110 Lever Systems + Muscles of the Head, Anterior Neck and Throat
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
3 components of lever system
Lever: rigid bar (bone) that moves on a fixed point, fulcrum (joint)
the fulcrum position is relative to load and effort
Effort: force (supplied by muscle contraction) applied to lever to move resistance (load)
Load: resistance (bone + tissues + any added weight) moved by the effort
Functional groups of skeletal muscles
prime mover of one movement
antagonist for different movement
synergist for third movement
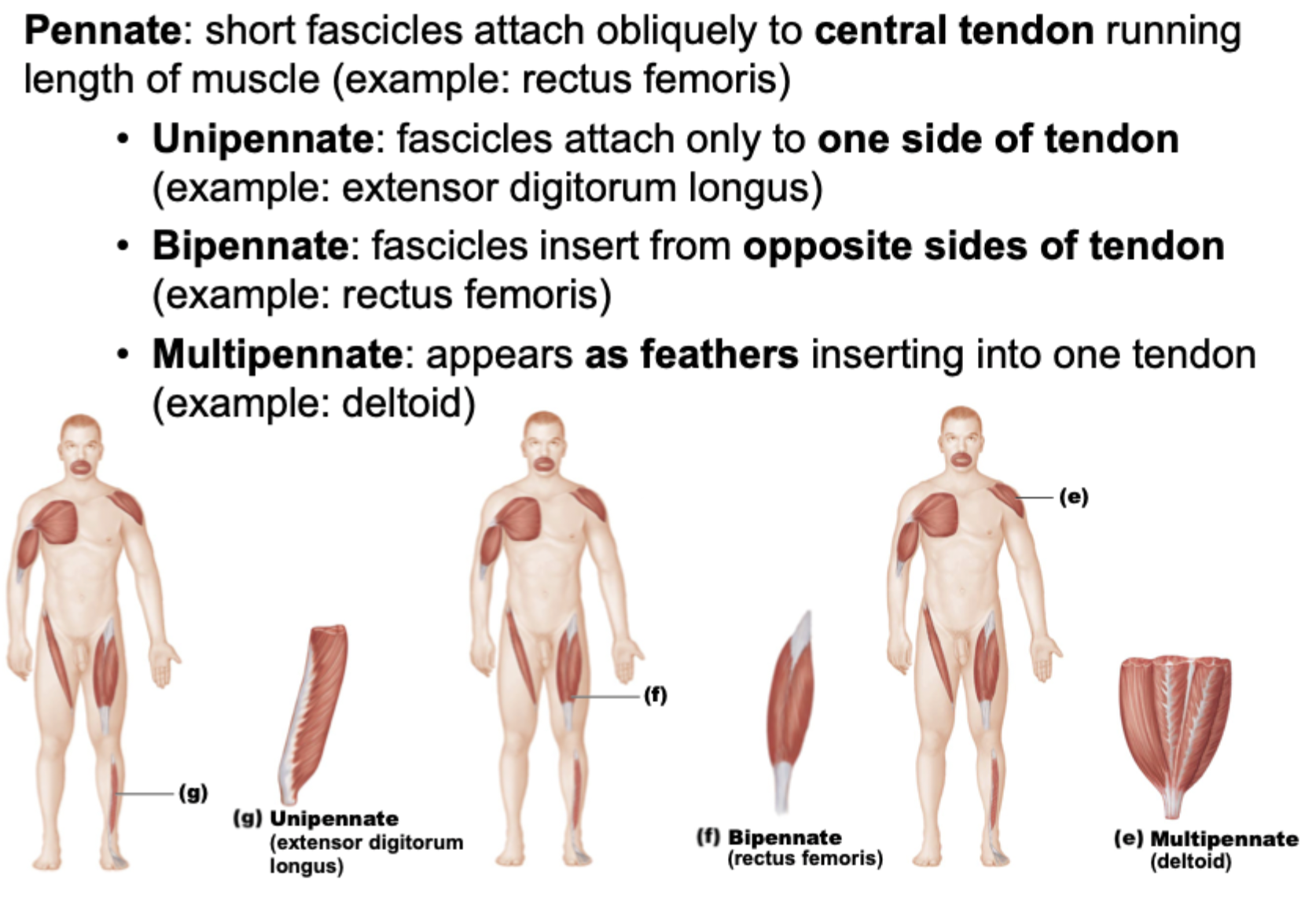
Example of a circular fascicle arrangement
