on the inside of the DNA molecule
c.) Bases on complementary strands are held together by hydrogen bonds
d.) Cytosine pairs with adenine
e.) Thymine pairs with guanine
c.) Bases on complementary strands are held together by hydrogen bonds
Which form of DNA has a left-handed helix and its sugar-phosphate backbone zigzags back and forth?
a.) A-DNA
b.) B-DNA
c.) Z-DNA
d.) All forms of DNA have this secondary structure
c.) Z-DNA
What secondary structures are formed when single-stranded DNA or RNA is inverted and complementary?
a.) double helix
b.) Z-DNA
c.) hairpin
d.) B-DNA
e.) None of the above, because single strands cannot form secondary structures
c.) hairpin
Which statement is true regarding negative supercoiled DNA?
a.) That negative supercoiled DNA is under-rotated and allows for easier strand separation during replication and transcription
b.) Negative supercoiled DNA is not usually seen in cells
c.) Negative supercoiled DNA has 10 base pairs per turn of its helix
d.) Negative supercoiled DNA carries more negative charges than positive supercoiled DNA does
e.) All of the above statements are true
Which is NOT true of most bacterial DNA?
a.) It is packaged into a confine space using proteins
b.) It appears as a distinct clump called a nucleiod
c.) It is linear
d.) It exists in a series of twisted loops
c.) It is linear
If a piece of chromatin contained 200 copies of the histone H4, then how many nucleosomes would be presnt?
a.) 100
b.) 200
c.) 400
d.) We cannot say: nucleosome structures are randomly placed throughout chromatin
Telomeres ___________ the end of chromosomes.
a.) transcribe
b.) replicate
c.) stabilize
d.) destabilize
c.) stabilize
Genetically speaking prokaryotes are different from eukaryotes because
a.) prokaryotes usually have a single chromosome
b.) prokaryotes do not usually have histone proteins to package their DNA
c.) prokaryotes do not have a nucleus to maintain their DNA
d.) all of the above
d.) all of the above
Which of the following is NOT true of cell reproduction?
a.) Genetic information needs to be copied
b.) Copies of genetic information do NOT separate during cell reproduction
c.) Cell division occurs
d.) Though prokaryotes and eukaryotes accomplish cell reproduction similarly, they require different process
Which of the following is not a part of the cell cycle?
a.) G1
b.) G2
c.) S0
d.) S
e.) M
c.) S0
_______________ chromosomes have their centromere located in the middle.
a.) Telocentric
b.) Acrocentric
c.) Submetacentric
d.) Metacentic
e.) None of the above
d.) Metacentic
Sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite poles during which phase of mitosis?
a.) Prophase
b.) Pro-metaphase
c.) Metaphase
d.) Anaphase
e.) Telophase
d.) Anaphase
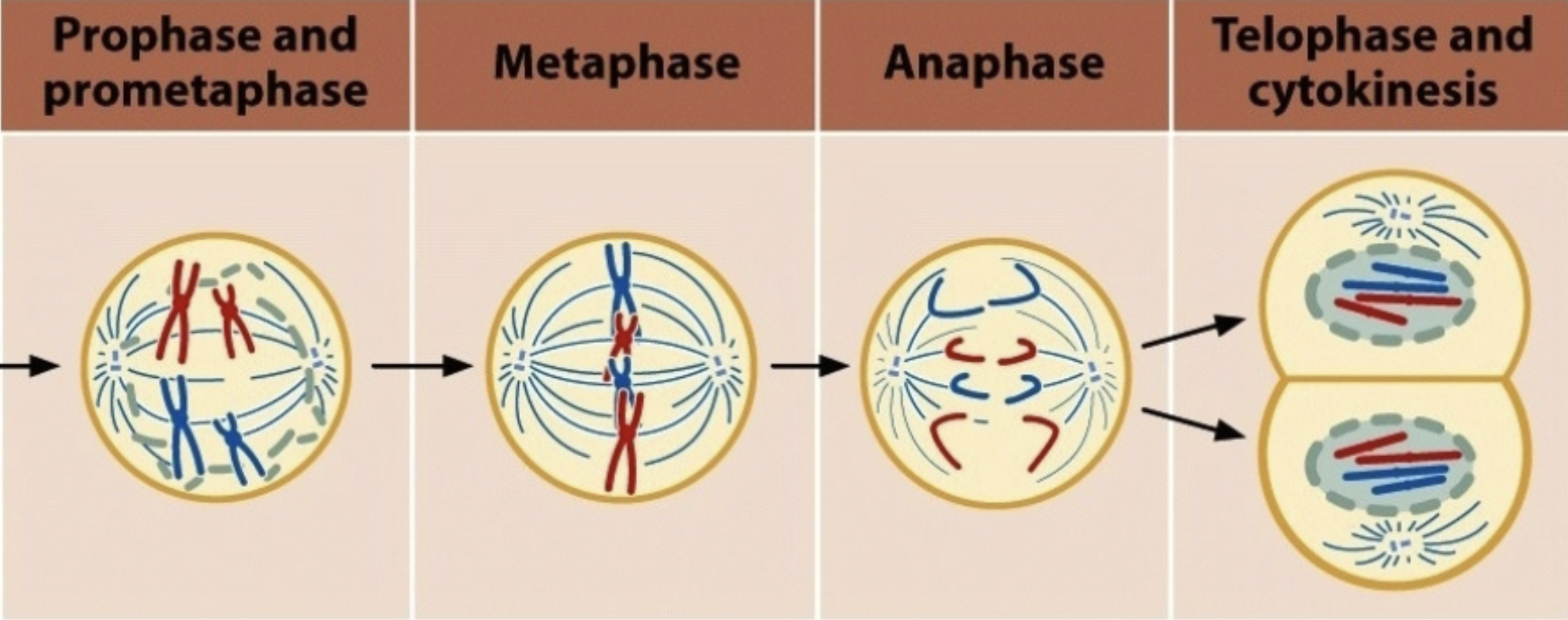
In the example below, how many chromosomes are in prophase and anaphase?
