Chapter 8: The Cerebrum: Cerebral Function
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
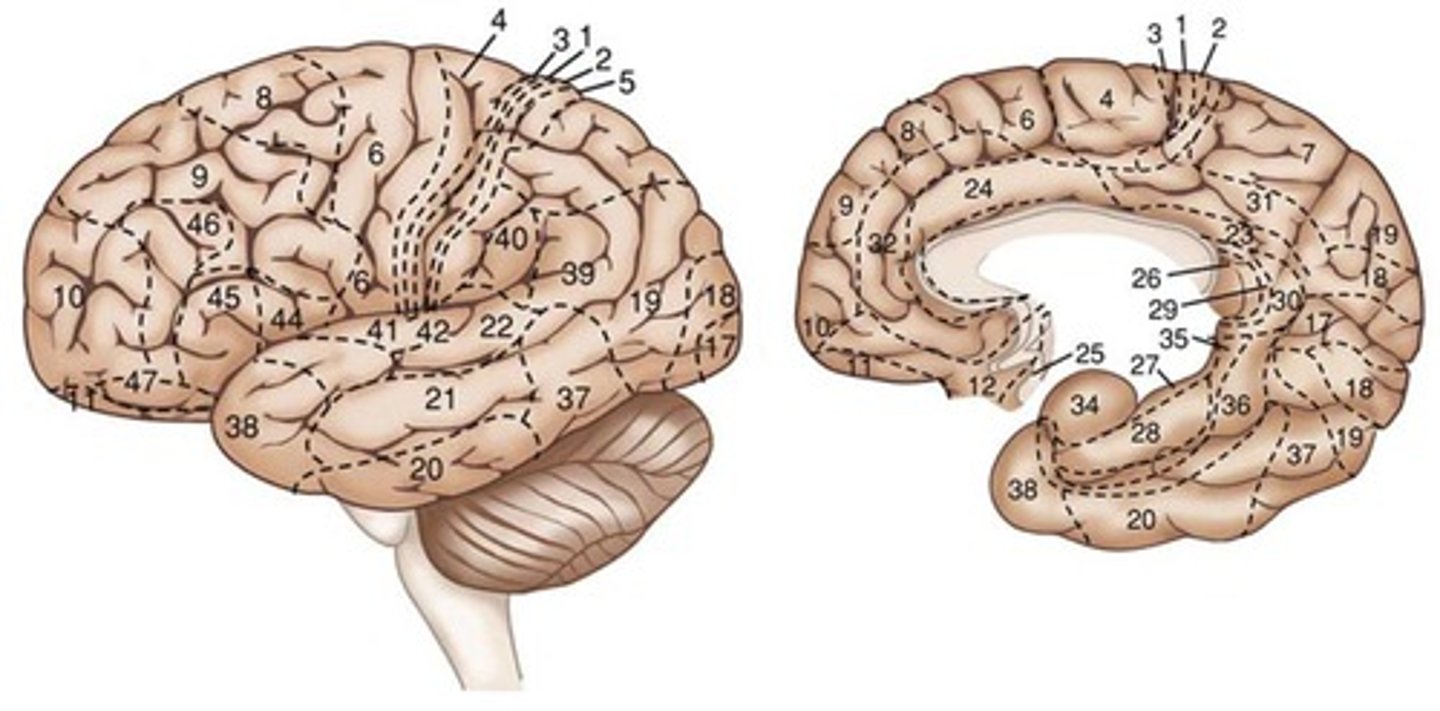
Brodmann Areas
52 brain regions based on gross anatomy and cellular structure of the brain.
Prefrontal Cortex
Involved in cognition (executive control), personality, decision making, and social structure
If there's damage to the Prefrontal cortex, it can cause what?