orbicularis oris
fascicles arranged in concentric rings
Example of a convergent fascicle arrangement
pectoralis major
fascicles converge toward single tendon insertion
Example of a fusiform fascicle arrangement
biceps brachii
spindle-shaped muscles with parallel fibers
Example of a parallel fascicle arrangement
sartorius
fascicles parallel to long axis of strap-like muscle
Pennates
Advantages of levers
allows given effort to move heavier load
moves the load farther or faster
Mechanical advantage
aka power lever
load is close to fulcrum
effort is far from fulcrum
small effort will move large load
slower
more stable
used where strength is a priority
Mechanical disadvantage
aka speed lever
load is far from fulcrum
effort is close to fulcrum
load moves rapidly over large distance; offers wider range of motion
force is lost
speed and range of movement are gained
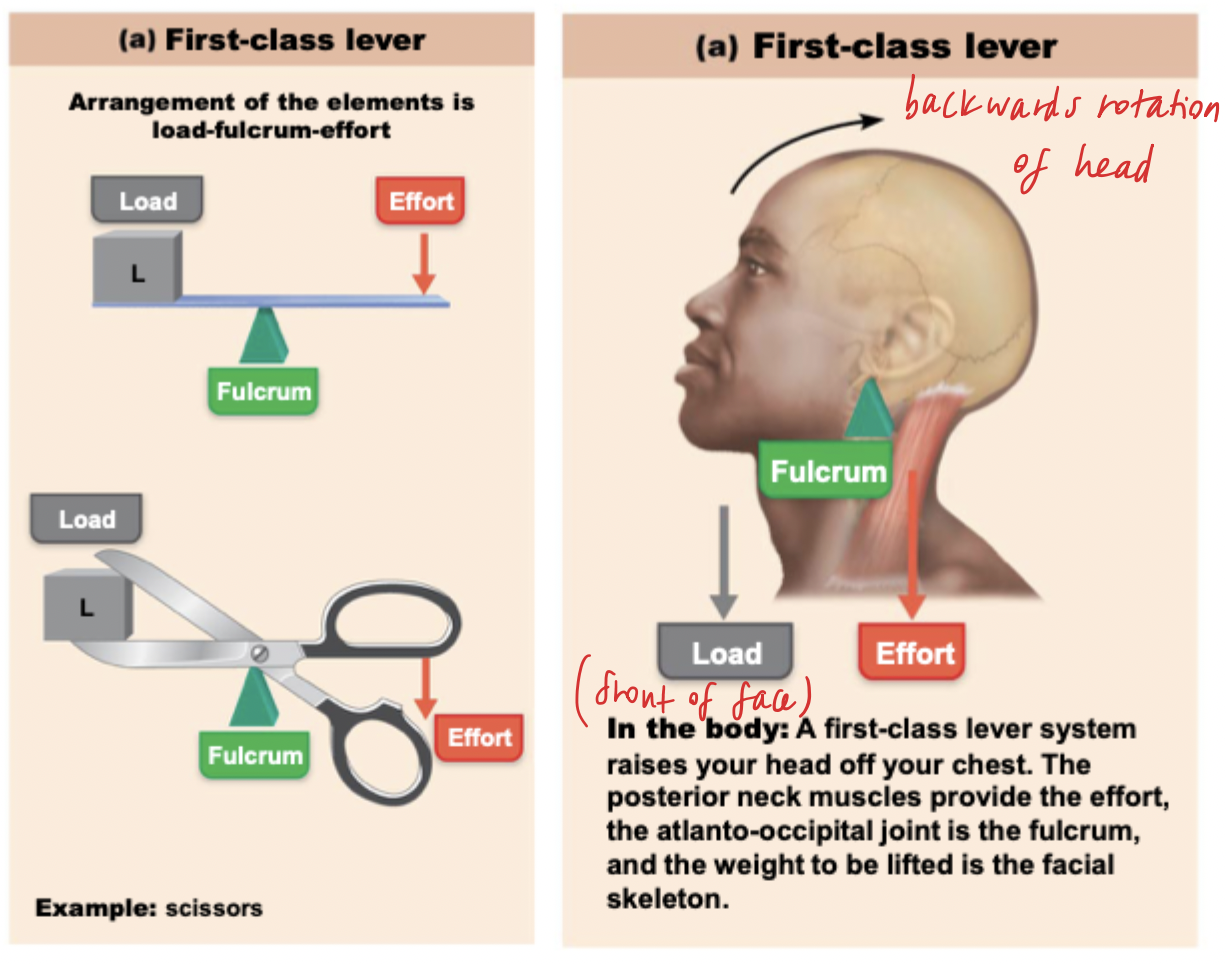
First-class lever system
aka CLASSICAL system
fulcrum is between load and effort
examples:
chin lowering and lifting (head nodding up and down)
load = weight of facial skeleton
fulcrum = atlanto-occipital joint
effort = posterior neck muscles
seesaw, scissors
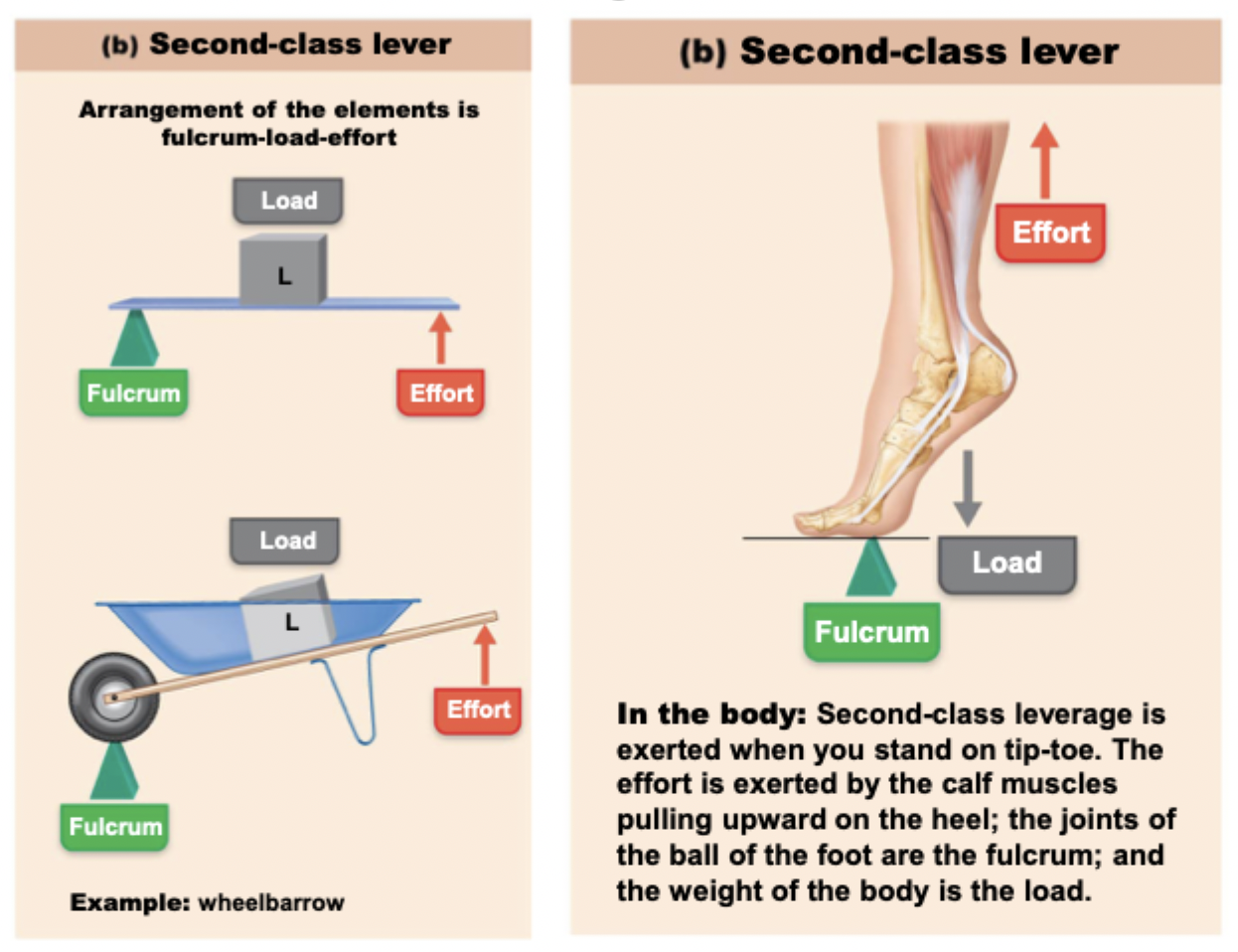
Second-class lever system
load is between fulcrum and effort
aka power system
