Dorsal columns, anterolateral sensory
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
The ascending pathway of the DC-ML includes the primary afferent with cell body in the _____
Second order neuron is in the _____ ____ ___ or ____
Fibers _____ as they exit the _____ to form the ____ ___
Third order neuron is in the ____ ___ ___ nucleus of the ____
The termination of the ____ ___ is in the _____ _ region of the ____ cortex (____ ___) Neurons in the ______ region project ____ to the _____ __ region
The ascending pathway of the DC-ML includes the primary afferent with cell body in the DRG
Second order neruon is in the dorsal nuclei cuneatus or gracilis
Fibers cross as the exit the nucleus to form the medial lemniscus
Third order neuron is in the ventral posterior lateral nucleus of the thalamus
The termination of the thalamic inputs is in the somatosensory I region of the ipsilateral cortex (Postcentral gyrus) Neurons in the somatosensory I region project bilaterally to the somatosensory II region
Trigeminal component of the DC-ML system has a primary afferent with cell body in the _____ ____
Second order neuron in the ____ ____ of ____
Fibers from the ____ ____ of ___ cross the ____ and ascend as the ____ ___ adjacent to the ____ ____
Trigeminal component of the DC-ML system has a primary afferent with cell body in the trigeminal ganglion
Second order neuron in the sensory nucleus of V
Fibers from the sensory nucleus of V cross the midline and ascend as the trigeminal lemniscus adjacent to the medial lemniscus
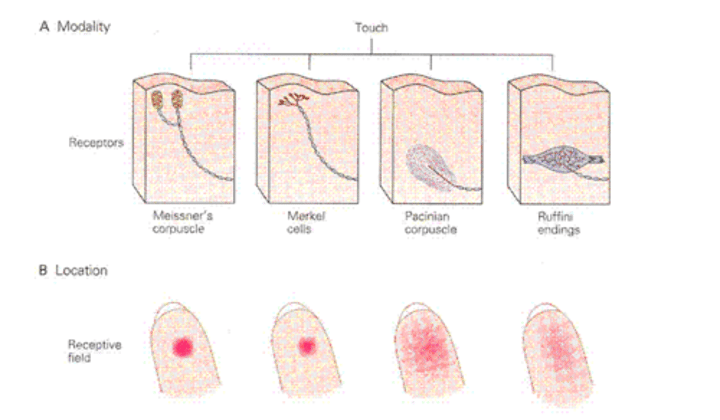
Receptors of the DC-ML system include ____ ___ which are sensitive to ____ and _____ ____
_____ ____ sensitive to ___ of lower ____ than ____ ___ and _____ ____
____ cells which are located at the base of the ___ and sensitive to ___ ___ and ____ ___
____ endings which are located in the ____ and sensitive to ____ ___ and _____ ____
These are ___-____ or ___-____ fibers
Receptors of the DC-ML system include pacinian corpuscles which are sensitive to vibration (deep dermis) and rapidly adapting
Meissner corpuscles sensitive to vibration of lower frequency pacinian corpuscles (dermal papillae) and rapidly adapting
Merkel cells which are located at the base of the epidermis and sensitive to sustained pressure and slowly adapting
Ruffini endings which are located in the dermis and sensitive to sustained pressure and slowly adapting
These are A-beta or A-delta fibers
Receptors of the DC-ML also include ___ ___ which detect ____ ___
_____ ___ ___ which detect ___ ___
____ ____ mechanoreceptors which detect ___ ____
Receptors of the DC-ML also include muscle spindles which detect muscle stretch (Ia)
Golgi tendon organs which detect Muscle tension (Ib)
Joint capsule mechanoreceptors - detect joint angle (AB fibers)
DC-ML receptors image
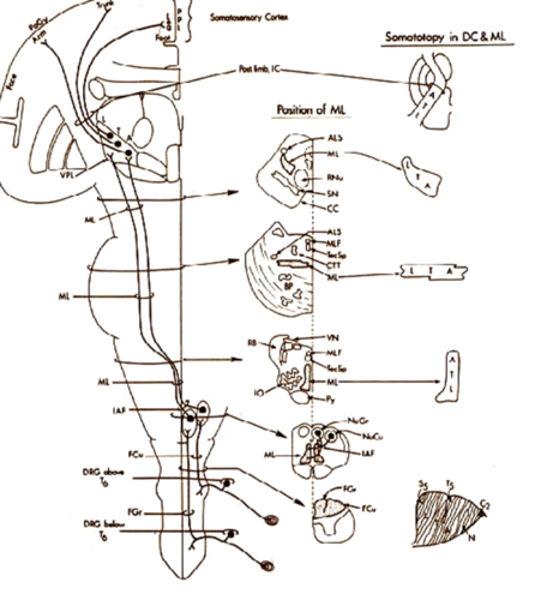
Somatotopy in the DC and ML?