It can change personality; Ex: Phineas Gage
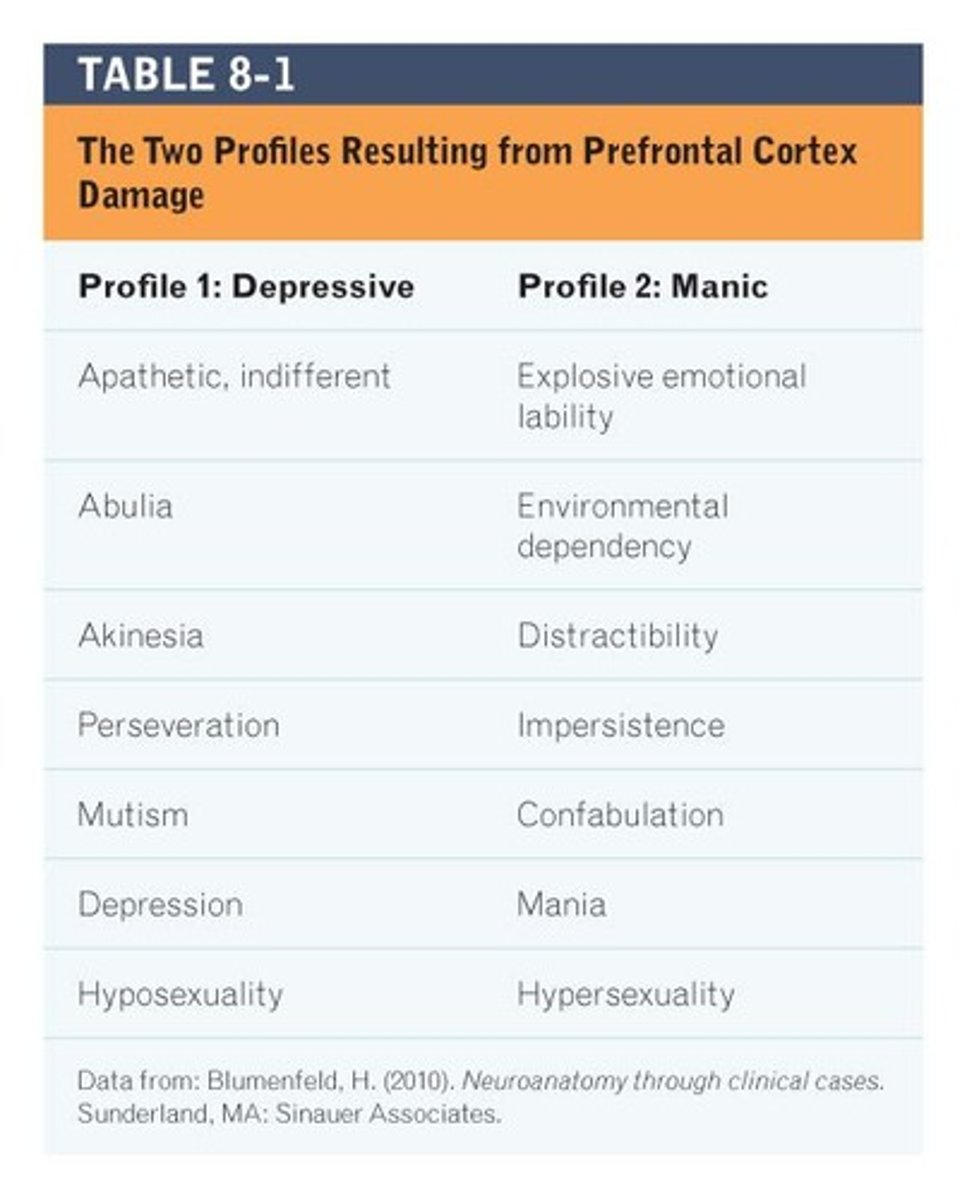
What are the two profiles resulting from damage in the Prefrontal Cortex?
Profile 1: Depressive
Profile 2: Manic
Broca's Area
BA 44 and 45; involved in interpretation of language (syntax) and planning/programming of verbal responses; involved in coordination of speech organs for language production
Damage to Broca's area can cause:
Broca's Aphasia or Apraxia of Speech Impairment leading to difficulty in speech production.
Broca's Aphasia
Impairment leading to difficulty in speech production
Premotor Cortex
plans and selects motor movements.
