Corporate Finance ch2
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Present Value
the current worth of a future sum of cash flows, discounted at a specific interest rate r
how much a future amount is worth today
(of a single cash flow at time n)
PV = FV/((1+r)^n)
Future Value
the amount of money an investment will grow to over time
how much an amount will be worth in the future
FV = PV * (1+r)^n
Net Present Value
sum of the present values of all incoming and outgoing cash flows over time, used to evaluate investment projects
should be positive to be profitable

how to evaluate if an investment is worth the opportunity cost interest rate?
calculate the present value of the cash inflow discounted at the opportunity cost interest rate. if NPV is positive, then it is better than dividends
what is the discount factor
1 / ((r+r)^t)
multiply this by Ct to find PV
opportunity cost of capital
the rate of return that shareholders could get by investing in securities with a similar risk.
use to evaluate if an investment will increase shareholder value compared to something with a similar level of risk.
net present value rule
accept investments that have positive net present valuesr
rate of return rule
accept investments that offer rates of return that are greater than opportunity cost of capital.
how do you calculate the present value of multiple cash flows?
Sum all of the PVs of the cash flows at each t=n.
for NPV, just subtract the initial cash outflow.
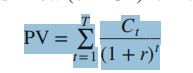
what are you doing when you discount the expected cash flows by the opportunity cost of capital?
You are asking how much investors are prepared to pay for a security that produces similar cash flows.
what is a peretuity
an investment that pays the same cash flow every year forever.
annual rate of return on a perpetuity
AKA discount rate or yield
pays r% of PV(price) every year
r = Cash flow / Present Value
note that this PV is a valuation of the point in time one year before payments begin.
what does the PV of a perpetuity represent
it is the amount that is needed to be able to regenerate its payments through interest yearly. the money made through interest is what is paid out.
valuing a perpetuity due
a perpetuity due is a perpetuity that begins immediately. To calculate the PV, simple add the first year’s cash flow to a regular perpetuity.
PV of a perpetuity due = C/r *(1+r)
valuing a delayed perpetuity
if payment begins in year 3, PV = C*(1/r)*(1/(1+r)³)
an annuity
pays a fixed sum each year for a specified number of years
how to value an annuity
PV of t-year annuity =
annuity factor is in brackets
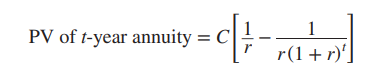
amortizing loans
part of the payment pays interest, part pays off (or amortizes) the loan
future value of an annuity
the same. it is PV*(1+r)^t
growing perpetuity
payments increase yearly by rate g
PV of a growing perpetuity = C1 / (r-g)
PV of a growing annuity
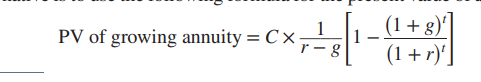
APR vs EAR
Annual Percentage Rate = interest rate over a year, ignoring how often its paid. ignores compounding
Effective Annual Rate= accounts for how often APR is paid and the effect of compounding.
How to calculate EAR
(1+r/m)^mn where m= how many times compounded in a year and n = how many years.
PV of $1 received at the end of the year t compounded continuously. use this to find the rate compounded annually equivalent to the rate compounded continuously over 1 year
PV = $1 / e^rt
how to get equivalent continuously compounded PV of annuity
replace (1+r)^t with e^rt