APUSH TERMS
1/226
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A complete guide to major terms in AP US history
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
227 Terms
Encomienda system(definition+time period)
Who were they used by?
Why?
Used in early Spanish colonization.
Forced labor of Native Americans, often brutalized and exploited.
It allowed Spanish settlers to demand tribute and labor from indigenous peoples in exchange for protection and Christianization, primarily during the 16th century.
The benefits were often not given. This system was predominant in the Americas from the early 1500s to the early 1700s.
Asiento System
What did it accomplish in legal stuff?
Required colonists to pay tax per imported slave, allowing legal slave trade in Spanish colonies from the 17th century onward.
These were Africans
Spanish Caste System
(Hierarchy)
Created in response to what?
A social hierarchy based on racial background in late Spanish colonization as the racial pool grew more diverse. Pure Whites were on top(as per usual)
Early colonization: Spanish treatment to Natives
Brought diseases that wiped out large populations of indigenous peoples.
Exploited labor through the encomienda system
Early colonization: English treatment to Natives
Met far less Natives(most were wiped out)
Initial relationships were mutually beneficial but then devolved into exploitation again as the Natives were deemed as “inferior”
Exploited land by driving many Natives off their territory
Early colonization: French treatment to Natives
Were not focused on colonizing
Far less conflict with Natives
Actually had a mutually beneficial relationship as they traded goods
Assisted Natives with their conflicts(allies)
Jamestown & Plymouth
What were they the 1st of?
First successful British colonies
Spanish-French-Dutch-British-Portuguese
What did these lads do in the Americas
European nations involved in colonization of the Americas
Corporate Colonies
Colonies funded by private companies, where investors aimed for profit. - Sole purpose was to generate MONEY $$$
Royal Colonies
Owned directly by the English Crown directly, and governed from officials of the Crown.
Proprietary Colonies
Land Charters given by the King in return for some form of service.
Operated by the person who got the charter. Not the King.
Plymouth(mayflower)-1620
Massachussets Bay-1629
Why and How were these two colonies founded
Was founded by dissident Protestants leaving England to flee from religious prosecution.
Was founded by Puritans also fleeing from persecution(after the Protestants)
Halfway Covenants
Why were these created?
A way for Puritan ministers to amass members in an age with weakened religious participation
You now no longer need a “full conversion” to be accepted
House of Burgesses(1619)
1st of what kind of idea?
Dominated by who?
Organized by settlers in Virginia to include more representation
Largely dominated by elite WHITE MALE planters
Trans-Atlantic Trade
The system of trade between Europe, Africa, and the Americas
involves the exchange of enslaved people, goods, and raw materials.
Very profitable
Mercantilism
Effects?
An economic theory that prioritizes feeding the “mother country” by trading exclusively with that country
Expected from the 13 colonies
The 13 colonies did not get fair import or export prices
Slow economic growth
Salutary Neglect
was a result of what?
England was so far away from the 13 colonies they couldn’t control everything(they also had larger problems to deal with)
Allowed for lax trade regulations
Smuggling and Pirates became commonplace
Bacon’s Rebellion
Why did it occur?(in protest of what?)
An armed uprising in 1676 by Virginia settlers led by Nathaniel Bacon against the colonial government,
Protested against injustices such as high taxes and lack of protection from Native American attacks.
RAHHHHHHH tensions increased
New England Confederation
What did it try to accomplish?
A brief alliance of New England colonies in 1643 to protect common interests like defending Native American attacks
Set a precedent of colonies uniting
Metacoms War(1675-1676)
Effects of the War?