Supplementary Motor Area
involved in sequencing and "turning on" motor plans
Primary Motor Cortex
Sends motor plans to muscles and integrates motor information form the supplementary motor area and premotor cortex to the muscles for them to act
Homunculus
A representation on the motor strip related to how much of the brain is dedicated to particular movements
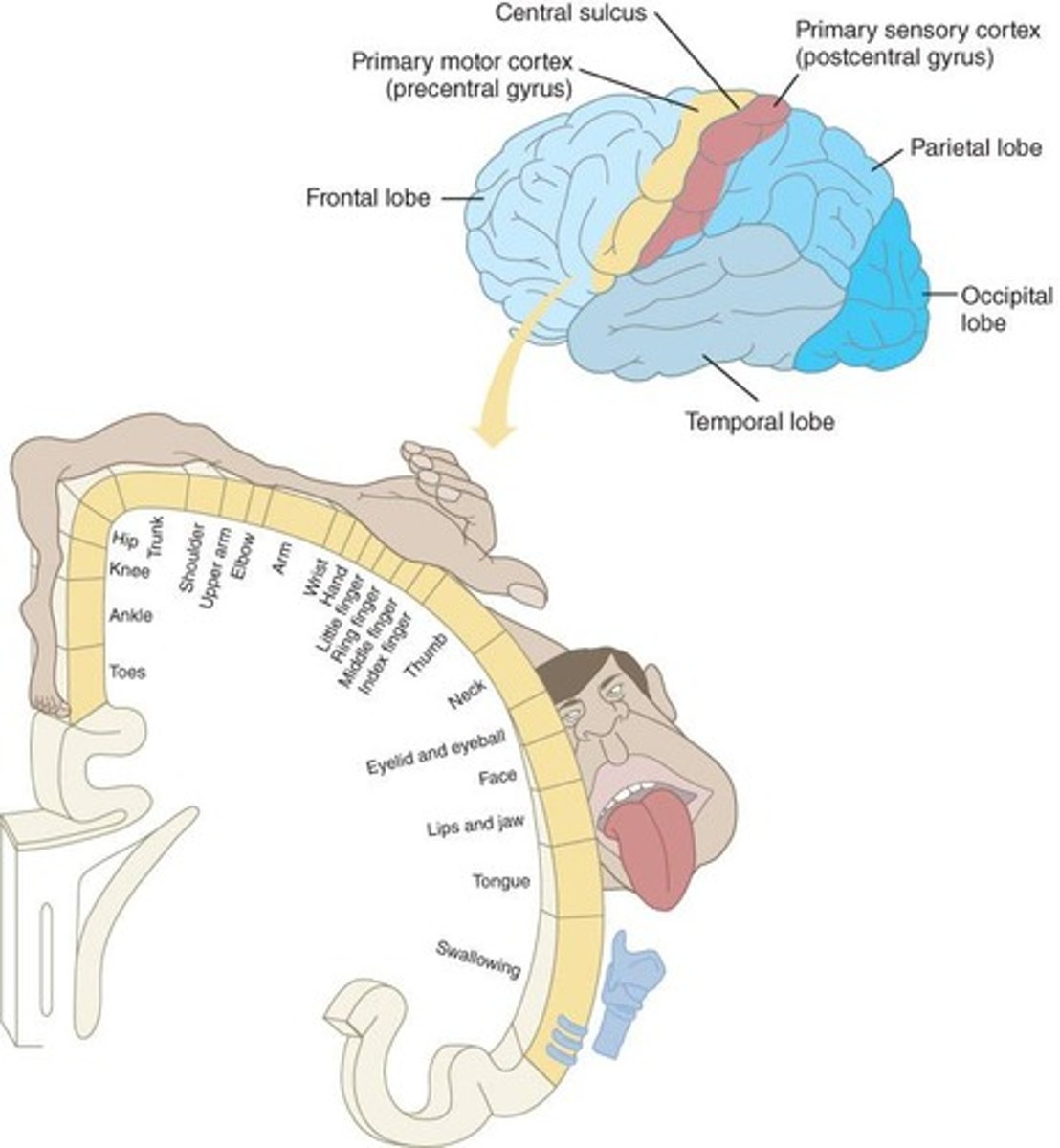
Primary Sensory Cortex is also known as
the somatosensory cortex
What somatosensory information does the primary sensory cortex process?
Vibration, proprioception, touch, and astereognosis
Astereognosis
Inability to recognize objects by touch.
Somatosensory Association Cortex
interprets sensory experience during motor movements; specifically used to refine motor action (writing) and it is involved in fine motor movements associated with speech
Angular Gyrus
involved in reading and math abilities.
Damage to the angular gyrus can lead to:
alexia and acalculia
Alexia
difficulty with reading
Acalculia
Difficulty with mathematical calculations.
Supramarginal Gyrus
involved in phonological processing, storing auditory representations and word sounding.
Phonological Dyslexia
Difficulty reading new and non-words.
Occipital Lobe
Processes and receives visual information from the eyes.
What are two streams in the occipital lobe?
dorsal stream and ventral stream
Dorsal Stream
Analyzes motion and spatial relationships in vision.
Ventral Stream
Analyzes forms, colors, and faces in vision.
Damage to occipital lobe can cause
simultanagnosia, proposopagnosia, and micro/macopsia
Simultanagnosia
Inability to perceive multiple elements of a scene.
