MKT CH 15
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Most advertising money is spent in
North America, Asia, and Europe
Producers of consumer products generally spend
a larger percentage on advertising than firms that produce business products
Advertising Agencies
Specialists in planning and handling mass-selling details for advertisers
independent of advertiser and have an outside viewpoint
bring experience and can do the job more economically
Every ad and advertising campaign should have
clearly defined objectives that grow out of the firm’s overall marketing strategy and the promotion jobs assigned to advertising.
Good advertising objectives are
specific
measurable
include a timeframe
Adoption Process Stages
Awareness
Interest
Evaluation & Trial
Decision
Confirmation
Adoption Process Stages: Awareness
Teaser campaigns
Pioneering ads
Jingles & slogans
Viral advertising
Announcements
Adoption Process Stages: Interest
Informative or descriptive ads
Image & celebrity ads
Email ads
Demonstration of benefits
Adoption Process Stages: Evaluation & Trial
Competitive ads
Persuasive copy
Comparative ads
Testimonials
Search ads
Adoption Process Stages: Decision
Direct-action retail ads
Point of purchase ads
Price deal offers
Adoption Process Stages: Confirmation
Reminder ads
Informative “why” ads
Firms should work closely with other _______________ to coordinate advertising efforts to get the best results.
channel members
Advertising Allowances
Price reductions to firms in the channel to encourage them to advertise or otherwise promote the firm’s products locally
Cooperative Advertising
Producers sharing in the cost of adds with wholesalers or retailers
2 Basic Types of Advertising
Product (includes pioneering, competitive, and reminder)
Institutional
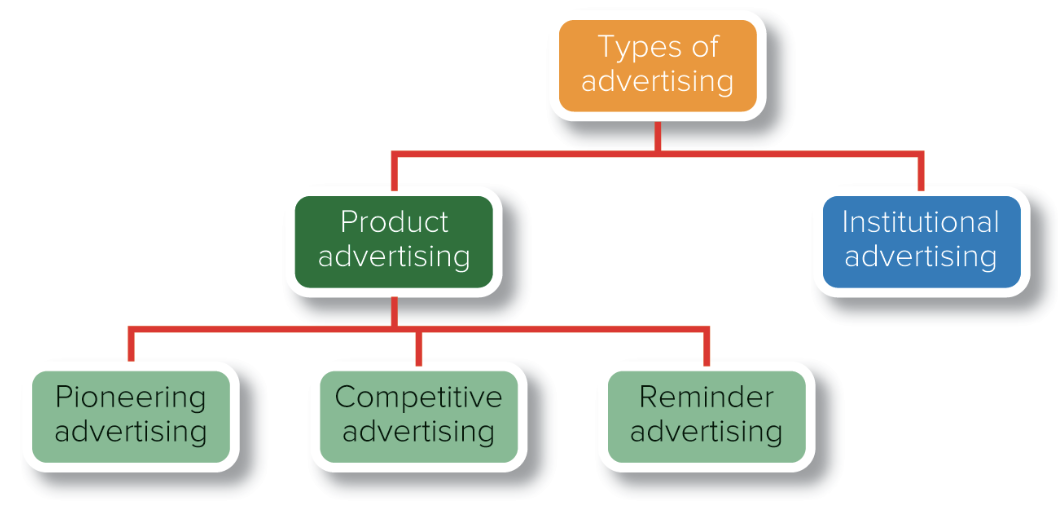
Product Advertising
Advertising that tries to sell a specific product
Institutional Advertising
Advertising that tries to promote an organization’s image, reputation, or ideas rather than a specific product (may inform, persuade, or remind)
Product Advertising: Pioneering
Advertising that tries to develop primary demand for a product category rather than demand for a specific brand
Pioneering Advertising is usually done in the
early stages of the product life cycle
turns potential customers into adopters
Product Advertising: Competitive
Advertising that tries to develop a selective demand for a specific brand rather than a product category
Competitive Advertising is forced onto a firm when
the product life cycle moves along - to hold its own against competitors.