examples
standing on tippy toe
fulcrum = joints of the ball of the foot
load = weight of the body
effort = calf muscles pulling upward on the heel
wheelbarrow
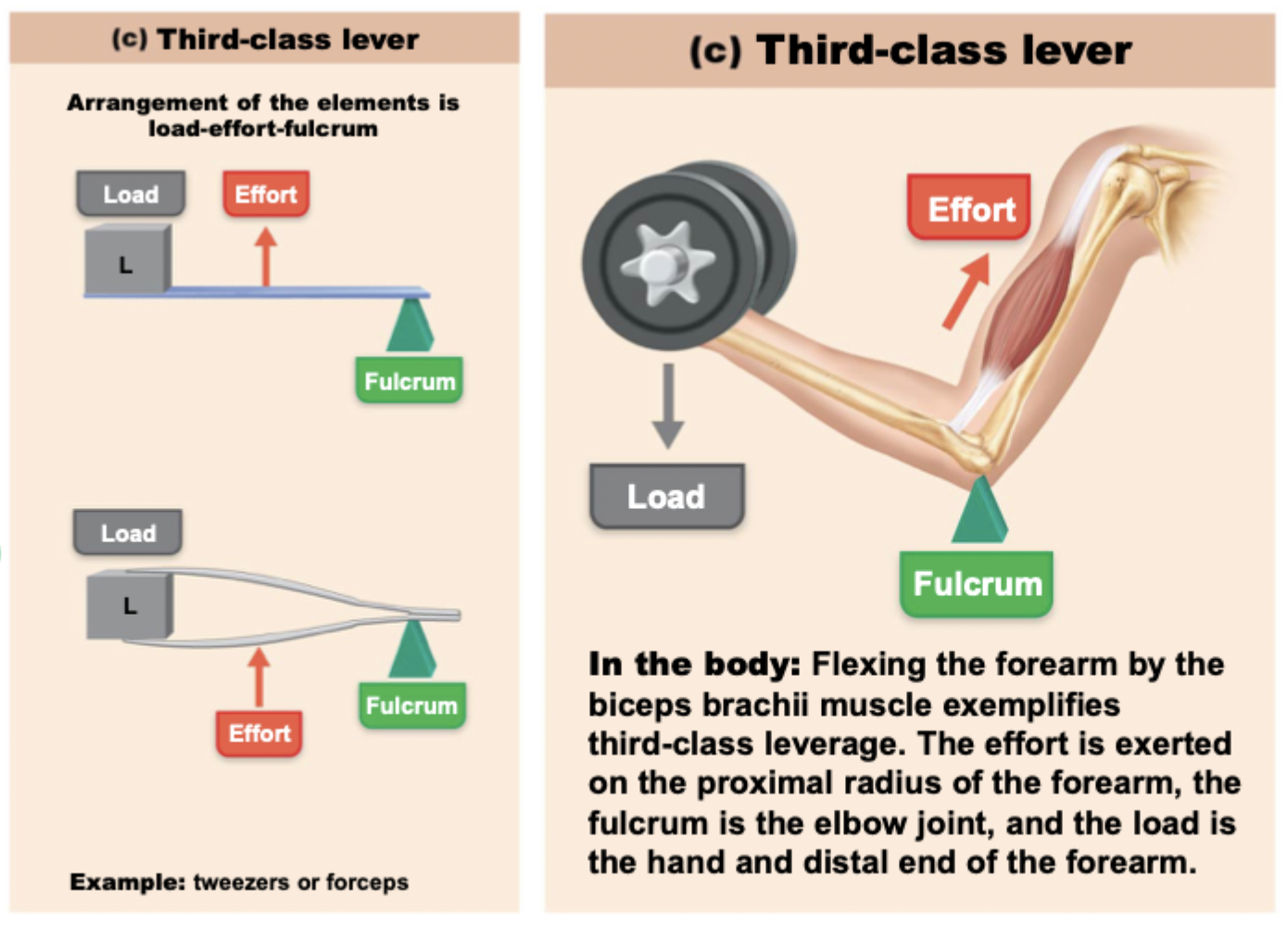
Third-class lever system
effort is applied between fulcrum and load
aka speed system
examples
flexing the forearm by the biceps brachii muscle
load = hand and distal end of forearm
effort = exerted on the proximal radius of the forearm (bicep muscle)
fulcrum = elbow joint
tweezers, forceps
Most skeletal muscles work by the _____ class lever system
third
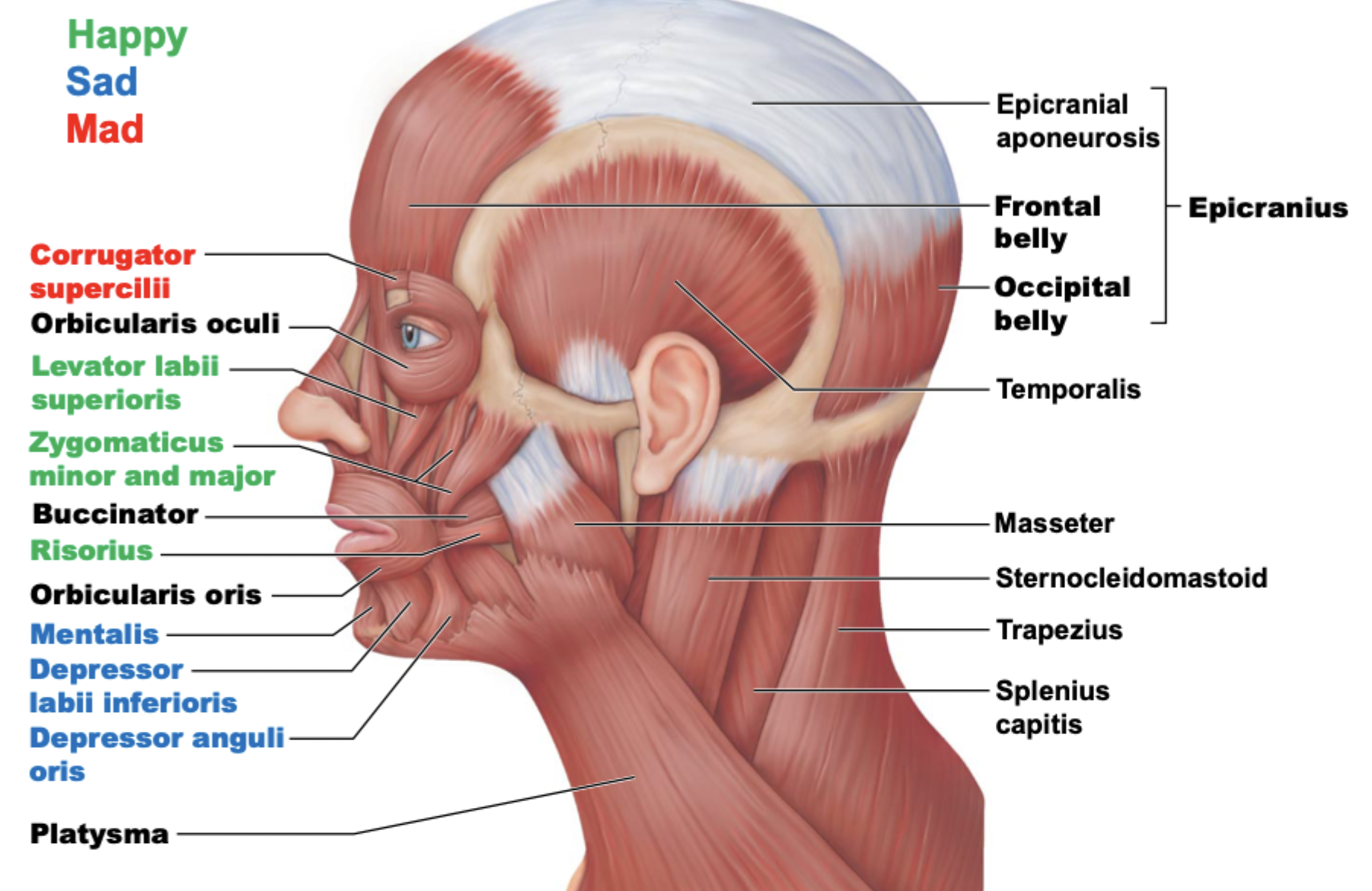
How are facial expression muscles different?
