Ectopic Pregnancy
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Ectopic Pregnancy
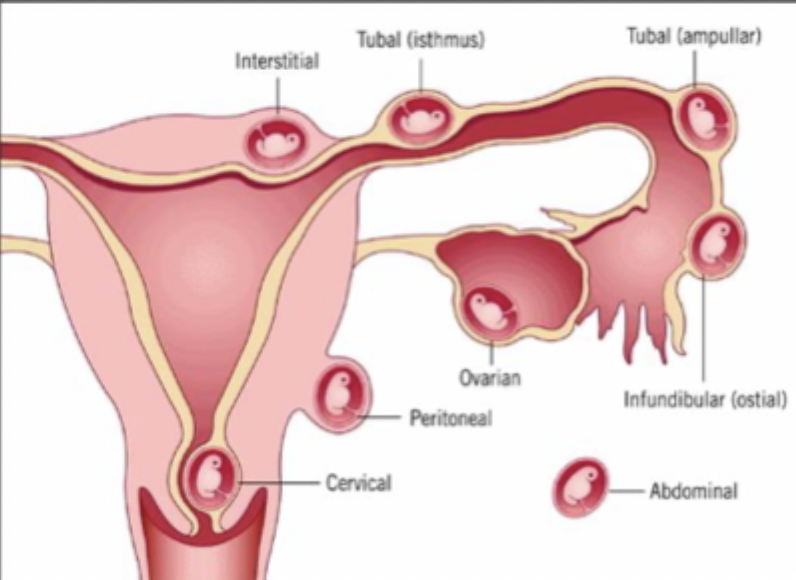
The implantation of a fertilized egg in a location outside of the uterine cavity including the fallopian tubes, cervix (under 1%), ovary (3% ), cornual, region of the uterus, and the abdominal cavity (1%) - 25% of all pregnancy related disease
Fallopian tube (70% in the ampulla, 12% Isthmus, 11% fimbria, 2% interstitial/cornual)
Most common spot for an ectopic pregnancy?
Previous Hx, previous tubal surgery, tubal ligation, tubal pathology, in utero DES exposure, current IUD use
High Risk factors for Ectopic pregnancy
Infertility, previous cervicitis, hx of PID (especially chlamydia), multiple sexual partners, smoking
Moderate risk factors for ectopic pregnancy
Previous pelvic/abdominal surgery, vaginal douching, early age of intercouse (under 18)
Low risk factors for ectopic pregnancy
hemorrhage in the 1st trimester
Ectopic pregnancy is the leading cause of maternal death due to
Conditions that delay/prevent passage of the fertilized oocyte, Factors that inherent in the embryo result in premature implanation
Pathophys for Ectopics
Abdominal pain, amenorrhea, spotting, normal pregnancy discomforts
Classic symptoms of Ectopics - a lot present atypically (50%)
UTI, kidney stones, diverticulitis, appendicitis, appendicitis, ovarian neoplasms, endometriosis, endometritis, leiomyomas, PID, pregnancy related conditions
DDX for lower abdominal pain in women includes
pregnant until proven otherwise (get a Hcg)
Say it with me - All females of childbearing age are…
No uterus (hysterectomy), confirmed menopause, young girls prior to menarche, XY genotype
Reasons to NOT order a pregnancy test
orthostatic changes, adnexal, cervical motion, and/or abdominal tenderness, adnexal mass and possible mild uterine enlargement
Physical Exam findings for Ectopics - often unremarkable if small
B-Hcg Quant (can be detected 8 days after the LH surge), transvaginal U/S
The eval for a suspected ectopic begins with a
Yolk sac, embryo, embryonic cardiac activity
Transvaginal U/S can be diagnostic alone if what is demonstrable
66% every 48 hours (basically doubles)
Beta Hcg should rise by at least ____________________ during the 1st 40 days of pregnancy
Discriminatory Zone
A serum HCG above which a gestational sac should be visualized by U/S examination if an intrauterine pregnancy is present - based on the correlation between visibility of the gestational sac and the HCG concentration
Pouch of Douglas (Cul-de-sac - can be sampled by a Culdocentesis)
A space behind the uterus that blood tends to pull
Serum HcG is 1500-2000 with TVUS OR 6500 with transabdominal U/S, visualization of an extrauterine gestational sac containing a yolk sac or embryo, a complex adnexal mass in the presence of a positive pregnancy test and empty uterus (most common), lower progesterone (less than 5), Higher blood flow to one fallopian tube (20-45%) on doppler (insufficient), Laparoscopy (RARE)
Diagnostic criteria for Ectopic
true gestational sac
What is the earliest sign of U/S of an intrauterine pregnancy is the presence of the
Sliding signs
What sign on U/S helps tell the difference between an ovarian cyst and an ectopic pregnancy?
trophoblastic tissue is obtained by uterine curettage (must r/o a viable pregnancy first)
The intrauterine location of a pregnancy is diagnosed with certainty IF
Methotrexate (MTX - 1 mg/kg or 50 mg/m² for ectopic), Laparoscopy (standard approach), Exploratory laparotomy, salpingectomy/salpingostomy (everybody with surgery gets one of these)
Treatment plan for Ectopic Pregnancy
folic acid antagonist that inhibits DNA synthesis and cell reproduction (usually in actively proliferating cells)
MOA for MTX
bone marrow, buccal/intestinal mucosa, respiratory epithelium, malignant cells, trophoblastic tissue
What tissues does MTX affect?
Stable, patient is willing and able to follow up, beta HCG under 5000, no fetal cardiac activity, ectopic mass under 3-4 cm
Optimal candidates for MTX
Breastfeeding, overt/lab evidence of immunodeficiency, Alcoholism, preexisting blood dyscrasia, known sensitivity, active pulmonary disease, peptic ulcer disease, hepatic/renal/hematologic dysfunction
Absolute C/I for MTX
Unstable, impending/ongoing rupture, C/I to MTX, coexisting intrauterine pregnancy, follow up is non-existent, lack of timely access to medical care, desire for permanent contraception, known tubal disease with planned IVF in the future, failed medical therapy
Indications for surgical treatment
hemoperitoneum, heterotopic preg, interstitial preg
Laparoscopy can be used even in the presence of a
Exploratory Laparotomy (Ex Lap)
What procedure can be performed if the patient is unstable, there is active bleeding, surgeon is inexperienced with laparoscopy or lack of equipment
Weekly measurement of beta-hCG, TVUS weekly until beta-hcg is undetectable, Counsel on starting birth control
Follow up for Ectopic pregnancy treated with MTX
Persistent Ectopic
If MTX or salpingotomy don’t work, what do we have on our hands
Intramural pregnancy
A pregnancy implanted within the myometrium of the uterus - extremely rare, less than 50 cases in the literature
Heterotopic pregnancy
The presence of simultaneous pregnancies at 2 different implantation sites - most often a combination of an intrauterine and ectopic