Module 1: Embracing Environmental Science
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:10 PM on 9/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
What is Environmental Science?
It is a science revealing the ***relationship*** between human activities and the environment.
2
New cards
What are the **three** **(3)** environmental processes?
* Physical Processes
* Biological Processes
* Chemical Processes
* Biological Processes
* Chemical Processes
3
New cards
What are ***physical*** processes?
These are processes shaping and influencing Earth’s physical features, creating constant change.
4
New cards
What are ***biological*** processes?
These are processes sustaining balance in ecosystems and are vital for organisms to function.
5
New cards
What are ***chemical*** processes?
These are processes producing or converting new chemical substances essential to humans and the environment.
6
New cards
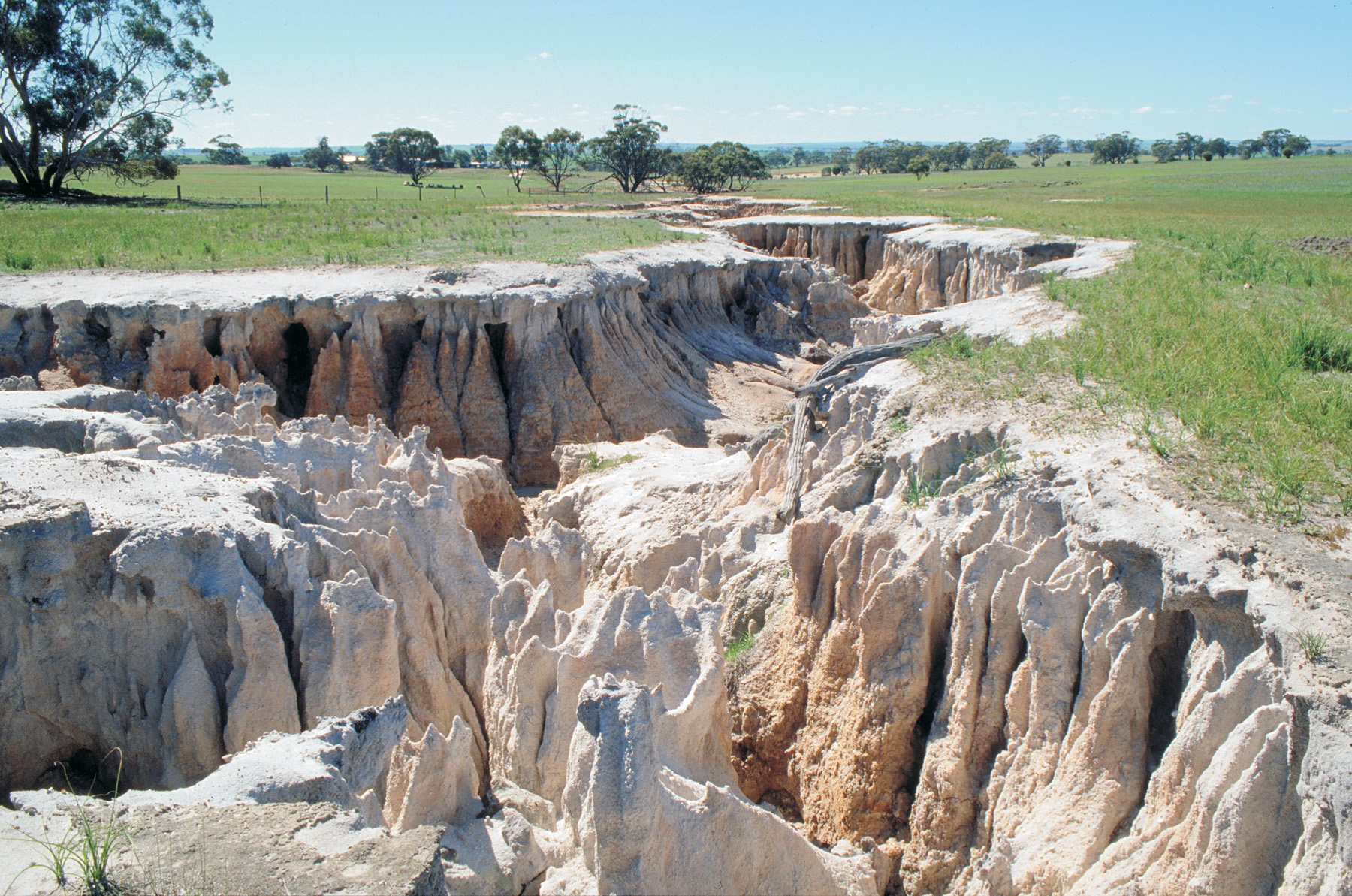

What kind of process is this?