Unlike most muscles, they insert into skin, not bone
Facial expression muscles are important in:
nonverbal communication
All facial expression muscles are _________________ by ____________ nerve ______.
innervated; cranial; 7
Cranial nerve VII is also known as?
facial nerve
Facial expression muscles consist of two groups: muscles of the __________ and ___________.
scalp; face
Key muscle of the scalp
Epicranius
Epicranius has 2 major ________.
bellies
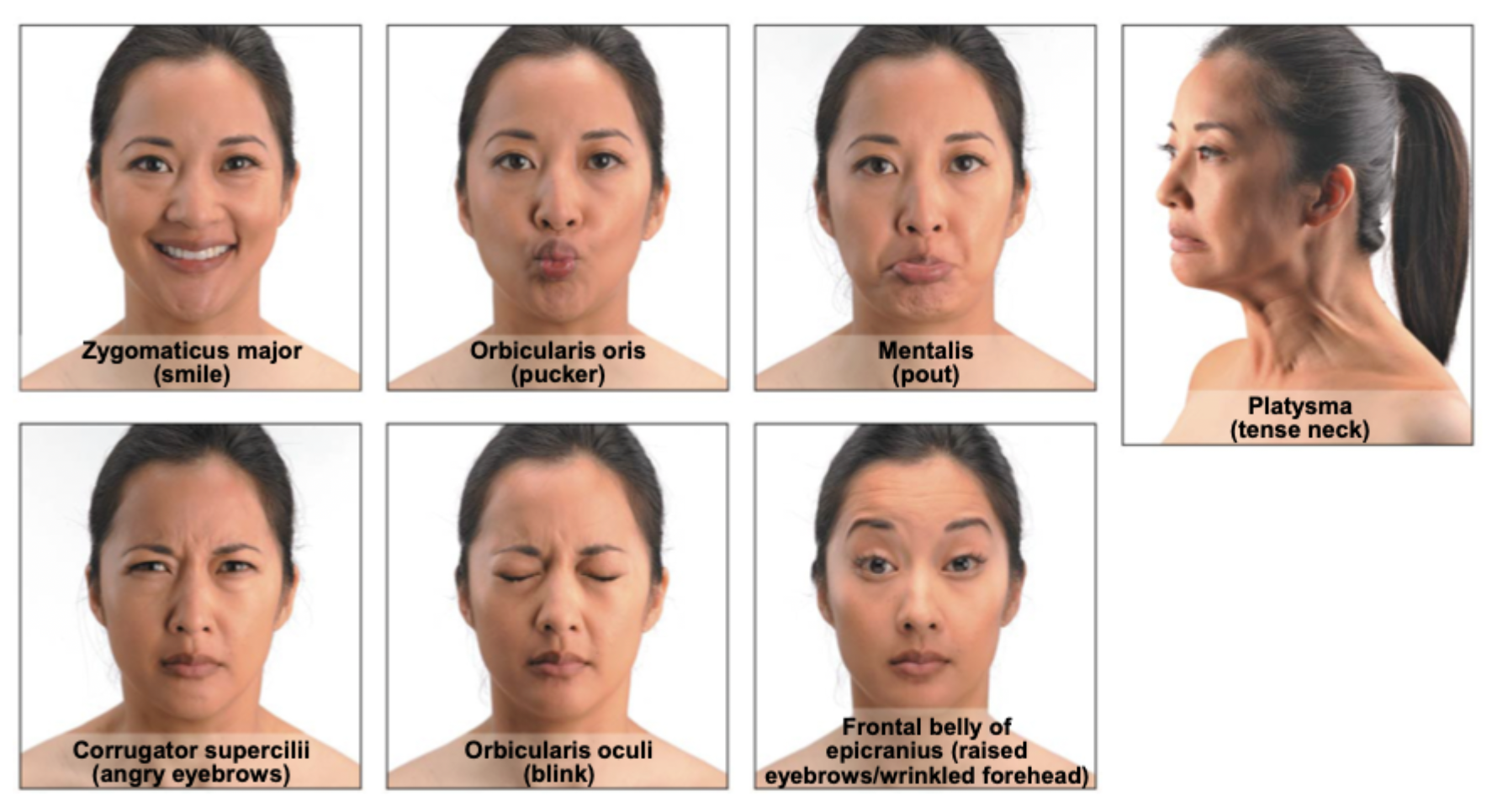
Frontal belly/frontalis muscle ==> raised eyebrows/wrinkled forehead
Occipital belly/occipitalis muscle
Frontalis and occipitalis muscles are connected by:
a specialized tendon, epicranial aponeurosis
Which muscle raises/lowers eyebrows? (ie. frowning)
Corrugator supercilii
Corrugator supercilii
has a frontal belly attachment
inserts into eyebrow
Which muscle closes/blinks eyes?
Orbicularis oculi
Which muscle raises lateral corners of mouth? (aka smiling muscle)
Zygomaticus major and minor
starts around zygomatic bone
inserts on the lateral edges of lips
Which muscle draws corner of lip laterally?
Risorius
masseter muscle
lateral edges of lips
Which muscle opens lips?
Levator labii superioris
zygomatic bone, maxilla
inserts onto lateral parts of upper lip
Which muscle draws lower lip inferiorly? (aka pout)
Depressor labii inferioris
mandible
inserts into the lower lip
Which muscle draws corners of mouth down and laterally?
Depressor anguli oris
mandible
inserts around the mouth
Which muscle closes lips? (pucker lips)
Orbicularis oris
origins around the maxilla and mandible
encircles the whole mouth
Which muscle wrinkles chin?