Competitive Advertising: Direct
Competitive advertising that aims for immediate buying action
Competitive Advertising: Indirect
Competitive advertising that points out product advantages - to affect future buying decisions
Comparative Advertising
Advertising that makes specific brand comparisons using actual product names
Product Advertising: Reminder
Advertising to keep the product’s name before the public
Reminder advertising may be useful when the product has achieved
brand preference or insistence, perhaps in the market maturity or sales decline stages
Institutional advertising usually focuses on the
name and prestige of an organization or industry
Institutional advertising’s basic objective is to
develop goodwill or improve an organization’s relations with various groups (customers, shareholders, employees, etc)
Advertising Media
The various means/ mediums by which a message is communicated to its target market
Effectiveness depends on how well the medium fits with
the rest of a marketing strategy
promotion objectives
target markets you want to reach
funds available for advertising
nature of the media
Nature of Media
whom they reach
with what frequency
with what impact
at what cost
Digital: Mobile → Advantages
Ads link to more detailed website
Some “pay for results”
Easier to track results
Can be highly targeted
Precise-location based
Digital: Mobile → Disadvantages
Hard to compare costs with other media
More focused on later stages of purchase process
Digital: Desktop/ Laptop → Advantages
Ads link to more detailed website
Some “pay for results”
Easier to track results
Can be highly targeted
Digital: Desktop/ Laptop → Disdvantages
Hard to compare costs with other media
More focused on later stages of purchase process
TV→ Advantages
Demonstrations
Image building
Good Attention
Wide reach
Cable can be targeted
TV→ Disadvantages
“Clutter”
Ads compete for attention
Expensive
Limited time (30 seconds or less)
Often skipped by viewers
Radio → Advantages
Wide reach
Segmented audience
Inexpensive
Use of sound & voices can help create certain image of business
Radio → Disdvantages
Weak attention
Many different rates
Short exposure
Declining audience
Listeners can’t review the ad
Ads interrupt entertainment
Magazines → Advantages
High reader involvement
Very targeted
Good detail
Some “pass along”
Image quality high
Magazines → Disdvantages
Inflexible
Long lead times
Cost can be high
Limited flexibility on location of ad within magazine
Out-of-Home (billboards,cinemas, bus stops, etc.) → Advantages
Captive audience
Can be geographic and local
Out-of-Home (billboards,cinemas, bus stops, etc.) → Disdvantages
Outdoor: “glance” medium
Cinema: primarily a younger audience
Advertisers pay for the
whole audience a chosen meda delivers, including those who aren’t potential customers
To ensure good media selection, the advertisers first must
clearly specify its target market. Then the advertiser can choose media to reach those target customers.