A conflict between colonists and Native Africans
The chief of the Wampanog tribe, Metacom (King Philip), led an uprising against English settlers in New England
He lost resulting in a devastating war that significantly weakened Native American resistance in New England
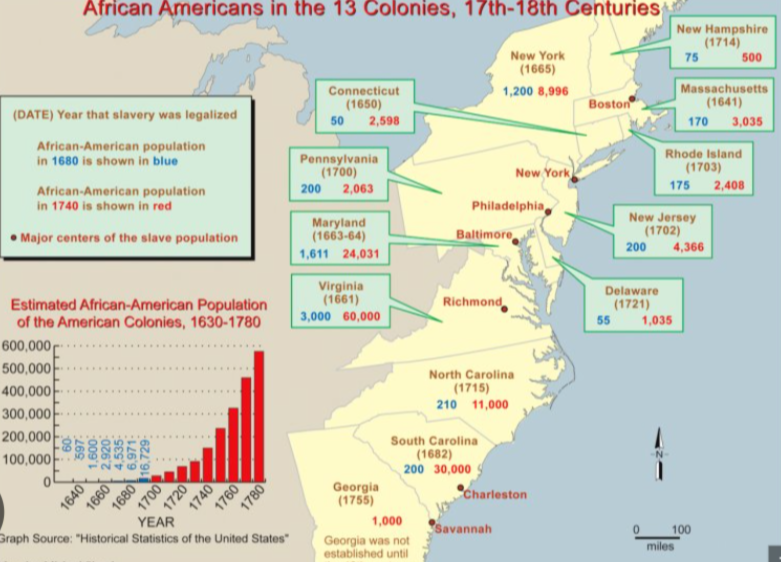
Slavery in the 1700’s
What were the different regions and their usage in Slavery
The North had more family farms and less use of Slavery
The South had more plantations and relied heavily on slave labor for cash crops like tobacco and rice.
The Great Awakening (1730-1770’s)
What was it?
Why was it important for the American Revolution?
A religious revival across all Europe and America
Drew emphasis on human sin and damnation
Increase in emotionalism
Ministers lost power and more power studied the Bible by themselves
Fueled ideas of autonomy and thinking for themselves to be independent thinkers, contributing to revolutionary sentiment.
Zenger Case
What did it accomplish?
During what time period?
Promoted the Freedom of Press
Colonial period(1734)
What were the colonies relationship with Britain before 1750?
What was gud?
What was bad?
Growing divergence from Britain as the colony’s self-governence led to a level of autonomy and independence
Surfacing tensions over trade policies
Was overall still good and colonists still considered themselves British citizens
What was the Treaty of Paris(1763) and what did it accomplish
(acquired land) as a result of Britain’s victories in the wars between 1689-1748?
Effects on the British empire
Effects on American colonies’
Ended _______ neglect
*note that there are many so called “Treaty of Paris’” and try not to get confused. This one is sometimes referred to as “Peace of Paris”
Great Britain became the supreme authority in North America
No more French influence(NOOOOO)
American colonies no longer faced threats
British demanded the American colonies to pay for the War. They justified it by stating that they protected the colonists which is honestly fair.
Ended Salutary Neglect and Britain became more attentive to trade regulations
Proclamation of 1763
(British induced)
Why did the British do this?
Was the first attempt made by the British to tax the colonies to pay for the 7 years war
Distinction between Great Awakening and Great Enlightenment
While both occurred during similar time periods
The Awakening emphasized emotionalism and a closer personal connection with God(drawing power away from ministers) and allowed people to believe in their own values
The Enlightenment emphasized science and reason but also allowed people to question the concepts on a Monarch(a “god-given” title/power)
Both fueled ideas of the American Revolution
Taxation w/o Representation
What did the Colonists think of this?
Colonies were unable to elect their own officials to the British parliament
Had no say on the taxes implemented
Fueled anti-british sentiments as colonists felt their rights were being violated by British rule.
Sugar Act
Quartering Act
Stamp Act
What did these have in common?
What reaction did the Colonists have?
Acts passed by King George III to pay for the War
Colonists were infuriated at THESE ATTEMPTS TO DENY THEM THEIR CIVIL LIBERTIES!!!
(1764-1765)
Stamp Act congress & Sons & Daughters of Liberty
Why were these organizations formed?
Organizations formed to oppose the Stamp Act and British oppression in general
Boycotts were very common
Declaratory Act of 1766
Why was this passed?(in response to what other act)
Repealed the controversial Stamp Act
Was a AWOOOO in a baaaaa clothing and it hid a sneaky term in there: Allowed parliament to create laws & taxes in any case
Colonists were just happy to be rid of the Stamp Act
Townshend Acts
Why were these Acts passed?
tried to gather more money and assert British dominance:
Placed tax on basic amenities like Chewbacca furry mugs
Allowed Bri’ish soldiers to search private homes
Upon public protest (and boycotts)was repealed and brought political peace for a brief moment of time
What was the Boston Tea Party and why did it happen?
