W6 - DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
passive transport
no energy
simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
water and solutes cross based on concentration on either side of the membrane (concentration gradient
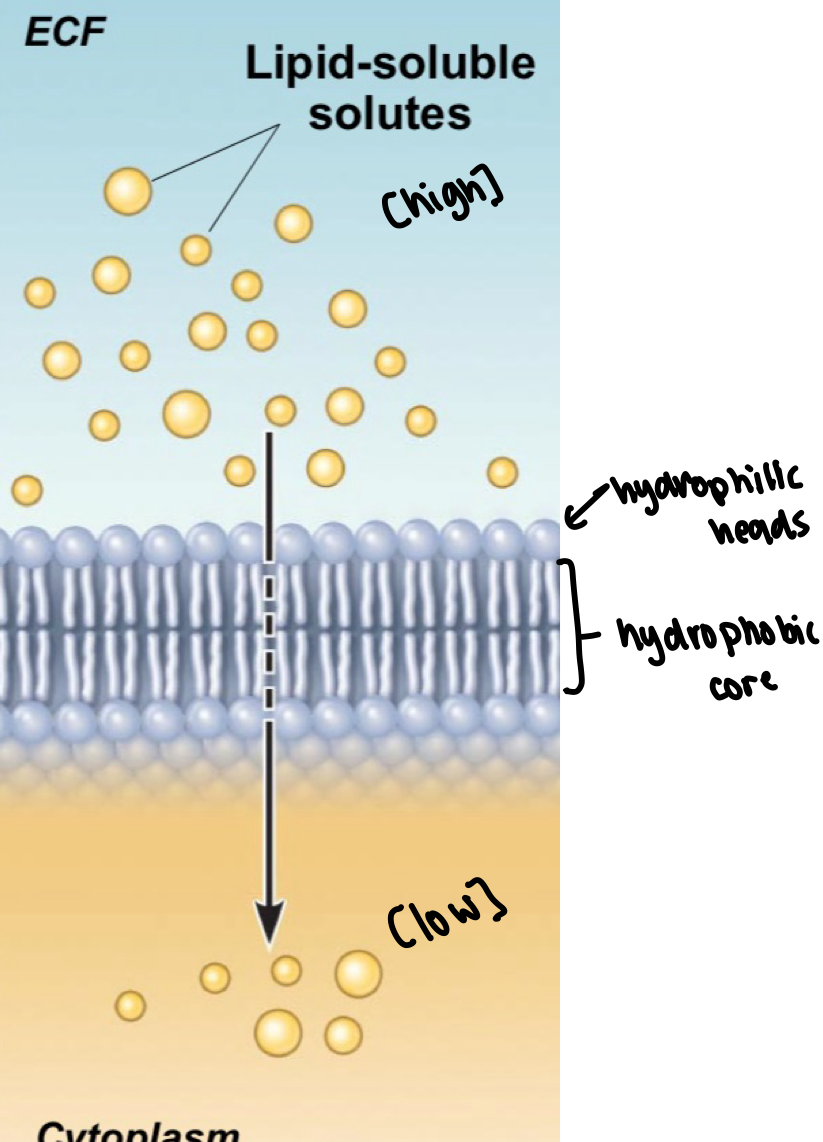
simple diffusion
lipid soluble
solute move down concentration gradient
high → low
speed influenced by size of solutes and gradient
larger difference between high and low gradient = solutes more quickly
larger solutes = slow pass through plasma membrane
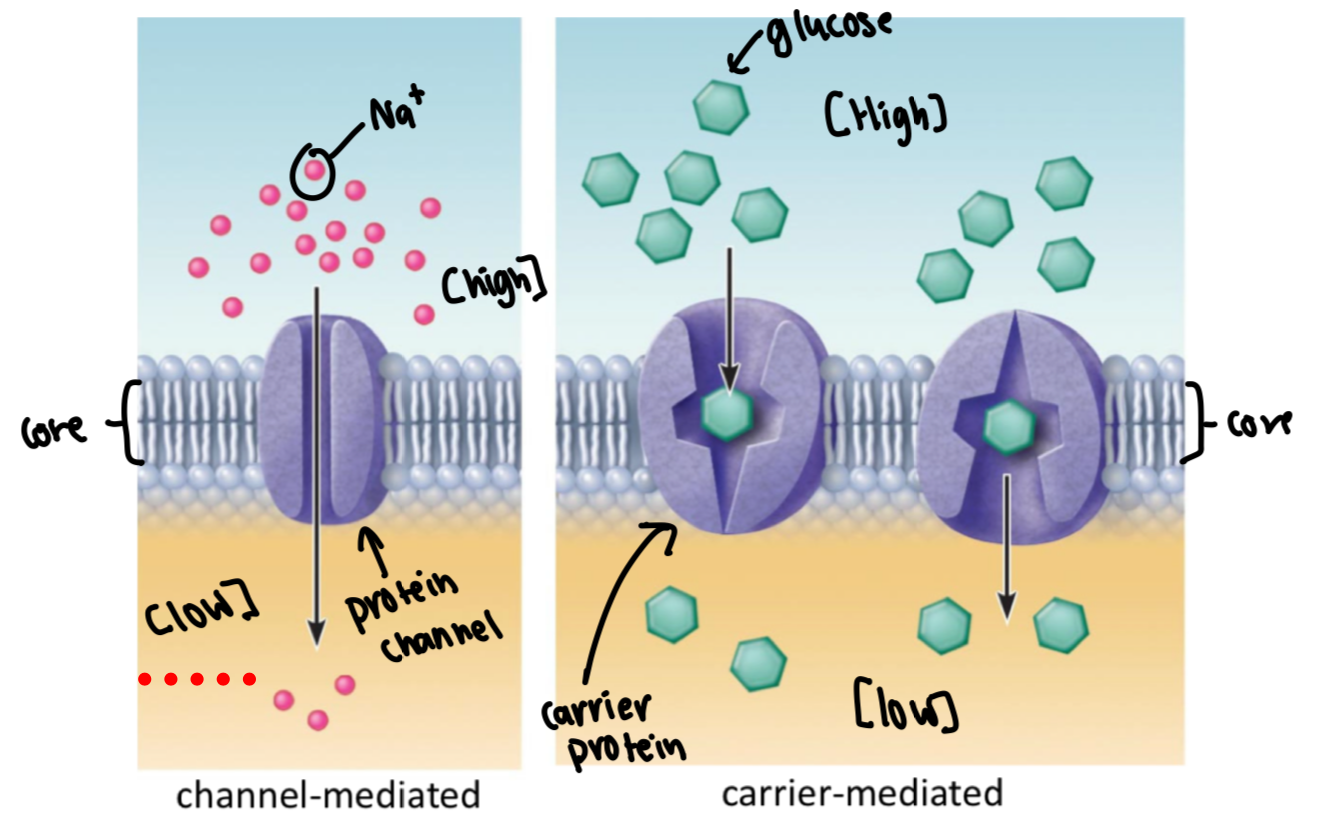
facilitated diffusion
channel- and carrier- mediated
water-soluable
solutes are “helped” across the membrane
solutes move down concentration gradient