a.) 8 and 8
b.) 4 and 4
c.) 4 and 8
d.) 8 and 4
e.) 2 and 8
Meiosis I is called the ________ division and Meiosis II is called the ________ division.
a.) reduction; equational
b.) interphase; prophase
c.) equational; interphase
d.) mitotic; interphase
e.) none of the above
a.) reduction; equational
All of the following make meiosis different from mitosis, EXCEPT:
a.) meiosis comprises 2 divisions
b.) chromosome number is reduced by half in meiosis
c.) resulting cells from meiosis are genetically different than the parent cell
d.) meiosis only occurs during embryonic development
Crossing over usually occurs during…
a.) Meiosis I
b.) Meiosis II
c.) Mitosis
d.) S-phase
e.) Occurs randomly in all division types
Crossing over and the random distribution of maternal and paternal chromosomes are responsible for:
a.) Genetic stability
b.) Cell division
c.) Genetic variation
d.) DNA synthesis
e.) None of the above
c.) Genetic variation
Cohesin is a protein that holds together chromosomes during…
a.) Interphase
b.) Anaphase I
c.) Anaphase II
d.) Anaphase I and II
e.) Breaks down before Meiosis
Why was the pea plant an ideal plant for Mendel to use?
a.) Produces few progeny
b.) Has clear and easy to identify characteristics
c.) Requires extensive care
d.) Required several seasons to complete a generation
e.) All of the above
b.) Has clear and easy to identify characteristics
Phenotypes are inherited.
a.) True
b.) False
b.) False
Alternate forms of a gene are called…
a.) loci
b.) phenotypes
c.) alleles
d.) genotypes
e.) heterozygotes
c.) alleles
An organism has the genotype Rr and the phenotype of R. This known has the concept of…
a.) segregation
b.) dominance
c.) recessive
d.) Mendel
b.) dominance
If T (tall) is dominant to t (short), then what proportion of the progeny will be tall in the following cross Tt x TT?
a.) 0/4
b.) 1/4
c.) 2/4
d.) 3/4
e.) 4/4
If an individual of genotype Aa is test crossed, what is the genotype of the test crossed individual?
a.) AA
b.) Aa
c.) aa
d.) The test crossed individual is unknown
In Mendel’s pea plants, how did he know each F1 generation contained two alleles encoding different characteristics?
a.) The F1 generation had a blended phenotype of the parental phenotypes
b.) Both parental phenotypes reappeared in the F2 generation
c.) Each F1 plant had a different phenotype
d.) The F1 plants did not have two alleles
e.) None of the above
Part (A) If there is a 1/2 probability of having a green seed and a 1/4 probability of having a round seed, then what is the probability that progeny will have both green and round seeds?
a.) 1/4
b.) 1/8
c.) 3/8
d.) 5/8
e.) 1/2
Part (B) From above (If there is a 1/2 probability of having a green seed and a 1/4 probability of having a round seed…), what is the probability that the progeny will have either green or round seeds?
a.) 1/4
b.) 1/2
c.) 3/8
d.) 3/4
e.) 5/8
According to Mendel’s Second Law, during meiosis the pea plant genes for seed color and texture assort…
a.) dependent upon how different alleles assort
b.) independently to how different alleles assort
c.) to prevent two mutant alleles occupying the same seed
b.) independently to how different alleles assort
What is the probability that in the cross Aa Bb x aa Bb that progeny will be aa BB?
a.) 1/8
b.) 1/4
c.) 1/2
d.) 2/3
e.) 3/4