Slope Failures - Falls, Slides, and Flows
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
1
New cards
what is mass wasting?
* gravitational downslope transport of rock, regolith (unconsolidated material), snow or ice
* also called mass movement
* also called mass movement
2
New cards
factors that affect slope shape?
* material strength
* ability to avoid failure
* material strength depends on if it is coherent or unconsolidated or has planes of weakness
* roundedness plays a part too
* climate
* affects which agents or erosion are at work (ice, water, wind) and how fast; also affects soil and vegetation formation on slopes
* more veg → more stability
* process of formation
* ex. glacially carved valley have a ‘U’ shape
* river erosion causes a ‘V’ shaped valleys
* ability to avoid failure
* material strength depends on if it is coherent or unconsolidated or has planes of weakness
* roundedness plays a part too
* climate
* affects which agents or erosion are at work (ice, water, wind) and how fast; also affects soil and vegetation formation on slopes
* more veg → more stability
* process of formation
* ex. glacially carved valley have a ‘U’ shape
* river erosion causes a ‘V’ shaped valleys
3
New cards
factors controlling downslope movement of material?
* slope angle
* critical angle of repose
* cohesion & water Saturation
* Material Strength
* critical angle of repose
* cohesion & water Saturation
* Material Strength
4
New cards
slope angle stress?
* Shear Stress (σd): stress resulting from application of force parallel to a surface (force pulling the boulder/grain downslope)
* Normal Stress σn): component of stress perpendicular to the Earth’s planar surface (force keeping the boulder/grain from moving)
* Normal Stress σn): component of stress perpendicular to the Earth’s planar surface (force keeping the boulder/grain from moving)
5
New cards
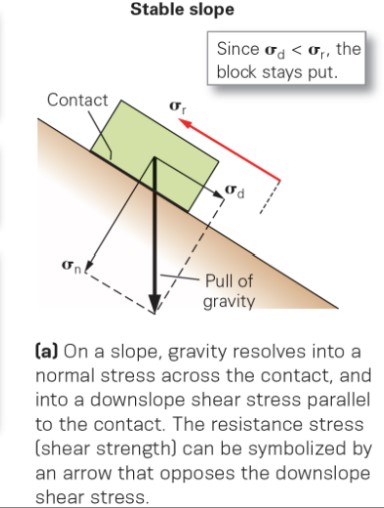
when is a slope stable?
* when σd
6
New cards
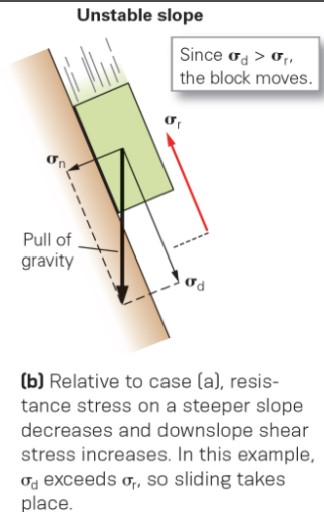
when is slope unstable?
* when σd>σr
* shear stress bigger than resistance
* shear stress bigger than resistance
7
New cards
what is the critical angle of repose?
* max angle at which sediment particles can stand w/o falling depends on:
* grain size
* grain angularity
* rounded grains (more friction) < angular grains
* moisture content
* dry sediments typic is less stable than damp sediment
* oversat sediment becomes less stable
* grain size
* grain angularity
* rounded grains (more friction) < angular grains
* moisture content
* dry sediments typic is less stable than damp sediment
* oversat sediment becomes less stable
8
New cards
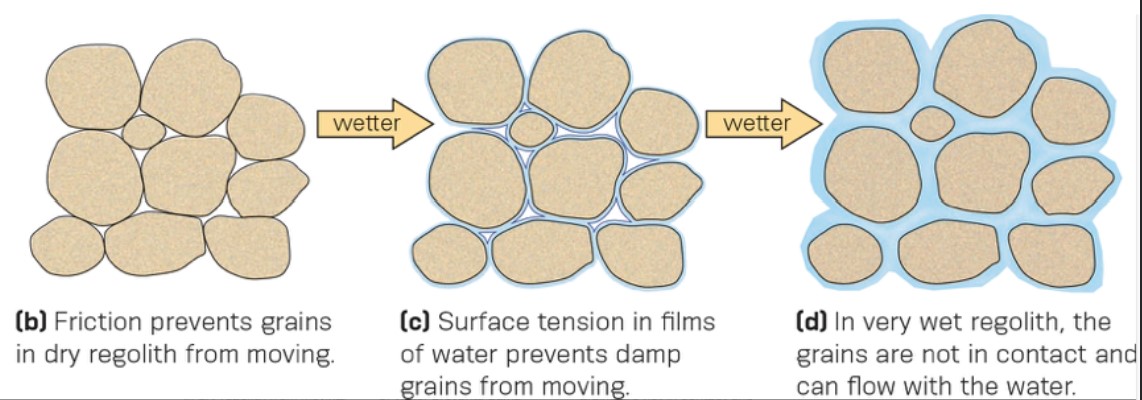
what is cohesion?
