Understanding Photosynthesis and Its Mechanisms
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Photosynthesis
the conversion of light energy to chemical energy
Autotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food (organic molecules) from simple substances in their surroundings
Heterotrophs
Organisms unable to make their own food so they live off of other organisms
Cyanobacteria
early prokaryotes capable of photosynthesis that oxygenated the atmosphere of early Earth
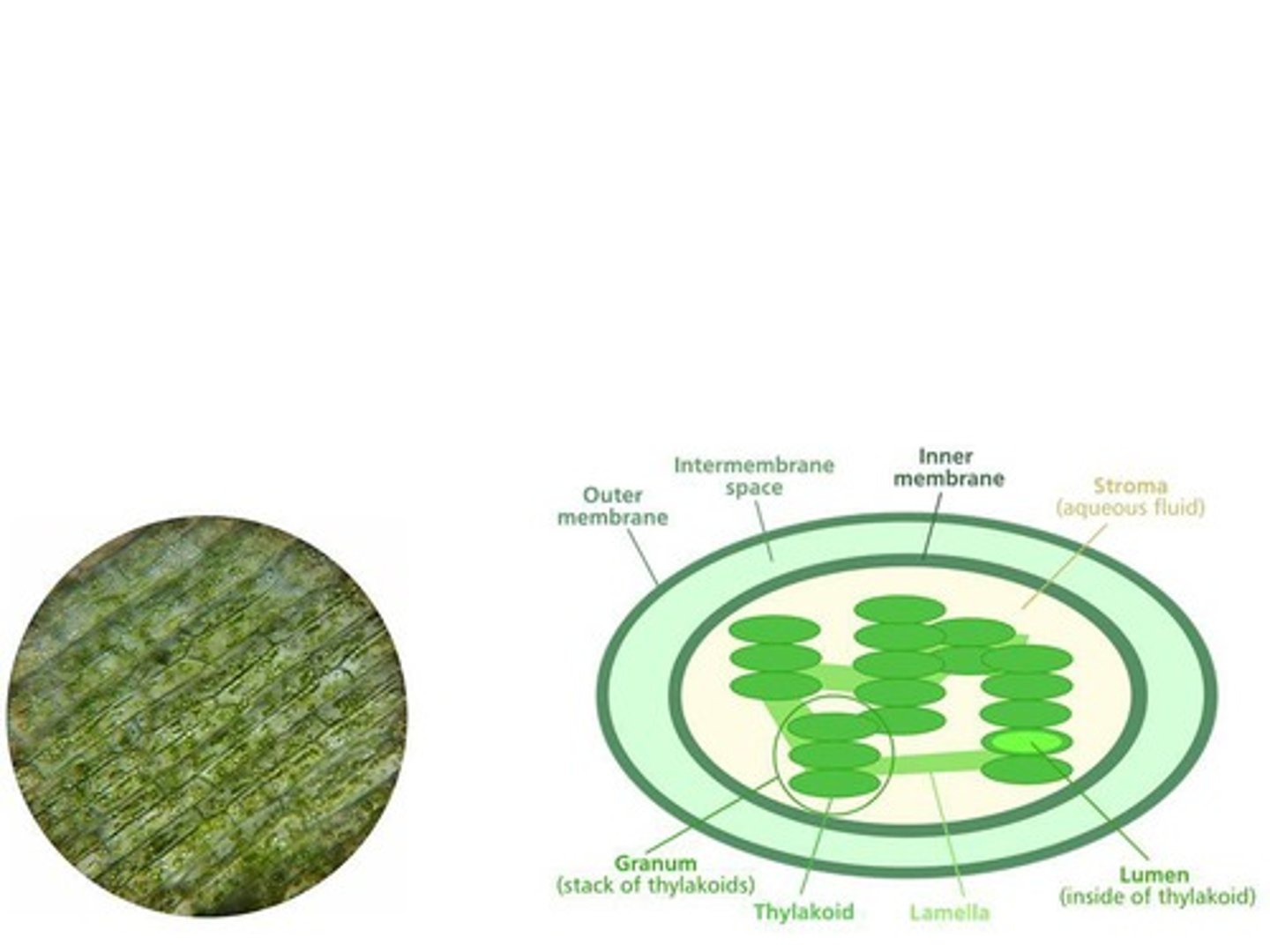
Chloroplast
organelle for the location of photosynthesis, found in the mesophyll, the cells that make up the interior tissue of the leaf
Stomata
pores in leaves that allow CO2 in and O2 out
Stroma
aqueous internal fluid of chloroplasts
Thylakoids
structures that form stacks known as grana in chloroplasts
Chlorophyll
green pigment in thylakoid membranes
Photosynthesis Simplified Formula
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
Redox reaction
