Understanding Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
ADHD
Neurodevelopmental disorder affecting attention and behavior.
Inattention
Difficulty sustaining focus and organizing tasks.
Hyperactivity
Excessive movement and inability to stay still.
Impulsivity
Acting without thinking, interrupting others.
Functional Impairment
Decreased performance in social or academic settings.
ADHD Combined
Presence of both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive symptoms.
ADHD Predominantly Inattentive
Mainly characterized by inattention symptoms.
ADHD Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive
Mainly characterized by hyperactivity and impulsivity.
Diagnosis Age
Symptoms must be present before age 12.
Prevalence in Children
7%-11% of US children diagnosed with ADHD.
Prevalence in Adults
4%-5% of US adults diagnosed with ADHD.
Etiology
Causes include genetic, environmental, and brain factors.
Genetic Influence
Siblings 5-7 times more likely to have ADHD.
Hallmark Symptoms
Inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity are key signs.
Associated Impairments
Includes executive function and academic underachievement.
Coexisting Conditions
80% of children may have additional disorders.
Social Determinants of Health
Conditions affecting health based on environment.
Screening Tools
Used for assessing ADHD in adults.

Severity Levels
Mild, moderate, and severe impairments in functioning.
Environmental Factors
Includes prenatal exposure and brain injuries.
Executive Function
Cognitive processes for attention and self-regulation.
Internalizing Symptoms
Anxiety and depression often hidden in ADHD.
Sleep Disturbances
Includes issues with sleep initiation and maintenance.
Developmental Coordination Disorder
Motor skill problems linked to ADHD.
Oppositional Defiant Disorder
Common coexisting condition with ADHD.
Tic Disorders
Involuntary movements or sounds often seen in ADHD.
Bipolar Disorder
Mood disorder that can coexist with ADHD.
Higher SES
Associated with better social functioning and reading ability.
ADHD Course
Lifelong disorder affecting attention and behavior.
Adult ADHD
Decreased hyperactivity; persistent attention limitations.
School Dropout Rates
Higher rates among children with ADHD.
Multimodal Approach
Combines education, medication, and therapy for treatment.
Stimulant Medications
Effective for 70-90% of ADHD patients.
Ritalin
Common stimulant medication for ADHD treatment.
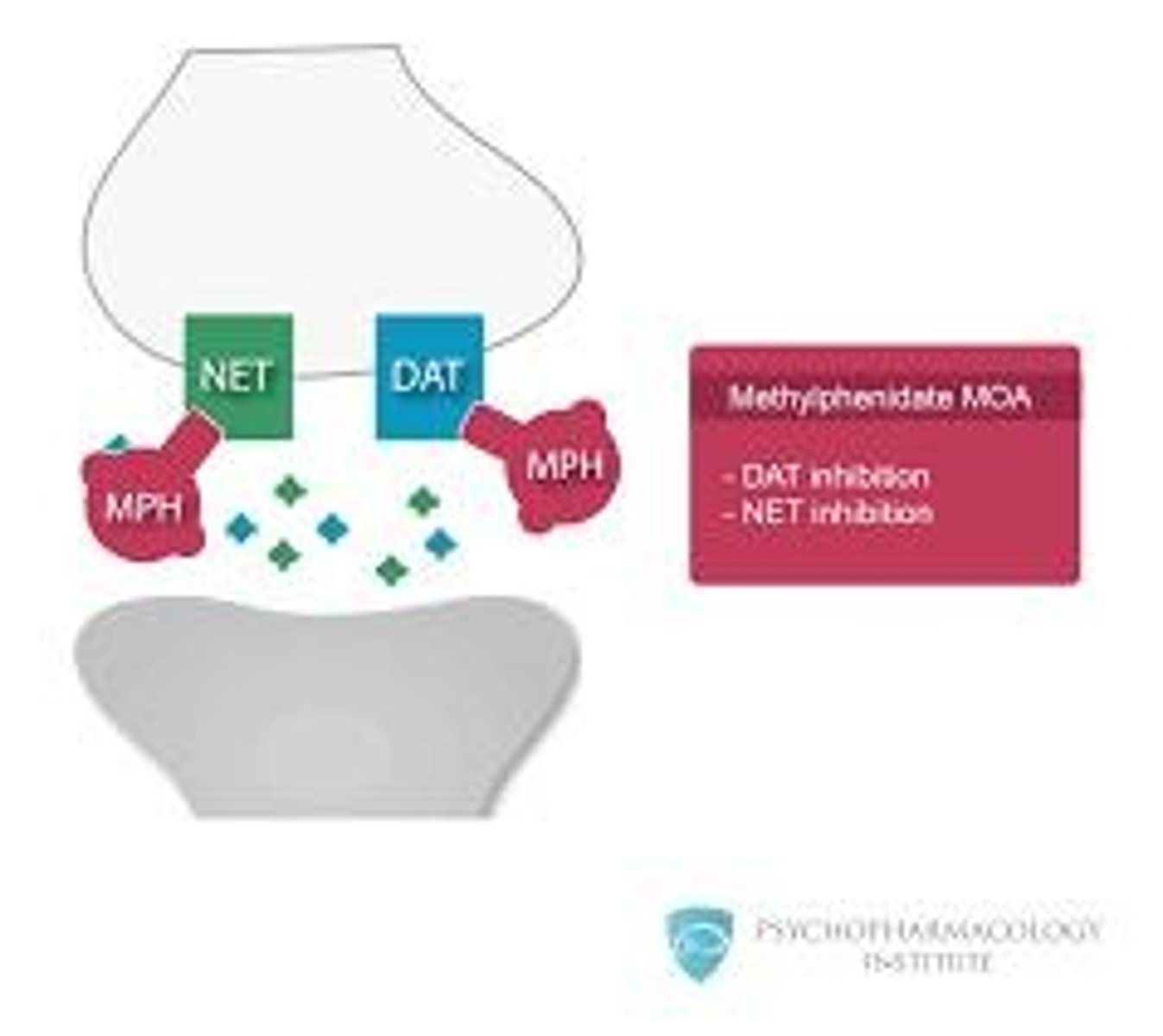
Medication Side Effects
Includes decreased appetite and sleep problems.
Nonstimulant Medications
Used when stimulants are ineffective; includes Strattera.
Behavioral Therapy
Targets behavior changes through environmental adjustments.
Cognitive-Behavior Therapy
Modifies thought processes to improve behavior.
Family Therapy
Addresses family dynamics affecting ADHD treatment.
IEP
Individualized Education Program for special education needs.
Mindfulness
Enhances attention and reduces impulsivity.
Dietary Interventions
Includes gluten-free and casein-free diets.
Occupational Therapy
Focuses on improving daily living skills.
ADLs
Activities of Daily Living; essential self-care tasks.
IADLs
Instrumental Activities of Daily Living; complex tasks.
Client Factors
Includes values, beliefs, and body functions.
Performance Skills
Skills needed for effective task execution.
Performance Patterns
Habits and routines affecting daily activities.
Social Skills Building
Enhances interpersonal interactions and relationships.
Peer Coaching
Group sessions focused on specific goals.
Parent Training
Educates parents on managing ADHD behaviors.
Support Groups
Provide emotional and practical support for families.
Technological Assistance
Tools to aid learning and task completion.

Rehabilitation Act of 1973
Legislation ensuring accommodations for disabilities.
IDEA of 2004
Ensures special education services for eligible children.
Contingency Approaches
Behavioral strategies like token economies and praise.