* attraction between small soil particles that is provided by the surface tension of water between the particles
* friction and surface tension of water can provide some resistance to sliding
* friction and surface tension of water can provide some resistance to sliding
9
New cards
material strength categories?
* loose, poorly cemented, dry material → weak
* solid, well-cemented material → stronger
* weak between sedimentary layers & along well dev factures
* diff types of rocks layer up → change between one type of rock to other can be failure
* solid, well-cemented material → stronger
* weak between sedimentary layers & along well dev factures
* diff types of rocks layer up → change between one type of rock to other can be failure
10
New cards
what are the diff types of slope failure?
* creep and solifluction
* slumps
* debris flows & mud flows
* rockslides and rockfalls
* sturzstroms (rock avalanches)
* slumps
* debris flows & mud flows
* rockslides and rockfalls
* sturzstroms (rock avalanches)
11
New cards
what is a creep?
* extremely slow downslope flow of sediment on the surface
* caused by cycles of freeze-thaw, wetting-drying and/or warming-cooling
* when water freeze, expands ground (rises) n continues
* so winter slope is higher than summer slope
* caused by cycles of freeze-thaw, wetting-drying and/or warming-cooling
* when water freeze, expands ground (rises) n continues
* so winter slope is higher than summer slope
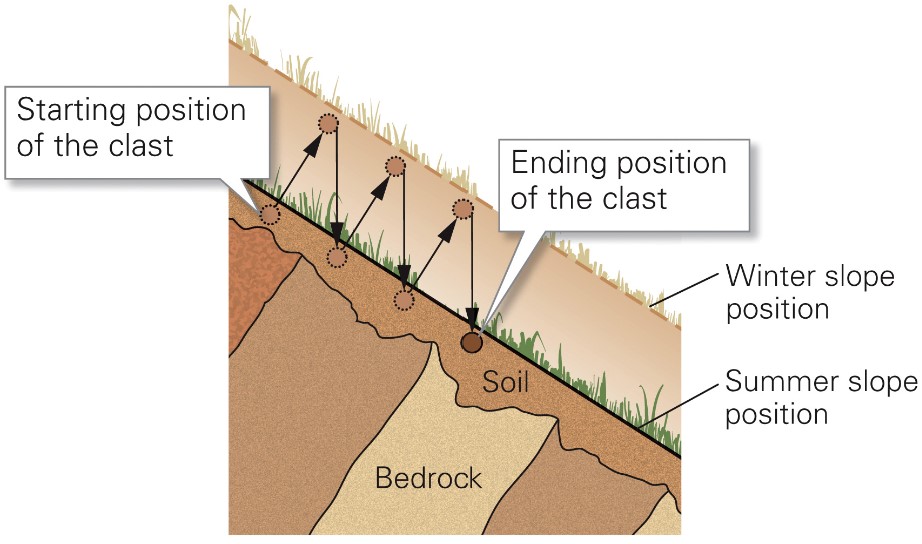
12
New cards
how do creep occur?
* slow, so loss is mostly from damage to buildings and infrastruct, rather than casualties
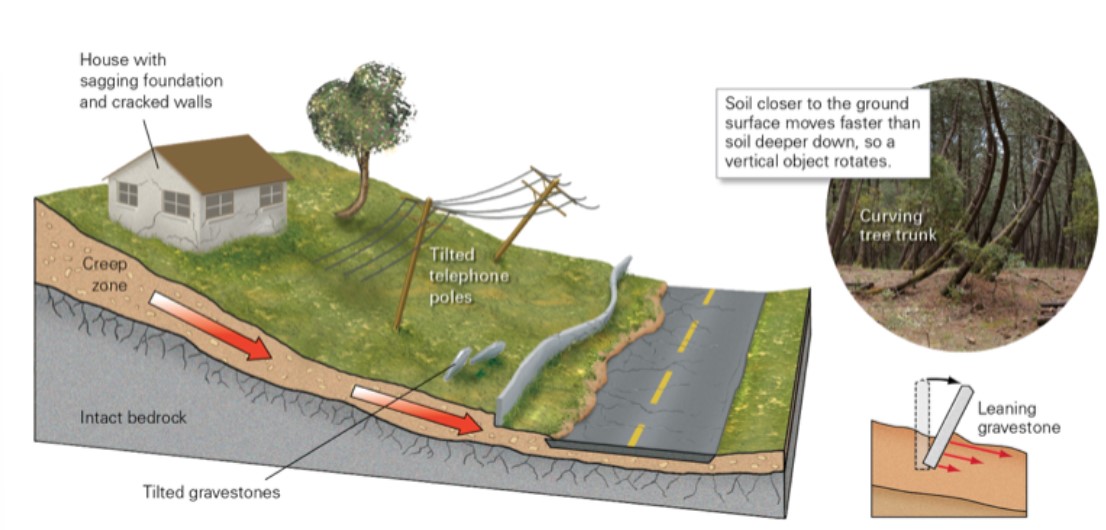
13
New cards
what is solifluction?