Colonists being petty and not wanting to buy British tea in protest to the Tea Act of 1773 that made it cheaper
They dumped lots of tea into the ocean
In retaliation parliament passed the Coercive acts
The Coercive Acts
Why were they passed?
What did it aim to happen and what actually happened?
Georgie III and Petty Parliament passed these acts to punish Massachusetts for the Boston Tea Party.
Closed Boston Harbor and restricted town meetings, aiming to reassert British control over the colony.
In reality, the Colonists just got mad
Dubbed the “intolerable acts” by the colonists
Quebec Act(1774)
Passed in tandem with what other act?
What did it do?
Passed with the Intolerable Acts
Repositioned all of the Canadian territories from the French, setting up a government WITHOUT A REPRESENTATIVE ASSEMBLY(OH NO) and took land from the American colonies
The Great Enlightenment
What influence did it have?
Major concepts of “Enlightenment”
Caused philosophical justifications to go against the British, inspired by ideas of liberty and equality
Deism- A belief in god but not in its intervention
Rationalism- Trusting human rationale rather than religious BS(science)
Social Contracts- A shared set of rules created by a group of people to promote liberty and equality(like a government)
“Common Sense” by Thomas Paine
What did it accomplish?
Through attacking the idiocracy of British rule over the colonies, argued for independence
Rallied and riled up colonists
First Continental Congress
Why were they assembled?
Who’s grievances did they try to avenge?
A assembled force on delegates from each colony except Georgia
Met at a convention in Philly in 1774 to discuss next steps to deal with Britain’s threat to their liberties
Most delegates wanted to keep British ties at this point which was very clear in their letter than they were willing to make concessions and collaborate
Declared grievances to the British Crown
The King said hell naw and declared MA to be in a state of rebellion, placing more troops in Boston
Bro’s just petty
Suffolk Resolves
Opposed who?
What did it detail?
Endorsed by 1st Continental Congress and opposed British oppression over the colonies
Called for immediate removal of Intolerable Acts(coercive Acts)
Called colonies to form militias and prepare for potential conflict.
Battle @ Lexington & Concord
Why did it happen?
Significance?
British came to take weapons from the colonists
They marched and achieved it, but not before severe fighting broke out
Signaled the start of armed conflict between Britain and the colonies, igniting the Revolutionary War.
“Declaration of the Causes and Necessities for Taking Up Arms”
Why was it declared?
What was it?
Who did it place in charge?
Was a response to the Battle of Bunker Hill(the first major full-scale conflict of the Revolutionary War)
Called for colonists to take up arms and become troops
Placed good ol Georgie Washington as commander-in-chief
The Declaraion of Independence?
Was in response to what specific action
Who’s ideas did they follow?
Was in response to Parliament’s Prohibitory Act, which declared all colonies in rebellion after they had a last ditch effort(olive branch) to make peace…
The Declaration of Independence:
Richard Henry Lee declared the colonies independent in June 7, 1776
T. Jefferson, amongst the 5 delegates drafted a statement in agreeance with Lee’s work
The Congress adopted these two and on July 4th, 1776, declared Independence
British in the Revolutionary War
Advantages?
Lots of resources'
Experienced in waging war
Wealthy economy
Trained Army
Strongest Navy
Support from loyalists(Tories)
Patriots in the Revolutionary War
Advantages?
What did troop enrollment look like?
Most were reluctant to travel outside home states
Would serve in local militia for short periods of time then go back to work their land
Washington never had more than 20,000 troops at one time
Were short on supplies
Were rarely paid
Had a strong commitment to independence → resilience
Battles of Saratoga(Oct 1777)
What was its significance?
A Patriot win against the British and persuaded the French to openly ally with the Colonists(they never liked the British)
Marks a turning point in the Revolutionary War
Treaty Of Paris 1783
Significance?
Why was it signed?
Formally ended the Revolutionary War, recognizing American independence and establishing boundaries for the new nation.