Prosopagnosia
Inability to recognize familiar faces.
micro/macropsia
things look abnormally small/large
Inferior Temporal Area
processes auditory, language info, and reading facial emotions
Parahippocampal gyrus
located on the medial surface of the temporal lobe
Hippocampus
Associated with declarative memory.
Entorhinal Cortex
major input/output relay between cerebral cortex and the hippocampus.
Fusiform Gyrus is also known as...
the occipitotemporal gyrus
Fusiform Gyrus
involved in remembering and naming seen objects acting as visual lexicon
Lesions in fusiform gyrus can cause:
anomia and lexical agraphia
Anomia
inability to name objects
Lexical agraphia
difficulty writing words
Primary Olfactory Cortex
receives and processes smell from the nose and emotional connections through the limbic system
Damage to the primary olfactory cortex can cause:
anosmia
Anosmia
Loss of smell due to damage.
Auditory Cortex
Receives auditory information from the ears through CN VII and the auditory pathway, processes sound intensity and frequency, organized by tones
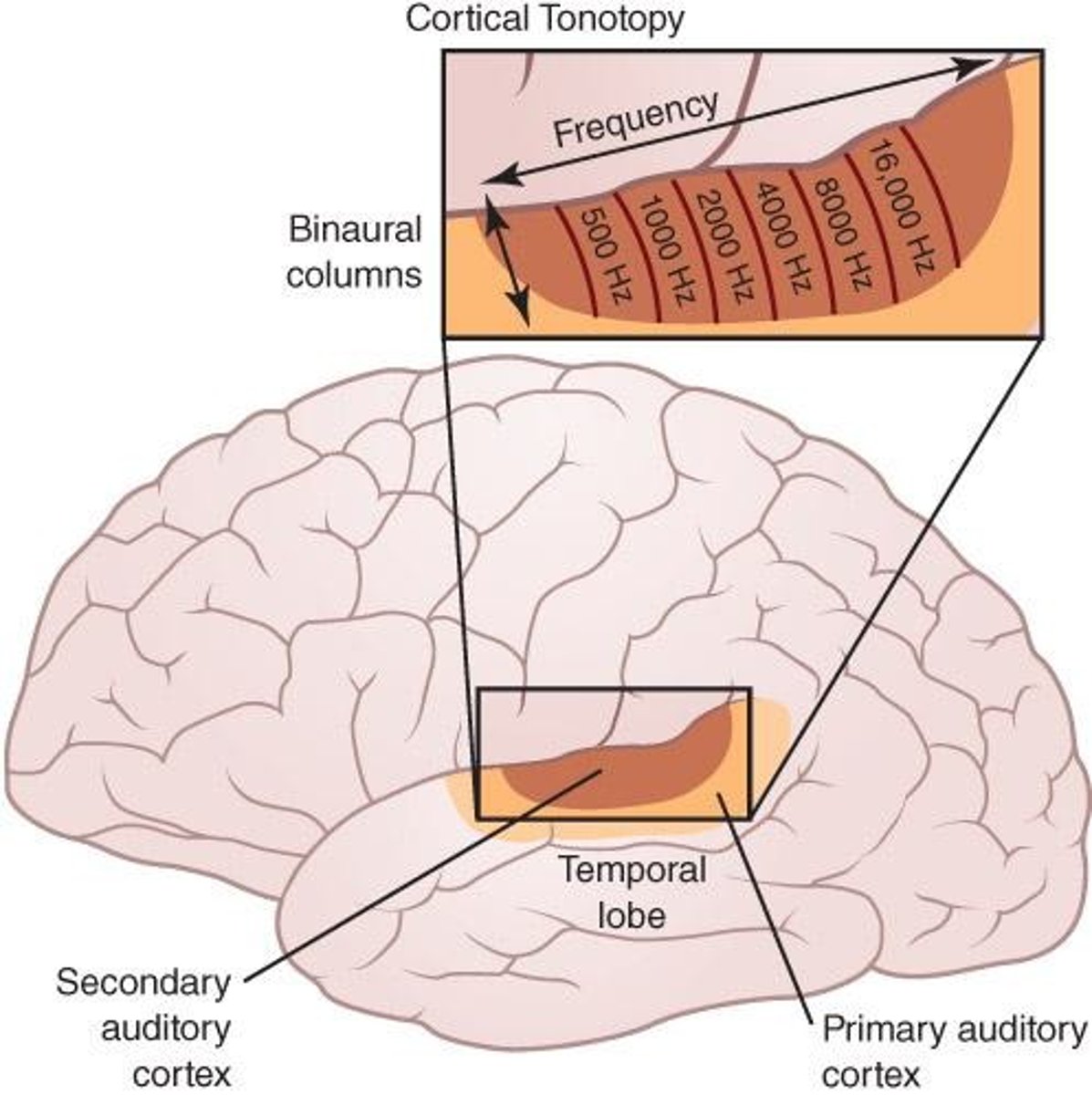
The auditory cortex is also known as
Heschl's gyrus
Wernicke's Area
BA 22; attaches meaning to auditory information.