* downslope creep driven by sequential freezing and thawing in tundra regions
* results in soggy layer of ground above frozen permafrost that then moves downhill
* this water can’t go back down
* results in soggy layer of ground above frozen permafrost that then moves downhill
* this water can’t go back down
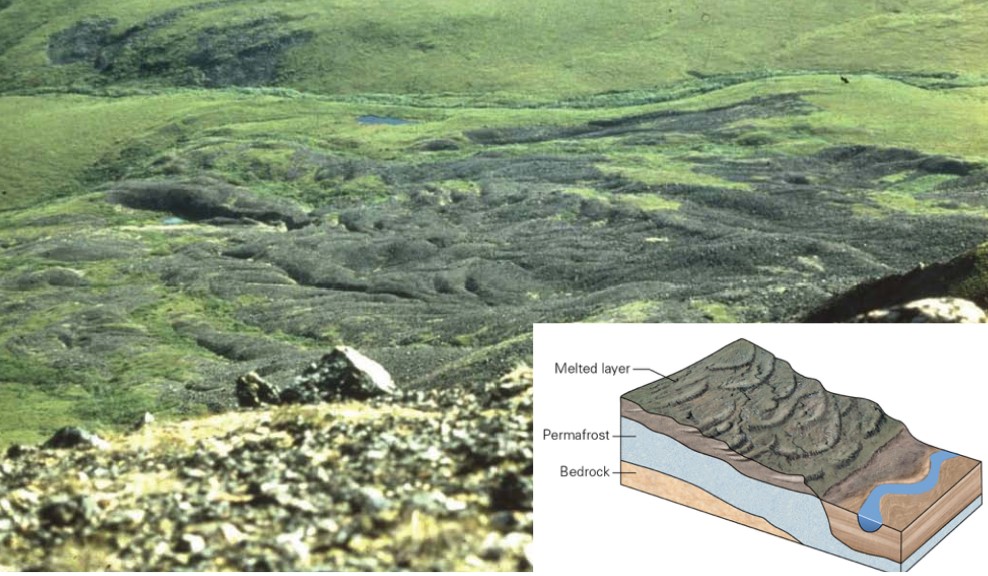
14
New cards
what are translational slump?
* landslide that moves along a regular sloping planar surface
* typic occurs when a block of material is underlain by a weak surface that is more or less parallel to the slope
* planes between sedimentary beds
* old faults and fractures
* debris or cohesive mud over underlying bedrocks
* block can travel down slope as a cohesive unit or lose internal cohesion and break up as it travels downslope
* if it breaks, turns into diff landslide
* typic occurs when a block of material is underlain by a weak surface that is more or less parallel to the slope
* planes between sedimentary beds
* old faults and fractures
* debris or cohesive mud over underlying bedrocks
* block can travel down slope as a cohesive unit or lose internal cohesion and break up as it travels downslope
* if it breaks, turns into diff landslide
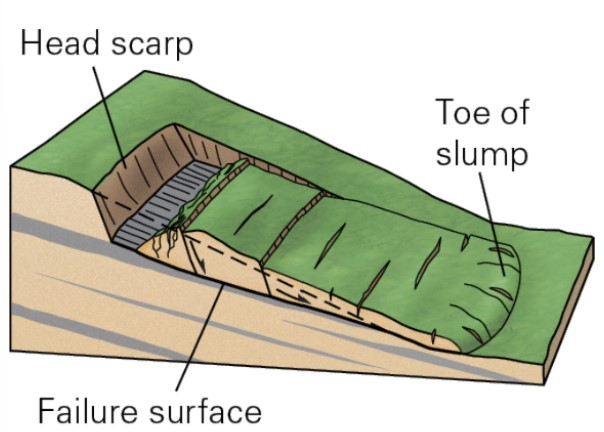
15
New cards
what are rotational slumps?
* landslide in which the mass rotates on a concave failure surface
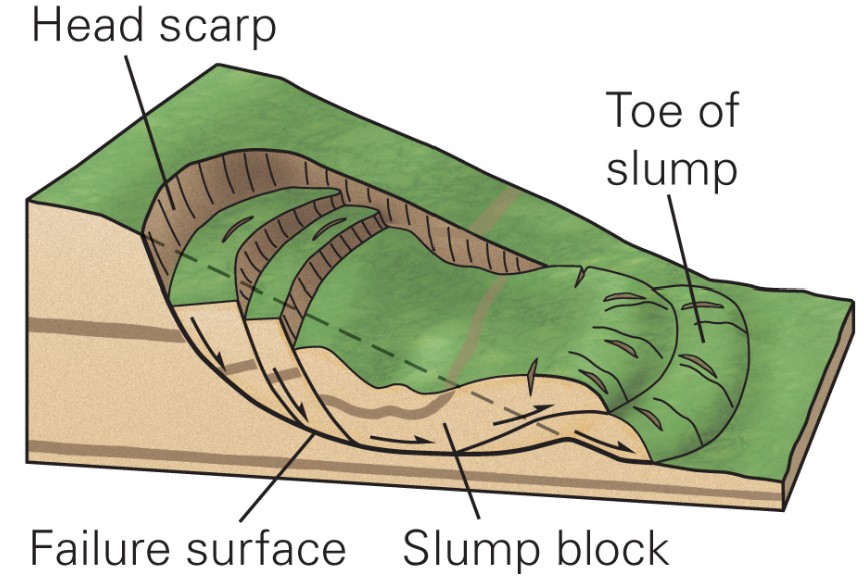
16
New cards
examples of slumps?