Physical Process
7
New cards
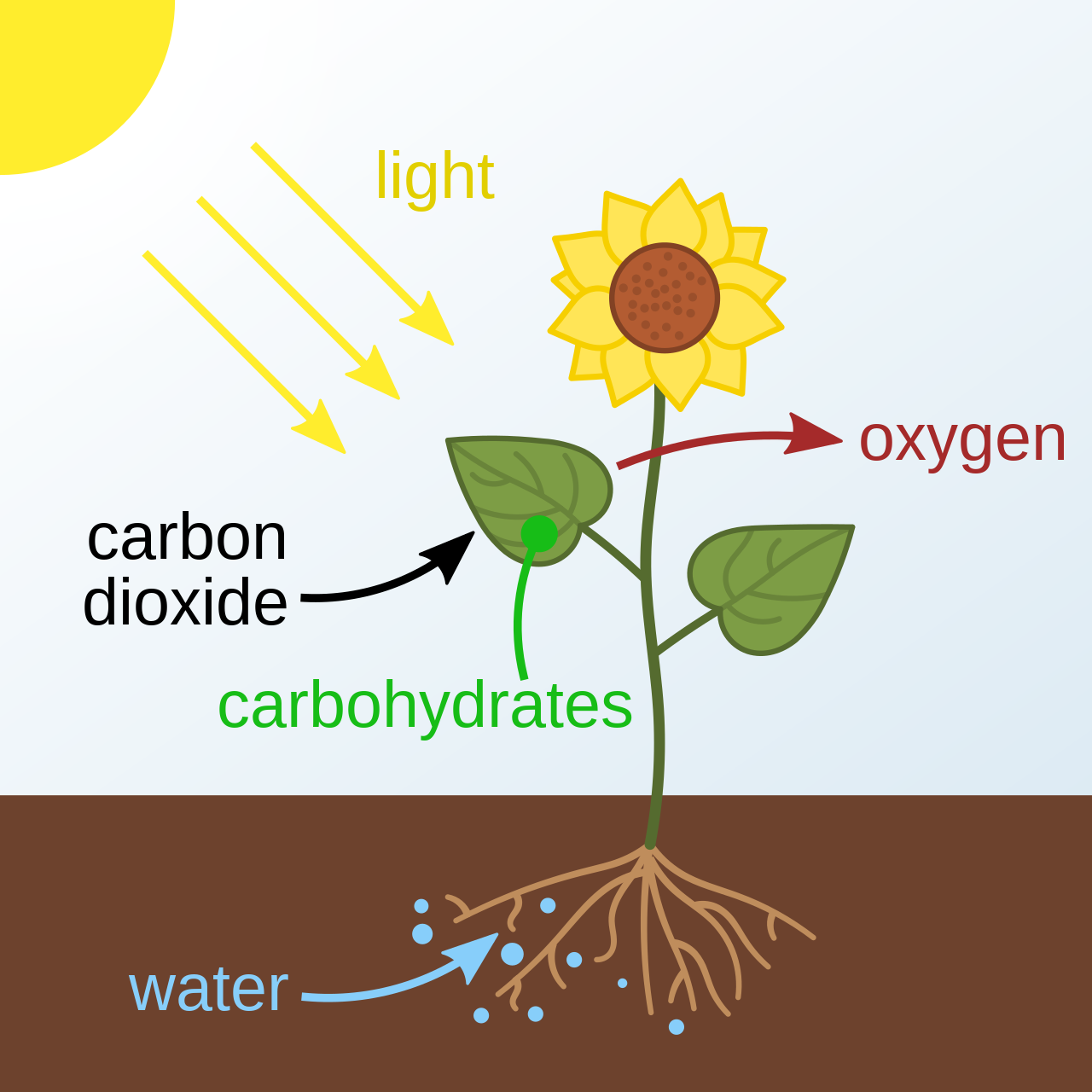
What kind of process is this?
