Module 5 - Transition metals
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Why are the 4s electrons removed first before the 3d ones?
Because 4s is filled first and as the first in, its the first out.
What are the exceptions to the Aufbau rule?
chromium - 3d and 4s are both half filled
copper 3d is completely filled
why are chromium and copper exceptions to the aufbau rule?
its thought that the repulsion between outer electrons is minimised by this arrangement so its makes them more stable
What is a transition metal?
A d-block element that forms an ion with an incomplete d subshell
Why do transition metals have variable oxidation states?
4s electrons are lost first from transition metals but because the 3d and 4s subshells are close together it means that the 3d electrons can also be lost too.
This makes them lose a variable number of electrons so they have a variable number of oxidation states
What colour is cobalt 2?
pink
What colour is iron 2?
pale green
What colour is iron 3?
yellow
What colour is chromium 3?
green
What colour is copper 2?
blue
What colour is manganese 7?
purple
What colour is manganese 2?
pale pink
What colour is chromium 6?
orange
How do the transition metals act as catalysts?
They provide a surface for the reaction to take place on so gases are absorbed and the reaction occurs and the products can then be deabsorbed from the metals surface
How do rhodium and platinum act as catalysts?
They are used in catalytic converted to convert No and Co into N2 and CO2
2NO + 2CO ——> N2 + 2CO2
Rh/Pt
How does iron act as catalyst?
Iron is used to catalyse the harber process
N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
Fe
How does MnO2 act as catalyst?
It catalyses the decomposition of H2O2
H2O2 ——> H2O + ½ O2
MnO2
How does nickle act as catalyst?
Its used to make margarine when sunsaturated oil or fat is hydrogenated
C2H4 + H2 ——> C2H6
Ni
What happens in a precipitation reaction of transition metals?
An aqueous transition metal reacts with aqueous NaOH and NH3 and a coloured precipitate gets formed
What are the safety concerns of copper 2 salt?
harmful
What are the safety concerns of manganese 2 salt?
toxic
What are the safety concerns of iron 2 and 3 salt?
irritant
What are the safety concerns of chromium 3 salt?
toxic
What are the observations of Cu2+ with NaOH?
blue ppt and insoluble when NaOH in excess
What are the observations of Mn2+ with NaOH?
buff ppt and insoluble when in excess
What are the observations of Fe2+ with NaOH?
green ppt and insoluble in excess
What are the observations of Fe3+ with NaOH?
orange-brown ppt and insoluble in excess
What are the observations of Cr3+ with NaOH?
grey-green ppt and dissolves to dark green solution in excess
What are the observations of Cu2+ with NH3?
blue ppt and dissolves to dark blue solution in excess
What are the observations of Mn2+ with NH3?
buff ppt insoluble in excess
What are the observations of Fe2+ with NH3?
green ppt insoluble in excess
What are the observations of Fe3+ with NH3?
orange brown ppt and insoluble in excess
What are the observations of Cr3+ with NH3?
green ppt that dissolves to form a purple solution in excess
What do precipitation ionic equations look like?
Ion + OH- → salt
Fe2+ + 2OH- → Fe(OH)2
What is a complex ion?
A transition metal ion thats bonded to one or more ligands by coordinate bonds
What is a ligand?
a molecule or ion that can donate a pair of electrons to the transition metal ion to forma a coordinate bond
What is the coordination number?
the total number of co-ordinate bonds that are formed between a central metal ion and its ligand
What is a coordinate bond?
A bond formed when one of the bonded atoms provides both of the electrons for the shaired pair
what is a monodentate ligand?
a ligand that is able to donate one pair of electrons to the central metal ion to form one coordinate bond
What is a square planar shape?
its a shape that occurs in complex ions with eight d electrons in their subshell
→ palladium2, gold 3, nickle 2, platinum 2
It has a bond angle of 90 and coordinate number of 4
what is a bidentate ligand?
each ligand can donate 2 pairs of electrons to the central metal ion to form 2 coordinate bonds
What are some common bidentate ligands and where are their lone pairs of electrons
(prefix en)ethane-1,2-diamine → e- on N
(prefix onoxolate)-oxolate ion → on O- ions
(prefix bipy) 2,2- bipyridine→ on N
(prefix pic) picolinate → on N and O-
What does an oxolate ion look like?
red= oxygen
white = carbon
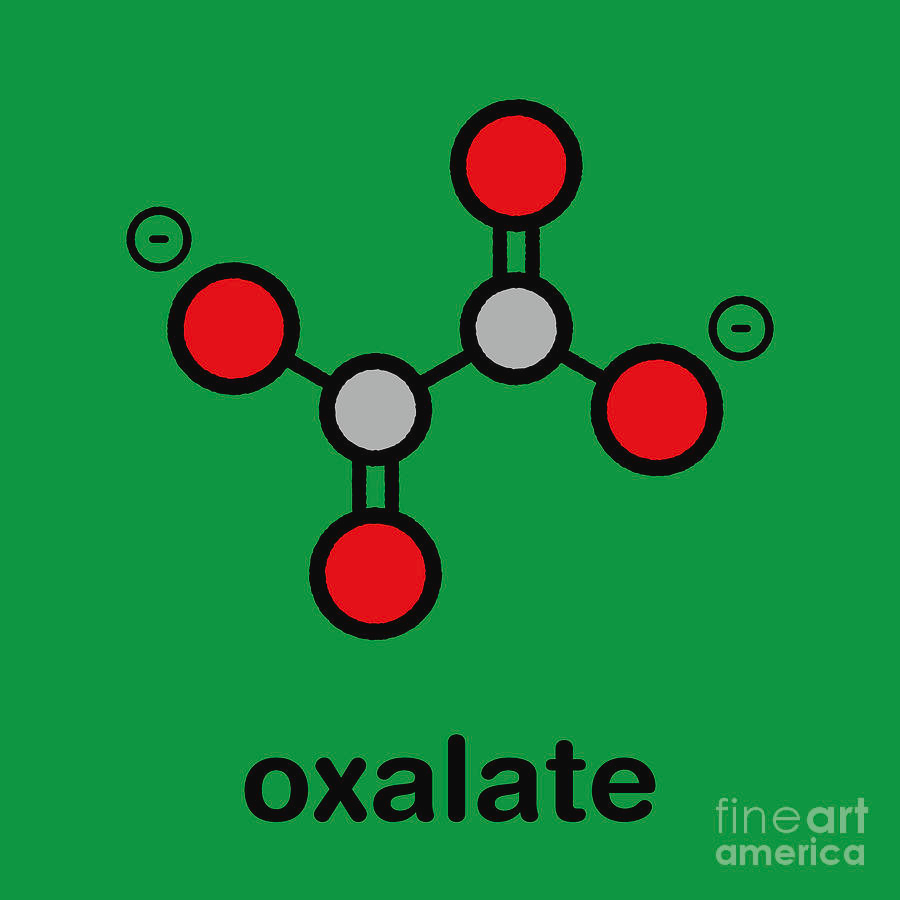
What are multidentate ligands?