* Slumps dev along the South Saskatchewan River near Medicine Hat, Alberta
* Slump destroyed Holbeck Hall in Scarborough, England, 1993
* Slump destroyed Holbeck Hall in Scarborough, England, 1993
17
New cards
what are flows?
* slope failures involving material that has lost internal cohesion
18
New cards
what is mud flow?
* flow of mud, rock, and water dominated by clay-sized particles
* includes lahars
* includes lahars
19
New cards
what is debris flow?
* slurry of rock, sand, and water flowing downslope; water usually makes up less than half of the flow vol
20
New cards
what does speed of flow depend on?
* steepness of the slope
* water content
* water content
21
New cards
example of debris flow?
* Andres of Northwest Argentina that was rich in cobble and boulders
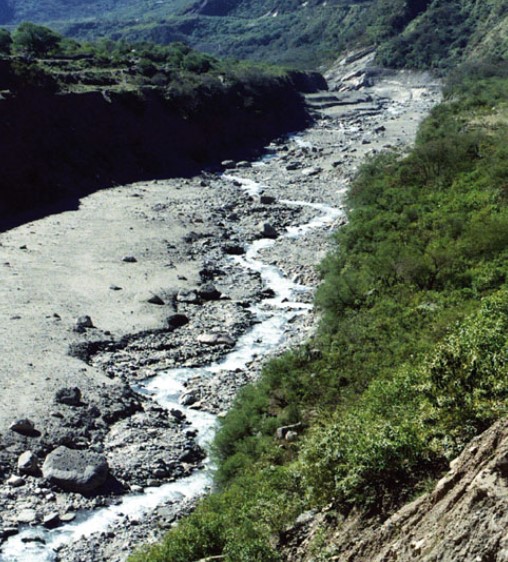

22
New cards
example mudflow?
* Afghanistan, 2014
* heavy rain turned a slump into a mudflow
* buried part of a village in Afghanistan
* heavy rain turned a slump into a mudflow
* buried part of a village in Afghanistan
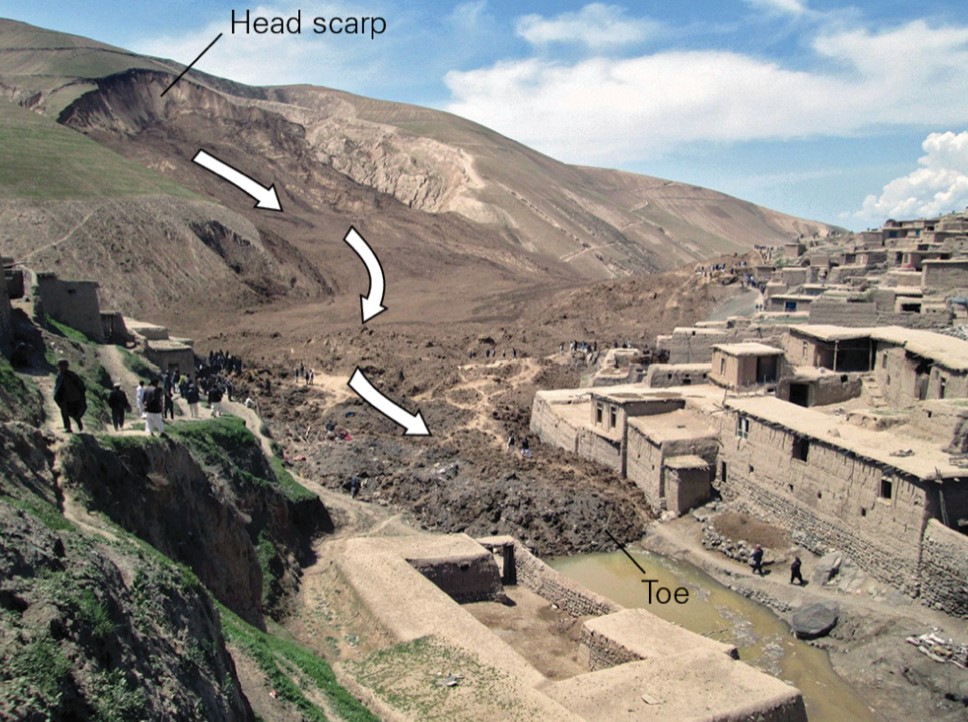

23
New cards
Rio De Janeiro and landslides
* highly weathered Sugarloaf mountains surround the city
* poor communities (favelas) built on material where landslides are common
* 8 million mostly poor Brazilians face mudflow risk
* wealthy communities build homes on stable ground
* poor communities (favelas) built on material where landslides are common
* 8 million mostly poor Brazilians face mudflow risk
