Autopsy: forensics I
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
coup
brain injury at the site of impact
countercoup
brain injury opposite the site of impact
larger
common in MVA
number
location
distribution
presence of satellite injuries
characteristics: length, shape, orientation, appearance of margins, marginal or adjacent abrasion, depth and structures injured, direction of wound track
clothing defects
List the important factors to document for stab wound injuries (6)
circular defect with marginal abrasion
inverted margins
soot and stippling
entrance wounds
irregular defect whose edges can be re-approximated
stellate, beveled, slit, crescent
everted margins
no marginal abrasion, but can be shored (collar of abrasion)
exit wound
entry wound
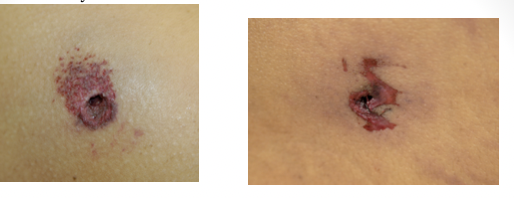
exit wound
congestive and heavy lungs
little food in GI tract
distended and full bladder
sedation
foam cone
drug users: track marks, skin popping
cocaine = MI with no other risk factors
list potential autopsy findings in overdoses cases as discussed in lecture.
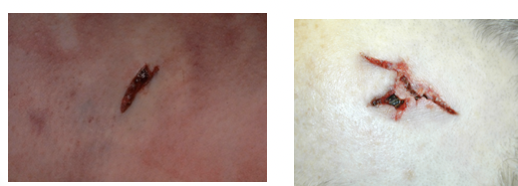
scratch
abrasion caused by sharp object passed across the skin
heaping of surface layers in front of the object leaves clean area at the start and tags at the end
e.g. fingernails, thorn, pin
graze
abrasion that occurs when there is movement between the skin and some rough surface (e.g. road rage)
impact abrasion
abrasion with more force and less duration
pressure abrasion
abrasion caused by crushing of superficial layers of skin; associated with bruise of surrounding area; force less, duration more
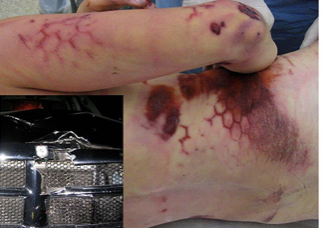
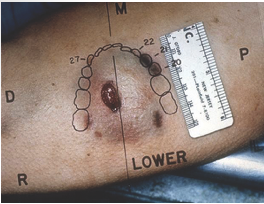
patterned abrasion
post mortem insect bites can mimic
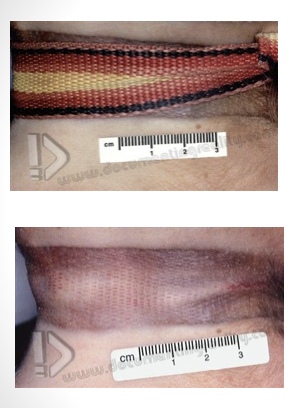
contusion
bruises due to rupture of vessels, usually capillaries; no loss of continuity of skin
pulmonary contusion
caused by extreme chest trauma; excess fluid interferes with gas exchange leading to hypoxia (e.g. explosions, traffic accidents, falls, sport injuries, falls)
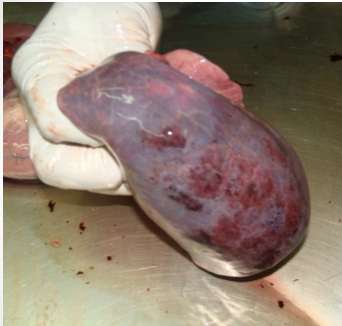
basilar skull fracture
battle’s sign behind ear and raccoon/panda eyes indicate?