Biological Process
8
New cards
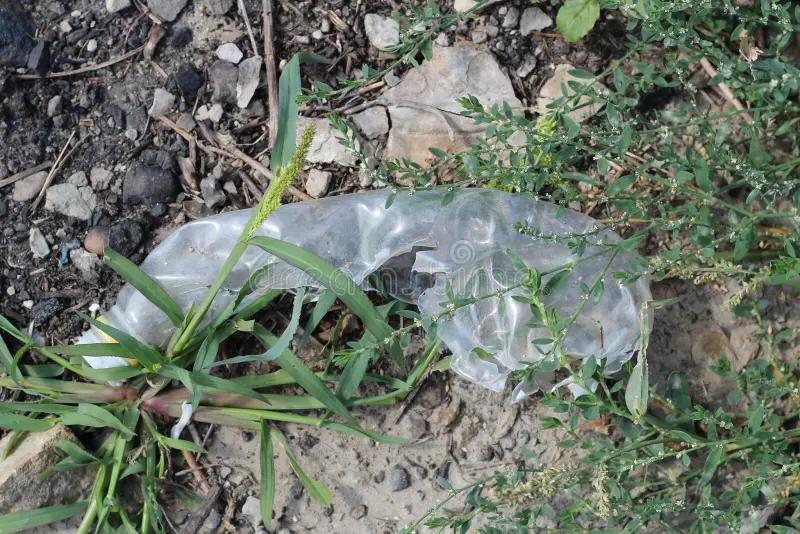

What kind of process is this?
Chemical Process
9
New cards
What **four** **(4)** topics make Environmental Science Interdisciplinary?
* Species Restoration
* Resource Management
* Environmental Laws
* Sustainability
* Resource Management
* Environmental Laws
* Sustainability
10
New cards
What are the **three (3)** tenets of sustainability?
* Environment
* Economy
* (Social) Equity
* Economy
* (Social) Equity
11
New cards
What are the **four (4)** types of ecosystem services?
* Provisioning Services
* Regulating Services
* Cultural Services
* Supporting Services
* Regulating Services
* Cultural Services
* Supporting Services
12
New cards
What is a Provisioning Service?
They are the direct products of an ecosystem.
13
New cards
What is a Regulating Service?
These are processes regulating natural systems.
14
New cards
What is a Cultural Service?
These are the non-material benefits contributing to the development and cultural advancement of peoples.
15
New cards
What is a Supporting Service?
These are processes supporting life.
16
New cards
“Food, Water, and Oxygen” are examples of?
Provisioning Services
17
New cards
“Aquifers and Wells and Pollination” are examples of?
Regulating Services
18
New cards
“Aesthetic Inspiration, Cultural Identity, Recreation, Spiritual Experience” are examples of?
Cultural Services
19
New cards
The “Water Cycle” is an example of?
Supporting Service
20
New cards
What ecosystem services does Photosynthesis belong to?
* Regulating Services
* Supporting Services
* Supporting Services
21
New cards
What are the **six (6)** important steps of the scientific method?
* Observation
* Research
* Hypothesis
* Experiment and Data Collection
* Data Analysis
* Drawing Conclusions
* Sharing Results
* Research
* Hypothesis
* Experiment and Data Collection
* Data Analysis
* Drawing Conclusions
* Sharing Results
22
New cards
What are the **two (2)** types of data that can be collected?
* Qualitative (Descriptive) Data
* Quantitative (Numeric) Data
* Quantitative (Numeric) Data
23
New cards
What are the **two (2)** types of variables in an experiment?
* Independent (changeable) Variable
* Dependent (measurable) Variable
* Dependent (measurable) Variable
24
New cards
What are the **two (2)** types of experiment groups?
* Experimental Group
* Control Group
* Control Group
25
New cards
What are the **seven (7)** warning signs of pseudoscience?
1. The Use of Psychobabble
2. Substantial Reliance on Anecdotal Evidence
3. Extraordinary Claims WITHOUT Extraordinary Evidence
4. *Unfalsifiable* Claims
5. Absence of Connectivity to Other Research
6. Absence of Adequate Peer Review
7. Lack of Self-Correction
26
New cards
What is Psychobabble?
These are words sounding scientific but are used incorrectly or misleadingly
27
New cards
What is Anecdotal Evidence?
Unverifiable evidence based on personal experiences and events
28
New cards
What does it mean when a claim is “unfalsifiable?”
A claim is “unfalsifiable” when it cannot be refuted “in principle”
29
New cards
How do you define, “in principle,” within the context of an unfalsifiable claim?
“In principle” → it cannot be rigorously tested or proven using the scientific method