* wealthy communities build homes on stable ground
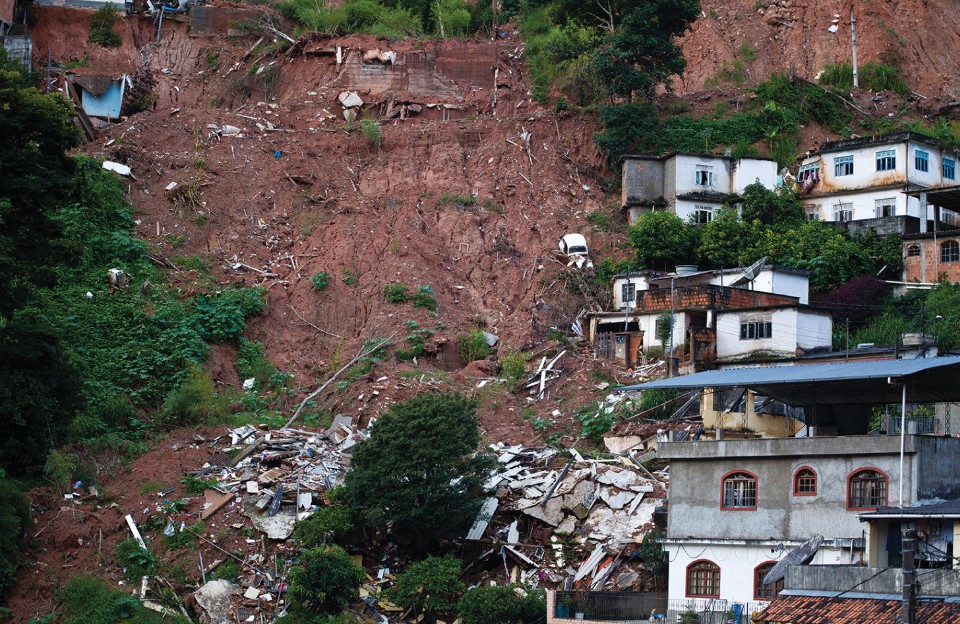

24
New cards
Vargas Tragedy - Venezuela 1999
* several debris and mudflows over a 2-day period caused by heave rainfall
* towns were built on debris from past flows
* 30,000 deaths
* 75,000 people displaces
* dutch helped out (Netherlands)
* Some buried to death
* mudline on clothes suggest that the landslide was much higher than what videographer saw next day
* towns were built on debris from past flows
* 30,000 deaths
* 75,000 people displaces
* dutch helped out (Netherlands)
* Some buried to death
* mudline on clothes suggest that the landslide was much higher than what videographer saw next day
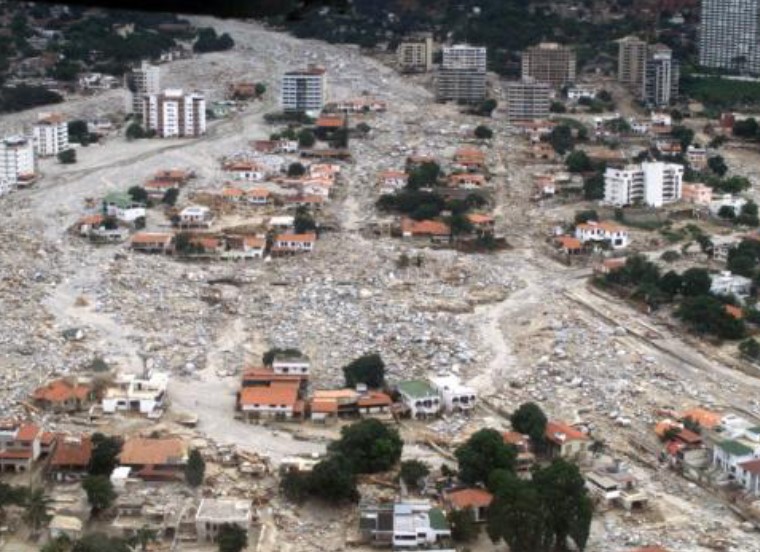

25
New cards
what is quick clay?
* water-sat mud deposited in salty water composed of clay flakes with large pore spaces between the flakes
* highly unstable
* highly unstable
26
New cards
example of quick clay landslides?
* Led Clay in the ST. Lawrence, Saguenay, and Ottawa Valleys
* Lemieux Landslide 1993 →
* The headscarp retrogressed 680 m into level
ground above the riverbank. About 2.8 million tons of clay and silt liquefied and flowed \n into the South Nation River valley, damming the river
* Alta, Norway 2020
* Lemieux Landslide 1993 →
* The headscarp retrogressed 680 m into level
ground above the riverbank. About 2.8 million tons of clay and silt liquefied and flowed \n into the South Nation River valley, damming the river
* Alta, Norway 2020
27
New cards
what is a rockslide?