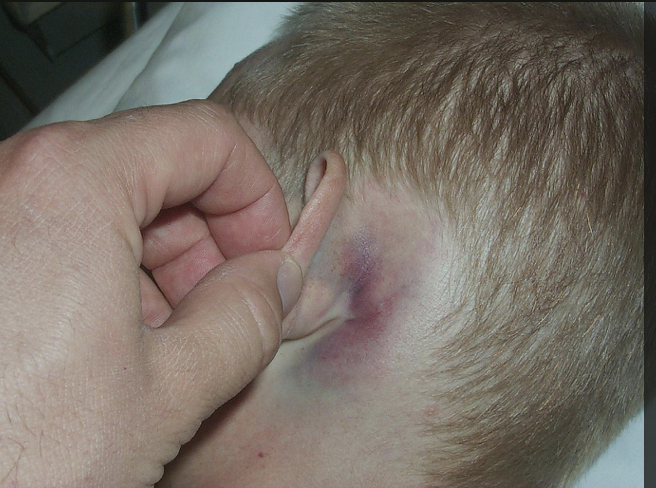
laceration
irregular edges, hair bulbs crushed, less hemorrhage, wound bridging, varying depth
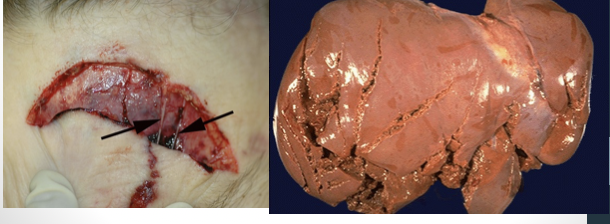
split laceration
occurs by crushing of the skin between two hard objects
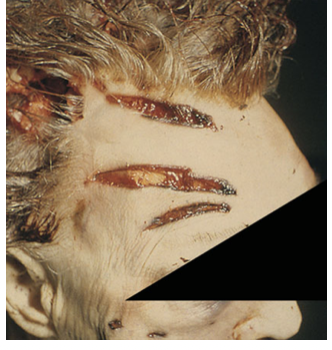
stretch laceration
common in high velocity intraoral GSW
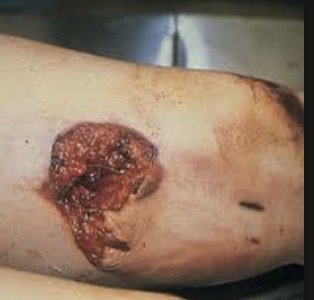
avulsion
degloving accidents

tearing laceration
ripping of skin and tissue from impact by or against object
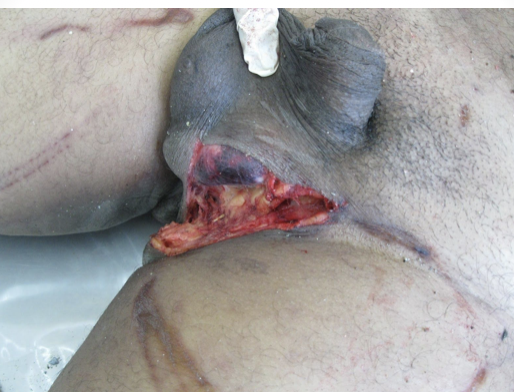
compound
fracture in which bone protrudes through skin
incised wound
clean, cut edges, well-defined, free from contusions
spindle-shaped
lots of hemorrhage from clean cut vessels
deeper at the beginning and more shallow at the end (“tailing”)
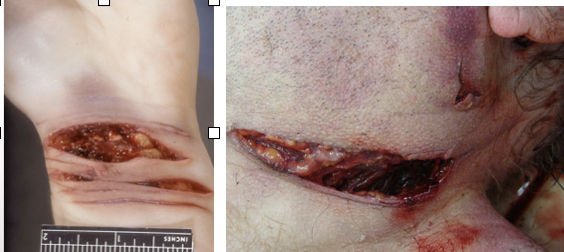
defensive wound
grasping surfaces of hands - flap wound created
ulnar border of forearm
dorsum or plantar surface of hand
lower limbs - sexual assault
stab wound
depth > length
width of wound < width of weapon - stretching of skin
clean cut edges
punctures around concealed parts of the body (axilla, vagina, rectum, nostrils)
abrasion
contusion
laceration
fracture
4 types of blunt force trauma
removing the tension caused by the elastic fibers in the skin is necessary to evaluate the true shape
isolating the area by cutting it from the surrounding skin and subcutis or with transparent tape
describe the procedure necessary to evaluate the true shape of a stab wound
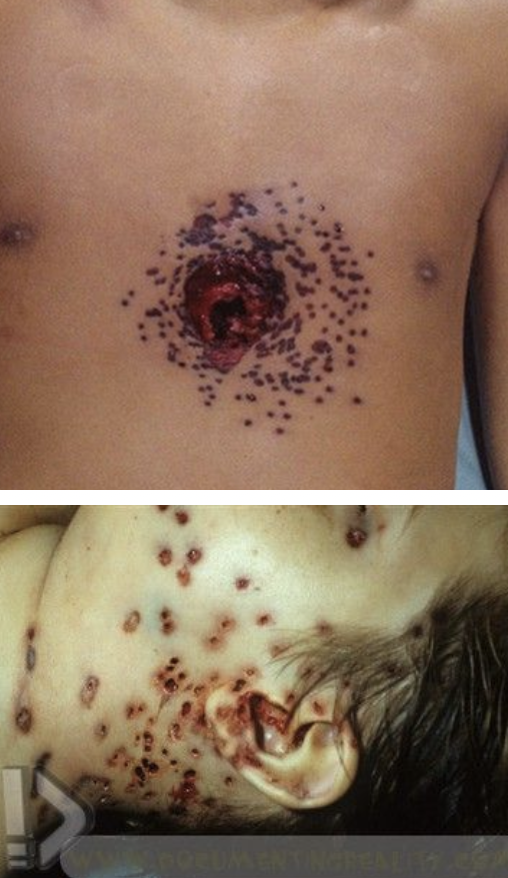
contact gunshot wound
circular and smaller
stellate over scalp
burning /blackening of immediate wound edges
soot within tissues
muzzle mark
inverted wound margins
back spatter = blood sucked up into the barrel of the weapon
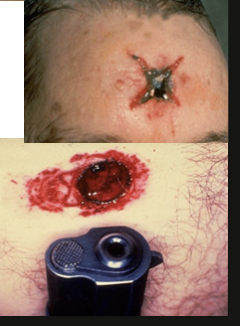
close range gunshot wound
almost always circular
inverted edges
collar of abrasion
burning effects
