Physics for Life Sciences
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 2: Foundations of Measurements and Motion
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Why are the foundations of units?
Accurate experiments
Safe medical dosages
Clear communication about the world
How many units are in the SI System?
7
Dimension/SI Unit/Symbol for 3 units
Length Meter m
Time Second s
Mass Kilogram kg
Metric Prefixes
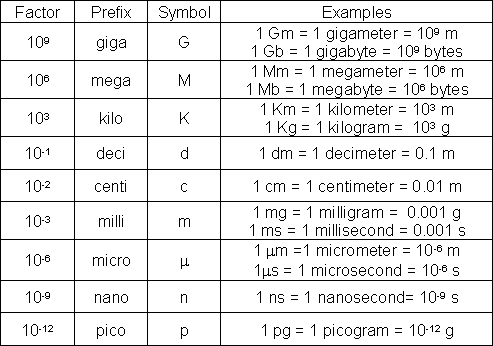
You can only compare two qualities if they have the same ____
Dimensions
You cannot compared ___ to ___, however you can compared ____ to ____, or ____ to ____
time; mass, seconds; years, kilograms; ounces
Dimensional Analysis (Factor-Label Method)
convert to the same unit
Unit conversion is the process ____
of expressing the same quality in a different unity of measurement. The actual amount of stuff (length, weight, time…) doesn’t change, just the way its labeled.
Position
the location of an object relative to a chosen reference point (the origin)
Distance
a scalar quantity. It represents the total length of the path traveled between two points, including units
Displacement
A vector quantity. It represents the change in an objects position, combining both a magnitude (distance) and direction. Mathematical difference between the final and initial position vectors
Scalar
physical quantity that has only magnitude (size). ex. distance, mass, time, speed
Vector
physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction. represented with arrows. ex, displacement, velocity, and force
Speed is ___
scalar
Speed
“how fast” something is moving. It is the rate of change of distance
Velocity is ____
vector
Velocity
Rate of change of displacement. How fast and in which direction an object is moving
Average speed
distance traveled/ elapsed time
Average velocity
Displacement/ elapsed time
instantaneous rate of change
how fast a quantity is changing at a single, specific instant time
Instantaneous speed
the magnitude of the instantaneous velocity
Instantaneous velocity
the average velocity in the limit as the change in time approaches zero