It was signed due to pressure from the Whig party in Parliament to end the War after it had been going south for them
Republican Motherhood
What did it call women to do?
Influenced by Revolutionary ideas
Called for women to educate their children on the values of liberty, equality and democracy
Articles of Confederation
Written by which group?
What did it state?
Where was its weakness(clue)?
Effects?
Was the first constitution of the United States written by the 2nd Continental Congress
Gave the federal government very weak powers to avoid another tyranny like Britain
One major weakness is it couldn’t directly tax states or regulate commerce(had no money power)
As a result, the U.S as a whole was weak, and struggled to pay debts and internal divisions emerged between states with conflicting interests
Shay’s Rebellion(1786)
Why did it happen?
Highlighted what weakness within the U.S at the time?
A revolt led by Daniel Shays to protest against the high state taxes and aggressive debt collection practices in Massachusetts
Highlighted the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation.
The CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION(1786)
Was a result of what weakness?(clue)
Made up of which specific demographic?
What was their main concern?
What did the convention decide on these topics:(Power-Representation-Slavery-Commerce-Presidency)
Persuaded by James Madison and Alexander Hamilton, 55 delegates from all states(except Rhode Island) met up to discuss the problems with the Articles of Confederation
Made up of rich old white men and bokchoys
The delegates wanted a stronger federal government in varying levels
Separation of Powers to reduce risk of tyranny
Representation through a bicameral legislature(Conneticut Plan/Great Compromise)
slavery was addressed with the Three-Fifths Compromise
The Commercial Compromise allowed congress to regulate commerce and place tax on imports(not exports though)
The President was decided to serve 4 years(with no limit to how many terms)
Ratification of the Constitution?(1787-1788)
What were the two sides?
What was the solution?
The two opposing sides were the Federalists and Anti-Federalists(not the most creative)
To appease the Anti-Feds and to achieve Ratification, the Feds promised a Bill of Rights to ensure basic freedoms
Main ideas of the Constitution:
Separation of powers(Legislative-Executive-Judicial)
Checks and balances
federalism(splitting state and federal powers)
individual rights
popular sovereignty.
idk if you want/need to memorize these, but could be useful to review: Government in 1788:
What are the 3 branches of the U.S
What did the Bill of Rights include
Legislative- created laws and taxes
Executive- Enforced those laws led by the president
Judicial- Interprets the laws and the Constitution as a check
Here is the original text directly from the Bill of Rights:
Freedom of speech, you can criticize anyone and anything ANYWHERE
People can have guns
Soldiers, even in times of war cannot come into your house without your permission slip
People cannot search you or your property without a warrant
If you have done bad things, you cannot be convicted without a fair trial with a jury and you cannot be double whammied for the same offense
If you have done bad things, you have the right to a speedy and public trial
If your bad thing has exceeded the value of 20 bucks you can still have a trial
You cannot be punished weirdly or have to pay unreasonable amounts of money
Constitution cannot be denied
Powers not given to the federal government are reserved for the states
Hamilton’s Financial Program
Why was it needed?
Who opposed it?
What did it do?
What version/alteration ended up getting passed?
Hammy’s program was created because the U.S was in a crippling amount of debt from the Revolutionary War
T.Jeff opposed it(saying it only benefited the rich)
Plan:
Pay off national debt fully & the debt of the states
Protect upcoming american industries
High tariffs on imports
Create a national bank for a stable U.S currency
The version that got passed had less “high” tariffs and a compromise on the location of the capital, which moved to Washington D.C
French Revolution
Controversial because?
Who supported it?
What did Washington do?
Coinciding with Washington’s term, was controversial because the U.S was allied with the French Monarch not the Revoultion(which the public supported because they too experienced their own revolution)
T.Jeff supported joining with the Revolution
Washington took a neutral stance
Jay Treaty
Why did Americans get mad?
What (hint) land opportunities did it give the U.S?
The Jay Treaty was unpopular due to perceived concessions to Britain, including the failure to address impressment of American sailors
It opened up land opportunities in the Northwest Territory by resolving lingering issues from the Revolutionary War(The Spanish respected the U.S more)
NorthWest Confederacy(1794)
Was a group of what specific demographic?