reaction involving complete or partial transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another
Oxidation
loss of electrons (e-)
Reduction
gain of electrons (e-)
Light
electromagnetic energy made up of particles of energy called photons
Wavelength
the distance from the crest of one wave to the crest of the next
Electromagnetic spectrum
the entire range of wavelengths of electromagnetic energy
Visible light
the range of light wavelengths from 380 nm to 750 nm
Photosynthetic Pigments
molecules that absorb visible light
Chlorophyll a
primary pigment involved in the light reactions, blue/green pigment
Chlorophyll b
accessory pigment, yellow/green pigment
Carotenoids
yellow/orange pigments that broaden the spectrum of colors that drive photosynthesis and provide photoprotection
Light Reactions
occur in the thylakoid membrane in the photosystems and convert solar energy to chemical energy
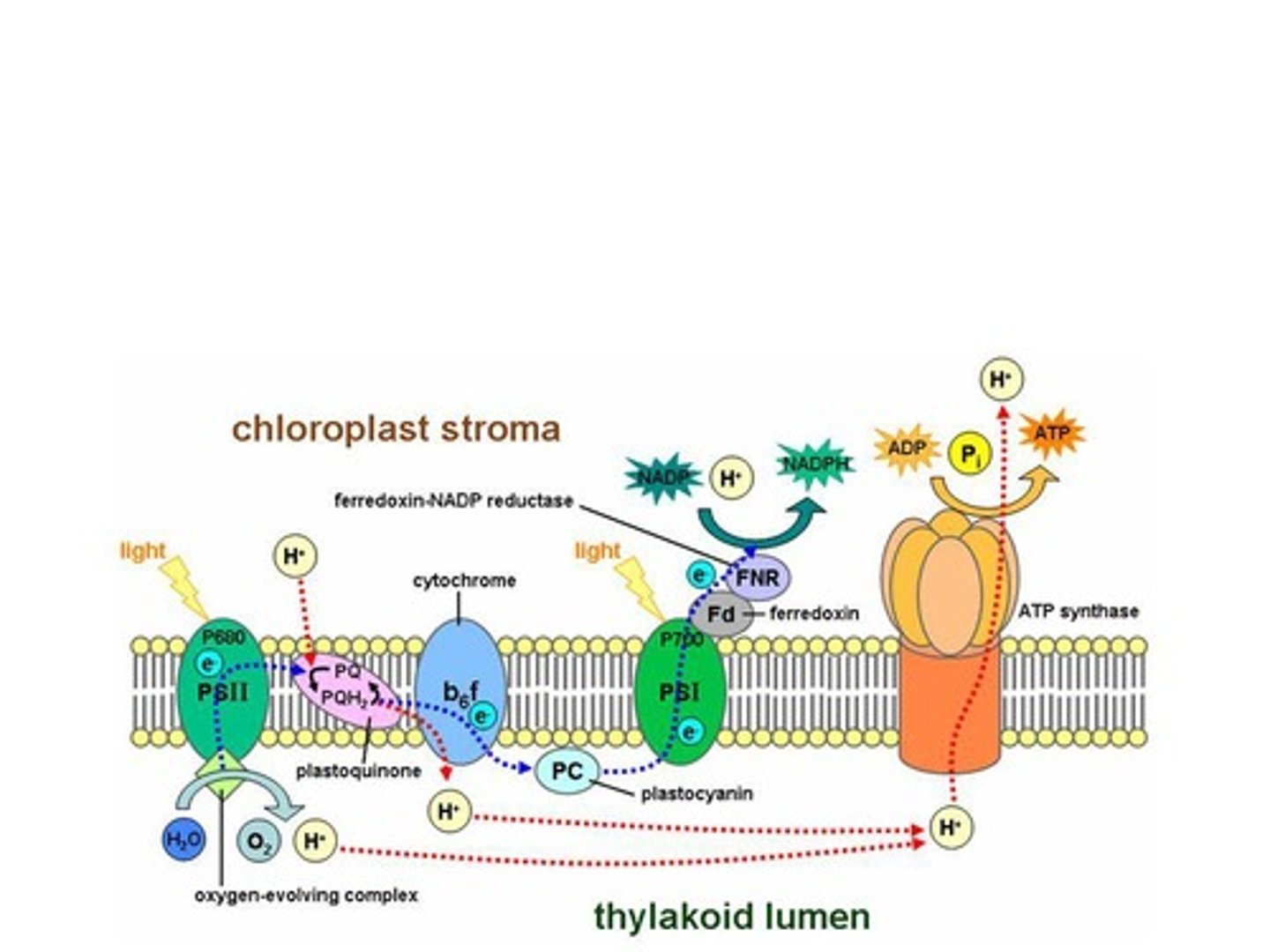
Photosystems
reaction center and light capturing complexes in the thylakoid membrane