Mentalis
origins in mandible
inserts into the chin
Which muscle compresses cheek? (sucking in)
Buccinator
inserts on the orbicularis oris muscle
Which muscle tenses skin of neck?
Platysma
Facial expression muscle diagram
Different facial expressions
Muscles of mastication
4 pairs [MTPB]
All innervated by cranial nerve V
What are the prime movers of jaw closure?
Temporalis and masseter
Which muscles are responsible for the mouth’s grinding movements?
Pterygoids
What extrinsic muscles promote tongue movement (anchor + move tongue)?
Genioglossus
Hyoglossus
Styloglossus
Which muscle moves and closes jaw?
Masseter
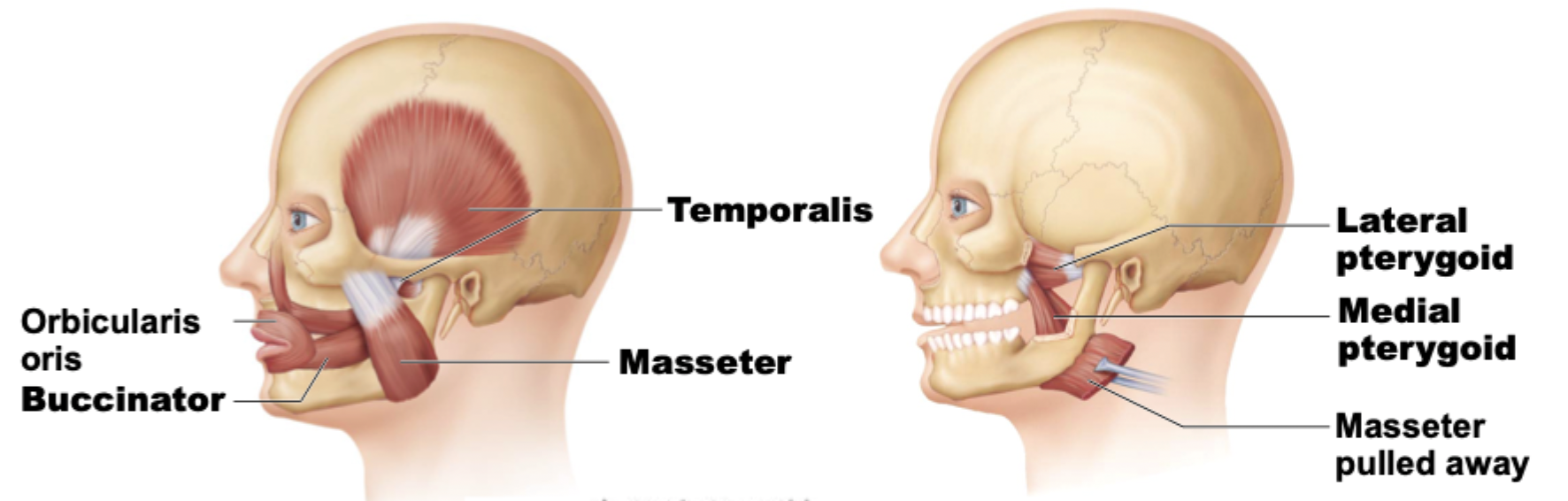
General location of temporalis?
O: temporal bone
inserts in the mandible

Temporalis muscle plays a role in ______ closure.
Jaw
What muscle protracts (pull anteriorly) the jaw/mandible and promotes side-to-side (grinding) movements?
Medial and lateral pterygoids

Which muscle compresses the cheeks and plays a role in chewing?
Buccinator
Purpose of buccinator muscle
keeps food in mouth
allows for good chewing surface
Which muscle protracts (stick out) tongue?
Genioglossus
Which muscle depresses tongue?
Hyoglossus
The styloglossus _______ and _______ the tongue.
retracts; elevates
The styloglossus origins at the
temporal bone
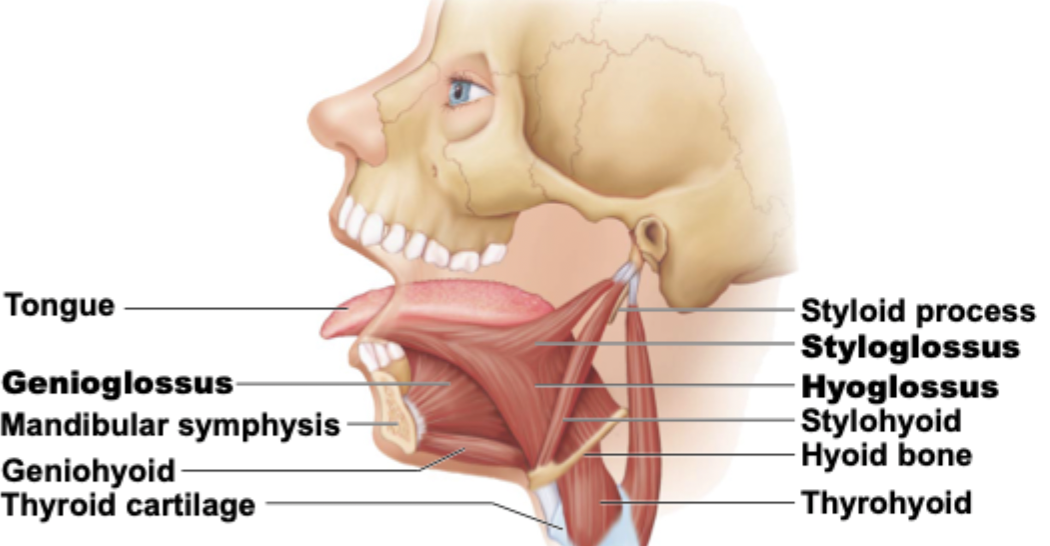
The lateral pterygoid has a _________ head and an ___________ head
superior; inferior
Styloglossus is ___________ to the hyoglossus
superior
Genioglossus is _________ to the hyoglossus
anterior
What muscle divides the neck into two triangles (anterior and posterior)?