Why was it formed?
Made up of tribes of Native Americans
To fight against the encroaching settlers stealing their land
In the Battle of Fallen Timbers, the confederacy was defeated by American forces, leading to the signing of the Treaty of Greenville.
Battle of Fallen Timbers(1794)
What treaty was made as a result?
Battle of Fallen Timbers was a conflict between settlers and the NorthWest Confederacy(Native Americans). The Natives lost.
The Treaty of Greenville, which new established boundaries
It resulted in the cession of significant territory to the United States.
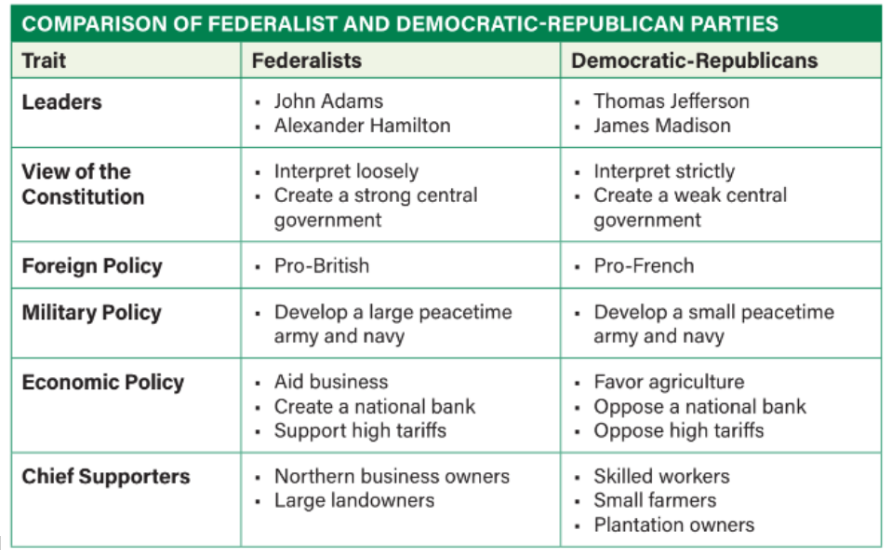
Review these: Early political parties in early United States
Reviewed? Good job!!
XYZ affair
What was it?
Influenced the American public in what way?(fueled what sentiments)
French ministers requested Bribes as a basis for negotiations for the issue of French warships seizing U.S merchant ships.
This angered the Americans and now disliked the French(no longer supported their revolution)
Naturalization Act(1790)
Alien Acts
Sedition Acts
What did these Acts do?
Why were they passed?
Made it harder for immigrants to become citizens, allowed the President to deport aliens considered “dangerous” and made it illegal for the media to criticize the Prez or Congress
Passed by the Federalist Party to weaken the base of the Demorcratic-Republican Party
Kentucky & Virginia resolutions(1790’s)
Why were they passed?
What did they accomplish?
Passed by the Democratic-Republican states to nullify the federal laws they deemed unconstitutional. (Due to Federalists passing Acts they didn’t like)
They asserted the principles of states' rights and set a precedent for future challenges to federal authority.
Growth of Slavery starting in 17__?
Due to the invention of ______ ___?
Started in 1793
The Cotton Gin(invented by Eli Whitney)
Revolution of 1800
Was the transfer of power between what 2 parties?
The Federalist Party and the Democratic-Republican Party as Jefferson won the Presidency
Peaceful
The Louisiana Purchase
Who oversaw this MASSIVE purchase?
Why was it made?
Effects?
Under Jefferson’s Presidency
Was made due to Napolean needing MONEY and Jefferson sent ministers to buy a small strip of land
Ended up getting the entire territory for a GREAT DEAL of 15 million
More than Doubled the size of U.S territory
Lewis & Clark expedition
What did it set out to do?
Who were they sent by?
Explore the Louisiana territories from St.Louis in 1804 for two years
Sent by T.Jeff
What was the influence of the Marbury Vs. Madison case in 1803?
Marshall set that the Supreme Court could exercise power to decide whether an act of Congress(or president) was allowed by the Constitution. Meaning, they could now overrule actions from the other 2 branches of government.
