NEW IMPERIALISM PT. 2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Manifest Destiny
The belief that the United States was destined to expand across the North American continent; used to justify westward expansion and displacement of Native peoples.
Spanish-American War
1898 conflict between the U.S. and Spain; the U.S. gained control of the Philippines, Guam, and Puerto Rico, marking its rise as an imperial power.

Roosevelt Corollary
Addition to the Monroe Doctrine stating that the U.S. could intervene in Latin America to maintain stability; justified American imperialism… in 1904 Roosevelt sent U.S. troops to occupy a Caribbean island nation, the Dominican Republic, until it repaid its foreign debts.

Great Game
Rivalry between Britain and Russia for influence in Central Asia during the 19th century, especially over Afghanistan.

Túpac Amaru II
José Gabriel Condorcanqui….Leader of a major indigenous uprising in Peru against Spanish colonial rule in the 1780s; claimed descent from Incan royalty…he was forced to watch as his wife and sons were executed before he was tortured and executed himself.

Benito Juárez
Mexican president and reformer who resisted French occupation and modernized the country in the mid-1800s.
Sepoys
Indian soldiers employed by the British East India Company; played a key role in the 1857 rebellion…made up the majority of the British armed forces in colonial India by the mid-19th century.
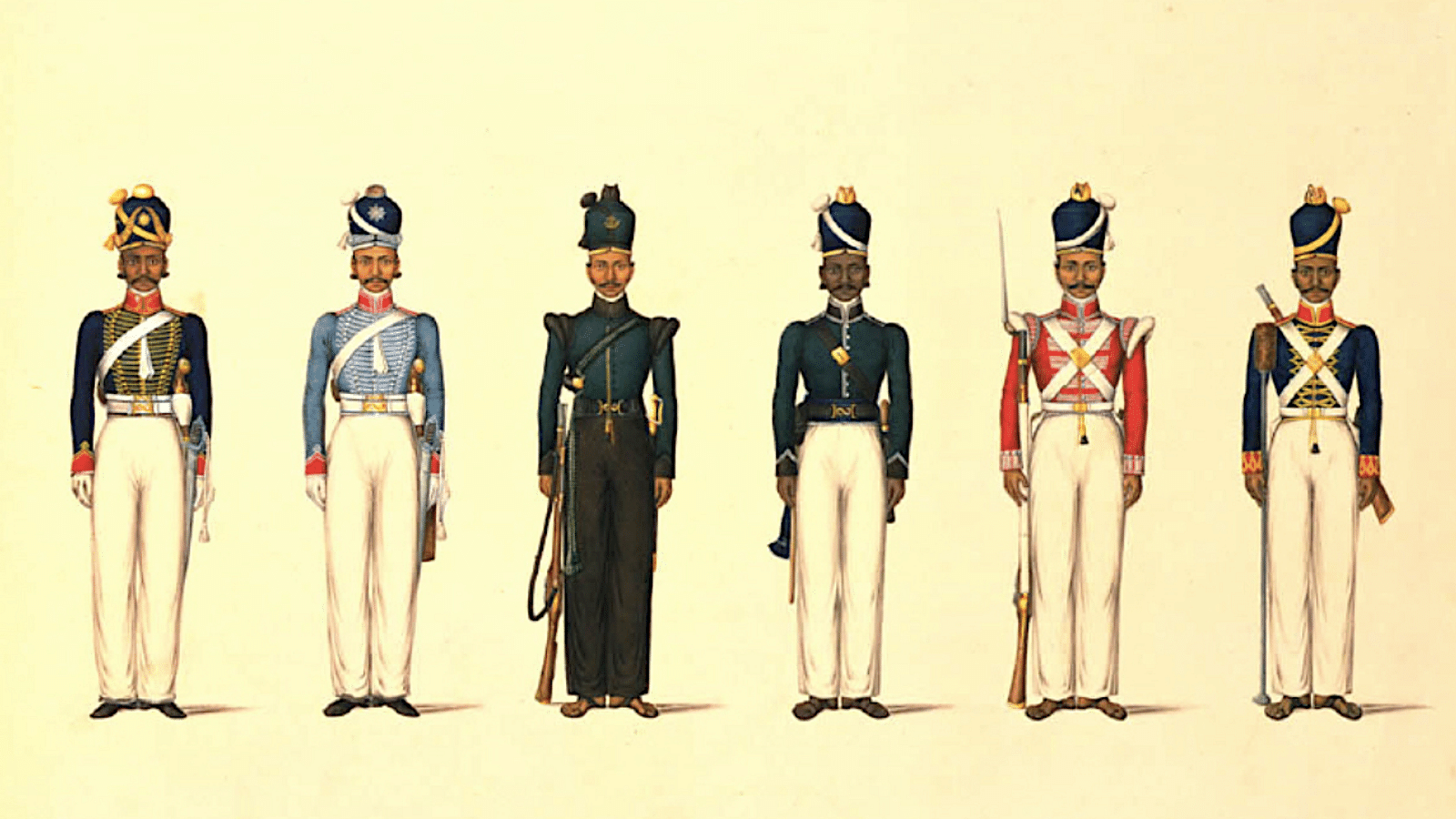
Indian Rebellion of 1857
In 1857, the British began using rifle cartridges that had been greased with a mixture of the fat of cows and pigs. Hindus, who view the cow as sacred, and Muslims, who refuse to slaughter pigs, were both furious….Major uprising against British rule in India, sparked by cultural insensitivity and exploitation; also called the Sepoy Mutiny.
Raj
The period of direct British rule in India from 1858 to 1947, following the suppression of the Indian Rebellion…( BRITISH COLONIAL GOVERNMENT)
Indian National Congress
Political party formed in 1885 to promote Indian self-rule; played a major role in the independence movement.
Aboriginal
The __________ people have been in Australia for an estimated 50,000 years and have the oldest continuous culture on Earth. At the time of European settlement, there may have been as many as 1 million people in 500 clans, speaking 700 languages.
Pan-Africanism
Movement promoting unity among all African people, often emphasizing shared history and a common destiny of liberation from colonialism.
Sokoto Caliphate
In West Africa in the 18th century, rulers often mixed Islamic and traditional religious practices. In 1804, a group of intellectuals led by Usman dan Fodio started a drive to purify Islam among the Hausa tribes of the region. He created a caliphate with its seat at the new town of Sokoto. This caliphate established the slave trade as a means if economic growth at a time when the British were trying to stop it. The British navy attempted to intercept the ships of this caliphate, free the enslaved people, and relocate them in their colony Sierra Leone. This caliphate was the largest African empire since the 16th century. It was finally subdued in 1903 when the British made it part of their colony of Nigeria.