Photosystem 2
reaction center P680 that absorbs light at 680 nm
Photosystem 1
reaction center P700 that absorbs light at 700 nm
Photosystem II
Initial stage of photosynthesis where light energy is absorbed.
P680
Chlorophyll a molecules in Photosystem II that absorb light.
Primary electron acceptor
Molecule that accepts excited electrons from P680.
H2O splitting
Process producing electrons, protons, and oxygen from water.
Linear electron flow
Pathway where electrons move from PS II to PS I.
ATP generation
Energy from electron flow used to synthesize ATP.
Photosystem I
Second stage of photosynthesis that further excites electrons.
P700
Chlorophyll a molecules in Photosystem I that absorb light.
NADP+ reductase
Enzyme that transfers electrons to NADP+, forming NADPH.
Calvin Cycle
Cyclic process using ATP and NADPH to synthesize sugars.
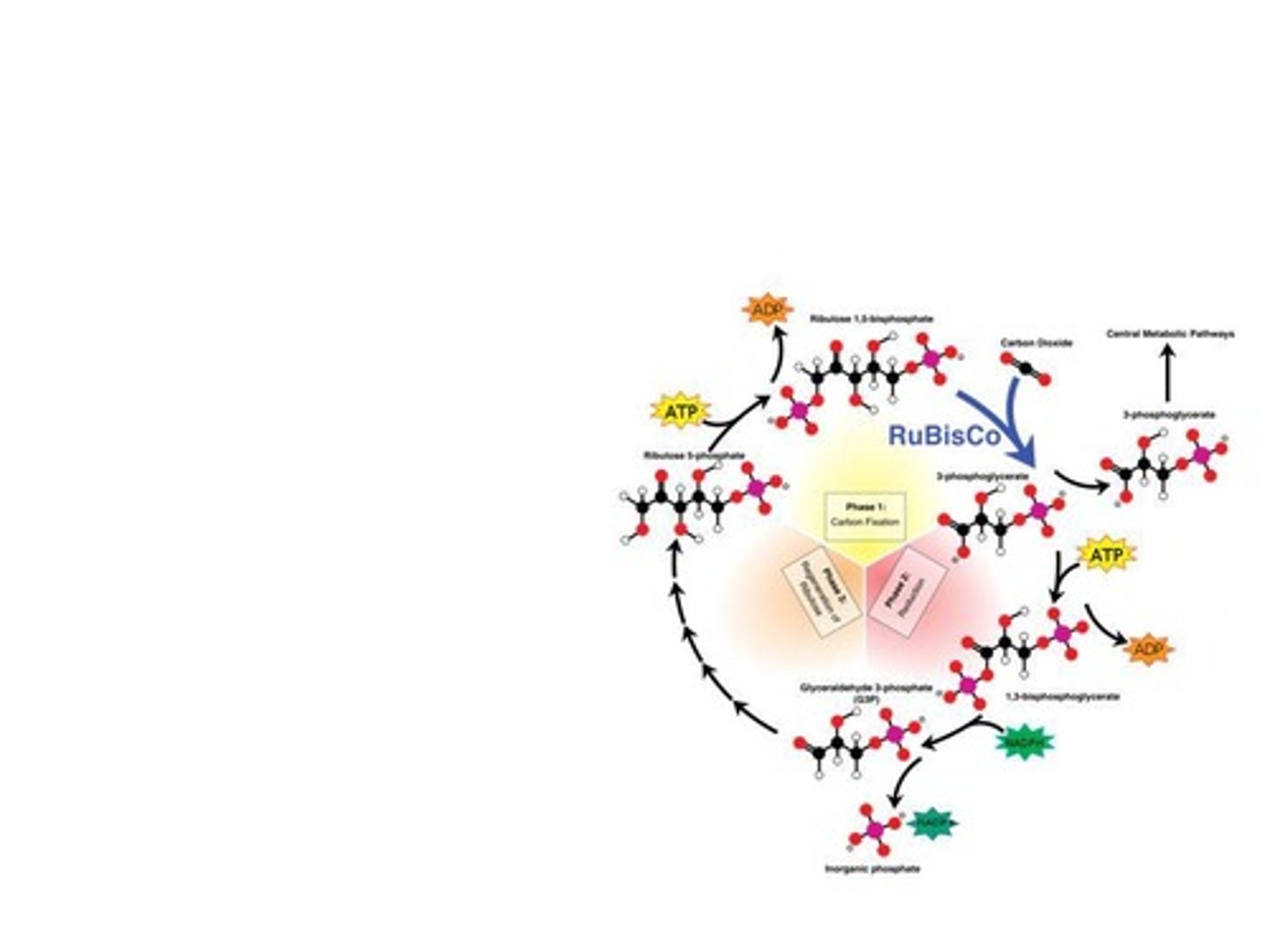
Carbon fixation
Incorporation of CO2 into organic molecules in Calvin Cycle.
Rubisco
Enzyme catalyzing the attachment of CO2 to RuBP.
3-phosphoglycerate
Product formed from CO2 and RuBP during carbon fixation.
G3P
3-carbon sugar produced in the Calvin Cycle.
Photorespiration
Inefficient process where Rubisco binds O2 instead of CO2.
C4 plants
Plants with spatial separation of carbon fixation steps.
CAM plants
Plants that fix CO2 at night to conserve water.
Electron transport chain
Series of proteins transferring electrons from PS II to PS I.
Thylakoid space
Compartment where protons accumulate during electron transport.
NADPH
Reduced form of NADP+, used in Calvin Cycle.
ATP synthase
Enzyme that synthesizes ATP using H+ gradient energy.
Oxygen release
By-product of water splitting during photosynthesis.
6 NADPH
Amount of NADPH needed to reduce 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
3 ATP
Amount of ATP used to regenerate RuBP in Calvin Cycle.
9 ATP
Total ATP required for one cycle of Calvin Cycle.
9 ADP
By-product of ATP usage in the Calvin Cycle.