Unit 2: #7 Genetics: Mutations (copy)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Genetic Mutations
Changes in DNA sequence that are caused by various mechanisms
Eg. radiation, chemicals, incorrect replication or random mutations
Can have a negative effect, no effect or a positive side effect (natural selection)
Small Scale Mutations
Include Point Mutations
Mutations of an individual base pair
Examples:
Substitution of one base for another
Insertion or deletion of a single base pair
Inversion of two adjoining base pairs
What are the four outcomes from a small scale mutation?
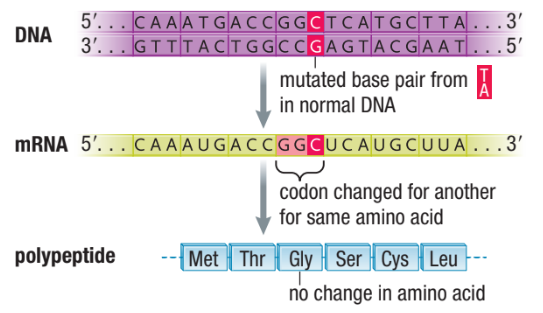
Silent Mutations
Missense Mutation
Nonsense Mutation
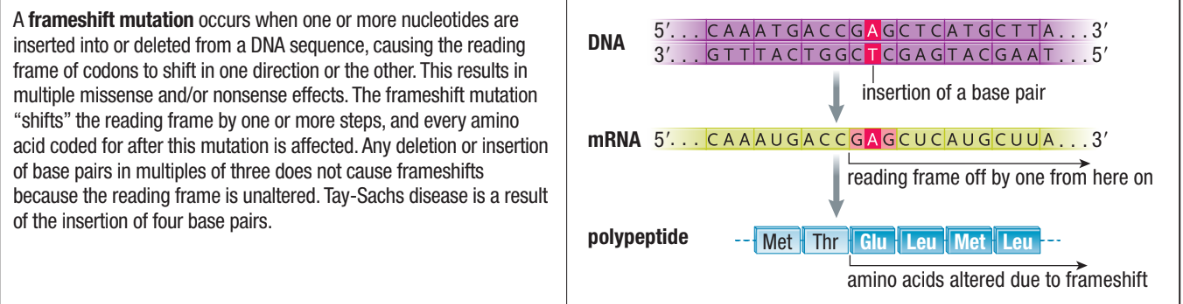
Frameshift Mutations
Silent Mutations
Has no effect on the operation of the cell (no consequences, will remain the same even with the mutations)
Usually occurs in non-coding regions (introns)
Change in codon can still represent same amino acid, since more than one codon code for same amino acid
Missense Mutations
Change in DNA bases alters a codon
This is substitution
Causes different amino acid to be placed in protein sequence

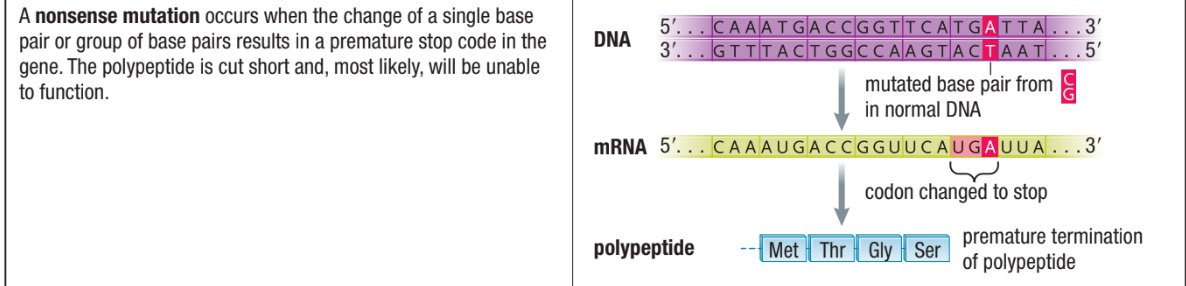
Nonsense Mutation
Occurs when a change in DNA base sequence causes a stop codon to be placed instead of an amino acid codon
This is a substitution
Only part of protein before “stop” is made and fragment may be digested
Often lethal to cell
Frameshift Mutations
Occurs when one or more nucleotides are inserted or deleted
Causes the reading frame of codons to shift one direction or another
Causes multiple missense or nonsense effects
Frameshift Mutation → Deletion
A frameshift occurs when one or more nucleotides are removed from the DNA sequence
Missing amino acids will alter the protein shape drastically
Frameshift Mutation → Insertion
Results in a frameshift by inserting a nucleotide
DNA read in triplets, inserting a nucleotide will modify the codons and different amino acids will be translated
Translocation
The relocation of entire genes or groups of genes from one of the chromosome to another
A segment of one chromosome breaks and releases a fragment. The same occurs at another unrelated chromosome
The two fragments then switch places
Results in a fusion protein with altered function.
Inversion
The reversal of a segment of DNA within a chromosome
No gain or loss of genetic material, but may interrupt a gene