tattooing/stippling
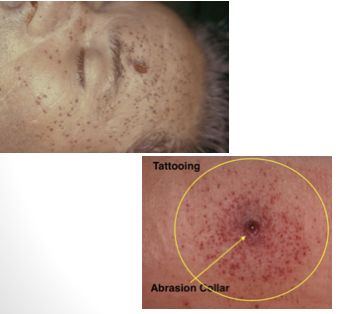
medium/distant range gunshot wound
from less than 0.5 meters to several kilometers away
abrasion collar around entry wound
wound is inverted
ring of dirt or grease ring
bullet striking sideways – may produce rectangular lacerated wound
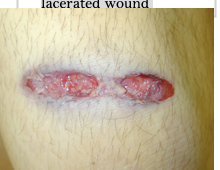
tangential gunshot wound
tears with skin tag formation
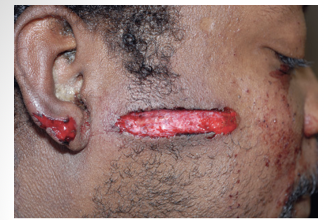
short range shotgun wound
6 inches – 6 feet
soot soiling vanishes after 1 foot
tattooing
single wound
rat hole injury
separate wad injury as an abrasion or bruise
distant range shotgun wound
>6 feet
no soot
number of separate pellet holes increase progressively around main wound
wad often takes lower trajectory
6-10 meters, central hole may shrink to nothing
suffocation
strangulation
chemical asphyxia
three types of asphyxial deaths
smothering
suffocation due to mechanical obstruction of the nose and mouth
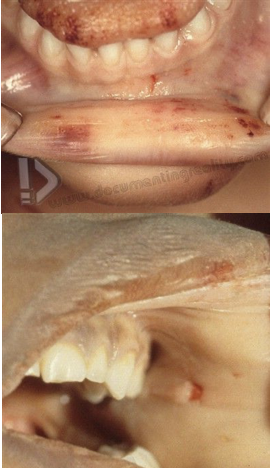
choking
suffocation due to obstruction of airway; no petechiae
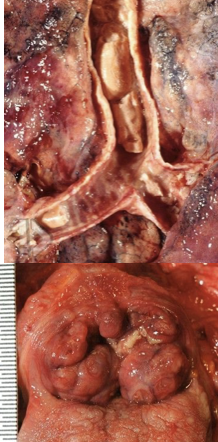
mechanical suffocation
pressure on chest and abdomen making it impossible to breath; most accidents
face and neck are deep purple from congestion; petechiae of conjunctiva and sclera, confluent scleral hemorrhage
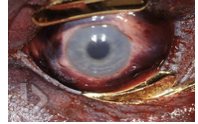
strangulation
occlusion of BV in neck secondary to external pressure
mechanism of death = cerebral hypoxia secondary to obstruction of vessels bringing oxygenated blood to the brain
NOT due to compression of the trachea
cyanosis, petechial hemorrhages of conjunctiva, sclera and periorbital skin
hanging
type of strangulation
usually pale face, protruding tongue and dried out mucus drips from nose with no petechiae depending on the degree
tardieu spots on heart and pooling of blood in the LE and forearms
furrow in neck
