Autonomic Nervous System
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What nutrient cannot be used to for ATP production
nucleic acids
During glycolysis ___ ATP are used and ___ ATP are produced per glucose
2;4
What happens to the ketone bodies often generated during fatty acid catabolism
They are split into two molecules of acetyl-CoA and used in oxidative catabolism
How are amino acids produced by the body
An amino acid group is added to molecules such as oxaloacetate
Would you expect to find a high level of ketone bodies in the blood during the absorptive state
No, because glucose is already available
What is the main heat transfer mechanism between the environment and the body
radiation
Compounds and molecules that cannot be synthesized by the body and can only be obtained from the diet are called
essential nutrients.
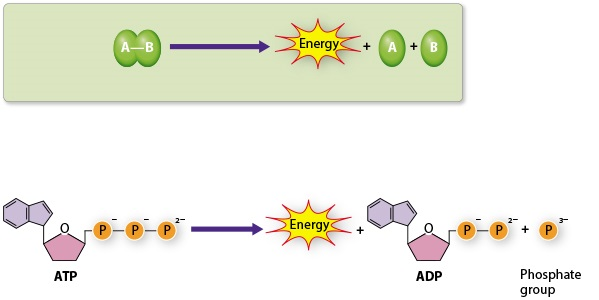
The reactions above are __________
reactions.
catabolic
If two stable chemicals were to react, what kind of reaction would this be?
The reaction would be endergonic because it uses energy to react.
The reaction A + B + energy → AB is a(n)
__________.
anabolic reaction
ATP production by direct transfer of a phosphate group from a phosphate-containing molecule to ADP is called
__________.
substrate-level phosphorylation.
The sum of all biochemical reactions that take place in the human body at any given time is called
__________.
metabolism.
A substance that is oxidized
__________.
loses electrons
The sum of the body's chemical reactions is known
as:
metabolism.
The breakdown of carbohydrates into glucose in the body is classified
as:
catabolism.
Which of the following is NOT a nutrient monomer used by the body to generate
ATP?
nucleic acids
Protein catabolism results in
amino acids
In order to proceed, endergonic reactions require an input
of:
energy
Which of the following reactions releases
energy?
exergonic reactions
Substances that lose electrons are said to
be:
oxidized
When NAD+ is ________ it becomes
NADH.
reduced
The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain is
__________.
oxygen
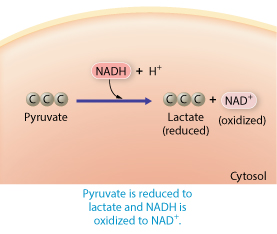
Rank the steps to describe first the anaerobic and then the aerobic pathways pyruvate would take after glycolysis
Pyruvate is reduced, pyruvate moves into the mitochondria, acetate is oxidized
Rank the steps from first to last to describe the correct order of events of the citric acid cycle starting with acetyl-CoA entering the cycle
Citrate synthesis, first oxidation, ATP synthesis, Second oxidation
Chemical reactions that release energy are called reactions.
The end product of a metabolic pathway needs which of the following to be made in abundance?
Specific starting reactant or substrate
all enzymes present & functional.
Specific intermediates produced throughout the pathway.
Cellular respiration is:
exergonic & produces ATP.
Which of the following is the formula for cellular respiration?
O2 + C6H12O6 ⟶ H2O + CO2
NAD+ & FAD are:
coenzymes that can accept or give up electrons.
Which phase of cellular respiration takes the energy products & produces ATP?
Electron Transport Chain
Which of the following stages are part of anaerobic respiration?
Glycolysis
Lactic acid fermentation
In which phase of cellular respiration is glucose broken down into pyruvate?
Glycolysis
H+ is pumped into the intermembrane space for what purpose?
To fuel ATP synthase
In which phase of cellular respiration is glucose broken down into lactate?
Lactic acid fermentation
How much ATP is produced in the intermediate stage? Citric Acid Cycle?
0;2
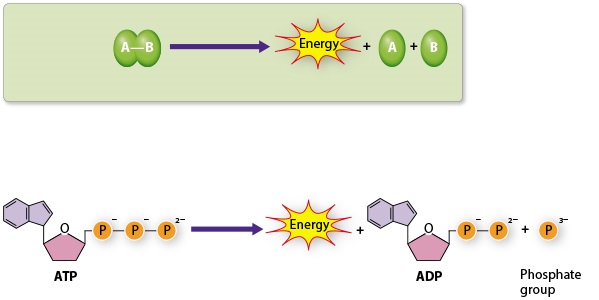
The reactions above are ___ reactions
catabolic
If two stable chemicals were to react, what kind of reaction would this be?
The reaction would be endergonic because it uses energy to react.
The reaction A + B + energy → AB is a(n)
__________.
anabolic reaction
ATP production by direct transfer of a phosphate group from a phosphate-containing molecule to ADP is called
__________.
substrate-level phosphorylation
The sum of all biochemical reactions that take place in the human body at any given time is called
__________.
metabolism
A substance that is oxidized
__________.
loses electrons
The sum of the body's chemical reactions is known
as:
metabolism.
The breakdown of carbohydrates into glucose in the body is classified
as:
catabolism.
Which of the following is NOT a nutrient monomer used by the body to generate
ATP?
nucleic acids
Protein catabolism results
in:
amino acids.
In order to proceed, endergonic reactions require an input
of
energy.
Which of the following reactions releases
energy?
exergonic reactions
Substances that lose electrons are said to
be:
oxidized.
When NAD+ is ________ it becomes
NADH.
reduced
The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain is
__________.
oxygen
Rank steps describing the anaerobic and aerobic pathways pyruvate would take after glycolysis
Pyruvate is reduced to lactate and NADH is oxidized to NAD
Pyruvate moves into the mitochondria and loses a carbon atom
Acetate is oxidized by NAD and combined with coenzyme A