Today, advertisers direct more attention to reaching
smaller, more defined target markets
TV tailors ads to individual households using
big data from consumers’ credit and loyalty cards, online activities
Addressable TV is a technology that allows cable television to
deliver specific ads to each household instead of advertising to everyone watching a particular show
Magazines sort readers by
special interests
Pay-per-Click
An advertiser pays media costs only when a customer clicks on the ad that leads to the advertiser’s website
Most media charge customers based on the
number of people who see an ad
Most websites use a
pay-per-click advertising model
Retargeting (aka behavioral retargeting)
Displaying ads to a web user based on sites he or she has previously visited
Programmatic Delivery refers to the
use of software and artificial intelligence to automate placing online advertising on websites or in social media to target users
Increases the efficiency and effectiveness of media planning
low cost makes it easier to target customers more precisely
Digital Ad: Banner Ads → Advantages
Relatively low cost
Banner ads work best for building a brand and image
Good tracking tools can measure effectiveness
Targeted ads can bring in customers
Digital Ad: Banner Ads → Disadvantages
Some types (ex:pop-up) can be intrusive
Browser ad blockers may limit reach
So relevant that people tend to ignore them
Digital Ad: Directories & Classifieds (ex: Craigslist) → Advantages
Low cost
Highly targeted
Best for customers ready to buy
Digital Ad: Directories & Classifieds (ex: Craigslist) → Disadvantages
Doesn’t work for brand building
Doesn’t fit for large companies
Digital Ad: Search Advertising (ex:Google ads) → Advantages
Easy to set budget and control costs
Targets users in information-gathering stage of the buying process
Easy to measure return on investment
Highly targeted
High credibility
Digital Ad: Search Advertising (ex:Google ads) → Disadvantages
Bidding process for keywords can become costly
Information overload for customers
Limited space for copy thrust
Limited/no image capability
Digital Ad: Social Media Advertising → Advantages
High knowledge of individuals
Potentially wide reach
Can stimulate viral
Can be narrowly targeted
Relatively low cost
Endorsement from friends (likes) can be powerful
Easy to set a budget
Digital Ad: Social Media Advertising → Disadvantages
Users of social media actively avoid advertising
Advertiser generally has fewer data than from other sources
Digital Ad: Mobile Advertising → Advantages
A large and growing audience
Works best for high-involvement/utilitarian products
Potential for location-based targeting
Works well for immediate purchase
Digital Ad: Mobile Advertising → Disadvantages
Technical limitations (small screen, bandwidth, data transfer)
No user friendly
Not very interactive
Measurement tools still emerging
Banner/ Display Ads
A type of online advertising that places an ad on a web page, often across the top or to the side of the page’s primary content
Click-through rate is low
Click-Through Rate
The number of people who click on the ad divided by the number of people this ad is presented to
Banner Ads often have the goal of
generating awareness and building a brand
Influencers
Trusted or well-known figures who can sway attitudes or purchase decisions among a particular target market - to promote a brand
Click Fraud
Occurs when a person or software program automatically clicks on an add without having any interest in the ad’s subject. The intent is to defraud the advertiser and make money for an unscrupulous website
Copy Thrust
What the words and illustrations of an ad should communicate
A guide to message planning: AIDA
getting Attention
holding Interest
arousing Desire
obtaining Action
AIDA: getting Attention
Anything different or eye-catching: shocking statements, special effects, etc.
AIDA: holding Interest
The tone and language of the ad must fit with the experiences and attitudes of the target customers and their reference groups
AIDA: arousing Desire
An ad should usually focus on a unique selling proposition, the main point of differentiation from competitors. It should aim at an important unsatisfied need.
AIDA: obtaining Action
Direct-response ads can sometimes promote action by encouraging interested consumers to do something even if they aren’t ready to make a purchase
Native Advertising
Advertising designed not to look like ads; it mimics the look and feel of the platform on which the ad appears
Corrective Advertising
Ads to correct deceptive advertising
If the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) decides that a particular practice is unfair or deceptive, it has the power to require
affirmative disclosures or cocrective advertising.
Sales Promotion
refers to Promotion activities (other than advertising, publicity, and personal selling) - that stimulate interest, trail, or purchase by final customers or others in the channel.
Sales Promotion Objectives
usually focus on prompting some short-term action.
Sales Promotion Activities: Aimed @ Final Consumers or Users
Contests
Coupons
Aisle Displays
Samples
Trade Shows
Point-of-purchase materials
Frequent buyer programs
Sponsored events
Partnering with causes
Limited availability products
Sales Promotion Activities: Aimed @ Wholesalers or Retailers
Price deals
Promotion allowances
Sales contests
Calendars
Gifts
Trade shows
Meetings
Catalogs
Merchandising Aids
Videos
Sales Promotion Activities: Aimed @ Company’s Own Sales Force
Contests
Bonuses
Meetings
Portfolios
Displays
Sales aid
Training Materials
Trade Promotion
Sales promotion aimed at intermediaries