may see sclera or conjunctival hemorrhage/strap muscle hemorrhage/hyoid bone or thyroid cartilage fracture but not always
ligature strangulation
pressure on neck applied by object tightened by force other than body weight
most commonly associated with rape
death due to occlusion of carotid arteries with cerebral hypoxia
blood gets to head but can’t drain = congested face, numerous petechiae of sclera and conjunctiva, periorbital and face skin too
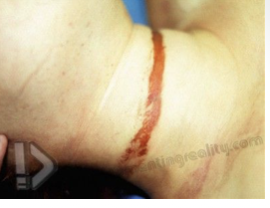
manual strangulation
strangulation from hand, forearm or another limb; occludes vessels on neck
congestion of face, petechial hemorrhages, fingernail marks, hemorrhage in the strap muscles, hyoid fracture, abrasions/contusions on neck
can’t say antemortem if no significant hemorrhage around hyoid/thyroid
chemical asphyxia
gases that prevent utilization of oxygen at the cellular level
carbon monoxide most common
helium, hydrogen cyanide, hydrogen sulfide
cyanide poisoning
bitter almond scent
tox - 200 mg lethal
internal organs = bright pink
damage, blood-stainined stomach lining
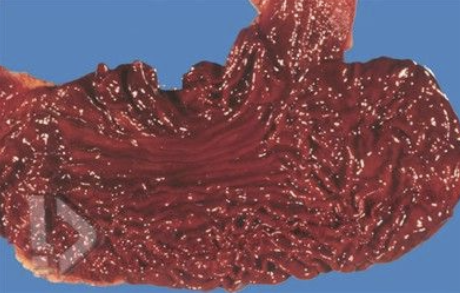
hydrogen sulfide
green discoloration of brain
exposure by proximity to waste water treatment facilities, landfills and farms with manure storage
supine, naked, spread, legs
bite marks and bruising - breasts, inner thighs
double swab method for bites! (wet then dry swab)
trauma to vagina/anus
contusions in posterior 5-7 o’clock
semen deposits - UV light (don’t need sperm to prove)
common COD - strangulation, BFT, stabbing
swabs of mouth, rectum, and vagina
fingernails
describe potential autopsy findings in a sexual assault/rape case as presented in lecture.
objectivity - based on facts and not personal opinions or other influences
internalize the importance of upholding professional ethical standards when arriving at a manner of death, as discussed in class
contact
what distance?