* sudden movement of rock and debris down a non-vertical slope
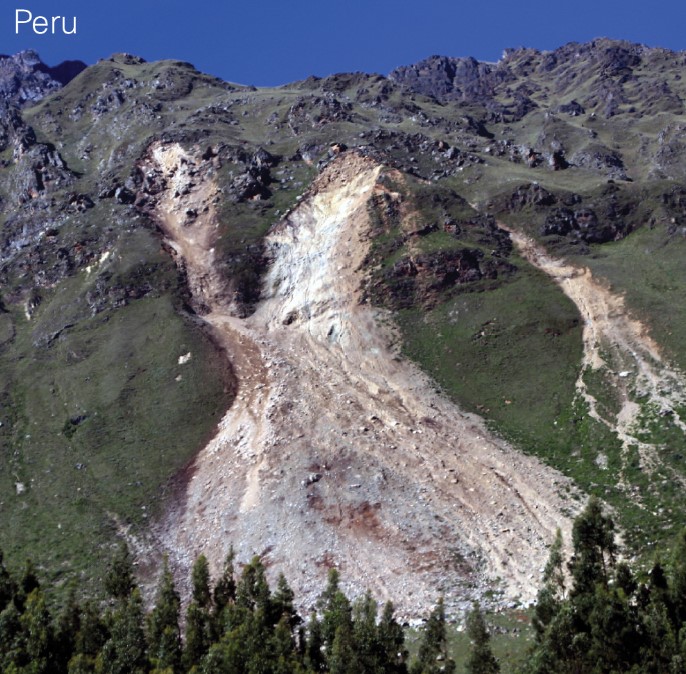

28
New cards
Vaiont Slide
* October 9, 1963; Southern alps in northwest Italy
* dam changed water tables (raised it) → caused surface above to get wet, making it unstable → cause slide + river was blocked
* slide displaced all the water in downstream half of the reservoir
* 125m high wave crashed over the dam
* tsunami rushed upstream
* 2500 lives lost due to water spilling over dam
* dam changed water tables (raised it) → caused surface above to get wet, making it unstable → cause slide + river was blocked
* slide displaced all the water in downstream half of the reservoir
* 125m high wave crashed over the dam
* tsunami rushed upstream
* 2500 lives lost due to water spilling over dam
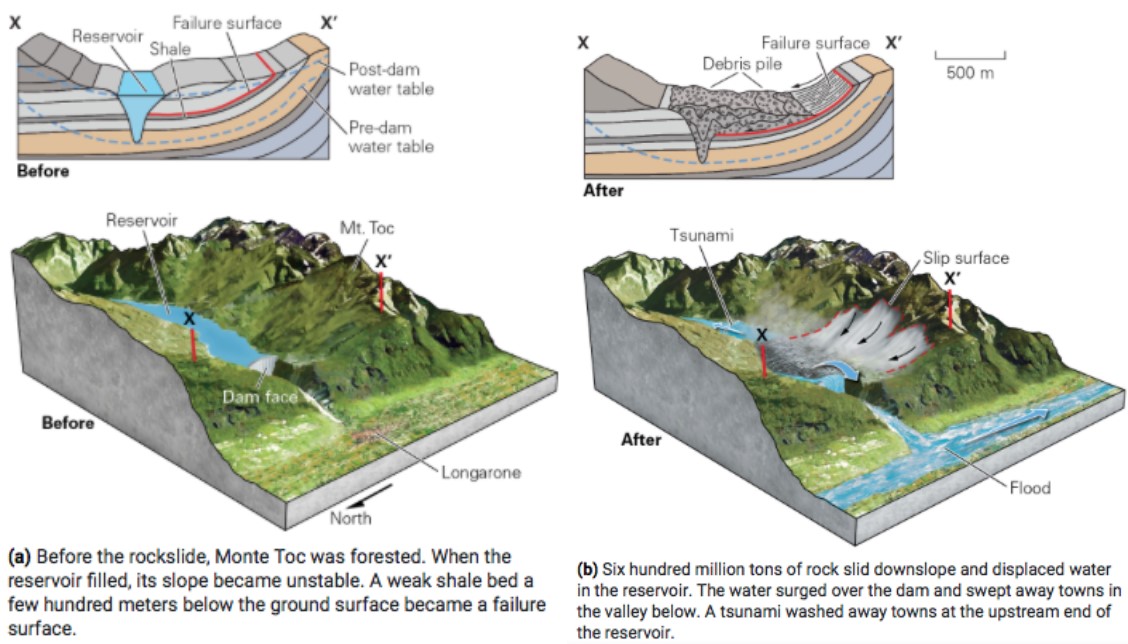
29
New cards
what is a rockfall?