The primary somatosensory cortex is ____ with respect to ____ ____ ____
3a is ___ ___
3b is _____
1 is ____
2 is ____ __ and ___
The primary somatosensory cortex is partitioned with respect to functional receptor classes
3a is deep tissue
3b is skin
1 is skin
2 is deep tissue and skin
Information encoded by particular cortical neurons includes more than the ____ ___ of the stimulus. For example, some cortical neurons are sensitive only to a ____ ____ and different neurons encode different ____ of ____
Feature extraction by higher order neurons involves combinations of ____ ____
Information encoded by particular cortical neurons includes more than the primary quality of the stimulus. For example, some cortical neurons are sensitive only to a moving stimulus and different neurons encode different directions of movement
Feature extraction by higher order neurons involves combinations of receptive fields
Feature extraction image receptive field
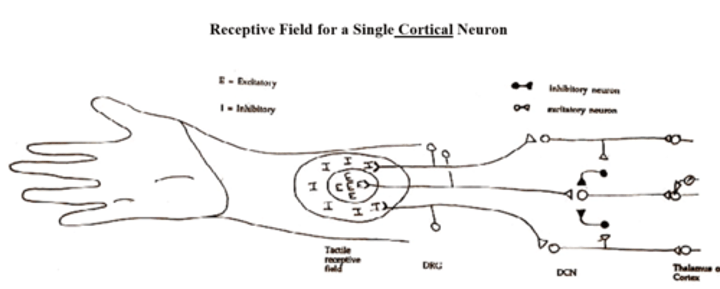
Excitation and inhibition from a cortical neuron field
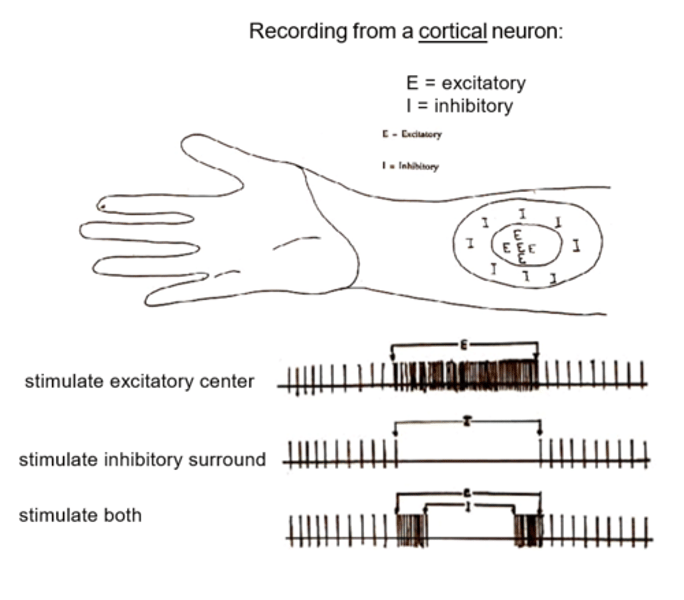
Some neurons in the somatic sensory cortex are _____ ____
Some neurons in the somatic sensory cortex are directionally sensitive
The neospinothalamic tract projects directly to the ____ and the paleospinothalamic tract relays through the ____ ____ ___ on the way to the ____
The neospinothalamic tract projects directly to the thalamus and the paleospinothalamic tract relays through the brainstem reticular formation on the way to the thalamus
The paleospinothalamic tract originates in ____ ___
This is ___ fibers (____)
It is ____ (___, ____) pain and chemically mediated ____ ___
Goes to the ____ ___, ____, and _____ ____ of the ____ - as well as the _____
The paleospinothalamic tract originates in lamina V
This is C fibers (afferents)
It is Protopathic (slow, burning) pain and chemically mediated pain sources
Goes to the reticular formation, mesencephalon, and intralaminar nucleus of the thalamus as well as the VPL
The neospinothalamic tract originates in ____ ___
This is ___ fibers (____)
This is _____ (___-____) pain and inputs induced by ____ and ____ ___
Goes to ____ ____ ___ (____ and ____ __)
Has a small _____ component
The neospinothalamic tract originates in Lamina I
This is A-delta fibers (afferents)
This is epicritic (well localized) pain and inputs induced by pressure and thermal extremes
Goes to the thalamic relay nuclei (VPL and posterior nuclei)
Has a small uncrossed component
Trigeminal components of the anterolateral tract include the primary afferents (___ and ____ fibers) with cell bodies in the ___ ____
Central process descend as the ____ ___ of ___ to synapse in the ___ ___ of ___
Neurons in the ___ ___ of __ send ____ across the ___ where they join in the _____ tract and project to the ____
_____ modalities synapse in the ____ ____ ____ ___ while _____ components synapse in the _____ _____
Trigeminal components of the anterolateral tract include the primary afferents (C and Adelta fibers) with cell bodies in the trigeminal ganglion
Central process descend as the spinal tract of V to synapse in the spinal nucleus of V
Neurons in the spinal nucleus of V send axons across the midline where they join in the anterolateral tract and project to the thalamus
Epicritic modalities synpase in the ventral posterior medial thalamus while protopathic components synapse in the intralaminar nucleus