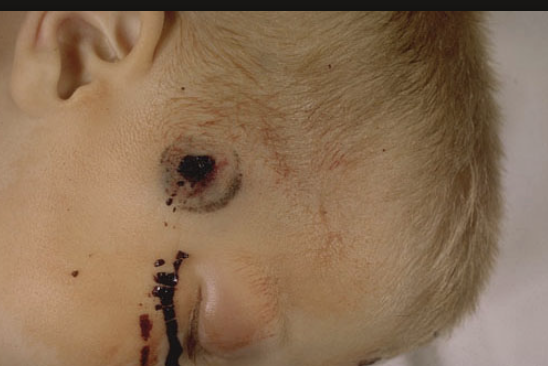
contact
what distance?
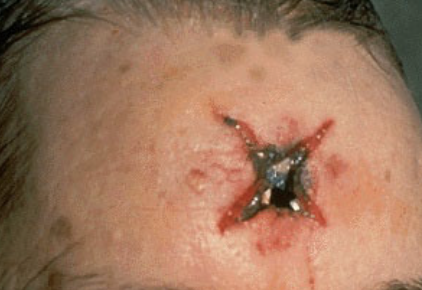
contact
what distance?
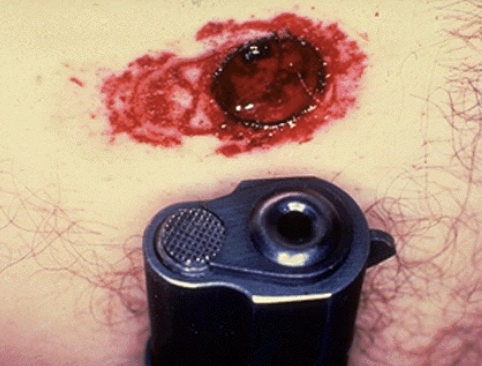
close range
what distance?
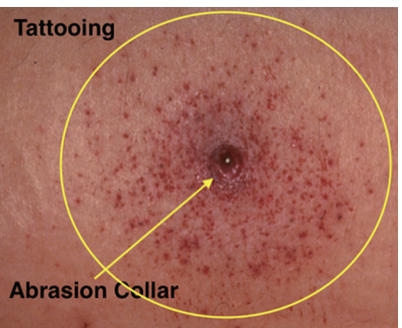
close range
what distance?
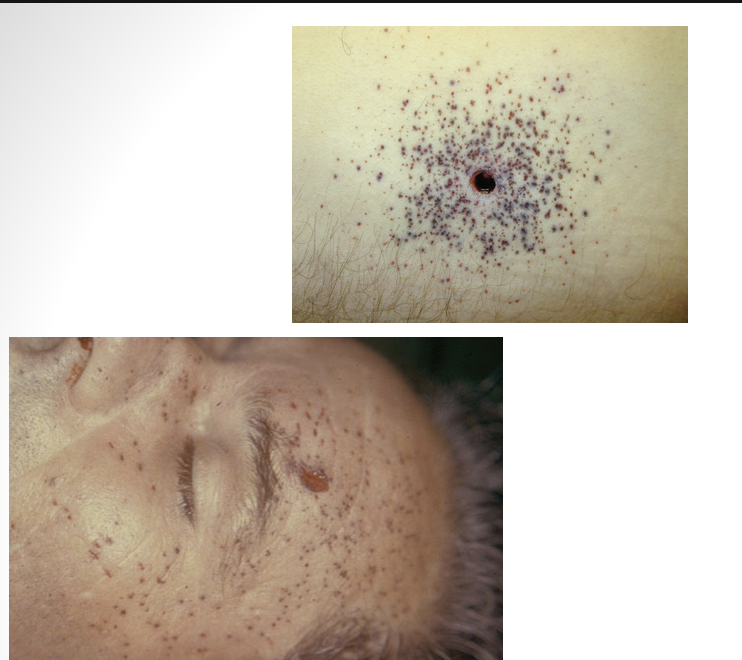
medium range
what distance?