* slope failure that occurs when a mass free-falls down a cliff or a steep slope; slope is often vertical
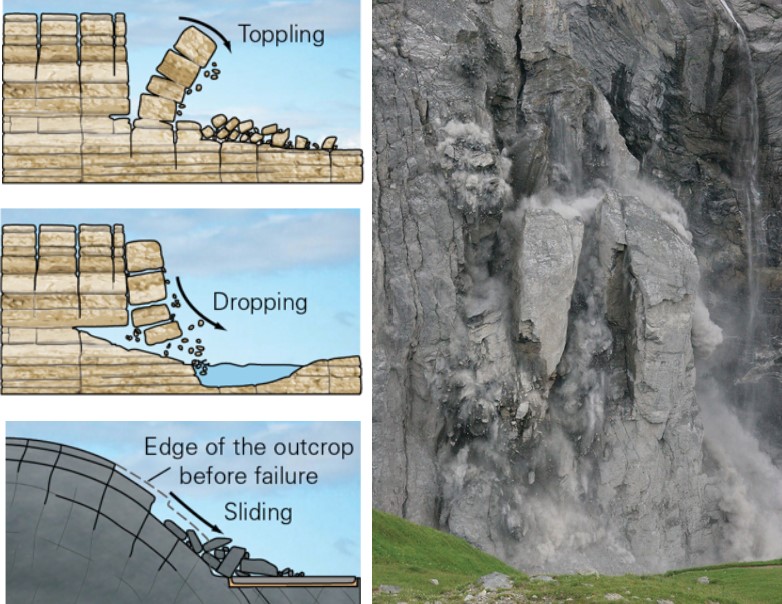
30
New cards
rock fall examples?
* Swiss Alps
* India
* India
31
New cards
what is frost wedging?
* splitting of rock thru pressure exerted when water freezes
* freezing water expands by 9.2%
* coastal areas prone to frost wedging where temperature oscillates around freezing pnt
* example: cliff in Torbay, Newfoundland and Labrador
* freezing water expands by 9.2%
* coastal areas prone to frost wedging where temperature oscillates around freezing pnt
* example: cliff in Torbay, Newfoundland and Labrador
32
New cards
what is Sturzstrom?
* extremely rapid downslope movement of large vols or rocks and debris
* largest and most destructive
* typic being as a rock slide, but breaks up, entraining air n water
* travel velocities as high as 100-300 km/hr
* can travel distances up to 20x their vertical fall
* mecha that causes sturzstroms to have such hig velocity and long flow paths is still under debate
* sturzstrom may flow as a fluid composed of rock fragment suspended in air (fluidization)
* largest and most destructive
* typic being as a rock slide, but breaks up, entraining air n water
* travel velocities as high as 100-300 km/hr
* can travel distances up to 20x their vertical fall
* mecha that causes sturzstroms to have such hig velocity and long flow paths is still under debate
* sturzstrom may flow as a fluid composed of rock fragment suspended in air (fluidization)
33
New cards
examples of struzstroms?
* 1903 Frank, Alberta
* 1965 Hope, BC
* 1965 Hope, BC
34
New cards
Frank, Alberta
* started as a translational slide
* grained speed and dev into sturzstrom
* event lasted less than 100 secs
* slope failure occurred along fractured limestone planes
* based on the speed and distance of the sturzstrom, it is thought to have traveled on a cushion of compressed air
* The rock moved from Turtle Mountain (lower \n left), buried the town of Frank, crossed the river and surged 120m up the other slope.
* The river eventually cut through and opened the channel again