Anterolateral tract conducts ____, _____ sensations, ____ touch, ___, ____, and ____ sensations
Anterolateral tract conducts pain, thermal sensations, crude touch, tickly, itch, and sexual sensations
Neurotransmitter associated with sensory afferents?
Substance P
mechanical afferents conducted through ____ ___ fibers
Thermal afferents conducted through _____ _____ fibers
Polymodal nociceptors conducted through ____ fibers
Mechanical afferents conducted through A delta fibers
Thermal afferents conducted through A delta fibers
Polymodal nociceptors conducted through C fibers
The mechanism by which nerve terminals sense specific modalities such as temp and specific chemicals depends on ____ channels which transduce _____, ____, and ____ stimuli into ____ ____ - these are _____ ____ ____ channels
The first to be ID'd was _____ which responds to _____
The mechanism by which nerve terminals sense specific modalities such as temp and specific chemicals depends on TRP channels which transduce thermal, chemical, and mechanical stimuli into inward currents - these are non selective cation channels
The first to be ID'd was TRPV which responds to capsacin
Nocireceptors are activated by compounds released when ___ is _____. They utilize the _____ channels to generate a potential. _____ ___ mediated processes carry sensations described as _____
_____ ____ mediate long lasting or ____ pain
Nocireceptors are activated by compounds released when tissue is damaged. They utilize the TRP channels to generate a potential. A delta mediated processes carry sensations described as epicritic
C fibers mediate long lasting or protopathic pain
Protopathic pain is the type of pain that is more clinically ____ to treat. All the receptors are ____ ___ ____
They can be responsive to ___, _____, _____, or ____ - they can also be _____ by ____ and ______ ___ so they are more responsive - this is called ____
Protopathic pain is the type of pain that is more clinically difficult to treat. All the receptors are free nerve endings
They can be responsive to K+, histamine, bradykinin, or serotonin - they can also be sensitized by prostaglandins and tissue damage so they are more responsive - this is called hyperalgesia
There are no CNS neurons specifically devoted to ____ ____ - instead _____ afferents converge onto the same _____ neurons that mediate ____ ___
The convergence takes place at the ____ of the ____ ___
Lamina _ and _ cells that give rise to the ____ ____ receive ____ input from both ____ and ____ receptors
There are no CNS neurons specifically devoted to visceral pain - instead visceral afferents converge onto the same CNS neurons that mediate somatic sensation
The convergence takes place at the level of the spinal cord
Lamina I and V cells that give rise to the anterolateral tract receive convergent input from both somatic and visceral receptors
The somatic stimulus takes _____ in ____ ___ - thus ____ __ is referred to the _____ ____ from which the ____ input arose
The somatic stimulus takes precedence in central processing - thus visceral pain is referred to the somatic site from which the convergent input arose
The ability of _____ activation to diminish traffic in the ____ pathways is the mechanism for ____ ___ ___ as a pain therapy
The ability of AB activation to diminish traffic in the pain pathways is the mechanism for transcutaneous nerve stimulation as a pain therapy