Na+ = water soluble and can’t come into contact w/ hydrophobic core
glucose binds to carrier protein (conformational change) = allows glucose to be released on other side
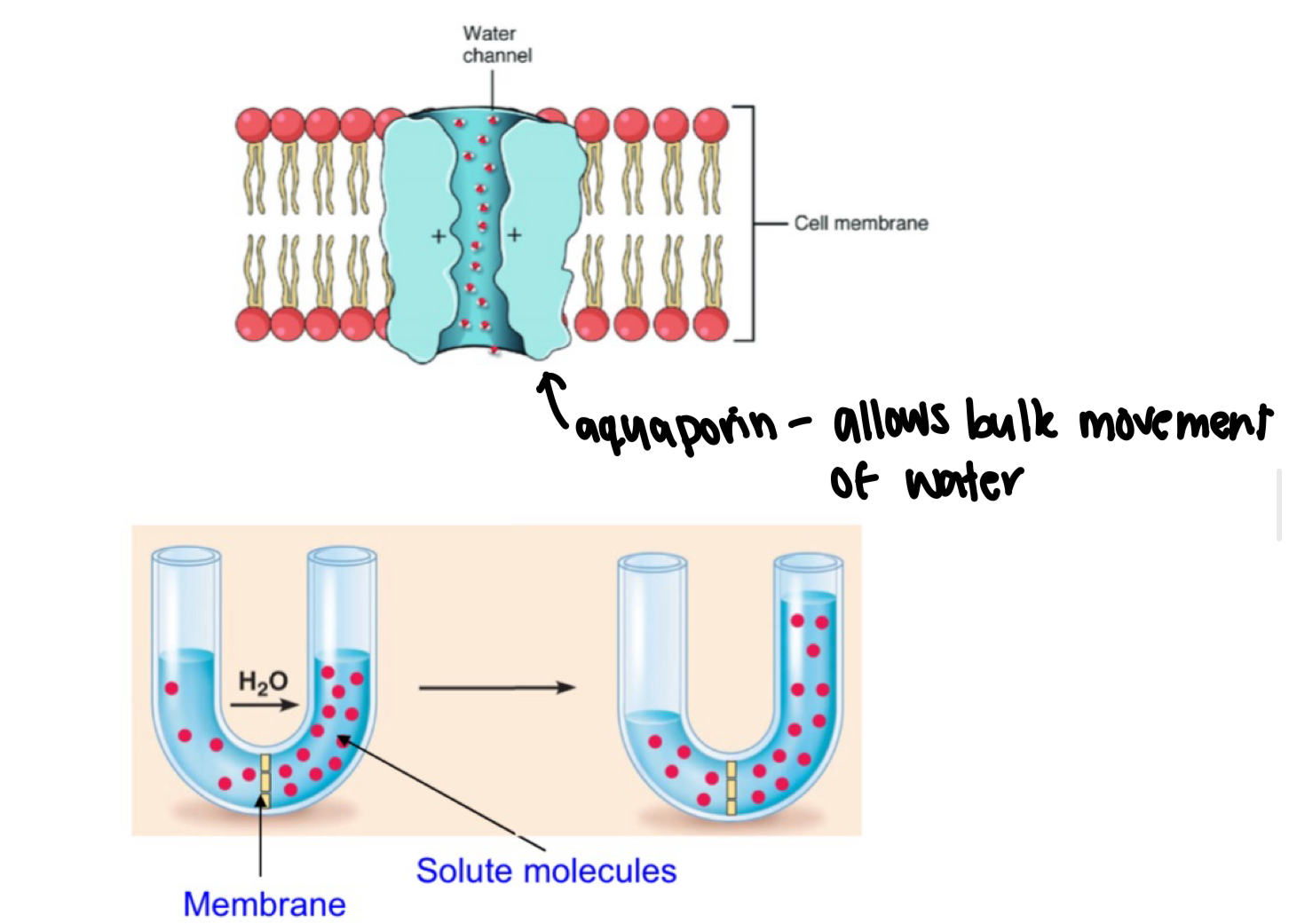
osmosis
passage of water across plasma membrane
moves through small gaps and aquaporin
helps balance concentration of penetrating and non-penetrating solutes
water touching core = disruptions to PM
PM = fluid mosaic model = movement creates gaps between phospholipid tails, allowing water to slip through
tails slight move apart
penetrating = can cross plasma membrane
non-penetrating = cannot cross plasma membrane
tonicity
the ability of a solution to change shape or tone of a cell
water moves across PM due to “non-penetrating” solutes