Sternocleidomastoid muscle
Anterior neck and throat muscles are divided based on __________ to the ________ bone: ______hyoid and ______hyoid
location; hyoid; supra; infra
What muscles push food back towards the pharynx during the swallowing process?
The tongue and buccinator muscles
Muscles in __________ mouth and __________ complete the swallowing process
posterior; pharynx
___________ closes over _________ while muscles in walls of _________ propel food forward to stomach
Epiglottis; larynx; pharynx
Functions of suprahyoid muscles
form floor of oral cavity
anchor tongue
elevate hyoid bone
move larynx during swallowing
Functions of infrahyoid muscles
depress hyoid bone and larynx during swallowing and speaking
Good Samaritan does marathon
suprahyoid muscles:
Geniohyoid
Stylohyoid
Digastric
Mylohyoid
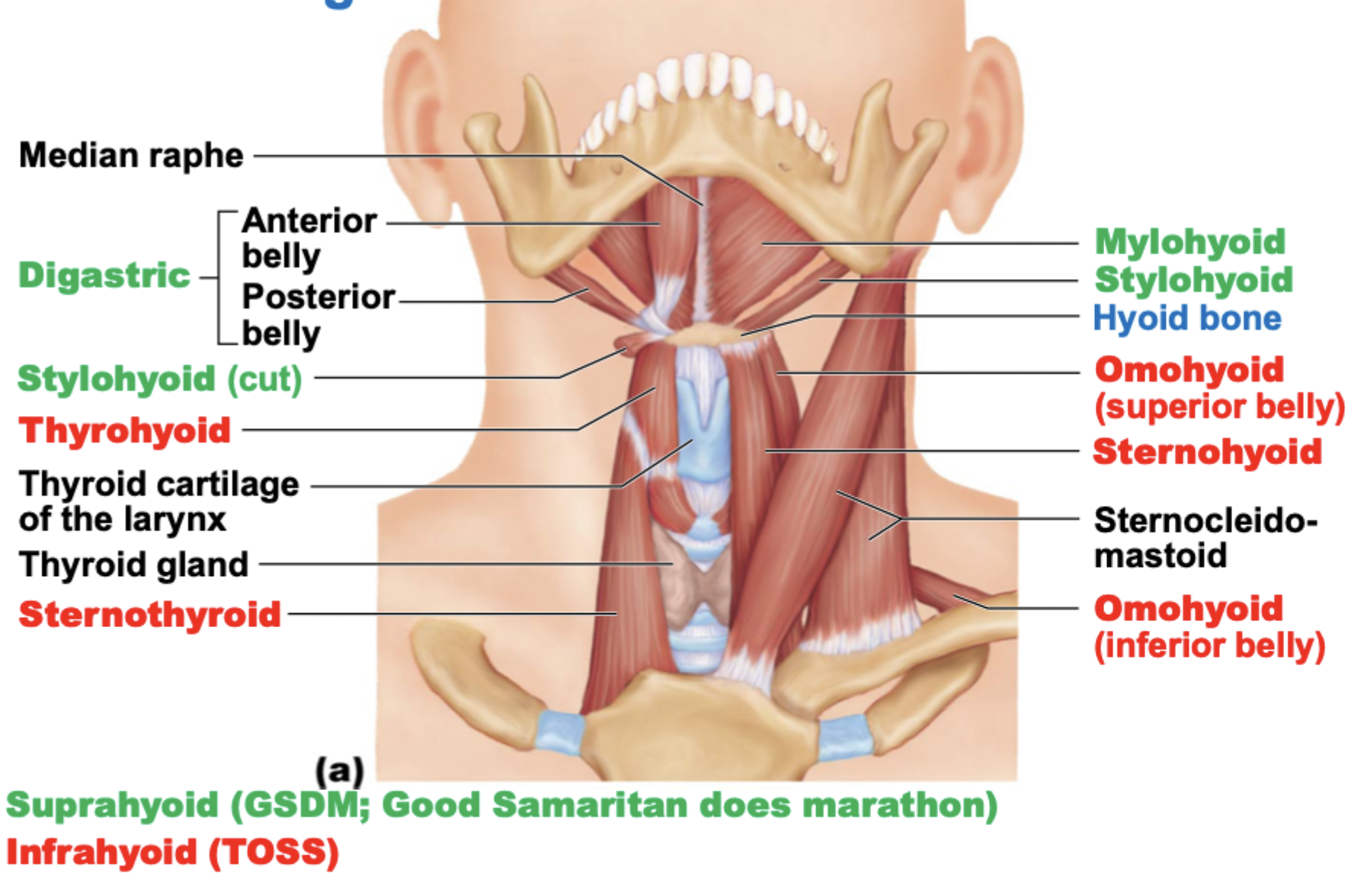
All 4 suprahyoid muscles insert into the
hyoid bone
Which of the suprahyoid muscles open mouth and depress mandible?