Embargo Act(1807)
Who created it?
Why was it bad
Was created by Thomas Jefferson in an attempt to stop the British from stealing merchant ships from the U.S
The British just ignored them and ended up hurting Americas merchants even more(was actually super bad)
Was hastily repealed and tried to be corrected with the Madison’s Non-intercourse act
THE WAR OF 1812
Causes of the War(why did the U.S get involved?)
Who opposed it?
What treaty came out of the War?
Effect on U.S economy?
The French & British were violating U.S shipping rights, Americans wanted more land, blaming the British for the Battle of Tippecanoe, War Hawks instigating the war
Quids, Merchants and some of the New England states
The Treaty of Ghent
Even prior to U.S involvement, U.S Independence strengthened as manufactured goods started to take place domestically
The Treaty of Ghent
What did it do?
Formally ended the War of 1812 between the United States and Britain, restoring pre-war boundaries and conditions. (Pretty much did nothing)
The Hartford Convention
Eradicated what political party?
Due to what event?
The Federalists, who opposed the War of 1812 and wanted seccesion(now in favor of the U.S) looked weak and whiny
Marked the decline of the Federalist Party
Monroe’s foreign policy
What was it characterized by?
VERY aggressive
VERY aggressive
Rush-Bagot Agreement(1817)
Treaty of 1818
What relations did these strengthen?
The Rush-Bagot allowed the Canana US border to be the largest unarmed border in the World
The Treaty of 1818 strengthened relations
Both signaled an era of cooperation and respect between Britain and the U.S
Florida Purchase Treaty
What time period?
1819
Spanish sold the Florida territory for 5 million
Monroe Doctrine (1823)
What did it assert?
Asserted that U.S properties & interests should not be messed with by European colonization powers.
Foreign policy was used by other Presidents in the future to justify their actions
MARKET REVOLUTION
(Industrialization)
During what period of time?
Shift from a __________ economy to a ___________ economy
This shift occurred due to what changes?
During 1815-1846
A shift from agrarian to industrial/commercial economy
Shift occurred due to improved technology and efficiency
(Farming became efficient, steamboats as tech, roads , railroads and canals developed for better transportation of goods)
Lowell System
During what period?
What was it?
During the industrial revolution
A system employing solely women and girls to work in really bad working conditions for low pay(textiles)
How did Politics change between 1824-1840’s
In terms of voting policies
Voting became less of a “rich white male thing” and became more of a “white male thing”(Universal White Male Suffrage)
Caucuses(closed to the public) were replaced by nominating conventions opened to the public
Spoils System
What is it?
A system where the Elected president would only appoint people federal jobs if they supported their party and campaign
If not, you're out of here
That’s why its called the “spoils” system, as in “spoils of war”
Peggy Eaton Affair
What effect did it have on _______ Cabinet?
Who stayed loyal(clue)?
Peggy Eaton was the wife of Jackson’s secretary of war and was the target of “malicious gossip” (she got with the secretary of war shortly after her previous husband died) and when Jackson appointed Eaton as his secretary of war, many cabinet members shunned her and some left.
However, Martin Van Buren stayed loyal and was chosen to replace the previous vice president(who left)
Indian Removal Act(1830)
Which President did this, and why?
What did this Act do?
Trail of _____ of the __________ tribe
Passed by President Jackson, and sided with the settlers to push Native Americans off their land
It authorized the forced(military force) removal of natives from their land to move further West
The Trial of Tears is considered a genocide of the Cherokee Tribe, due to its high death rate in 1838
Tariff of Abominations
Who revolted, against what?
How was it dealt with and how does it speak to ______ Presidency in general?
In 1828, South Carolina declared the “Tariff of Abominations” to be unconstitutional due to how high it was, seeking to nullify it(Kansas-Nebraska Act)
Jackson favored States rights, but NOT disunion and threatened with Military force, and declared South Carolina treasonous
What did the ever-changing “Frontier” represent to the American people?
While the physical frontier kept changing due to expansions to westward, the frontier remained a beacon of hope and opportunity for discontent or ambitious Americans seeking a new start
Cultural Nationalism
When did it really start gaining traction?