Wernicke's Aphasia
Characterized by verbal jargon and comprehension issues.
Cingulate Cortex
between the corpus callosum and frontal and parietal lobes; involved in the limbic system having connections to the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus
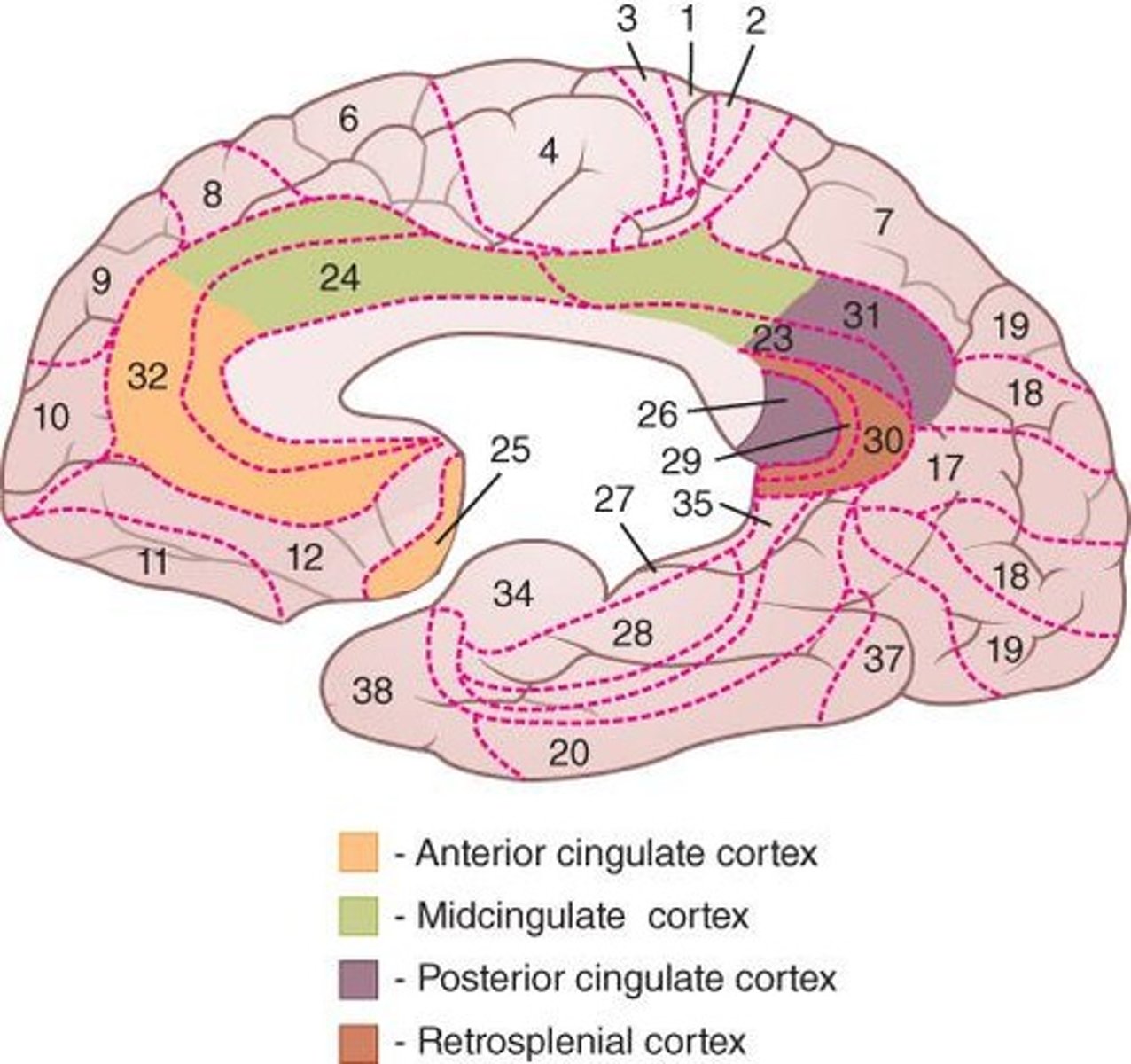
Functionally what do the anterior and posterior parts of the cingulate cortex do?