medium range
what distance?
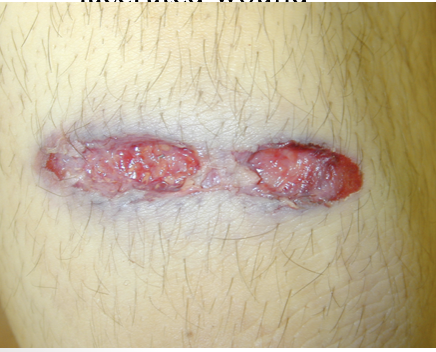
tangential
what distance?
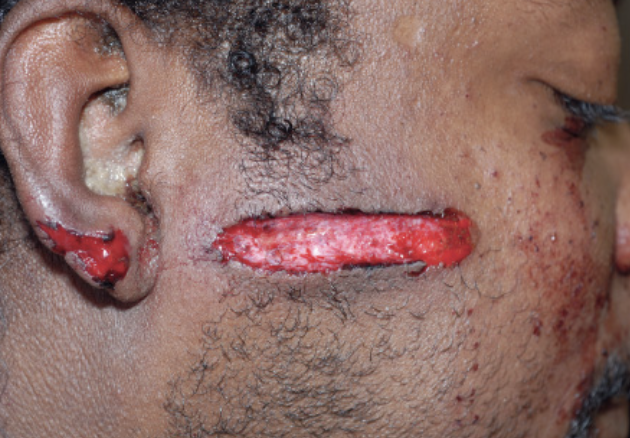
contact
what distance?
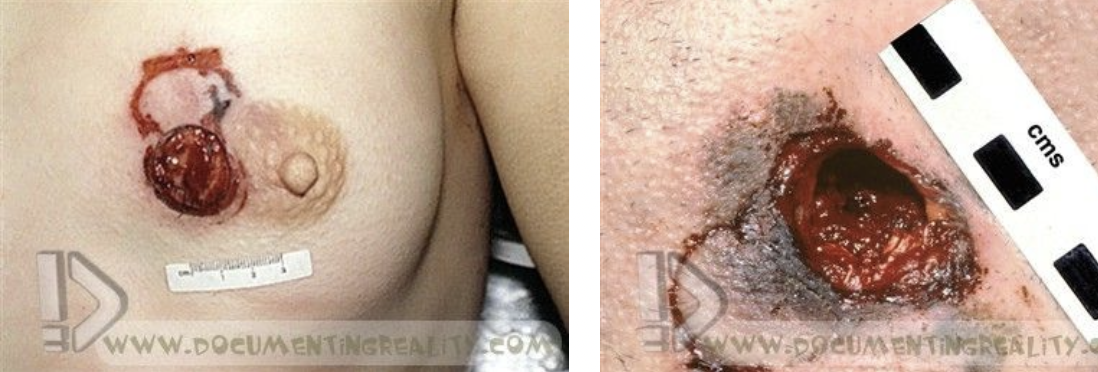
near contact
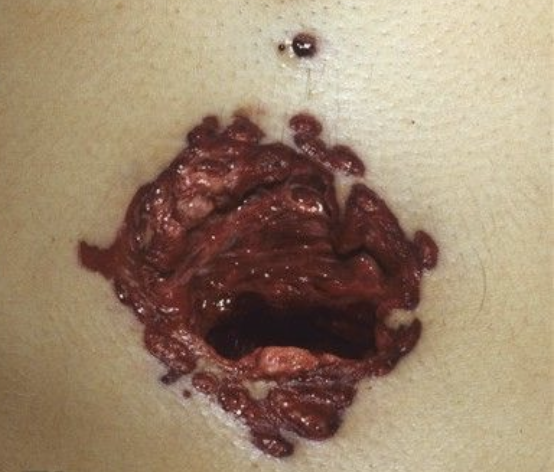
short range
what distance?