ligands that can donate more than one lone pair of electrons to central metal ion so can form more than one coordinate bond
What si an example ofa multidentate ligand?
EDTA or ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
its a hexadentate ligands
What is stertioisomerism?
A species with the same structural formula but different arrangement of atoms in space
What happens is cisisomerism?
ligands are next to eachother or adjacent
ONLY HAPPENS IN OCTAHEDRAL AND SQUARE PLANAR
What happens in transisomerism?
the lignads are opposite eachother
ONLY HAPPENS IN OCTAHEDRAL AND SQUARE PLANAR
What is cisplatin and what does it do?
Its the cis-siomer of the platinum complex [PtCl2(NH3)2]
its used in cancer treatment as it binds to the DNA in fast growing cancer cells and alters the DNA structure and prevents cell divison.
What is optical isomerism?
non superimposable mirror images
What are conditions of optical isomerism?
3 bidentate ligands
2 bidentate and one monodentate
one hexadentate ligand
What are ligand substitution reactions?
a reaction where one ligand in a complex is replaced by another ligand
—→ they are often accompanied by colour changes
What happens when Cu2+ reacts with concentrated HCl?
a yellow solution is produced
What happens in the ligand substitution of copper with ammonia?
Excess ammonia is added to aqueous copper2 ions and colour change from pale blue to dark blue as ammonia replaces 4 water ligands
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 4NH3 → [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ + 4H2O
SHAPE - OCT to OCT
What happens in the ligand substitution of copper with conc. HCl?
conc. HCl is added to a solution of copper 2 ions and the colour changes from blue to green initially then to yellow as cl replaces all 6 water ligands
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl- → [CuCl4]2- + 6H2O
SHAPE - OCT to TETRA
What happens in the ligand substitution of chromium with ammonia?
excess ammonia is added to a solution of chromium 3 ions and the solution turns from violet to purple as six water molecules are replaced by 6 ammonia molecules
[Cr(H2O)6]3+ + 5NH3 → [Cr(NH3)]3+ + 6H2O
What are the problems in the ligand substitution of chromium with ammonia?
[Cr(H2O)6]3+ rarely exist because the water molecules will typically swap with a negative ion in the solution so can be hard to carry out
What is Hb?
an oxygen carrying molecule in red blood cells that can bin reversibly with O2 molecules
How does Hb bind with O2?
It has 4 polypeptide chains with a haem group at the centre which contains Fe2+ which binds with oxygen by dative bonding as the oxygen donates the lone pair of electrons to Fe2+
What happens in the ligand substitution of CO and O2?
CO acts as a ligand as it can donate a pair of electrons to Fe2+ and so it can bind with Hb at the same site as O2 but as it bonds more strongly when they are both present it will be CO that binds.
What are the implicationsof ligand substitution of Co and O2?
CO cant unbind from Hb so less oxygen can be carried which means less respiration and this can be fatal if occurs lots
What happens in the oxidation of fe2+ to fe3+?
A strong ox agent like KMnO4 oxidises fe2+ and gets reduced to Mn2+ ion
5Fe2+ + MnO4- + 8H- + → 5Fe3+ Mn2+ + 4H2O
What happens in the reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+?
A solution of fe3+ reacts with I- ions and they are reduced to fe2+
the change of colour is brown to green in iron but its often obscured by the iodide ions which form a brown colour when oxidised
What happens during the reduction of Cr2O72- to Cr3+?
Acidified dichromate ions can be reduced to cr3+ when zinc is added and if its added in excess they can be further reduced to cr2+ which is pale blue
Cr2O72- + 14H+ _ 3Zn → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O + 3Zn2+
Zn + 2Cr3+ → Zn2+ + 2Cr2+
What happens in the oxidation of Cr3+ to Cr2O72-?
H2O2 is the most powerful ox agent and is used to oxidise cr3+ to Cr2O72-
2Cr3+ + 3H2O2 + H2O → Cr2O72- + 8H+
What happens when copper 2 ions react with excess iodide ions?
I- is oxidised to I2
Cu2+ is reduced to CU+ which then forms a precipitate of copper 1 iodide
2Cu2+ + 4I- → 2CUI + I2
What happens during the disproportionation reaction of copper 1 ions?
When Cu2O reacts with hot dilute sulfuric acid, copper solid is formed with blue copper2 sulfate solution and water
Cu+ is oxidised in CuSO4 and reduced in Cu
Cu2O + H2SO4 → Cu + CuSO4 + H2O