What movements did it inspire?
A strong patriotic feeling in the Americas that started gaining traction in the 1850’s
Inspired many art and literary movements that celebrated American culture and identity.
Romanticism
A shift from _____________
Expressed through ____________
A shift away from Enlightenment ideas towards more individualism and intuition
Expressed through Transcendentalists like Ralph Waldo Emerson and Henry David Thoreau(supported reforms and emphasized indivisualism)
Second Great Awakening(1780-1850)
Promoted what?
Led to _______ movements
Led by who?
Reasserted traditional Puritan teachings while also promoting new religious fervor
Also led to many social reform movements, including temperance(reducing drinking), abolition and women's rights.
Activist Religious Groups(believing in perfection)
What are some Reforms made before the Civil War?
(antebellum period)
Temperance- Reducing the sale and drinking of alcohol
Humanitarian help in Public Asylums- Jails, mental hospitals and specialized care for the disabled
Public Education- higher education and emphasis on virtues
Seneca Falls Convention(1848)
Meeting of who?
What did they publish?
What other issue within the United States shadowed the movement they represented?
A meeting of feminists
Published the Declaration of Sentiments declaring that all men AND women are created equal
The issue of women’s rights was overshadowed by the issue of Slavery at the time
American Colonization Society
What was their approach to ______?
Was it successful? Why or why not?
They figured it would be a good idea to “return” African Americans back to Africa
First attempted in 1817
Only managed to move 12,000 and was not significant to the massive 2.5 million enslaved population
What are some ways enslaved African Americans resisted Slavery?
What effect did these have on White slaveowners
Slowing/Sabotaging work
Running away(faced severe consequences)
Organizing revolts or uprisings
Creating and maintaining a distinct culture through music and oral traditions
Made slave codes more strict and southerners got more and more defensive on Slavery.
Foundation of the Southern economy during the 1850 era
KING COTTON(and other cash crops but mainly cotton)
Manifest Destiny
What was it used to describe?
Was supported by who?
Used by expansionalists to justify the U.S acquiring land as part of its divine right to expand across the continent from coast to coast(entitled butts)
The general public(especially during the 1840’s)
Webster-Ashburton Treaty (1842)
Was made due to what War?
What did it do?
The Aroostook War, which was between Maine and British ruled Canada
It settled the boundary disputes
The expansionalist zeal was captured by which political party and candidate during the 1844 election?
What did “Fifty-Four Forty or Fight” mean?
James K. Polk from the democratic party appealed to Western and southern expansionalist and won the election
Democratic Party slogan of the latitude line they wanted the border of Oregon to be
Mexican-American War
Effects?
Instigated by which Prez?
A war between Mexican and American forces that resulted in the U.S. acquiring significant territory including present-day California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas.
President James K. Polk, who sought to expand U.S. territory.
Treaty of Guadalpe Hidalgo(1848)
What did it do((objectively)
What did it do(effects on politics)
Due to what?
Mexico recognized the border to be at the Rio Grande(what the U.S wanted)
Sold the provinces of Mexico and California in the Mexican Cession, and the United States paid 15 million for this.
The newly acquired lands renewed debates on the expansion of Slavery, becoming a major cause of the upcoming Civil War
Was the result of the Mexican-America War which the U.S won
Ostend Manifesto(1854)
Who?
Why did it stop?
Highlights what debate within the U.S at the time?
Franklin Pierce(Prez) sent iplomats in secret to buy Cuba
News was leaked and the operation had to stop due to Anti-Slavery members getting MAD
Highlights how intense the topic of Slavery was getting
Wilmot Proviso
What did it attempt to do?
Why did it fail(clue)?
Was a failed attempt after the Mexican War to prohibit Slavery from the new territories
Defeated by a majority Southern senate, increasing tensions
Free-Soil Movement
What did they advocate for
(Hint: Right cause, wrong reason)
They advocated for the prohibition of Slavery to create a land of opportunity solely for White guys
Popular Sovereignty
What did it try to compromise and how?
Concept introduced by Lewis Cass to settle issues on the expansion of Slavery by allowing settlers of a territory to decide on the legality of slavery within that territory.
Appealed to moderates