ACC: filters out irrelevant information
PCC: detects important information
Insular Cortex
Deep in lateral sulcus; role in language, lexical decision making, and possibly global aphasia
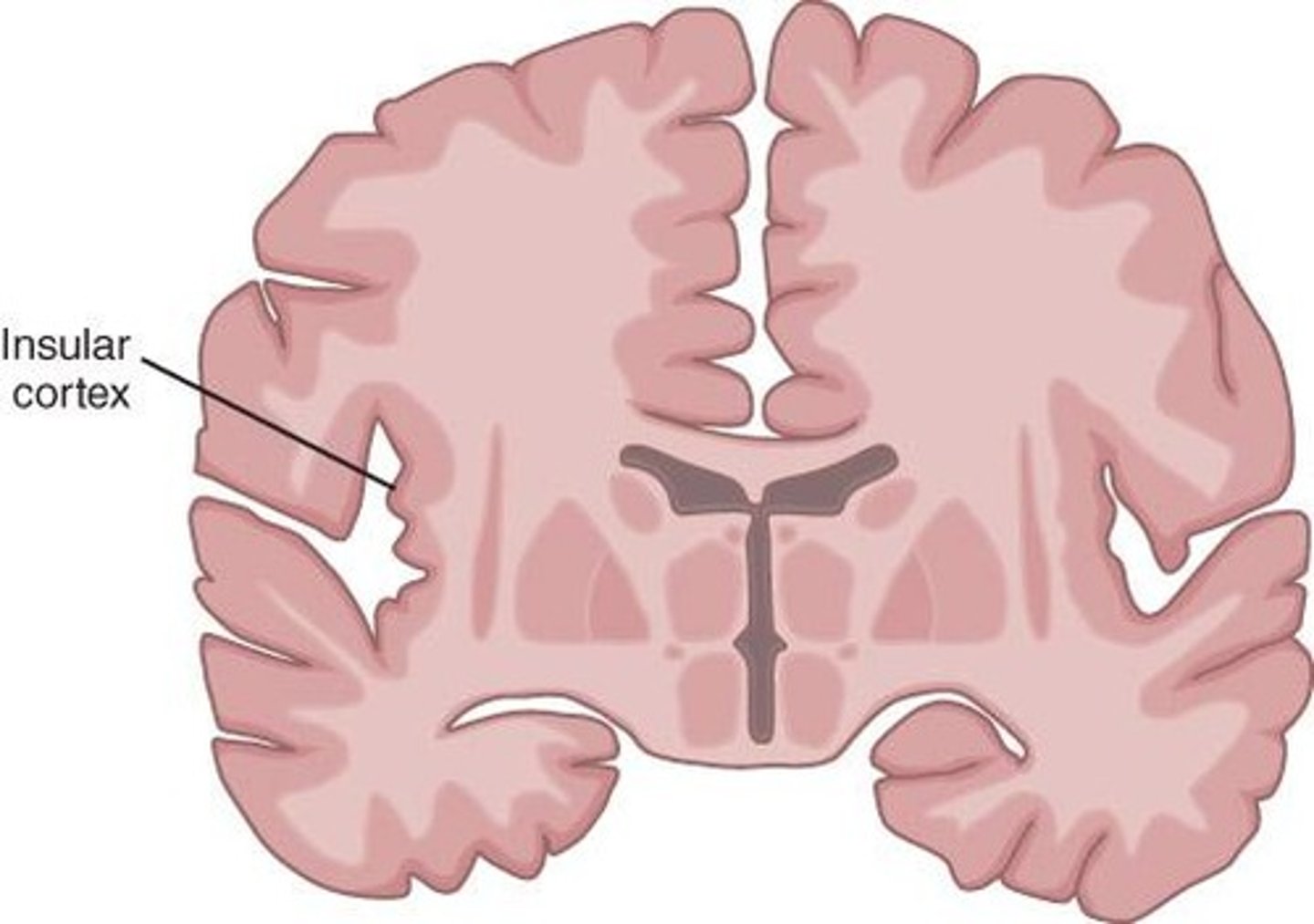
Global aphasia
large parts of the brain are impaired causing lots of impairments