* grained speed and dev into sturzstrom
* event lasted less than 100 secs
* slope failure occurred along fractured limestone planes
* based on the speed and distance of the sturzstrom, it is thought to have traveled on a cushion of compressed air
* The rock moved from Turtle Mountain (lower \n left), buried the town of Frank, crossed the river and surged 120m up the other slope.
* The river eventually cut through and opened the channel again
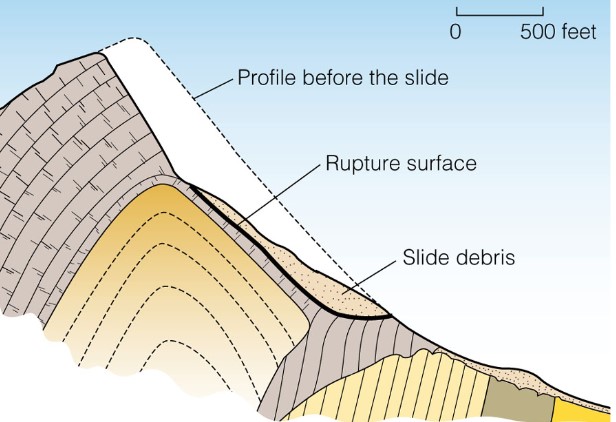
35
New cards
hazard mapping & assessment
* GIS software can help identify areas of past and potential failures by mapping attributes that contribute to slope failures
* slope
* bedrock type (lithology)
* sediment texture and depth
* vegetation
* drainage
* historic slope failures
* slope
* bedrock type (lithology)
* sediment texture and depth
* vegetation
* drainage
* historic slope failures
36
New cards
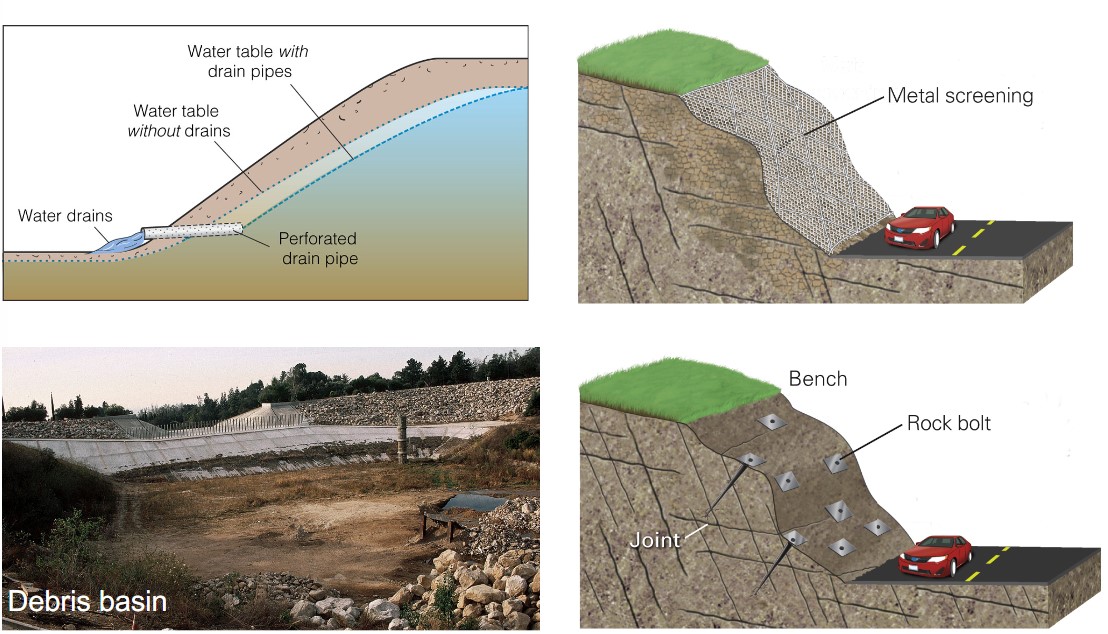
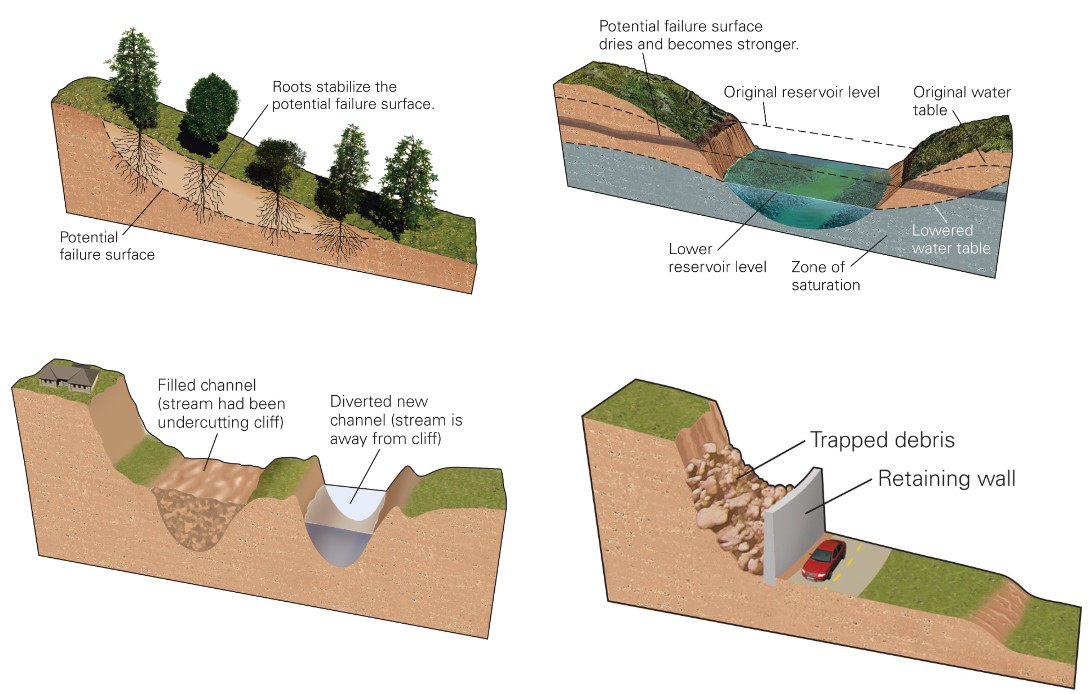
reducing or mitigating risk?
* roots of plants
* reservoir lowering
* river undercutting flow
* retaining wall
* pipes
* metal screening
* debris basin
* rock bolt
* reservoir lowering
* river undercutting flow
* retaining wall
* pipes
* metal screening
* debris basin
* rock bolt
37
New cards
how to reduce risk from slope failures?
* installation of detection devices, such as acoustic flow monitors
* only gives a couple of mins of warning
* not enough time to evacuate peep downslope
* prohibit building at the base of mountains and is dangerous areas along steep slopes
* zone hazardous area as open space for parks, golf courses and agriculture
* construct walls and dams to deflect or slow debris flows
* construct debris basins large enough to channel and contain debris
* only gives a couple of mins of warning
* not enough time to evacuate peep downslope
* prohibit building at the base of mountains and is dangerous areas along steep slopes
* zone hazardous area as open space for parks, golf courses and agriculture
* construct walls and dams to deflect or slow debris flows
* construct debris basins large enough to channel and contain debris