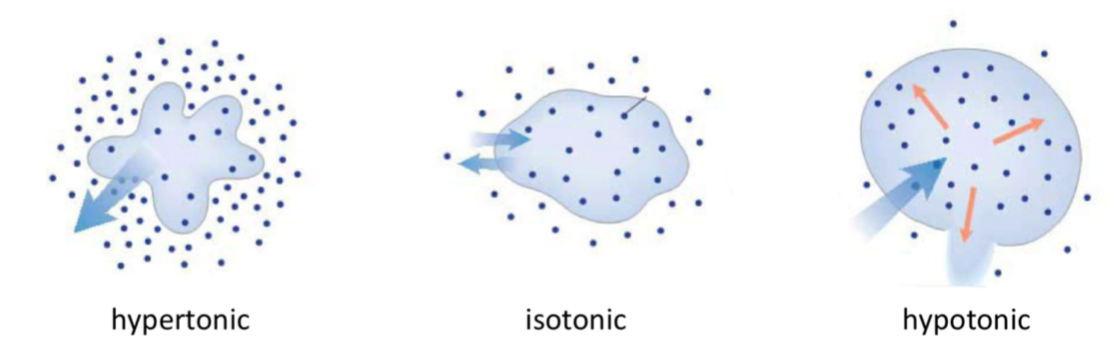
isotonic
solution on the outside of the cell is isotonic in respect to the inside of the cell
same concentration inside and out
no net movement of water - amount moving in = amount moving out
hypertonic
solution is hypertonic on the outside compared to the inside of the cell.
high concentration on outside of cell
high concentration = solutes can’t cross (non-penetrating(
water drawn out to try dilute outside concentration
cell shrinks, changing shape of cell
hypotonic
solution is hypotonic on the outside compared to the inside
low concentration on outside of cell
water pushed inside cell to balance out concentration
push PM = sell swells = too much water = burst