Xhosa
Ethnic group in South Africa that resisted British colonization during the 19th century through a series of wars. did not want to be ruled by Europeans whether Dutch or English
Zulu
Powerful South African kingdom that resisted British and Boer invasions under leaders like Shaka Zulu.In the 1870s, the British fought the Zula Kingdom, located on the South African coast of the Indian Ocean, which had become a well-organized and centralized state.
Asante Empire
A West African empire in modern-day Ghana that resisted British colonization before being annexed in the early 1900s.pre-colonial West African state
Yaa Asantewaa
Queen mother of the Asante who led rebellion against British imperial forces in 1900. Last African War led by a woman
Cecil Rhodes
British imperialist who promoted colonization of southern Africa; founder of De Beers and the colony of Rhodesia.
Guano
Natural fertilizer made from bird droppings; highly valuable and exported by Peru and other countries in the 1800s.

Export Economies
Economies focused on exporting raw materials to industrialized nations, often at the expense of local development.
Rubber
Made from the latex sap of trees or vines. It softens when warm and hardens when cold. A valuable resource harvested in Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Amazon; associated with brutal labor conditions, especially under King Leopold in the Congo.
De Beers Mining Company
Major diamond company founded by Cecil Rhodes in South Africa; helped expand British economic power in the region.
Apartheid
System of institutionalized racial segregation in South Africa, officially beginning in 1948 but rooted in earlier colonial policies, Cecil Rhodes became the prim minister and paved the way for this racist segregation.
Monocultures
Economic systems that rely on the cultivation of a single crop, often leading to soil depletion and economic vulnerability.

Opium War (1839-1842)
Two wars fought between Western Powers and China (1839-1842 and 1856-1858) after China tried to restrict the importation of foreign goods, especially opium; China lost both wars and was forced to make major concessions, ended with British victory and the Treaty of Nanjing, opening Chinese ports.
"Banana Republics"
Term for Central American countries whose economies were dominated by foreign fruit companies, especially the U.S.-based United Fruit Company.
Great Famine (1845-1849)
Massive famine in Ireland caused by potato crop failure; worsened by British neglect and led to mass emigration and death, disease, and starvation.
Mohandas Gandhi
Leader of the Indian independence movement who promoted nonviolent resistance against British colonial rule.
Natal Indian Congress
Organization founded by Gandhi in South Africa to fight discrimination against Indians living under British rule.
Chinese Exclusion Act
1882 U.S. law banning Chinese immigration; first major federal law to restrict a specific ethnic group.
White Australia Policy
A set of Australian laws aimed at restricting non-European immigration and preserving a "white" national identity.