Digastric
Which of the suprahyoid muscles elevates and retracts hyoid?
Stylohyoid
Which of the suprahyoid muscles elevates hyoid bone and floor of mouth?
Mylohyoid
Which of the suprahyoid muscles pulls hyoid bone superiorly and anteriorly?
Geniohyoid
Stylohyoid muscle origins at the
temporal bone
Which of the suprahyoid muscles origin at the mandible?
Mylohyoid and geniohyoid
All but 1 of the 4 infrahyoid muscles inserts into the hyoid bone. What muscle is it and where does it insert into instead?
Sternothyroid; thyroid cartilage
If mandible is fixed, which muscle depresses larynx and hyoid bone?
Sternohyoid
Sternohyoid origins at
manubrium and clavicle
Which muscle depresses larynx and hyoid bone?
Sternothyroid
Which muscle depresses and retracts hyoid bone?
Omohyoid
If hyoid is fixed, which muscle depresses hyoid bone or elevates larynx?
Thyrohyoid
Which muscle plays a role in constricting pharynx during swallowing?
Pharyngeal constrictor muscles
How many pharyngeal constrictor muscles are there?
3: superior, middle, inferior
Where do pharyngeal constrictor muscles originate from and insert into?
O: mandible (superior), hyoid bone (middle), and laryngeal cartilages (inferior)
I: pharynx
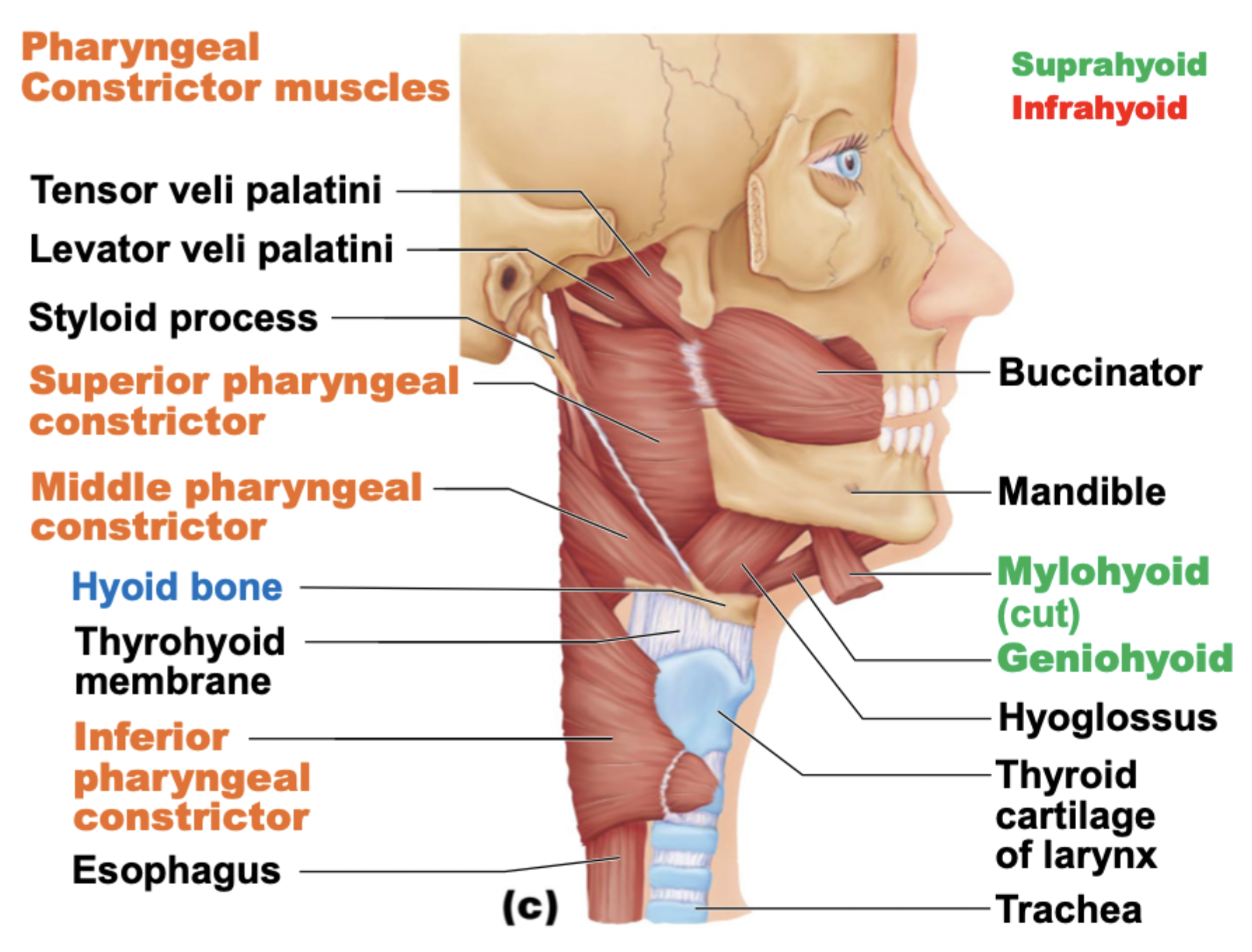
TOSS
infrahyoid muscles:
Thyrohyoid
Omohyoid
Sternohyoid
Sternothyroid

Digastric muscle
has anterior and posterior belly
U-shaped
Omohyoid muscle
has superior and inferior belly
Geniohyoid is ________ to mylohyoid muscle
posterior